Abstract
As a member of the Catharanthus roseus receptor-like kinase 1-like (CrRLK1L) protein kinase subfamily, FERONIA (FER) has emerged as a versatile player regulating multifaceted functions in growth and development, as well as responses to environmental factors and pathogens. With the concerted efforts of researchers, the molecular mechanism underlying FER-dependent signaling has been gradually elucidated. A number of cellular processes regulated by FER-ligand interactions have been extensively reported, implying cell type-specific mechanisms for FER. Here, we provide a review on the roles of FER in male-female gametophyte recognition, cell elongation, hormonal signaling, stress responses, responses to fungi and bacteria, and present a brief outlook for future efforts.
1. Introduction
Plants are persistently perceiving, recognizing and transducing extracellular environmental signals, such as light, temperature, nutrients, and pathogens, during their lifetime [1,2,3,4], which have received extensive interest worldwide to dissect the underlying molecular basis. Plant cells usually utilize receptors to interpret diverse signals into cellular responses [5]. Plant receptor-like kinases (RLKs) compose one of the largest subfamilies in membrane proteins, which involve more than 600 members in Arabidopsis thaliana and Solanum lycopersicum, respectively [6,7]. To date, most of the ligands for these receptor-like kinases have not been identified. A typical RLK contains an extracellular domain, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic kinase domain [8]. According to the differences in the extracellular domains, plant RLKs are divided into several subgroups, including the Catharanthus roseus RLK1-like (CrRLK1L) family, the leucine-rich repeat (LRR) RLK family, the LysM RLK family, the proline-rich extensin-like RLK family, and the lectin RLK family [6,9]. Named after the identification of CrRLK1 in Catharanthus roseus [10], members in the CrRLK1L family are characterized by one or two malectin-like domains, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular Ser/Thr kinase domain [9]. The CrRLK1L members always harbor two malectin-like domains, which have been hypothesized to be capable of interacting with cell wall polysaccharides (oligogalacturonides, OGAs) or glycosylated proteins. Currently, a total of 17, 23, and 20 putative CrRLK1L members have been retrieved in the genomes of A. thaliana, S. lycopersicum, and Oryza sativa, respectively [6,11,12], some of which have been functionally identified (Figure 1). Among them, FERONIA (FER) is, above all, the most extensively investigated, which is named from the Etruscan fertility goddess for its originally identified role in fertilization [13,14]. Here, we focus on recent advances in underpinning multifaceted functions of FER (AtFER, unless indicated otherwise) and try to explore further challenges in future studies on this RLK.
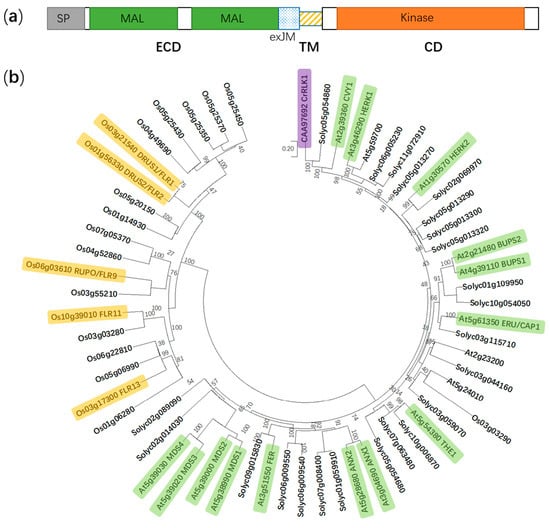
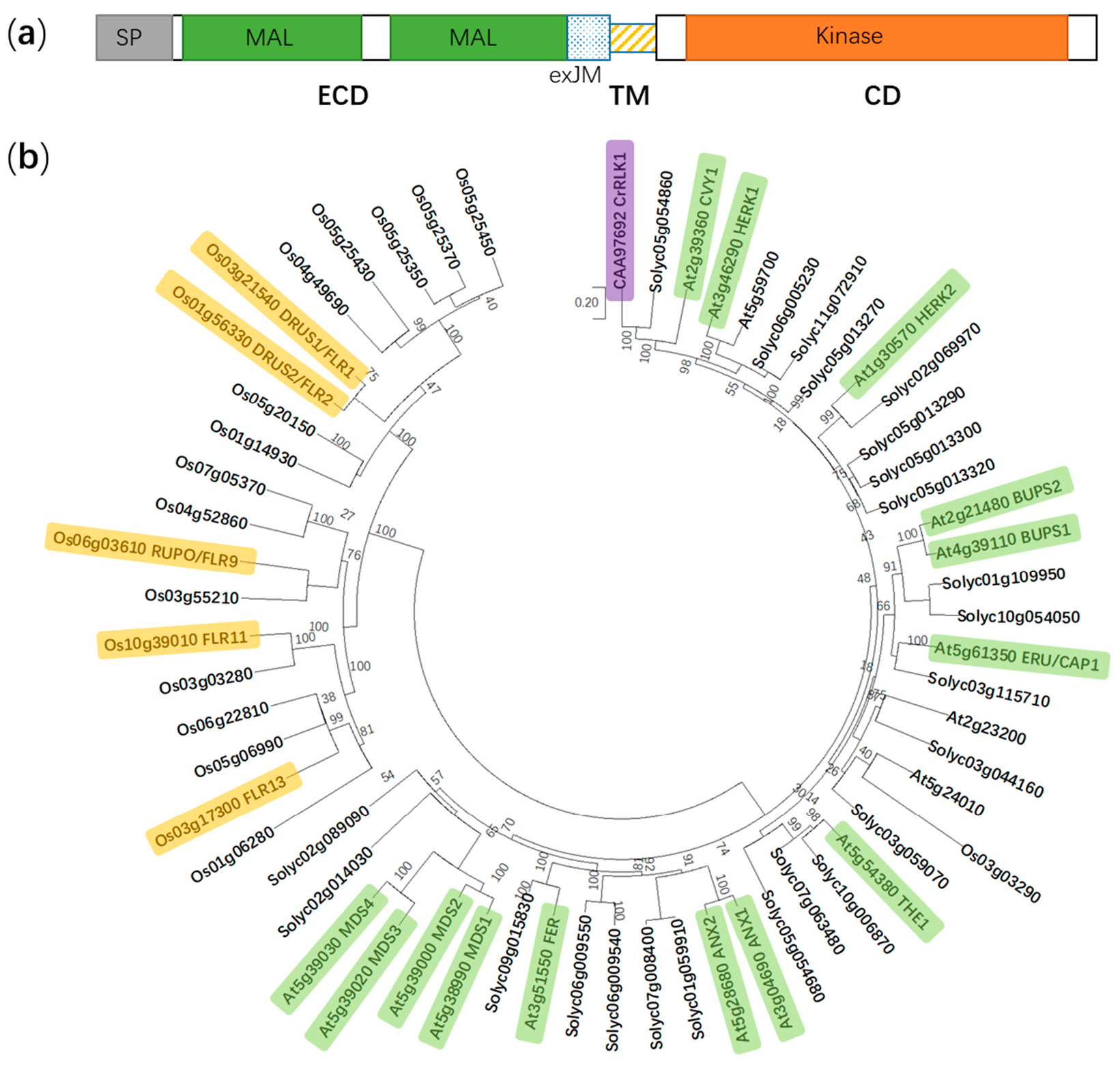
Figure 1.
Protein domain structure of FER and a phylogenetic tree of the CrRLK1L subfamily in Arabidopsis thaliana, Solanum lycopersicum, and Oryza sativa. (a) FER is composed of an extracellular domain (ECD), a transmembrane domain (TM), and a cytosolic domain (CD). SP, signal peptide; MAL, malectin-like; and exJM, extracellular juxtamembrane region. (b) The phylogenetic tree is generated using the neighbor-joining method in MEGA X. Boot-strap values (1000 replicates) are shown for each branch. FER, FERONIA; ANX1 to 2, ANXUR1 to 2; THE1, THESEUS1; ERU/CAP1, ERULUS/(Ca2+)cyt-ASSOCIATED PROTEIN KINASE; BUPS1 to 2, BUDDHA’S PAPER SEAL 1 to 2; HERK1 to 2, HERCULES1 to 2; CVY1, CURVY1; CrRLK1, Catharanthus roseus receptor-like kinase 1; MDS1 to 4, MEDOS1 to 4; FLR1, 2, 9, 11, and 13, FERONIA-LIKE RECEPTOR1, 2, 9, 11, and 13; RUPO, RUPTURED POLLEN TUBE; and DRUS1 to 2, DWARF AND RUNTISH SPIKELET1 to 2. Yellow, green and purple color indicate functionally identified CrRLK1L members in Oryza sativa, A. thaliana and Catharanthus roseus, respectively.
2. FER is Involved in Multiple Aspects in Plant Growth and Development
2.1. FER Mediates Male-Female Gametophyte Recognition During Sexual Reproduction
Precise guidance and penetration of pollen tubes are crucial for successful sexual reproduction, which requires the coordination of extracellular signaling molecules and their receptors [15,16]. The polarized growth of pollen tubes is mainly guided by the chemical inducer LURE [17,18], whereas FER has a dual role in guaranteeing the normal delivery of sperm cells and blocking polyspermy [19,20,21,22]. As early as 2003, Huck et al. isolated a semi-sterile gametophytic mutant affected in female gametophyte development, feronia (fer), for which the pollen tubes failed to burst and release the sperm cells [14]. Further studies showed that the mutation in fer was mapped to At3g51550, which encoded a membrane-resided receptor-like kinase composed of a signal peptide (SP), two extracellular malectin-like domains (MAL), an extracellular juxtamembrane region (exJM), a transmembrane domain (TM), and an intracellular kinase domain (Kinase) (Figure 1A) [19,20,23]. Normal pollen tube growth, arrest, and the release of sperm cells require the FER-dependent signaling pathway in the synergid cell membrane, during which reactive oxygen species (ROS) are key mediators [14,19,22]. LORELEI (LRE) encodes a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored protein with a modified eight-cysteine motif (M8CM). In the lorelei (lre) mutant, pollen tube reception fails in most female gametophytes, whereas the ectopic expression of LRE in pollen tubes could complement the defect in pollen tube reception in lre female gametophytes in a non-cell-autonomous manner, which is dependent on FERONIA but nondependent on the GPI anchor. These findings imply that FERONIA and LRE are synergistically involved in pollen tube reception [24]. Moreover, FER interacts with RHO GTPase signaling pathway proteins ROP2 (RHO OF PLANTS 2) and GEF1 (GUANINE EXCHANGE FACTORS 1) to generate ROS burst at the filiform apparatus/synergid cell region, further inducing pollen tube rupture and sperm release [20,21]. Importantly, a point mutation in FER-K565 resulted in the abolishment of its in vitro kinase activity, but it can complement the defect in pollen tube reception of fer-1, suggesting that the kinase activity may be not essential for FER function [25].
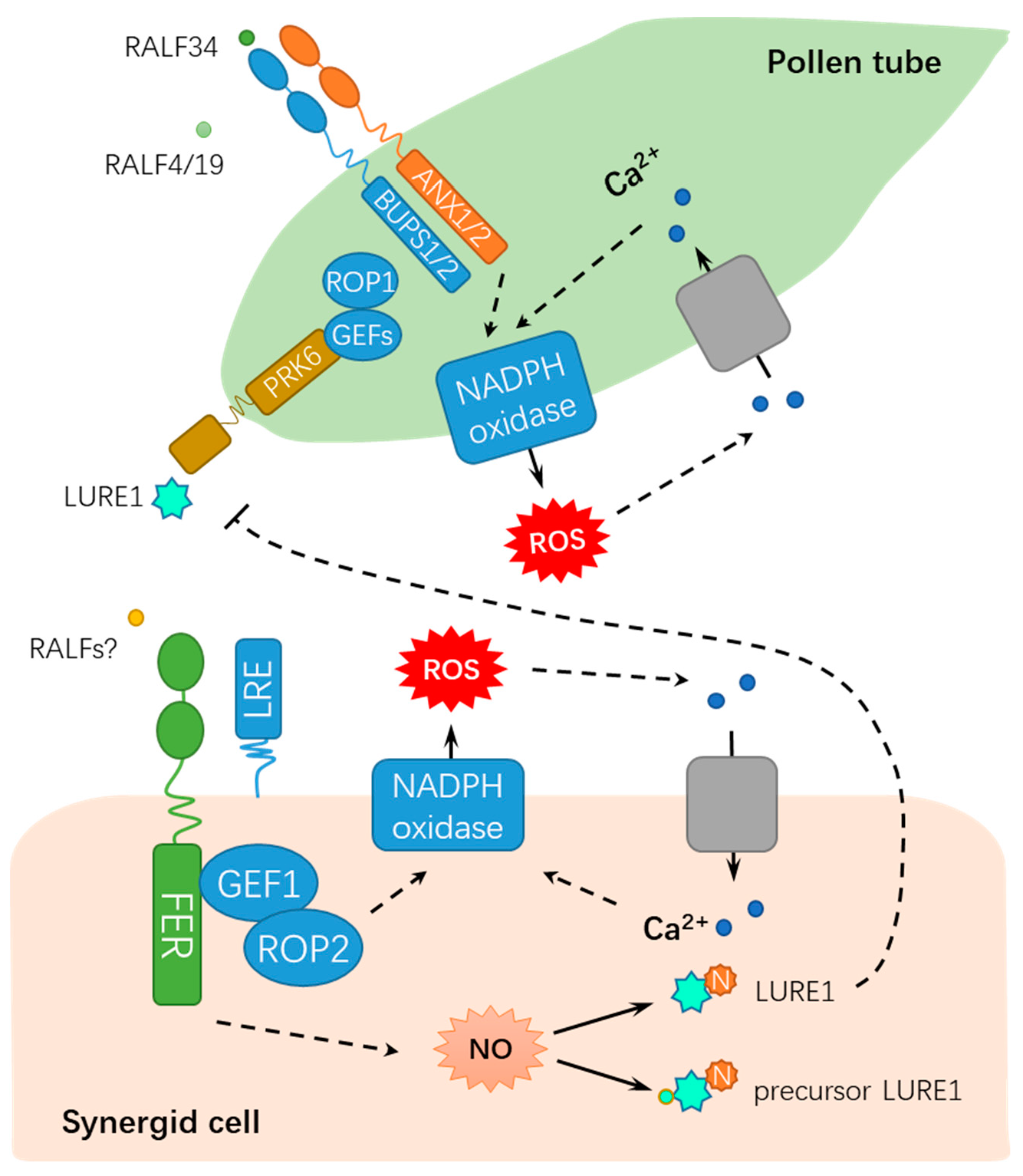
Originally identified to be capable of inducing apoplastic alkalization in a tobacco cell culture, rapid alkalinization factors (RALFs) compose a family of 34 RALF-like genes in Arabidopsis [26,27], which are involved in CrRLK1L receptors/FER signaling. Among the CrRLK1L receptors, BUDDHA’S PAPER SEAL l (BUPS1) and BUPS2 (BUPS1/2) and ANXUR1 and ANXUR2 (ANX1/2) have been shown to regulate pollen tube wall stiffness, whereas RALF4 and RALF19 may function in maintaining cell integrity [28,29]. BUPS1/2 and ANX1/2 bind to RALF4 and RALF19 for maintaining pollen tube integrity, whereas RALF34 is capable of binding to BUPS1/2 and ANX1/2 and inducing pollen tube burst at nanomolar concentrations [16]. These findings propose a novel working model by which RALF34 takes over RALF4 and RALF19 during male–female gametophyte communication, thereby triggering pollen tube rupture by deregulating BUPS-ANXUR signaling. In addition to the function for facilitating fertilization, FER also inhibits the entry of supernumerary pollen tubes into the female gametophyte by regulating ovular pectin and nitric oxide [22]. FER maintains de-esterified pectin at the filiform apparatus, whereas pollen tube arrival triggers the FER-dependent accumulation of nitric oxide (NO). Subsequently, NO blocks LURE1 secretion and interaction with its receptor POLLEN-SPECIFIC RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE 6 (PRK6) by nitrosating both the precursor and mature forms of LURE1, ultimately suppressing pollen tube attraction [22]. Moreover, FER-mediated synergic calcium responses are also involved in the orchestrated programmed cell death events of pollen tubes and receptive synergid, which accurately controls sperm delivery [30]. The dual roles of FER in fertilization demonstrates that FER maintains the homeostasis of the internal female gametophyte environment to fine-tune sperm delivery and block polyspermy, which is crucial for the sexual reproduction of flowering plants. As described above, FER modulates the synergid function by perceiving LURE and modulating ROS and Ca2+ signaling, whereas BUPS/ANXUR regulates pollen tube wall stiffness by differentially responding to RALFs, suggesting that these events might be integrated by common ligands of FER and BUPS/ANXUR (e.g., LORELEI, RALFs, or other unknown factors) (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
A schematic diagram for the functions of FER in regulating male-female gametophyte recognition during sexual reproduction. FER mediates male-female interaction by ROS, NO, and Ca2+ signaling. RALF, rapid alkalinization factor; ROP, RHO OF PLANTS; ROS, reactive oxygen species; GEFs, GUANINE EXCHANGE FACTORS; LRE: LORELEI; PRK6: POLLEN-SPECIFIC RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE 6; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; N, nitrosation; and NO: nitric oxide. Solid lines indicate previously defined signaling pathways. Dash lines indicate transport or speculative steps.
2.2. FER Modulates Cellular Expansion and Other Developmental Processes
Plants largely depend on cell expansion or elongation for normal growth and development [31]. Root hair is well-known as an excellent model system for investigating cell morphogenesis and polar growth. The mutants of two guanine nucleotide exchange factors for ROPs (RopGEF4 and RopGEF10), gef4 and gef10, displayed decreased cellular ROS levels and compromised root hair initiation and elongation. Further genetic and biochemical evidence indicated that RopGEF4 and RopGEF10 were developmental modulators in FER-mediated root hair growth (Figure 3) but not dependent for the FER-mediated environmental regulation of root hair development [32]. As compared to wild-type Col-0, the null mutant fer-4 shows defects in the development of root hairs and trichomes [20]. FER associates with LORELEI-LIKE GLYCOSYLPHOSPHATIDYLINOSITOL-ANCHORED PROTEIN 1 (LLG1), ROPGEF1 and RAC/ROP2, mediating NADPH oxidase-dependent ROS production, and modulating polarized root hair growth [20,33] (Figure 3). LLG1 acts as a chaperone to maintain normal localization of FER for its proper function in the plasma membrane. Moreover, fer and llg1 mutants share common phenotypes for less ROS accumulation in roots as compared with that in wild-type seedlings. Meanwhile, Huang et al. reported that ROPGEF4 and ROPGEF10 contributed to FER-mediated ROS production during root hair growth [32]. Furthermore, a recent study showed that RALF1-bound FER modulated the mRNA translation and protein synthesis of ROOT HAIR DEFECTIVE 6-LIKE 4 (RSL4) to repress RALF1 expression and promote root hair tip growth by phosphorylating eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E 1 (eIF4E1) [34,35].
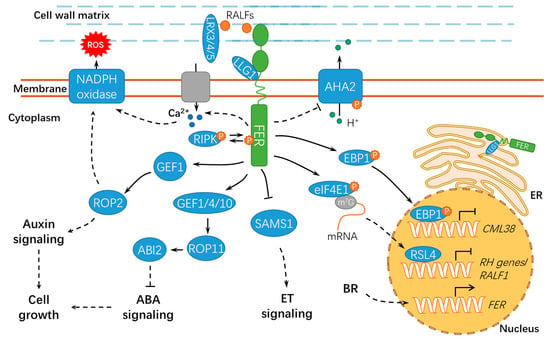
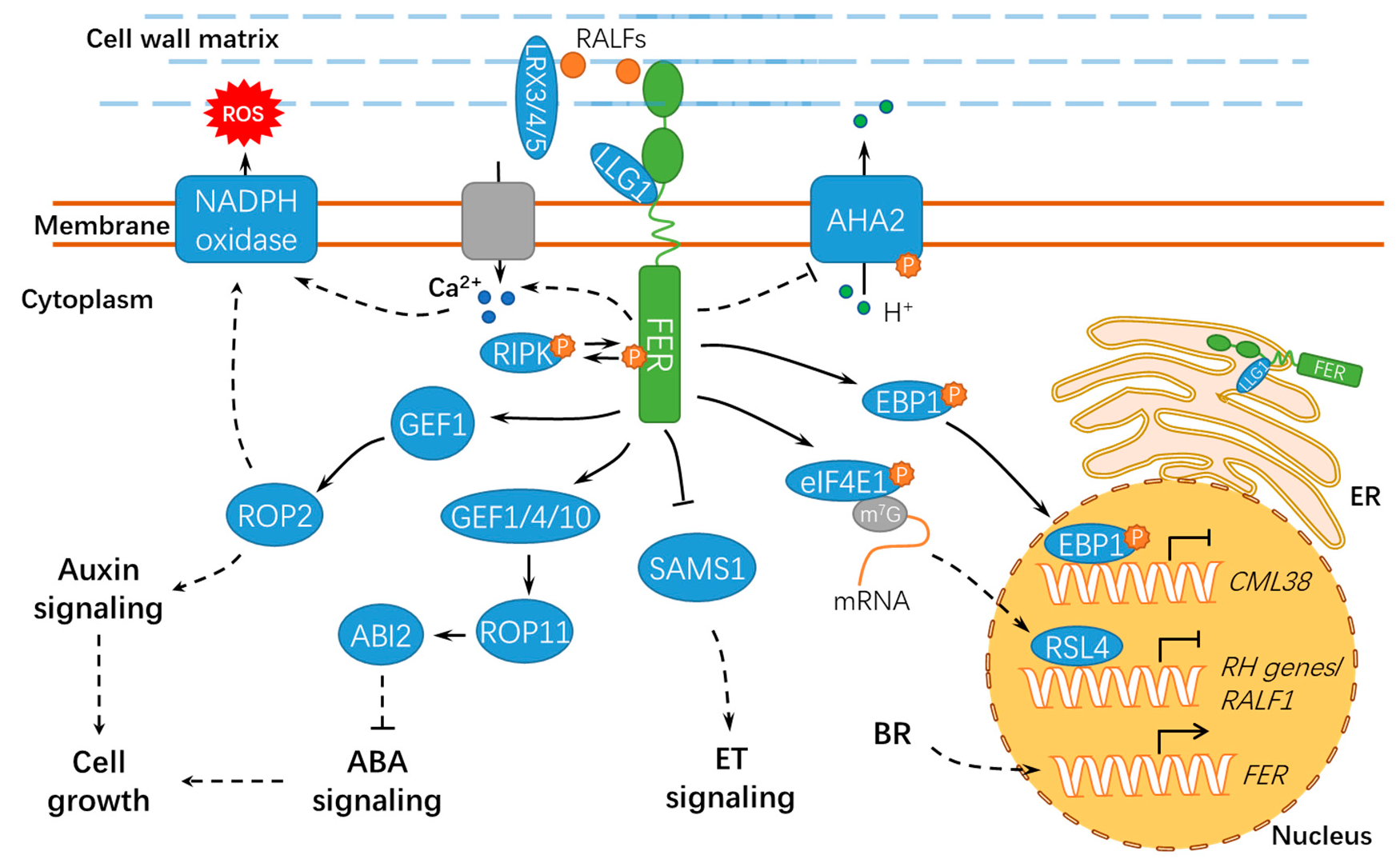
Figure 3.
A schematic diagram for the functions of FER in regulating cell growth and hormonal responses. FER regulates cell growth by hormone signaling (such as auxin, ABA, and BR) and RALF signaling. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; ET, ethylene; BR, brassinosteroid; ABA, abscisic acid; ABI2, ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE 2; LLG1, LORELEI-LIKE GLYCOSYLPHOSPHATIDYLINOSITOL-ANCHORED PROTEIN 1; RIPK, RESISTANCE TO Pseudomonas syringae pv. maculicola 1–INDUCED PROTEIN KINASE; P, phosphate group; m7G, 7-methylguanine triphosphate nucleoside (m7GpppN); SAMS1, S-ADENOSYLMETHIONINE SYNTHASE1; AHA2, H+–ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE 2; EBP1, ErbB3-binding protein 1; eIF4E1, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E 1; RSL4, ROOT HAIR DEFECTIVE 6-LIKE 4; LRX3/4/5, LEUCINE-RICH REPEAT EXTENSIN3/4/5; CML38, CALMODULIN-LIKE PROTEIN 38; and RH, ROOT HAIR. Solid lines indicate previously defined signaling pathways. Dashed lines indicate transport or speculative steps.
Notably, RALFs also play important roles in cell expansion (Figure 3). RALF1 interacts with the extracellular domain of the receptor kinase FER, further inhibiting cell elongation by phosphorylating Ser899 of H+–ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE 2 (AHA2) to prevent proton transport [31]. Under normal conditions, FER undergoes clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent endocytosis, and RALF1 substantially stimulated its endocytic internalization [36]. Alternatively, a plant peptide containing the sulfated tyrosine1 (PSY1)-receptor module phosphorylates and activates the plasma membrane H+-ATPase, thus displaying antagonistic action to the RALF-FER pathway. PSY1 could trigger a rapid burst of cellular Ca2+ and apoplastic alkalinization in Arabidopsis roots by activating RALF33 and RALF36. As expected, fer mutants did not respond to RALF33 but responded to RALF36 and activated both Ca2+ and H+ signatures. These results suggest the existence of negative feedback machinery involving different RALF peptides and receptors [37]. Cell elongation mainly relies on the expansion of central vacuoles [38]. Extracellular LEUCINE-RICH REPEAT EXTENSION 3/4/5 (LRX3/4/5) and RALF1 interact with FER, jointly inhibiting vacuolar expansion and preventing cell elongation [38] (Figure 3). Moreover, the RALF1-mediated FER function requires the cytoplasmic kinase RESISTANCE TO Pseudomonas syringae pv. maculicola 1–INDUCED PROTEIN KINASE (RIPK), and they likely form together a receptor complex downstream of RALF1 [39]. In response to RALF1, FER also facilitates mRNA translation of ErbB3-binding protein 1 (EBP1) and phosphorylates EBP1, resulting in EBP1 accumulation in the nucleus and suppressing CALMODULIN-LIKE PROTEIN 38 (CML38) transcription [40,41]. CML38 serves as a component of the RALF1 signaling pathway via a negative feedback loop to regulate root growth (Figure 3).
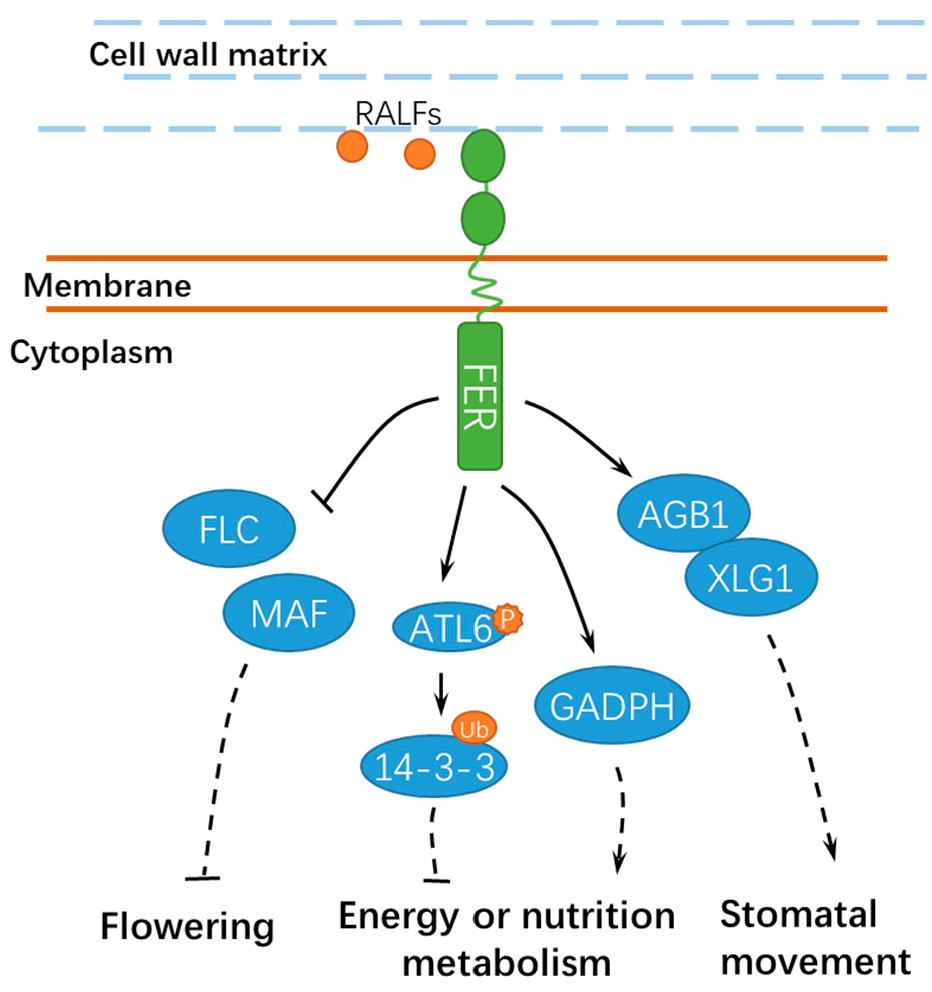
Mechanical force and cellular energy metabolism also affect cell growth [42,43] (Figure 4). fer-4 displayed severely altered Ca2+ signature and growth responses upon mechanical stimuli, indicating that FER may be a key regulator of mechanical Ca2+ signaling [44]. However, further studies are still required to explore the underlying mechanisms and the specific calcium signaling components involved. FER also contributes to the energy production in glycolysis by interacting with GLYCERALDEHYDE-3-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASEs (GAPDH, GAPC1, and GAPC2), which are responsible for starch accumulation and cell expansion [45]. Moreover, FER-mediated E3 ubiquitin ligase ATL6 (Arabidopsis Tóxicos en Levadura 6) phosphorylation mediates the stability of 14-3-3 proteins to control the primary carbon and nitrogen response and plant growth [46]. Notably, FER also interacts with XLG1, a core component in heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide-binding (G) proteins, to regulate stomatal movement (Figure 4). By contrast, RALF1 inhibited stomatal opening and promoted stomatal closure in wild-type seedlings but not in the agb1 mutant [47]. Importantly, further studies show that FER responses may be either kinase-dependent or kinase-independent, deducing from the phenotypes in rosette leaves of the fer complementation lines employing a kinase-dead FERK565R [48], which further confirmed the complexity for the functional mechanisms of FER. A recent study shows that FER also modulates the mRNA alternative splicing and transcript accumulation of FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC) and MADS AFFECTING FLOWERING (MAF) to positively control the flowering time in Arabidopsis, which is important for reproductive growth and development [49] (Figure 4). FER and GEF1 (possibly other GEFs) are involved in an undefined signaling pathway to negatively regulate the elongation of integument cells and, ultimately, the seed size in Arabidopsis [50].

Figure 4.
A schematic diagram for the functions of FER in regulating other developmental processes. FER is involved in flowering, energy, or nutrition metabolism and stomatal movement. Ub, ubiquitin; ATL6, Arabidopsis Tóxicos en Levadura 6; GADPH, GLYCERALDEHYDE-3-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE; FLC, FLOWERING LOCUS C; and MAF, MADS AFFECTING FLOWERING. Solid lines indicate previously defined signaling pathways. Dashed lines indicate transport or speculative steps.
2.3. FER Has Pivotal Roles in Hormone Signaling
Hormones are key regulators for the growth, development, and defenses of plants [9], among which, auxin is well-known for promoting root hair elongation [20,51]. FER functions in a ROPGEF1/ RAC/ROP2 signaling pathway and serves as a modulator for auxin-regulated root hair development [20] (Figure 3). In addition, FER also regulates the F-actin-dependent polar localization of PIN2 and polar auxin transport, thus modulating lateral root branching and the gravitropic response [52]. A recent study showed that FER mediates the root nutating growth via PIN2- and AUX1-mediated auxin transport [53], thus providing new evidence for the correlation of FER to auxin signaling. Moreover, fer-4 is hypersensitive to abscisic acid (ABA), which can be mimicked by the mutations in GEF1/4/10 or ROP11/ARAC10 (RHO OF PLANTS 11/RAC-LIKE GTP BINDING PROTEIN 10) [54]. These results suggested that FER utilize diverse ROPGEFs in auxin and ABA signaling [54] (Figure 3). In addition, when RALF23 is downregulated in Arabidopsis in response to brassinolide (BL) treatment, FER negatively regulates the brassinosteroid (BR) response in hypocotyl growth and promotes the BR response in etiolated seedlings [55]. FER, THESEUS1, and HERCULES1, three RLKs in the CrRLK1L family, are transcriptionally activated by BRs [56]. The FER transcripts are downregulated in the BR-insensitive mutant bri1-5 and upregulated in the gain-of-function mutant bes1-D [56]. Microarray studies revealed that these RLKs regulated the expression of a set of genes, including those involved in cell elongation [56], thus implying the existence of gene sets that are commonly and independently regulated by FER and BR to regulate cell elongation.
In addition, the null mutant fer-4 showed higher levels of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM, ethylene precursor) and ethylene, whereas the S-ADENOSYLMETHIONINE SYNTHASE1 (SAMS1) and SAMS2 overexpression lines could mimic the dwarf phenotype of fer-4 [57]. Coincidently, T-DNA insertion in FER (fer-2 and fer-3) led to an enhanced ethylene response in Arabidopsis, indicating that FER is a negative regulator of the ethylene response and ethylene is a negative regulator of FER [55]. SAMS is a key enzyme catalyzing the production of SAM in the ethylene biosynthesis pathway [58]. Mao et al. found that SAMS1 and SAMS2 interacted with FER at the plasma membrane in A. thaliana [57], repressing SAMS activity and, thus, ethylene production (Figure 3). A similar result was reported for the putative homologs in apples (Malus × domestica), in which MdFERL6 and MdFERL1 physically interacted with MdSAMS, thus negatively affecting ethylene biosynthesis [59]. However, given the importance of ethylene biosynthesis in climacteric fruit ripening, it is pivotal to examine the specific expression patterns for the putative homologs during the ripening process. Additional efforts are still required to examine whether FER may directly phosphorylate SAMSs to modulate their enzymatic activities. Possibilities for the involvements of other post-translational modifications on SAMSs should not be ruled out. Zermiani and colleagues also reported that ethylene downregulated the transcript abundance of genes involved in ROP-GAP rheostat and further affected apoplastic ROS homeostasis in apple fruits in cold storage, whereas the 1-MCP treatment activated a gene encoding a FERONIA-like kinase [60], suggesting FER homologs in fruit may also have certain regulatory roles in ethylene signaling. In terms of nonclimacteric fruit, ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE 1 (ABI1) negatively regulated the fruit ripening of strawberries (Fragaria × ananassa) [61]. FaMRLK47, a homolog of AtFER, negatively regulated ABA biosynthesis by interacting with FaABI1, thus inhibiting strawberry fruit ripening [62]. However, it is still uncertain how these putative FER homologs mediate fruit ripening as a kinase or just merely a scaffolding protein.
3. Potential Functions of FER in Stress Tolerance
As sessile organisms, plants are confronted with unfavorable environmental conditions, such as high temperatures, salinity, and heavy metals [63,64]. Arabidopsis FER and its homologs in other species are also implicated in the responses to stress conditions [63,65,66] (Figure 5).
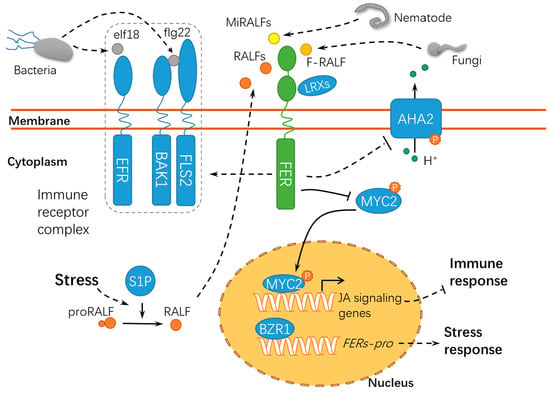
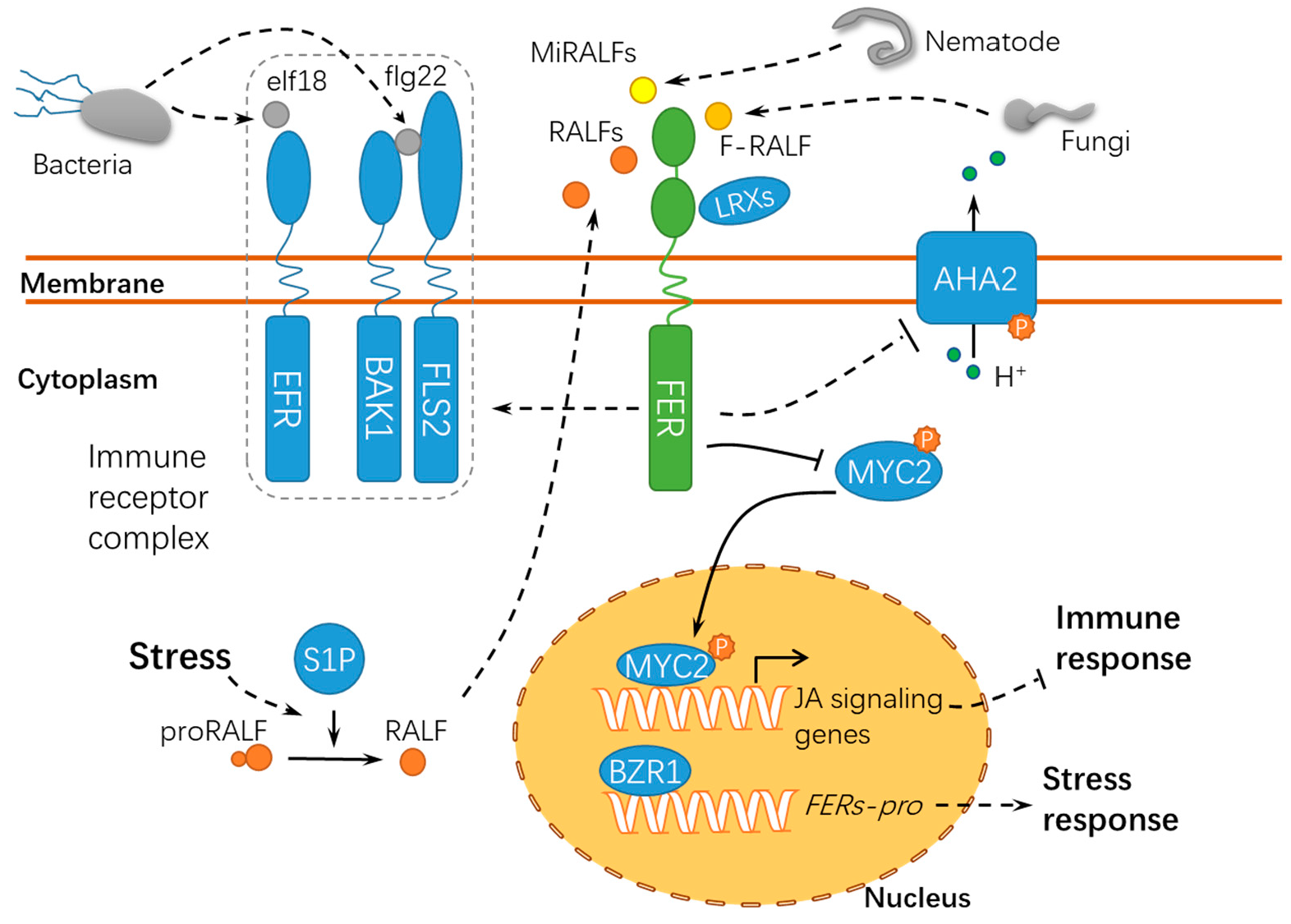
Figure 5.
A schematic diagram for the functions of FER in responding to abiotic and biotic stress. FER acts as a scaffold protein to mediate the assembly of the immune receptor complex, during which FER serves as a target of diverse RALFs. proRALF, RALF propeptides; BAK1, BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE 1–ASSOCIATED KINASE 1; EFR, ELONGATION FACTOR THERMO-UNSTABLE RECEPTOR; elf18, elongation factor Tu peptide (first 18 amino acids); flg22, flagellin epitope 22; FLS2, FLAGELLIN SENSING 2; F-RALF, Fusarium oxysporum RALF; MiRALFs: Meloidogyne incognita RALFs; S1P, SITE-1 PROTEASE; MYC2, MYELOCYTOMATOSIS PROTEINS 2; LRXs, LEUCINE-RICH REPEAT EXTENSINs; BZR1, BRASSINAZOLE RESISTANT 1; and FERs-pro, FERONIAs promoter. Solid lines indicate previously defined signaling pathways. Dashed lines indicate transport or speculative steps.
RLKs may regulate heterotrimeric G-protein signaling in plants [47,67]. The G protein β subunits AGB1 and FER act synergistically to regulate the salt response by stimulating the net K+ uptake but inhibiting the net Na+ uptake, which requires salt-induced ROS production. AGB1 is involved in inhibiting root-to-shoot Na+ translocation under transpiring conditions, whereas FER is mainly involved in inhibiting the net Na+ uptake under nontranspiring conditions [67]. During this process, RALF1 enhances the salt toxicity by stimulating Na+ accumulation, which is independent of AGB1 and ROS production. Importantly, RALF1 probably inhibits the activity of AHA2 by a FER-dependent mechanism, thus suppressing the Na+/H+ antiporter activity and leading to salt injuries [67].
fer-4, lrx345 (leucine-rich repeat extension 345) triple mutants, and RALF22/23 overexpression lines are hypersensitive to salt stress, suggesting that these components may function synergistically in response to high salt [65]. LRXs physically interact with RALFs, demonstrating that these proteins function together with FER as a module in salt stress tolerance [65]. High salinity facilitates the cleavage of the RALF22 propeptide by SITE-1 PROTEASE (S1P), resulting in the release of mature RALF22. Mature RALF22/23 peptides interact with FER and then cause its endocytosis [65], and this may represent a different endocytic mechanism as compared to the RALF1-stimulated FER endocytosis [36]. Another report shows that FER can protect seedlings from injuries upon salt stress by modulating cell-specific calcium transients, and this process requires the integration of FER-dependent calcium signaling and cell integrity signaling [66]. The defects in the cell wall integrity of fer-2 and fer-4 can be rescued by exogenous calcium and borate treatments, which also facilitate pectin crosslinking possibly by the “egg-box” model [15], suggesting that the perception of cell wall injuries caused by salt stress may directly result from the connection between the extracellular domain of FER and pectin.
Moreover, it is reported that BZR1 (BRASSINAZOLE RESISTANT 1) binds to the promoter region of the genes encoding FER homologs of tomatoes and, thus, regulate the heat stress tolerance in tomatoes by the FER-dependent ROS signaling pathway [63]. FER may be also be involved in metal ion stress [64]; however, the underlying mechanisms are still not elucidated. Recently, it was demonstrated that the interaction of FER with RALF1 resulted in the phosphorylation of the GLYCINE-RICH RNA-BINDING PROTEIN 7 (GRP7) to promote GRP7 nuclear accumulation, thus triggering a rapid and massive RNA alternative splicing response. GRP7 phosphorylation enhanced its mRNA binding ability and its association with the spliceosome component U1-70K, which depends on FER [68].
4. FER Has Pivotal Roles in Host-Pathogen Interactions
Membrane-localized and intracellular immune receptors have crucial roles in the surveillance system recognizing or responding to non-self-components during host-pathogen interactions [69]. Pathogens, particularly necrotrophic pathogens, secrete cell wall hydrolases and form specific infection structures to facilitate host cell invasion, whereas plants have evolved elaborate surveillance machinery to perceive these changes and ward off these invaders [70,71,72]. FER acts as a sensor of cell wall integrity challenged by the host-pathogen interaction and further triggers downstream immune responses in the host cell [73] (Figure 5). Similar to nta (nortia) mutants, fer mutants are insensitive to Golovinomyces (syn. Erysiphe) orontii, indicating that FER may negatively regulate plant immunity to biotrophic pathogens. The fer-mediated resistance may be attributed to the activation of the ethylene/jasmonic acid pathways [74]. As compared with the functions of FER in pollen tube guidance and powdery mildew resistance, FER may regulate the susceptibility of plants to symbiotic organisms in the early years of evolution [74]. Another study revealed that OsFLR2 and OsFLR11, two rice FERONIA-LIKE RECEPTOR (FLR) genes, attenuated the resistance of rice seedlings to Magnaporthe grisea by downregulating defense-related genes and suppressing ROS bursts at the penetration sites [75]. It is noteworthy that fungal pathogens secrete peptides with homology to RALF23 [76,77]. During the interaction between host plants and the root-infecting fungus Fusarium oxysporum, FER is targeted by a small peptide F-RALF secreted by F. oxysporum, leading to extracellular alkalinization and defense response inhibition [76]. This may result from the phosphorylation of PM-resided AHA2 following the F-RALF-FER interaction [31]. The increase in extracellular pH activates a fungal mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), Fmk1, which is indispensable for mycelial growth, plant infection, and the pathogenicity of F. oxysporum. Similar RALFs have been found in 26 species of phytopathogenic fungi [77], suggesting an interesting possibility that different RALF peptides may be employed by microorganisms to override plant defenses to facilitate successful infections. Similarly, FER can also bind and respond to the small peptides MiRALF1 and MiRALF3 from Meloidogyne incognita, thus modulating the cell expansion and downstream immune responses [78], suggesting that the FER-RALF modules may have similar roles in the responses of plants to developmental cues, pathogen infections, and nematode invasions. As a scaffold protein, FER is recruited into the receptor kinase complex with ELONGATION FACTOR THERMO UNSTABLE RECEPTOR (EFR), FLAGELLIN SENSING 2 (FLS2), and BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE 1–ASSOCIATED KINASE 1 (BAK1) to initiate immune signaling [79]. Arabidopsis SITE-1 PROTEASE (S1P) cleaves the endogenous RALF23 precursor to deliver mature RALF23 and, thus, inhibits the scaffolding function of FER, finally dampening the immune signaling [79]. Meanwhile, FER suppresses the jasmonic acid (JA) and coronatine (COR) signaling pathway by phosphorylating the transcription factor MYC2 (MYELOCYTOMATOSIS PROTEINS 2) [80], thus revealing the RALF23-FER-MYC2 signaling pathway. Xiao et al. reported after X-ray crystallography and a biochemical assay that LLG1 and LLG2 directly bound RALF23 to induce the assembly of RALF23–LLG1–FER and RALF23–LLG2–FER heterocomplexes, respectively, which depends on the conserved N-terminal of RALF23 [81]. Collectively, FER may act as positive or negative regulator in immune responses by binding to RALFs or modulating the immune receptor kinase complex assembly, indicating that FER functions diversely in response to pathogens of different trophic types (Figure 5). It was recently found using high-resolution live cell imaging and single-particle tracking that FER regulates FLS2 dynamics in the nanoscale domains in the plasma membrane, further supporting the hypothesis that FER has crucial roles in recruiting and maintaining the immune receptor complex [82]. Interestingly, immune signaling regulated by FER in response to P. syringae is independent of its kinase activity. However, whether this is also applicable to the pathogens of other life strategies remains unknown. Moreover, the fer-2 mutant incapable of binding pectin is still functional in regulating immune signaling, whereas the wall-associated LRXs are required for this process. Up to now, given the characteristics for FER as a membrane-residing receptor-like kinase, the partners for FER in the host-pathogen interaction still need to be identified.
5. Future Outlook
In summary, FER may employ cell type-specific mechanisms by functioning with other protein kinases or simply working as a scaffolding protein to facilitate the recruitment/assembly of signaling complexes [83,84]. In vitro and in vivo kinase assays indicate that FER undergoes autophosphorylation and transphosphorylation [19,40,80]. However, the kinase dead version of FER (FER K565R) influences RALF1-caused root growth inhibition rather than ovule fertilization in Arabidopsis [85], indicating that the kinase activity of FER may not account for male-female gametophyte interactions or FER may have cell type-specific functions in different biological contexts. However, deducing from the currently available data, FER may phosphorylate a number of downstream substrates; a high-throughput quantitative phosphor-proteomic analysis may facilitate the identification of kinase substrates and specific phosphorylation sites. Another important aspect in the kinase activity of FER is the dephosphorylation of FER, which has been scarcely reported. When FER is phosphorylated upon RALF1 and ABA stimuli, ABI2 inhibits FER activity by directly dephosphorylating FER [86]. Further studies on the attenuation of FER activity by dephosphorylation merit further investigation in other cellular and physiological contexts.
FER/CrRLK1Ls-RALFs may display opposite effects in different cell types or in response to pathogens of different life strategies. Moreover, different CrRLK1L members may function in coordination in response to diversified environmental stimuli. THESEUS (THE1) functions upstream of GEF4, thus contributing to the resistance of Arabidopsis seedlings to the necrotrophic pathogen Botrytis cinerea [87], whereas HERK1, THE1, and FER function independent of BR signaling in cell elongation, as FER-RNAi seedlings and herk1 the1 double mutants showed similar dwarf phenotypes during vegetative growth [56]. Therefore, substantial functions of other CrRLK1L members in host-pathogen interactions also deserve further in-depth investigation. The identification of interacting partners and downstream substrates/signaling may greatly facilitate the elucidation of diversified roles of FER in different vital processes, whereas the interaction between extracellular domains of different CrRLK1L members may also become a focus of research interests. In addition to phosphorylation, the FER protein may also have other types of post-translational modifications to exert its functions, which deserves additional work for clarification.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.J., T.C., and S.T.; supervision, S.T.; visualization, D.J.; writing—original draft, D.J. and T.C.; and writing—review and editing, T.C., Z.Z., B.L., and S.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors are sorry for inadvertent omission of any pertinent reference. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31930086, 31530057, 31722043, and 31672210).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest for declaration.
Abbreviations
| FER | FERONIA |
| ANX1 to 2 | ANXUR1 to 2 |
| THE1 | THESEUS1 |
| BUPS1 to 2 | BUDDHA’S PAPER SEAL 1 to 2 |
| HERK1 to 2 | HERCULES1 to 2 |
| CVY1 | CURVY1 |
| CrRLK1 | Catharanthus roseus receptor-like kinase 1 |
| FLR | FERONIA-LIKE RECEPTOR |
| RALF | rapid alkalinization factor |
| ROP | RHO OF PLANTS |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| GEFs | GUANINE EXCHANGE FACTORS |
| LRE | LORELEI |
| PRK6 | POLLEN-SPECIFIC RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE 6 |
| NADPH | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| ET | ethylene |
| BR | brassinosteroid |
| ABA | abscisic acid |
| ABI2 | ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE 2 |
| LLG1 | LORELEI-LIKE GLYCOSYLPHOSPHATIDYLINOSITOL-ANCHORED PROTEIN 1 |
| RIPK | RESISTANCE TO Pseudomonas syringae pv. maculicola 1–INDUCED PROTEIN KINASE |
| SAMS1 | S-ADENOSYLMETHIONINE SYNTHASE1 |
| AHA2 | H+–ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE 2 |
| EBP1 | ErbB3-binding protein 1 |
| eIF4E1 | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E 1 |
| RSL4 | ROOT HAIR DEFECTIVE 6-LIKE 4 |
| LRX3/4/5 | LEUCINE-RICH REPEAT EXTENSIN3/4/5 |
| CML38 | CALMODULIN-LIKE PROTEIN 38 |
| ATL6 | Arabidopsis Tóxicos en Levadura 6 |
| GADPH | GLYCERALDEHYDE-3-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE |
| FLC | FLOWERING LOCUS C |
| MAF | MADS AFFECTING FLOWERING |
| proRALF | RALF propeptides |
| BAK1 | BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE 1–ASSOCIATED KINASE 1 |
| EFR | ELONGATION FACTOR THERMO-UNSTABLE RECEPTOR |
| elf18 | elongation factor Tu peptide (first 18 amino acids) |
| flg22 | flagellin epitope 22 |
| FLS2 | FLAGELLIN SENSING 2 |
| F-RALF | Fusarium oxysporum RALF |
| MiRALFs | Meloidogyne incognita RALFs |
| S1P | SITE-1 PROTEASE |
| MYC2 | MYELOCYTOMATOSIS PROTEINS 2 |
| LRXs | LEUCINE-RICH REPEAT EXTENSINs |
| BZR1 | BRASSINAZOLE RESISTANT 1. |
References
- Tian, S.; Qin, G.; Li, B. Reactive oxygen species involved in regulating fruit senescence and fungal pathogenicity. Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 82, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, D.; Chen, T.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, G.; Tian, S. Production, signaling, and scavenging mechanisms of reactive oxygen species in fruit–pathogen interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tian, S. Crucial contribution of membrane lipids’ unsaturation to acquisition of chilling-tolerance in peach fruit stored at 0 °C. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tian, S. Peach fruit acquired tolerance to low temperature stress by accumulation of linolenic acid and N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine in plasma membrane. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Tang, R.; Zhang, X.; Luan, S.; Yu, F. FERONIA receptor kinase at the crossroads of hormone signaling and stress responses. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Deguchi, M.; Brustolini, O.J.B.; A Santos, A.; Silva, F.F.; Fontes, E.P.B. The tomato RLK superfamily: Phylogeny and functional predictions about the role of the LRRII-RLK subfamily in antiviral defense. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiu, S.H.; Bleecker, A.B. Receptor-like kinases from Arabidopsis form a monophyletic gene family related to animal receptor kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10763–10768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiu, S.H.; Bleecker, A.B. Plant receptor-like kinase gene family: diversity, function, and signaling. Sci. Signal. 2001, 2001, re22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franck, C.M.; Westermann, J.; Boisson-Dernier, A. Plant malectin-like receptor kinases: from cell wall integrity to immunity and beyond. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 301–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze-Muth, P.; Irmler, S.; Schröder, G.; Schröder, J. Novel type of receptor-like protein kinase from a higher plant (Catharanthus roseus). J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 26684–26689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.F.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, S.W.; Sun, D.Y.; Sun, Y. Receptor-like kinase CrRLK1-L subfamily: novel motifs in extracellular domain and biological functions in plants. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 38, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, C.X.; Han, Y.F.; Zhu, S.; Song, F.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.C.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J.; Bu, S.L.; et al. The rice receptor-like kinases DWARF AND RUNTISH SPIKELET1 and 2 repress cell death and affect sugar utilization during reproductive development. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Wu, D.; Yu, F. RALF–FERONIA signaling: linking plant immune response with cell growth. Plant Commun. 2020, 1, 100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huck, N.; Moore, J.M.; Federer, M.; Grossniklaus, U. The Arabidopsis mutant feronia disrupts the female gametophytic control of pollen tube reception. Development 2003, 130, 2149–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Teng, N.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, W.; Šamaj, J.; Baluška, F.; Lin, J. Disruption of actin filaments by Latrunculin B affects cell wall construction in Picea meyeri pollen tube by disturbing vesicle trafficking. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007, 48, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Bergonci, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zou, Y.; Du, S.; Liu, M.C.; Luo, X.; Ruan, H.; García-Valencia, L.E.; Zhong, S.; et al. Arabidopsis pollen tube integrity and sperm release are regulated by RALF-mediated signaling. Science 2017, 358, 1596–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, S.; Tsutsui, H.; Shiina, K.; Sprunck, S.; Takeuchi, H.; Yui, R.; Kasahara, R.D.; Hamamura, Y.; Mizukami, A.; Susaki, D.; et al. Defensin-like polypeptide LUREs are pollen tube attractants secreted from synergid cells. Nature 2009, 458, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, S.; Higashiyama, T. Pollen tube guidance by attractant molecules: LUREs. Cell Struct. Funct. 2010, 35, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar-Restrepo, J.M.; Huck, N.; Kessler, S.; Gagliardini, V.; Gheyselinck, J.; Yang, W.C.; Grossniklaus, U. The FERONIA receptor-like kinase mediates male-female interactions during pollen tube reception. Science 2007, 317, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Kita, D.; Li, C.; Cheung, A.Y.; Wu, H.M. FERONIA receptor-like kinase regulates RHO GTPase signaling of root hair development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17821–17826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Q.; Kita, D.; Johnson, E.A.; Aggarwal, M.; Gates, L.; Wu, H.M.; Cheung, A.Y. Reactive oxygen species mediate pollen tube rupture to release sperm for fertilization in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Q.; Liu, M.C.; Kita, D.; Jordan, S.S.; Yeh, F.L.J.; Yvon, R.; Carpenter, H.; Federico, A.N.; García-Valencia, L.E.; Eyles, S.J.; et al. FERONIA controls pectin- and nitric oxide-mediated male–female interaction. Nature 2020, 579, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, H.M.; Cheung, A.Y. FERONIA and her pals: functions and mechanisms. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 2379–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Castro, C.A.; Wang, Y.; Noble, J.A.; Ponvert, N.D.; Bundy, M.G.; Hoel, C.R.; Shpak, E.D.; Palanivelu, R. The role of LORELEI in pollen tube reception at the interface of the synergid cell and pollen tube requires the modified eight-cysteine motif and the receptor-like kinase FERONIA. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 1035–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, S.A.; Lindner, H.; Jones, D.S.; Grossniklaus, U. Functional analysis of related CrRLK1L receptor-like kinases in pollen tube reception. EMBO Rep. 2014, 16, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, G.; Moura, D.S.; Stratmann, J.; Ryan, C.A. RALF, a 5-kDa ubiquitous polypeptide in plants, arrests root growth and development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12843–12847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, A.N.; Mundy, J.; Skriver, K. Peptomics, identification of novel cationic Arabidopsis peptides with conserved sequence motifs. Silico Biol. 2002, 2, 441–451. [Google Scholar]
- Canto, A.M.D.; Ceciliato, P.H.; Ribeiro, B.; Morea, F.A.O.; Garcia, A.A.F.; Silva-Filho, M.C.; Moura, D.S. Biological activity of nine recombinant AtRALF peptides: Implications for their perception and function in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 75, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecchia, M.A.; Santos-Fernandez, G.; Duss, N.N.; Somoza, S.C.; Boisson-Dernier, A.; Gagliardini, V.; Martínez-Bernardini, A.; Fabrice, T.N.; Ringli, C.; Muschietti, J.P.; et al. RALF4/19 peptides interact with LRX proteins to control pollen tube growth in Arabidopsis. Science 2017, 358, 1600–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, Q.A.; Vogler, H.; Lituiev, D.S.; Nestorova, A.; Grossniklaus, U. A calcium dialog mediated by the FERONIA signal transduction pathway controls plant sperm delivery. Dev. Cell 2014, 29, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruta, M.; Sabat, G.; Stecker, K.; Minkoff, B.B.; Sussman, M.R. A peptide hormone and its receptor protein kinase regulate plant cell expansion. Science 2014, 343, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.Q.; Li, E.; Ge, F.R.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, C.Q.; Zhang, Y. Arabidopsis RopGEF4 and RopGEF10 are important for FERONIA-mediated developmental but not environmental regulation of root hair growth. New Phytol. 2013, 200, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Yeh, F.L.; Cheung, A.Y.; Duan, Q.; Kita, D.; Liu, M.C.; Maman, J.; Luu, E.J.; Wu, B.W.; Gates, L.; et al. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins as chaperones and co-receptors for FERONIA receptor kinase signaling in Arabidopsis. eLife 2015, 4, e06587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Estévez, J.M.; Liao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, T.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Pacheco, J.M.; et al. The RALF1–FERONIA complex phosphorylates eIF4E1 to promote protein synthesis and polar root hair growth. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 698–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Pacheco, J.M.; Estevez, J.M.; Yu, F. Autocrine regulation of root hair size by the RALF-FERONIA-RSL4 signaling pathway. New Phytol. 2020, 227, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Li, R.; Cui, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Bu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Xing, J.; Jewaria, P.K.; et al. The RALF1-FERONIA interaction modulates endocytosis to mediate control of root growth in Arabidopsis. Development 2020, 147, dev189902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjetting, S.K.; Mahmood, K.; Shabala, L.; Kristensen, A.; Shabala, S.; Palmgren, M.G.; Fuglsang, A.P.D.A.T. Evidence for multiple receptors mediating RALF-triggered Ca2+ signaling and proton pump inhibition. Plant J. 2020, 14935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dünser, K.; Gupta, S.; Herger, A.; I Feraru, M.; Ringli, C.; Kleine-Vehn, J. Extracellular matrix sensing by FERONIA and leucine-rich repeat extensins controls vacuolar expansion during cellular elongation in Arabidopsis thaliana. EMBO J. 2019, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, W.; Li, B.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Lin, J.; et al. Receptor kinase complex transmits RALF peptide signal to inhibit root growth in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E8326–E8334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, X.; Qiang, X.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liao, H.; Luan, S.; et al. EBP1 nuclear accumulation negatively feeds back on FERONIA-mediated RALF1 signaling. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2006340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, W.F.; Dressano, K.; Ceciliato, P.H.O.; Guerrero-Abad, J.C.; Silva, A.L.; Fiori, C.S.; Canto, A.M.D.; Bergonci, T.; Claus, L.A.N.; Silva-Filho, M.C.; et al. Arabidopsis thaliana rapid alkalinization factor 1–mediated root growth inhibition is dependent on calmodulin-like protein 38. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 293, 2159–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Bertomeu, J.; Cascales-Miñana, B.; Mulet, J.M.; Baroja-Fernández, E.; Pozueta-Romero, J.; Kuhn, J.M.; Segura, J.; Ros, R. Plastidial glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency leads to altered root development and affects the sugar and amino acid balance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monshausen, G.B.; Haswell, E.S. A force of nature: Molecular mechanisms of mechanoperception in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 4663–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, H.-W.; Miller, N.D.; Dai, C.; Spalding, E.P.; Monshausen, G.B. The receptor-like kinase FERONIA is required for mechanical signal transduction in Arabidopsis seedlings. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Qi, Y.; Liu, X.; Lin, Q.; Luan, S.; Yu, F. Receptor protein kinase FERONIA controls leaf starch accumulation by interacting with glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 465, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Chen, W.; Song, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Liao, H.; Zhao, G.; Lin, F.; Zhou, H.; Yu, F. FERONIA phosphorylates E3 ubiquitin ligase ATL6 to modulate the stability of 14-3-3 proteins in response to the carbon/nitrogen ratio. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 6375–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chakravorty, D.; Assmann, S.M. The G protein β-subunit, AGB1, interacts with FERONIA in RALF1-regulated stomatal movement. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 2426–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravorty, D.; Yu, Y.; Assmann, S.M. A kinase-dead version of FERONIA receptor-like kinase has dose-dependent impacts on rosette morphology and RALF 1-mediated stomatal movements. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 3429–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, T.; Lin, Q.; Wang, B.; Li, X.; Luan, S.; Yu, F. Receptor kinase FERONIA regulates flowering time in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, D.; Chen, L.; Luan, S. FERONIA receptor kinase controls seed size in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 920–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, R.J.; Cernac, A.; Estelle, M. Auxin and ethylene promote root hair elongation in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 1998, 16, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tao, L.; Liu, H. FERONIA regulates auxin-mediated lateral root development and primary root gravitropism. FEBS Lett. 2018, 593, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, Z.; Li, S. FERONIA mediates root nutating growth. Plant J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Qian, L.; Nibau, C.; Duan, Q.; Kita, D.; Levasseur, K.; Li, X.; Lu, C.; Li, H.; Hou, C.; et al. FERONIA receptor kinase pathway suppresses abscisic acid signaling in Arabidopsis by activating ABI2 phosphatase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14693–14698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DesLauriers, S.D.; Larsen, P.B. FERONIA is a key modulator of brassinosteroid and ethylene responsiveness in Arabidopsis hypocotyls. Mol. Plant 2010, 3, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Li, L.; Ye, H.; Yu, X.; Algreen, A.; Yin, Y. Three related receptor-like kinases are required for optimal cell elongation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7648–7653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, D.; Yu, F.; Li, J.; Van De Poel, B.; Tan, D.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Dong, M.; Chen, L.; et al. FERONIA receptor kinase interacts with S-adenosylmethionine synthetase and suppresses S-adenosylmethionine production and ethylene biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 2566–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcmurchie, E.J.; Mcglasson, W.B.; Eaks, I.L. Treatment of fruit with propylene gives information about the biogenesis of ethylene. Nature 1972, 237, 235–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Du, P.; Ding, N.; Zhang, Q.; Xing, S.; Wei, L.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, W.; Li, J.; Li, B.; et al. Two FERONIA-like receptor kinases regulate apple fruit ripening by modulating ethylene production. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zermiani, M.; Zonin, E.; Nonis, A.; Begheldo, M.; Ceccato, L.; Vezzaro, A.; Baldan, B.; Trentin, A.; Masi, A.; Pegoraro, M.; et al. Ethylene negatively regulates transcript abundance of ROP-GAP rheostat-encoding genes and affects apoplastic reactive oxygen species homeostasis in epicarps of cold stored apple fruits. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 7255–7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Lu, D.; Sun, J.; Li, C.; Xing, Y.; Qin, L.; Shen, Y. Type 2C protein phosphatase ABI1 is a negative regulator of strawberry fruit ripening. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 1677–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, M.; Ding, N.; Zhang, Q.; Xing, S.; Wei, L.; Zhao, Y.; Du, P.; Mao, W.; Li, J.; Li, B.; et al. A FERONIA-like receptor kinase regulates strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) fruit ripening and quality formation. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Qin, K.; Song, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, X.; Yu, J. BZR1 transcription factor regulates heat stress tolerance through FERONIA receptor-like kinase-mediated reactive oxygen species signaling in tomato. Plant Cell Physiol. 2018, 59, 2239–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, J.; Ploderer, M.; Mongelard, G.; Gutierrez, L.; Hauser, M.T. Role of CrRLK1L cell wall sensors HERCULES1 and 2, THESEUS1, and FERONIA in growth adaptation triggered by heavy metals and trace elements. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zayed, O.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Zhu, P.; Hsu, C.C.; Zhang, L.; Andy Tao, W.; Lozano-Durán, R.; Zhu, J.K. Leucine-rich repeat extensin proteins regulate plant salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 13123–13128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Kita, D.; Peaucelle, A.; Cartwright, H.N.; Doan, V.; Duan, Q.; Liu, M.C.; Maman, J.; Steinhorst, L.; Schmitz-Thom, I.; et al. The FERONIA receptor kinase maintains cell-wall integrity during salt stress through Ca2+ signaling. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Assmann, S.M. Inter-relationships between the heterotrimeric Gβ subunit AGB1, the receptor-like kinase FERONIA, and RALF1 in salinity response. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 2475–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, T.; Wang, B.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, S.; Li, C.; Ma, Y.; Tang, J.; Xing, J.; Li, X.; et al. RALF1-FERONIA complex affects splicing dynamics to modulate stress responses and growth in plants. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, D.; Zipfel, C. Regulation of pattern recognition receptor signalling in plants. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, B.; Li, B.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, G.; Tian, S. Aquaporin8 regulates cellular development and reactive oxygen species production, a critical component of virulence in Botrytis cinerea. New Phytol. 2016, 209, 1668–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, G.; Chen, T.; Tian, S. Molecular basis and regulation of pathogenicity and patulin biosynthesis in Penicillium expansum. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Torres, R.; Ballester, A.R.; Li, B.; González-Candelas, L. Molecular aspects in pathogen-fruit interactions: Virulence and resistance. Postharvest Biol. Tec. 2016, 122, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, A.Y.; Wu, H.M. THESEUS 1, FERONIA and relatives: A family of cell wall-sensing receptor kinases? Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011, 14, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, S.A.; Shimosato-Asano, H.; Keinath, N.F.; Wuest, S.E.; Ingram, G.; Panstruga, R.; Grossniklaus, U. Conserved molecular components for pollen tube reception and fungal invasion. Science 2010, 330, 968–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Xing, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Qu, J.; Tan, Y.; Fu, X.; Lin, Q.; Deng, H.; Yu, F. Mutations of two FERONIA-like receptor genes enhance rice blast resistance without growth penalty. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 2112–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masachis, S.; Segorbe, D.; Turrà, D.; Leon-Ruiz, M.; Fürst, U.; El Ghalid, M.; Leonard, G.; López-Berges, M.S.; Richards, T.A.; Felix, G.; et al. A fungal pathogen secretes plant alkalinizing peptides to increase infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thynne, E.; Saur, I.M.L.; Simbaqueba, J.; Ogilvie, H.A.; Gonzalez-Cendales, Y.; Mead, O.; Taranto, A.; Catanzariti, A.M.; McDonald, M.C.; Schwessinger, B.; et al. Fungal phytopathogens encode functional homologues of plant rapid alkalinization factor (RALF) peptides. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2017, 18, 811–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Peng, H.; Zhu, S.; Xing, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; et al. Nematode-encoded RALF peptide mimics facilitate parasitism of plants through the FERONIA receptor kinase. Mol. Plant 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegmann, M.; Monaghan, J.; Smakowska-Luzan, E.; Rovenich, H.; Lehner, A.; Holton, N.; Belkhadir, Y.; Zipfel, C. The receptor kinase FER is a RALF-regulated scaffold controlling plant immune signaling. Science 2017, 355, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Nolan, T.M.; Song, G.; Liu, S.; Xie, Z.; Chen, J.; Schnable, P.S.; Walley, J.W.; Yin, Y. FERONIA receptor kinase contributes to plant immunity by suppressing jasmonic acid signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 3316–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Stegmann, M.; Han, Z.; DeFalco, T.A.; Parys, K.; Xu, L.; Belkhadir, Y.; Zipfel, C.; Chai, J. Mechanisms of RALF peptide perception by a heterotypic receptor complex. Nature 2019, 572, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronnier, J.; Franck, C.M.; Stegmann, M.; DeFalco, T.A.; Cifuentes, A.A.; Dünser, K.; Lin, W.; Yang, Z.; Kleine-Vehn, J.; Ringli, C.; et al. FERONIA regulates FLS2 plasma membrane nanoscale dynamics to modulate plant immune signaling. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Cheung, A.Y. Context-specific dependence on FERONIA kinase activity. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 2392–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo-Trigo, S.; Blümke, P.; Simon, R.; Butenko, M.A. Emerging mechanisms to fine-tune receptor kinase signaling specificity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2020, 57, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruta, M.; Gaddameedi, V.; Burch, H.; Fernandez, D.; Sussman, M.R. Comparison of the effects of a kinase-dead mutation of FERONIA on ovule fertilization and root growth of Arabidopsis. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 2395–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yu, F.; Liu, Y.; Du, C.; Li, X.; Zhu, S.; Wang, X.; Lan, W.; Rodriguez, P.L.; Liu, X.; et al. FERONIA interacts with ABI2-type phosphatases to facilitate signaling cross-talk between abscisic acid and RALF peptide in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E5519–E5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Lin, J.; Shan, X. THESEUS1 positively modulates plant defense responses against Botrytis cinerea through GUANINE EXCHANGE FACTOR4 signaling: THE1 functions in plant defense responses. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2017, 59, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).