Abstract
Clusterin (CLU) is one of the risk genes most associated with late onset Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and several genetic variants in CLU are associated with AD risk. However, the functional role of known AD risk genetic variants in CLU has been little explored. We investigated the effect of an AD risk variant (rs7982) in the 5th exon of CLU on alternative splicing by using an integrative approach of brain-tissue-based RNA-Seq and whole genome sequencing data from Accelerating Medicines Partnership—Alzheimer’s Disease (AMP-AD). RNA-Seq data were generated from three regions in the temporal lobe of the brain—the temporal cortex, superior temporal gyrus, and parahippocampal gyrus. The rs7982 was significantly associated with intron retention (IR) of the 5th exon of CLU; as the number of alternative alleles (G) increased, the IR rates decreased more significantly in females than in males. Our results suggest a sex-dependent role of rs7982 in AD pathogenesis via splicing regulation.
1. Introduction
Alternative splicing (AS) is associated with many neurodegenerative disorders, including AD [1,2,3], and many genetic variants that contribute to diseases affect splicing regulation [4]. Accumulating evidence further suggests that AD susceptibility variants may affect alternative splicing [5].
CLU (clusterin) is associated with AD and is known to influence the neurotoxic effects of Aβ deposition [6,7]. CLU is largely regulated by AS mechanisms [3,8]. Most importantly, CLU may be a factor that contributes to greater AD vulnerability in females, suggesting that risk variants of CLU could have sex-specific effects [9]. While gene-level expression represents the sum of all isoform expression, an AS study explores isoform-level expression. Indeed, spliced isoforms can be affected by SNPs located in a gene body (i.e., in exons and introns), with those effects being connected to the binding affinity of splicing factors for the RNA. Thus, rather than overall gene expression, the expression ratio of CLU isoforms may provide new additional insights into the functional analysis of associated SNPs. However, the functional effects of known AD risk loci in CLU on alternative splicing remain largely unexplored.
One such variant, rs7982, is located within the 5th exon of CLU; an alternative splicing event divides this exon into two parts separated by a short intron [6]. Retention of this intron as part of the 5th exon encodes a cleavage site [10]. Therefore, we investigated a sex-specific functional role of rs7982 in AS regulation using brain-tissue-based RNA-sequencing (RNA-Seq) and whole genome sequencing (WGS) data from two independent cohorts.
2. Results
2.1. Regulatory Function of rs7982 in Splicing
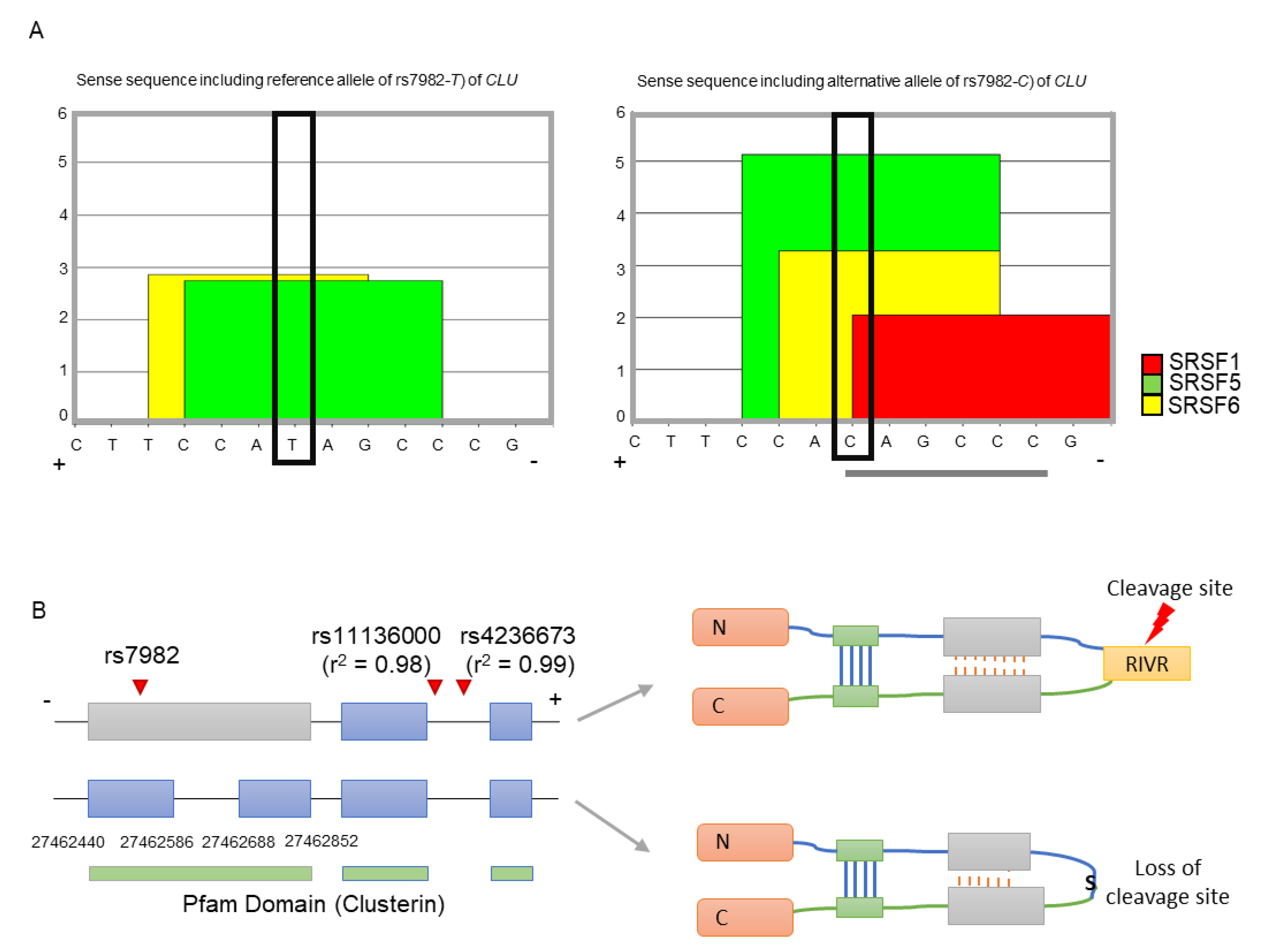
As CLU is a minus-stranded gene, we used the sense sequence of CLU (i.e., the reference allele is T and alternative allele is C) for the splicing regulatory element (SRE) and splicing binding site analyses (see Methods and Materials). We found that the only alternative allele (C, major) of rs7982 has exonic splicing enhancer (ESE) hexamers, namely CAGCCC (Figure 1A). Furthermore, the C allele corresponded to the binding motifs of three splicing factors (SRSF5, SRSF6, and SRSF1), while the T allele contributed to a motif for two splicing factors (SRSF5 and SRSF6) (Figure 1A). Furthermore, the binding affinities of SRSF5 and SRSF6 are greater in the alternative allele C than the reference allele T. This suggests that even though both may form splicing enhancers, the alternative allele may constitute the stronger enhancer. Therefore, rs7982G may promote alternative splicing, specifically division of the 5th exon of CLU. Transcripts without the retained intron may be dysfunctional due to loss of a functional cleavage site, RIVR (Arg-Ile-Val-Arg) (Figure 1B).
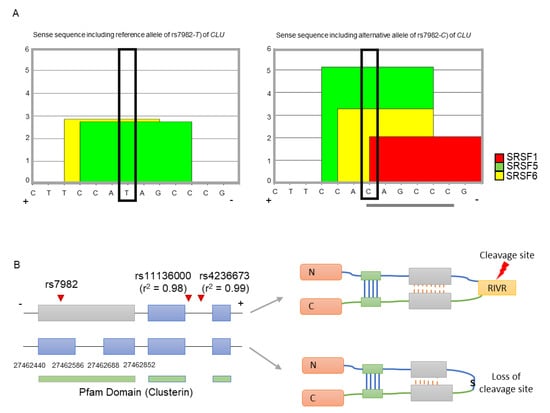
Figure 1.
Splicing modulation and functional impact of rs7982. (A) The reference allele (T) is involved in two binding motif, SRSF5 and SRSF6 (left figure), while the alternative allele (C) is involved in three motifs, SRSF1, SRSF5, and SRSF6 (right figure). Gray lines underneath indicate each hexameric exonic splicing enhancer (ESE) sequence. The black box indicates allele rs7982 in the binding motif. (B) The SNP is located in the 5th exon of CLU. Isoforms retaining the intron (upper transcript) are translated into normally functioning proteins containing the RIVR (Arg-Ile-Val-Arg) sequence, which is part of a key cleavage site; isoforms without the retained intron (lower transcript) produce dysfunctional proteins lacking the cleavage site. The + and – refers a DNA strand as a template. N and C is the N-terminal and C-terminal domain respectively. S indicates serine amino acid.
2.2. Association of Intron Retention (IR) with rs7982
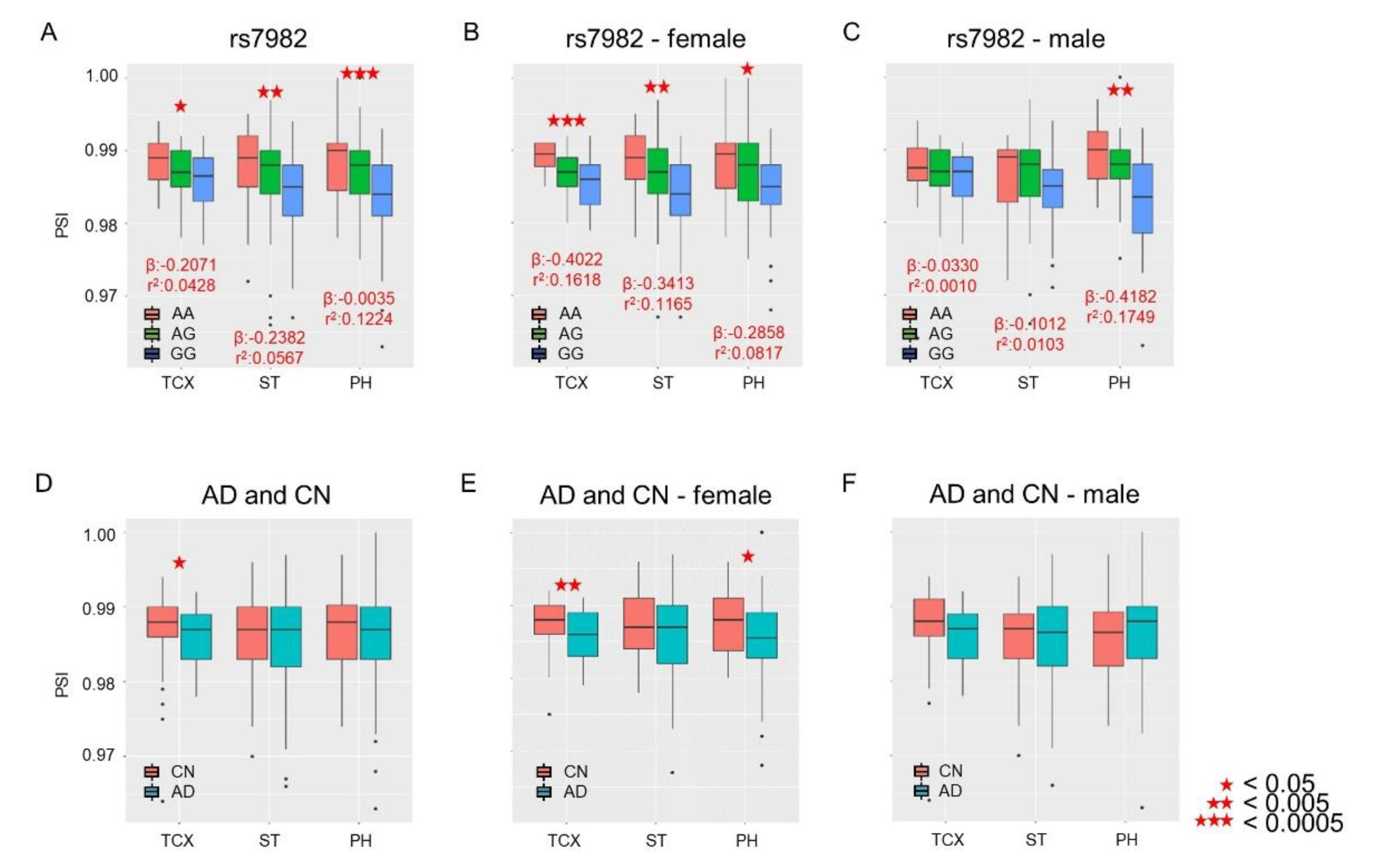
We performed splicing quantitative trait loci (sQTLs) analysis to evaluate the associations of percent-spliced-in (PSI) from the 5th exon of CLU with the rs7982 genotype and of AD diagnosis with sex as a covariate. Significant associations between PSI and rs7982 were observed in all three brain regions (Figure 2A; temporal cortex (TCX): p = 1.02 × 10−2; superior temporal gyrus (ST): p = 2.34 × 10−3; and Parahippocampal gyrus (PH): p = 7.03 × 10−6). IR rates decreased as the number of G alleles increased (Figure 2A). Lower IR levels were also observed in AD in the TCX but not ST and PH regions (Figure 2D; TCX: p = 0.041, OR = 0.88; ST: p = 0.369, OR = 0.92; and PH: p = 0.549, OR = 0.93).
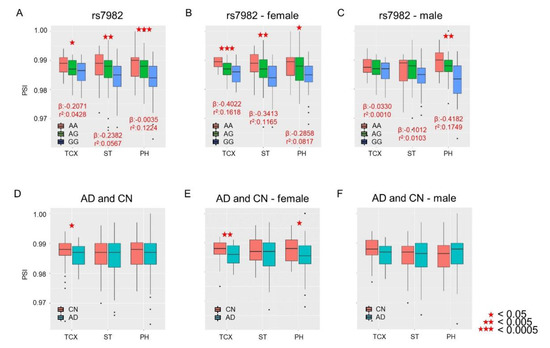
Figure 2.
Associations of PSI levels of the 5th exon of CLU with rs7982 and AD diagnosis. The X-axis represents temporal lobe regions: temporal cortex (TCX), superior temporal gyrus (ST), and Parahippocampal gyrus (PH). The Y-axis represents the PSI level, i.e., rate of intron retention (IR). Top: Association of IR with the rs7982 genotype as a continuous variable, with the numbers of alternative alleles (i.e., AA = 0, AG = 1, GG = 2) tallied for all samples (A): females only (B); males only (C). Bottom: Association of IR with AD (cognitively normal older adults (CN) vs. AD) for all samples (D): females only (E); males only (F). Black dots indicate outliers.
2.3. Sex-Dependent Association of IR with rs7982
We examined whether sex is a potential biological factor in rs7982-modulated IR and whether there is an effect of an interaction between rs7982 and sex on IR. Our analysis identified no significant sex-by-rs7982 interaction (TCX: p = 0.10; ST: p = 0.25; PH: p = 0.48). However, in female participants, IR was associated with rs7982 in all three brain regions (TCX: p = 1.90 × 10−4; ST: p = 9.91 × 10−4; PH: p = 5.74 × 10−3, Figure 2B); in male participants, IR was associated with rs7982 only in PH (TCX: p = 0.762; ST: p = 0.401; PH: p = 5.26 × 10−4, Figure 2C). In addition, female AD patients had less intron retention in TCX and PH regions (TCX: p = 9.10 × 10−3; ST: p = 0.165; PH: p = 0.042, Figure 2E), while male participants demonstrated no difference in IR rates in any of the three temporal lobe regions (TCX: p = 0.260; ST: p = 0.785; PH: p = 0.625, Figure 2F).
3. Discussion
Here, we functionally annotated rs7982, a SNP within the 5th exon of CLU that is associated with AD and Aβ accumulation. Of the seven exons in CLU that encode clusterin domains, only the 5th exon undergoes alternative splicing (i.e., intron retention), conferring a key part of a cleavage site. The full-length mRNA of CLU is translated into extracellular secreted CLU (sCLU), while other shorter mRNAs generate intracellular forms (iCLU). A recent study showed that mutations in the 5th exon reduced the sCLU protein and increased iCLU protein [11], and even an absence of the 5th exon tends to be associated with an increased generation of iCLU form [11,12]. However, the function of CLU in AD pathology is controversial. Unlike the protective effect associated with a higher extracellular clusterin concentration (sCLU), iCLU is related to cell cytotoxicity, which may be involved in AD progression through interactions with tau and BIN1 [11,13]; that is, an rs7982G-dependent alternative splicing event may be implicated in AD by affecting the subcellular CLU localization, whose iCLU form is involved in AD progression generated via a partial loss (i.e., less intron retention) of the 5th exon.
We showed a significant sex-dependent association of rs7982 with IR levels in three temporal lobe regions, suggesting that rs7982 may be an important factor underlying AD susceptibility by modulation of IR in the 5th exon of CLU. Interestingly, we observed that rs7982 might have a sex-specific effect on IR levels, with IR showing a significantly greater decrease in female AD patients relative to cognitively normal older adults (CN). This difference was significant in two brain regions (TCX and PH; cohort-independent difference), and although not significant in ST, the same tendency was observed. Notably, the alternative splicing event is tissue-dependent, and these events are associated with brain site-specific functions, meaning that splicing may contribute to generating an mRNA isoform that is translated into a protein version specific to the brain site [14,15,16,17]. Therefore, this observation may need to be replicated with a larger sample size and to be validated with further experimental study to investigate why such intron retention is regulated to be brain-region-specific and to discover the underlying mechanism.
The sample size of females is larger than that of males, as shown in Table S1. This difference in the sample size between male and female groups may lead to differing statistical power. However, such a difference in sample sizes between groups may not be a bias in our study, as the sex-dependent effect of rs7982 was much stronger when examining a comparison of the similar sizes between females and males in TCX (Figure 2). Moreover, the sample sizes of both groups in the CN group were similar for each brain region (Table S1). The significant effect of rs7982 in the female CN group was replicated in two similar brain regions, TCX and ST (Figure S1B,E), while the significant effect of rs7982 was not replicated in the CN male group (Figure S1C,F). For AD cases, we observed similar results. In addition, the standardized beta and r2 values were higher in females than males in three sample groups, namely CN only (Figure S1), AD only (Figure S2), and CN and AD together (Figure 2). Therefore, we believe that this sex-dependent functional effect of rs7982 may not be due to the difference in sample sizes between sexes. Additionally, we evaluated the potential presence of baseline genotype differences between groups, such as the AD male and AD female groups (Table S2), and none of these comparisons showed a statistical difference (see Materials and Methods and Table S3). CLU is considered a factor for increased amyloid dyshomeostasis associated with the earliest female brain transition, providing a mechanistic rationale that the female brain is more vulnerable to AD [9].
Our finding in CLU is consistent with the sex-dependency of AD and provides a molecular basis for understanding mechanisms underlying the functional association of risk variants with AD pathogenesis. Notably, rs7982 is in strong linkage disequilibrium with the well-known AD susceptibility SNPs rs11136000 (r2 = 0.98) [6] and rs4236673 (r2 = 0.99) [18]. Our results may, therefore, indirectly explain other AD-associated variation. It is well-known that SNPs located within a given AS exon and its flanking introns are likely to be able to affect AS regulation. Thus, AS of the 5th exon could be regulated by rs7982, which is located in that exon. In addition, there is evidence that the haplotypes of these SNPs (GCG and ATC; rs7982, rs11136000, and rs933188, respectively) are related to amyloid beta deposition, thereby influencing the risk of AD in vivo [19]. Thus, there is a possibility that these SNPs have a haplotype-based effect on splicing [20].
There are seven known AD-associated SNPs in CLU, according to a previous study [19]. We summarized their minor allele frequencies (Figure S3). As mentioned above, rs7982 is in strong linkage disequilibrium (LD) with rs11136000 and rs4236673, and the minor allele frequencies of those SNPs were greater than those of the other AD-associated SNPs in CLU.
Since there is a possibility that our results concerning the splicing rate may be dependent on the analysis method used, we repeated our integrative analysis using another method, MISO, to define and calculate the splicing rate (PSI) based on the Bayesian approach [21]; this method yielded the same results (Figure S4).
We evaluated the ability of rs7982 to enhance a splicing event (less intron retention) within the 5th exon of CLU using two different splicing-regulation-related datasets: (1) cis-acting regulatory elements, i.e., ESEs; (2) SR splicing factor binding motifs. Both showed consistent indications that the rs7982G allele may increase splicing within the 5th exon of CLU. In addition, we analyzed RNA-Seq data generated from three temporal lobe regions in two independent cohorts and identified consistent associations across them. In other words, we integrated RNA-Seq and WGS data to present a priori knowledge- and data-driven evidence that rs7982G (risk allele) tends to elevate AS efficiency (less intron retention). Consistently, decreased IR (loss of functional exon regions) was observed in AD.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. RNA-Seq and WGS Analysis
We downloaded RNA-Seq (BAM files) and WGS data (VCF files) from the Synapse database (www.synapse.org). Data were generated from two independent cohorts in the Accelerating Medicines Partnership–Alzheimer’s Disease (AMP-AD) project: the Mayo Clinic Brain Bank [22] and the Mount Sinai Brain Bank (MSBB) [23]. The participant demographics and included brain regions are described in Table S1. RNA-Seq data were generated from three regions in the temporal lobes of CN and AD patients: TCX, ST, and PH. We converted the binary version of the Sequence Alignment/Map (SAM) file (BAM) files into FASTQ files, then mapped the reads to the human reference genome (GRCh37.75) using STAR [24]. We identified AS events and quantified their incidences as the PSI, the fraction of mRNAs including an AS exon, using rMATs [25].
4.2. Implication of rs7982 in Splicing Regulation
First, we investigated whether the synonymous variant rs7982 in the 5th exon of CLU was located within a splicing regulatory element (SRE, i.e., ESE or exonic splicing silencer (ESS) [26]), a hexameric regulatory sequence in an exonic region. We scanned the surrounding sequence for SREs according to our previously published method [26]. Second, using ESEfinder, we determined whether rs7982 coincided with any splicing factor binding motifs. Because CLU is transcribed into minus-stranded RNA, we used the sense sequence (i.e., reverse complimentary sequence of reference DNA sequence) of CLU exon 5 (Table S4) in the SRE and splicing binding motif analyses. We compared the surrounding sequence against a database of nucleotide frequency matrices for SR family proteins generated from in vitro tests [27].
4.3. Statistical Analysis
We determined allele-specific associations of rs7982 with AS levels (PSI) for each brain region using linear regression with respect to the genotype of rs7982 as a continuous variable, tallying the numbers of alternative alleles (i.e., AA = 0, AG = 1, GG = 2). We then compared PSI values between CN and AD groups by logistic regression, including sex as a covariate. We performed parametric t-tests to compare PSI values between CN and AD in each sex group. In addition, we performed ANOVA to evaluate the effect of an interaction between sex and rs7982 on PSI values. We further performed a 2 × 2 Chi-square test on the minor allele frequency to evaluate baseline genotype differences between groups (i.e., AD male vs. AD female, CN male vs. CN female, AD male vs. CN male, and AD female vs. CN female).
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we present new insights into the molecular mechanism of action for rs7982 in CLU, which potentially acts as a sex-dependent AD risk factor via alternative splicing.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Materials can be found at https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/19/7079/s1.
Author Contributions
S.H., K.N., and Y.L. were involved in the conception and design of the study. All authors were involved in data collection and statistical analyses. All authors prepared all figures and tables and wrote the manuscript. K.N. and Y.L. supervised the study overall. All of the authors approved the final manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by development funding for Younghee Lee from the Department of Biomedical Informatics, University of Utah School of Medicine, RAG063250A, R03 AG063250, R03 AG054936, and R01 LM012535. This research was also supported by the Collaborative Genome Program for Fostering New Post-Genome Industry of the National Research Foundation (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) (NRF-2017M3C9A6047623), and the MSIT under the Information Technology Research Center (ITRC) support program (IITP-2018-2018-0-01833), supervised by the Institute for Information and Communications Technology Promotion (IITP).
Acknowledgments
The support and resources from the Center for High-Performance Computing and Vice President’s Clinical and Translational Research Scholar Program at the University of Utah are gratefully acknowledged. The results published here are in whole or in part based on data obtained from the AMP-AD Knowledge Portal (doi:10.7303/syn2580853). Study data were provided by the following sources: The Mayo Clinic Alzheimer’s Disease Genetic Studies, led by Nilufer Taner and Steven G. Younkin, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL using samples from the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging, the Mayo Clinic Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center, and the Mayo Clinic Brain Bank. Data collection was supported through funding by NIA grants P50 AG016574, R01 AG032990, U01 AG046139, R01 AG018023, U01 AG006576, U01 AG006786, R01 AG025711, R01 AG017216, R01 AG003949, NINDS grant R01 NS080820, the CurePSP Foundation, and support from the Mayo Foundation. Study data include samples collected through the Sun Health Research Institute Brain and Body Donation Program of Sun City, Arizona. The Brain and Body Donation Program is supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (U24 NS072026 National Brain and Tissue Resource for Parkinson’s Disease and Related Disorders), the National Institute on Aging (P30 AG19610 Arizona Alzheimer’s Disease Core Center), the Arizona Department of Health Services (contract 211002, Arizona Alzheimer’s Research Center), the Arizona Biomedical Research Commission (contracts 4001, 0011, 05-901, and 1001 to the Arizona Parkinson’s Disease Consortium), and the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research. The results published here are in whole or in part based on data obtained from the AMP-AD Knowledge Portal (doi:10.7303/syn2580853). These data were generated from post-mortem brain tissue collected through the Mount Sinai VA Medical Center Brain Bank and were provided by Eric Schadt from Mount Sinai School of Medicine.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| TCX | Temporal cortex |
| ST | Superior temporal gyrus |
| PH | Parahippocampal gyrus |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| AMP-AD | Accelerating Medicines Partnership–Alzheimer’s Disease |
| ESE | Exon skipping enhancer |
| IR | Intron retention |
| AS | Alternative splicing |
| sQTLs | Splicing quantitative trait loci |
References
- Buee, L.; Bussiere, T.; Buee-Scherrer, V.; Delacourte, A.; Hof, P.R. Tau protein isoforms, phosphorylation and role in neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Res. Rev. 2000, 33, 95–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockenstein, E.M.; McConlogue, L.; Tan, H.; Power, M.; Masliah, E.; Mucke, L. Levels and alternative splicing of amyloid beta protein precursor (APP) transcripts in brains of APP transgenic mice and humans with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 28257–28267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koch, L. Altered splicing in Alzheimer transcriptomes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 738–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.S.; Cooper, T.A. Splicing in disease: Disruption of the splicing code and the decoding machinery. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, T.; Li, Y.I.; Wong, G.; Humphrey, J.; Wang, M.; Ramdhani, S.; Wang, Y.C.; Ng, B.; Gupta, I.; Haroutunian, V.; et al. Integrative transcriptome analyses of the aging brain implicate altered splicing in Alzheimer’s disease susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harold, D.; Abraham, R.; Hollingworth, P.; Sims, R.; Gerrish, A.; Hamshere, M.L.; Pahwa, J.S.; Moskvina, V.; Dowzell, K.; Williams, A.; et al. Genome-Wide association study identifies variants at CLU and PICALM associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.T.; Tan, L. The role of clusterin in Alzheimer’s disease: Pathways, pathogenesis, and therapy. Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 45, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymanski, M.; Wang, R.; Bassett, S.S.; Avramopoulos, D. Alzheimer’s risk variants in the clusterin gene are associated with alternative splicing. Transl. Psychiatry 2011, 1, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Mao, Z.; Woody, S.K.; Brinton, R.D. Sex differences in metabolic aging of the brain: Insights into female susceptibility to Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 42, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohne, P.; Prochnow, H.; Wolf, S.; Renner, B.; Koch-Brandt, C. The chaperone activity of clusterin is dependent on glycosylation and redox environment. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 1626–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettens, K.; Vermeulen, S.; Van Cauwenberghe, C.; Heeman, B.; Asselbergh, B.; Robberecht, C.; Engelborghs, S.; Vandenbulcke, M.; Vandenberghe, R.; De Deyn, P.P.; et al. Reduced secreted clusterin as a mechanism for Alzheimer-associated CLU mutations. Mol. Neurodegener. 2015, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, K.; Yamamoto, M. Modification of the alternative splicing process of testosterone-repressed prostate message-2 (TRPM-2) gene by protein synthesis inhibitors and heat shock treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1307, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hayashi, I.; Wong, J.; Tugusheva, K.; Renger, J.J.; Zerbinatti, C. Intracellular clusterin interacts with brain isoforms of the bridging integrator 1 and with the microtubule-associated protein Tau in Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyn-Vanhentenryck, S.M.; Feng, H.; Ustianenko, D.; Duffie, R.; Yan, Q.; Jacko, M.; Martinez, J.C.; Goodwin, M.; Zhang, X.; Hengst, U.; et al. Precise temporal regulation of alternative splicing during neural development. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.H.; Tarn, W.Y. Alternative Splicing in Neurogenesis and Brain Development. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, J.M.E.; Kim, Y.; von Jonquieres, G.; Housley, G.D. Human Brain Region-Specific Alternative Splicing of TRPC3, the Type 3 Canonical Transient Receptor Potential Non-Selective Cation Channel. Cerebellum 2019, 18, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, B.; Blencowe, B.J. Alternative Splicing in the Mammalian Nervous System: Recent Insights into Mechanisms and Functional Roles. Neuron 2015, 87, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, I.; Savage, J.; Watanabe, K.; Bryois, J.; Williams, D.; Steinberg, S.; Sealock, J.; Karlsson, I.; Hagg, S.; Athanasiu, L.; et al. Genetic meta-analysis identifies 10 novel loci and functional pathways for Alzheimer’s disease risk. bioRxiv 2018, 258533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Wang, H.F.; Tan, M.S.; Tan, C.C.; Zhu, X.C.; Miao, D.; Yu, W.J.; Jiang, T.; Tan, L.; Yu, J.T.; et al. Effect of CLU genetic variants on cerebrospinal fluid and neuroimaging markers in healthy, mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease cohorts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kralovicova, J.; Houngninou-Molango, S.; Kramer, A.; Vorechovsky, I. Branch site haplotypes that control alternative splicing. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 3189–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, Y.; Wang, E.T.; Airoldi, E.M.; Burge, C.B. Analysis and design of RNA sequencing experiments for identifying isoform regulation. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.; Carrasquillo, M.M.; Funk, C.; Heavner, B.D.; Zou, F.; Younkin, C.S.; Burgess, J.D.; Chai, H.S.; Crook, J.; Eddy, J.A.; et al. Human whole genome genotype and transcriptome data for Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Beckmann, N.D.; Roussos, P.; Wang, E.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Q.; Ming, C.; Neff, R.; Ma, W.; Fullard, J.F.; et al. The Mount Sinai cohort of large-scale genomic, transcriptomic and proteomic data in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Park, J.W.; Lu, Z.X.; Lin, L.; Henry, M.D.; Wu, Y.N.; Zhou, Q.; Xing, Y. rMATS: Robust and flexible detection of differential alternative splicing from replicate RNA-Seq data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E5593–E5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Gamazon, E.R.; Rebman, E.; Lee, Y.; Lee, S.; Dolan, M.E.; Cox, N.J.; Lussier, Y.A. Variants affecting exon skipping contribute to complex traits. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Chew, S.L.; Zhang, M.Q.; Krainer, A.R. An increased specificity score matrix for the prediction of SF2/ASF-specific exonic splicing enhancers. Hum. Mol Genet. 2006, 15, 2490–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).