Strain-Dependent Prion Infection in Mice Expressing Prion Protein with Deletion of Central Residues 91–106
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Generation of Tg(PrP∆91–106)/Prnp0/0 Mice
2.2. PrP∆91–106 Does Not Alter Its Localization at Raft Micromembrane Domains
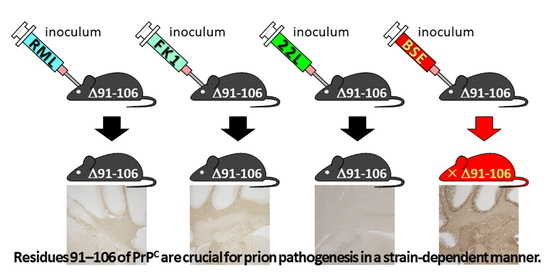
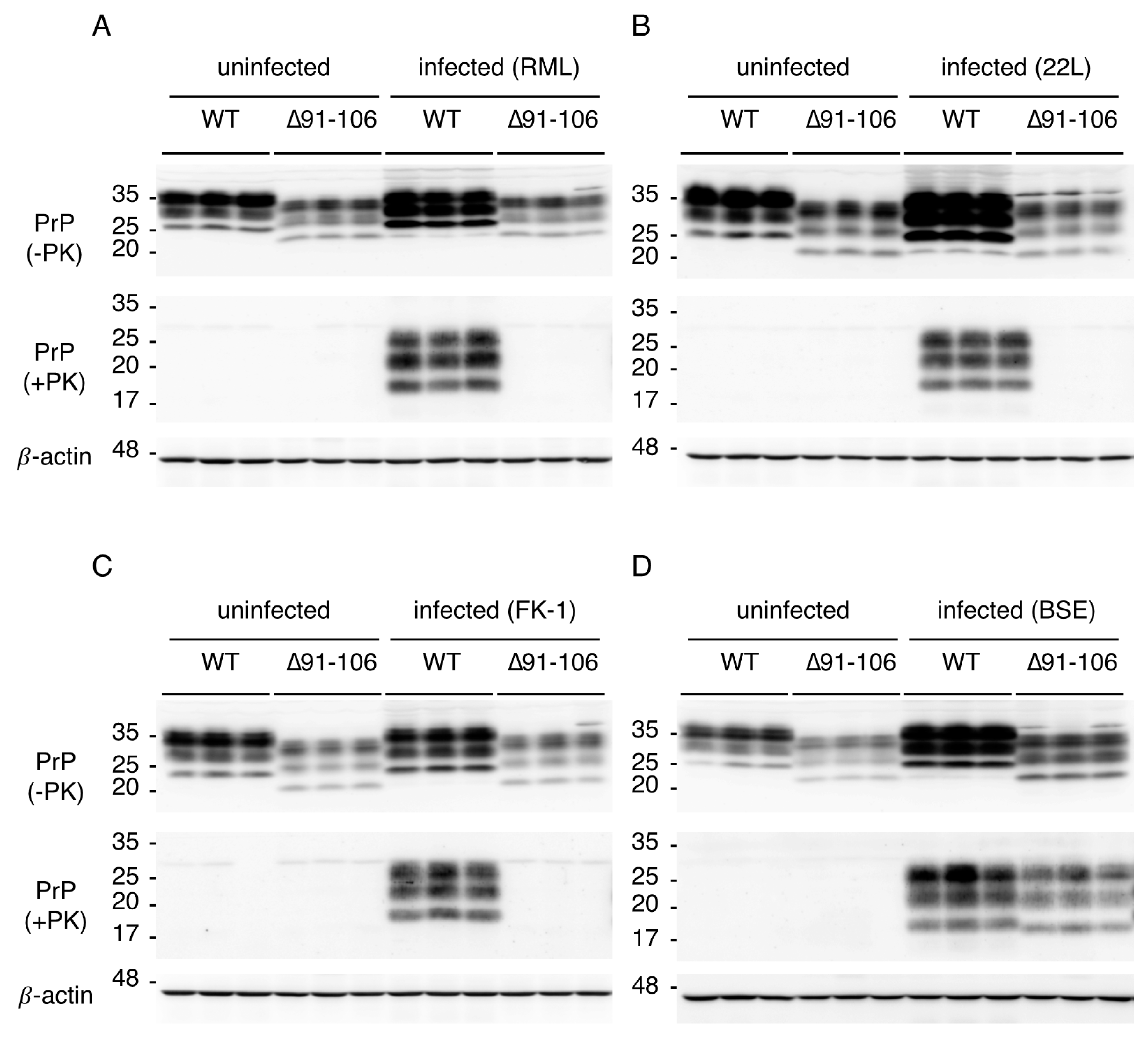
2.3. Tg(PrP∆91–106)/Prnp0/0 Mice Are Resistant to RML, 22L and FK-1 Prions but Still Susceptible to BSE Prions
2.4. Tg(PrP∆91–106)/Prnp0/0 Mice Propagate BSE Prions but Not RML, 22L, FK-1 Prions
2.5. Digitonin and Heparin Stimulate the Conversion of PrP∆91–104 into PrPSc∆91–104 Even after Incubation with RML- and 22L-PrPSc-Prions In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statements
4.2. Generation of Tg(PrP∆91–106)/Prnp0/0 Mice
4.3. Prion Inoculation
4.4. Establishment of N2a∆PrP/PrP∆91–106 Cells
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. HE Staining
4.7. Immunohistochemistry
4.8. Fractionation of Membrane Microdomains
4.9. Preparation of Insect Cell Suspension Expressing Recombinant WT PrP and PrP∆91–104
4.10. PMCA
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aguzzi, A.; Baumann, F.; Bremer, J. The prion’s elusive reason for being. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 31, 439–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prusiner, S.B. The prion diseases. Brain Pathol. 1998, 8, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueler, H.; Aguzzi, A.; Sailer, A.; Greiner, R.A.; Autenried, P.; Aguet, M.; Weissmann, C. Mice devoid of PrP are resistant to scrapie. Cell 1993, 73, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusiner, S.B.; Groth, D.; Serban, A.; Koehler, R.; Foster, D.; Torchia, M.; Burton, D.; Yang, S.L.; DeArmond, S.J. Ablation of the prion protein (PrP) gene in mice prevents scrapie and facilitates production of anti-PrP antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10608–10612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manson, J.C.; Clarke, A.R.; McBride, P.A.; McConnell, I.; Hope, J. PrP gene dosage determines the timing but not the final intensity or distribution of lesions in scrapie pathology. Neurodegeneration 1994, 3, 331–340. [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi, S.; Katamine, S.; Shigematsu, K.; Nakatani, A.; Moriuchi, R.; Nishida, N.; Kurokawa, K.; Nakaoke, R.; Sato, H.; Jishage, K.; et al. Accumulation of proteinase K-resistant prion protein (PrP) is restricted by the expression level of normal PrP in mice inoculated with a mouse-adapted strain of the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease agent. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 7586–7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turnbaugh, J.A.; Unterberger, U.; Saa, P.; Massignan, T.; Fluharty, B.R.; Bowman, F.P.; Miller, M.B.; Supattapone, S.; Biasini, E.; Harris, D.A. The N-terminal, polybasic region of PrP(C) dictates the efficiency of prion propagation by binding to PrP(Sc). J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 8817–8830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, M.; Rulicke, T.; Raeber, A.; Sailer, A.; Moser, M.; Oesch, B.; Brandner, S.; Aguzzi, A.; Weissmann, C. Prion protein (PrP) with amino-proximal deletions restoring susceptibility of PrP knockout mice to scrapie. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Miyata, H.; Uchiyama, K.; Ootsuyama, A.; Inubushi, S.; Mori, T.; Muramatsu, N.; Katamine, S.; Sakaguchi, S. Biological and biochemical characterization of mice expressing prion protein devoid of the octapeptide repeat region after infection with prions. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, H.; Miyata, H.; Das, N.R.; Chida, J.; Yoshimochi, T.; Uchiyama, K.; Watanabe, H.; Kondoh, G.; Yokoyama, T.; Sakaguchi, S. Prion protein devoid of the octapeptide repeat region delays bovine spongiform encephalopathy pathogenesis in mice. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01368-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flechsig, E.; Shmerling, D.; Hegyi, I.; Raeber, A.J.; Fischer, M.; Cozzio, A.; von Mering, C.; Aguzzi, A.; Weissmann, C. Prion protein devoid of the octapeptide repeat region restores susceptibility to scrapie in PrP knockout mice. Neuron 2000, 27, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weissmann, C.; Flechsig, E. PrP knock-out and PrP transgenic mice in prion research. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 66, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scott, M.R.; Kohler, R.; Foster, D.; Prusiner, S.B. Chimeric prion protein expression in cultured cells and transgenic mice. Protein Sci. 1992, 1, 986–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uchiyama, K.; Tomita, M.; Yano, M.; Chida, J.; Hara, H.; Das, N.R.; Nykjaer, A.; Sakaguchi, S. Prions amplify through degradation of the VPS10P sorting receptor sortilin. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uchiyama, K.; Muramatsu, N.; Yano, M.; Usui, T.; Miyata, H.; Sakaguchi, S. Prions disturb post-Golgi trafficking of membrane proteins. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hara, H.; Okemoto-Nakamura, Y.; Shinkai-Ouchi, F.; Hanada, K.; Yamakawa, Y.; Hagiwara, K. Mouse prion protein (PrP) segment 100 to 104 regulates conversion of PrP(C) to PrP(Sc) in prion-infected neuroblastoma cells. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5626–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murayama, Y.; Yoshioka, M.; Yokoyama, T.; Iwamaru, Y.; Imamura, M.; Masujin, K.; Yoshiba, S.; Mohri, S. Efficient in vitro amplification of a mouse-adapted scrapie prion protein. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 413, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, M.; Tabeta, N.; Kato, N.; Matsuura, Y.; Iwamaru, Y.; Yokoyama, T.; Murayama, Y. Heparan sulfate and heparin promote faithful prion replication in vitro by binding to normal and abnormal prion proteins in protein misfolding cyclic amplification. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 26478–26486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, H.; Takata, M.; Iwamaru, Y.; Ushiki, Y.; Kimura, K.M.; Tagawa, Y.; Shinagawa, M.; Yokoyama, T. Effect of tissue deterioration on postmortem BSE diagnosis by immunobiochemical detection of an abnormal isoform of prion protein. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2004, 66, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collinge, J.; Clarke, A.R. A general model of prion strains and their pathogenicity. Science 2007, 318, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wadsworth, J.D.; Asante, E.A.; Collinge, J. Review: Contribution of transgenic models to understanding human prion disease. Neuropath. Appl. Neurol. 2010, 36, 576–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, H.K.; Yokoyama, T.; Takata, M.; Iwamaru, Y.; Imamura, M.; Ushiki, Y.K.; Shinagawa, M. The N-terminal cleavage site of PrPSc from BSE differs from that of PrPSc from scrapie. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 328, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, M.; Foster, D.; Mirenda, C.; Serban, D.; Coufal, F.; Walchli, M.; Torchia, M.; Groth, D.; Carlson, G.; DeArmond, S.J.; et al. Transgenic mice expressing hamster prion protein produce species-specific scrapie infectivity and amyloid plaques. Cell 1989, 59, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, R.G.; Hundt, C.; Weiss, S.; Turnbull, J.E. Identification of the heparan sulfate binding sites in the cellular prion protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 18421–18430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bazar, E.; Jelinek, R. Divergent heparin-induced fibrillation pathways of a prion amyloidogenic determinant. Chembiochem 2010, 11, 1997–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yin, S.; Wang, X.; Zha, L.; Sy, M.S.; Ma, J. Role of the highly conserved middle region of prion protein (PrP) in PrP-lipid interaction. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 8169–8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prusiner, S.B. Genetic and infectious prion diseases. Arch. Neurol. 1993, 50, 1129–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenbrod, S.; Frick, P.; Bertsch, U.; Mitteregger-Kretzschmar, G.; Mielke, J.; Maringer, M.; Piening, N.; Hepp, A.; Daude, N.; Windl, O.; et al. Substitutions of PrP N-terminal histidine residues modulate scrapie disease pathogenesis and incubation time in transgenic mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshikawa, D.; Yamaguchi, N.; Ishibashi, D.; Yamanaka, H.; Okimura, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Mori, T.; Miyata, H.; Shigematsu, K.; Katamine, S.; et al. Dominant-negative effects of the N-terminal half of prion protein on neurotoxicity of prion protein-like protein/doppel in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 24202–24211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brinster, R.L.; Chen, H.Y.; Trumbauer, M.E.; Yagle, M.K.; Palmiter, R.D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 4438–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilmut, I.; Hooper, M.L.; Simons, J.P. Genetic manipulation of mammals and its application in reproductive biology. J. Reprod. Fertil. 1991, 92, 245–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bueler, H.; Fischer, M.; Lang, Y.; Bluethmann, H.; Lipp, H.P.; DeArmond, S.J.; Prusiner, S.B.; Aguet, M.; Weissmann, C. Normal development and behaviour of mice lacking the neuronal cell-surface PrP protein. Nature 1992, 356, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Sakaguchi, S.; Shigematsu, K.; Okimura, N.; Katamine, S. Doppel-induced Purkinje cell death is stoichiometrically abrogated by prion protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 319, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, M.; Kato, N.; Yoshioka, M.; Okada, H.; Iwamaru, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Mohri, S.; Yokoyama, T.; Murayama, Y. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor-dependent stimulation pathway required for generation of baculovirus-derived recombinant scrapie prion protein. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 2582–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Prions | Recipient Mouse | Expression Level of PrP (Fold) 1 | Diseased Mice/Total Mice | Times to the Onset of Disease (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RML | WT | 1 | 8/8 | 171 ± 4 |
| Tg(PrP∆91–106)/Prnp0/0 | 0.4 | 0/11 | >765 | |
| 22L | WT | 1 | 10/10 | 143 ± 1 |
| Tg(PrP∆91–106)/Prnp0/0 | 0.4 | 0/9 | >623 | |
| FK-1 | WT | 1 | 10/10 | 187 ± 3 |
| Tg(PrP∆91–106)/Prnp0/0 | 0.4 | 0/4 | >604 | |
| BSE | WT | 1 | 10/10 | 174 ± 4 |
| Tg(PrP∆91–106)/Prnp0/0 | 0.4 | 10/10 | 538 ± 24 |
| Prions | Donor Mouse | Recipient Mouse | Diseased Mice /Total Mice | Incubation Times 1 (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RML | Tg(PrP∆91–106)/Prnp0/0 | WT | 0/6 | >730 |
| Tg(PrP∆91–106)/Prnp0/0 | 0/4 | >730 | ||
| 22L | Tg(PrP∆91–106)/Prnp0/0 | WT | 0/9 | >732 |
| Tg(PrP∆91–106)/Prnp0/0 | 0/4 | >732 | ||
| FK-1 | Tg(PrP∆91–106)/Prnp0/0 | WT | 0/6 | >730 |
| Tg(PrP∆91–106)/Prnp0/0 | 0/6 | >730 | ||
| BSE | Tg(PrP∆91–106)/Prnp0/0 | WT | 10/10 | 326 ± 29 |
| Tg(PrP∆91–106)/Prnp0/0 | 9/9 | 343 ± 28 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uchiyama, K.; Miyata, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Imamura, M.; Okazaki, M.; Pasiana, A.D.; Chida, J.; Hara, H.; Atarashi, R.; Watanabe, H.; et al. Strain-Dependent Prion Infection in Mice Expressing Prion Protein with Deletion of Central Residues 91–106. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197260
Uchiyama K, Miyata H, Yamaguchi Y, Imamura M, Okazaki M, Pasiana AD, Chida J, Hara H, Atarashi R, Watanabe H, et al. Strain-Dependent Prion Infection in Mice Expressing Prion Protein with Deletion of Central Residues 91–106. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(19):7260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197260
Chicago/Turabian StyleUchiyama, Keiji, Hironori Miyata, Yoshitaka Yamaguchi, Morikazu Imamura, Mariya Okazaki, Agriani Dini Pasiana, Junji Chida, Hideyuki Hara, Ryuichiro Atarashi, Hitomi Watanabe, and et al. 2020. "Strain-Dependent Prion Infection in Mice Expressing Prion Protein with Deletion of Central Residues 91–106" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 19: 7260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197260
APA StyleUchiyama, K., Miyata, H., Yamaguchi, Y., Imamura, M., Okazaki, M., Pasiana, A. D., Chida, J., Hara, H., Atarashi, R., Watanabe, H., Kondoh, G., & Sakaguchi, S. (2020). Strain-Dependent Prion Infection in Mice Expressing Prion Protein with Deletion of Central Residues 91–106. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(19), 7260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197260