Novel Insights on the Corpus Luteum Function: Role of Vaspin on Porcine Luteal Cell Angiogenesis, Proliferation and Apoptosis by Activation of GRP78 Receptor and MAP3/1 Kinase Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
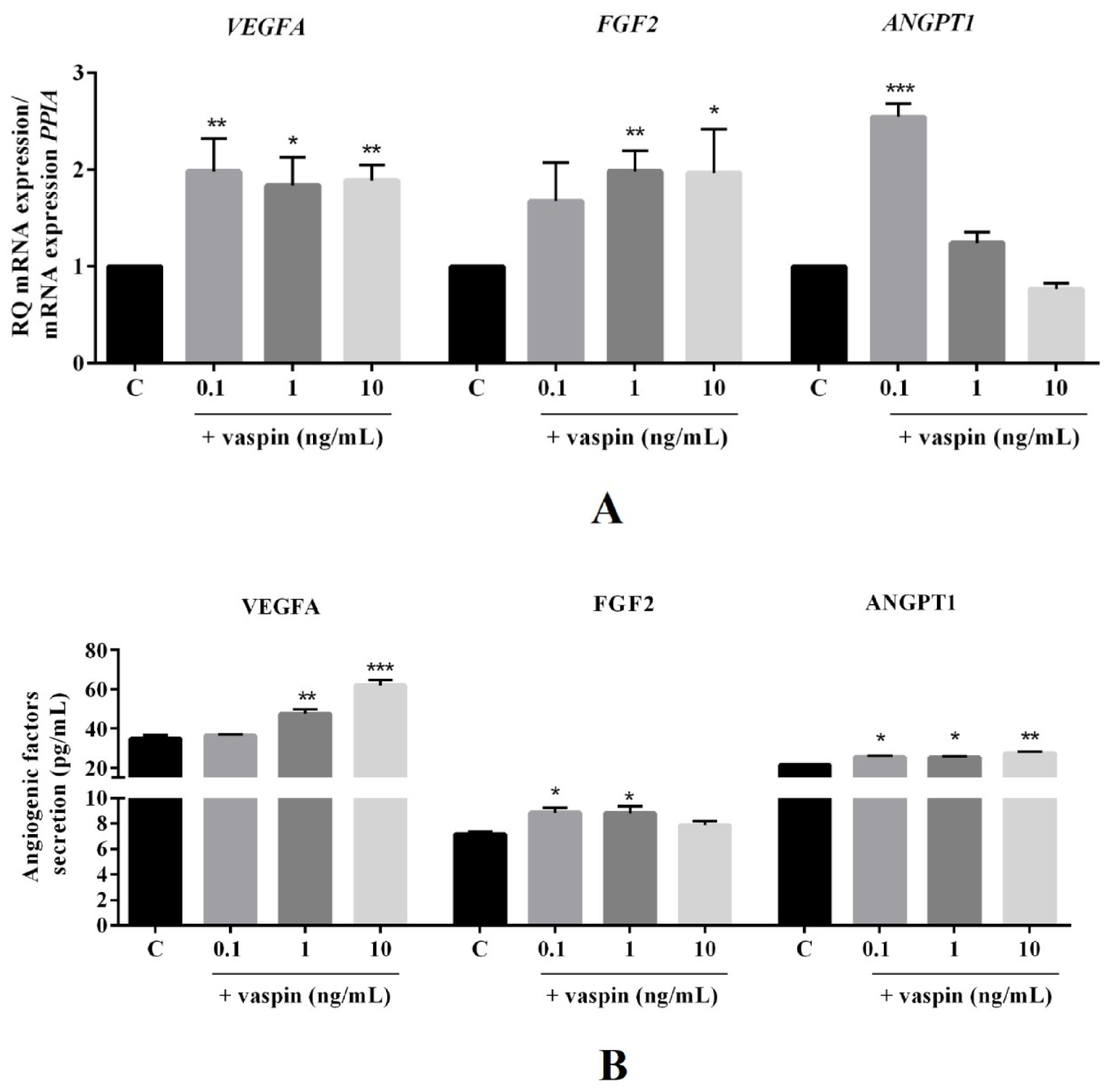
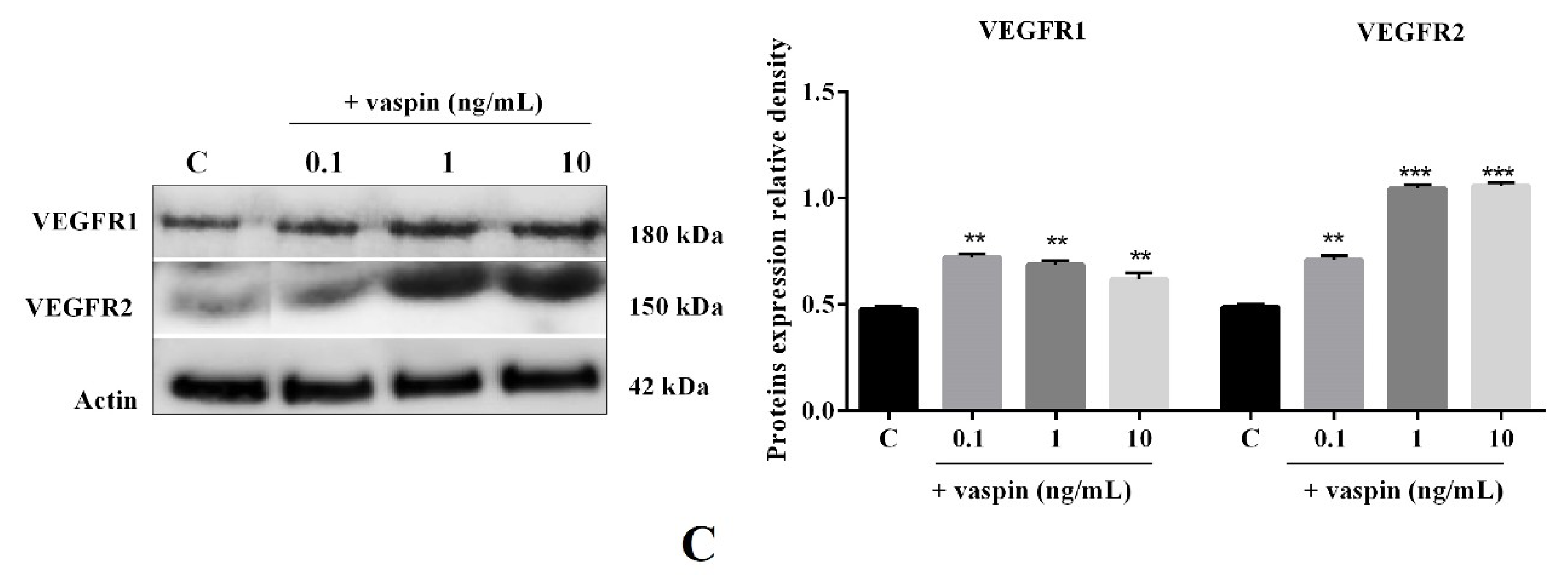
2.1. Dose-Dependent Effect of Vaspin on Luteal Cell Angiogenesis
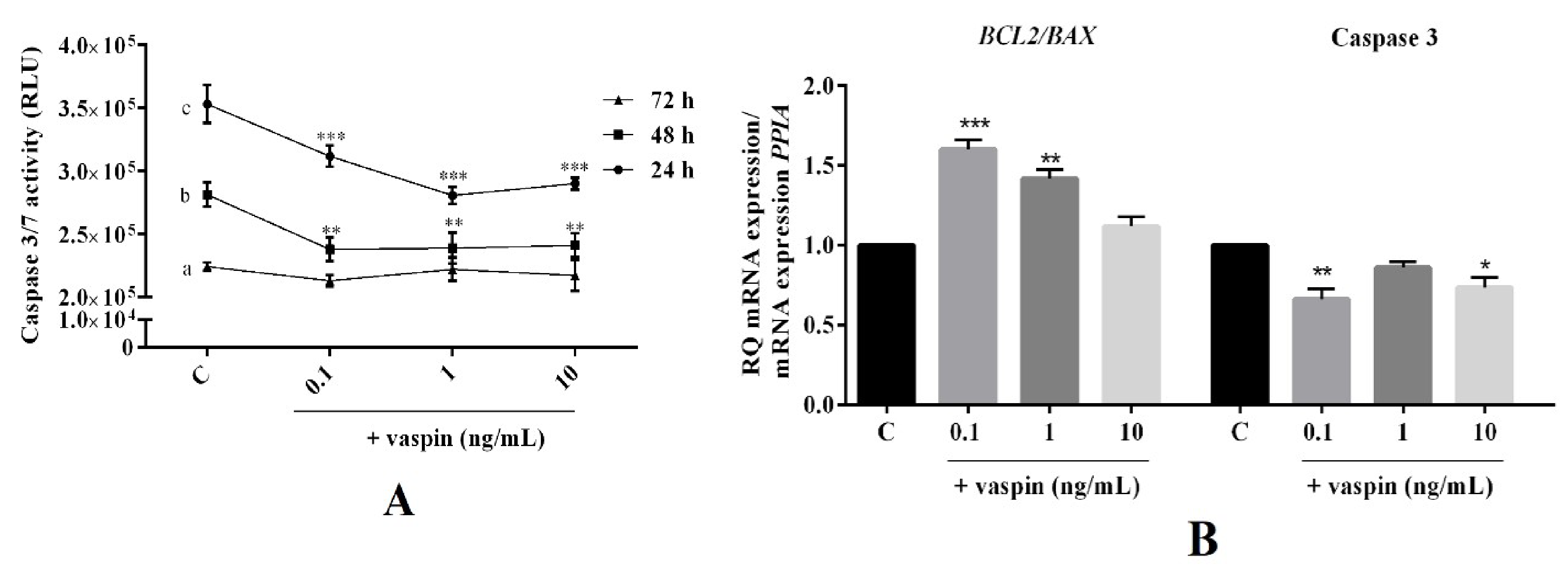
2.2. Dose- and Time-Dependent Effect of Vaspin on Luteal Cell Apoptosis
2.3. Dose- and Time-Dependent Effect of Vaspin on Luteal Cell Proliferation
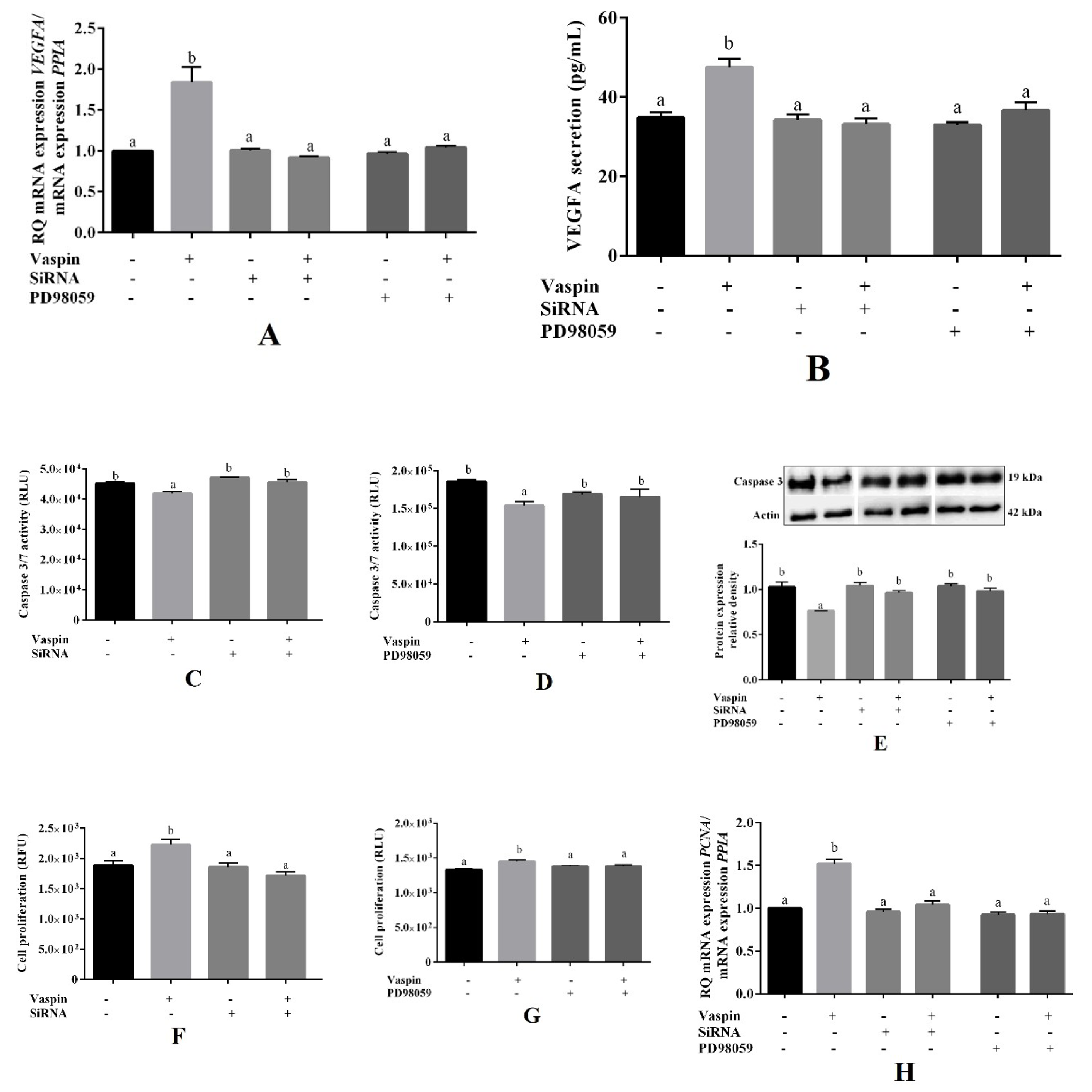
2.4. Involvement of the GRP78 Receptor and MAP3/1 Kinase in the Effects of Vaspin on Luteal Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Luteal Cells In Vitro Culture
Experimental Procedures
4.3. Gene Silencing
4.4. AlamarBlue Assay
4.5. Caspase-Glo 3/7 Assay
4.6. Real-Time PCR
4.7. Western Blot
4.8. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKT | protein kinase B |
| ANGPT1 | angiopoietin 1 |
| BAX | bcl-2-like protein 4 |
| BCL2 | B-cell lymphoma |
| C | control |
| CL | corpus luteum |
| E2 | estradiol |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| FGF2 | fibroblast growth factor 2 |
| GRP78 | 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein |
| MAP3/1 | mitogen activated kinase |
| OLETF | Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty |
| P4 | progesterone |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| PCNA | proliferating cells nuclear antigen |
| PGE2 | prostaglandin E2 |
| PGF2α | prostaglandin F2 alpha |
| PPIA | cyclophylin A |
| RFU | relative fluorescence units |
| RLU | relative luminescence units |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| SEM | standard error of mean |
| STAT3 | Janus kinase |
| VEGFA | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VEGFR1/2 | endothelial growth factor receptors |
References
- Stocco, C.; Telleria, C.; Gibori, G. The molecular control of corpus luteum formation, function, and regression. Endocr. Rev. 2007, 28, 117–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amsterdam, A.; Dantes, A.; Selvaraj, N.; Aharoni, D. Apoptosis in steroidogenic cells: Structure-function analysis. Steroids 1997, 62, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bopp, B.; Shoupe, D. Luteal phase defects. J. Reprod. Med. 1993, 38, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coomarasamy, A.; Williams, H.; Truchanowicz, E.; Seed, P.T.; Small, R.; Quenby, S.; Gupta, P.; Dawood, F.; Koot, Y.; Atik, R.B.; et al. A randomized trial of progesterone in women with recurrent miscarriages. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, L.P.; Redmer, D.A. Expression of the angiogenic factors, basic fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor, in the ovary. J. Anim. Sci. 1998, 76, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, F.; Rossant, J.; Yamaguchi, T.P.; Gertsenstein, M.; Wu, X.F.; Breitman, M.L.; Schuh, A.C. Failure of blood-island formation and vasculogenesis in Flk-1 deficient mice. Nature 1995, 376, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przygrodzka, E.; Witek, K.J.; Kaczmarek, M.M.; Andronowska, A.; Ziecik, A.J. Expression of factors associated with apoptosis in the porcine corpus luteum throughout the luteal phase of the estrous cycle and early pregnancy: Their possible involvement in acquisition of luteolytic sensitivity. Theriogenology 2015, 83, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Haldar, S. The relationship between BcI2, Bax and p53: Consequences for cell cycle progression and cell death. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 1998, 4, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.S.; Rueda, B.R.; Spanel-Borowski, K. Microvascular endothelial cells of the corpus luteum. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2003, 1, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montón, M.; Castilla, M.A.; Alvarez Arroyo, M.V.; Tan, D.; González-Pacheco, F.R.; López Farré, A.; Casado, S.; Caramelo, C. Effects of angiotensin II on endothelial cell growth: Role of AT-1 and AT-2 receptors. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1998, 9, 969–974. [Google Scholar]
- Pru, J.K.; Lynch, M.P.; Davis, J.S.; Rueda, B.R. Signaling mechanisms in tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced death of microvascular endothelial cells of the corpus luteum. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2003, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiles, J.R.; Katchko, R.A.; Benavides, E.A.; O’Gorman, C.W.; Escudero, J.M.; Keisler, D.H.; Stanko, R.L.; Garcia, M.R. The effect of leptin on luteal angiogenic factors during the luteal phase of the estrous cycle in goats. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2014, 148, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gregoraszczuk, E.Ł.; Ptak, A. In vitro effect of leptin on growth hormone (GH)- and insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I)-stimulated progesterone secretion and apoptosis in developing and mature corpora lutea of pig ovaries. J. Reprod. Dev. 2005, 51, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hida, K.; Wada, J.; Eguchi, J.; Zhang, H.; Baba, M.; Seida, A.; Hashimoto, I.; Okada, T.; Yasuhara, A.; Nakatsuka, A.; et al. Visceral adipose tissue-derived serine protease inhibitor: A unique insulin-sensitizing adipocytokine in obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10610–10615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klöting, N.; Kovacs, P.; Kern, M.; Heiker, J.T.; Fasshauer, M.; Schön, M.R.; Stumvoll, M.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G.; Blüher, M. Central vaspin administration acutely reduces food intake and has sustained blood glucose-lowering effects. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 1819–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Li, G.; Wu, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Han, W.; Lv, Y.; Sun, C. Vaspin promotes 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2015, 240, 1520–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wada, J. Vaspin: A novel serpin with insulin-sensitizing effects. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2008, 17, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Luo, C.; Liu, L.; Chuo, F.; Li, Q.; Sun, C. Higher vaspin levels in subjects with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 106, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, C.R.; Caminos, J.E.; Vázquez, M.J.; Garcés, M.F.; Cepeda, L.A.; Angel, A.; González, A.C.; García-Rendueles, M.E.; Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; López, M.; et al. Regulation of visceral adipose tissue-derived serine protease inhibitor by nutritional status, metformin, gender and pituitary factors in rat white adipose tissue. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 3741–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurowska, P.; Mlyczyńska, E.; Barbe, A.; Staub, C.; Gregoraszczuk, E.; Dupont, J.; Rak, A. Vaspin in the pig ovarian follicles: Expression and regulation by different hormones. Reproduction 2019, 158, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurowska, P.; Mlyczyńska, E.; Dawid, M.; Grzesiak, M.; Dupont, J.; Rak, A. The role of vaspin in porcine corpus luteum. J. Endocrinol. 2020. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Kukla, M.; Berdowska, A.; Gabriel, A.; Sawczyn, T.; Mazur, W.; Sobala-Szczygieł, B.; Grzonka, D.; Zajęcki, W.; Tomaszek, K.; Bułdak, R.J.; et al. Association between hepatic angiogenesis and serum adipokine profile in non-obese chronic hepatitis C patients. Pol. J. Pathol. 2011, 62, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakatsuka, A.; Wada, J.; Iseda, I.; Teshigawara, S.; Higashio, K.; Murakami, K.; Kanzaki, M.; Inoue, K.; Terami, T.; Katayama, A.; et al. Visceral adipose tissue-derived serine proteinase inhibitor inhibits apoptosis of endothelial cells as a ligand for the cell-surface GRP78/voltage-dependent anion channel complex. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurowska, P.; Mlyczyńska, E.; Dawid, M.; Opydo-Chanek, M.; Dupont, J.; Rak, A. In Vitro Effects of Vaspin on Porcine Granulosa Cell Proliferation, Cell Cycle Progression, and Apoptosis by Activation of GRP78 Receptor and Several Kinase Signaling Pathways Including MAP3/1, AKT, and STAT3. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arosh, J.A.; Banu, S.K.; Chapdelaine, P.; Madore, E.; Sirois, J.; Fortier, M.A. Prostaglandin biosynthesis, transport, and signaling in corpus luteum: A basis for autoregulation of luteal function. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 2551–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenbaum, D.; Colangelo, C.; Williams, K.; Gerstein, M. Comparing protein abundance and mRNA expression levels on a genomic scale. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koussounadis, A.; Langdon, S.P.; Um, I.H.; Harrison, D.J.; Smith, V.A. Relationship between differentially expressed mRNA and mRNA-protein correlations in a xenograft model system. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, E.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C. Inflammation and angiogenesis in the corpus luteum. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2019, 45, 1967–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, R.; LeCouter, J.; Kowalski, J.; Ferrara, N. Characterization of endocrine gland-derived vascular endothelial growth factor signaling in adrenal cortex capillary endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 8724–8729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamashita, H.; Kamada, D.; Shirasuna, K.; Matsui, M.; Shimizu, T.; Kida, K.; Berisha, B.; Schams, D.; Miyamoto, A. Effect of local neutralization of basic fibroblast growth factor or vascular endothelial growth factor by a specific antibody on the development of the corpus luteum in the cow. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2008, 75, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belair, D.G.; Khalil, A.S.; Miller, M.J.; Murphy, W.L. Serum-dependence of affinity-mediated VEGF release from biomimetic microspheres. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 2038–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stouffer, R.; Hennebold, J. Structure, Function, and Regulation of the Corpus Luteum. In Knobil and Neill’s Physiology of Reproduction, 4th ed.; Plant, T., Zeleznik, A., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 1023–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Zorrilla, L.M.; D’Annibale, M.A.; Swing, S.E.; Gadsby, J.E. Expression of genes associated with apoptosis in the porcine corpus luteum during the oestrous cycle. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2013, 48, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, M.R. Apoptosis in the ovary: Molecular mechanisms. Hum. Reprod. Update 2005, 11, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, M.D. Apoptosis: Bcl-2-related proteins get connected. Curr. Biol. 1997, 7, R277–R281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurki, P.; Ogata, K.; Tan, E.M. Monoclonal antibodies to proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)/cyclin as probes for proliferating cells by immunofluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry. J. Immunol. Methods 1988, 109, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruo, T.; Laoag-Fernandez, J.B.; Takekida, S.; Peng, X.; Deguchi, J.; Samoto, T.; Kondo, H.; Matsuo, H. Regulation of granulosa cell proliferation and apoptosis during follicular development. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 1999, 13, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoli, C.; Skotheim, J.M.; de Bruin, R.A. Control of cell cycle transcription during G1 and S phases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolesarova, A.; Capcarova, M.; Sirotkin, A.V.; Medvedova, M.; Kalafova, A.; Filipejova, T.; Kovacik, J. In vitro assessment of molybdenum-induced secretory activity, proliferation and apoptosis of porcine ovarian granulosa cells. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard Subst. Environ. Eng. 2011, 46, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, B.R.; Hendry, I.R.; Hendry, W.J., III; Stormshak, F.; Slayden, O.D.; Davis, J.S. Decreased progesterone levels and progesterone receptor antagonists promote apoptotic cell death in bovine luteal cells. Biol. Reprod. 2000, 62, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rak, A.; Drwal, E.; Wróbel, A.; Gregoraszczuk, E.Ł. Resistin is a survival factor for porcine ovarian follicular cells. Reproduction 2015, 150, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ke, X.; Hao, Y.; Li, B.; Zou, J.; Li, X.; Wei, C.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z. Vaspin Prevents Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Induced Apoptosis in Cardiomyocytes by Promoting Autophagy. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2018, 77, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, B.; Huang, H.; Lv, J.; Hu, S.; Shen, J. Vaspin protects mouse mesenchymal stem cells from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis through the MAPK/p38 pathway. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2019, 462, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Shan, P.F.; Shen, J.; Liang, Q.H.; Cui, R.R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G.Y.; Wu, S.S.; Lu, Q.; et al. Vaspin attenuates the apoptosis of human osteoblasts through ERK signaling pathway. Amino Acids 2013, 44, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C. Roles of Grp78 in Female Mammalian Reproduction. Adv. Anat. Embryol. Cell Biol. 2017, 222, 129–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Gong, L.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Zheng, Z. Diosgenin inhibits tumor angiogenesis through regulating GRP78-mediated HIF-1α and VEGF/VEGFR signaling pathways. Pharmazie 2019, 74, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurowska, P.; Mlyczyńska, E.; Dawid, M.; Dupont, J.; Rak, A. Role of vaspin in porcine ovary: Effect on signaling pathways and steroid synthesis via GRP78 receptor and protein kinase A†. Biol. Reprod. 2020, 102, 1290–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagnol, S.; Chambard, J.C. ERK and cell death: Mechanisms of ERK-induced cell death—apoptosis, autophagy and senescence. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rak, A.; Drwal, E.; Rame, C.; Knapczyk-Stwora, K.; Słomczyńska, M.; Dupont, J.; Gregoraszczuk, E.L. Expression of apelin and apelin receptor (APJ) in porcine ovarian follicles and in vitro effect of apelin on steroidogenesis and proliferation through APJ activation and different signaling pathways. Theriogenology 2017, 96, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoraszczuk, E. Steroid hormone release in cultures of pig corpus luteum and granulosa cells: Effect of LH, hCG, PRL and estradiol. Endocrinol. Exp. 1983, 17, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Rak-Mardyła, A.; Gregoraszczuk, E.L.; Karpeta, A.; Duda, M. Expression of ghrelin and the ghrelin receptor in different stages of porcine corpus luteum development and the inhibitory effects of ghrelin on progesterone secretion, 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3β-honestly significant difference (HSD)) activity and protein expression. Theriogenology 2012, 77, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Yang, S.G.; Jung, J.M.; Kim, M.J.; Park, J.J.; Koo, D.B. Regulation of the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress by BIP/GRP78 is involved in Meiotic Maturation of Porcine Oocytes In Vitro. Dev. Reprod. 2017, 21, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Antibody | Host | Dilution | Vendor |
|---|---|---|---|
| VEGFR1 | rabbit | 1:250 | Abcam, GB, product no. ab2350 |
| VEGFR2 | rabbit | 1:250 | Abcam, GB, product no. ab45010 |
| caspase 3 | rabbit | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling Technology, USA, product no. 9662S |
| BCL2 | rabbit | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling Technology, USA, product no. 4223S |
| BAX | rabbit | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling Technology, USA, product no. 2772S |
| cyclin A | mouse | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling Technology, USA, product no. 4656S |
| PCNA | mouse | 1:250 | ThermoFisher Scientific, USA, product no. 13-3900 |
| actin | mouse | 1:5000 | Sigma-Aldrich, USA, product no. A5316 |
| anti-rabbit | goat | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling Technology, USA, product no. 7074 |
| anti-mouse | horse | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling Technology, USA, product no. 7076 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kurowska, P.; Mlyczyńska, E.; Dupont, J.; Rak, A. Novel Insights on the Corpus Luteum Function: Role of Vaspin on Porcine Luteal Cell Angiogenesis, Proliferation and Apoptosis by Activation of GRP78 Receptor and MAP3/1 Kinase Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6823. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186823
Kurowska P, Mlyczyńska E, Dupont J, Rak A. Novel Insights on the Corpus Luteum Function: Role of Vaspin on Porcine Luteal Cell Angiogenesis, Proliferation and Apoptosis by Activation of GRP78 Receptor and MAP3/1 Kinase Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(18):6823. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186823
Chicago/Turabian StyleKurowska, Patrycja, Ewa Mlyczyńska, Joelle Dupont, and Agnieszka Rak. 2020. "Novel Insights on the Corpus Luteum Function: Role of Vaspin on Porcine Luteal Cell Angiogenesis, Proliferation and Apoptosis by Activation of GRP78 Receptor and MAP3/1 Kinase Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 18: 6823. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186823
APA StyleKurowska, P., Mlyczyńska, E., Dupont, J., & Rak, A. (2020). Novel Insights on the Corpus Luteum Function: Role of Vaspin on Porcine Luteal Cell Angiogenesis, Proliferation and Apoptosis by Activation of GRP78 Receptor and MAP3/1 Kinase Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(18), 6823. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186823






