Differential Expression of SMAD Genes and S1PR1 on Circulating CD4+ T Cells in Multiple Sclerosis and Crohn’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patients Characteristics
2.2. StellARrays
2.3. Gene Expression of Th17-Selected Genes in MS
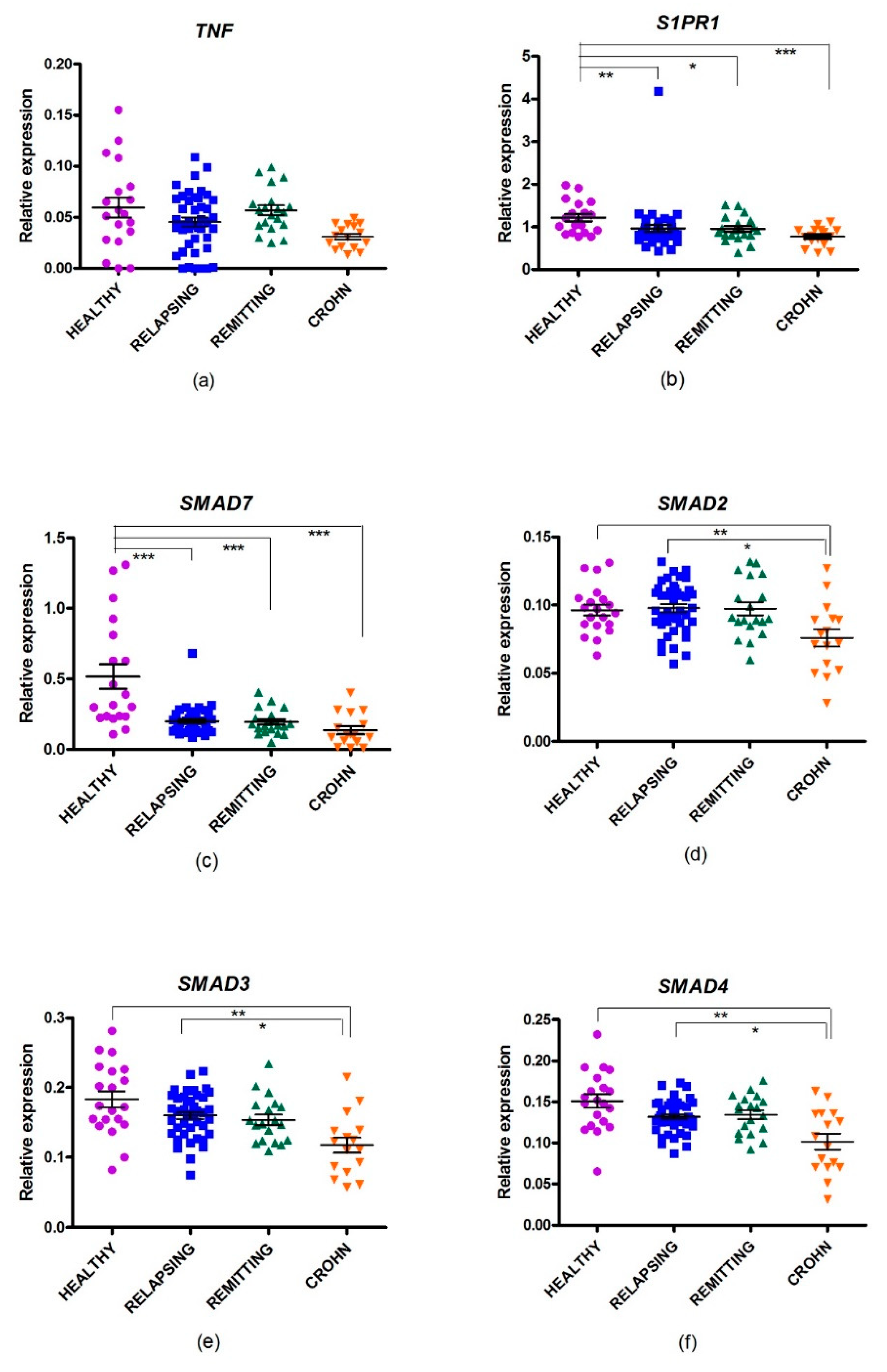
2.4. Gene Expression of SMAD Genes in MS
2.5. Changes in Gene Expression in CD
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
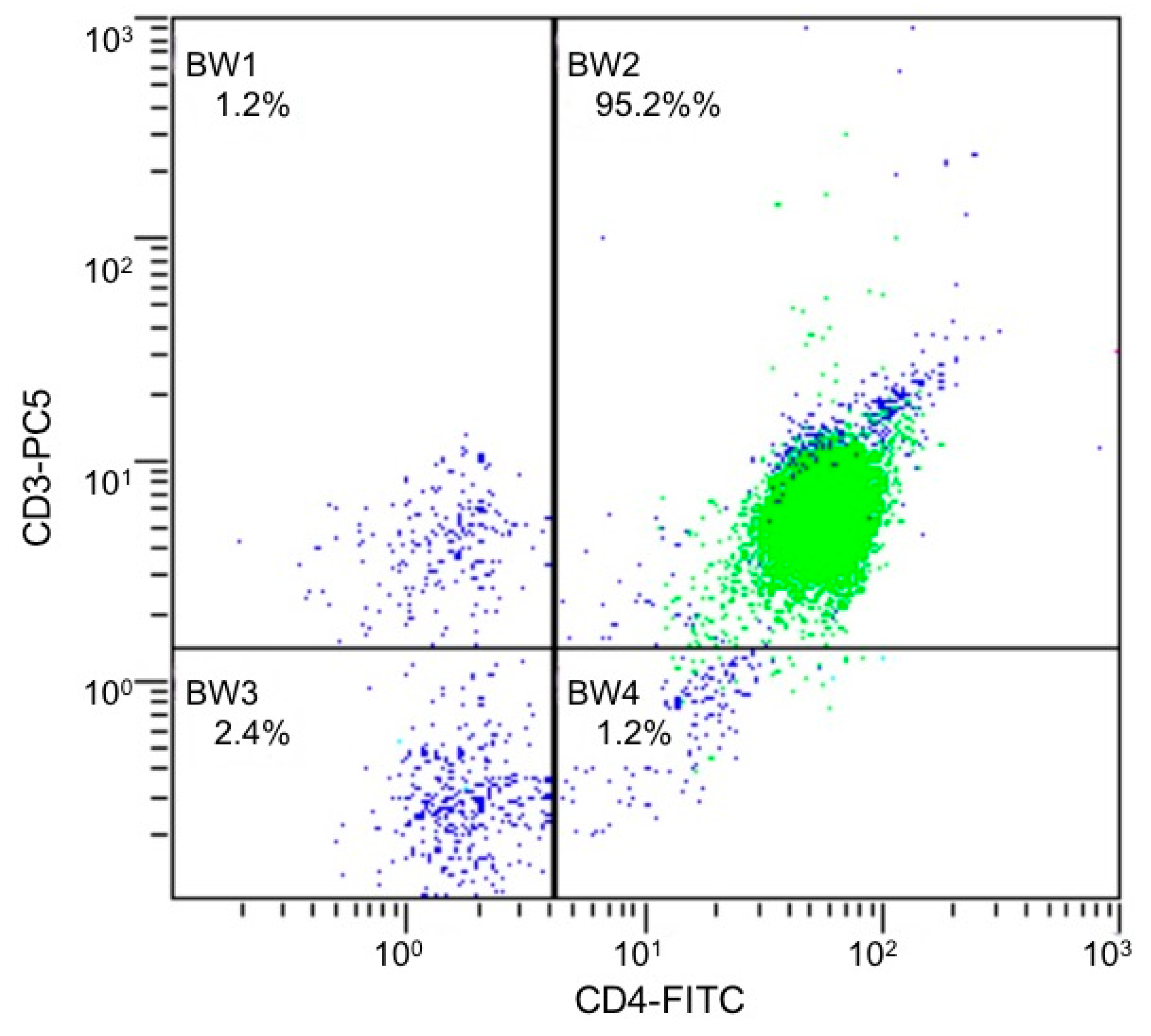
4.2. Isolation and Culture of CD4+ T cells
4.3. Isolation of RNA and Synthesis of cDNA
4.4. StellARrays Procedure
4.5. Real Time qRT-PCR
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MS | Multiple sclerosis |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| CD | Crohn’s disease |
| Th17 | Human T helper 17 |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| IFN | Interferon |
| EAE | Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis |
| RRMS | Remittent recurrent multiple sclerosis |
| HD | Healthy donors |
| CIS | Clinically isolated syndrome |
| mAb | Monoclonal antibody |
| Tregs | Anti-inflammatory regulatory T |
| S1PPBMCs | Sphingosine-1 phosphate Peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| GPR | Global Pattern Recognition |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
Appendix A
| Rank | Gene Name | p-Value | GPR Fold Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SMAD7 | 0.023116 | −4.121045 |
| 2 | TNF | 0.097984 | −1.975738 |
| 3 | CSF3 | 0.115770 | 3.099492 |
| 4 | S1PR1 | 0.169676 | −1.489735 |
| 5 | CEBPD | 0.173658 | 2.447022 |
| 6 | IL18R1 | 0.181638 | 1.741877 |
| 7 | MMP9 | 0.183453 | 2.454003 |
| 8 | ICAM1 | 0.204162 | −1.397425 |
| 9 | IL10 | 0.217187 | −1.478354 |
| 10 | MAP3K14 | 0.227840 | −1.232434 |
| 12 | IL15 | 0.230006 | 1.914874 |
| 13 | IL12RB2 | 0.230664 | 1.408320 |
| 14 | IL17RC | 0.230917 | −2.236766 |
| 15 | IL22 | 0.236646 | 2.149112 |
| 16 | CCR2 | 0.236910 | 1.298827 |
| 17 | PTGES2 | 0.238409 | 1.286509 |
| 19 | CLEC7A | 0.260678 | 1.849452 |
| 21 | CCR5 | 0.280039 | 1.463742 |
| 22 | IL27 | 0.280070 | 2.076678 |
| 23 | PRKCQ | 0.280210 | −1.203029 |
| 24 | PTGS2 | 0.287147 | −1.292593 |
| 25 | CCL5 | 0.288848 | 1.868512 |
| 30 | STAT5A | 0.302796 | 1.180038 |
| 31 | TGFB1 | 0.303116 | −1.169076 |
| 32 | IL6R | 0.305101 | −1.075965 |
| 33 | S100A9 | 0.310143 | 2.053510 |
| 36 | ITGAL | 0.312514 | −1.163330 |
| 37 | IL1B | 0.317977 | −1.351223 |
| 38 | IL1R1 | 0.323904 | −1.318258 |
| 39 | CD28 | 0.326297 | −1.154887 |
| 40 | S100A8 | 0.326948 | 2.071241 |
| 42 | IL17RE | 0.333320 | 2.006149 |
| 43 | IFNG | 0.337986 | 1.213963 |
| 44 | IL17C | 0.342972 | 1.415405 |
| 45 | FAS | 0.348147 | 1.289762 |
| 46 | CD4 | 0.354280 | −1.157741 |
| 47 | IL18 | 0.368094 | −1.327924 |
| 48 | IL12RB1 | 0.374193 | −1.151614 |
| 49 | MAF | 0.380837 | −1.055353 |
| 50 | LIF | 0.380977 | −3.1015170 |
| 51 | RORC | 0.385640 | 1.290307 |
| 52 | JAK2 | 0.388477 | 1.082868 |
| 53 | IL17D | 0.389396 | −1.094554 |
| 54 | IL23A | 0.392817 | −1.192429 |
| 55 | CXCL2 | 0.400369 | −1.428309 |
| 56 | FOXP3 | 0.409157 | 1.087963 |
| 57 | ICOS | 0.422018 | −1.134658 |
| 58 | IL17RB | 0.430393 | 1.039733 |
| 59 | CSF2 | 0.433523 | 1.478325 |
| 60 | IL23R | 0.444508 | 1.133804 |
| 61 | EOMES | 0.445174 | 1.038471 |
| 62 | CCR4 | 0.446667 | 1.160488 |
| 63 | CCL20 | 0.448723 | −2.306566 |
| 64 | CCR6 | 0.468722 | 1.107297 |
| 65 | SYK | 0.471252 | 1.434643 |
| 66 | ITGAX | 0.482659 | 1.562096 |
| 67 | CD8A | 0.482678 | −1.206777 |
| 68 | SOCS3 | 0.484580 | −1.111256 |
| 69 | LCN2 | 0.502556 | 1.358341 |
| 70 | IL21 | 0.515282 | 1.572404 |
| 71 | IL2 | 0.532927 | 1.719894 |
| 72 | ITGAM | 0.546400 | 1.047556 |
| 73 | FASLG | 0.546997 | 1.224576 |
| 74 | HLX | 0.558206 | 1.118766 |
| 75 | CXCL3 | 0.563145 | 1.062506 |
| 76 | MUC5AC | 0.567032 | 2.128834 |
| 77 | IL13 | 0.568119 | 1.404698 |
| 78 | IL4 | 0.594178 | 1.031688 |
| 79 | CARD9 | 0.599793 | 1.587336 |
| 80 | TBX21 | 0.615106 | 1.006864 |
| 81 | CXCL10 | 0.620610 | 1.085097 |
| 82 | DEFB4 | 0.673370 | −1.204941 |
| 83 | IL17RD | 0.711636 | −2.334528 |
| 84 | GZMB | 0.713332 | 1.303447 |
| 85 | CCL11 | 0.755471 | −1.509432 |
| 87 | MMP3 | NS | −1.328030 |
| 88 | MMP13 | NS | −1.605307 |
| 89 | CCL13 | NS | 1.166980 |
| 90 | CXCL12 | NS | 1.726135 |
| 91 | IL17F | NS | 1.173435 |
| 92 | IL6 | NS | −1.988051 |
| 93 | IL12B | NS | −1.152891 |
| 94 | CRP | NS | −1.287846 |
| 95 | IL17A | NS | −1.526223 |
| 96 | IL25 | NS | 1.342714 |
References
- Yadav, S.K.; Mindur, J.E.; Ito, K.; Dhib-Jalbut, S. Advances in the immunopathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2015, 28, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, A.; Yousaf, W.; Giannella, R.; Shata, M.T. Th17 cells: Interactions with predisposing factors in the immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 8, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, G.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Mirshafiey, A. Th17 Cells in Immunopathogenesis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 16, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwabara, T.; Ishikawa, F.; Kondo, M.; Kakiuchi, T. The Role of IL-17 and Related Cytokines in Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangan, P.R.; Harrington, L.E.; O’Quinn, D.B.; Helms, W.S.; Bullard, D.C.; Elson, C.O.; Hatton, R.D.; Wahl, S.M.; Schoeb, T.R.; Weaver, C.T. Transforming growth factor-beta induces development of the T(H)17 lineage. Nature 2006, 441, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustakas, A.; Heldin, C.-H. Non-Smad TGF- signals. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 3573–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budi, E.H.; Duan, D.; Derynck, R. Transforming Growth Factor-β Receptors and Smads: Regulatory Complexity and Functional Versatility. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 658–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhurst, R.J.; Hata, A. Targeting the TGFβ signalling pathway in disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 790–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockinger, B.; Veldhoen, M. Differentiation and function of Th17 T cells. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boniface, K.; Blumenschein, W.M.; Brovont-Porth, K.; McGeachy, M.J.; Basham, B.; Desai, B.; Pierce, R.; McClanahan, T.K.; Sadekova, S.; de Waal Malefyt, R. Human Th17 cells comprise heterogeneous subsets including IFN-gamma-producing cells with distinct properties from the Th1 lineage. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Lee, Y.; Kuchroo, V.K. The many faces of Th17 cells. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2011, 23, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasebinia, F.; Pourgholaminejad, A. The role of Th17 cells in auto-inflammatory neurological disorders. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacology Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 79, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushansky, N.; Bakos, E.; Becker-Herman, S.; Shachar, I.; Ben-Nun, A. Circulating Picomolar Levels of CCL2 Downregulate Ongoing Chronic Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Induction of Regulatory Mechanisms. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 1857–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kebir, H.; Kreymborg, K.; Ifergan, I.; Dodelet-Devillers, A.; Cayrol, R.; Bernard, M.; Giuliani, F.; Arbour, N.; Becher, B.; Prat, A. Human TH17 lymphocytes promote blood-brain barrier disruption and central nervous system inflammation. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1173–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waisman, A.; Hauptmann, J.; Regen, T. The role of IL-17 in CNS diseases. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lock, C.; Hermans, G.; Pedotti, R.; Brendolan, A.; Schadt, E.; Garren, H.; Langer-Gould, A.; Strober, S.; Cannella, B.; Allard, J.; et al. Gene-microarray analysis of multiple sclerosis lesions yields new targets validated in autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebir, H.; Ifergan, I.; Alvarez, J.I.; Bernard, M.; Poirier, J.; Arbour, N.; Duquette, P.; Prat, A. Preferential recruitment of interferon-γ-expressing T H 17 cells in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 66, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garris, C.S.; Wu, L.; Acharya, S.; Arac, A.; Blaho, V.A.; Huang, Y.; Moon, B.S.; Axtell, R.C.; Ho, P.P.; Steinberg, G.K.; et al. Defective sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1P1) phosphorylation exacerbates TH17-mediated autoimmune neuroinflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-F.; Zhang, S.-X.; Ma, X.-W.; Xue, Y.-L.; Gao, C.; Li, X.-Y. Levels of peripheral Th17 cells and serum Th17-related cytokines in patients with multiple sclerosis: A meta-analysis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2017, 18, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, P.; Chen, N.; Su, L.; Peng, T.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y. Local level of TGF-β1 determines the effectiveness of dexamethasone through regulating the balance of Treg/Th17 cells in TNBS-induced mouse colitis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 3639–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.-F.; Leng, R.-X.; Feng, C.-C.; Li, X.-P.; Chen, G.-M.; Li, B.-Z.; Xu, W.-D.; Zheng, S.G.; Ye, D.-Q. Expression profiles of Th17 pathway related genes in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gras, R.; Relloso, M.; García, M.I.; de la Mata, F.J.; Gómez, R.; López-Fernández, L.A.; Muñoz-Fernández, M.A. The inhibition of Th17 immune response in vitro and in vivo by the carbosilane dendrimer 2G-NN16. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 4002–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, L.M.; Antel, J.P. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptors in the Central Nervous and Immune Systems. Curr. Drug Targets 2016, 17, 1841–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, F.S.; Hofereiter, J.; Rübsamen, H.; Melms, J.; Schwarz, S.; Faber, H.; Weber, P.; Pütz, B.; Loleit, V.; Weber, F.; et al. Fingolimod induces neuroprotective factors in human astrocytes. J. Neuroinflammation 2015, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagida, K.; Liu, C.H.; Faraco, G.; Galvani, S.; Smith, H.K.; Burg, N.; Anrather, J.; Sanchez, T.; Iadecola, C.; Hla, T. Size-selective opening of the blood–brain barrier by targeting endothelial sphingosine 1–phosphate receptor 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4531–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Jin, H.; Yue, X.; Luo, Z.; Liu, C.; Rosenberg, A.J.; Tu, Z. PET Imaging Study of S1PR1 Expression in a Rat Model of Multiple Sclerosis. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2016, 18, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shi, D.; Cao, K.; Wu, F.; Zhu, X.; Wen, S.; You, Q.; Zhang, K.; Liu, L.; Zhou, H. Fingolimod targets cerebral endothelial activation to block leukocyte recruitment in the central nervous system. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 103, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Cao, R.; Quan, M.; Sun, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Guo, L.; Song, X. Rapamycin and fingolimod modulate Treg/Th17 cells in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by regulating the Akt-mTOR and MAPK/ERK pathways. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 324, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.; Li, J.; Dang, J.; Bian, X.; Shan, S.; Yuan, J.; Qian, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, G.; Yuan, Q.; et al. miR-155 Deficiency Ameliorates Autoimmune Inflammation of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus by Targeting S1pr1 in Fas lpr/lpr Mice. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 5437–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Lee, W.-W.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, S.W.; Craft, J.; Kang, I. Dysregulated balance of Th17 and Th1 cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejas, P.J.; Walsh, M.C.; Pearce, E.L.; Han, D.; Harms, G.M.; Artis, D.; Turka, L.A.; Choi, Y. TRAF6 inhibits Th17 differentiation and TGF-beta-mediated suppression of IL-2. Blood 2010, 115, 4750–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xue, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, L.; Da, Y.; Yao, Z.; et al. MicroRNA-181c promotes Th17 cell differentiation and mediates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2018, 70, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meoli, E.M.; Oh, U.; Grant, C.W.; Jacobson, S. TGF-β signaling is altered in the peripheral blood of subjects with multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 230, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achiron, A.; Gurevich, M.; Friedman, N.; Kaminski, N.; Mandel, M. Blood transcriptional signatures of multiple sclerosis: Unique gene expression of disease activity. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 55, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomprezzi, R.; Ringnér, M.; Kim, S.; Bittner, M.L.; Khan, J.; Chen, Y.; Elkahloun, A.; Yu, A.; Bielekova, B.; Meltzer, P.S.; et al. Gene expression profile in multiple sclerosis patients and healthy controls: Identifying pathways relevant to disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003, 12, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiter, I.; Song, J.; Lukas, D.; Hasan, M.; Neumann, B.; Croxford, A.L.; Pedré, X.; Hövelmeyer, N.; Yogev, N.; Mildner, A.; et al. Smad7 in T cells drives T helper 1 responses in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain 2010, 133, 1067–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, S.; Talebi, F.; Chan, W.F.; Masoumi, F.; Vojgani, M.; Power, C.; Noorbakhsh, F. MicroRNA-181 Variants Regulate T Cell Phenotype in the Context of Autoimmune Neuroinflammation. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, G.; Del Vecchio Blanco, G.; Monteleone, I.; Fina, D.; Caruso, R.; Gioia, V.; Ballerini, S.; Federici, G.; Bernardini, S.; Pallone, F.; et al. Post-transcriptional Regulation of Smad7 in the Gut of Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, G.; Neurath, M.F.; Ardizzone, S.; Di Sabatino, A.; Fantini, M.C.; Castiglione, F.; Scribano, M.L.; Armuzzi, A.; Caprioli, F.; Sturniolo, G.C.; et al. Mongersen, an Oral SMAD7 Antisense Oligonucleotide, and Crohn’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzone, S.; Bevivino, G.; Monteleone, G. Mongersen, an oral Smad7 antisense oligonucleotide, in patients with active Crohn’s disease. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2016, 9, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feagan, B.G.; Sands, B.E.; Rossiter, G.; Li, X.; Usiskin, K.; Zhan, X.; Colombel, J.-F. Effects of Mongersen (GED-0301) on Endoscopic and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Active Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupeltshofer, S.; Leichsenring, T.; Berg, S.; Pedreiturria, X.; Joachim, S.C.; Tischoff, I.; Otte, J.-M.; Bopp, T.; Fantini, M.C.; Esser, C.; et al. Smad7 in intestinal CD4+ T cells determines autoimmunity in a spontaneous model of multiple sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 25860–25869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitzer, M.; von Gersdorff, G.; Liang, D.; Dominguez-Rosales, A.; Beg, A.A.; Rojkind, M.; Böttinger, E.P. A mechanism of suppression of TGF-beta/SMAD signaling by NF-kappa B/RelA. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- De Andres, C.; García, M.I.; Goicoechea, H.; Martínez-Ginés, M.L.; García-Domínguez, J.M.; Martín, M.L.; Romero-Delgado, F.; Benguría, A.; Sanjurjo, M.; López-Fernández, L.A. Genes differentially expressed by methylprednisolone in vivo in CD4 T lymphocytes from multiple sclerosis patients: Potential biomarkers. Pharmacogenomics J. 2018, 18, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raphael, I.; Nalawade, S.; Eagar, T.N.; Forsthuber, T.G. T cell subsets and their signature cytokines in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Cytokine 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arellano, G.; Acuña, E.; Reyes, L.I.; Ottum, P.A.; De Sarno, P.; Villarroel, L.; Ciampi, E.; Uribe-San Martín, R.; Cárcamo, C.; Naves, R. Th1 and Th17 Cells and Associated Cytokines Discriminate among Clinically Isolated Syndrome and Multiple Sclerosis Phenotypes. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muls, N.; Nasr, Z.; Dang, H.A.; Sindic, C.; van Pesch, V. IL-22, GM-CSF and IL-17 in peripheral CD4+ T cell subpopulations during multiple sclerosis relapses and remission. Impact of corticosteroid therapy. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akilesh, S.; Shaffer, D.J.; Roopenian, D. Customized molecular phenotyping by quantitative gene expression and pattern recognition analysis. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 1719–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickles, D.; Chen, H.P.; Li, M.M.; Khankhanian, P.; Madireddy, L.; Caillier, S.J.; Santaniello, A.; Cree, B.A.C.; Pelletier, D.; Hauser, S.L.; et al. Blood RNA profiling in a large cohort of multiple sclerosis patients and healthy controls. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 4194–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | RRMS Rel (n = 43) | RRMS Rem (n = 21) | HD (n = 20) | CD (n =16) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median age, years (IQR, range) | 35 (14; 22–53) | 40 (14.5; 25–52) | 29.5 (17.5; 25–61) | 28.5 (21.3; 18–69) |
| Gender Women n, (%) Men n, (%) | 38 (88.4%) 5 (11.6%) | 19 (90.5%) 2 (9.5%) | 16 (80%) 4 (20%) | 7 (43.8%) 9 (56.2%) |
| Months from diagnosisto sample collection, median (IQR, range) | 9 (144; 0–36) | 12 (70.5; 0–216) | 192 (231; 1–456) | |
| Type of MS/CIS MS n, (%) CIS n, (%) | 33 (76.7%) 10 (23.3%) | 13 (61.9%) 8 (38.1%) | ||
| Naïve Yes n, (%) No n, (%) | 24 (55.8%) 19 (44.2%) | 16 (76.2%) 5 (23.8%) | 0 16 (100%) | |
| Type of treatment in non-naïve (n) | ||||
| Interferon beta-1a sc | 4 | 2 | ||
| Glatitamer Acetate | 5 | 1 | ||
| Interferon beta-1b | 2 | 1 | ||
| Azathioprine | 1 | 1 | ||
| Interferon beta-1b im | 5 | |||
| Methylprednisolone | 1 | |||
| Dimethyl fumarate | 1 | 1 | ||
| Adalimumab | 5 | |||
| Adalimumab + azathioprine | 2 | |||
| Infliximab | 1 | |||
| Vedolizumab | 4 | |||
| Certolizumab + Methylprednisolone | 1 | |||
| Azathioprine + Prednisone | 1 | |||
| Prednisone | 1 |
| Rank | Gene Name | p-Value | GPR Fold Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SMAD7 | 0.023116 | −4.121045 |
| 2 | TNF | 0.097984 | −1.975738 |
| 3 | CSF3 | 0.115770 | 3.099492 |
| 4 | S1PR1 | 0.169676 | −1.489735 |
| 5 | CEBPD | 0.173658 | 2.447022 |
| 6 | IL18R1 | 0.181638 | 1.741877 |
| 7 | MMP9 | 0.183453 | 2.454003 |
| 8 | ICAM1 | 0.204162 | −1.397425 |
| 9 | IL10 | 0.217187 | −1.478354 |
| 10 | MAP3K14 | 0.227840 | −1.232434 |
| Comparison | SMAD7 FC (PFDR) | S1PR1 FC (PFDR) | TNF FC (PFDR) | SMAD2 FC (PFDR) | SMAD3 FC (PFDR) | SMAD4 FC (PFDR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HD vs. RRMS rem | −2.29 (0.001) | −1.28 (0.041) | −1.19 (0.405) | −1.28 (0.870) | −1.17 (0.720) | −1.12 (0.155) |
| HD vs. RRMS rel | −2.17 (0.001) | −1.31 (0.010) | −1.34 (0.123) | −1.05 (0.372) | −1.18 (0.130) | −1.17 (0.110) |
| HD vs.CD rel | −4.65 (0.001) | −1.59 (0.001) | −2.25 (0.001) | −1.40 (0.001) | −1.64 (0.001) | −1.60 (< 0.001) |
| RRMS rem vs. RRMS rel | 1.05 (1.000) | −1.02 (1.000) | −1.13 (0.690) | 1.02 (1.000) | 1.01 (1.000) | −1.04 (1.738) |
| RRMS rem vs. CD rel | −2.02 (0.101) | −1.24 (0.158) | −1.89 (0.003) | −1.3 (0.008) | −1.40 (0.023) | −1.43 (0.004) |
| RRMS rel vs. CD rel | −2.14 (0.046) | −1.22 (0.137) | −1.67 (0.006) | −1.33 (0.006) | −1.38 (0.016) | −1.40 (0.006) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abarca-Zabalía, J.; García, M.I.; Lozano Ros, A.; Marín-Jiménez, I.; Martínez-Ginés, M.L.; López-Cauce, B.; Martín-Barbero, M.L.; Salvador-Martín, S.; Sanjurjo-Saez, M.; García-Domínguez, J.M.; et al. Differential Expression of SMAD Genes and S1PR1 on Circulating CD4+ T Cells in Multiple Sclerosis and Crohn’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020676
Abarca-Zabalía J, García MI, Lozano Ros A, Marín-Jiménez I, Martínez-Ginés ML, López-Cauce B, Martín-Barbero ML, Salvador-Martín S, Sanjurjo-Saez M, García-Domínguez JM, et al. Differential Expression of SMAD Genes and S1PR1 on Circulating CD4+ T Cells in Multiple Sclerosis and Crohn’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(2):676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020676
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbarca-Zabalía, Judith, Ma Isabel García, Alberto Lozano Ros, Ignacio Marín-Jiménez, Maria L. Martínez-Ginés, Beatriz López-Cauce, María L. Martín-Barbero, Sara Salvador-Martín, María Sanjurjo-Saez, Jose M. García-Domínguez, and et al. 2020. "Differential Expression of SMAD Genes and S1PR1 on Circulating CD4+ T Cells in Multiple Sclerosis and Crohn’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 2: 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020676
APA StyleAbarca-Zabalía, J., García, M. I., Lozano Ros, A., Marín-Jiménez, I., Martínez-Ginés, M. L., López-Cauce, B., Martín-Barbero, M. L., Salvador-Martín, S., Sanjurjo-Saez, M., García-Domínguez, J. M., & López Fernández, L. A. (2020). Differential Expression of SMAD Genes and S1PR1 on Circulating CD4+ T Cells in Multiple Sclerosis and Crohn’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(2), 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020676







