Effects of PIN on Osteoblast Differentiation and Matrix Mineralization through Runt-Related Transcription Factor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. PIN Increases Cell Migration during the Differentiation of Pre-Osteoblasts
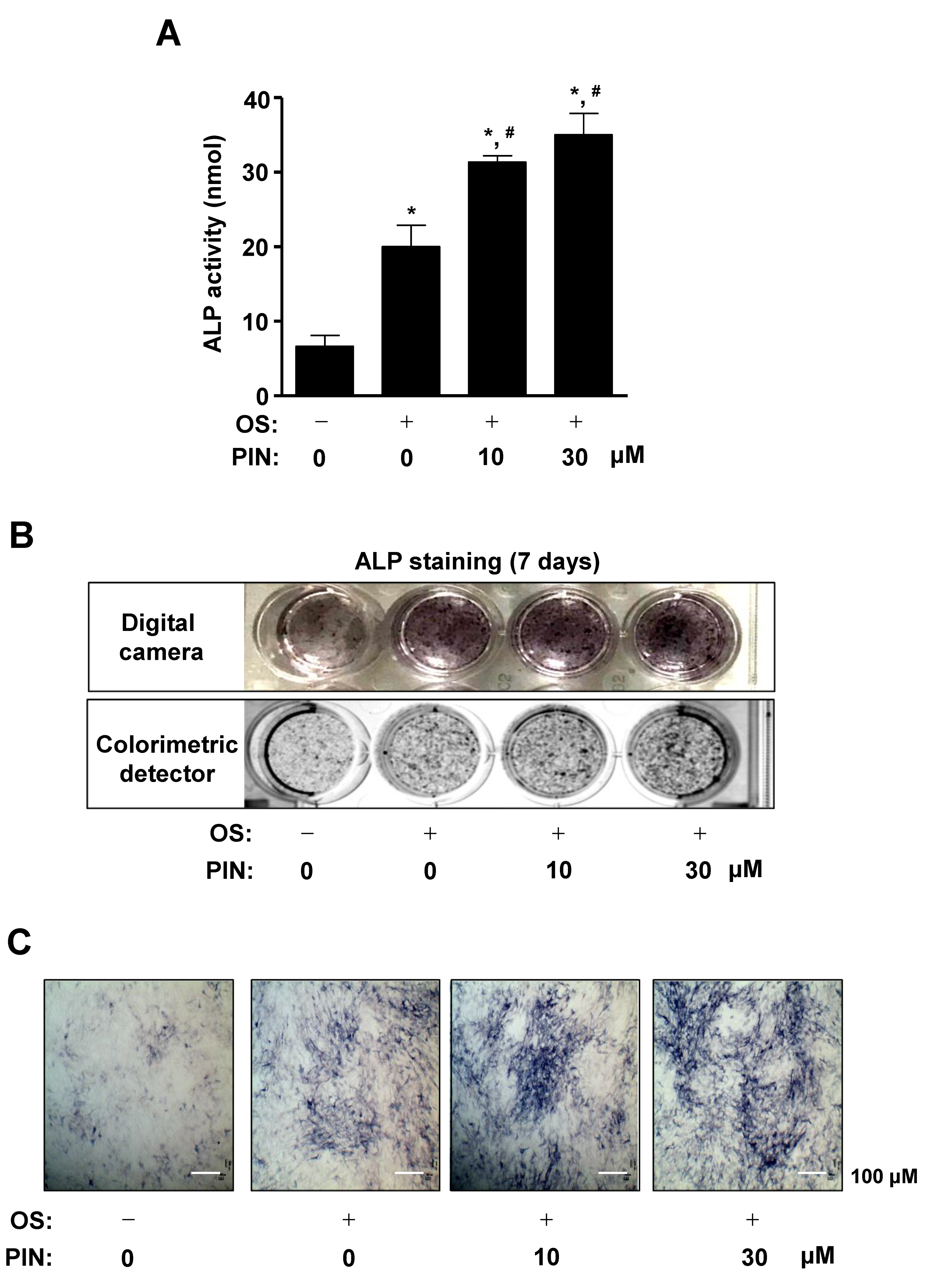
2.2. PIN Increases the Early Differentiation of Pre-Osteoblasts
2.3. PIN Increases Mineralized Nodule Formation during Differentiation of Pre-Osteoblasts
2.4. PIN Increases BMP2 Expression and Activates Its Signaling during Differentiation of Pre-Osteoblasts
2.5. PIN Increases Non-Canonical BMP2 Signaling and β-Catenin Sigaling during Differentiation of Pre-Osteoblasts
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General
4.2. Plant Material
4.3. Extraction and Isolation of Compound
4.4. PIN
4.5. Cell Culture
4.6. Osteoblast Differentiation
4.7. MTT Assay
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Cell Migration Assay
4.10. Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) Activity Assay
4.11. ALP Staining Assay
4.12. Alizarin Red S (ARS) Staining
4.13. Immunofluorescence
4.14. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.15. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raisz, L.G. Pathogenesis of osteoporosis: Concepts, conflicts, and prospects. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 3318–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guiglia, R.; Di Fede, O.; Lo Russo, L.; Sprini, D.; Rini, G.B.; Campisi, G. Osteoporosis, jawbones and periodontal disease. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2013, 18, e93–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marie, P.J. Osteoblast dysfunctions in bone diseases: From cellular and molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 1347–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, R.; Bahmaee, H.; Claeyssens, F.; Reilly, G.C. Comparison of the Anabolic Effects of Reported Osteogenic Compounds on Human Mesenchymal Progenitor-derived Osteoblasts. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, W.C.; Guntur, A.R.; Long, F.; Rosen, C.J. Energy Metabolism of the Osteoblast: Implications for Osteoporosis. Endocr. Rev. 2017, 38, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russow, G.; Jahn, D.; Appelt, J.; Mardian, S.; Tsitsilonis, S.; Keller, J. Anabolic Therapies in Osteoporosis and Bone Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawai, M.; Modder, U.I.; Khosla, S.; Rosen, C.J. Emerging therapeutic opportunities for skeletal restoration. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marie, P.J.; Kassem, M. Osteoblasts in osteoporosis: Past, emerging, and future anabolic targets. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 165, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, B. Natural products for treatment of osteoporosis: The effects and mechanisms on promoting osteoblast-mediated bone formation. Life Sci. 2016, 147, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.P.; Xia, Y. Chinese herbal medicines for treating osteoporosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.M.; Lee, M.K.; Min, B.S.; Kim, J.C.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, H.K. Two Lignans from the Stem Bark of Styrax japonica. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. 2009, 52, 560–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Hirai, H.; Tanaka, M.; Arihara, S. Antisweet natural products. XV. Structures of Jegosaponins A-D from Styrax japonica Sieb. et Zucc. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 48, 1093–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, A.F. Elementos da Flora Aromática: O Laboratório de Farmacognosia no Estudo dos Óleos Essenciais de Portugal e Angola; Junta de Investigações Científicas do Ultramar: Lisboa, Portugal, 1975; p. 295. [Google Scholar]
- Min, B.S.; Oh, S.R.; Ahn, K.S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, H.K. Anti-complement activity of norlignans and terpenes from the stem bark of Styrax japonica. Planta Med. 2004, 70, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, K.J.; Min, B.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, K.T. Styraxoside A isolated from the stem bark of Styrax japonica inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in RAW 264.7 cells by suppressing nuclear factor-kappa B activation. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, H.I.; Kim, M.R.; Woo, E.R.; Chung, J.H. Triterpenoid from Styrax japonica SIEB. et ZUCC, and its effects on the expression of matrix metalloproteinases-1 and type 1 procollagen caused by ultraviolet irradiated cultured primary human skin fibroblasts. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 2003–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Do, K.H.; Choi, Y.W.; Kim, E.K.; Yun, S.J.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Ha, J.M.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, C.D.; Son, B.G.; et al. Pinoresinol-4,4′-di-O-beta-D-glucoside from Valeriana officinalis root stimulates calcium mobilization and chemotactic migration of mouse embryo fibroblasts. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.R.; Ko, H.J.; Chowdhury, M.A.; Chang, Y.S.; Woo, E.R. Chemical constituents on the aerial parts of Artemisia selengensis and their IL-6 inhibitory activity. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2015, 38, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Dai, J.; Zhang, H.; Ge, Z. MicroRNA-221 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation by regulation of ZFPM2 in osteoblasts. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, e7574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Histing, T.; Stenger, D.; Kuntz, S.; Scheuer, C.; Tami, A.; Garcia, P.; Holstein, J.H.; Klein, M.; Pohlemann, T.; Menger, M.D. Increased osteoblast and osteoclast activity in female senescence-accelerated, osteoporotic SAMP6 mice during fracture healing. J. Surg. Res. 2012, 175, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guntur, A.R.; Rosen, C.J. The skeleton: A multi-functional complex organ: New insights into osteoblasts and their role in bone formation: The central role of PI3Kinase. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 211, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsenty, G.; Kronenberg, H.M.; Settembre, C. Genetic control of bone formation. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2009, 25, 629–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsenty, G.; Wagner, E.F. Reaching a genetic and molecular understanding of skeletal development. Dev. Cell 2002, 2, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.S.; Jung, E.Y.; Bae, S.H.; Kwon, K.H.; Kim, J.M.; Suh, H.J. Stimulation of osteoblastic differentiation and mineralization in MC3T3-E1 cells by yeast hydrolysate. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.B.; Song, Y.; Hwang, J.K. Kirenol stimulates osteoblast differentiation through activation of the BMP and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways in MC3T3-E1 cells. Fitoterapia 2014, 98, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Deng, C.; Li, Y.P. TGF-beta and BMP signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Artigas, N.; Urena, C.; Rodriguez-Carballo, E.; Rosa, J.L.; Ventura, F. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-regulated interactions between Osterix and Runx2 are critical for the transcriptional osteogenic program. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27105–27117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ducy, P.; Zhang, R.; Geoffroy, V.; Ridall, A.L.; Karsenty, G. Osf2/Cbfa1: A transcriptional activator of osteoblast differentiation. Cell 1997, 89, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kern, B.; Shen, J.; Starbuck, M.; Karsenty, G. Cbfa1 contributes to the osteoblast-specific expression of type I collagen genes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7101–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishimura, R.; Wakabayashi, M.; Hata, K.; Matsubara, T.; Honma, S.; Wakisaka, S.; Kiyonari, H.; Shioi, G.; Yamaguchi, A.; Tsumaki, N.; et al. Osterix regulates calcification and degradation of chondrogenic matrices through matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP13) expression in association with transcription factor Runx2 during endochondral ossification. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 33179–33190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fakhry, M.; Hamade, E.; Badran, B.; Buchet, R.; Magne, D. Molecular mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation towards osteoblasts. World J. Stem Cells 2013, 5, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhoff, M.A.; Serrels, B.; Fincham, V.J.; Frame, M.C.; Carragher, N.O. SRC-mediated phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase couples actin and adhesion dynamics to survival signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 8113–8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.M.; Shih, Y.T.; Chen, Y.S.; Liu, C.L.; Fang, W.K.; Tsai, C.H.; Tsai, F.J.; Kuo, W.W.; Lai, T.Y.; Huang, C.Y. Schwann Cell Migration Induced by Earthworm Extract via Activation of PAs and MMP2/9 Mediated through ERK1/2 and p38. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2011, 2011, 395458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Liu, F.C.; Chou, P.Y.; Chien, Y.C.; Chang, W.S.; Huang, G.J.; Wu, C.H.; Sheu, M.J. Ethanol extracts of fruiting bodies of Antrodia cinnamomea suppress CL1-5 human lung adenocarcinoma cells migration by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 through ERK, JNK, p38, and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2012, 2012, 378415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, X.; Lu, S.; Zhuo, Y.; Winter, C.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y. Visualization of Src and FAK activity during the differentiation process from HMSCs to osteoblasts. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikkavilli, R.K.; Malbon, C.C. Mitogen-activated protein kinases and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Molecular conversations among signaling pathways. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2009, 2, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, T.F.; Guo, X.; Garrett-Beal, L.; Yang, Y. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in mesenchymal progenitors controls osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation during vertebrate skeletogenesis. Dev. Cell 2005, 8, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Oyajobi, B.O.; Harris, S.E.; Chen, D.; Tsao, C.; Deng, H.W.; Zhao, M. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling activates bone morphogenetic protein 2 expression in osteoblasts. Bone 2013, 52, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rawadi, G.; Vayssiere, B.; Dunn, F.; Baron, R.; Roman-Roman, S. BMP-2 controls alkaline phosphatase expression and osteoblast mineralization by a Wnt autocrine loop. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2003, 18, 1842–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Kokabu, S.; Ohte, S.; Sasanuma, H.; Kanomata, K.; Yoneyama, K.; Kato, H.; Akita, M.; Oda, H.; Katagiri, T. Canonical Wnts and BMPs cooperatively induce osteoblastic differentiation through a GSK3beta-dependent and beta-catenin-independent mechanism. Differentiation 2010, 80, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.M.; Nakashima, A.; Nashimoto, M.; Yawaka, Y.; Tamura, M. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 enhances Wnt/beta-catenin signaling-induced osteoprotegerin expression. Genes Cells 2009, 14, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Whetstone, H.C.; Youn, A.; Nadesan, P.; Chow, E.C.; Lin, A.C.; Alman, B.A. Beta-catenin signaling pathway is crucial for bone morphogenetic protein 2 to induce new bone formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soelaiman, I.N.; Das, S.; Shuid, A.N.; Mo, H.; Mohamed, N. Use of medicinal plants and natural products for treatment of osteoporosis and its complications. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 764701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, A.M.; Jurgens, T.M.; Bowles, S.K. Natural health products in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis: Systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Ann. Pharmacother. 2006, 40, 836–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, M.A.; Wein, Y.S.; Zhang, Z.K.; Kuo, Y.H. Inhibitory activity against tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) replication of pinoresinol and syringaresinol lignans and their glycosides from the root of Rhus javanica var. roxburghiana. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 6460–6465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.R.; Lee, H.; Cho, M.; Yun, H.M. A Phytochemical Constituent, (E)-Methyl-Cinnamate Isolated from Alpinia katsumadai Hayata Suppresses Cell Survival, Migration, and Differentiation in Pre-Osteoblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.R.; Yun, H.M. RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in bone marrow-derived macrophages is suppressed by cisapride. Toxicology 2019, 422, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.R.; Kim, E.C.; Hong, J.T.; Yun, H.M. Dysregulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine 6 receptor accelerates maturation of bone-resorbing osteoclasts and induces bone loss. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3087–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.R.; Yun, H.M.; Hong, J.T. G721-0282 inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in human osteosarcoma through down-regulation of the STAT3 pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, K.-R.; Kim, S.; Cho, M.; Kang, S.W.; Yun, H.-M. Effects of PIN on Osteoblast Differentiation and Matrix Mineralization through Runt-Related Transcription Factor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249579
Park K-R, Kim S, Cho M, Kang SW, Yun H-M. Effects of PIN on Osteoblast Differentiation and Matrix Mineralization through Runt-Related Transcription Factor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(24):9579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249579
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Kyung-Ran, SooHyun Kim, MyoungLae Cho, Sang Wook Kang, and Hyung-Mun Yun. 2020. "Effects of PIN on Osteoblast Differentiation and Matrix Mineralization through Runt-Related Transcription Factor" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 24: 9579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249579
APA StylePark, K. -R., Kim, S., Cho, M., Kang, S. W., & Yun, H. -M. (2020). Effects of PIN on Osteoblast Differentiation and Matrix Mineralization through Runt-Related Transcription Factor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(24), 9579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249579




