The Fluoro-Thiazolylhydrazone Compound TSC-3C Inhibits Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cell Line Activity by Promoting Apoptosis, Regulating the MAPK Pathway and Inducing Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
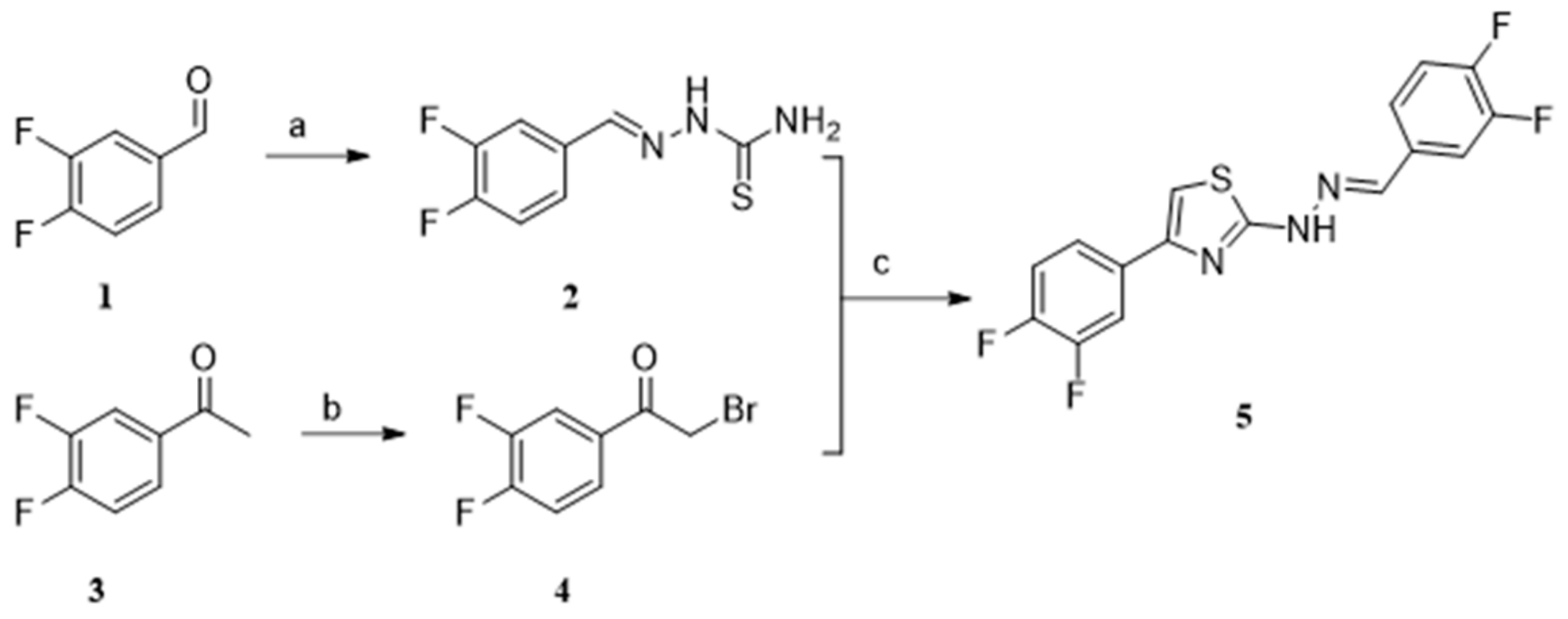
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Anti-Proliferative Activity
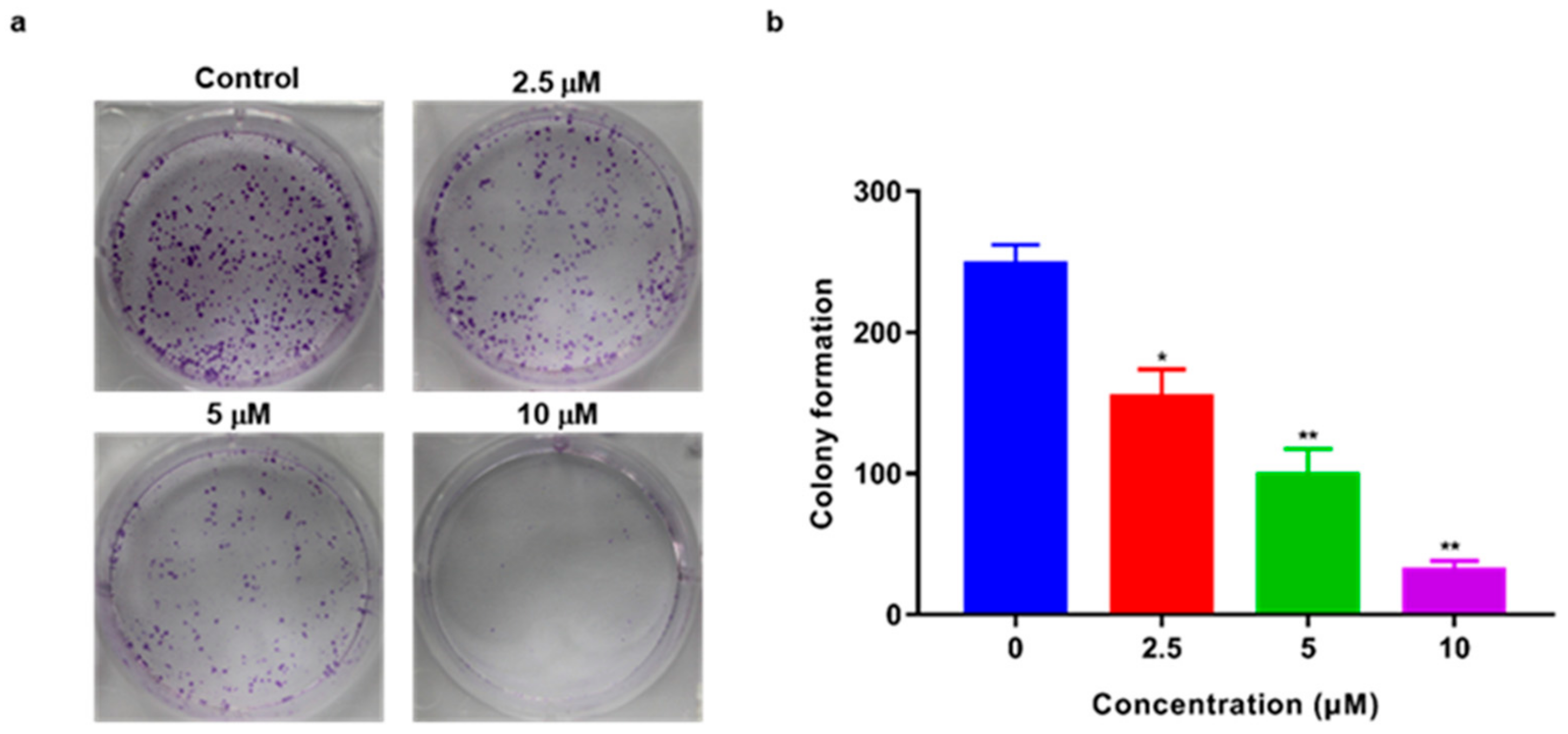
2.3. TSC-3C Inhibited the Proliferation of MDA-MB-231 Cells
2.4. Effect of TSC-3C on MDA-MB-231 Cell Migration
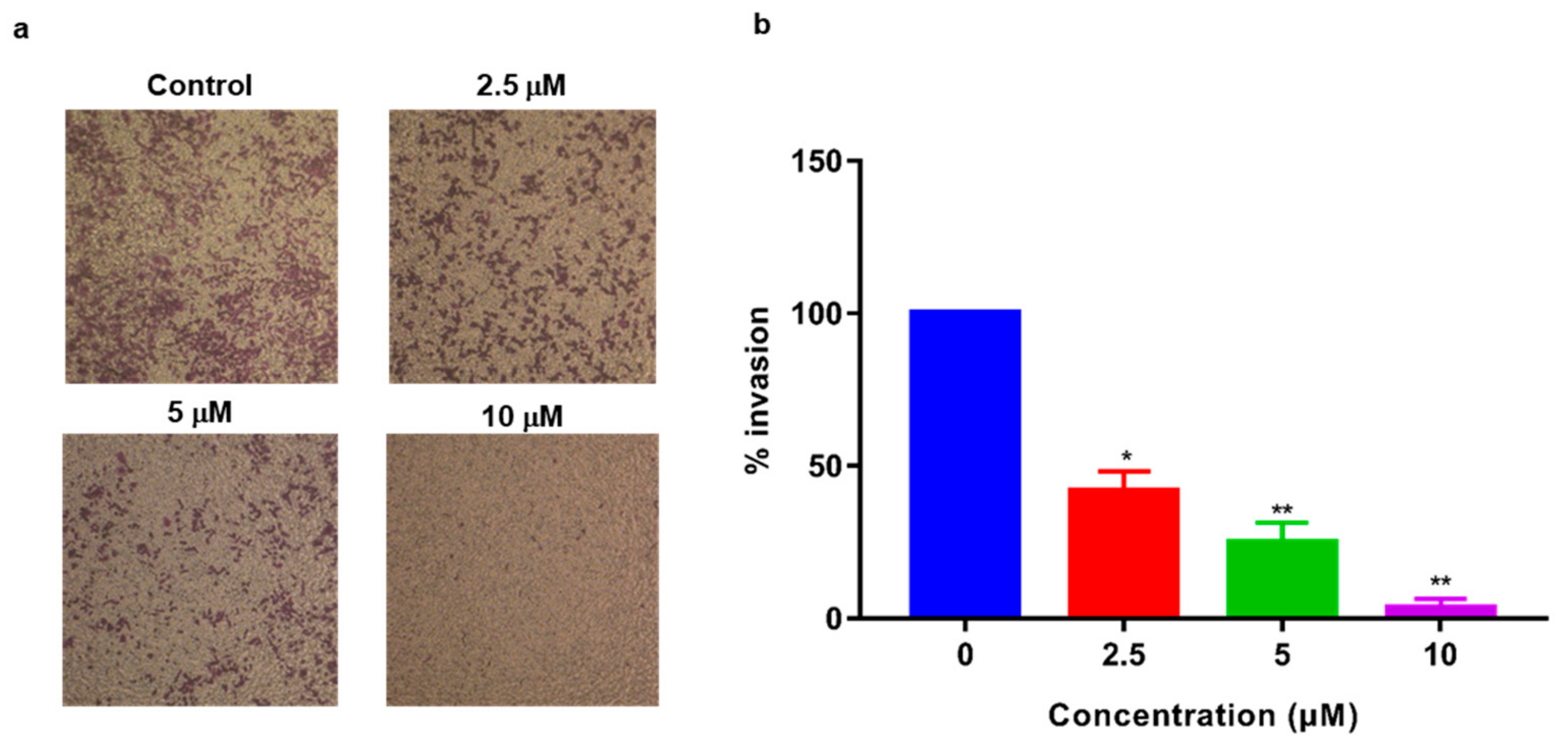
2.5. Inhibition of MDA-MB-231 Cell Invasion
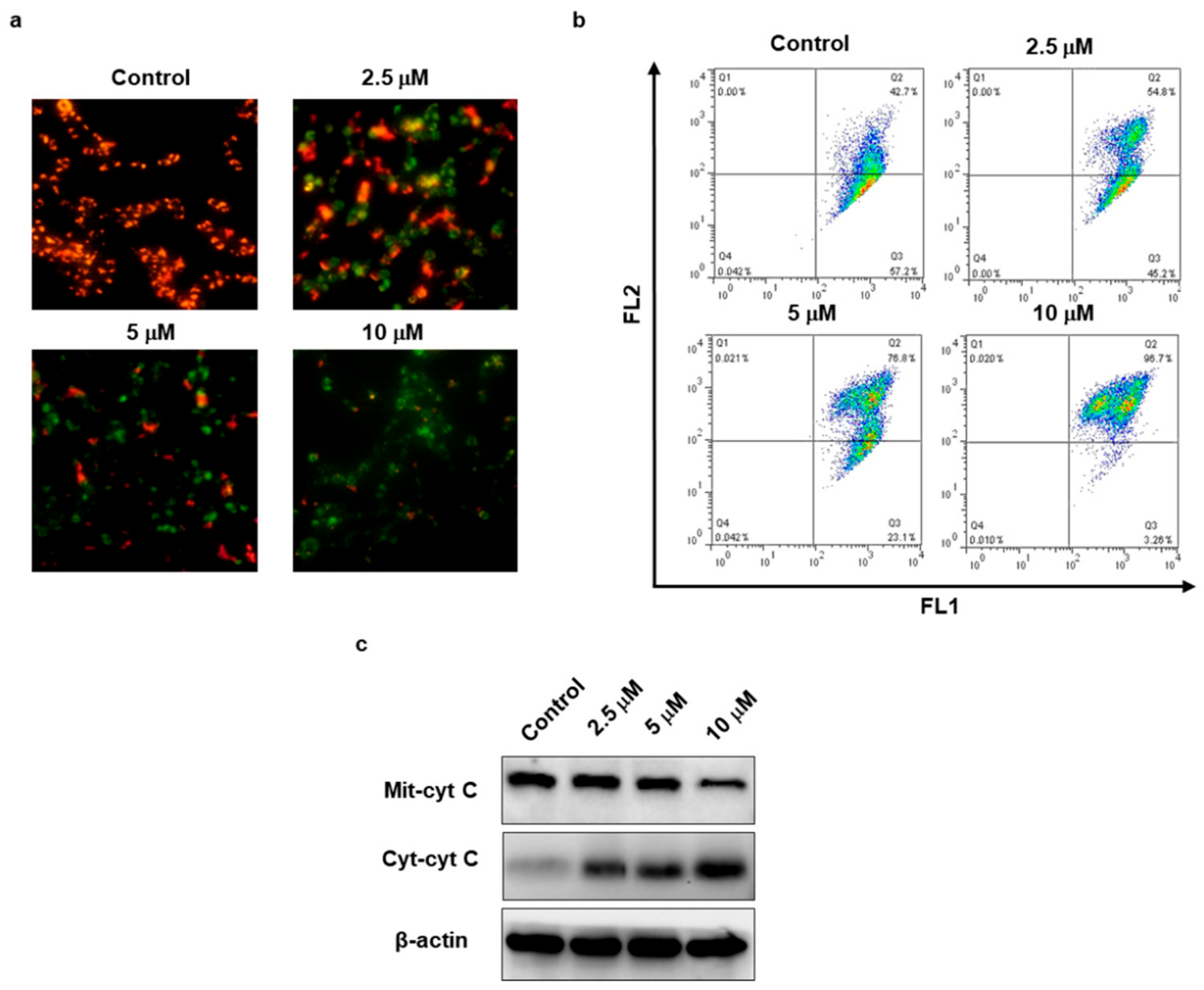
2.6. TSC-3C Decreased the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
2.7. TSC-3C Induces Apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 Cells
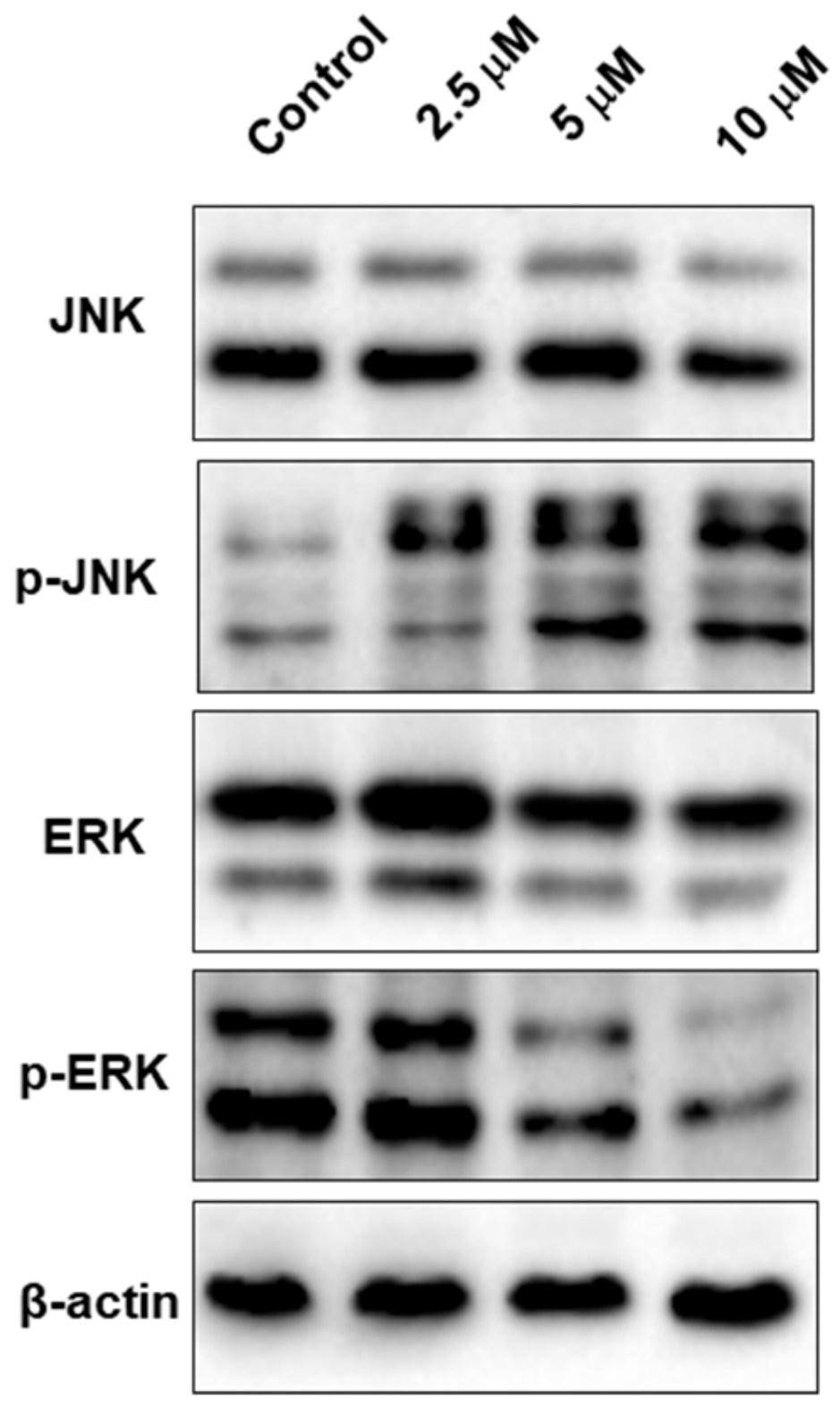
2.8. TSC-3C Affects the MAPK Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
4.1.1. Procedure for the Synthesis of Compound 2
4.1.2. Procedure for the Synthesis of Compound 4
4.1.3. Procedure for the Synthesis of Compound 5
4.2. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.4. Colony Forming Assay
4.5. Cell Migration Assay
4.6. Cell Invasion Assay
4.7. Measurement of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (Δφm)
4.8. Fluorescence Probe JC-1 and Fluorescence Microscopy
4.9. Detection of Apoptosis
4.10. Western Blotting
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TNBC | Triple negative breast cancer |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| PR | Progesterone receptor |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
References
- Mansoori, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Ghasabi, M. miR-142-3p as tumor suppressor miRNA in the regulation of tumorigenicity, invasion and migration of human breast cancer by targeting Bach-1 expression. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 9816–9825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Shi, A.; Lu, C. Breast Cancer: Epidemiology and Etiology. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 72, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perou, C.M.; Sørlie, T.; Eisen, M.B. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Adams, S.; Rugo, H.S. Atezolizumab and Nab-Paclitaxel in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2108–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, N.; Lee, S.-J.; Ohtani, S. Adjuvant Capecitabine for Breast Cancer after Preoperative Chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2147–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foulkes, W.D.; Smith, I.E. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1938–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlader, N.; Cronin, K.A.; Kurian, A.W. Differences in Breast Cancer Survival by Molecular Subtypes in the United States. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2018, 27, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yu, K.; Pang, D. Adjuvant Capecitabine in Combination with Docetaxel and Cyclophosphamide Plus Epirubicin for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (cbcsg010): An Open-Label, Randomised, Multicentre, Phase 3 Trial; Gonzalez Convention Center: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2019; p. GS1-08. [Google Scholar]
- Delea, T.E.; Kartashov, A.; Sharma, P.P. PCN123 Retrospective Stupdy of Health Care Utilization and Costs in Women with Metastatic Breast Cancer (MBC) Receiving Lapatinib After Treament with Trastuzumab. Value Health 2012, 15, A230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, N.; Sharma, J.R.; Yadav, U.C.S. Induction of growth cessation by acacetin via beta-catenin pathway and apoptosis by apoptosis inducing factor activation in colorectal carcinoma cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Zhou, M.; Chen, J. Hyperelodiones A-C, monoterpenoid polyprenylated acylphoroglucinols from Hypericum elodeoides, induce cancer cells apoptosis by targeting RXRalpha. Phytochemistry 2020, 170, 112216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S. Mechanism and current progress of Poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors in the treatment of ovarian cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 123, 109661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, H.; He, G. Discovery of Novel Dual Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase and Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Inhibitors as a Promising Strategy for Cancer Therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.L.; Le, K.H.; Xu, M. Combined MEK inhibition and tumor-associated macrophages depletion suppresses tumor growth in a triple-negative breast cancer mouse model. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 76, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, R.; Taha, R.Z.; Nair, V.S. PD-L1 Blockade by Atezolizumab Downregulates Signaling Pathways Associated with Tumor Growth, Metastasis, and Hypoxia in Human Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lim, B.; Pearson, T. Anti-tumor and anti-metastasis efficacy of E6201, a MEK1 inhibitor, in preclinical models of triple-negative breast cancer. Breast. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 175, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Qi, Y.X.; Qi, Z.H. TRPC3 Regulates the Proliferation and Apoptosis Resistance of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells through the TRPC3/RASA4/MAPK Pathway. Cancers 2019, 11, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.; Ramamurthy, V.P.; Gediya, L.K. The Novel Mnk1/2 Degrader and Apoptosis Inducer VNLG-152 Potently Inhibits TNBC Tumor Growth and Metastasis. Cancers 2019, 11, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Thodey, K. Complete biosynthesis of noscapine and halogenated alkaloids in yeast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3922–E3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takino, T.; Yasui, H.; Yoshitake, A. A new halogenated antidiabetic vanadyl complex, bis(5-iodopicolinato)oxovanadium(IV): In vitro and in vivo insulinomimetic evaluations and metallokinetic analysis. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 6, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentzer, M.; Riedel, K.; Rasmussen, T.B. Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm bacteria by a halogenated furanone compound. Microbiology 2002, 148, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, K.; Zubair, M.; Rasool, N. Regioselective synthesis of 2-(bromomethyl)-5-aryl-thiophene derivatives viapalladium (0) catalyzed suzuki cross-coupling reactions: As antithrombotic and haemolytically active molecules. Chem. Cent. J. 2014, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, I.S.; Kim, M.; Son, K.T.; Jeong, Y.; Jeon, Y.J. Antioxidant Activity of Marine Algal Polyphenolic Compounds: A Mechanistic Approach. J. Med. Food 2016, 19, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, D.H.A.; Seca, A.M.L.; Pinto, D.C.G.A. Seaweed Secondary Metabolites in vitro and in vivo Anticancer Activity. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Hamann, M.T. Marine pharmacology in 2001–2002: Marine compounds with anthelmintic, antibacterial, anticoagulant, antidiabetic, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiplatelet, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; affecting the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C 2005, 140, 265–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, M.H.M.; Salem, M.A.; El-Gaby, M.S.A. Synthesis and biological evaluation of some novel thiazole compounds as potential anti-inflammatory agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 65, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefranc, F.; Koutsaviti, A.; Ioannou, E. Algae metabolites: From in vitro growth inhibitory effects to promising anticancer activity. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 810–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-J.; Guo, C.-L.; Li, X.-Q. Discovery of Novel Bromophenol Hybrids as Potential Anticancer Agents through the Ros-Mediated Apoptotic Pathway: Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-J.; Wang, S.-Y.; Jiang, B. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Bromophenol Derivatives Incorporating Indolin-2-One Moiety as Potential Anticancer Agents. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 806–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Discovery of Novel Bromophenol–Thiosemicarbazone Hybrids as Potent Selective Inhibitors of Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase-1 (PARP-1) for Use in Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 3051–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moerke, N.J.; Aktas, H.; Chen, H. Small-Molecule Inhibition of the Interaction between the Translation Initiation Factors eIF4E and eIF4G. Cell 2007, 128, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takrouri, K.; Chen, T.; Papadopoulos, E. Structure–activity relationship study of 4EGI-1, small molecule eIF4E/eIF4G protein–protein interaction inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 77, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalingam, P.; Takrouri, K.; Chen, T. Synthesis of Rigidified eIF4E/eIF4G Inhibitor-1 (4EGI-1) Mimetic and Their in Vitro Characterization as Inhibitors of Protein–Protein Interaction. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 5094–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillis, E.P.; Eastman, K.J.; Hill, M.D. Applications of Fluorine in Medicinal Chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 8315–8359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Guo, C.; Li, X. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of bromophenol-thiazolylhydrazone hybrids inhibiting the interaction of translation initiation factors eIF4E/eIF4G as multifunctional agents for cancer treatment. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 177, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- English, J.; Pearson, G.; Wilsbacher, J. New Insights into the Control of MAP Kinase Pathways. Exp. Cell Res. 1999, 253, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.J. Signal Transduction by the JNK Group of MAP Kinases. Cell 2000, 103, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Chiba, K. Induction of apoptosis in starfish eggs requires spontaneous inactivation of MAPK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase) followed by activation of p38MAPK. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huot, J.; Houle, F.; Rousseau, S. SAPK2/p38-dependent F-Actin Reorganization Regulates Early Membrane Blebbing during Stress-induced Apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 1361–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier, C.; Hess, P.; Yang, D.D. Requirement of JNK for Stress- Induced Activation of the Cytochrome c-Mediated Death Pathway. Science 2000, 288, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurada, P.; White, K. Ras Promotes Cell Survival in Drosophila by Downregulating hid Expression. Cell 1998, 95, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Dickens, M.; Raingeaud, J. Opposing Effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP Kinases on Apoptosis. Science 1995, 270, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.-L.; Wang, L.-J.; Zhao, Y. A Novel Bromophenol Derivative BOS-102 Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Human A549 Lung Cancer Cells via ROS-Mediated PI3K/Akt and the MAPK Signaling Pathway. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sa, P.N.; Lino, C.I.; Fonseca, N.C. Thiazole compounds with activity against Cryptococcus gattii and Cryptococcus neoformans in vitro. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 102, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dykhuizen, E.C.; May, J.F.; Tongpenyai, A. Inhibitors of UDP-Galactopyranose Mutase Thwart Mycobacterial Growth. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 6706–6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Liu, S.V.; Subramaniam, D.S. Refining the treatment of NSCLC according to histological and molecular subtypes. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Cell Lines | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|
| MDA-MB-231 | 2.79 ± 0.71 |
| A549 | 8.12 ± 1.22 |
| Capanc-1 | 8.45 ± 1.21 |
| Caco-2 | 12.33 ± 1.31 |
| MCF-7 | 22.77 ± 1.16 |
| PANC-1 | 26.32 ± 1.35 |
| HepG2 | 27.10 ± 1.98 |
| SK-OV-3 | 33.81 ± 1.87 |
| U87 MG | 40.00 ± 2.03 |
| L-02 | not reached |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Dai, J.; Zheng, Q.; Guo, S.; Yu, Y.; Hu, W.; Gao, Y.; Shi, D. The Fluoro-Thiazolylhydrazone Compound TSC-3C Inhibits Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cell Line Activity by Promoting Apoptosis, Regulating the MAPK Pathway and Inducing Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031038
Zhang J, Dai J, Zheng Q, Guo S, Yu Y, Hu W, Gao Y, Shi D. The Fluoro-Thiazolylhydrazone Compound TSC-3C Inhibits Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cell Line Activity by Promoting Apoptosis, Regulating the MAPK Pathway and Inducing Mitochondrial Dysfunction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(3):1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031038
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiajia, Jiajia Dai, Qingxuan Zheng, Shuju Guo, Yanyan Yu, Wenpeng Hu, Yanan Gao, and Dayong Shi. 2020. "The Fluoro-Thiazolylhydrazone Compound TSC-3C Inhibits Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cell Line Activity by Promoting Apoptosis, Regulating the MAPK Pathway and Inducing Mitochondrial Dysfunction" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 3: 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031038
APA StyleZhang, J., Dai, J., Zheng, Q., Guo, S., Yu, Y., Hu, W., Gao, Y., & Shi, D. (2020). The Fluoro-Thiazolylhydrazone Compound TSC-3C Inhibits Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cell Line Activity by Promoting Apoptosis, Regulating the MAPK Pathway and Inducing Mitochondrial Dysfunction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031038






