Identification and Characterization of Glycoproteins and Their Responsive Patterns upon Ethylene Stimulation in the Rubber Latex
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
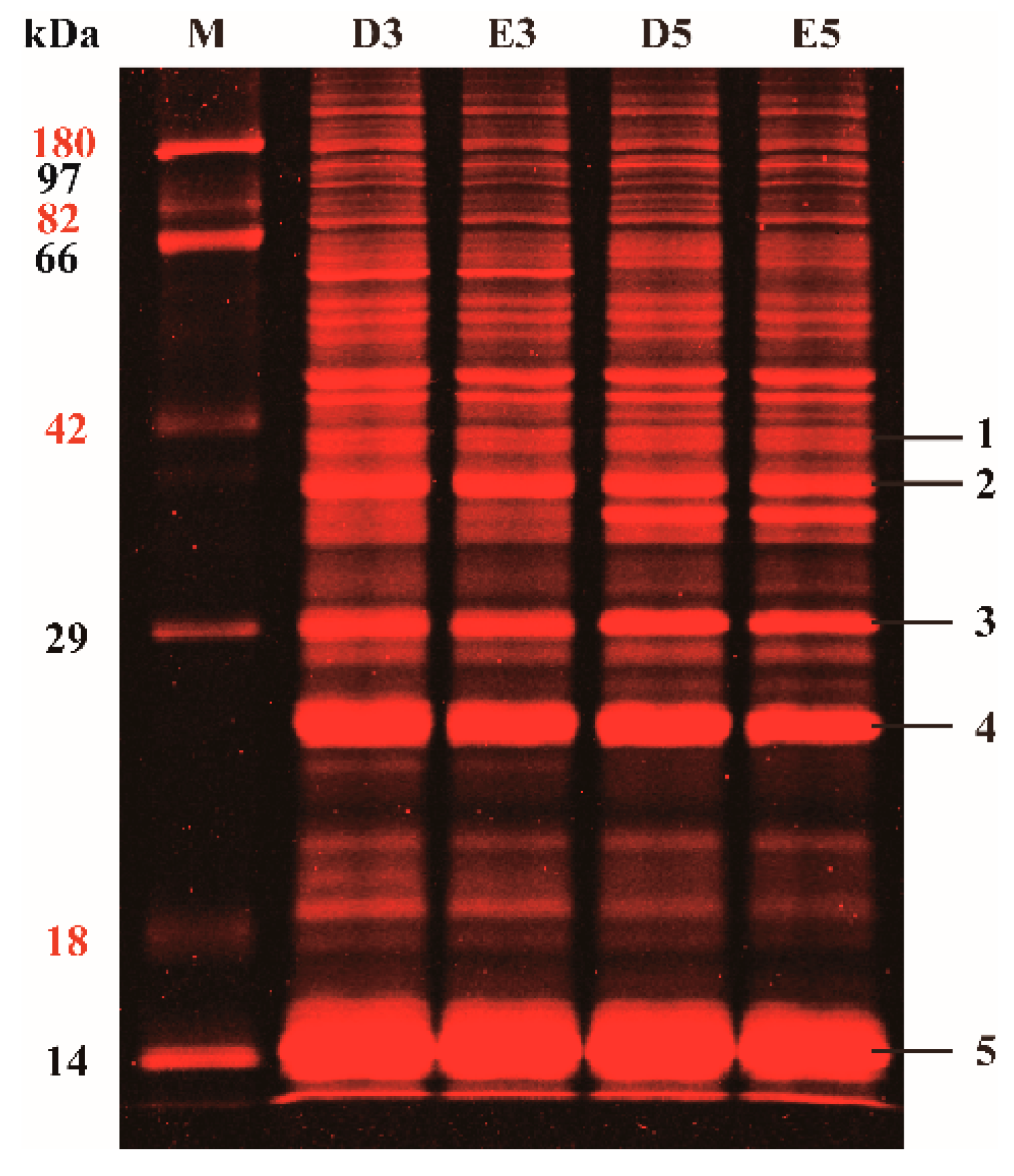
2.1. Profiles of the Glycosylated Proteins from Rubber Latex in One-Dimensional Gel
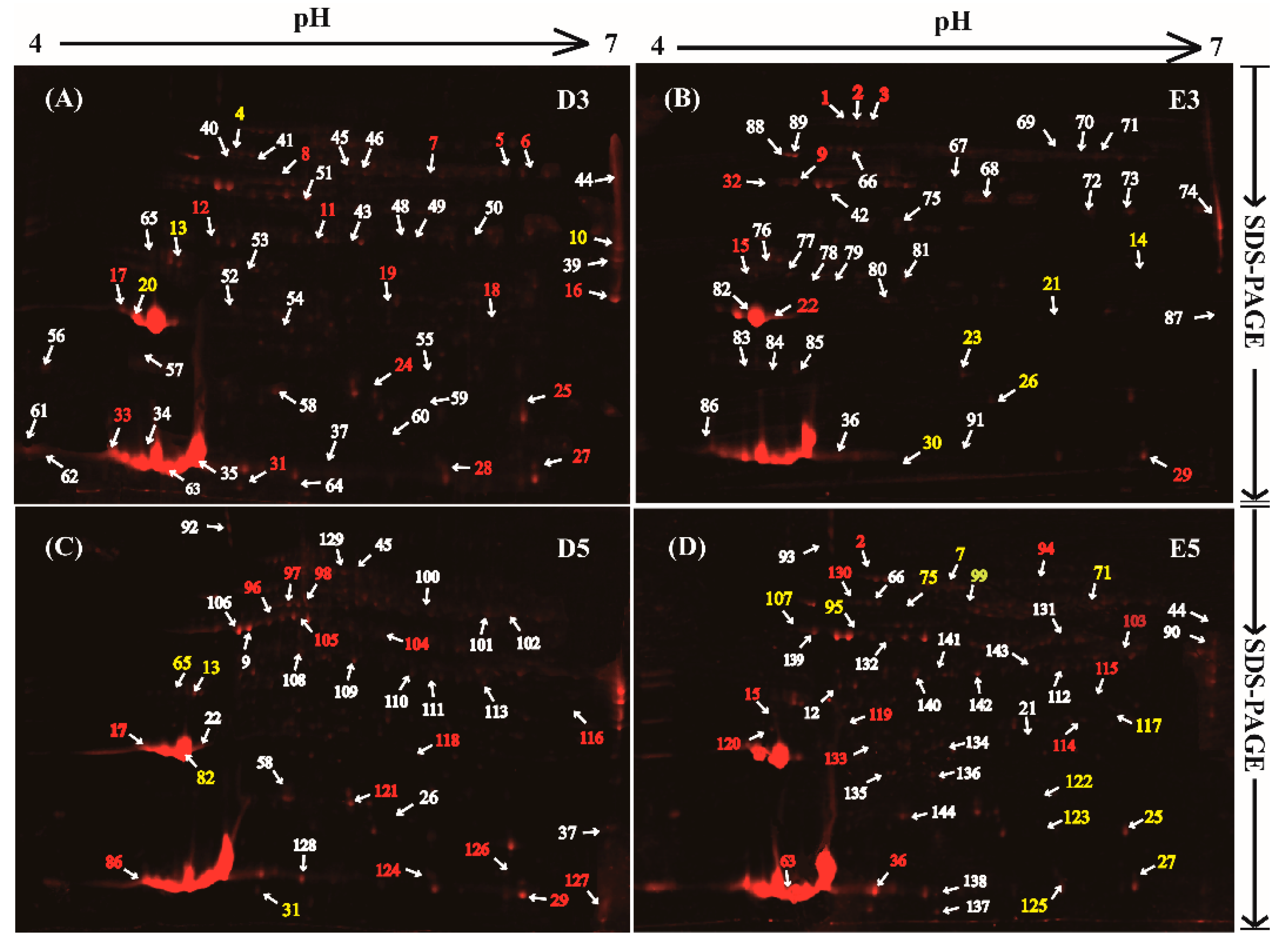
2.2. Profiles of Glycosylated Proteins Abundance in the Reference 2-DE Proteome Map for the Rubber Latex
2.3. Determinnation of Isoforms for the Glycosylated Proteins in 2-DE Gels
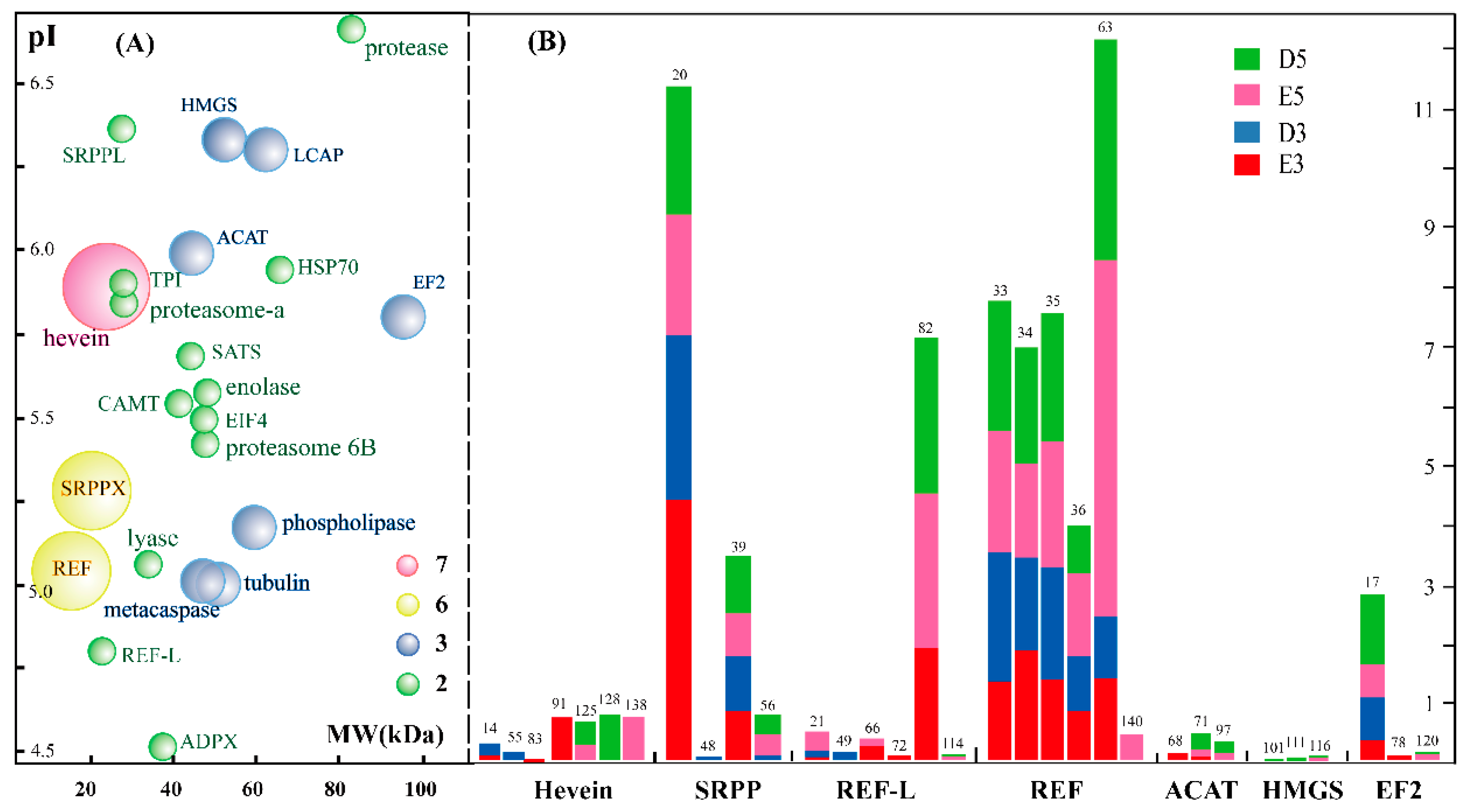
2.4. Characterization and Identification of Differentially Accumulated Glycoproteins in the Rubber Latex upon Ethylene Stimulation
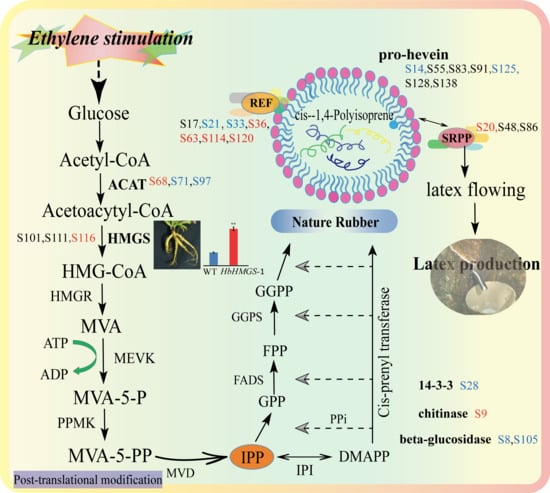
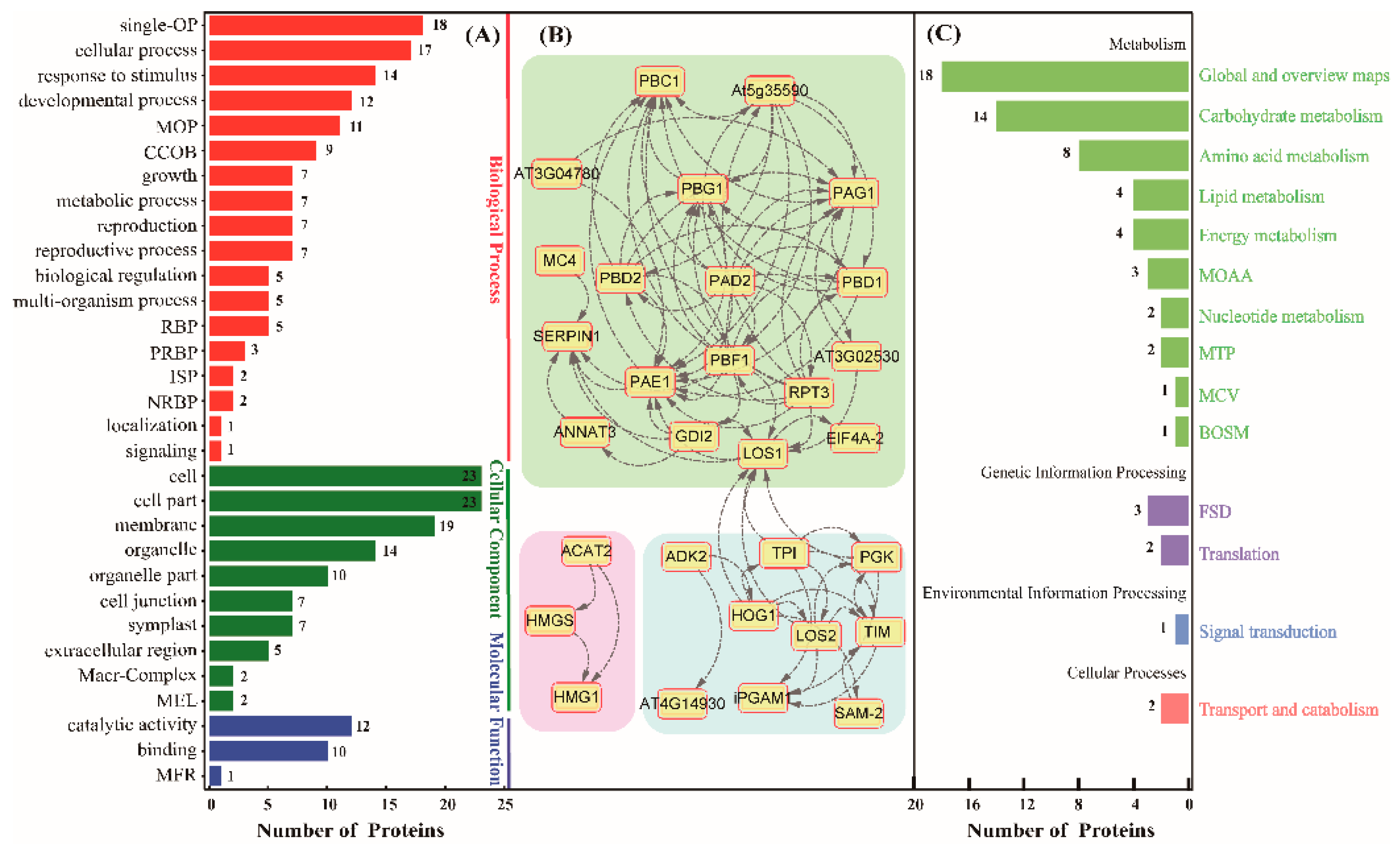
2.5. Functinal Analysis of Differential Glycoproteins in the Rubber Latex upon Ethylene Stimulation
2.6. Functional Verification of the HbHMGS2 Gene
3. Discussion
3.1. The First Visual Profiling of Glycoproteomics Based on 2-DE Gel Determined Lots of Proteins Involved in Carbohydrate Metabolism in Rubber Latex
3.2. Glycoproteomics of Rubber Latex Revealed Many Ethylene-Responsive Glycoproteins are Important for Nature Rubber Biosynthesis
3.3. Glycosylation of Different Isforms of NRB-Ralated Proteins Mgiht Play Different Roles and HbHMGS2 Gene Is Crucial for Nature Rubber Production
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Ethylene Treatments
4.2. Protein Extraction and Electrophoresis
4.3. Glycoproteomics Analysis
4.4. Protein Identification via Mass Spectrometry
4.5. GO and KEGG Annotations for the Identified Glycosylated Proteins
4.6. Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) Analysis
4.7. Phenotypic Analysis of the Transgenic Plants and Determination of Photosynthetic Pigment and Latex Content
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACAT | acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase |
| DMAPP | elongation factor 2-like protein |
| EF2 | Three letter acronym |
| FPP | farnesyl pyrophosphate |
| FPS | farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase |
| GGPP | geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate |
| GPP | geranyl pyrophosphate |
| GPS | geranyl pyrophosphate synthase |
| Hevein | pro-hevein |
| HMG-CoA | hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA |
| HMGR | HMG-CoA reductase |
| HMGS | hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase |
| IPP | isopentenyl pyrophosphate |
| IPI | IPP isomerase |
| MEVK | mevalonate kinase |
| MVA | mevalonate acid |
| MVA-5-P | mevalonate-5-phosphate |
| MVA-5-PP | mevalonate pyrophosphate |
| MVD | mevalonate pyrophosphate decarboxylase |
| PPMK | MVA-5-P kinase |
| SRPP | small rubber particle protein |
| REF | rubber elongation factor |
| REF-L | rubber elongation factor-like protein |
| 14-3-3 | 14-3-3 protein |
References
- Cornish, K. Biochemistry of natural rubber, a vital raw material, emphasizing biosynthetic rate, molecular weight and compartmentalization, in evolutionarily divergent plant species. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2001, 18, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.C.; Shi, M.J.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y.Y.; Cai, F.G.; Zhang, S.X.; Wang, L.M.; Tong, Z.; Tian, W.M. Comparative proteomics of primary and secondary lutoids reveals that chitinase and glucanase play a crucial combined role in rubber particle aggregation in Hevea brasiliensis. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 5146–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.P.; Zhuang, Y.F.; Guo, X.L.; Li, Y.J. Molecular mechanism of ethylene stimulation of latex yield in rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) revealed by de novo sequencing and transcriptome analysis. BMC Genomics. 2016, 17, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.H.; Zhang, Z.L. Ethylene stimulation of latex production in Hevea brasiliensis. Plant Signal. Behav. 2009, 4, 1072–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coupe, M.; Chrestin, H. Physico-chemical and biochemical mechanisms of hormonal (ethylene) stimulation. Physiol. Rubber Tree Latex 1989, 295–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, R.; Rio, M.; Martin, F.; Leclercq, J.; Woraathasin, N.; Roques, S.; Dessailly, F.; Clément-Vidal, A.; Sanier, C.; Fabre, D.; et al. Overexpression of Hevea brasiliensis ethylene response factor HbERF-IXc5 enhances growth, tolerance to abiotic stress and affects laticifer differentiation. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.C.; Wang, D.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Q.; Chang, L.L.; Wang, L.M.; Meng, X.R.; Huang, Q.X.; Jin, X.; Tong, Z. Comprehensive proteomics analysis of laticifer latex reveals new insights into ethylene stimulation of natural rubber production. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Xie, Q.L.; Sun, Y.; Tong, Z.; Chang, L.L.; Yu, L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yuan, B.X.; He, P.; Jin, X.; et al. Proteomic landscape has revealed small rubber particles are crucial rubber biosynthetic machines for ethylene-stimulation in natural rubber production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeang, H.Y.; Arif, S.M.; Yusof, F.; Sunderasan, E. Allergenic proteins of natural rubber latex. Methods 2002, 27, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.L.; Xia, K.C.; Dai, L.J.; Kang, G.J.; Li, Y.; Nie, Z.Y.; Duan, C.F.; Zeng, R.Z. Proteome analysis of the large and the small rubber particles of Hevea brasiliensis using 2D-DIGE. Plant Phys. Biochem. 2012, 60, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.J.; Kang, G.J.; Li, Y.; Nie, Z.Y.; Duan, C.F.; Zeng, R.Z. In-depth proteome analysis of the rubber particle of Hevea brasiliensis (para rubber tree). Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 82, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, S.; Yamaguchi, H.; Waki, T.; Aoki, Y.; Mizuno, M.; Yanbe, F.; Ishii, T.; Funaki, A.; Tozawa, Y.; Miyagi-Inoue, Y.; et al. Identification and reconstitution of the rubber biosynthetic machinery on rubber particles from Hevea brasiliensis. eLife 2016, 5, 19022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Habib, M.H.; Yuen, G.C.; Othman, F.; Zainudin, N.N.; Latiff, A.A.; Ismail, M.N. Proteomics analysis of latex from Hevea brasiliensis (clone RRIM 600). Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 95, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, X.; Wang, F.; Chen, G.Q.; Zhang, H.B.; Xian, M. Biosynthesis of natural rubber: Current state and perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, L.J.; Kang, G.J.; Nie, Z.Y.; Li, Y.; Zeng, R.Z. Comparative proteomic analysis of latex from Hevea brasiliensis treated with ethrel and methyl jasmonate using iTRAQ-coupled two-dimensional LC-MS/MS. J. Proteom. 2016, 132, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Z.; Wang, D.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Q.; Meng, X.R.; Wang, L.M.; Feng, W.Q.; Li, L.; Wurtele, E.S.; Wang, X.C. Comparative proteomics of rubber latex revealed multiple protein species of REF/SRPP family respond diversely to ethylene stimulation among different rubber tree clones. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linding, R.; Jensen, L.J.; Ostheimer, G.J.; van Vugt, M.A.; Jorgensen, C.; Miron, I.M.; Diella, F.; Colwill, K.; Taylor, L.; Elder, K.; et al. Systematic discovery of in vivo phosphorylation networks. Cell 2007, 129, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zielinska, D.F.; Gnad, F.; Schropp, K.; Wisniewski, J.R.; Mann, M. Mapping N-glycosylation sites across seven evolutionarily distant species reveals a divergent substrate proteome despite a common core machinery. Mol. Cell 2012, 46, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-May, E.; Hucko, S.; Howe, K.J.; Zhang, S.; Sherwood, R.W.; Thannhauser, T.W.; Rose, J.K. A comparative study of lectin affinity-based plant N-glycoproteome profiling using tomato fruit as a model. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lige, B.; Ma, S.; Van-huystee, R.B. The effects of the site-directed removal of N-glycosylation from cationic peanut peroxidase on its function. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 386, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, A. Plant protein glycosylation. Glycobiology 2016, 26, 926–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ceriotti, A.; Duranti, M.; Bollini, R. Effects of N-glycosylation on the folding and structure of plant proteins. J. Exp. Bot. 1998, 49, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattison, R.J.; Amtmann, A. N-glycan production in the endoplasmic reticulum of plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haweker, H.; Rips, S.; Koiwa, H.; Salomon, S.; Saijo, Y.; Chinchilla, D.; Robatzek, S.; Schaewen, A.V. Pattern recognition receptors require N-glycosylation to mediate plant immunity. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 4629–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catala, C.; Howe, K.J.; Hucko, S.; Rose, J.C.; Thannhauser, T.W. Towards characterization of the glycoproteome of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruit using Concanavalin A lectin affinity chromatography and LC-MALDI-MS/MS analysis. Proteomics 2011, 11, 1530–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligat, L.; Lauber, E.; Albenne, C.; Clemente, H.S.; Valot, B.; Zivy, M.; Pont-Lezica, R.; Arlat, M.; Jamet, E. Analysis of the xylem sap proteome of Brassica oleracea reveals a high content in secreted proteins. Proteomics 2011, 11, 1798–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melo-braga, M.N.; Verano-braga, T.; Leon, I.R.; Antonacci, D.; Nogueira, F.C.; Thelen, J.J.; Larsen, M.R.; Palmisano, G. Modulation of protein phosphorylation, N-glycosylation and lys-acetylation in grape mesocarp and exocarp owing to Lobesia botrana infection. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palmisano, G.; Antonacci, D.; Larsen, M.R. Glycoproteomic profile in wine: A sweet molecular renaissance. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 6148–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, C.; Schulenberg, B.; Steinberg, T.H.; Leung, W.Y.; Patton, W.F. Detection of glycoproteins in polyacrylamide gels and on electroblots using Pro-Q Emerald 488 dye, a fluorescent periodate Schiff-base stain. Electrophoresis 2003, 24, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlmeier, S.; Mazur, W.; Salmenkivi, K.; Myllärniemi, M.; Bergmann, U.; Kinnula, V.L. Proteomic studies on receptor for advanced glycation end product variants in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proteomics 2010, 4, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, W.T.; Zhou, A.; Liu, Z.G.; Shen, J.; Zhou, X.; Ye, W.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Lin, J.J.; Jin, L.T. Highly sensitive method for specific, brief, and economical detection of glycoproteins in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis by the synthesis of a new hydrazide derivative. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1462–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Shi, M.; Lu, X.; Ma, R.; Wu, C.; Guo, A.; Peng, M.; Tian, W. A method for protein extraction from different subcellular fractions of laticifer latex in Hevea brasiliensis compatible with 2-DE and MS. Proteome Sci. 2010, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Putranto, R.A.; Herlinawati, E.; Rio, M.; Leclercq, J.; Piyatrakul, P.; Gohet, E.; Sanier, C.; Oktavia, F.; Pirrello, J.; Montoro, P. Involvement of ethylene in the latex metabolism and tapping panel dryness of Hevea brasiliensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 17885–17908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adiwilaga, K.; Kush, A. Cloning and characterization of cDNA encoding farnesyl diphosphate synthase from rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis). Plant Mol. Biol. 1996, 30, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.W.; Deng, L.H.; Yi, X.P.; Zeng, H.C.; Xiao, S.H. Cloning and sequence analysis of a novel cis-prenyltransferases gene from Hevea brasiliensis. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2009, 17, 223–228. [Google Scholar]
- Chye, M.L.; Tan, C.T.; Chua, N.H. Three genes encode 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase in Hevea brasiliensis: Hmg1 and hmg3 are differentially expressed. Plant Mol. Biol. 1992, 19, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tungngoen, K.; Kongsawadworakul, P.; Viboonjun, U.; Katsuhara, M.; Brunel, N.; Sakr, S.; Narangajavana, J.; Chrestin, H. Involvement of HbPIP2;1 and HbTIP1;1 aquaporins in ethylene stimulation of latex yield through regulation of water exchanges between inner liber and latex cells in Hevea brasiliensis. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pluang, S.; Nualpun, S.; Wallie, S. Regulation of the expression of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase gene in Hevea brasiliensis (B.H.K.) Mull. Arg. Plant Sci. 2004, 166, 531–537. [Google Scholar]
- Sirinupong, N.; Suwanmanee, P.; Doolittle, R.F.; Suvachitanont, W. Molecular cloning of a new cDNA and expression of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase gene from Hevea brasiliensis. Planta 2005, 221, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sardar, H.S.; McGovern, K.R.; Zhang, Y.; Showalter, A.M. A lysine-rich arabinogalactan protein in Arabidopsis is essential for plant growth and development, including cell division and expansion. Plant J. 2007, 49, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minic, Z.; Jamet, E.; Négroni, L.; Arsene der Garabedian, P.; Zivy, M.; Jouanin, L. A sub-proteome of Arabidopsis thaliana mature stems trapped on Concanavalin A is enriched in cell wall glycoside hydrolases. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 2503–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Giboulot, A.; Zivy, M.; Valot, B.; Jamet, E.; Albenne, C. Combining various strategies to increase the coverage of the plant cell wall glycoproteome. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sultana, N.; Florance, H.V.; Johns, A.; Smirnoff, N. Ascorbate deficiency influences the leaf cell wall glycoproteome in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hunter, J.R. Reconsidering the functions of latex. Trees 1994, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrot, R.; Kalinowski, A.; Gozdzicka-Jozefiak, A. Proteomic analysis of Chelidonium majus milky sap using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and tandem mass spectrometry. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 1612–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Rahman, N.; Kamarrudin, M.F. Proteomic profiling of Hevea latex serum induced by ethephon stimulation. J. Trop. Plant Physiol. 2018, 10, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, W.K.; Chen, X.Y.; Rim, Y.; Chu, H.; Jo, Y.; Kim, S.; Park, Z.Y.; Kim, J.Y. Extended latex proteome analysis deciphers additional roles of the lettuce laticifer. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2010, 4, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Sun, Y.; Chang, L.L.; Tong, Z.; Xie, Q.L.; Jin, X.; Zhu, L.P.; He, P.; Li, H.B.; Wang, X.C. Subcellular proteome profiles of different latex fractions revealed washed solutions from rubber particles contain crucial enzymes for natural rubber biosynthesis. J. Proteom. 2018, 182, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.K.; Jo, Y.; Chu, H.; Park, S.H.; Kim, K.H. Integration of latex protein sequence data provides comprehensive functional overview of latex proteins. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 1469–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Buitrago, J.M.; Ferreira, L.; Isidoro-Garcia, M.; Sanz, C.; Lorente, F.; Davila, I. Proteomic approaches for identifying new allergens and diagnosing allergic diseases. Clinica Chim. Acta 2007, 385, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, A.; Bachi, A.; Fasoli, E.; Boschetti, E.; Peltre, G.; Sénéchal, H.; Sutra, J.P.; Citterio, A.; Righetti, P.G. In-depth exploration of Hevea brasiliensis latex proteome and “hidden allergens” via combinatorial peptide ligand libraries. J. Proteom. 2010, 73, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagami, T.; Haishima, Y.; Tsuchiya, T.; Tomitaka-Yagami, A.; Kano, H.; Matsunaga, K. Proteomic analysis of putative latex allergens. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2004, 135, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Sun, Y.; Tong, Z.; Yang, Q.; Chang, L.L.; Meng, X.R.; Wang, L.M.; Tian, W.M.; Wang, X.C. A protein extraction method for low protein concentration solutions compatible with the proteomic analysis of rubber particles. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 2930–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.R.; Xiao, X.H.; Li, H.P.; Fan, Y.J.; Yang, J.H.; Qi, J.Y.; Li, H.B. Comparative analysis of latex transcriptome reveals putative molecular mechanisms underlying super productivity of Hevea brasiliensis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.; Sun, Y.; Wu, M.; Wang, D.; Wei, J.S.; Wu, B.S.; Wang, G.H.; Wu, W.G.; Jin, X.; Wang, X.C.; et al. Physiological and proteomic analyses of molybdenum- and ethylene-responsive mechanisms in rubber latex. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; An, B.; Hou, X.; Guo, Y.; Luo, H.L.; He, C.Z. Dicer-like proteins regulate the growth, conidiation, and pathogenicity of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides from Hevea brasiliensis. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.J.; Deng, Z.; Chen, C.L.; Xia, Z.H.; Wu, M.; He, P.; Chen, S.C. Identification and characterization of genes associated with tapping panel dryness from Hevea brasiliensis latex using suppression subtractive hybridization. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, W.K.; Chen, X.Y.; Uddin, N.M.; Rim, Y.; Moon, J.; Jung, J.H.; Shi, C.; Chu, H.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.W.; et al. Comprehensive proteome analysis of lettuce latex using multidimensional protein-identification technology. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havanapan, P.; Bourchookarn, P.; Ketterman, A.J.; Krittanai, C. Comparative proteome analysis of rubber latex serum from pathogenic fungi tolerant and susceptible rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis). J. Proteom. 2016, 131, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujade-Renaud, V.; Clement, A.; Perrot-Rechenmann, C.; Prevot, J.C.; Chrestin, H.; Jacob, J.L.; Guern, J. Ethylene-induced increase in glutamine synthetase activity and mRNA levels in Hevea brasiliensis latex cells. Plant Physiol. 1994, 105, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sando, T.; Takaoka, C.; Mukai, Y.; Yamashita, A.; Hattori, M.; Ogasawara, N.; Fukusaki, E.; Kobayashi, A. Cloning and characterization of mevalonate pathway genes in a natural rubber producing plant, Hevea brasiliensis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 2049–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puskas, J.E.; Gautriaud, E.; Deffieux, A.; Kennedy, J.P. Natural rubber biosynthesis-A living carbocationic polymerization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.R.; Yang, M.; Fang, Y.J.; Luo, Y.F.; Gao, S.H.; Xiao, X.H.; An, Z.W.; Zhou, B.H.; Zhang, B.; Tan, X.Y.; et al. The rubber tree genome reveals new insights into rubber production and species adaptation. Nature Plants. 2016, 6, 16073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oh, S.K.; Kang, H.; Shin, D.H.; Yang, J.; Chow, K.S.; Yeang, H.Y.; Wagner, B.; Breiteneder, H.; Han, K.H. Isolation, characterization, and functional analysis of a novel cDNA clone encoding a small rubber particle protein from Hevea brasiliensis. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 17132–17138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rojruthai, P.; Sakdapipanich, J.T.; Takahashi, S.; Hyegin, L.; Noike, M.; Koyama, T.; Tanaka, Y. In vitro synthesis of high molecular weight rubber by Hevea small rubber particles. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2010, 109, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.J.; Nie, Z.Y.; Kang, G.J.; Li, Y.; Zeng, R.Z. Identification and subcellular localization analysis of two rubber elongation factor isoforms on Hevea brasiliensis rubber particles. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 111, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.; Feeney, M.; Ahmadi, M.; Lonoce, C.; Sajari, R.; Di Cola, A.; Frigerio, L. Subcellular localization and interactions among rubber particle proteins from Hevea brasiliensis. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 5045–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, C.; Pan, S.; Zouhar, J.; Avila, E.L.; Girke, T.; Raikhel, N.V. The vegetative vacuole proteome of Arabidopsis thaliana reveals predicted and unexpected proteins. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 3285–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wititsuwannakul, R.; Rukseree, K.; Kanokwiroon, K.; Wititsuwannakul, D. A rubber particle protein specific for Hevea latex lectin binding involved in latex coagulation. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Broekaert, W.F.; Raikhel, N.V. Co-and post-translational processing of the hevein preproprotein of latex of the rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis). J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 15944–15946. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.X.; Yan, B.Y.; Tan, Y.R.; Gao, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; Li, S.J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.Y.; et al. Identification of cis-regulatory regions responsible for developmental and hormonal regulation of HbHMGS1 in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 41, 1077–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Nagegowda, D.A.; Rawat, R.; Bouvier-Nave, P.; Guo, D.; Bach, T.J.; Chye, M.L. Overexpression of Brassica juncea wild-type and mutant HMG-CoA synthase 1 in Arabidopsis up-regulates genes in sterol biosynthesis and enhances sterol production and stress tolerance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2012, 10, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putter, K.M.; Deenen, N.V.; Unland, K.; Prufer, D.; Gronover, C.S. Isoprenoid biosynthesis in dandelion latex is enhanced by the overexpression of three key enzymes involved in the mevalonate pathway. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.W. Study on rapid determination of chlorophyll content of leaves. Chin. J. Spect. Lab. 2002, 4, 478–481. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, T.; Xiang, T.; Dong, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Zhang, L.Q. Quantitation of isoprenoids for natural rubber biosynthesis in natural rubber latex by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1558, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, L.; Yuan, B.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Ding, G.; Souleymane, O.A.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Q.; Wang, X. Identification and Characterization of Glycoproteins and Their Responsive Patterns upon Ethylene Stimulation in the Rubber Latex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5282. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155282
Yu L, Yuan B, Wang L, Sun Y, Ding G, Souleymane OA, Zhang X, Xie Q, Wang X. Identification and Characterization of Glycoproteins and Their Responsive Patterns upon Ethylene Stimulation in the Rubber Latex. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(15):5282. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155282
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Li, Boxuan Yuan, Lingling Wang, Yong Sun, Guohua Ding, Ousmane Ahmat Souleymane, Xueyan Zhang, Quanliang Xie, and Xuchu Wang. 2020. "Identification and Characterization of Glycoproteins and Their Responsive Patterns upon Ethylene Stimulation in the Rubber Latex" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 15: 5282. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155282
APA StyleYu, L., Yuan, B., Wang, L., Sun, Y., Ding, G., Souleymane, O. A., Zhang, X., Xie, Q., & Wang, X. (2020). Identification and Characterization of Glycoproteins and Their Responsive Patterns upon Ethylene Stimulation in the Rubber Latex. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(15), 5282. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155282