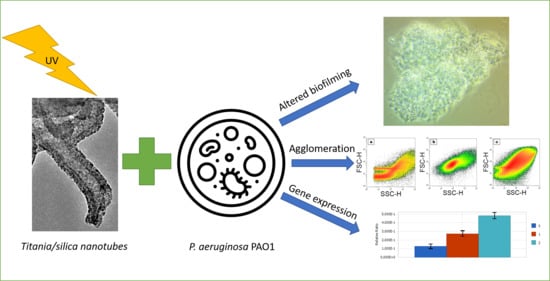
The Response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 to UV-activated Titanium Dioxide/Silica Nanotubes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Physical and Chemical Characterization of Studied Nanomaterial
2.2. Viability and Agglomeration
2.3. Biofilm Formation
2.4. Relative Expression of Selected Genes
2.5. Antibiotic Susceptibility on Media Containing Activated Nanomaterials
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Synthesis of Titanium Dioxide/Silica Nanotubes (mt-SiO2/TiO2)
4.3. Preparation of Bacteria
4.4. Viability Testing and Observation of Cells Agglomeration
4.5. Biofilm Viability and Biomass
4.6. Gene Expression Studies
4.7. Antibiotic Susceptibility on Media Containing Activated Nanomaterials
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Branski, L.K.; Al-Mousawi, A.; Rivero, H.; Jeschke, M.G.; Sanford, A.P.; Herndon, D.N. Emerging Infections in Burns. Surg. Infect. (Larchmt) 2009, 10, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winstanley, C.; O’Brien, S.; Brockhurst, M.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Evolutionary Adaptation and Diversification in Cystic Fibrosis Chronic Lung Infections. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Newman, J.W.; Floyd, R.V.; Fothergill, J.L. The contribution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factors and host factors in the establishment of urinary tract infections. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2017, 364, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, V.D.; Al-Abdely, H.M.; Ali El-Kholy, A.; Aziz AlKhawaja, S.A.; Leblebicioglu, H.; Mehta, Y.; Rai, V.; Viet Hung, N.; Sami Kanj, S.; Foda Salama, M.; et al. International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium report, data summary of 50 countries for 2010–2015: Device-associated module. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2016, 44, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojciuk, B.; Salabura, A.; Grygorcewicz, B.; Kędzierska, K.; Ciechanowski, K.; Dołęgowska, B. Urobiome: In Sickness and in Health. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lotfabad, T.B.; Shahcheraghi, F.; Shooraj, F. Assessment of antibacterial capability of rhamnolipids produced by two indigenous Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2013, 6, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panghal, M.; Singh, K.; Kadyan, S.; Chaudary, U.; Yadav, J.P. The analysis of distribution of multidrug resistant Pseudomonas and Bacillus species from burn patients and burn ward environment. Burns 2015, 41, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Cao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Han, L.; Zhan, S. Prevalence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and antimicrobial-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with pneumonia in mainland China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 49, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. Global Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria to Guide Research, Discovery, and Development of New Antibiotics. Available online: www.who.int/medicines/publications/global-priority-list-antibiotic-resistant-bacteria/en/ (accessed on 5 October 2020).
- Sikora, P.; Cendrowski, K.; Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Horszczaruk, E.; Mijowska, E. The effects of silica/titania nanocomposite on the mechanical and bactericidal properties of cement mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 150, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, P.; Augustyniak, A.; Cendrowski, K.; Horszczaruk, E.; Rucinska, T.; Nawrotek, P.; Mijowska, E. Characterization of Mechanical and Bactericidal Properties of Cement Mortars Containing Waste Glass Aggregate and Nanomaterials. Materials (Basel) 2016, 9, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iavicoli, I.; Leso, V.; Beezhold, D.H.; Shvedova, A.A. Nanotechnology in agriculture: Opportunities, toxicological implications, and occupational risks. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 329, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trukawka, M.; Cendrowski, K.; Peruzynska, M.; Augustyniak, A.; Nawrotek, P.; Drozdzik, M.; Mijowska, E. Carbonized metal–organic frameworks with trapped cobalt nanoparticles as biocompatible and efficient azo-dye adsorbent. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrotek, P.; Augustyniak, A. Nanotechnology in microbiology—Selected aspects | Nanotechnologia w mikrobiologii—wybrane aspekty. Postep. Mikrobiol. 2015, 54, 275–282. [Google Scholar]
- Cendrowski, K.; Peruzynska, M.; Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Chen, X.; Wajda, A.; Lapczuk, J.; Kurzawski, M.; Kalenczuk, R.J.; Drozdzik, M.; Mijowska, E. Antibacterial performance of nanocrystallined titania confined in mesoporous silica nanotubes. Biomed. Microdevices. 2014, 16, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borkowski, A.; Cłapa, T.; Szala, M.; Gąsiński, A.; Selwet, M. Synthesis of SiC/Ag/Cellulose Nanocomposite and Its Antibacterial Activity by Reactive Oxygen Species Generation. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piszczek, P.; Lewandowska, Ż.; Radtke, A.; Jędrzejewski, T.; Kozak, W.; Sadowska, B.; Szubka, M.; Talik, E.; Fiori, F. Biocompatibility of Titania Nanotube Coatings Enriched with Silver Nanograins by Chemical Vapor Deposition. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Mahendra, S.; Lyon, D.Y.; Brunet, L.; Liga, M.V.; Li, D.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Antimicrobial nanomaterials for water disinfection and microbial control: Potential applications and implications. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4591–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, P.; Schimel, J.P.; Godwin, H. Five reasons to use bacteria when assessing manufactured nanomaterial environmental hazards and fates. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 27, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xie, W.; Huang, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, N.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. The graphene oxide and chitosan biopolymer loads TiO2 for antibacterial and preservative research. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemire, J.; Harrison, J.J.; Turner, R.J. Antimicrobial activity of metals: Mechanisms, molecular targets and applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Schimel, J.P.; Holden, P. a Evidence for negative effects of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles on soil bacterial communities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1659–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Schimel, J.P.; Holdena, P. Identification of soil bacteria susceptible to TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 6749–6758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maurer-Jones, M.A.; Gunsolus, I.L.; Meyer, B.M.; Christenson, C.J.; Haynes, C.L. Impact of TiO2 nanoparticles on growth, biofilm formation, and flavin secretion in Shewanella oneidensis. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 5810–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Augustyniak, A.; Cendrowski, K.; Nawrotek, P.; Barylak, M.; Mijowska, E. Investigating the Interaction Between Streptomyces sp. and Titania/Silica Nanospheres. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Y.-C.; Wu, X.-Y.; Sun, J.-Z.; Cao, Y.-X.; Song, H. Engineering quorum sensing signaling of Pseudomonas for enhanced wastewater treatment and electricity harvest: A review. Chemosphere 2015, 140, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.Y.; Koh, E.; Wong, A.; March, J.C.; Bentley, W.E.; Lee, Y.S.; Chang, M.W. Engineered probiotic Escherichia coli can eliminate and prevent Pseudomonas aeruginosa gut infection in animal models. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mccaughey, L.C.; Josts, I.; Grinter, R.; White, P.; Byron, O.; Tucker, N.P.; Matthews, J.M.; Kleanthous, C.; Whitchurch, C.B.; Walker, D. Discovery, characterization and in vivo activity of pyocin SD2, a protein antibiotic from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 2345–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Mathieu, J.M.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Miller, J.T.; Wu, T.; Shibata, T.; Guo, W.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Defense mechanisms of pseudomonas aeruginosa pao1 against quantum dots and their released heavy metals. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6091–6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horst, A.M.; Neal, A.C.; Mielke, R.E.; Sislian, P.R.; Suh, W.H.; Mädler, L.; Stucky, G.D.; Holden, P. Dispersion of TiO2 nanoparticle agglomerates by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7292–7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shivaji, S.; Madhu, S.; Singh, S. Extracellular synthesis of antibacterial silver nanoparticles using psychrophilic bacteria. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 1800–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husseiny, M.I.; El-Aziz, M.A.; Badr, Y.; Mahmoud, M.A. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2007, 67, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, C.B.B.; Silva, A.F.; Rufino, R.D.; Luna, J.M.; Souza, J.E.G.; Sarubbo, L.A. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using a biosurfactant produced in low-cost medium as stabilizing agent. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 17, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cendrowski, K. Titania/mesoporous silica nanotubes with efficient photocatalytic properties. Polish, J. Chem. Technol. 2018, 20, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verdier, T.; Bertron, A.; Erable, B.; Roques, C. Bacterial Biofilm Characterization and Microscopic Evaluation of the Antibacterial Properties of a Photocatalytic Coating Protecting Building Material. Coatings 2018, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baptista, P.V.; McCusker, M.P.; Carvalho, A.; Ferreira, D.A.; Mohan, N.M.; Martins, M.; Fernandes, A.R. Nano-strategies to fight multidrug resistant bacteria-”A Battle of the Titans”. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borkowski, A.; Syczewski, M.; Czarnecka-Skwarek, A. Ionic liquids strongly affect the interaction of bacteria with magnesium oxide and silica nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 28724–28734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, X.; Li, J.; Ma, S.; Liu, G.; Yang, K.; Tong, M.; Lin, D. Toxicity of TiO2 Nanoparticles to Escherichia coli: Effects of Particle Size, Crystal Phase and Water Chemistry. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, G.S.; Kumar, A.; Shanker, R.; Dhawan, A. Assessment of agglomeration, co-sedimentation and trophic transfer of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in a laboratory-scale predator-prey model system. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouyang, K.; Mortimer, M.; Holden, P.; Cai, P.; Wu, Y.; Gao, C.; Huang, Q. Towards a better understanding of Pseudomonas putida biofilm formation in the presence of ZnO nanoparticles (NPs): Role of NP concentration. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capdevila, D.A.; Wang, J.; Giedroc, D.P. Bacterial strategies to maintain zinc metallostasis at the host-pathogen interface. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 20858–20868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teitzel, G.M.; Geddie, A.; De Long, S.K.; Jo Kirisits, M.; Whiteley, M.; Parsek, M.R.; Cu, H.; Cu, H. Survival and Growth in the Presence of Elevated Copper: Transcriptional Profiling of Copper-Stressed Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 7242–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salunkhe, P.; Töpfer, T.; Buer, J.; Tümmler, B. Genome-Wide Transcriptional Pro ling of the Steady-State Response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 2565–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palma, M.; DeLuca, D.; Worgall, S.; Quadri, L.E.N. Transcriptome Analysis of the Response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sikora, P.; Augustyniak, A.; Cendrowski, K.; Nawrotek, P.; Mijowska, E. Antimicrobial Activity of Al2O3, CuO, Fe3O4, and ZnO Nanoparticles in Scope of Their Further Application in Cement-Based Building Materials. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palleroni, N.J. Pseudomonas; John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2015; ISBN 9781118960608. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/book/10.1002/9781118960608 (accessed on 16 October 2020).
- Augustyniak, A. The Influence of Nanomaterials on the Environmental Bacteria of Potential Biotechnological Significance. Ph.D. Thesis, West Pomeranian University of Technology, Szczecin, Poland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Merritt, J.H.; Kadouri, D.E.; O’Toole, G.A. Growing and Analyzing Static Biofilms. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2015, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savli, H.; Karadenizli, A.; Kolayli, F.; Gundes, S.; Ozbek, U.; Vahaboglu, H. Expression stability of six housekeeping genes: A proposal for resistance gene quantification studies of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by real-time quantitative RT-PCR. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 52, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alqarni, B.; Colley, B.; Klebensberger, J.; McDougald, D.; Rice, S.A. Expression stability of 13 housekeeping genes during carbon starvation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Microbiol. Methods 2016, 127, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabestani, M.R.; Rajabpour, M.; Mashouf, R.Y.; Alikhani, M.Y.; Mousavi, S.M. Expression of efflux pump mexab-oprm and oprd of pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from clinical samples using qrt-pcr. Arch. Iran. Med. 2014, 18, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Aedekerk, S.; Diggle, S.P.; Song, Z.; Høiby, N.; Cornelis, P.; Williams, P.; Cámara, M. The MexGHI-OpmD multidrug efflux pump controls growth, antibiotic susceptibility and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa via 4-quinolone-dependent cell-to-cell communication. Microbiology 2005, 151, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bragonzi, A.; Worlitzsch, D.; Pier, G.B.; Timpert, P.; Ulrich, M.; Hentzer, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Givskov, M.; Conese, M.; Döring, G. Nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa Expresses Alginate in the Lungs of Patients with Cystic Fibrosis and in a Mouse Model. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Antibiotic | Control (mm) | SD | Treated (mm) | SD | EUCAST * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN | 21.00 | ±0.00 | 19.33 | ±0.58 | 15 |
| FEP | 30.67 | ±0.58 | 29.67 | ±0.58 | 21 |
| ATM | 28.67 | ±0.58 | 29.00 | ±0.00 | 18 |
| MEM | 36.50 | ±0.71 | 35.00 | ±0.00 | 18 |
| CIP | 35.00 | ±1.00 | 36.00 | ±0.00 | 26 |
| Primer Name | Gene Function | Sequence (5′–3′) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| ampC-f | Chromosomal beta lactamase | AGATTCCCCTGCCTGTGC | [49] |
| ampC-r | GGCGGTGAAGGTCTTGCT | ||
| recA-f | Recombinase A | TCCGCAGGTAGCACTCAGTTC | [50] |
| recA-r | AAGCCGGATTCATAGGTGGTG | ||
| oprD-f | Outer membrane protein | ATCTACCGCACAAACGATGAG | [51] |
| oprD-r | GCCGAAGCCGATATAATCAAACG | ||
| oprL-f | Peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein | ATGGAAATGCTGAAATTCGGC | [52] |
| oprL-r | CTTCTTCAGCTCGACGCGACG | ||
| gyrA-f | Gyrase | TGTGCTTTATGCCATGAGCGA | [53] |
| gyrA-r | TCCACCGAACCGAAGTTGC | ||
| mexA-f | Efflux pump | CTCGACCCGATCTACGTC | [51] |
| mexA-r | GTCTTCACCTCGACACCC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Augustyniak, A.; Cendrowski, K.; Grygorcewicz, B.; Jabłońska, J.; Nawrotek, P.; Trukawka, M.; Mijowska, E.; Popowska, M. The Response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 to UV-activated Titanium Dioxide/Silica Nanotubes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207748
Augustyniak A, Cendrowski K, Grygorcewicz B, Jabłońska J, Nawrotek P, Trukawka M, Mijowska E, Popowska M. The Response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 to UV-activated Titanium Dioxide/Silica Nanotubes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(20):7748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207748
Chicago/Turabian StyleAugustyniak, Adrian, Krzysztof Cendrowski, Bartłomiej Grygorcewicz, Joanna Jabłońska, Paweł Nawrotek, Martyna Trukawka, Ewa Mijowska, and Magdalena Popowska. 2020. "The Response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 to UV-activated Titanium Dioxide/Silica Nanotubes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 20: 7748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207748
APA StyleAugustyniak, A., Cendrowski, K., Grygorcewicz, B., Jabłońska, J., Nawrotek, P., Trukawka, M., Mijowska, E., & Popowska, M. (2020). The Response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 to UV-activated Titanium Dioxide/Silica Nanotubes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(20), 7748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207748