Silver Nanoparticles Protect Skin from Ultraviolet B-Induced Damage in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Shielding Effect of AgNP- and TiO2NP-Coated Plastic Films against UVB Irradiation
2.2. Shielding Effect of AgNPs Protects Cells from UVB Damage
2.3. Shielding Effect of AgNPs Protects Skin from UVB-Induced Elevations of Cellular ROS and Proinflammatory Cytokines
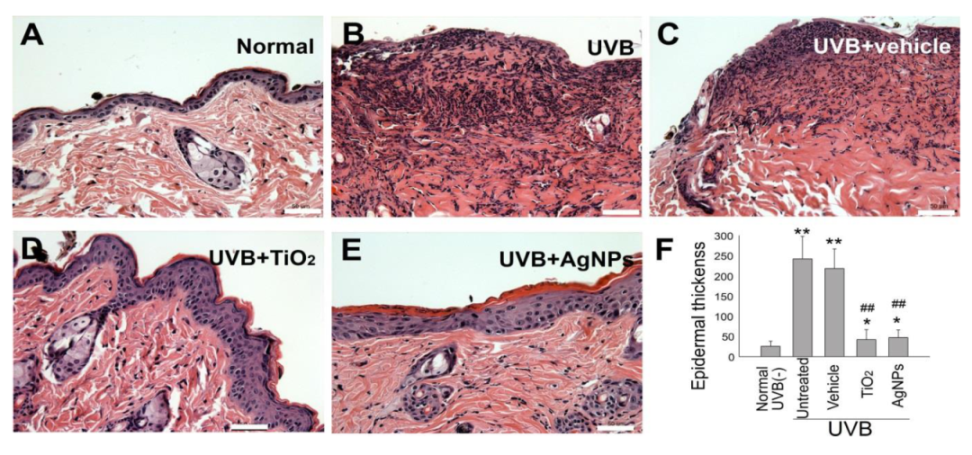
2.4. Shielding Effect of AgNPs Ameliorates UVB-Induced Skin Hyperplasia and Cell Damage in Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. UV-Related Equipment and Nanoparticles (NPs)
4.2. Human HaCaT Keratinocyte Cell Cultures
4.3. Animal Study
4.4. Measurement of UVB Shielding by Nanoparticle-Coated Films
4.5. Cell Viability, Cell Death, ROS, and Cytokine Analyses in HaCaT Cells
4.6. Cytokine and Histology Examinations of Mouse Skin
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UVB | Ultraviolet B |
| UVI | UV Index |
| AgNPs | Silver nanoparticles |
| TiO2 | Titanium dioxide |
| ZnO | Zinc oxide |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TNF–α | Tumor necrosis factor–α |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| MED | minimal erythema dose |
| TUNEL | Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling |
References
- Lautenschlager, S.; Wulf, H.C.; Pittelkow, M.R. Photoprotection. Lancet 2007, 370, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korac, R.R.; Khambholja, K.M. Potential of herbs in skin protection from ultraviolet radiation. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2011, 5, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.Q.; Tooley, I.R. Photoprotection in the era of nanotechnology. Semin. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2011, 30, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polefka, T.G.; Meyer, T.A.; Agin, P.P.; Bianchini, R.J. Effects of solar radiation on the skin. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2012, 11, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Solar UV Index: A Practical Guide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. INTERSUN: The Global UV Project: A Guide and Compendium; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, G.M. Sunblocks: Mechanisms of action. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 1999, 15, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, M.E.; Hu, J.Y.; Wang, S.Q. Sunscreens: Obtaining adequate photoprotection. Dermatol. Ther. 2012, 25, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smijs, T.G.; Pavel, S. Titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles in sunscreens: Focus on their safety and effectiveness. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2011, 4, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, J.J.; Liu, J.; Ehrenshaft, M.; Roberts, J.E.; Fu, P.P.; Mason, R.P.; Zhao, B. Phototoxicity of nano titanium dioxides in HaCaT keratinocytes—Generation of reactive oxygen species and cell damage. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 263, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silver, S.; Phung le, T.; Silver, G. Silver as biocides in burn and wound dressings and bacterial resistance to silver compounds. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 33, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, N.; Srivastava, S.K.; Arora, S.; Omar, Y.; Ijaz, Z.M.; Al-Ghadhban, A.; Deshmukh, S.K.; Carter, J.E.; Singh, A.P.; Singh, S. Comparative analysis of the relative potential of silver, Zinc-oxide and titanium-dioxide nanoparticles against UVB-induced DNA damage for the prevention of skin carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2016, 383, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, P.; Mohanty, S.; Mallick, R.; Jacob, B.; Sonawane, A. Toxicity and antibacterial assessment of chitosan-coated silver nanoparticles on human pathogens and macrophage cells. Int. J. Nanomedicine. 2012, 7, 1805–1818. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Mohsen, A.M.; Abdel-Rahman, R.M.; Fouda, M.M.; Vojtova, L.; Uhrova, L.; Hassan, A.F.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; El-Shamy, I.E.; Jancar, J. Preparation, characterization and cytotoxicity of schizophyllan/silver nanoparticle composite. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, K.; Edwards-Jones, V. The role of Acticoat with nanocrystalline silver in the management of burns. Burns 2004, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, S. Bacterial silver resistance: Molecular biology and uses and misuses of silver compounds. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, M.S.; Stern, J.M.; Vanni, A.J.; Kelley, R.S.; Baumgart, E.; Field, D.; Libertino, J.A.; Summerhayes, I.C. In vitro analysis of a nanocrystalline silver-coated surgical mesh. Surg. Infect. (Larchmt) 2007, 8, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaloupka, K.; Malam, Y.; Seifalian, A.M. Nanosilver as a new generation of nanoproduct in biomedical applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Schluesener, H.J. Nanosilver: A nanoproduct in medical application. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 176, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, T.; Nigusse, T.; Dhanaraju, M.D. Silver nanoparticles as real topical bullets for wound healing. J. Am. Coll. Clin. Wound Spec. 2011, 3, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kokura, S.; Handa, O.; Takagi, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Naito, Y.; Yoshikawa, T. Silver nanoparticles as a safe preservative for use in cosmetics. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Boil. Med. 2010, 6, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, C.H.; Walters, R.; Stein, J.A. Infectious eccrine hidradenitis associated with intense sun exposure. Cutis 2013, 92, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Termorshuizen, F.; Hogewoning, A.A.; Bouwes Bavinck, J.N.; Goettsch, W.G.; de Fijter, J.W.; van Loveren, H. Skin infections in renal transplant recipients and the relation with solar ultraviolet radiation. Clin. Transpl. 2003, 17, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martineau, L.; Dosch, H.M. In vitro bactericidal efficacy of a new sun- and heat burn gel. Burns 2006, 32, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, R.; Mankad, V.; Gupta, S.; Jha, P. Size Distribution of Silver Nanoparticles: UV-Visible Spectroscopic Assessment. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2012, 4, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.; Abdullah, O.G.; Saber, D.R.; Rasheed, M.A.; Ahmed, H.M. Investigation of Metallic Silver Nanoparticles through UV-Vis and Optical Micrograph Techniques. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.S.; Sun, D.S.; Chang, H.H. Bactericidal performance of visible-light responsive titania photocatalyst with silver nanostructures. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.S.; Chen, C.W.; Hsieh, C.C.; Hung, S.C.; Sun, D.S.; Chang, H.H. Antibacterial property of Ag nanoparticle-impregnated N-doped titania films under visible light. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salleh, A.; Naomi, R.; Utami, N.D.; Mohammad, A.W.; Mahmoudi, E.; Mustafa, N.; Fauzi, M.B. The Potential of Silver Nanoparticles for Antiviral and Antibacterial Applications: A Mechanism of Action. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2020, 10, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanki, R.; Arora, S.; Tyagi, N.; Rusu, L.; Singh, A.P.; Palanki, S.; Carter, J.E.; Singh, S. Size is an essential parameter in governing the UVB-protective efficacy of silver nanoparticles in human keratinocytes. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, M.S.; Sun, D.S.; Lin, Y.C.; Cheng, C.L.; Hung, S.C.; Chen, P.K.; Yang, J.H.; Chang, H.H. Nanodiamonds protect skin from ultraviolet B-induced damage in mice. J. Nanobiotechnology 2015, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryu, H.C.; Kim, C.; Kim, J.Y.; Chung, J.H.; Kim, J.H. UVB radiation induces apoptosis in keratinocytes by activating a pathway linked to “BLT2-reactive oxygen species”. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glady, A.; Tanaka, M.; Moniaga, C.S.; Yasui, M.; Hara-Chikuma, M. Involvement of NADPH oxidase 1 in UVB-induced cell signaling and cytotoxicity in human keratinocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2018, 14, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, K.; Kadoya, K.; Kajiya, K.; Hong, Y.K.; Detmar, M. Ultraviolet B irradiation of human skin induces an angiogenic switch that is mediated by upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and by downregulation of thrombospondin-1. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 152, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, Y.; Cheng, L.; Li, R.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Qin, Y. Potential antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and the optimization of orthopedic implants by advanced modification technologies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3311–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Ouay, B.; Stellacci, F. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: A surface science insight. Nanotoday 2015, 10, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, M.R.; Werth, B.; Werth, V.P. Animal models of acute photodamage: Comparisons of anatomic, cellular and molecular responses in C57BL/6J, SKH1 and Balb/c mice. Photochem. Photobiol. 2011, 87, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barr, R.M.; Walker, S.L.; Tsang, W.; Harrison, G.I.; Ettehadi, P.; Greaves, M.W.; Young, A.R. Suppressed alloantigen presentation, increased TNF-alpha, IL-1, IL-1Ra, IL-10, and modulation of TNF-R in UV-irradiated human skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 112, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKenzie, R.; Smale, D.; Kotkamp, M. Relationship between UVB and erythemally weighted radiation. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2004, 3, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumiyoshi, M.; Kimura, Y. Effects of olive leaf extract and its main component oleuroepin on acute ultraviolet B irradiation-induced skin changes in C57BL/6J mice. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.Y.; Hu, C.T.; Sun, D.S.; Lien, T.S.; Chang, H.H. Thioacetamide-induced liver damage and thrombocytopenia is associated with induction of antiplatelet autoantibody in mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, P.K.; Chang, H.H.; Lin, G.L.; Wang, T.P.; Lai, Y.L.; Lin, T.K.; Hsieh, M.C.; Kau, J.H.; Huang, H.H.; Hsu, H.L.; et al. Suppressive effects of anthrax lethal toxin on megakaryopoiesis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, G.L.; Chang, H.H.; Lien, T.S.; Chen, P.K.; Chan, H.; Su, M.T.; Liao, C.Y.; Sun, D.S. Suppressive effect of dengue virus envelope protein domain III on megakaryopoiesis. Virulence 2017, 8, 1719–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eruslanov, E.; Kusmartsev, S. Identification of ROS using oxidized DCFDA and flow-cytometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 594, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.L.; Sun, D.S.; Su, M.T.; Lien, T.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Huang, C.H.; King, C.C.; Li, C.R.; Chen, T.H.; et al. Suppressed humoral immunity is associated with dengue nonstructural protein NS1-elicited anti-death receptor antibody fractions in mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, Y.-Y.; Sun, D.-S.; Chang, H.-H. Silver Nanoparticles Protect Skin from Ultraviolet B-Induced Damage in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197082
Ho Y-Y, Sun D-S, Chang H-H. Silver Nanoparticles Protect Skin from Ultraviolet B-Induced Damage in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(19):7082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197082
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Yu-Yi, Der-Shan Sun, and Hsin-Hou Chang. 2020. "Silver Nanoparticles Protect Skin from Ultraviolet B-Induced Damage in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 19: 7082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197082
APA StyleHo, Y.-Y., Sun, D.-S., & Chang, H.-H. (2020). Silver Nanoparticles Protect Skin from Ultraviolet B-Induced Damage in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(19), 7082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197082





