Horizontal Combination of MEK and PI3K/mTOR Inhibition in BRAF Mutant Tumor Cells with or without Concomitant PI3K Pathway Mutations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
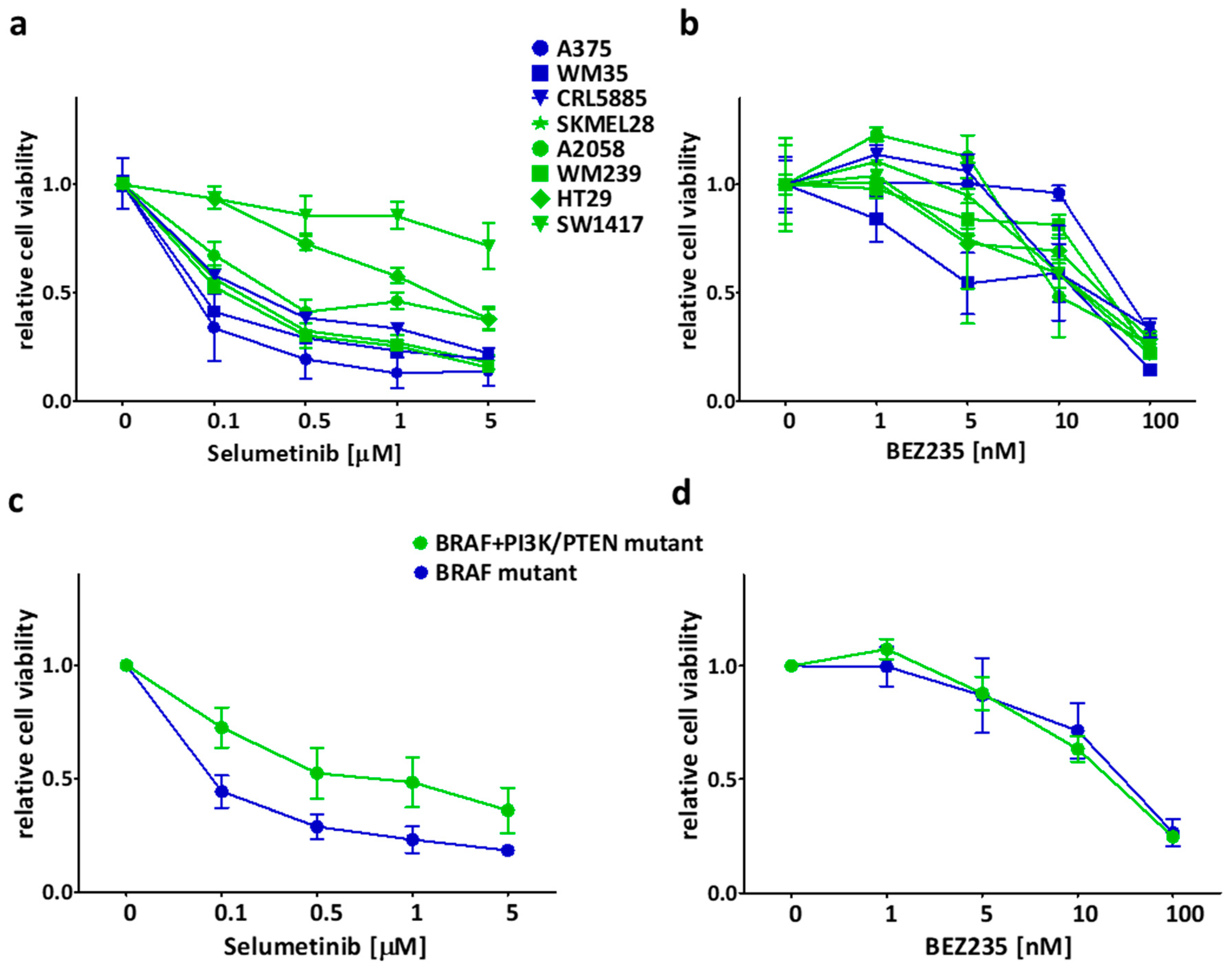
2.1. Sensitivity of the Cancer Cell Lines in Short-Term Treatments
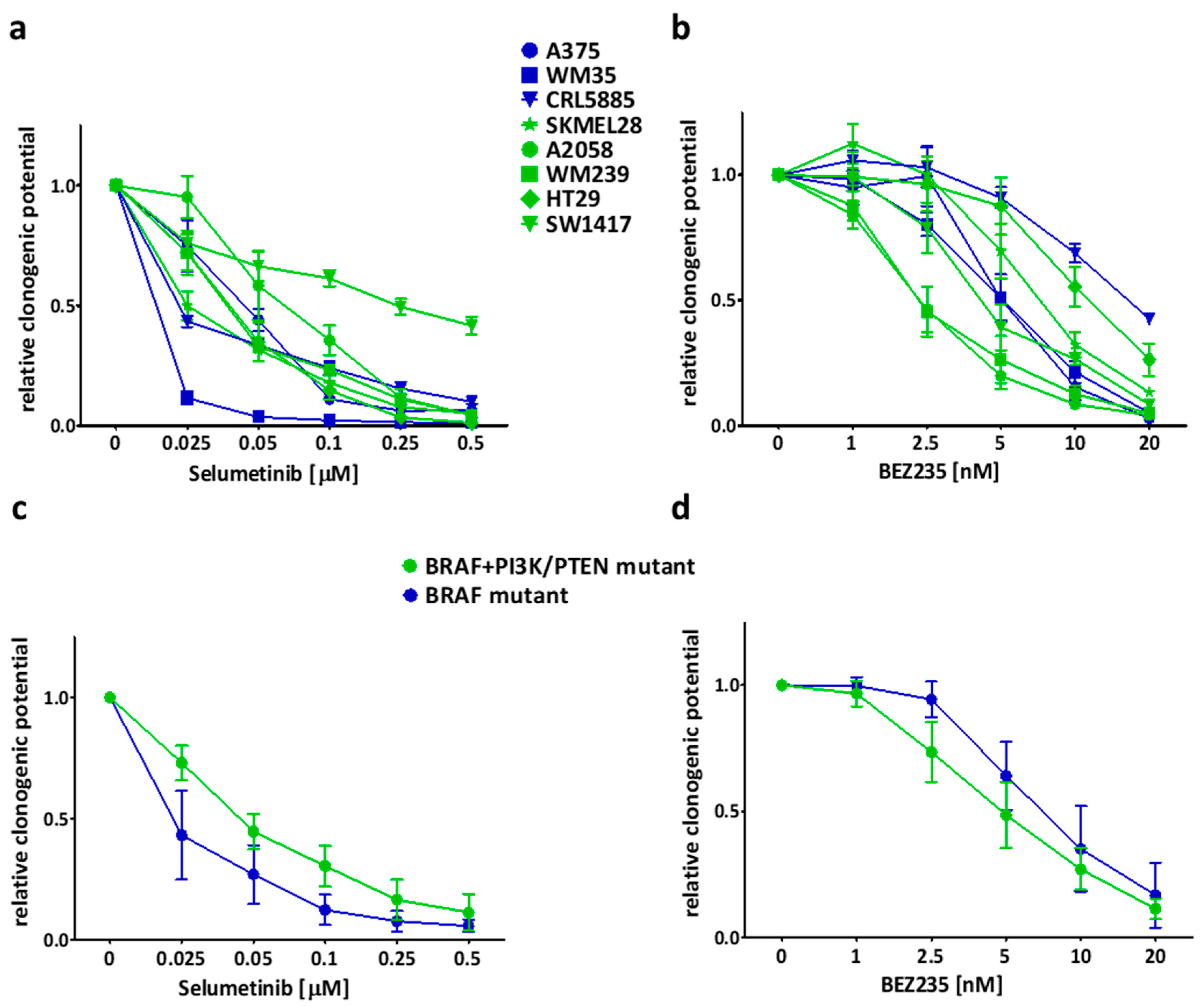
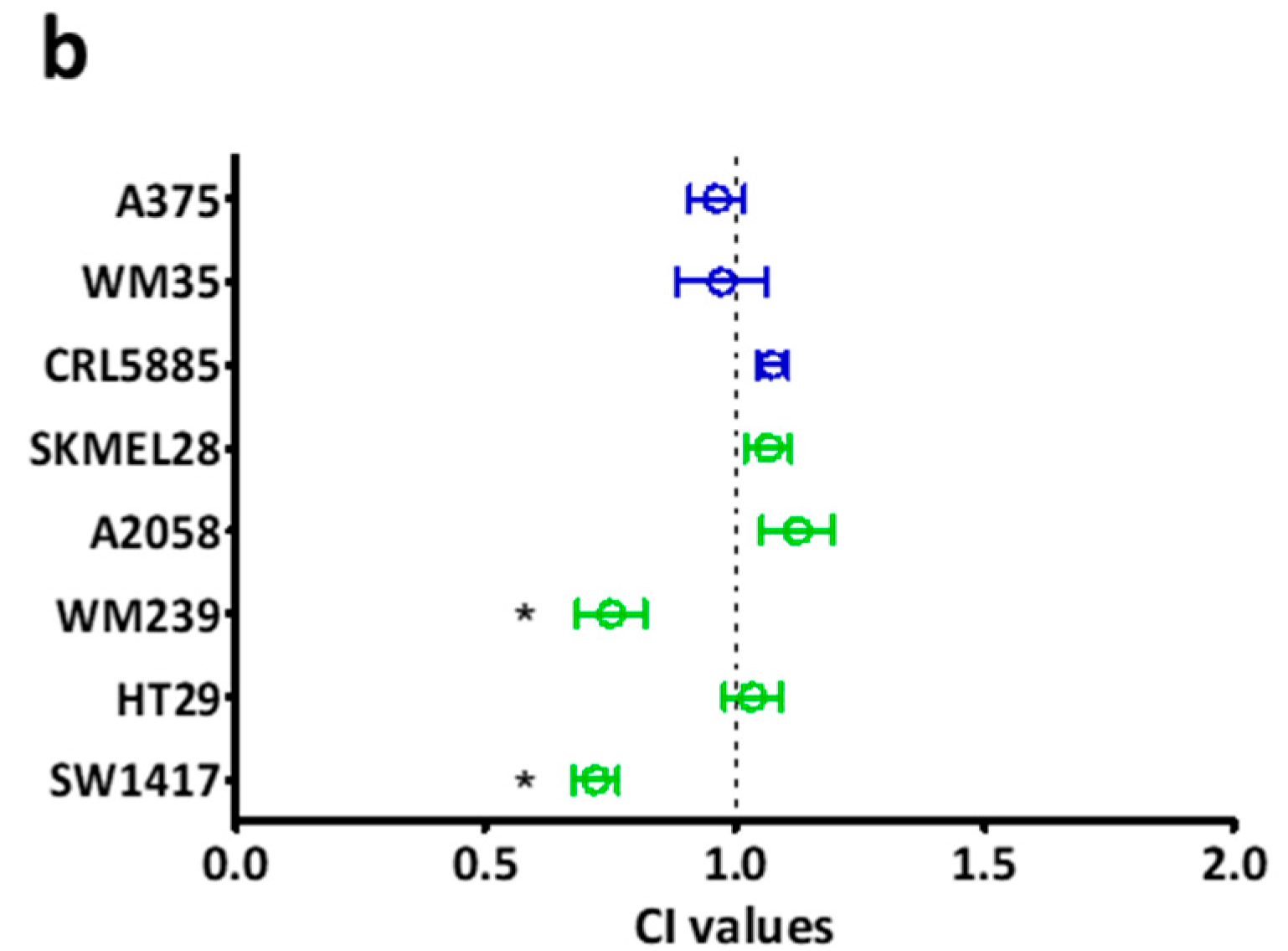
2.2. Long Term Effect of the Inhibitors Alone and in Combinations
2.3. Effect of the Inhibitors on Spheroid Growth
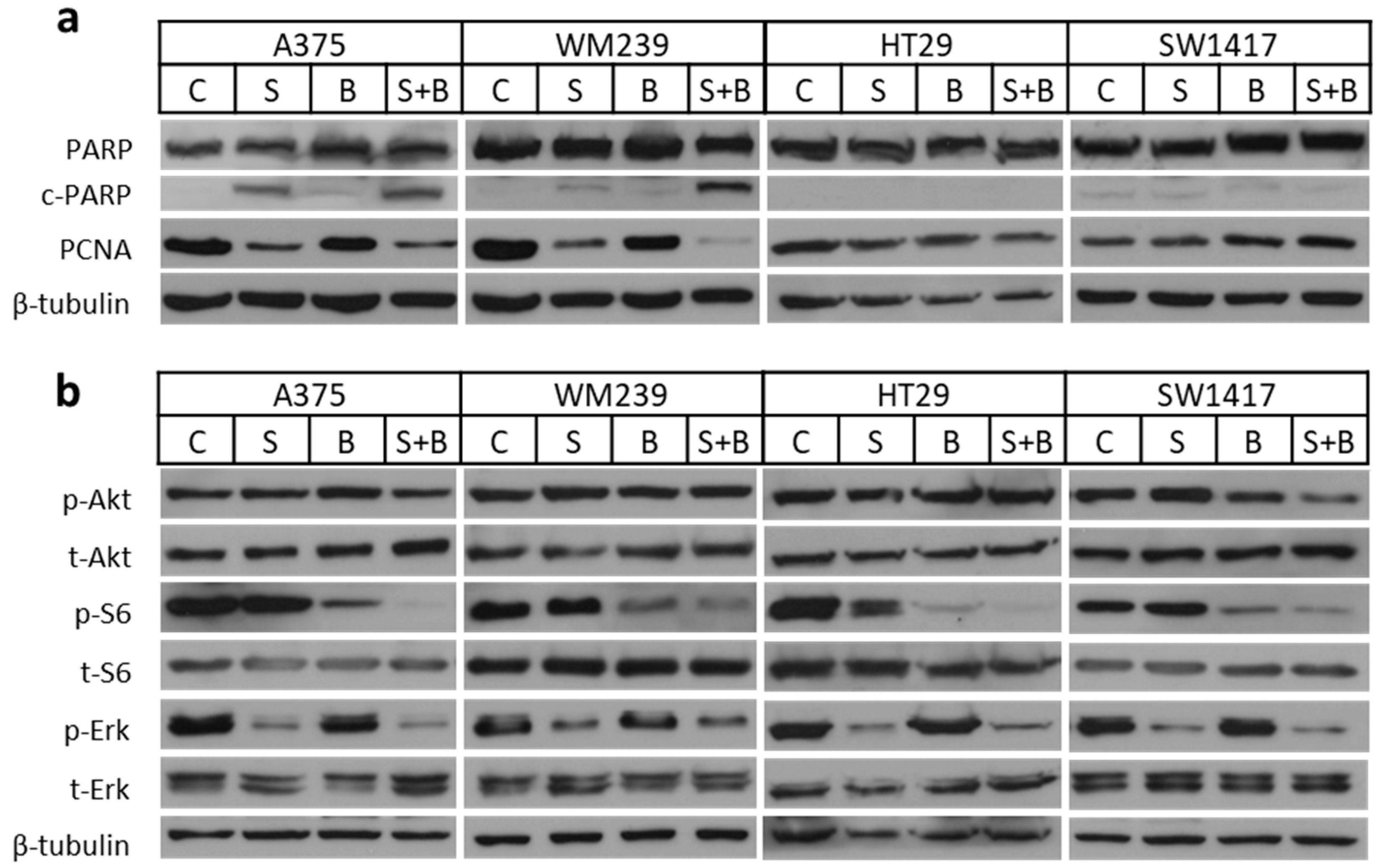
2.4. Apoptosis Induction and Decreased Signaling Upon Treatment
2.5. Baseline Activation of Certain Proteins in the Five Double Mutant Cell Lines
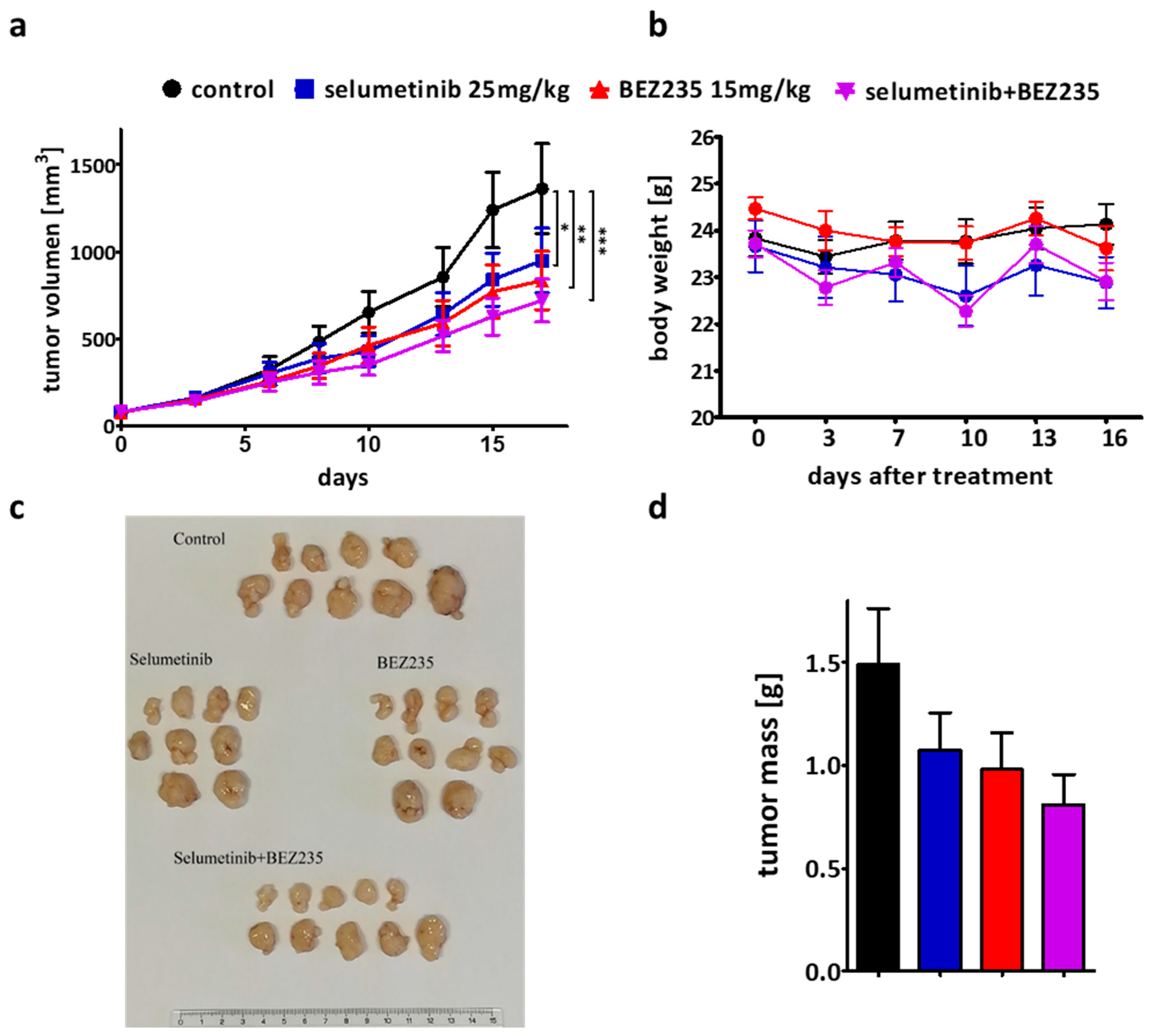
2.6. The Efficacy of the Combination Therapy Was Recapitulated in the SW1417 Xenograft Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Reagents
4.2. Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Assay
4.3. Colony Formation Inhibition and Combinatory Index Evaluation
4.4. Spheroid Growth Inhibition
4.5. Immunoblot Analysis
4.6. Cell Cycle and Cell Number Analysis
4.7. In Vivo Xenograft Experiment
4.8. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yap, T.A.; Garrett, M.D.; Walton, M.I.; Raynaud, F.; De Bono, J.S.; Workman, P. Targeting the PI3K–AKT–mTOR pathway: Progress, pitfalls, and promises. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.T. MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyamoorthy, K.; Li, G.; Gerrero, M.R.; Brose, M.S.; Volpe, P.; Weber, B.L.; Van Belle, P.; E Elder, D.; Herlyn, M. Constitutive mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in melanoma is mediated by both BRAF mutations and autocrine growth factor stimulation. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 756–759. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Steinmetz, R.; Wagoner, H.A.; Zeng, P.; Hammond, J.R.; Hannon, T.S.; Meyers, J.L.; Pescovitz, O.H. Mechanisms Regulating the Constitutive Activation of the Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase (ERK) Signaling Pathway in Ovarian Cancer and the Effect of Ribonucleic Acid Interference for ERK1/2 on Cancer Cell Proliferation. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 2570–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stemke-Hale, K.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Lluch, A.; Neve, R.M.; Kuo, W.-L.; Davies, M.; Carey, M.; Yinghui, G.; Guan, Y.; Sahin, A.; et al. An Integrative Genomic and Proteomic Analysis of PIK3CA, PTEN, and AKT Mutations in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6084–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, H.; Bignell, G.R.; Cox, C.; Stephens, P.; Edkins, S.; Clegg, S.; Teague, J.; Woffendin, H.; Garnett, M.J.; Bottomley, W.; et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 417, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turski, M.L.; Vidwans, S.J.; Janku, F.; Garrido-Laguna, I.; Munoz, J.; Schwab, R.; Subbiah, V.; Rodon, J.; Kurzrock, R. Genomically Driven Tumors and Actionability across Histologies: BRAF-Mutant Cancers as a Paradigm. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holderfield, M.; Deuker, M.M.; McCormick, F.; McMahon, M. Targeting RAF kinases for cancer therapy: BRAF-mutated melanoma and beyond. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molnár, E.; Rittler, D.; Baranyi, M.; Grusch, M.; Berger, W.; Dome, B.; Tóvári, J.; Aigner, C.; Tímár, J.; Garay, T.; et al. Pan-RAF and MEK vertical inhibition enhances therapeutic response in non-V600 BRAF mutant cells. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tissot, C.; Couraud, S.; Tanguy, R.; Bringuier, P.-P.; Girard, N.; Souquet, P.-J. Clinical characteristics and outcome of patients with lung cancer harboring BRAF mutations. Lung Cancer 2016, 91, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, S.A.; Beare, D.; Boutselakis, H.; Bamford, S.; Bindal, N.; Tate, J.; Cole, C.G.; Ward, S.; Dawson, E.; Ponting, L.; et al. COSMIC: Somatic cancer genetics at high-resolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, D777–D783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caunt, C.J.; Sale, M.J.; Smith, P.D.; Cook, S.J. MEK1 and MEK2 inhibitors and cancer therapy: The long and winding road. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 577–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carracedo, A.; Alimonti, A.; Pandolfi, P.P. PTEN Level in Tumor Suppression: How Much Is Too Little? Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hollander, M.C.; Blumenthal, G.M.; Dennis, P.A. PTEN loss in the continuum of common cancers, rare syndromes and mouse models. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, M.S.; Stojanov, P.; Mermel, C.H.; Robinson, J.T.; Garraway, L.A.; Golub, T.R.; Meyerson, M.L.; Gabriel, S.B.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G. Discovery and saturation analysis of cancer genes across 21 tumour types. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 505, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samuels, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bardelli, A.; Silliman, N.; Ptak, J.; Szabo, S.; Yan, H.; Gazdar, A.; Powell, S.M.; Riggins, G.J.; et al. High Frequency of Mutations of the PIK3CA Gene in Human Cancers. Science 2004, 304, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cole, P.A.; Chu, N.; Salguero, A.L.; Bae, H. AKTivation mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2019, 59, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldus, S.E.; Schaefer, K.-L.; Engers, R.; Hartleb, D.; Stoecklein, N.H.; Gabbert, H.E. Prevalence and Heterogeneity of KRAS, BRAF, and PIK3CA Mutations in Primary Colorectal Adenocarcinomas and Their Corresponding Metastases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, G.; Tseng, L.-H.; Chen, G.; Haley, L.; Illei, P.; Gocke, C.D.; Eshleman, J.R.; Lin, M.-T. Clinical detection and categorization of uncommon and concomitant mutations involving BRAF. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janku, F.; Lee, J.J.; Tsimberidou, A.M.; Hong, D.S.; Naing, A.; Falchook, G.S.; Fu, S.; Luthra, R.; Garrido-Laguna, I.; Kurzrock, R. PIK3CA Mutations Frequently Coexist with RAS and BRAF Mutations in Patients with Advanced Cancers. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shull, A.Y.; Latham-Schwark, A.; Ramasamy, P.; Leskoske, K.; Oroian, D.; Birtwistle, M.R.; Buckhaults, P.J. Novel Somatic Mutations to PI3K Pathway Genes in Metastatic Melanoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dankort, D.; Curley, D.P.; Cartlidge, R.A.; Nelson, B.; Karnezis, A.N.; Damsky, W.E., Jr.; You, M.J.; Depinho, R.A.; McMahon, M.; Bosenberg, M. BrafV600E cooperates with Pten loss to induce metastatic melanoma. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsao, H.; Goel, V.; Wu, H.; Yang, G.; Haluska, F.G. Genetic interaction between NRAS and BRAF mutations and PTEN/MMAC1 inactivation in melanoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendoza, M.C.; Er, E.E.; Blenis, J. The Ras-ERK and PI3K-mTOR pathways: Cross-talk and compensation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Viciana, P.; Warne, P.H.; Dhand, R.; Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Gout, I.; Fry, M.J.; Waterfield, M.D.; Downward, J. Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase direct target of Ras. Nat. Cell Biol. 1994, 370, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, F.; Schittek, B.; Busch, S.; Garbe, C.; Smalley, K.; Satyamoorthy, K.; Li, G.; Herlyn, M. The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways present molecular targets for the effective treatment of advanced melanoma. Front. Biosci. A J. Virtual Libr. 2005, 10, 2986–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, S. Phosphorylation and Regulation of Raf by Akt (Protein Kinase B). Science 1999, 286, 1741–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turke, A.B.; Song, Y.; Costa, C.; Cook, R.; Arteaga, C.L.; Asara, J.M.; Engelman, J.A. MEK Inhibition Leads to PI3K/AKT Activation by Relieving a Negative Feedback on ERBB Receptors. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 3228–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gopal, Y.V.; Deng, W.; Woodman, S.E.; Komurov, K.; Ram, P.; Smith, P.D.; Davies, M.A. Basal and Treatment-Induced Activation of AKT Mediates Resistance to Cell Death by AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in Braf-Mutant Human Cutaneous Melanoma Cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8736–8747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuo, Q.; Liu, J.; Huang, L.; Qin, Y.; Hawley, T.; Seo, C.; Merlino, G.; Yu, Y. AXL/AKT axis mediated-resistance to BRAF inhibitor depends on PTEN status in melanoma. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3275–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarian, R.; Shi, H.; Wang, Q.; Kong, X.; Koya, R.C.; Lee, H.; Chen, Z.; Lee, M.-K.; Attar, N.; Sazegar, H.; et al. Melanomas acquire resistance to B-RAF(V600E) inhibition by RTK or N-RAS upregulation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 468, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Roberto, M.; Panebianco, M.; Botticelli, A.; Mazzuca, F.; Marchetti, P. Drug resistance of BRAF-mutant melanoma: Review of up-to-date mechanisms of action and promising targeted agents. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 862, 172621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, R.B.; Homayouni, T.S.; Baluch, N.; Morgatskaya, E.; Kumar, S.; Das, B.; Yeger, H. Combination therapy in combating cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38022–38043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Nandi, S. Rare Genetic Diseases with Defects in DNA Repair: Opportunities and Challenges in Orphan Drug Development for Targeted Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2018, 10, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeh, T.C.; Marsh, V.; Bernat, B.A.; Ballard, J.; Colwell, H.; Evans, R.J.; Parry, J.; Smith, D.; Brandhuber, B.J.; Gross, S.; et al. Biological Characterization of ARRY-142886 (AZD6244), a Potent, Highly Selective Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase 1/2 Inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1576–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, B.R.; Logie, A.; McKay, J.S.; Martin, P.; Steele, S.; Jenkins, R.; Cockerill, M.; Cartlidge, S.; Smith, P.D. AZD6244 (ARRY-142886), a potent inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1/2 kinases: Mechanism of action in vivo, pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship, and potential for combination in preclinical models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 2209–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huynh, H.; Soo, K.C.; Chow, P.K.; Tran, E. Targeted inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase pathway with AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryu, S.-H.; Heo, S.-H.; Park, E.Y.; Choi, K.-C.; Lee, S.H. Selumetinib Inhibits Melanoma Metastasis to Mouse Liver via Suppression of EMT-targeted Genes. Anticancer. Res. 2017, 37, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartholomeusz, C.; Xie, X.; Pitner, M.K.; Kondo, K.; Dadbin, A.; Lee, J.; Saso, H.; Smith, P.D.; Dalby, K.N.; Ueno, N.T. MEK Inhibitor Selumetinib (AZD6244; ARRY-142886) Prevents Lung Metastasis in a Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Xenograft Model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 2773–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, S.R.; Hall, A.; Buckley, H.L.; Flanagan, L.; De Castro, D.G.; Farnell, K.; Moss, L.; Gregory, R.; Newbold, K.; Du, Y.; et al. Investigating the potential clinical benefit of Selumetinib in resensitising advanced iodine refractory differentiated thyroid cancer to radioiodine therapy (SEL-I-METRY): Protocol for a multicentre UK single arm phase II trial. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emelosky, B.; Bradbury, P.; Tu, D.; Florescu, M.; Reiman, A.; Nicholas, G.; Basappa, N.; Rothenstein, J.; Goffin, J.R.; Laurie, S.A.; et al. Selumetinib in patients receiving standard pemetrexed and platinum-based chemotherapy for advanced or metastatic KRAS wildtype or unknown non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer: A randomized, multicenter, phase II study. Canadian Cancer Trials Group (CCTG) IND.219. Lung Cancer 2019, 133, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, T.; Hirai, F.; Saka, H.; Kogure, Y.; Yoh, K.; Niho, S.; Fukase, K.; Shimada, H.; Sasai, M.; Fukino, K. Safety and tolerability of selumetinib as a monotherapy, or in combination with docetaxel as second-line therapy, in Japanese patients with advanced solid malignancies or non-small cell lung cancer. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 48, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gross, A.M.; Wolters, P.L.; Dombi, E.; Baldwin, A.; Whitcomb, P.; Fisher, M.J.; Weiss, B.; Kim, A.; Bornhorst, M.; Shah, A.C.; et al. Selumetinib in Children with Inoperable Plexiform Neurofibromas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1430–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maira, S.-M.; Stauffer, F.; Brueggen, J.; Furet, P.; Schnell, C.; Fritsch, C.; Brachmann, S.; Chène, P.; De Pover, A.; Schoemaker, K.; et al. Identification and characterization of NVP-BEZ235, a new orally available dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor with potent in vivo antitumor activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1851–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serra, V.; Markman, B.; Scaltriti, M.; Eichhorn, P.J.; Valero, V.; Guzman, M.; Botero, M.L.; Llonch, E.; Atzori, F.; Di Cosimo, S.; et al. NVP-BEZ235, a Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor, Prevents PI3K Signaling and Inhibits the Growth of Cancer Cells with Activating PI3K Mutations. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8022–8030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, S.A.; Jilaveanu, L.B.; Zito, C.; Camp, R.L.; Rimm, D.L.; Conrad, P.; Kluger, H. Vertical targeting of the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase pathway as a strategy for treating melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 6029–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Niu, B.; Wang, L.; Chen, M.; Kang, X.; Wang, L.; Ji, Y.; Zhong, J. Autophagy inhibition enhances colorectal cancer apoptosis induced by dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor NVP-BEZ235. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinelli, E.; Troiani, T.; D’Aiuto, E.; Morgillo, F.; Vitagliano, D.; Capasso, A.; Costantino, S.; Ciuffreda, L.P.; Merolla, F.; Vecchione, L.; et al. Antitumor activity of pimasertib, a selective MEK 1/2 inhibitor, in combination with PI3K/mTOR inhibitors or with multi-targeted kinase inhibitors in pimasertib-resistant human lung and colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 2089–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, R.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Libutti, S.K.; Hendifar, A.E.; Custodio, A.; Guimbaud, R.; Lombard-Bohas, C.; Ricci, S.; Klümpen, H.; Capdevila, J.; et al. Phase II Study of BEZ235 versus Everolimus in Patients with Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Inhibitor-Naïve Advanced Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Oncologist 2017, 23, e766–e790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fazio, N.; Buzzoni, R.; Baudin, E.; Antonuzzo, L.; Hubner, R.A.; Lahner, H.; De Herder, W.W.; Raderer, M.; Teulé, A.; Capdevila, J.; et al. A Phase II Study of BEZ235 in Patients with Everolimus-resistant, Advanced Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours. Anticancer. Res. 2016, 36, 713–719. [Google Scholar]
- Bedard, P.L.; Tabernero, J.; Janku, F.; Wainberg, Z.A.; Paz-Ares, L.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Pérez-García, J.; Stathis, A.; Britten, C.D.; et al. A Phase Ib Dose-Escalation Study of the Oral Pan-PI3K Inhibitor Buparlisib (BKM120) in Combination with the Oral MEK1/2 Inhibitor Trametinib (GSK1120212) in Patients with Selected Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 21, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juric, D.; Soria, J.-C.; Sharma, S.; Banerji, U.; Azaro, A.; Desai, J.; Ringeisen, F.P.; Kaag, A.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Hourcade-Potelleret, F.; et al. A phase 1b dose-escalation study of BYL719 plus binimetinib (MEK162) in patients with selected advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 9051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolcher, A.W.; Khan, K.; Ong, M.; Banerji, U.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.; Gandara, D.R.; Patnaik, A.; Baird, R.D.; Olmos, D.; Garrett, C.R.; et al. Antitumor activity in RAS-driven tumors by blocking AKT and MEK. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 21, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacinto, E.; Loewith, R.; Schmidt, A.; Lin, S.; Rüegg, M.A.; Hall, A.; Hall, M.N. Mammalian TOR complex 2 controls the actin cytoskeleton and is rapamycin insensitive. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, A.K.S.; Li, S.; Macrae, E.R.; Park, J.-I.; Mitchell, E.P.; Zwiebel, J.A.; Chen, H.X.; Gray, R.J.; McShane, L.M.; Rubinstein, L.V.; et al. Dabrafenib and Trametinib in Patients with Tumors with BRAFV600E Mutations: Results of the NCI-MATCH Trial Subprotocol H. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Zaoui, I.; Bucher, M.; Rimoldi, D.; Nicolas, M.; Kaya, G.; Gobert, R.P.; Bedoni, N.; Schalenbourg, A.; Sakina, E.; Zografos, L.; et al. Conjunctival Melanoma Targeted Therapy: MAPK and PI3K/mTOR Pathways Inhibition. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 2764–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sweetlove, M.; Wrightson, E.; Kolekar, S.; Rewcastle, G.W.; Baguley, B.C.; Shepherd, P.R.; Jamieson, S.M.F. Inhibitors of pan-PI3K Signaling Synergize with BRAF or MEK Inhibitors to Prevent BRAF-Mutant Melanoma Cell Growth. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, Y.; Wu, X.; Yin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ma, D.; Li, H. Antitumor activity of selective MEK1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 in combination with PI3K/mTOR inhibitor BEZ235 in gefitinib-resistant NSCLC xenograft models. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 33, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuger, S.; Flentje, M.; Djuzenova, C.S. Simultaneous perturbation of the MAPK and the PI3K/mTOR pathways does not lead to increased radiosensitization. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grazia, G.; Vegetti, C.; Benigni, F.; Penna, I.; Perotti, V.; Tassi, E.; Bersani, I.; Nicolini, G.; Canevari, S.; Carlo-Stella, C.; et al. Synergistic anti-tumor activity and inhibition of angiogenesis by cotargeting of oncogenic and death receptor pathways in human melanoma. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, H.; Kong, X.; Ribas, A.; Lo, R.S. Combinatorial treatments that overcome PDGFRβ-driven resistance of melanoma cells to V600EB-RAF inhibition. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5067–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montero, J.; Dutta, C.; Van Bodegom, D.; Weinstock, D.; Letai, A. p53 regulates a non-apoptotic death induced by ROS. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deb, S.; Jackson, C.T.; Subler, M.A.; Martin, D.W. Modulation of cellular and viral promoters by mutant human p53 proteins found in tumor cells. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 6164–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasudevan, K.M.; Barbie, D.A.; Davies, M.A.; Rabinovsky, R.; McNear, C.J.; Kim, J.J.; Hennessy, B.T.; Tseng, H.; Pochanard, P.; Kim, S.Y.; et al. AKT-Independent Signaling Downstream of Oncogenic PIK3CA Mutations in Human Cancer. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engelman, J.A.; Chen, L.; Tan, X.; Crosby, K.; Guimaraes, A.R.; Upadhyay, R.; Maira, M.; McNamara, K.; Perera, S.A.; Song, Y.; et al. Effective use of PI3K and MEK inhibitors to treat mutant Kras G12D and PIK3CA H1047R murine lung cancers. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spano, J.-P.; Lagorce, C.; Atlan, D.; Milano, G.; Domont, J.; Benamouzig, R.; Attar, A.; Benichou, J.; Martin, A.; Morere, J.-F.; et al. Impact of EGFR expression on colorectal cancer patient prognosis and survival. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayyed, M.F.; El-Maqsoud, N.M.R.A.; El-Heeny, A.A.E.-H.; Mohammed, M.F. c-MET expression in colorectal adenomas and primary carcinomas with its corresponding metastases. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2015, 6, 618–627. [Google Scholar]
- Thakuri, P.S.; Tavana, H. Single and Combination Drug Screening with Aqueous Biphasic Tumor Spheroids. SLAS Discov. Adv. Life Sci. R D 2017, 22, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Migliardi, G.; Sassi, F.; Torti, D.; Galimi, F.; Zanella, E.R.; Buscarino, M.; Ribero, D.; Muratore, A.; Massucco, P.; Pisacane, A.; et al. Inhibition of MEK and PI3K/mTOR Suppresses Tumor Growth but Does Not Cause Tumor Regression in Patient-Derived Xenografts of RAS-Mutant Colorectal Carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 2515–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khaleghpour, K. Involvement of the PI 3-kinase signaling pathway in progression of colon adenocarcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2003, 25, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-C. Drug Combination Studies and Their Synergy Quantification Using the Chou-Talalay Method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Cell Line | Tissue | BRAF | PI3K/PTEN | RAS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A375 | melanoma | V600E | wild type | wild type |
| WM35 | melanoma | V600E | wild type | wild type |
| CRL5885 | lung | G466V | wild type | wild type |
| SKMEL28 | melanoma | V600E | PTEN T167A | wild type |
| A2058 | melanoma | V600E | PTEN null | wild type |
| WM239 | melanoma | V600D | PTEN null | wild type |
| HT29 | colon | V600E | PI3KCA P449T | wild type |
| SW1417 | colon | V600E | delPI3KR1 [70] | wild type |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rittler, D.; Molnár, E.; Baranyi, M.; Garay, T.; Hegedűs, L.; Aigner, C.; Tóvári, J.; Tímár, J.; Hegedűs, B. Horizontal Combination of MEK and PI3K/mTOR Inhibition in BRAF Mutant Tumor Cells with or without Concomitant PI3K Pathway Mutations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207649
Rittler D, Molnár E, Baranyi M, Garay T, Hegedűs L, Aigner C, Tóvári J, Tímár J, Hegedűs B. Horizontal Combination of MEK and PI3K/mTOR Inhibition in BRAF Mutant Tumor Cells with or without Concomitant PI3K Pathway Mutations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(20):7649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207649
Chicago/Turabian StyleRittler, Dominika, Eszter Molnár, Marcell Baranyi, Tamás Garay, Luca Hegedűs, Clemens Aigner, József Tóvári, József Tímár, and Balázs Hegedűs. 2020. "Horizontal Combination of MEK and PI3K/mTOR Inhibition in BRAF Mutant Tumor Cells with or without Concomitant PI3K Pathway Mutations" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 20: 7649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207649
APA StyleRittler, D., Molnár, E., Baranyi, M., Garay, T., Hegedűs, L., Aigner, C., Tóvári, J., Tímár, J., & Hegedűs, B. (2020). Horizontal Combination of MEK and PI3K/mTOR Inhibition in BRAF Mutant Tumor Cells with or without Concomitant PI3K Pathway Mutations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(20), 7649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207649





