Tfh Cells in Health and Immunity: Potential Targets for Systems Biology Approaches to Vaccination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Role of the T Cell Receptor
3. Lymphocyte Development in the Thymus
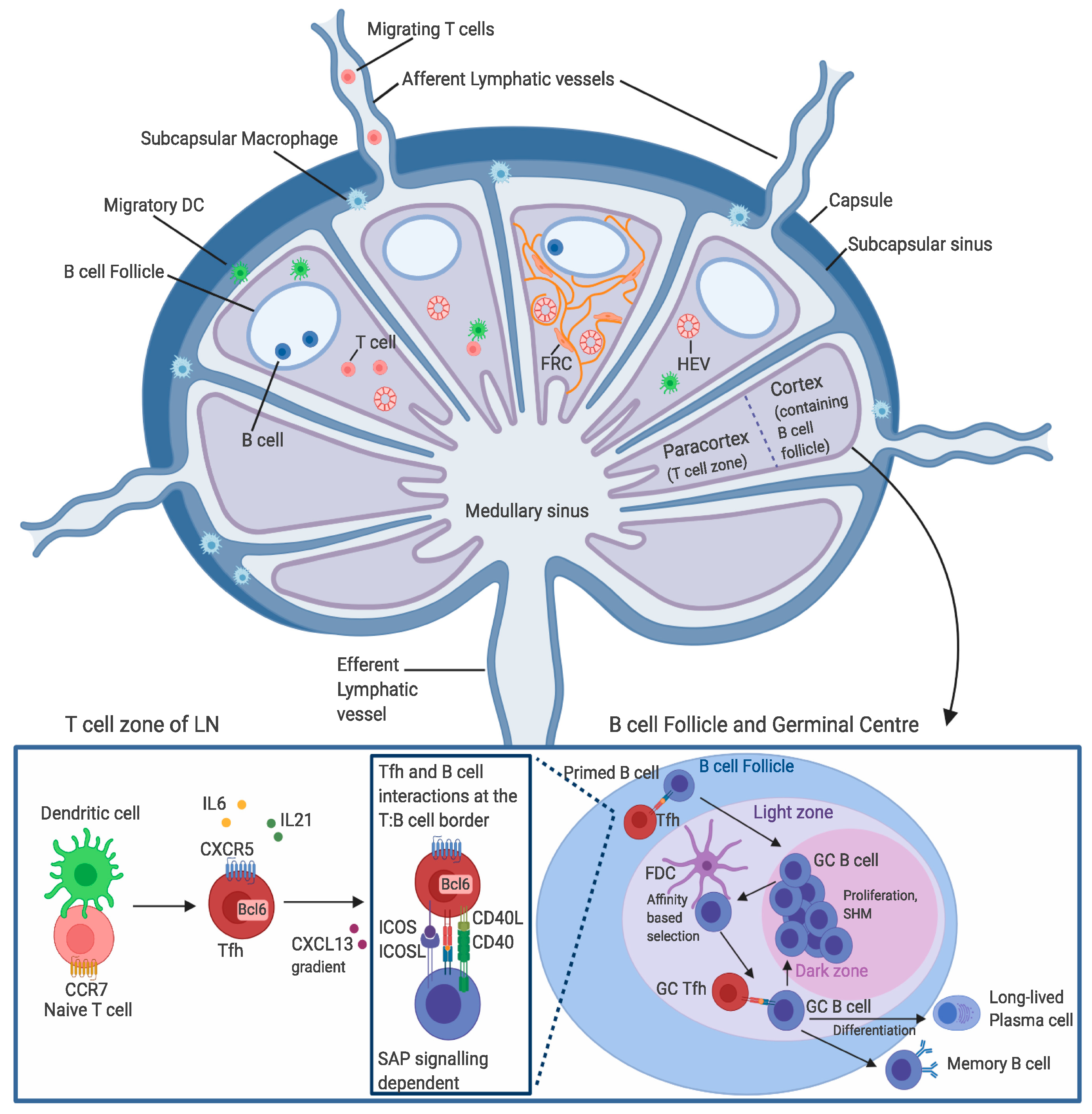
4. T Cell Entry into the Lymph Nodes
5. Tfh Cell Migration through the Lymph Nodes
6. T Cell Egress from the Lymph Node
7. Stages of Tfh Cell Differentiation
8. The GC Response and Tfh Cell Function in the Immune Response
9. Utilisation of c-Tfh Cells to Study Disease States
10. Role of Tfh Cells in Vaccination
11. The Future Role of Systems Biology Approaches in Characterising Tfh Cells
12. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Control of infectious diseases. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 1999, 48, 621–629. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkander, J.; Hojyo, S.; Tokoyoda, K. Vaccination to gain humoral immune memory. Clin. Transl. Immunology 2016, 5, e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ndhlovu, Z.M.; Liu, D.; Porter, L.C.; Fang, J.W.; Darko, S.; Brockman, M.A.; Miura, T.; Brumme, Z.L.; Schneidewind, A.; et al. TCR clonotypes modulate the protective effect of HLA class I molecules in HIV-1 infection. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davenport, M.P.; Price, D.A.; McMichael, A.J. The T cell repertoire in infection and vaccination: Implications for control of persistent viruses. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piepenbrink, K.H.; Blevins, S.J.; Scott, D.R.; Baker, B.M. The basis for limited specificity and MHC restriction in a T cell receptor interface. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrisekoop, N.; Monteiro, J.P.; Mandl, J.N.; Germain, R.N. Revisiting thymic positive selection and the mature T cell repertoire for antigen. Immunity 2014, 41, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, M.G.; Stanfield, R.L.; Wilson, I.A. How TCRs bind MHCs, peptides, and coreceptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 24, 419–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, J.D.; Warren, R.L.; Webb, J.R.; Nelson, B.H.; Holt, R.A. Profiling the T-cell receptor beta-chain repertoire by massively parallel sequencing. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1817–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, N.A.; Ely, L.K.; Beddoe, T.; Macdonald, W.A.; Reid, H.H.; Clements, C.S.; Purcell, A.W.; Kjer-Nielsen, L.; Miles, J.J.; Burrows, S.R.; et al. The CDR3 regions of an immunodominant T cell receptor dictate the ‘energetic landscape’ of peptide-MHC recognition. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.M.; Bjorkman, P.J. T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition. Nature 1988, 334, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, M.R. Site-specific recombination in the immune system. FASEB J. 1991, 5, 2934–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arstila, T.P.; Casrouge, A.; Baron, V.; Even, J.; Kanellopoulos, J.; Kourilsky, P. A direct estimate of the human alphabeta T cell receptor diversity. Science 1999, 286, 958–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhanen, R.; Heikkila, N.; Aggarwal, K.; Hamm, D.; Tarkkila, H.; Patila, T.; Jokiranta, T.S.; Saramaki, J.; Arstila, T.P. T cell receptor diversity in the human thymus. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 76, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sewell, A.K. Why must T cells be cross-reactive? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciofani, M.; Knowles, G.C.; Wiest, D.L.; von Boehmer, H.; Zuniga-Pflucker, J.C. Stage-specific and differential notch dependency at the alphabeta and gammadelta T lineage bifurcation. Immunity 2006, 25, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfer, A.; Wilson, A.; Nemir, M.; MacDonald, H.R.; Radtke, F. Inactivation of Notch1 impairs VDJbeta rearrangement and allows pre-TCR-independent survival of early alpha beta Lineage Thymocytes. Immunity 2002, 16, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krangel, M.S. Mechanics of T cell receptor gene rearrangement. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2009, 21, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, E.C.; Petrie, H.T.; Shah, L.M.; Owen, M.J.; Hayday, A.C. T cell receptor beta chain gene rearrangement and selection during thymocyte development in adult mice. Immunity 1994, 1, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, C.A.; Dudley, E.C.; Viney, J.L.; Owen, M.J.; Hayday, A.C. Rearrangement and diversity of T cell receptor beta chain genes in thymocytes: A critical role for the beta chain in development. Cell 1993, 73, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, M.; Hockett, R.D., Jr.; Zlotnik, A. Kinetics of T cell receptor beta, gamma, and delta rearrangements during adult thymic development: T cell receptor rearrangements are present in CD44(+)CD25(+) Pro-T thymocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 12522–12527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warmflash, A.; Dinner, A.R. A model for TCR gene segment use. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 3857–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Huang, C.Y.; Kanagawa, O. Rapid deletion of rearranged T cell antigen receptor (TCR) Valpha-Jalpha segment by secondary rearrangement in the thymus: Role of continuous rearrangement of TCR alpha chain gene and positive selection in the T cell repertoire formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 11834–11839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Hawwari, A.; Li, H.; Sun, Z.; Mahanta, S.K.; Littman, D.R.; Krangel, M.S.; He, Y.W. Regulation of the TCRalpha repertoire by the survival window of CD4(+)CD8(+) thymocytes. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shortman, K.; Egerton, M.; Spangrude, G.J.; Scollay, R. The generation and fate of thymocytes. Semin. Immunol. 1990, 2, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Surh, C.D.; Sprent, J. T-cell apoptosis detected in situ during positive and negative selection in the thymus. Nature 1994, 372, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, E. Negative selection—Clearing out the bad apples from the T-cell repertoire. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley, S.R.; Hu, D.Y.; Goodnow, C.C. Helios marks strongly autoreactive CD4+ T cells in two major waves of thymic deletion distinguished by induction of PD-1 or NF-kappaB. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, K.; Ohigashi, I.; Takahama, Y. Thymus machinery for T-cell selection. Int. Immunol. 2019, 31, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, L.; Kyewski, B.; Allen, P.M.; Hogquist, K.A. Positive and negative selection of the T cell repertoire: What thymocytes see (and don’t see). Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueni, L.N.; Detmar, M. The lymphatic system in health and disease. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2008, 6, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, R.; Braun, A.; Worbs, T. Lymph node homing of T cells and dendritic cells via afferent lymphatics. Trends Immunol. 2012, 33, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaahtomeri, K.; Brown, M.; Hauschild, R.; De Vries, I.; Leithner, A.F.; Mehling, M.; Kaufmann, W.A.; Sixt, M. Locally Triggered Release of the Chemokine CCL21 Promotes Dendritic Cell Transmigration across Lymphatic Endothelia. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, V.; Chaluvadi, V.S.; Ramos-Perez, W.D.; Mendoza, A.; Baeyens, A.; Rivera, R.; Chun, J.; Cammer, M.; Schwab, S.R. Gradients of the signaling lipid S1P in lymph nodes position natural killer cells and regulate their interferon-gamma response. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigl, B.; Aebischer, D.; Nitschke, M.; Iolyeva, M.; Rothlin, T.; Antsiferova, O.; Halin, C. Tissue inflammation modulates gene expression of lymphatic endothelial cells and dendritic cell migration in a stimulus-dependent manner. Blood 2011, 118, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, A.; Fang, V.; Chen, C.; Serasinghe, M.; Verma, A.; Muller, J.; Chaluvadi, V.S.; Dustin, M.L.; Hla, T.; Elemento, O.; et al. Lymphatic endothelial S1P promotes mitochondrial function and survival in naive T cells. Nature 2017, 546, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, S.D. Ligands for L-selectin: Homing, inflammation, and beyond. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 22, 129–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, J.P.; Moussion, C.; Forster, R. HEVs, lymphatics and homeostatic immune cell trafficking in lymph nodes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novkovic, M.; Onder, L.; Cupovic, J.; Abe, J.; Bomze, D.; Cremasco, V.; Scandella, E.; Stein, J.V.; Bocharov, G.; Turley, S.J.; et al. Topological Small-World Organization of the Fibroblastic Reticular Cell Network Determines Lymph Node Functionality. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, A.; Worbs, T.; Moschovakis, G.L.; Halle, S.; Hoffmann, K.; Bolter, J.; Munk, A.; Forster, R. Afferent lymph-derived T cells and DCs use different chemokine receptor CCR7-dependent routes for entry into the lymph node and intranodal migration. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.G.; Green, J.A.; Gray, E.E.; Xu, Y.; Cyster, J.G. Immune complex relay by subcapsular sinus macrophages and noncognate B cells drives antibody affinity maturation. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirosue, S.; Dubrot, J. Modes of Antigen Presentation by Lymph Node Stromal Cells and Their Immunological Implications. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwood, N.E.; Batista, F.D. The antigen expressway: Follicular conduits carry antigen to B cells. Immunity 2009, 30, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sixt, M.; Kanazawa, N.; Selg, M.; Samson, T.; Roos, G.; Reinhardt, D.P.; Pabst, R.; Lutz, M.B.; Sorokin, L. The conduit system transports soluble antigens from the afferent lymph to resident dendritic cells in the T cell area of the lymph node. Immunity 2005, 22, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, T.G.; Grigorova, I.; Okada, T.; Cyster, J.G. Subcapsular encounter and complement-dependent transport of immune complexes by lymph node B cells. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomura, M.; Yoshida, N.; Tanaka, J.; Karasawa, S.; Miwa, Y.; Miyawaki, A.; Kanagawa, O. Monitoring cellular movement in vivo with photoconvertible fluorescence protein “Kaede” transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10871–10876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerner, M.Y.; Casey, K.A.; Kastenmuller, W.; Germain, R.N. Dendritic cell and antigen dispersal landscapes regulate T cell immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 3105–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazilleau, N.; Eisenbraun, M.D.; Malherbe, L.; Ebright, J.N.; Pogue-Caley, R.R.; McHeyzer-Williams, L.J.; McHeyzer-Williams, M.G. Lymphoid reservoirs of antigen-specific memory T helper cells. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ise, W.; Inoue, T.; McLachlan, J.B.; Kometani, K.; Kubo, M.; Okada, T.; Kurosaki, T. Memory B cells contribute to rapid Bcl6 expression by memory follicular helper T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11792–11797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerner, M.Y.; Torabi-Parizi, P.; Germain, R.N. Strategically localized dendritic cells promote rapid T cell responses to lymph-borne particulate antigens. Immunity 2015, 42, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyster, J.G.; Schwab, S.R. Sphingosine-1-phosphate and lymphocyte egress from lymphoid organs. Annu Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, M.C.; Teijeira, A.; Halin, C. T Cell Trafficking through Lymphatic Vessels. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crotty, S. T follicular helper cell differentiation, function, and roles in disease. Immunity 2014, 41, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trub, M.; Barr, T.A.; Morrison, V.L.; Brown, S.; Caserta, S.; Rixon, J.; Ivens, A.; Gray, D. Heterogeneity of Phenotype and Function Reflects the Multistage Development of T Follicular Helper Cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goenka, R.; Barnett, L.G.; Silver, J.S.; O’Neill, P.J.; Hunter, C.A.; Cancro, M.P.; Laufer, T.M. Cutting edge: Dendritic cell-restricted antigen presentation initiates the follicular helper T cell program but cannot complete ultimate effector differentiation. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaerli, P.; Willimann, K.; Lang, A.B.; Lipp, M.; Loetscher, P.; Moser, B. CXC chemokine receptor 5 expression defines follicular homing T cells with B cell helper function. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardtke, S.; Ohl, L.; Forster, R. Balanced expression of CXCR5 and CCR7 on follicular T helper cells determines their transient positioning to lymph node follicles and is essential for efficient B-cell help. Blood 2005, 106, 1924–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Eto, D.; Yang, J.A.; Lao, C.; Crotty, S. Cutting edge: STAT1 is required for IL-6-mediated Bcl6 induction for early follicular helper cell differentiation. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3049–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, R.J.; Poholek, A.C.; DiToro, D.; Yusuf, I.; Eto, D.; Barnett, B.; Dent, A.L.; Craft, J.; Crotty, S. Bcl6 and Blimp-1 are reciprocal and antagonistic regulators of T follicular helper cell differentiation. Science 2009, 325, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzi, K.; Nance, J.P.; Kroenke, M.A.; Bothwell, M.; Haddad, E.K.; Melnick, A.; Crotty, S. BCL6 orchestrates Tfh cell differentiation via multiple distinct mechanisms. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurieva, R.I.; Chung, Y.; Hwang, D.; Yang, X.O.; Kang, H.S.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.H.; Watowich, S.S.; Jetten, A.M.; Tian, Q.; et al. Generation of T follicular helper cells is mediated by interleukin-21 but independent of T helper 1, 2, or 17 cell lineages. Immunity 2008, 29, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramatsu, Y.; Suto, A.; Kashiwakuma, D.; Kanari, H.; Kagami, S.; Ikeda, K.; Hirose, K.; Watanabe, N.; Grusby, M.J.; Iwamoto, I.; et al. c-Maf activates the promoter and enhancer of the IL-21 gene, and TGF-beta inhibits c-Maf-induced IL-21 production in CD4+ T cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 87, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroenke, M.A.; Eto, D.; Locci, M.; Cho, M.; Davidson, T.; Haddad, E.K.; Crotty, S. Bcl6 and Maf cooperate to instruct human follicular helper CD4 T cell differentiation. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3734–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andris, F.; Denanglaire, S.; Anciaux, M.; Hercor, M.; Hussein, H.; Leo, O. The Transcription Factor c-Maf Promotes the Differentiation of Follicular Helper T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.S.; Kageyama, R.; Eto, D.; Escobar, T.C.; Johnston, R.J.; Monticelli, L.; Lao, C.; Crotty, S. ICOS receptor instructs T follicular helper cell versus effector cell differentiation via induction of the transcriptional repressor Bcl6. Immunity 2011, 34, 932–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.S.; Suryani, S.; Avery, D.T.; Chan, A.; Nanan, R.; Santner-Nanan, B.; Deenick, E.K.; Tangye, S.G. Early commitment of naive human CD4(+) T cells to the T follicular helper (T(FH)) cell lineage is induced by IL-12. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2009, 87, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, N.; Morita, R.; Bourdery, L.; Bentebibel, S.E.; Zurawski, S.M.; Banchereau, J.; Ueno, H. Human dendritic cells induce the differentiation of interleukin-21-producing T follicular helper-like cells through interleukin-12. Immunity 2009, 31, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.P.; Fuhrmann, F.; Feist, R.K.; Lahmann, A.; Al Baz, M.S.; Gentz, L.J.; Vu Van, D.; Mages, H.W.; Haftmann, C.; Riedel, R.; et al. ICOS maintains the T follicular helper cell phenotype by down-regulating Kruppel-like factor 2. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Skon, C.N.; Lee, Y.J.; Oh, S.; Taylor, J.J.; Malhotra, D.; Jenkins, M.K.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Hogquist, K.A.; Jameson, S.C. The transcription factor KLF2 restrains CD4(+) T follicular helper cell differentiation. Immunity 2015, 42, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, S.; Delon, J.; Brotz, T.M.; Germain, R.N. Dynamic imaging of T cell-dendritic cell interactions in lymph nodes. Science 2002, 296, 1873–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celli, S.; Lemaitre, F.; Bousso, P. Real-time manipulation of T cell-dendritic cell interactions in vivo reveals the importance of prolonged contacts for CD4+ T cell activation. Immunity 2007, 27, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazilleau, N.; McHeyzer-Williams, L.J.; Rosen, H.; McHeyzer-Williams, M.G. The function of follicular helper T cells is regulated by the strength of T cell antigen receptor binding. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, N.M.; Allen, C.D.; Lesley, R.; Ansel, K.M.; Killeen, N.; Cyster, J.G. Role of CXCR5 and CCR7 in follicular Th cell positioning and appearance of a programmed cell death gene-1high germinal center-associated subpopulation. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 5099–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ma, W.; Zhang, T.; Wu, L.; Qi, H. Phenotypic Tfh development promoted by CXCR5-controlled re-localization and IL-6 from radiation-resistant cells. Protein Cell 2015, 6, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamperschroer, C.; Roberts, D.M.; Zhang, Y.; Weng, N.P.; Swain, S.L. SAP enables T cells to help B cells by a mechanism distinct from Th cell programming or CD40 ligand regulation. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 3994–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Cannons, J.L.; Klauschen, F.; Schwartzberg, P.L.; Germain, R.N. SAP-controlled T-B cell interactions underlie germinal centre formation. Nature 2008, 455, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foy, T.M.; Laman, J.D.; Ledbetter, J.A.; Aruffo, A.; Claassen, E.; Noelle, R.J. gp39-CD40 interactions are essential for germinal center formation and the development of B cell memory. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, T.D.; Heath, A.W.; Santos-Argumedo, L.; Howard, M.C.; Weissman, I.L.; Lund, F.E. Arrest of B lymphocyte terminal differentiation by CD40 signaling: Mechanism for lack of antibody-secreting cells in germinal centers. Immunity 1998, 8, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, J.; Kim, H.S.; Zhang, X.; Armitage, R.J.; Choi, Y.S. Cellular and molecular factors that regulate the differentiation and apoptosis of germinal center B cells. Anti-Ig down-regulates Fas expression of CD40 ligand-stimulated germinal center B cells and inhibits Fas-mediated apoptosis. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 1006–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, M.; Fujihara, C.; Radtke, A.J.; Chiang, Y.J.; Bhatia, S.; Germain, R.N.; Hodes, R.J. Co-stimulatory function in primary germinal center responses: CD40 and B7 are required on distinct antigen-presenting cells. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 2795–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, X.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Hou, S.; Peng, L.; Xu, C.; Liu, W.; et al. Follicular T-helper cell recruitment governed by bystander B cells and ICOS-driven motility. Nature 2013, 496, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiba, H.; Takeda, K.; Kojima, Y.; Usui, Y.; Harada, N.; Yamazaki, T.; Ma, J.; Tezuka, K.; Yagita, H.; Okumura, K. The role of ICOS in the CXCR5+ follicular B helper T cell maintenance in vivo. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2340–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmeister, Y.; Lischke, T.; Dahler, A.C.; Mages, H.W.; Lam, K.P.; Coyle, A.J.; Kroczek, R.A.; Hutloff, A. ICOS controls the pool size of effector-memory and regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinuesa, C.G.; Cook, M.C.; Angelucci, C.; Athanasopoulos, V.; Rui, L.; Hill, K.M.; Yu, D.; Domaschenz, H.; Whittle, B.; Lambe, T.; et al. A RING-type ubiquitin ligase family member required to repress follicular helper T cells and autoimmunity. Nature 2005, 435, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deenick, E.K.; Chan, A.; Ma, C.S.; Gatto, D.; Schwartzberg, P.L.; Brink, R.; Tangye, S.G. Follicular helper T cell differentiation requires continuous antigen presentation that is independent of unique B cell signaling. Immunity 2010, 33, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Chen, X.; Chu, C.; Lu, P.; Xu, H.; Yan, J. Follicular T-helper cells: Controlled localization and cellular interactions. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2014, 92, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, Z.; Gitlin, A.D.; Targ, S.; Jankovic, M.; Pasqual, G.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; Victora, G.D. T follicular helper cell dynamics in germinal centers. Science 2013, 341, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, I.; Kageyama, R.; Monticelli, L.; Johnston, R.J.; Ditoro, D.; Hansen, K.; Barnett, B.; Crotty, S. Germinal center T follicular helper cell IL-4 production is dependent on signaling lymphocytic activation molecule receptor (CD150). J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannons, J.L.; Qi, H.; Lu, K.T.; Dutta, M.; Gomez-Rodriguez, J.; Cheng, J.; Wakeland, E.K.; Germain, R.N.; Schwartzberg, P.L. Optimal germinal center responses require a multistage T cell:B cell adhesion process involving integrins, SLAM-associated protein, and CD84. Immunity 2010, 32, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, R.; Cannons, J.L.; Zhao, F.; Yusuf, I.; Lao, C.; Locci, M.; Schwartzberg, P.L.; Crotty, S. The receptor Ly108 functions as a SAP adaptor-dependent on-off switch for T cell help to B cells and NKT cell development. Immunity 2012, 36, 986–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morra, M.; Barrington, R.A.; Abadia-Molina, A.C.; Okamoto, S.; Julien, A.; Gullo, C.; Kalsy, A.; Edwards, M.J.; Chen, G.; Spolski, R.; et al. Defective B cell responses in the absence of SH2D1A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4819–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCausland, M.M.; Yusuf, I.; Tran, H.; Ono, N.; Yanagi, Y.; Crotty, S. SAP regulation of follicular helper CD4 T cell development and humoral immunity is independent of SLAM and Fyn kinase. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffey, A.J.; Brooksbank, R.A.; Brandau, O.; Oohashi, T.; Howell, G.R.; Bye, J.M.; Cahn, A.P.; Durham, J.; Heath, P.; Wray, P.; et al. Host response to EBV infection in X-linked lymphoproliferative disease results from mutations in an SH2-domain encoding gene. Nat. Genet. 1998, 20, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.S.; Deenick, E.K. Human T follicular helper (Tfh) cells and disease. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2014, 92, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, K.E.; Harkin, D.P.; Levitz, S.; Krainer, M.; Kolquist, K.A.; Genovese, C.; Bernard, A.; Ferguson, M.; Zuo, L.; Snyder, E.; et al. Inactivating mutations in an SH2 domain-encoding gene in X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13765–13770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suan, D.; Nguyen, A.; Moran, I.; Bourne, K.; Hermes, J.R.; Arshi, M.; Hampton, H.R.; Tomura, M.; Miwa, Y.; Kelleher, A.D.; et al. T follicular helper cells have distinct modes of migration and molecular signatures in naive and memory immune responses. Immunity 2015, 42, 704–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurieva, R.I.; Chung, Y.; Martinez, G.J.; Yang, X.O.; Tanaka, S.; Matskevitch, T.D.; Wang, Y.H.; Dong, C. Bcl6 mediates the development of T follicular helper cells. Science 2009, 325, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Moran, I.; Shinnakasu, R.; Phan, T.G.; Kurosaki, T. Generation of memory B cells and their reactivation. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 283, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinnakasu, R.; Kurosaki, T. Regulation of memory B and plasma cell differentiation. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2017, 45, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsakos, M.; Nguyen, T.H.O.; Kedzierska, K. With a Little Help from T Follicular Helper Friends: Humoral Immunity to Influenza Vaccination. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattoretti, G.; Angelin-Duclos, C.; Shaknovich, R.; Zhou, H.; Wang, D.; Alobeid, B. PRDM1/Blimp-1 is expressed in human B-lymphocytes committed to the plasma cell lineage. J. Pathol. 2005, 206, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogerson, B.; Hackett, J., Jr.; Peters, A.; Haasch, D.; Storb, U. Mutation pattern of immunoglobulin transgenes is compatible with a model of somatic hypermutation in which targeting of the mutator is linked to the direction of DNA replication. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 4331–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.J.; Xu, J.; de Bouteiller, O.; Parham, C.L.; Grouard, G.; Djossou, O.; de Saint-Vis, B.; Lebecque, S.; Banchereau, J.; Moore, K.W. Follicular dendritic cells specifically express the long CR2/CD21 isoform. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, D.; Wu, J.; Vora, K.A.; Ravetch, J.V.; Szakal, A.K.; Manser, T.; Tew, J.G. Fc gamma receptor IIB on follicular dendritic cells regulates the B cell recall response. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 6268–6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Good-Jacobson, K.L.; Szumilas, C.G.; Chen, L.; Sharpe, A.H.; Tomayko, M.M.; Shlomchik, M.J. PD-1 regulates germinal center B cell survival and the formation and affinity of long-lived plasma cells. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victora, G.D.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Germinal centers. Annu Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 429–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulman, Z.; Gitlin, A.D.; Weinstein, J.S.; Lainez, B.; Esplugues, E.; Flavell, R.A.; Craft, J.E.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Dynamic signaling by T follicular helper cells during germinal center B cell selection. Science 2014, 345, 1058–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blink, E.J.; Light, A.; Kallies, A.; Nutt, S.L.; Hodgkin, P.D.; Tarlinton, D.M. Early appearance of germinal center-derived memory B cells and plasma cells in blood after primary immunization. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.G.; Paus, D.; Chan, T.D.; Turner, M.L.; Nutt, S.L.; Basten, A.; Brink, R. High affinity germinal center B cells are actively selected into the plasma cell compartment. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2419–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heesters, B.A.; Myers, R.C.; Carroll, M.C. Follicular dendritic cells: Dynamic antigen libraries. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.D.; Okada, T.; Tang, H.L.; Cyster, J.G. Imaging of germinal center selection events during affinity maturation. Science 2007, 315, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwickert, T.A.; Lindquist, R.L.; Shakhar, G.; Livshits, G.; Skokos, D.; Kosco-Vilbois, M.H.; Dustin, M.L.; Nussenzweig, M.C. In Vivo imaging of germinal centres reveals a dynamic open structure. Nature 2007, 446, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hams, E.; McCarron, M.J.; Amu, S.; Yagita, H.; Azuma, M.; Chen, L.; Fallon, P.G. Blockade of B7-H1 (programmed death ligand 1) enhances humoral immunity by positively regulating the generation of T follicular helper cells. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 5648–5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gitlin, A.D.; Shulman, Z.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Clonal selection in the germinal centre by regulated proliferation and hypermutation. Nature 2014, 509, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivino, L.; Messi, M.; Jarrossay, D.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Sallusto, F.; Geginat, J. Chemokine receptor expression identifies Pre-T helper (Th)1, Pre-Th2, and nonpolarized cells among human CD4+ central memory T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenna, E.; Davydov, A.N.; Ladell, K.; McLaren, J.E.; Bonaiuti, P.; Metsger, M.; Ramsden, J.D.; Gilbert, S.C.; Lambe, T.; Price, D.A.; et al. CD4(+) T Follicular Helper Cells in Human Tonsils and Blood Are Clonally Convergent but Divergent from Non-Tfh CD4(+) Cells. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 137–152.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heit, A.; Schmitz, F.; Gerdts, S.; Flach, B.; Moore, M.S.; Perkins, J.A.; Robins, H.S.; Aderem, A.; Spearman, P.; Tomaras, G.D.; et al. Vaccination establishes clonal relatives of germinal center T cells in the blood of humans. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 2139–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, L.A.; Buggert, M.; Manne, S.; Herati, R.S.; Sayin, I.; Kuri-Cervantes, L.; Bukh Brody, I.; O’Boyle, K.C.; Kaprielian, H.; Giles, J.R.; et al. T follicular helper cells in human efferent lymph retain lymphoid characteristics. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3185–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, P.; Ueno, H.; Schmitt, N. T follicular helper (Tfh) cells in lupus: Activation and involvement in SLE pathogenesis. Eur J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangye, S.G.; Ma, C.S.; Brink, R.; Deenick, E.K. The good, the bad and the ugly—TFH cells in human health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 412–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oli, A.N.; Obialor, W.O.; Ifeanyichukwu, M.O.; Odimegwu, D.C.; Okoyeh, J.N.; Emechebe, G.O.; Adejumo, S.A.; Ibeanu, G.C. Immunoinformatics and Vaccine Development: An Overview. Immunotargets Ther. 2020, 9, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, N.; Gatenby, P.A.; Wilson, A.; Malik, S.; Fulcher, D.A.; Tangye, S.G.; Manku, H.; Vyse, T.J.; Roncador, G.; Huttley, G.A.; et al. Expansion of circulating T cells resembling follicular helper T cells is a fixed phenotype that identifies a subset of severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Coz, C.; Joublin, A.; Pasquali, J.L.; Korganow, A.S.; Dumortier, H.; Monneaux, F. Circulating TFH subset distribution is strongly affected in lupus patients with an active disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieth, B.; Parekh, S.; Ziegenhain, C.; Enard, W.; Hellmann, I. A systematic evaluation of single cell RNA-seq analysis pipelines. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, K.U.; Edelmann, S.L.; Jeltsch, K.M.; Bertossi, A.; Heger, K.; Heinz, G.A.; Zoller, J.; Warth, S.C.; Hoefig, K.P.; Lohs, C.; et al. Roquin paralogs 1 and 2 redundantly repress the Icos and Ox40 costimulator mRNAs and control follicular helper T cell differentiation. Immunity 2013, 38, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratama, A.; Ramiscal, R.R.; Silva, D.G.; Das, S.K.; Athanasopoulos, V.; Fitch, J.; Botelho, N.K.; Chang, P.P.; Hu, X.; Hogan, J.J.; et al. Roquin-2 shares functions with its paralog Roquin-1 in the repression of mRNAs controlling T follicular helper cells and systemic inflammation. Immunity 2013, 38, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubas, R.A.; Mudd, J.C.; Savoye, A.L.; Perreau, M.; van Grevenynghe, J.; Metcalf, T.; Connick, E.; Meditz, A.; Freeman, G.J.; Abesada-Terk, G., Jr.; et al. Inadequate T follicular cell help impairs B cell immunity during HIV infection. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Weatherall, C.; Bailey, M.; Alcantara, S.; De Rose, R.; Estaquier, J.; Wilson, K.; Suzuki, K.; Corbeil, J.; Cooper, D.A.; et al. Simian immunodeficiency virus infects follicular helper CD4 T cells in lymphoid tissues during pathogenic infection of pigtail macaques. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 3760–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreau, M.; Savoye, A.L.; De Crignis, E.; Corpataux, J.M.; Cubas, R.; Haddad, E.K.; De Leval, L.; Graziosi, C.; Pantaleo, G. Follicular helper T cells serve as the major CD4 T cell compartment for HIV-1 infection, replication, and production. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaunders, J.; Xu, Y.; Kent, S.J.; Koelsch, K.K.; Kelleher, A.D. Divergent Expression of CXCR5 and CCR5 on CD4(+) T Cells and the Paradoxical Accumulation of T Follicular Helper Cells during HIV Infection. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, M.; van Lunzen, J.; Soghoian, D.Z.; Kuhl, B.D.; Ranasinghe, S.; Kranias, G.; Flanders, M.D.; Cutler, S.; Yudanin, N.; Muller, M.I.; et al. Expansion of HIV-specific T follicular helper cells in chronic HIV infection. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3271–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessl, J.; Baxter, A.E.; Morou, A.; Brunet-Ratnasingham, E.; Sannier, G.; Gendron-Lepage, G.; Richard, J.; Delgado, G.G.; Brassard, N.; Turcotte, I.; et al. Persistent expansion and Th1-like skewing of HIV-specific circulating T follicular helper cells during antiretroviral therapy. EBioMedicine 2020, 54, 102727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, H. Human Circulating T Follicular Helper Cell Subsets in Health and Disease. J. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 36 (Suppl. 1), 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buranapraditkun, S.; Pissani, F.; Teigler, J.E.; Schultz, B.T.; Alter, G.; Marovich, M.; Robb, M.L.; Eller, M.A.; Martin, J.; Deeks, S.; et al. Preservation of Peripheral T Follicular Helper Cell Function in HIV Controllers. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cubas, R.; van Grevenynghe, J.; Wills, S.; Kardava, L.; Santich, B.H.; Buckner, C.M.; Muir, R.; Tardif, V.; Nichols, C.; Procopio, F.; et al. Reversible Reprogramming of Circulating Memory T Follicular Helper Cell Function during Chronic HIV Infection. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 5625–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colineau, L.; Rouers, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Xu, Y.; Urrutia, A.; Pham, H.P.; Cardinaud, S.; Samri, A.; Dorgham, K.; Coulon, P.G.; et al. HIV-Infected Spleens Present Altered Follicular Helper T Cell (Tfh) Subsets and Skewed B Cell Maturation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Waseem, T.C.; Sahoo, A.; Bieerkehazhi, S.; Zhou, H.; Galkina, E.V.; Nurieva, R. Insights Into the Molecular Mechanisms of T Follicular Helper-Mediated Immunity and Pathology. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Iijima, K.; Dent, A.L.; Kita, H. Follicular helper T cells mediate IgE antibody response to airborne allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 300–313.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, K.; Gaspar, K.; Dajnoki, Z.; Papp, G.; Fabos, B.; Szegedi, A.; Zeher, M. Expansion of circulating follicular T helper cells associates with disease severity in childhood atopic dermatitis. Immunol. Lett. 2017, 189, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnowicki, T.; Esaki, H.; Gonzalez, J.; Renert-Yuval, Y.; Brunner, P.; Oliva, M.; Estrada, Y.; Xu, H.; Zheng, X.; Talasila, S.; et al. Alterations in B-cell subsets in pediatric patients with early atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 134–144.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Qian, C.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, J.; Pan, Y.; Dong, Q.; Jiang, D. Circulating follicular T-helper cell subset distribution in patients with asthma. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2016, 37, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, A.; Zhao, J. Follicular helper T cells are responsible for IgE responses to Der p 1 following house dust mite sensitization in mice. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentebibel, S.E.; Lopez, S.; Obermoser, G.; Schmitt, N.; Mueller, C.; Harrod, C.; Flano, E.; Mejias, A.; Albrecht, R.A.; Blankenship, D.; et al. Induction of ICOS+CXCR3+CXCR5+ TH cells correlates with antibody responses to influenza vaccination. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 176ra132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herati, R.S.; Muselman, A.; Vella, L.; Bengsch, B.; Parkhouse, K.; Del Alcazar, D.; Kotzin, J.; Doyle, S.A.; Tebas, P.; Hensley, S.E.; et al. Successive annual influenza vaccination induces a recurrent oligoclonotypic memory response in circulating T follicular helper cells. Sci. Immunol. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herati, R.S.; Reuter, M.A.; Dolfi, D.V.; Mansfield, K.D.; Aung, H.; Badwan, O.Z.; Kurupati, R.K.; Kannan, S.; Ertl, H.; Schmader, K.E.; et al. Circulating CXCR5+PD-1+ response predicts influenza vaccine antibody responses in young adults but not elderly adults. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 3528–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutsakos, M.; Wheatley, A.K.; Loh, L.; Clemens, E.B.; Sant, S.; Nussing, S.; Fox, A.; Chung, A.W.; Laurie, K.L.; Hurt, A.C.; et al. Circulating TFH cells, serological memory, and tissue compartmentalization shape human influenza-specific B cell immunity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilkinton, M.A.; Nicholas, K.J.; Warren, C.M.; Smith, R.M.; Yoder, S.M.; Talbot, H.K.; Kalams, S.A. Greater activation of peripheral T follicular helper cells following high dose influenza vaccine in older adults forecasts seroconversion. Vaccine 2017, 35, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Tsai, L.M.; Leong, Y.A.; Hu, X.; Ma, C.S.; Chevalier, N.; Sun, X.; Vandenberg, K.; Rockman, S.; Ding, Y.; et al. Circulating precursor CCR7(lo)PD-1(hi) CXCR5(+) CD4(+) T cells indicate Tfh cell activity and promote antibody responses upon antigen reexposure. Immunity 2013, 39, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentebibel, S.E.; Khurana, S.; Schmitt, N.; Kurup, P.; Mueller, C.; Obermoser, G.; Palucka, A.K.; Albrecht, R.A.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Golding, H.; et al. ICOS(+)PD-1(+)CXCR3(+) T follicular helper cells contribute to the generation of high-avidity antibodies following influenza vaccination. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spensieri, F.; Borgogni, E.; Zedda, L.; Bardelli, M.; Buricchi, F.; Volpini, G.; Fragapane, E.; Tavarini, S.; Finco, O.; Rappuoli, R.; et al. Human circulating influenza-CD4+ ICOS1+IL-21+ T cells expand after vaccination, exert helper function, and predict antibody responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14330–14335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stebegg, M.; Bignon, A.; Hill, D.L.; Silva-Cayetano, A.; Krueger, C.; Vanderleyden, I.; Innocentin, S.; Boon, L.; Wang, J.; Zand, M.S.; et al. Rejuvenating conventional dendritic cells and T follicular helper cell formation after vaccination. eLife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pape, K.A.; Taylor, J.J.; Maul, R.W.; Gearhart, P.J.; Jenkins, M.K. Different B cell populations mediate early and late memory during an endogenous immune response. Science 2011, 331, 1203–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havenar-Daughton, C.; Carnathan, D.G.; Torrents de la Pena, A.; Pauthner, M.; Briney, B.; Reiss, S.M.; Wood, J.S.; Kaushik, K.; van Gils, M.J.; Rosales, S.L.; et al. Direct Probing of Germinal Center Responses Reveals Immunological Features and Bottlenecks for Neutralizing Antibody Responses to HIV Env Trimer. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 2195–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havenar-Daughton, C.; Carnathan, D.G.; Boopathy, A.V.; Upadhyay, A.A.; Murrell, B.; Reiss, S.M.; Enemuo, C.A.; Gebru, E.H.; Choe, Y.; Dhadvai, P.; et al. Rapid Germinal Center and Antibody Responses in Non-human Primates after a Single Nanoparticle Vaccine Immunization. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 1756–1766 e1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.L.; Pierson, W.; Bolland, D.J.; Mkindi, C.; Carr, E.J.; Wang, J.; Houard, S.; Wingett, S.W.; Audran, R.; Wallin, E.F.; et al. The adjuvant GLA-SE promotes human Tfh cell expansion and emergence of public TCRbeta clonotypes. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 1857–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, P.; Fiore-Gartland, A.J.; Hertz, T.; Wang, G.C.; Sharma, S.; Souquette, A.; Crawford, J.C.; Clemens, E.B.; Nguyen, T.H.O.; Kedzierska, K.; et al. Quantifiable predictive features define epitope-specific T cell receptor repertoires. Nature 2017, 547, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerson, R.O.; DeWitt, W.S.; Vignali, M.; Gravley, J.; Hu, J.K.; Osborne, E.J.; Desmarais, C.; Klinger, M.; Carlson, C.S.; Hansen, J.A.; et al. Immunosequencing identifies signatures of cytomegalovirus exposure history and HLA-mediated effects on the T cell repertoire. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanville, J.; Huang, H.; Nau, A.; Hatton, O.; Wagar, L.E.; Rubelt, F.; Ji, X.; Han, A.; Krams, S.M.; Pettus, C.; et al. Identifying specificity groups in the T cell receptor repertoire. Nature 2017, 547, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.J.; Liu, Y.; Roskin, K.M.; Glanville, J.; Hoh, R.A.; Seo, K.; Marshall, E.L.; Gurley, T.C.; Moody, M.A.; Haynes, B.F.; et al. Human responses to influenza vaccination show seroconversion signatures and convergent antibody rearrangements. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 16, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becattini, S.; Latorre, D.; Mele, F.; Foglierini, M.; De Gregorio, C.; Cassotta, A.; Fernandez, B.; Kelderman, S.; Schumacher, T.N.; Corti, D.; et al. T cell immunity. Functional heterogeneity of human memory CD4(+) T cell clones primed by pathogens or vaccines. Science 2015, 347, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.; Glanville, J.; Hansmann, L.; Davis, M.M. Linking T-cell receptor sequence to functional phenotype at the single-cell level. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaf, M.; Huseby, E.; Sewell, A.K. alphabeta T cell receptors as predictors of health and disease. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2015, 12, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Pesenacker, A.M.; Stansfield, A.; King, D.; Barge, D.; Foster, H.E.; Abinun, M.; Wedderburn, L.R. Immunological characteristics and T-cell receptor clonal diversity in children with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis undergoing T-cell-depleted autologous stem cell transplantation. Immunology 2014, 142, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lossius, A.; Johansen, J.N.; Vartdal, F.; Robins, H.; Jurate Saltyte, B.; Holmoy, T.; Olweus, J. High-throughput sequencing of TCR repertoires in multiple sclerosis reveals intrathecal enrichment of EBV-reactive CD8+ T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 3439–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, T.; Teichmann, S.A.; Talavera-Lopez, C. Immunology Driven by Large-Scale Single-Cell Sequencing. Trends Immunol. 2019, 40, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.M.; Tato, C.M.; Furman, D. Systems immunology: Just getting started. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querec, T.D.; Akondy, R.S.; Lee, E.K.; Cao, W.; Nakaya, H.I.; Teuwen, D.; Pirani, A.; Gernert, K.; Deng, J.; Marzolf, B.; et al. Systems biology approach predicts immunogenicity of the yellow fever vaccine in humans. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, E.A.; Grill, D.E.; Zimmermann, M.T.; Simon, W.L.; Ovsyannikova, I.G.; Kennedy, R.B.; Poland, G.A. Transcriptomic signatures of cellular and humoral immune responses in older adults after seasonal influenza vaccination identified by data-driven clustering. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaya, H.I.; Hagan, T.; Duraisingham, S.S.; Lee, E.K.; Kwissa, M.; Rouphael, N.; Frasca, D.; Gersten, M.; Mehta, A.K.; Gaujoux, R.; et al. Systems Analysis of Immunity to Influenza Vaccination across Multiple Years and in Diverse Populations Reveals Shared Molecular Signatures. Immunity 2015, 43, 1186–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.T.; Oberg, A.L.; Grill, D.E.; Ovsyannikova, I.G.; Haralambieva, I.H.; Kennedy, R.B.; Poland, G.A. System-Wide Associations between DNA-Methylation, Gene Expression, and Humoral Immune Response to Influenza Vaccination. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizukami, T.; Momose, H.; Kuramitsu, M.; Takizawa, K.; Araki, K.; Furuhata, K.; Ishii, K.J.; Hamaguchi, I.; Yamaguchi, K. System vaccinology for the evaluation of influenza vaccine safety by multiplex gene detection of novel biomarkers in a preclinical study and batch release test. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralambieva, I.H.; Zimmermann, M.T.; Ovsyannikova, I.G.; Grill, D.E.; Oberg, A.L.; Kennedy, R.B.; Poland, G.A. Whole Transcriptome Profiling Identifies CD93 and Other Plasma Cell Survival Factor Genes Associated with Measles-Specific Antibody Response after Vaccination. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Rouphael, N.; Duraisingham, S.; Romero-Steiner, S.; Presnell, S.; Davis, C.; Schmidt, D.S.; Johnson, S.E.; Milton, A.; Rajam, G.; et al. Molecular signatures of antibody responses derived from a systems biology study of five human vaccines. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonnberg, T.; Svensson, V.; James, K.R.; Fernandez-Ruiz, D.; Sebina, I.; Montandon, R.; Soon, M.S.; Fogg, L.G.; Nair, A.S.; Liligeto, U.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq and computational analysis using temporal mixture modelling resolves Th1/Tfh fate bifurcation in malaria. Sci. Immunol. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Receptor/Ligand | Corresponding Gene | Reciprocal Receptor/Ligand | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCR7 | CCR7 | CCL21 | Promotes naïve T cell homing to the T cell zone (paracortex) of the LN [31,47,54,56]. |
| CXCR5 | CXCR5 | CXCL13 | Essential for T and B cell homing to the B cell follicle, within the cortex of the LN [55,72,73]. |
| Bcl6 | BCL6 | - | Master transcription factor for Tfh cell lineage. Limits Th1 differentiation through Blimp-1 pathway and supports Tfh cell differentiation [96]. |
| IL-21 | IL21 | IL-21R | Regulates ICOSL expression on B cells essential for Tfh and B cell interactions through ICOS/ICOSL signalling [60]. Regulates Tfh differentiation through c-Maf promotion of IL-21 production [61]. |
| ICOS | ICOS | ICOSL | Interacts with ICOSL expressed on B cells, influencing Tfh and B cell positioning within the LN [84]. Necessary for persistent T cell migration to the T–B cell border of the B cell follicle and optimal germinal centre responses [80]. |
| TCR | - | MCH-II | T cell receptor that binds with peptide–MHC-II complexes. Higher TCR affinity results in longer TCR–MHC-II interactions, ultimately influencing cell fate decisions [69,70,71]. |
| SAP | SH2D1A | SLAMF6 and SLAMF5 | Necessary for forming stable T–B cell conjugates via SLAMF6 binding within the GC [75]. Supports Tfh cell adhesion and development and B cell responses when bound to SLAMF6 [90,91]. Essential for optimal GC responses by SLAMF5 binding [88]. |
| CD40L | CD40LG | CD40 | Essential for formation and maintenance of the GC, promotes antibody class switching and provides crucial survival signals to GC B cells [76,77,78,79]. |
| EBI2 | GPR183 | 7α,25-dihydroxycholesterol (7α,25-OHC) | Involved in temporospatial guidance of B cells and Tfh cells through the LN follicle mantle and GC [95]. |
| S1PR1 | S1PR1 | S1P | Binds to S1P secreted by lymphatic vessels, facilitating T cell migration into the LN [33,34,35]. High concentrations of S1P in efferent lymph promotes Tfh cell egress from the LN via S1PR1 binding [50]. |
| S1PR2 | S1PR2 | S1P | Involved in guidance and retention of Tfh cells within the GC via repelling them from S1P-rich lymph [95]. |
| CD62L | SELL | GlyCAM-1 | Facilitates adhesion and rolling of T cells along high endothelial venules as they migrate into the LN [36]. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Law, H.; Venturi, V.; Kelleher, A.; Munier, C.M.L. Tfh Cells in Health and Immunity: Potential Targets for Systems Biology Approaches to Vaccination. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8524. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228524
Law H, Venturi V, Kelleher A, Munier CML. Tfh Cells in Health and Immunity: Potential Targets for Systems Biology Approaches to Vaccination. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(22):8524. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228524
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaw, Hannah, Vanessa Venturi, Anthony Kelleher, and C. Mee Ling Munier. 2020. "Tfh Cells in Health and Immunity: Potential Targets for Systems Biology Approaches to Vaccination" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 22: 8524. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228524
APA StyleLaw, H., Venturi, V., Kelleher, A., & Munier, C. M. L. (2020). Tfh Cells in Health and Immunity: Potential Targets for Systems Biology Approaches to Vaccination. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(22), 8524. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228524





