Genetic Background Underlying 5-HT1A Receptor Functioning Affects the Response to Fluoxetine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Open Field Test (OF)
2.2. Forced Swim Test
2.3. Expression of Genes
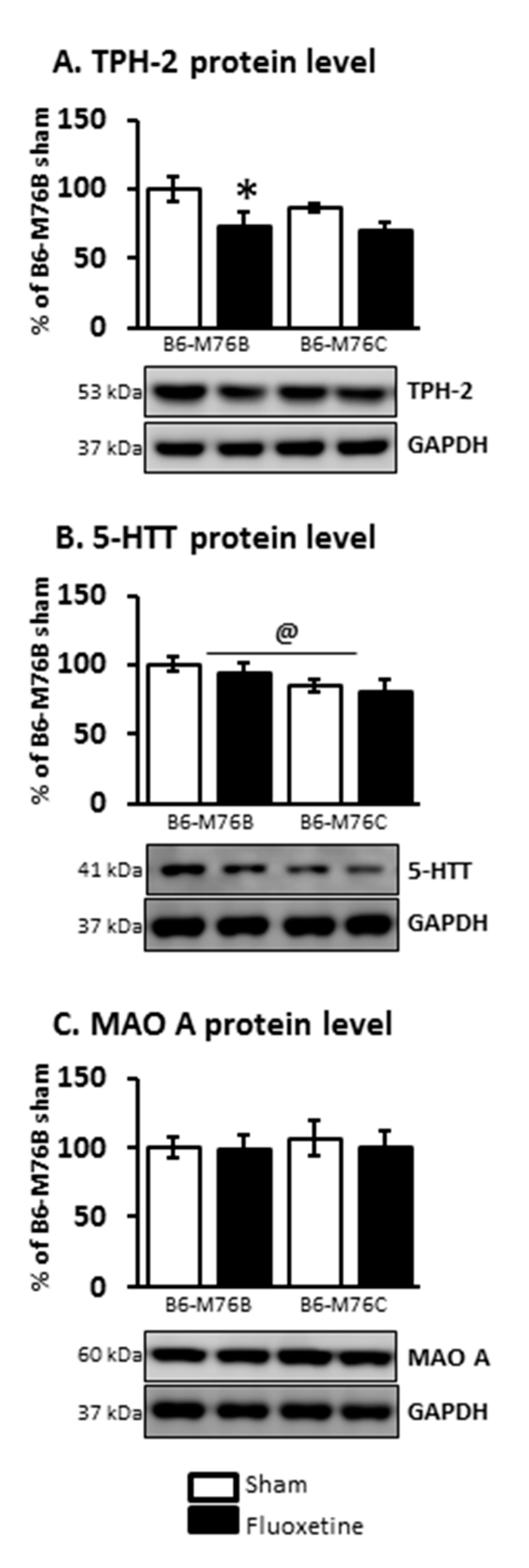
2.4. Protein Levels
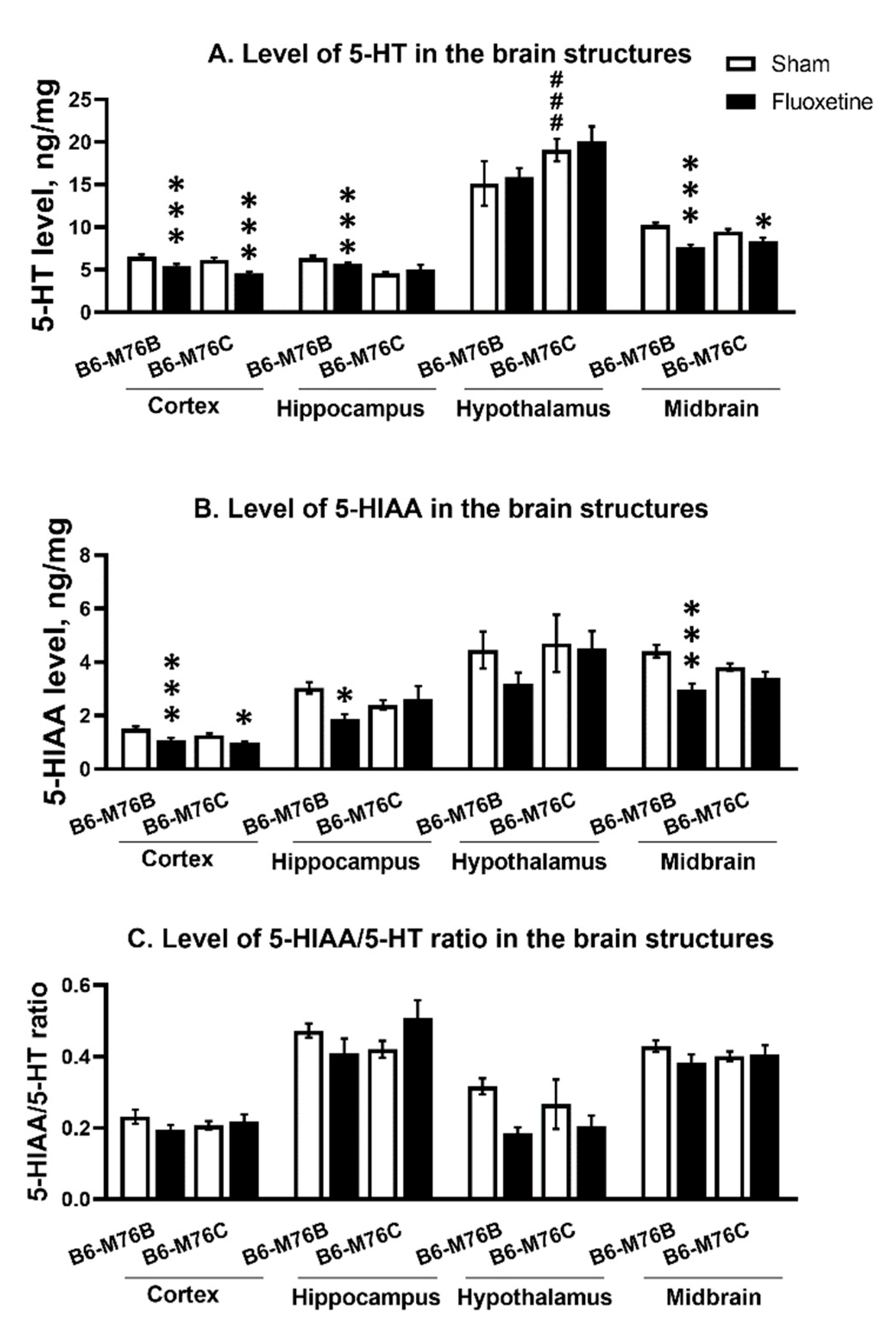
2.5. The Levels of 5-HT, 5-HIAA and 5-HIAA/5-HT Ratio
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Drug
4.3. Design of the Experiment
4.4. Open Field Test
4.5. Forced Swim Test
4.6. Brain Structures Isolation
4.7. Tissue Extraction for Isolation Total mRNA and for HPLC
4.8. Real-Time PCR
4.9. HPLC Protocol
4.10. Western blot
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duman, R.S.; Heninger, G.R.; Nestler, E.J. A Molecular and Cellular Theory of Depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1997, 54, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harro, J.; Oreland, L. Depression as a spreading neuronal adjustment disorder. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 1996, 6, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jans, L.A.W.; Riedel, W.J.; Markus, C.R.; Blokland, A. Serotonergic vulnerability and depression: Assumptions, experimental evidence and implications. Mol. Psychiatry 2006, 12, 522–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, N.K.; Naumenko, V.S. 5-HT1A receptor as a key player in the brain 5-HT system. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 24, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, P.R.; Le François, B.; Millar, A.M. Transcriptional dysregulation of 5-HT1A autoreceptors in mental illness. Mol. Brain 2011, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fuller, R.W. Role of serotonin in therapy of depression and related disorders. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1991, 52, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Heisler, L.K.; Chu, H.-M.; Brennan, T.J.; Danao, J.A.; Bajwa, P.; Parsons, L.H.; Tecott, L.H. Elevated anxiety and antidepressant-like responses in serotonin 5-HT1A receptor mutant mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 15049–15054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Overstreet, D.H.; Commissaris, R.C.; De La Garza, R.; File, S.E.; Knapp, D.J.; Seiden, L.S. Involvement of 5-HT 1A Receptors in Animal Tests of Anxiety and Depression: Evidence from Genetic Models. Stress 2003, 6, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramboz, S.; Oosting, R.; Amara, D.A.; Kung, H.F.; Blier, P.; Mendelsohn, M.; Mann, J.J.; Brunner, D.; Hen, R. Serotonin receptor 1A knockout: An animal model of anxiety-related disorder. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14476–14481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson-Jones, J.W.; Craige, C.P.; Guiard, B.P.; Stephen, A.; Metzger, K.L.; Kung, H.F.; Gardier, A.M.; Dranovsky, A.; David, D.J.; Beck, S.G.; et al. 5-HT1A Autoreceptor Levels Determine Vulnerability to Stress and Response to Antidepressants. Neuron 2010, 65, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maes, M.; Meltzer, H.Y. The serotonin hypothesis of major depression. In Psychopharmacology. The Fourth Generation of Progress Bloom; Bloom, F.E., Kupfer, D.J., Bunney, B.S., Ciaranello, R.D., Davis, K.L., Koob, G.F., Meltzer, H.Y., Schuster, C.R., Shader, R.I., Watson, S.J., Eds.; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 933–944. [Google Scholar]
- Arango, V.; Underwood, M.D.; Boldrini, M.; Tamir, H.; Kassir, S.A.; Hsiung, S.-C.; Chen, J.J.-X.; Mann, J.J. Serotonin 1A Receptors, Serotonin Transporter Binding and Serotonin Transporter mRNA Expression in the Brainstem of Depressed Suicide Victims. Neuropsychopharmacology 2001, 25, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowther, S.; De Paermentier, F.; Cheetham, S.C.; Crompton, M.; Katona, C.L.; Horton, R.W. 5-HT1A Receptor binding sites in post-mortem brain samples from depressed suicides and controls. J. Affect. Disord. 1997, 42, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockmeier, C.A.; Shapiro, L.A.; Dilley, G.E.; Kolli, T.N.; Friedman, L.; Rajkowska, G. Increase in Serotonin-1A Autoreceptors in the Midbrain of Suicide Victims with Major Depression—Postmortem Evidence for Decreased Serotonin Activity. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 7394–7401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albert, P.R.; Lemonde, S. 5-HT1A Receptors, Gene Repression, and Depression: Guilt by Association. Neuroscience 2004, 10, 575–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumenko, V.S.; Popova, N.K.; LaCivita, E.; Leopoldo, M.; Ponimaskin, E. Interplay between Serotonin 5-HT1Aand 5-HT7Receptors in Depressive Disorders. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2014, 20, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrini, M.; Underwood, M.D.; Mann, J.J.; Arango, V. Serotonin-1A autoreceptor binding in the dorsal raphe nucleus of depressed suicides. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2008, 42, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Jiang, Z.-Z.; Shang, J.; Zhang, L. Differential involvement of 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B/1D receptors in human interferon-alpha-induced immobility in the mouse forced swimming test. Arzneimittelforschung 2011, 60, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blier, P.; Ward, N.M. Is there a role for 5-HT1A agonists in the treatment of depression? Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 53, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, L.; Rothe, J.; Rex, A.; Voigt, J.-P.; Millan, M.J.; Fink, H.; Gilbert, S. 5-HT1A-receptor over-expressing mice: Genotype and sex dependent responses to antidepressants in the forced swim-test. Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ou, X.-M.; Jafar-Nejad, H.; Storring, J.M.; Meng, J.-H.; Lemonde, S.; Albert, P.R. Novel Dual Repressor Elements for Neuronal Cell-specific Transcription of the Rat 5-HT1A Receptor Gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 8161–8168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ou, X.-M.; Lemonde, S.; Jafar-Nejad, H.; Bown, C.D.; Goto, A.; Rogaeva, A.; Albert, P.R. Freud-1: A Neuronal Calcium-Regulated Repressor of the 5-HT1A Receptor Gene. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 7415–7425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rogaeva, A.; Albert, P.R. The mental retardation gene CC2D1A/Freud-1 encodes a long isoform that binds conserved DNA elements to repress gene transcription. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 26, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogaeva, A.; Galaraga, K.; Albert, P.R. The Freud-1/CC2D1A family: Transcriptional regulators implicated in mental retardation. J. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 85, 2833–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuxe, K.; Narváez, M.; Ambrogini, P.; Ferraro, L.; Brito, I.; Romero-Fernández, W.; Talavera, Y.; Flores-Burgess, A.; Millón, C.; Gago, B.; et al. Receptor–Receptor Interactions in Multiple 5-HT1A Heteroreceptor Complexes in Raphe-Hippocampal 5-HT Transmission and Their Relevance for Depression and Its Treatment. Molecules 2018, 23, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naumenko, V.S.; Bazovkina, D.V.; Kondaurova, E.M. On the Functional Cross-Talk between Brain 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A Receptors. Zhurnal Vyss. Nervn. Deiatelnosti Im. I P Pavlov. 2015, 65, 240–247. [Google Scholar]
- Naumenko, V.S.; Bazovkina, D.V.; Kondaurova, E.M.; Zubkov, E.A.; Kulikov, A.V. The role of 5-HT2Areceptor and 5-HT2A/5-HT1Areceptor interaction in the suppression of catalepsy. Genes Brain Behav. 2010, 9, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, U.; Zeug, A.; Woehler, A.; Niebert, M.; Dityatev, A.; Dityateva, G.; Gorinski, N.; Guseva, D.; Abdel-Galil, D.; Döring, F.; et al. Heterodimerization of serotonin receptors 5-HT1A and 5-HT7 differentially regulates receptor signalling and trafficking. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 2486–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbott, A. With your genes? Take one of these, three times a day. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 425, 760–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondaurova, E.M.; Bazovkina, D.V.; Kulikov, A.V. Study of the association between catalepsy, anxiety, aggression and depressive-like behavior in congenic mice. Ross. Fiziol. Zhurnal Im. I.M. Sechenova 2010, 96, 464–471. [Google Scholar]
- Kulikova, E.A.; V.Bazovkina, D.; A.Kulov, A.; S.Tsybko, A.; V.Fursenko, D.; V.Kulikov, A.; S.Naumenko, V.; Ponimaskin, E.; M.Kondaurova, E. Alterations in pharmacological and behavioural responses in recombinant mouse line with an increased predisposition to catalepsy: Role of the 5-HT1Areceptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 2147–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucki, I.; Dalvi, A.; Mayorga, A.J. Sensitivity to the effects of pharmacologically selective antidepressants in different strains of mice. Psychopharmacology 2001, 155, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, D.J.P.; Bourin, M.; Jego, G.; Przybylski, C.; Jolliet, P.; Gardier, A.M. Effects of acute treatment with paroxetine, citalopram and venlafaxine in vivo on noradrenaline and serotonin outflow: A microdialysis study in Swiss mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 140, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cervo, L.; Canetta, A.; Calcagno, E.; Burbassi, S.; Sacchetti, G.; Caccia, S.; Fracasso, C.; Albani, D.; Forloni, G.; Invernizzi, R.W. Genotype-Dependent Activity of Tryptophan Hydroxylase-2 Determines the Response to Citalopram in a Mouse Model of Depression. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 8165–8172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzzetti, S.; Calcagno, E.; Canetta, A.; Sacchetti, G.; Fracasso, C.; Caccia, S.; Cervo, L.; Invernizzi, R.W. Strain differences in paroxetine-induced reduction of immobility time in the forced swimming test in mice: Role of serotonin. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 594, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, A.V.; Tikhonova, M.A.; Osipova, D.V.; Kulikov, V.A.; Popova, N.K. Association between tryptophan hydroxylase-2 genotype and the antidepressant effect of citalopram and paroxetine on immobility time in the forced swim test in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 99, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, J.K.; Tripathi, A.; Nischal, A.; Nischal, A. Suicide and antidepressants: What current evidence indicates. Mens Sana Monogr. 2012, 10, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianchi, M.; Moser, C.; Lazzarini, C.; Vecchiato, E.; Crespi, F. Forced swimming test and fluoxetine treatment: In vivo evidence that peripheral 5-HT in rat platelet-rich plasma mirrors cerebral extracellular 5-HT levels, whilst 5-HT in isolated platelets mirrors neuronal 5-HT changes. Exp. Brain Res. 2002, 143, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccia, S.; Anelli, M.; Codegoni, A.M.; Fracasso, C.; Garattini, S. The effects of single and repeated anorectic doses of 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake inhibitors on indole levels in rat brain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 110, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popa, D.; Cerdan, J.; Reperant, C.; Guiard, B.P.; Guilloux, J.-P.; David, D.J.; Gardier, A.M. A longitudinal study of 5-HT outflow during chronic fluoxetine treatment using a new technique of chronic microdialysis in a highly emotional mouse strain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 628, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siesser, W.B.; Sachs, B.D.; Ramsey, A.J.; Sotnikova, T.D.; Beaulieu, J.-M.; Zhang, X.; Caron, M.G.; Gainetdinov, R.R. Chronic SSRI Treatment Exacerbates Serotonin Deficiency in HumanizedTph2Mutant Mice. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2012, 4, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stenfors, C.; Ross, S.B. Evidence for involvement of 5-hydroxytryptamine1B autoreceptors in the enhancement of serotonin turnover in the mouse brain following repeated treatment with fluoxetine. Life Sci. 2002, 71, 2867–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, N.M.; Sharp, T. A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology 1999, 38, 1083–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, A.V.; Tikhonova, M.A.; Kulikov, V.A. Automated measurement of spatial preference in the open field test with transmitted lighting. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 170, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khotskin, N.V.; Plyusnina, A.V.; Kulikova, E.A.; Bazhenova, E.Y.; Fursenko, D.V.; Sorokin, I.E.; Kolotygin, I.; Mormede, P.; Terenina, E.E.; Shevelev, O.B.; et al. On association of the lethal yellow (A) mutation in the agouti gene with the alterations in mouse brain and behavior. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 359, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulikov, A.V.; Morozova, M.V.; Kulikov, V.A.; Kirichuk, V.S.; Popova, N.K. Automated analysis of antidepressants’ effect in the forced swim test. J. Neurosci. Methods 2010, 191, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, A.V.; Naumenko, V.S.; Voronova, I.P.; Tikhonova, M.A.; Popova, N.K. Quantitative RT-PCR assay of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A serotonin receptor mRNAs using genomic DNA as an external standard. J. Neurosci. Methods 2005, 141, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumenko, V.S.; Kulikov, A.V. Quantitative assay of 5-HT1A receptor gene expression in the brain. Mol. Biol. 2006, 40, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumenko, V.S.; Osipova, D.V.; Kostina, E.V.; Kulikov, A.V. Utilization of a two-standard system in real-time PCR for quantification of gene expression in the brain. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 170, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, N.K.; Ilchibaeva, T.V.; Antonov, E.V.; Pershina, A.V.; Bazovkina, D.V.; Naumenko, V.S. On the interaction between BDNF and serotonin systems: The effects of long-term ethanol consumption in mice. Alcohol 2020, 87, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, W.J. Processing Data for Outliers. Biometrics 1953, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
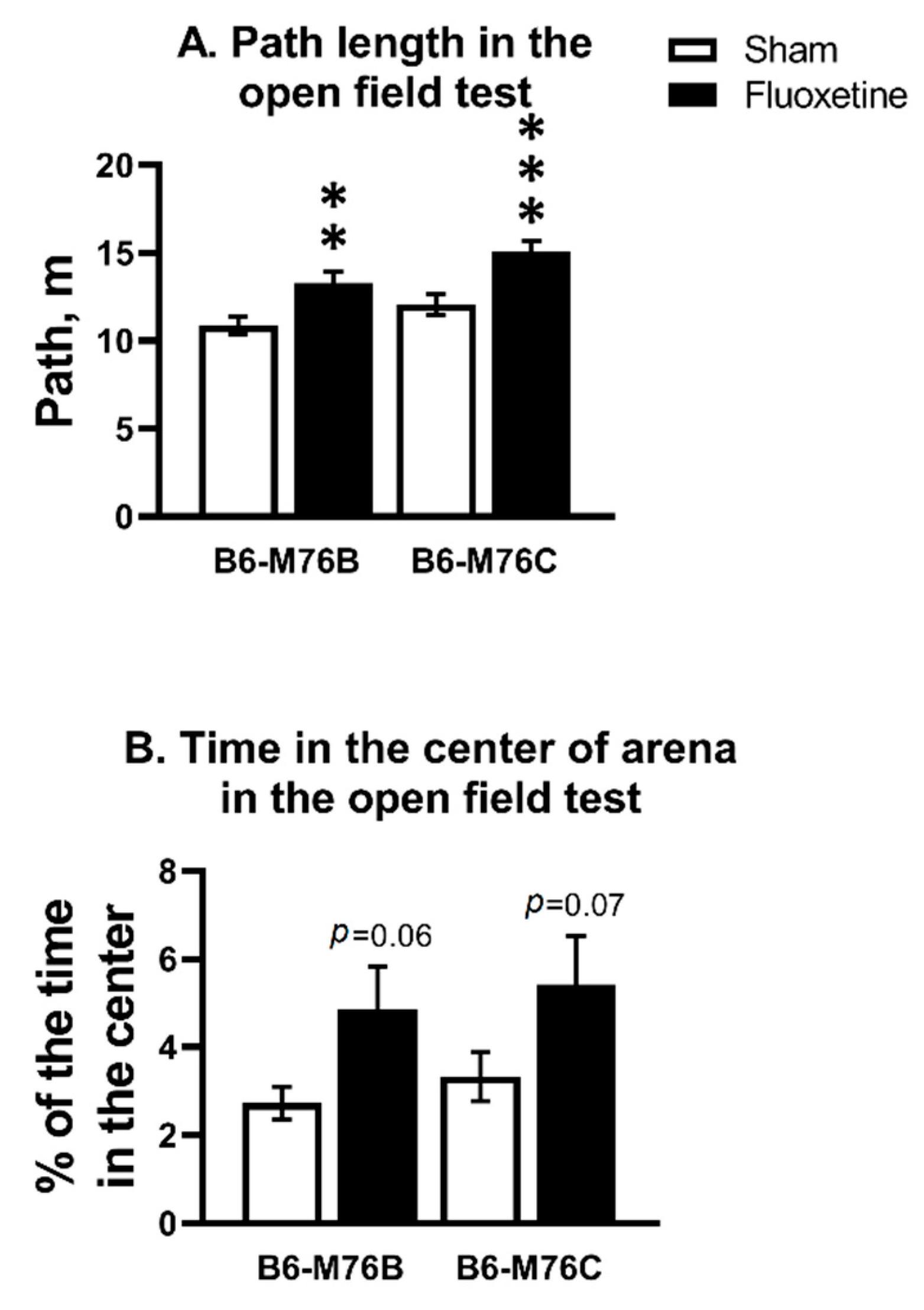

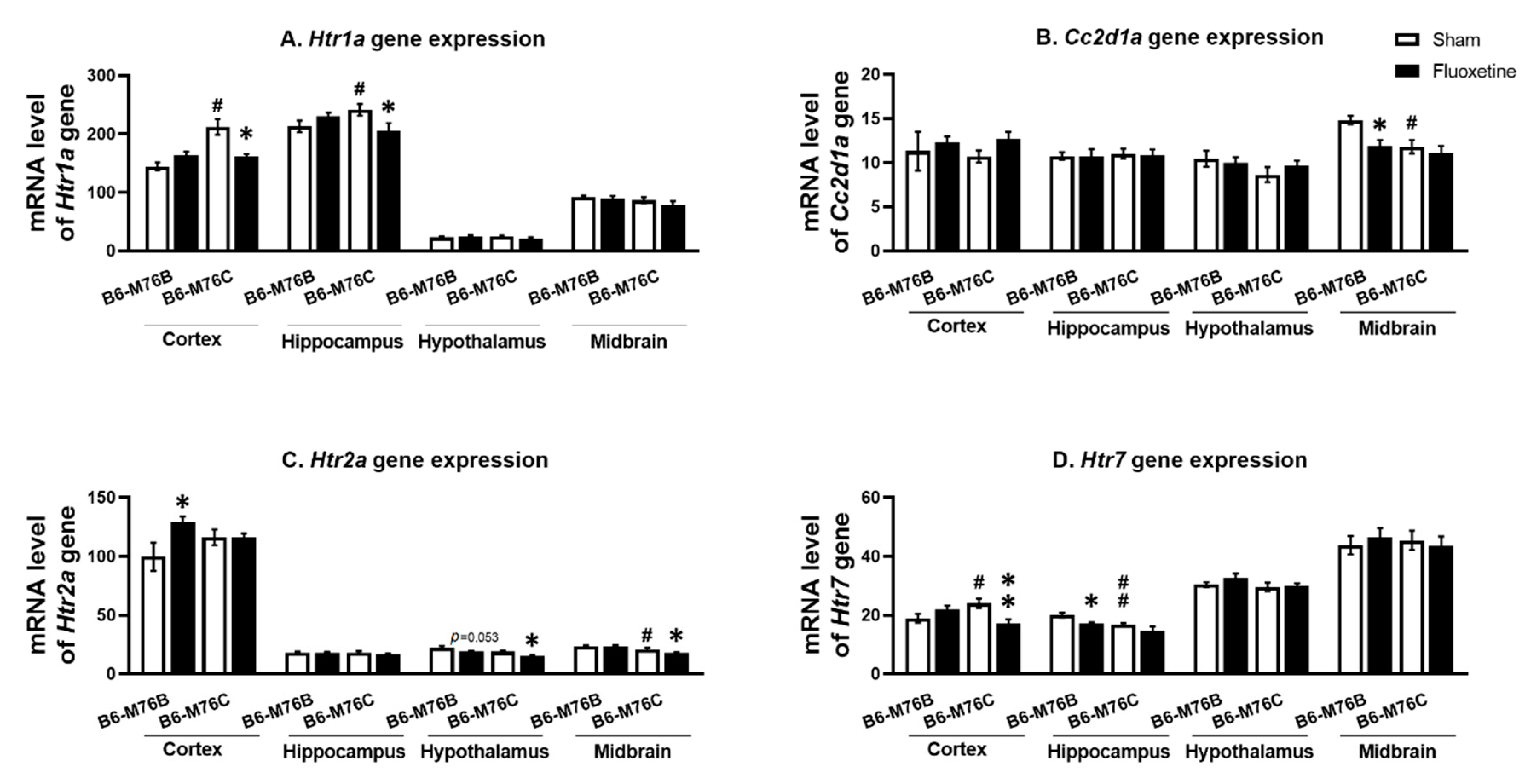
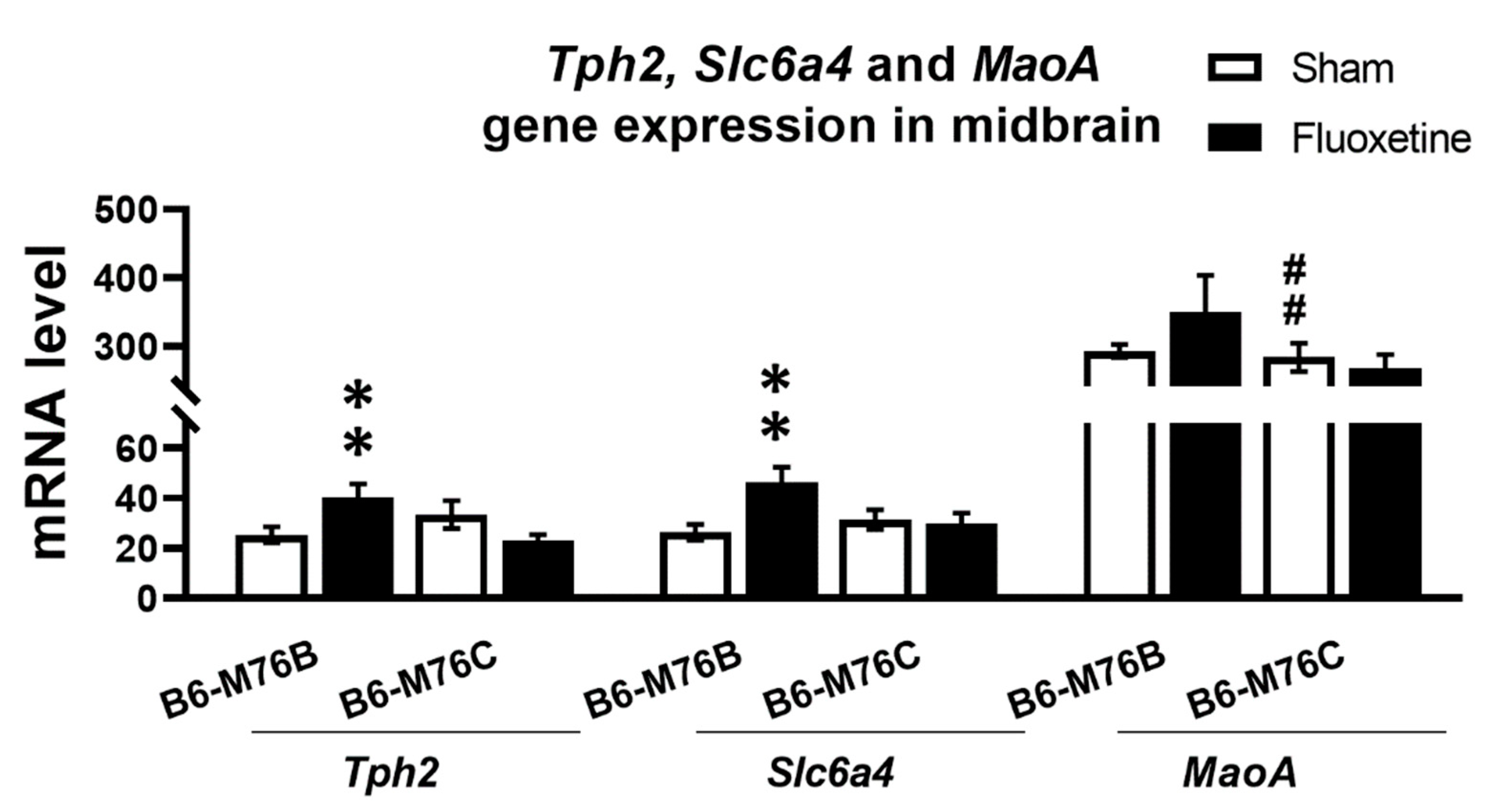
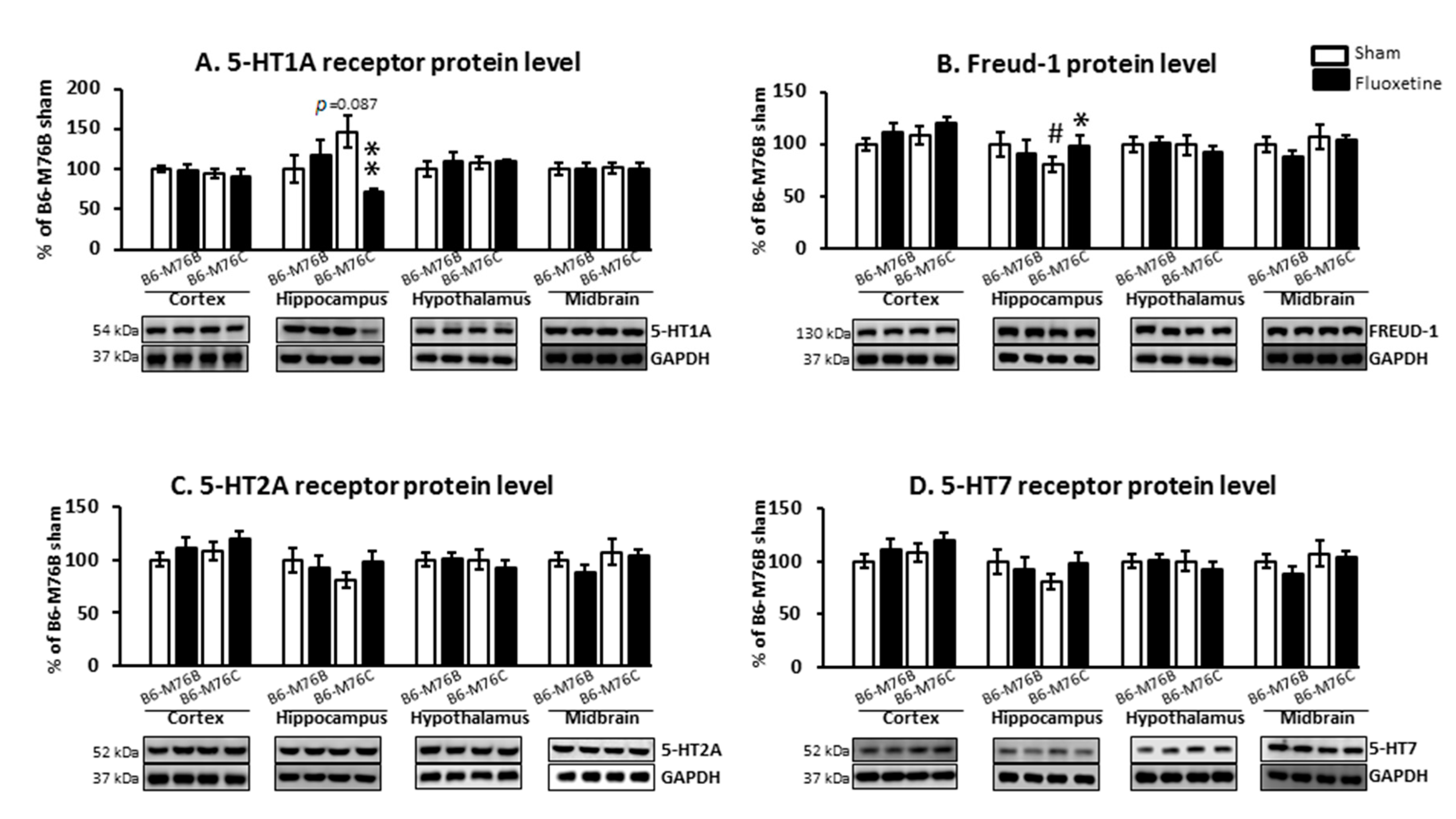
| B6-M76B CFT Group Compared to Sham | B6-M76C CFT Group Compared to Sham | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Open field test | Path length | ↑ | ↑ |
| Time in center | = | = | |
| Forced swim test | Mobility | = | ↓ |
| 5-HT1A mRNA/Protein | Frontal cortex | =/= | ↓/= |
| Hippocampus | =/= | ↓/↓ | |
| Freud-1 mRNA/Protein | Hippocampus | =/= | =/↑ |
| Midbrain | ↓/= | =/= | |
| 5-HT2A mRNA/Protein | Frontal cortex | ↑/= | =/= |
| Hypothalamus | ↓/= | ↓/= | |
| Midbrain | =/= | ↓/= | |
| 5-HT7 mRNA/Protein | Frontal cortex | =/= | ↓/= |
| Hippocampus | ↓/= | =/= | |
| TPH2 mRNA/Protein | Midbrain | ↑/↓ | =/= |
| 5-HTT mRNA/Protein | Midbrain | ↑/= | =/= |
| MAO A mRNA/Protein | Midbrain | =/= | =/= |
| 5-HTT level | Frontal cortex | ↓ | ↓ |
| Hippocampus | ↓ | = | |
| Hypothalamus | = | = | |
| Midbrain | ↓ | ↓ | |
| 5-HIAA level | Frontal cortex | ↓ | ↓ |
| Hippocampus | ↓ | = | |
| Hypothalamus | = | = | |
| Midbrain | ↓ | = |
| Gene | Sequence | Annealing Temperature, °C | Product Length, bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| Htr1a | F 5′-ctgtgacctgtttatcgccctg-3′ R 5′-gtagtctatagggtcggtgattgc-3′ | 62 | 200 |
| Htr2a | F 5′-agaagccaccttgtgtgtga-3′ R 5′-ttgctcattgctgatggact-3′ | 61 | 169 |
| Htr7 | F5′-ggctacacgatctactccaccg-3′ R5′-cgcacactcttccacctccttc-3′ | 65 | 198 |
| Tph2 | F 5′-cattcctcgcacaattccagtcg-3′ R 5′- cttgacatattcaactagacgctc -3′ | 61 | 239 |
| Slc6a4 | F 5′-cgctctactacctcatctcctcc-3′ R 5′- gtcctgggcgaagtagttgg -3′ | 63 | 101 |
| Maoa | F 5′-aatgaggatgttaaatgggtagatgttggt-3′ R 5′-cttgacatattcaactagacgctc-3′ | 61 | 138 |
| Cc2d1a | F 5′-gcaaagccgggcaacatcatc-3′ R 5′-tagcagaggtgggtgtagtgg-3′ | 60 | 181 |
| rPol2 | F 5′-tgtgacaactccatacaatgc-3′ R 5′-ctctcttagtgaatttgcgtact-3′ | 60 | 194 |
| Antibodies, Manufacturer | Breeding | Incubation Time, Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Rabbit polyclonal primary antibodies to 5-HT1A protein, Abcam, United Kingdom, ab85615 | 1:1000 in 5% milk powder with Tris-Buffered Saline with Tween 20 (TBST) | Night at 4 °C |
| Rabbit polyclonal primary antibodies to 5-HT2A protein, Novus Biologicals, USA, Novus NBP1-49172 | 1:250 in 5% milk powder with TBST | Night at 4 °C |
| Rabbit monoclonal primary antibodies to 5-HT7 protein, Abcam, United Kingdom, ab128892 | 1:500 in 5% milk powder with TBST | Night at 4 °C |
| Rabbit monoclonal primary antibodies to Freud-1 protein, Abcam, United Kingdom, ab191472 | 1:2000 in 5% milk powder with TBST | Night at 4 °C |
| Rabbit polyclonal primary antibodies to TPH-2 protein, Abcam, United Kingdom, ab111828 | 1:1000 in 5% milk powder with TBST | Night at 4 °C |
| Rabbit polyclonal primary antibodies to 5-HTT protein, US Biological Life Sciences, 303614 | 1:1000 in 5% milk powder with TBST | Night at 4 °C |
| Rabbit monoclonal primary antibodies to MAOA protein, Abcam, United Kingdom, ab126751 | 1:250 in 5% milk powder with TBST | Night at 4 °C |
| Rabbit polyclonal primary antibodies to GAPDH protein, conjugated to horseradish peroxidase, Santa Cruz, USA, sc-25778 | 1:500 in 5% milk powder with TBST | 2 h at Room Temperature |
| Secondary goat antibodies against rabbit immunoglobulins conjugated to horseradish peroxidase, Invitrogen, USA, G-21234 | 1:10,000 in 5% milk powder with TBST | 1 h at Room Temperature |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kondaurova, E.M.; Rodnyy, A.Y.; Ilchibaeva, T.V.; Tsybko, A.S.; Eremin, D.V.; Antonov, Y.V.; Popova, N.K.; Naumenko, V.S. Genetic Background Underlying 5-HT1A Receptor Functioning Affects the Response to Fluoxetine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228784
Kondaurova EM, Rodnyy AY, Ilchibaeva TV, Tsybko AS, Eremin DV, Antonov YV, Popova NK, Naumenko VS. Genetic Background Underlying 5-HT1A Receptor Functioning Affects the Response to Fluoxetine. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(22):8784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228784
Chicago/Turabian StyleKondaurova, Elena M., Alexander Ya. Rodnyy, Tatiana V. Ilchibaeva, Anton S. Tsybko, Dmitry V. Eremin, Yegor V. Antonov, Nina K. Popova, and Vladimir S. Naumenko. 2020. "Genetic Background Underlying 5-HT1A Receptor Functioning Affects the Response to Fluoxetine" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 22: 8784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228784





