NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation Is Involved in LPA1-Mediated Brain Injury after Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
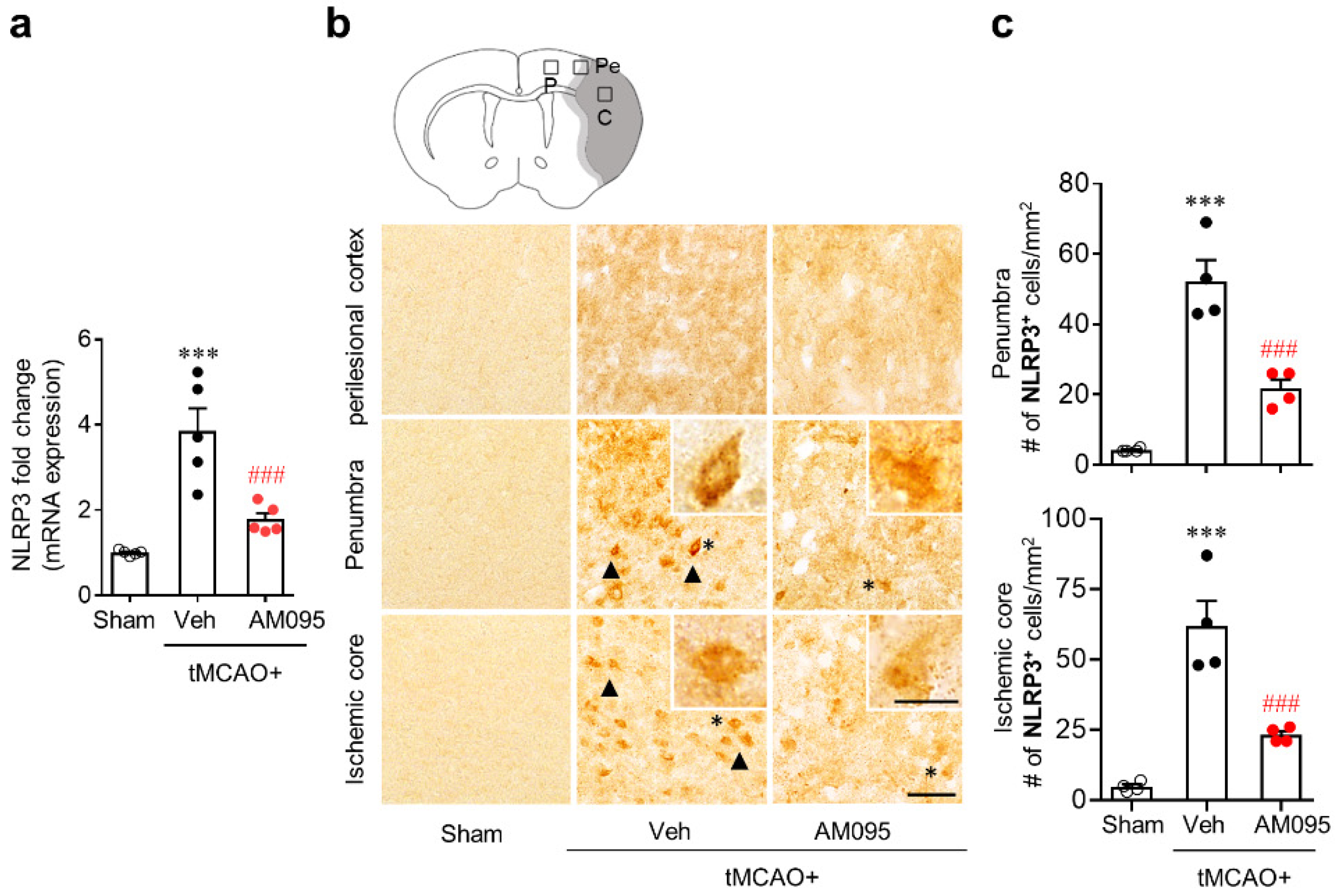
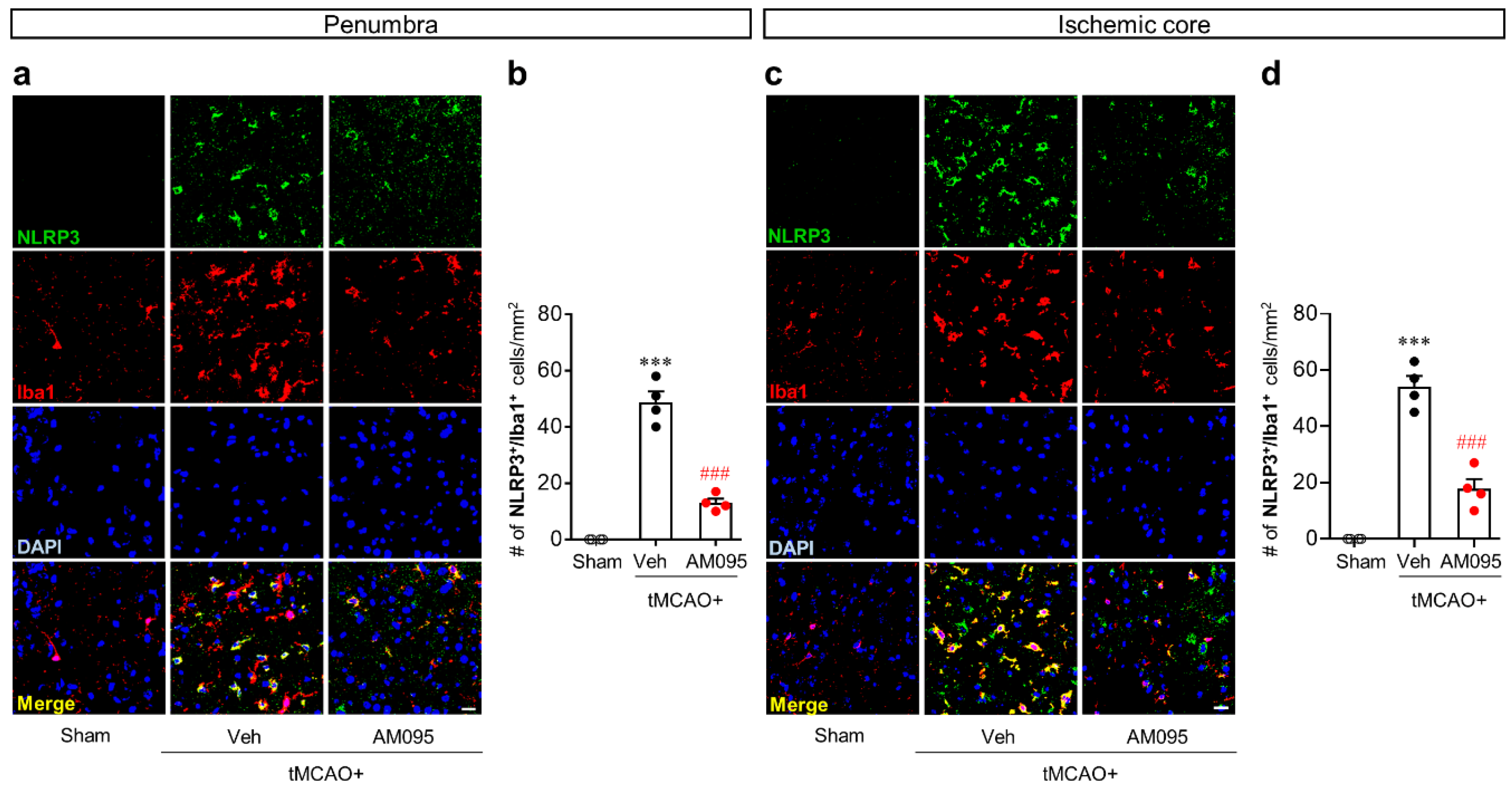
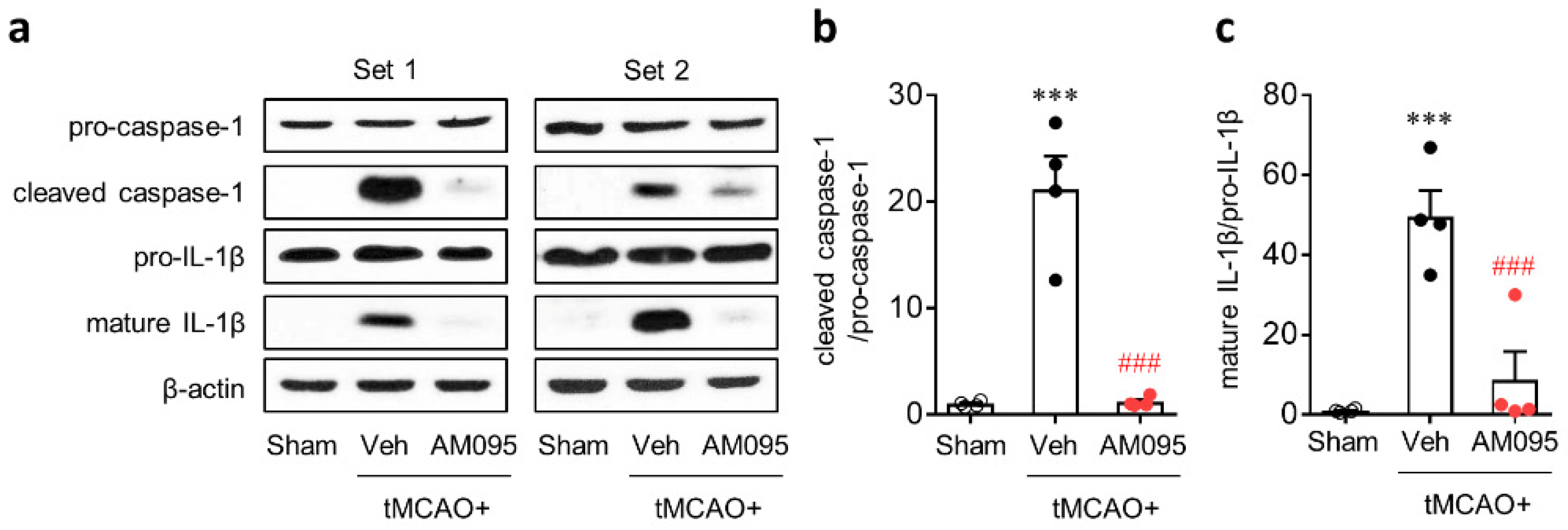
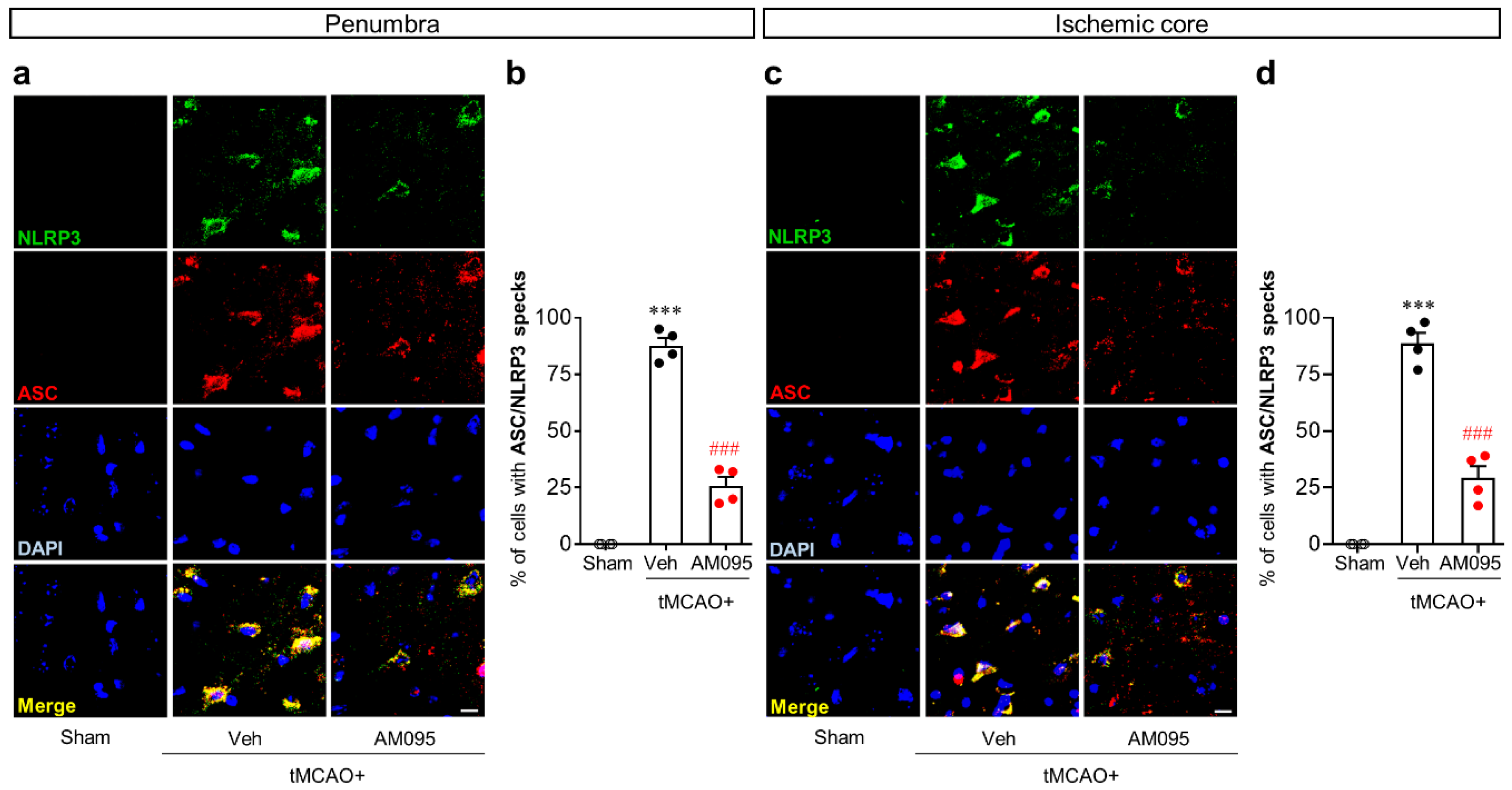
2.1. Suppressing LPA1 Activity Attenuates NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in an Injured Brain after tMCAO Challenge
2.2. LPA1 Contributes to NLRP3 Upregulation and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in LPS-Primed Macrophages Followed by LPA Exposure
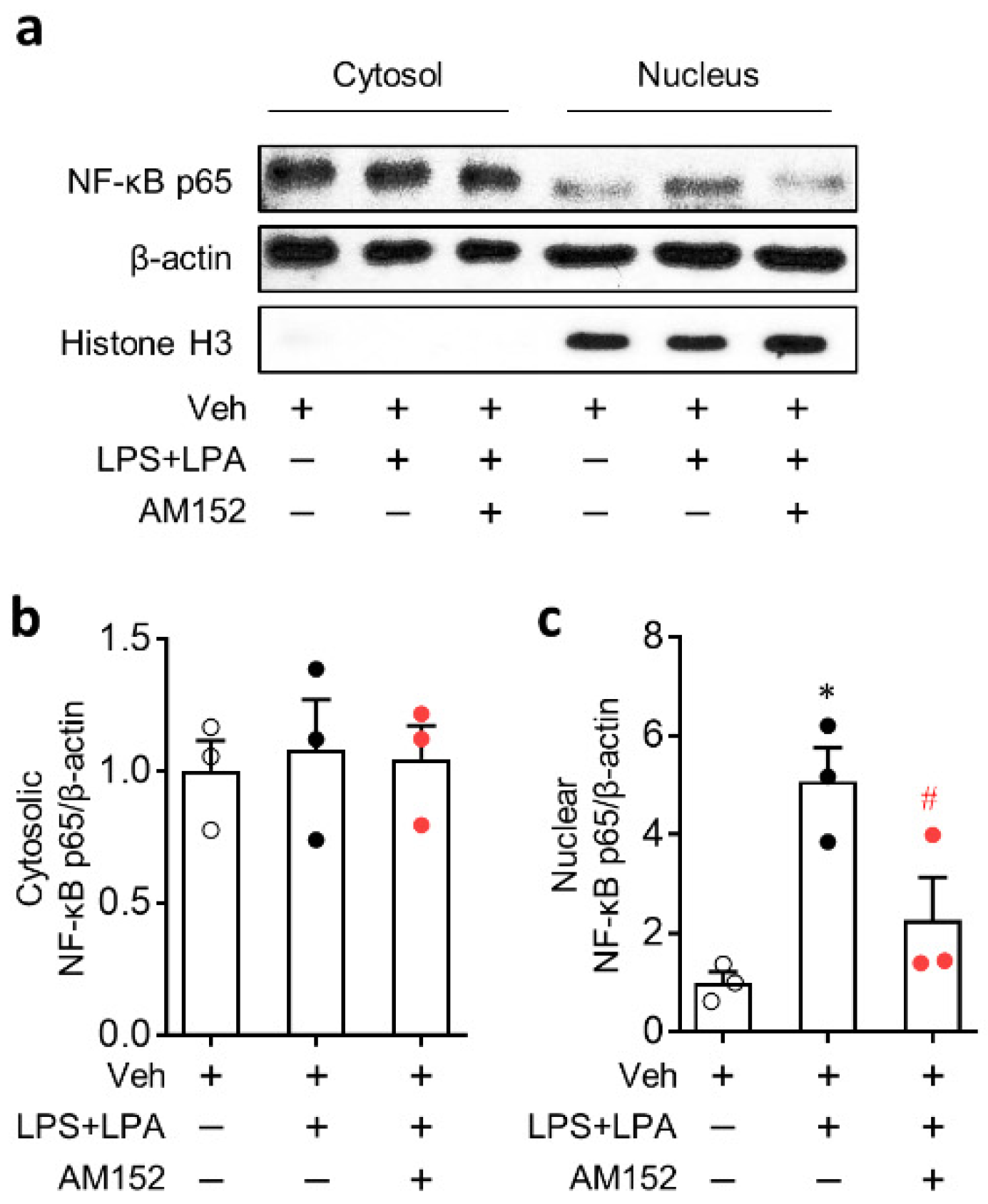
2.3. LPA1 Regulates NLRP3 Upregulation in LPS-Primed Macrophages Followed by LPA Exposure by Enhancing Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB) Translocation and Activating Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK)
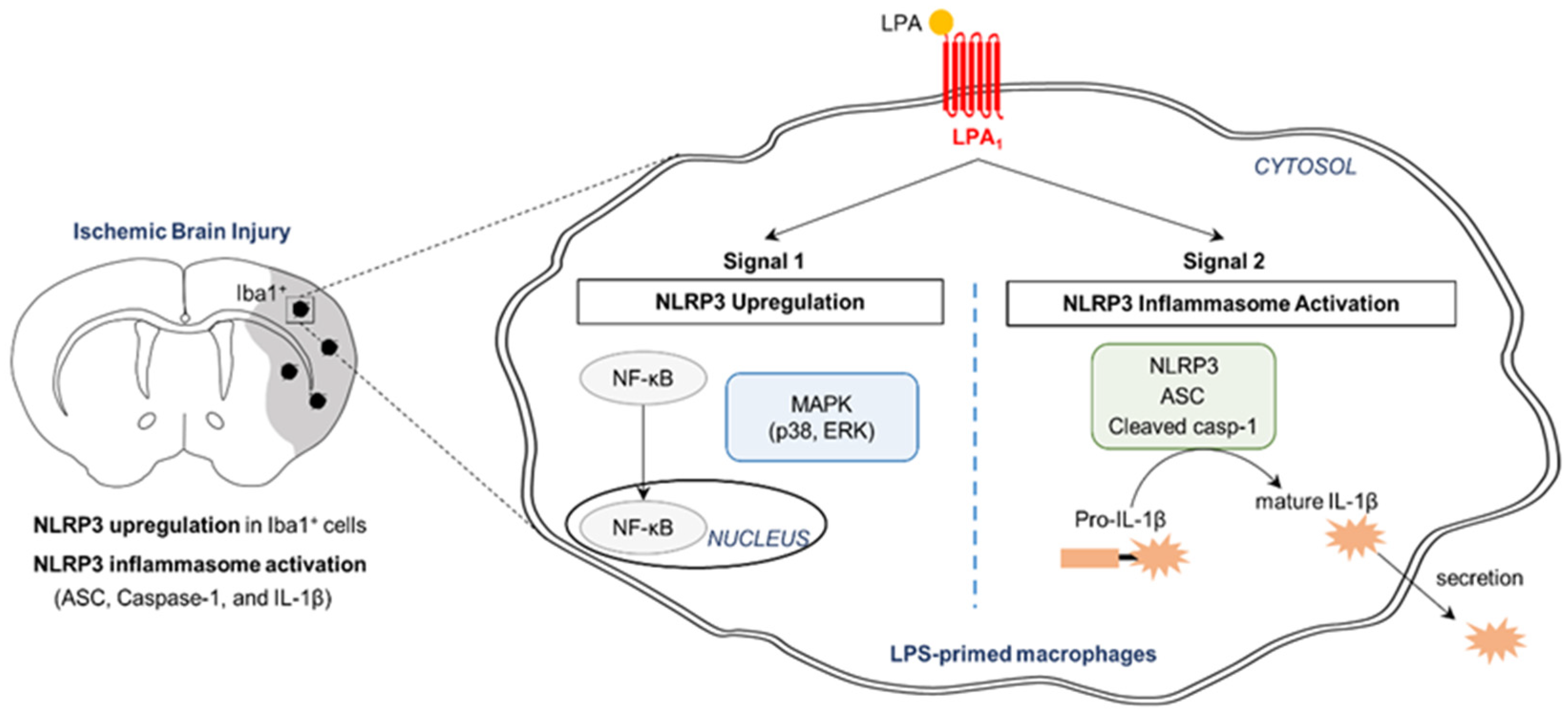
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia Challenge and AM095 Administration
4.3. Determination of Functional Neurological Deficit Score
4.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR) Analysis
4.5. Immunohistochemistry for NLRP3 and Double Immunofluorescence for NLRP3/Iba1 or ASC/NLRP3
4.6. BMDMs Primary Culture, Treatment, and LPA1 Knockdown
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Measurement of IL-1β in Conditioned Medium
4.9. Determination of NF-κB Translocation
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASC | Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain |
| BMDMs | Bone marrow-derived macrophages |
| CCA | Common carotid artery |
| DAPI | 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ERK1/2 | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| Iba1 | Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1β |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| LPA1 | Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| α-MEM | Minimum Essential Medium alpha |
| mNSS | Modified neurological severity score |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-κB |
| NLRP3 | Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene difluoride |
| siRNA | Small interfering RNA |
| tMCAO | Transient middle cerebral artery occlusion |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
References
- Choi, J.W.; Chun, J. Lysophospholipids and their receptors in the central nervous system. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta 2013, 1831, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yung, Y.C.; Stoddard, N.C.; Chun, J. LPA receptor signaling: Pharmacology, physiology, and pathophysiology. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1192–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoddard, N.C.; Chun, J. Promising Pharmacological Directions in the World of Lysophosphatidic Acid Signaling. Biomol. Ther. 2015, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaire, B.P.; Sapkota, A.; Song, M.-R.; Choi, J.W. Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 (LPA1) plays critical roles in microglial activation and brain damage after transient focal cerebral ischemia. J. Neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, H.; Neyama, H.; Sasaki, K.; Miyama, C.; Iwamoto, R. Lysophosphatidic acid LPA1 and LPA3 receptors play roles in the maintenance of late tissue plasminogen activator-induced central poststroke pain in mice. Neurobiol. Pain 2019, 5, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halder, S.; Yano, R.; Chun, J.; Ueda, H. Involvement of LPA1 receptor signaling in cerebral ischemia-induced neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 2013, 235, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Miao, E.A.; Ting, J.P.-Y. Mechanisms of NOD-like Receptor-Associated Inflammasome Activation. Immunity 2013, 39, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinon, F.; Mayor, A.; Tschopp, J. The Inflammasomes: Guardians of the Body. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 229–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Kouadir, M.; Song, H.; Shi, F. Recent advances in the mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and its inhibitors. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, H.; Ting, J.P.-Y.; O’Neill, L.A. A role for the NLRP3 inflammasome in metabolic diseases—did Warburg miss inflammation? Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nardo, D.; De Nardo, C.M.; Latz, E. New Insights into Mechanisms Controlling the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Its Role in Lung Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szabo, G.; Csak, T. Inflammasomes in liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anders, H.-J.; Muruve, D.A. The Inflammasomes in Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youm, Y.-H.; Grant, R.W.; McCabe, L.R.; Albarado, D.C.; Nguyen, K.Y.; Ravussin, A.; Pistell, P.; Newman, S.; Carter, R.; Laque, A.; et al. Canonical Nlrp3 Inflammasome Links Systemic Low-Grade Inflammation to Functional Decline in Aging. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abulafia, D.P.; Vaccari, J.P.D.R.; Lozano, J.D.; Lotocki, G.; Keane, R.W.; Dietrich, W.D. Inhibition of the Inflammasome Complex Reduces the Inflammatory Response after Thromboembolic Stroke in Mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 29, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, J.; Xiang, P.; Li, T.; Lan, L.; Xu, X.; Lu, G.; Ji, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. NOSH-NBP, a Novel Nitric Oxide and Hydrogen Sulfide- Releasing Hybrid, Attenuates Ischemic Stroke-Induced Neuroinflammatory Injury by Modulating Microglia Polarization. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, X.; Shen, T.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, L.; Cui, C.; Jin, G.; Zan, K.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Purinergic 2X7 receptor/NLRP3 pathway triggers neuronal apoptosis after ischemic stroke in the mouse. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 292, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaire, B.P.; Lee, C.-H.; Kim, W.; Sapkota, A.; Lee, D.Y.; Choi, J.W. Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 5 Contributes to Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Lesions through NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Macrophages. Cells 2020, 9, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-G.; Yu, Z.-C.; Wang, D.-Z.; Ju, W.-P.; Zhan, X.; Wu, Q.-Z.; Wu, X.-J.; Cong, H.-M.; Man, H.-H. Influence of acetylsalicylate on plasma lysophosphatidic acid level in patients with ischemic cerebral vascular diseases. Neurol. Res. 2008, 30, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Tang, J.; Li, Y.-Y.; Gu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xiong, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, T.-T.; et al. Lysophosphatidic acid induces neuronal cell death via activation of asparagine endopeptidase in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 306, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hara, H.; Núñez, G. Mechanism and Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schroder, K.; Sagulenko, V.; Zamoshnikova, A.; Richards, A.A.; Cridland, J.A.; Irvine, K.M.; Stacey, K.J.; Sweet, M.J. Acute lipopolysaccharide priming boosts inflammasome activation independently of inflammasome sensor induction. Immunobiololgy 2012, 217, 1325–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juliana, C.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Kang, S.; Farias, A.; Qin, F.; Alnemri, E.S. Non-transcriptional Priming and Deubiquitination Regulate NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 36617–36622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ito, D.; Tanaka, K.; Suzuki, S.; Dembo, T.; Fukuuchi, Y. Enhanced Expression of Iba1, Ionized Calcium-Binding Adapter Molecule 1, After Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Rat Brain. Stroke 2001, 32, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, Z.; Shaw, G.; Sharma, V.P.; Yang, C.; McGowan, E.; Dickson, D.W. Actin-binding Proteins Coronin-1a and IBA-1 are Effective Microglial Markers for Immunohistochemistry. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2007, 55, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, B.H.; Onizawa, M.; Oses-Prieto, J.A.; Advincula, R.; Burlingame, A.; Malynn, B.A.; Ma, A. A20 restricts ubiquitination of pro-interleukin-1beta protein complexes and suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activity. Immunity 2015, 42, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Fei, D.; Gong, R.; Yang, W.; Yu, W.; Pan, S.; Zhao, M. CORM-2 inhibits TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Inflamm. Res. 2016, 65, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M. NLRP3 inflammasome activation regulated by NF-κB and DAPK contributed to paraquat-induced acute kidney injury. Immunol. Res. 2017, 65, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campillo-Gimenez, L.; Renaudin, F.; Jalabert, M.; Gras, P.; Gosset, M.; Rey, C.; Sarda, S.; Collet, C.; Cohen-Solal, M.; Combes, C.; et al. Inflammatory Potential of Four Different Phases of Calcium Pyrophosphate Relies on NF-kappaB Activation and MAPK Pathways. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Ren, W.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, L. Regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and macrophage pyroptosis by the p38 MAPK signaling pathway in a mouse model of acute lung injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 4399–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Jiao, F.; Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Luan, W.; Ma, F.; Ni, L.; Tang, X.; et al. Activation of ROS/MAPKs/NF-kappaB/NLRP3 and inhibition of efferocytosis in osteoclast-mediated diabetic osteoporosis. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 12515–12527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Z. Lysophosphatidic Acid Induces Apoptosis of PC12 Cells Through LPA1 Receptor/LPA2 Receptor/MAPK Signaling Pathway. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tager, A.M.; LaCamera, P.; Shea, B.S.; Campanella, G.S.; Selman, M.; Zhao, Z.; Polosukhin, V.; Wain, J.; Karimi-Shah, B.A.; Kim, N.D.; et al. The lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA1 links pulmonary fibrosis to lung injury by mediating fibroblast recruitment and vascular leak. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, S.M.; Snyder, L.; Todd, J.L.; Soule, B.; Christian, R.; Anstrom, K.; Luo, Y.; Gagnon, R.; Rosen, G. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Trial of BMS-986020, a Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor Antagonist for the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Chest 2018, 154, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lei, L.; Su, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, W.; Chen, X.; Peng, C. The role of lysophosphatidic acid in the physiology and pathology of the skin. Life Sci. 2019, 220, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kihara, Y.; Mizuno, H.; Chun, J. Lysophospholipid receptors in drug discovery. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 333, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Wang, Z.; Wei, X.; Han, H.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W.; Li, F.; Xin, T.; Pang, Q.; et al. NLRP3 Deficiency Ameliorates Neurovascular Damage in Experimental Ischemic Stroke. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 34, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ismael, S.; Zhao, L.; Nasoohi, S.; Ishrat, T. Inhibition of the NLRP3-inflammasome as a potential approach for neuroprotection after stroke. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benhadou, F.; Mintoff, D.; Del Marmol, V. Psoriasis: Keratinocytes or Immune Cells—Which Is the Trigger? Dermatology 2018, 235, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, G.A.; Ritter, J.L.; Baracka, C.A. Lysophosphatidic Acid Induction of Transforming Growth Factors α and β: Modulation of Proliferation and Differentiation in Cultured Human Keratinocytes and Mouse Skin. Exp. Cell Res. 1995, 216, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casciano, F.; Pigatto, P.D.; Secchiero, P.; Gambari, R.; Reali, E. T Cell Hierarchy in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis and Associated Cardiovascular Comorbidities. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chi, O.Z.; Mellender, S.J.; Kiss, G.K.; Chiricolo, A.; Liu, X.; Patel, N.; Jacinto, E.; Weiss, H.R. Lysophosphatidic acid increased infarct size in the early stage of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion with increased BBB permeability. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Yang, G.; Li, G. Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: Role of inflammatory cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 87, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levard, D.; Buendia, I.; Lanquetin, A.; Glavan, M.; Vivien, D.; Rubio, M. Filling the gaps on stroke research: Focus on inflammation and immunity. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, F.; A Parsons, A. Therapeutic potential of anti-inflammatory drugs in focal stroke. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2000, 9, 2281–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Di Sciacca, R.; Di Raimondo, D.; Renda, C.; Pinto, A.; Licata, G. Inflammation as a Therapeutic Target in Acute Ischemic Stroke Treatment. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 1240–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaraj, R.L.; Azimullah, S.; Beiram, R.; Jalal, F.Y.; Rosenberg, G.A. Neuroinflammation: Friend and foe for ischemic stroke. J. Neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sochocka, M.; Diniz, B.S.; Leszek, J. Inflammatory Response in the CNS: Friend or Foe? Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 8071–8089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sapkota, A.; Lee, C.-H.; Park, S.J.; Choi, J.W. Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 5 Plays a Pathogenic Role in Brain Damage after Focal Cerebral Ischemia by Modulating Neuroinflammatory Responses. Cells 2020, 9, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, A.; Hatcher, J.; Virley, D.; Nelson, P.; Irving, E.; Hadingham, S.J.; A Parsons, A. Functional assessments in mice and rats after focal stroke. Neuropharmacology 2000, 39, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melani, A.; Pantoni, L.; Bordoni, F.; Gianfriddo, M.; Bianchi, L.; Vannucchi, M.G.; Bertorelli, R.; Monopoli, A.; Pedata, F. The selective A2A receptor antagonist SCH 58261 reduces striatal transmitter outflow, turning behavior and ischemic brain damage induced by permanent focal ischemia in the rat. Brain Res. 2003, 959, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Nogueira, E.; Francos-Quijorna, I.; Hernández, J.; Lago, N.; Astudillo, A.M.; Balsinde, J.; Estivill-Torrús, G.; De Fonseca, F.R.; Chun, J.; López-Vales, R. Activation of Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor Type 1 Contributes to Pathophysiology of Spinal Cord Injury. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 10224–10235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakai, N.; Chun, J.; Duffield, J.S.; Wada, T.; Luster, A.D.; Tager, A.M. LPA 1 -induced cytoskeleton reorganization drives fibrosis through CTGF-dependent fibroblast proliferation. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1830–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castelino, F.V.; Seiders, J.; Bain, G.; Brooks, S.F.; King, C.D.; Swaney, J.S.; Lorrain, D.S.; Chun, J.; Luster, A.D.; Tager, A.M. Amelioration of dermal fibrosis by genetic deletion or pharmacologic antagonism of lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 in a mouse model of scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sanberg, P.R.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Lu, M.; Willing, A.E.; Sanchez-Ramos, J.; Chopp, M. Intravenous Administration of Human Umbilical Cord Blood Reduces Behavioral Deficits After Stroke in Rats. Stroke 2001, 32, 2682–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francke, A.; Herold, J.; Weinert, S.; Strasser, R.H.; Braun-Dullaeus, R.C. Generation of Mature Murine Monocytes from Heterogeneous Bone Marrow and Description of Their Properties. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2011, 59, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, C.-H.; Sapkota, A.; Gaire, B.P.; Choi, J.W. NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation Is Involved in LPA1-Mediated Brain Injury after Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228595
Lee C-H, Sapkota A, Gaire BP, Choi JW. NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation Is Involved in LPA1-Mediated Brain Injury after Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(22):8595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228595
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Chi-Ho, Arjun Sapkota, Bhakta Prasad Gaire, and Ji Woong Choi. 2020. "NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation Is Involved in LPA1-Mediated Brain Injury after Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 22: 8595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228595
APA StyleLee, C.-H., Sapkota, A., Gaire, B. P., & Choi, J. W. (2020). NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation Is Involved in LPA1-Mediated Brain Injury after Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(22), 8595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228595






