Chitin Biosynthesis Inhibition of Meloidogyne incognita by RNAi-Mediated Gene Silencing Increases Resistance to Transgenic Tobacco Plants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
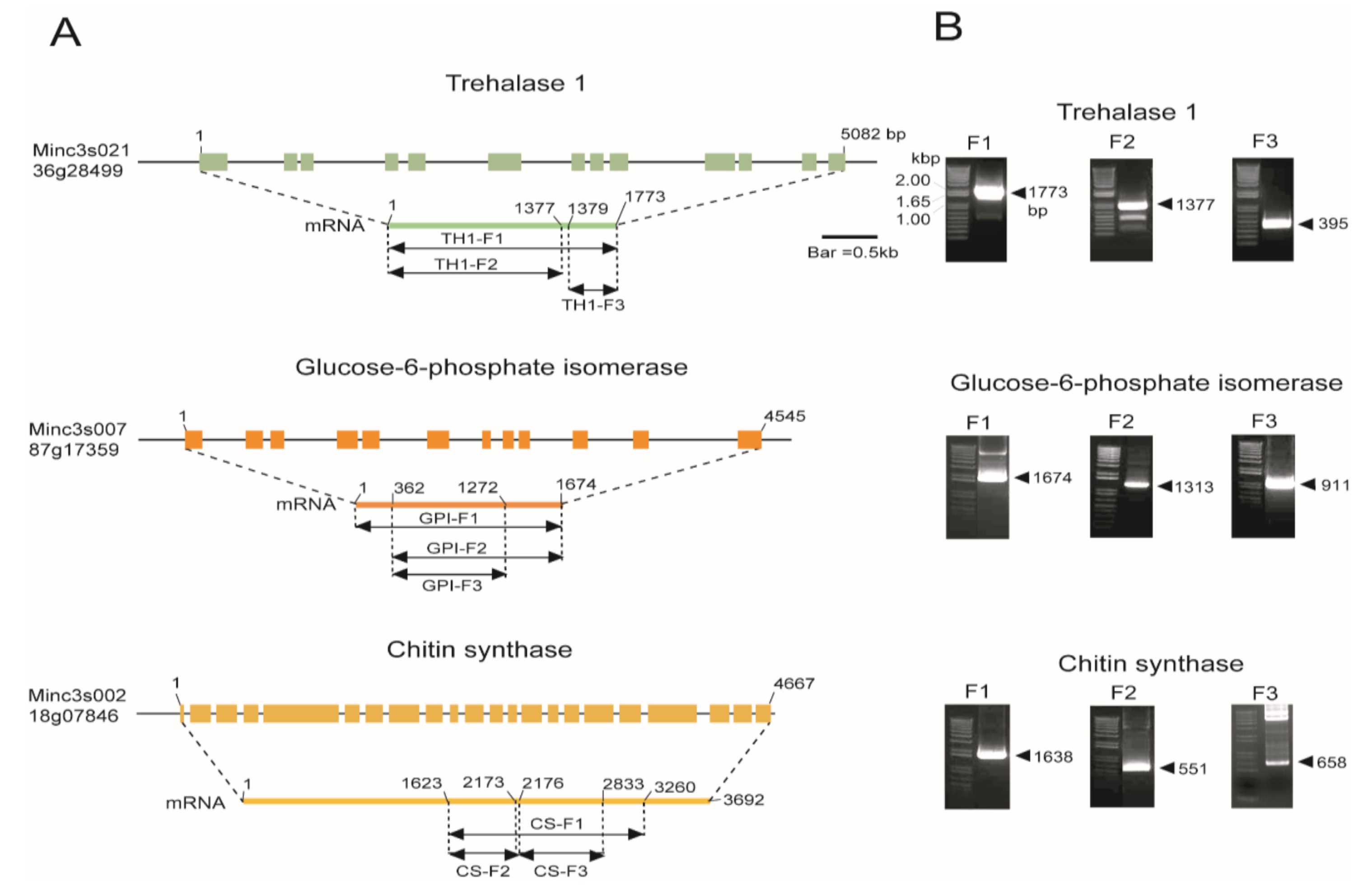
2.1. In Silico Mining and Cloning of Chitin Biosynthesis Pathway Genes
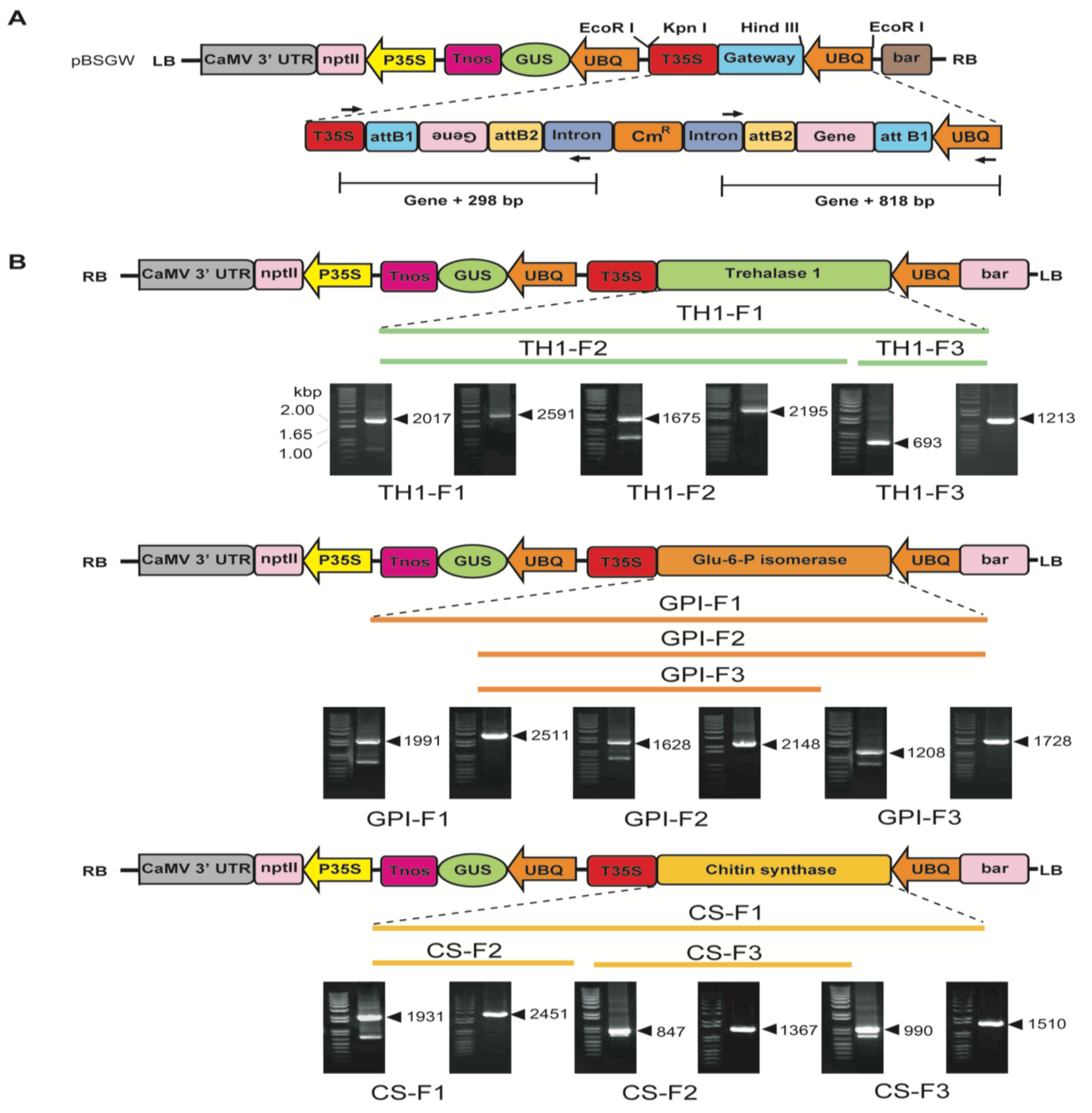
2.2. Plant Transformation Vector Construction and Tobacco Transformation
2.3. Chitin Genes Expression Analysis by qRT-PCR
2.4. Efficiency of Regeneration and GUS Staining of Transgenic Plants
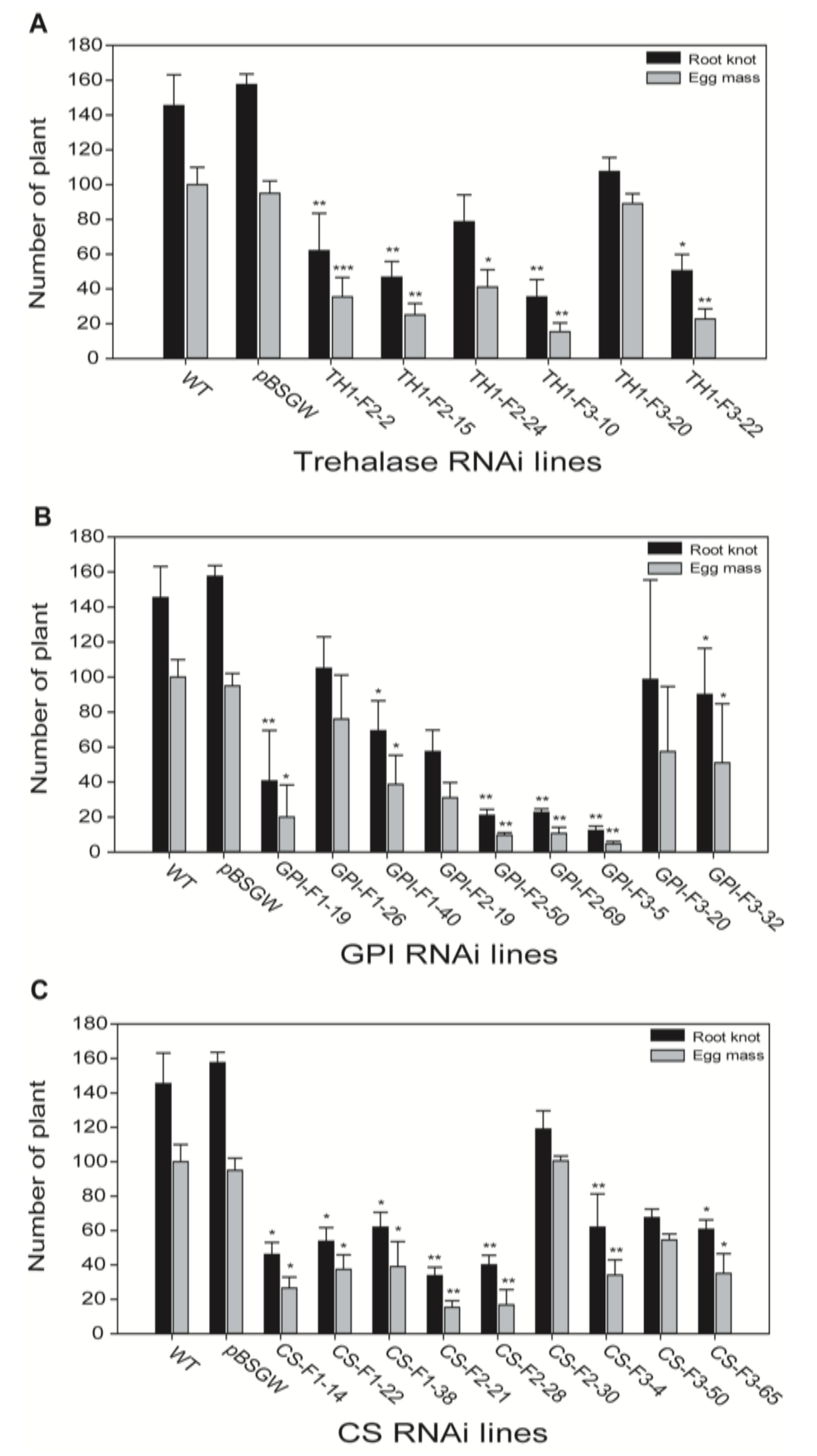
2.5. RKN Inoculation of Transgenic Lines and Suppression Analysis
2.6. Downregulation of Chitin Biosynthetic Genes of the Female Nematode in RNAi Transgenic Roots
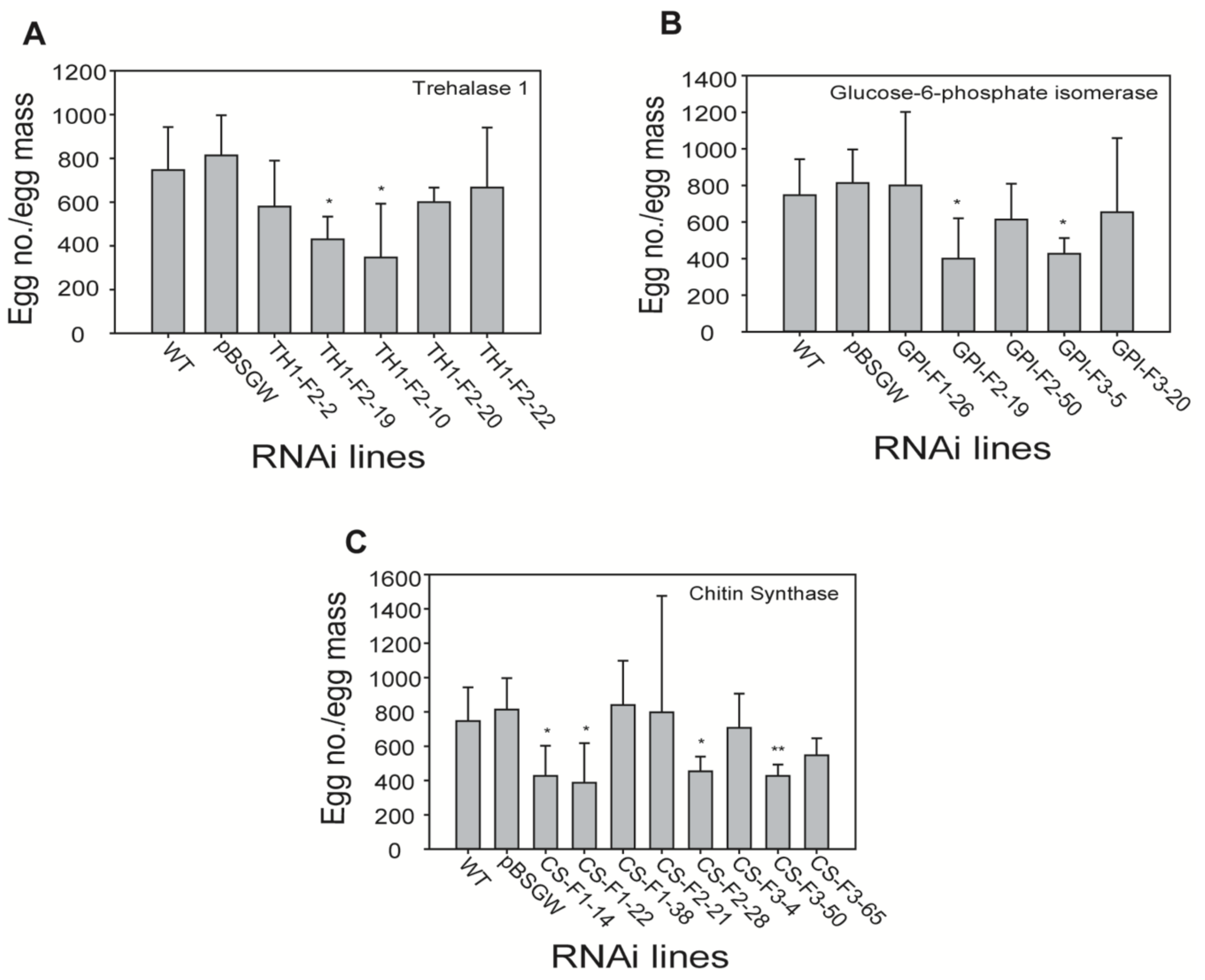
2.7. Effect of RNAi-Mediated Gene Silencing on Egg Number and Female Morphology in Transgenic Lines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation and Cloning of Chitin Synthesis Genes
4.2. RNAi Vector Construction
4.3. Stage-Wise Nematode Sample Preparation
4.4. RNA Isolation from Nematode
4.5. cDNA Synthesis
4.6. Quantitative Real-Time-PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
4.7. Plant Transformation and PCR Analysis
4.8. RKN Inoculation and Suppression Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RKN | Root knot nematode |
| J2 | Juvenile 2 |
| RNAi | RNA interference |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| UBQ | Ubiquitin |
| GPI | Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase |
| dsRNA | Double-stranded RNA |
References
- Singh, S.; Singh, B.; Singh, A.P. Nematodes: A threat to sustainability of agriculture. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 29, 215–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanian, P.; Choi, I.C.; Mani, V.; Park, J.; Subramaniyam, S.; Choi, K.H.; Sim, J.S.; Lee, C.M.; Koo, J.C.; Hahn, B.S. Stage-wise identification and analysis of miRNA from root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, P.; Shukla, N.; Joshi, G.; VijayaKumar, C.; Jagannath, A.; Agarwal, M.; Goel, S.; Kumar, A. Genome-wide identification and characterization of miRNAome from tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) roots and root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne incognita) during susceptible interaction. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ling, J.; Mao, Z.; Zhai, M.; Zeng, F.; Yang, Y.; Xie, B. Transcriptome profiling of Cucumis metuliferus infected by Meloidogyne incognita provides new insights into putative defense regulatory network in Cucurbitaceae. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Medina, A.; Fernandez, I.; Lok, G.B.; Pozo, M.J.; Pieterse, C.M.; Van Wees, S.C. Shifting from priming of salicylic acid- to jasmonic acid-regulated defences by Trichoderma protects tomato against the root knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 1363–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ajjappala, H.; Chung, H.Y.; Sim, J.S.; Choi, I.; Hahn, B.S. Disruption of prefoldin-2 protein synthesis in root-knot nematodes via host-mediated gene silencing efficiently reduces nematode numbers and thus protects plants. Planta 2015, 241, 773–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbashir, S.M.; Lendeckel, W.; Tuschl, T. RNA interference is mediated by 21- and 22-nucleotide RNAs. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fairbairn, D.J.; Cavallaro, A.S.; Bernard, M.; Mahalinga-Iyer, J.; Graham, M.W.; Botella, J.R. Host-delivered RNAi: An effective strategy to silence genes in plant parasitic nematodes. Planta 2007, 226, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennerdell, J.R.; Carthew, R.W. Use of dsRNA-mediated genetic interference to demonstrate that frizzled and frizzled 2 act in the wingless pathway. Cell 1998, 95, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Napoli, C.; Lemieux, C.; Jorgensen, R. Introduction of a chimeric chalcone synthase gene into petunia results in reversible co-suppression of homologous genes in trans. Plant Cell 1990, 2, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romano, N.; Macino, G. Quelling: Transient inactivation of gene expression in Neurospora crassa by transformation with homologous sequences. Mol. Microbiol. 1992, 6, 3343–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urwin, P.E.; Lilley, C.J.; Atkinson, H.J. Ingestion of double stranded RNA by preparasitic juvenile cyst nematodes leads to RNA interference. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2002, 15, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Rehman, S.; Smant, G.; Jones, J.T. Functional analysis of pathogenicity proteins of the potato cyst nematode Globodera rostochiensis using RNAi. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2005, 18, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakhetia, M.; Charlton, W.; Atkinson, H.J.; McPherson, M.J. RNA interference of dual oxidase in the plant nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2005, 18, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosso, M.N.; Dubrana, M.P.; Cimbolini, N.; Jaubert, S.; Abad, P. Application of RNA interference to root-knot nematode genes encoding esophageal gland proteins. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2005, 18, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalzell, J.J.; McMaster, S.; Fleming, C.C.; Maule, A.G. Short interfering RNA-mediated gene silencing in Globodera pallida and Meloidogyne incognita infective stage juveniles. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Allen, R.; Davis, E.L.; Baum, T.J.; Hussey, R.S. Engineering broad root-knot resistance in transgenic plants by RNAi silencing of a conserved and essential root-knot nematode parasitism gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14302–14306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steeves, R.M.; Todd, T.C.; Essig, J.S.; Trick, H.N. Transgenic soybeans expressing siRNAs specific to a major sperm protein gene suppress Heterodera glycines reproduction. Funct. Plant Biol. 2006, 33, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.C.; Veluthambi, K.; Subramaniam, K. Host-generated double stranded RNA induces RNAi in plant-parasitic nematodes and protects the host from infection. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2006, 148, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheysen, G.; Vanholme, B. RNAi from plants to nematodes. Trends Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, P.T.; Brown, C.R.; Elling, A.A. RNA interference of effector gene Mc16D10L confers resistance against Meloidogyne chitwoodi in Arabidopsis and potato. Phytopathology 2014, 104, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chi, Y.; Wang, X.; Le, X.; Ju, Y.; Guan, T.; Li, H. Exposure to double-stranded RNA mediated by tobacco rattle virus leads to transcription up-regulation of effector gene Mi-vap-2 from Meloidogyne incognita and promotion of pathogenicity in progeny. Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenço-Tessutti, I.T.; Souza Junior, J.D.; Martins-de-Sa, D.; Viana, A.A.; Carneiro, R.M.; Togawa, R.C.; de Almeida-Engler, J.; Batista, J.A.; Silva, M.C.; Fragoso, R.R.; et al. Knock-down of heat-shock protein 90 and isocitrate lyase gene expression reduced root-knot nematode reproduction. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roderick, H.; Urwin, P.E.; Atkinson, H.J. Rational design of biosafe crop resistance to a range of nematodes using RNA interference. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antonino de Souza Júnior, J.D.; Ramos Coelho, R.; Tristan Lourenço, I.; da Rocha Fragoso, R.; Barbosa Viana, A.A.; Lima Pepino de Macedo, L.; Mattar da Silva, M.C.; Gomes Carneiro, R.M.; Engler, G.; de Almeida-Engler, J.; et al. Knocking-down Meloidogyne incognita proteases by plant-delivered dsRNA has negative pleiotropic effect on nematode vigor. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papolu, P.K.; Gantasala, N.P.; Kamaraju, D.; Banakar, P.; Sreevathsa, R.; Rao, U. Utility of host delivered RNAi of two FMRF amide like peptides, flp-14 and flp-18, for the management of root knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, B.; Hamamouch, N.; Li, C.; Huang, G.; Hussey, R.S.; Baum, T.J.; Davis, E.L. The 8D05 parasitism gene of Meloidogyne incognita is required for successful infection of host roots. Phytopathology 2013, 103, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinh, P.T.; Zhang, L.; Brown, C.R.; Elling, A.A. Plant-mediated RNA interference of effector gene Mc16D10L confers resistance against Meloidogyne chitwoodi in diverse genetic backgrounds of potato and reduces pathogenicity of nematode offspring. Nematology 2014, 16, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jittayasothorn, Y.; Chronis, D.; Wang, X.; Cousins, P.; Zhong, G.Y. Molecular characteristics and efficacy of 16D10 siRNAs in inhibiting root-knot nematode infection in transgenic grape hairy roots. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Foster, J.M.; Nelson, L.S.; Ma, D.; Carlow, C.K. The chitin synthase genes chs-1 and chs-2 are essential for C. elegans development and responsible for chitin deposition in the eggshell and pharynx, respectively. Dev. Biol. 2005, 285, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bird, A.F.; Mcclure, M.A. The tylenchid (Nematoda) egg shell: Structure, composition and permeability. Parasitology 1976, 72, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brydon, L.J.; Gooday, G.W.; Chappell, L.H.; King, T.P. Chitin in egg shells of Onchocerca gibsoni and Onchocerca volvulus. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1987, 25, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, L.S.; Gamble, H.R.; Fetterer, R.H. Characterization of the eggshell of Haemonchus contortus—I. Structural components. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 1992, 103, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, A.F.; Self, P.G. Chitin in Meloidogyne javanica. Fundam. Appl. Nematol. 1995, 18, 235–239. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Wei, P.; Zhao, L.; Shi, Z.; Shen, Q.; Yang, M.; Xie, G.; Wang, S. Knockdown of five trehalase genes using RNA interference regulates the gene expression of the chitin biosynthesis pathway in Tribolium castaneum. BMC Biotechnol. 2016, 16, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McElroy, D.; Zhang, W.; Cao, J.; Wu, R. Isolation of an efficient actin promoter for use in rice transformation. Plant Cell 1990, 2, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benfey, P.N.; Chua, N.H. The cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter—Combinatorial regulation of transcription in plants. Science 1990, 250, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hershko, A. Ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 263, 15237–15240. [Google Scholar]
- Norris, S.R.; Meyer, S.E.; Callis, J. The intron of Arabidopsis thaliana polyubiquitin genes is conserved in location and is a quantitative determinant of chimeric gene expression. Plant Mol. Biol. 1993, 21, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzendorfer, H.; Zimoch, L. Chitin metabolism in insects: Structure, function and regulation of chitin synthases and chitinases. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 4393–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abad, P.; Gouzy, J.; Aury, J.M.; Castagnone-Sereno, P.; Danchin, E.G.; Deleury, E.; Perfus-Barbeoch, L.; Anthouard, V.; Artiguenave, F.; Blok, V.C.; et al. Genome sequence of the metazoan plant-parasitic nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Nat. Biotchnol. 2008, 26, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kamath, R.S.; Fraser, A.G.; Dong, Y.; Poulin, G.; Durbin, R.; Gotta, M.; Kanapin, A.; Le Bot, N.; Moreno, S.; Sohrmann, M.; et al. Systematic functional analysis of the Caenorhabditis elegans genome using RNAi. Nature 2003, 421, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsumasu, K.; Azuma, M.; Niimi, T.; Yamashita, O.; Yaginuma, T. Changes in the expression of soluble and integral-membrane trehalases in the midgut during metamorphosis in Bombyx mori. Zool. Sci. 2008, 25, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, A.; Vecchi, M.; Mandrioli, M.; Manicardi, G.C. The evolutionary history and functional divergence of trehalase (treh) genes in insects. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Jiang, Y.D.; An, X.; Yang, L.; Shang, F.; Niu, J.; Wang, J.J. Effects of RNAi-based silencing of chitin synthase gene on moulting and fecundity in pea aphids (Acyrthosiphon pisum). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fanelli, E.; Di Vito, M.; Jones, J.T.; De Giorgi, C. Analysis of chitin synthase function in a plant parasitic nematode, Meloidogyne artiellia, using RNAi. Gene 2005, 349, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.Y.; Merzendorfer, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Muthukrishnan, S. Biosynthesis, turnover, and functions of chitin in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Fosu-Nyarko, J.; Jone, M.G.K. Attempt to silence genes of the RNAi pathways of the root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita results in diverse response including increase and no change in expression of some genes. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fragoso, R.R.; Batista, J.A.; Grossi de Sá, M.F. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding a serine proteinase from the roo-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Exp. Parasitol. 2005, 110, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fragoso, R.R.; Lourenço, I.T.; Batista, J.A.; Oliveira-Neto, O.B.; Silva, M.C.; Rocha, T.L.; Coutinho, M.V.; Grossi-de-Sa, M.F. Meloidogyne incognita: Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding a cathepsin D–like aspartic proteinase. Exp. Parasitol. 2009, 121, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Song, X.S.; Li, H.P.; Cao, L.H.; Sun, K.; Qiu, X.L.; Xu, Y.B.; Yang, P.; Huang, T.; Zhang, J.B.; et al. Host-induced gene silencing of an essential chitin synthase gene confers durable resistance to Fusarium head blight and seedling blight in wheat. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 1335–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulovic, A.; Streit, A. RNAi-mediated knockdown of daf-12 in the model parasitic nematode Strongyloides ratti. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shingles, J.; Lilley, C.J.; Atkinson, H.J.; Urwin, P.E. Meloidogyne incognita: Molecular and biochemical characterization of a cathepsin L cysteine proteinase and the effect on parasitism following RNAi. Exp. Parasitol. 2007, 115, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Todd, T.C.; Oakley, T.R.; Lee, J.; Trick, H.N. Host-derived suppression of nematode reproductive and fitness gene decrease fecundity of Heterodera glycines Ichinohe. Planta 2010, 232, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Hahn, B.S. Expressed sequence tag analysis generated from a normalized full-length cDNA library of the root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne incognita). Genes Genom. 2010, 32, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.; Subramanian, P.; Shim, D.; Oh, B.J.; Hahn, B.S. RNA-Seq of Plant-parasitic nematode Meloidogyne incognita at various stages of its development. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, K.R.; Ausubel, F.M. Characterization of elicitor-induced defense responses in suspension-cultured cells of Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 1989, 2, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-DDCt method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsch, R.B.; Fry, J.E.; Hoffmann, N.; Eicholz, D.; Rogers, S.G.; Fraley, R.T. A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science 1985, 227, 1229–1231. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, J.; Liu, P.; Liu, Q.; Chen, C.; Guo, Q.; Yin, J.; Yang, G.; Jian, H. Msp40 effector of root-knot nematode manipulates plant immunity to facilitate parasitism. Sci. Rep. 2015, 6, 19443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basyony, A.G.; Abo-Zaid, G.A. Biocontrol of the root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita, using an eco-friendly formulation from Bacillus subtilis, lab. and greenhouse studies. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2018, 28, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| CS-F1-F | ATGGTTAAAGGCCCCTCAACTG |
| CS-F1-R | TTATAAAAAAACCTGTGACCACC |
| CS-F2-F | ATGGTTAAAGGCCCCTCAACTG |
| CS-F2-R | CTCATAAAGTTCTTGAAAAAGACC |
| CS-F3-F | AAATATGGCATGAGAAAGCTCAATC |
| CS-F3-R | ATTCGAAGAGGGCTTTCCTCAG |
| GPI-F1-F | ATGACTTCAACAATTACTGGTCTA |
| GPI-F1-R | TCAATCCTTGTAATTTTTAATTAAATTA |
| GPI-F2-F | ATGCCTGATGTTAATGCTGTTC |
| GPI-F2-R | TCAATCTTTGTAATTTTTAATTAAATT |
| GPI-F3-F | ATGCCTGATGTTAATGCTGTTC |
| GPI-F3-R | CGTATGGTGAAGACC TCCAC |
| TH1-F1-F | ATGCTTTATTATGTTGTTTCTTTGC |
| TH1-F1-R | TTAAAATACATTATTTAAATAAATTCTTT |
| TH1-F2-F | ATGCTTTATTATGTTGTTTCATTGC |
| TH1-F2-R | TCAATTCATATGCACCATTGGAG |
| TH1-F3-F | TAATTGAAGGCTTCCGTACCAG |
| TH1-F3-R | TTAAAATACATTATTTAAATAAATTCTTT |
| Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| Phos-gusf1 | ATGTTACGTCCTGTAGAAACCCC |
| Phos-gusr1 | TCATTGTTTGCCTCCCTGCTGC |
| RNAi UBQ1 F9 | cggaattcAGGTGCCAAATCTTTGATTGGAGTTG |
| RNAi UBQ1 R12 | aagcttCTTTTGTGTTTCGTCTTCTCTCACG |
| RNAi UBQ1 R13 | ggtaccctcgagaagcttCTTTTGTGTTTCGTCTTCTC |
| RNAi UBQ1 R14 | cggaattcggtaccctcgagaagcttCTTTTGTG |
| MCSF8 | CCGAGCTCGCCCAAGCTTACGCGTGGATCCCTGCAG |
| MCSR8 | CTGCAGGGATCCACGCGTAAGCTTGGGCGAGCTCGG |
| Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| pK7-F | TTTGCGGACTCTAGCATGGCCGCG |
| Int-R1 | CTTGAAAGTCAAATTGTCGAATTTG |
| Int-R2 | GATCGGTGTGATACAAAACCTAATC |
| UBQ-F | CCATCTTAGACTTAGCTAAGTTT |
| Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| Mi-actin F | TTATTCTTTCACCGCAACCG |
| Mi-actin R | TTGACCGTCAGGCAATTCAT |
| CS-F | CACTTGTGCCTTTCACTGTTTC |
| CS-R | TGATGGTAGACTTGCGGTAATG |
| GPI-F | TGGCCAATGGACTGGTTATAC |
| GPI-R | TTGAGTGCTTCAGTGACCATTA |
| TH1-F | CAGAAGGGTAAAGGACGATGTT |
| TH1-R | AACGACCACCAGGAATGATAAA |
| CS-RNAi-F | CGTATTTGGAGACCAAGCAAAG |
| CS-RNAi-R | ACACTGGATGGATACACGTAAA |
| GPI-RNAi-F | TACTCCAAATACATTGGGCTCTT |
| GPI-RNAi-R | GCTAATTGTTTGCCTAATTCAACAC |
| TH1-RNAi-F | CCCTGGACATGAACTACAAGAA |
| TH1-RNAi-R | CCCAACGCCGAAGTTGATA |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mani, V.; Reddy, C.S.; Lee, S.-K.; Park, S.; Ko, H.-R.; Kim, D.-G.; Hahn, B.-S. Chitin Biosynthesis Inhibition of Meloidogyne incognita by RNAi-Mediated Gene Silencing Increases Resistance to Transgenic Tobacco Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186626
Mani V, Reddy CS, Lee S-K, Park S, Ko H-R, Kim D-G, Hahn B-S. Chitin Biosynthesis Inhibition of Meloidogyne incognita by RNAi-Mediated Gene Silencing Increases Resistance to Transgenic Tobacco Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(18):6626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186626
Chicago/Turabian StyleMani, Vimalraj, Chinreddy Subramanyam Reddy, Seon-Kyeong Lee, Soyoung Park, Hyoung-Rai Ko, Dong-Gwan Kim, and Bum-Soo Hahn. 2020. "Chitin Biosynthesis Inhibition of Meloidogyne incognita by RNAi-Mediated Gene Silencing Increases Resistance to Transgenic Tobacco Plants" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 18: 6626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186626
APA StyleMani, V., Reddy, C. S., Lee, S.-K., Park, S., Ko, H.-R., Kim, D.-G., & Hahn, B.-S. (2020). Chitin Biosynthesis Inhibition of Meloidogyne incognita by RNAi-Mediated Gene Silencing Increases Resistance to Transgenic Tobacco Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(18), 6626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186626







