Disparate Phenotypes Resulting from Mutations of a Single Histidine in Switch II of Geobacillus stearothermophilus Translation Initiation Factor IF2
Abstract
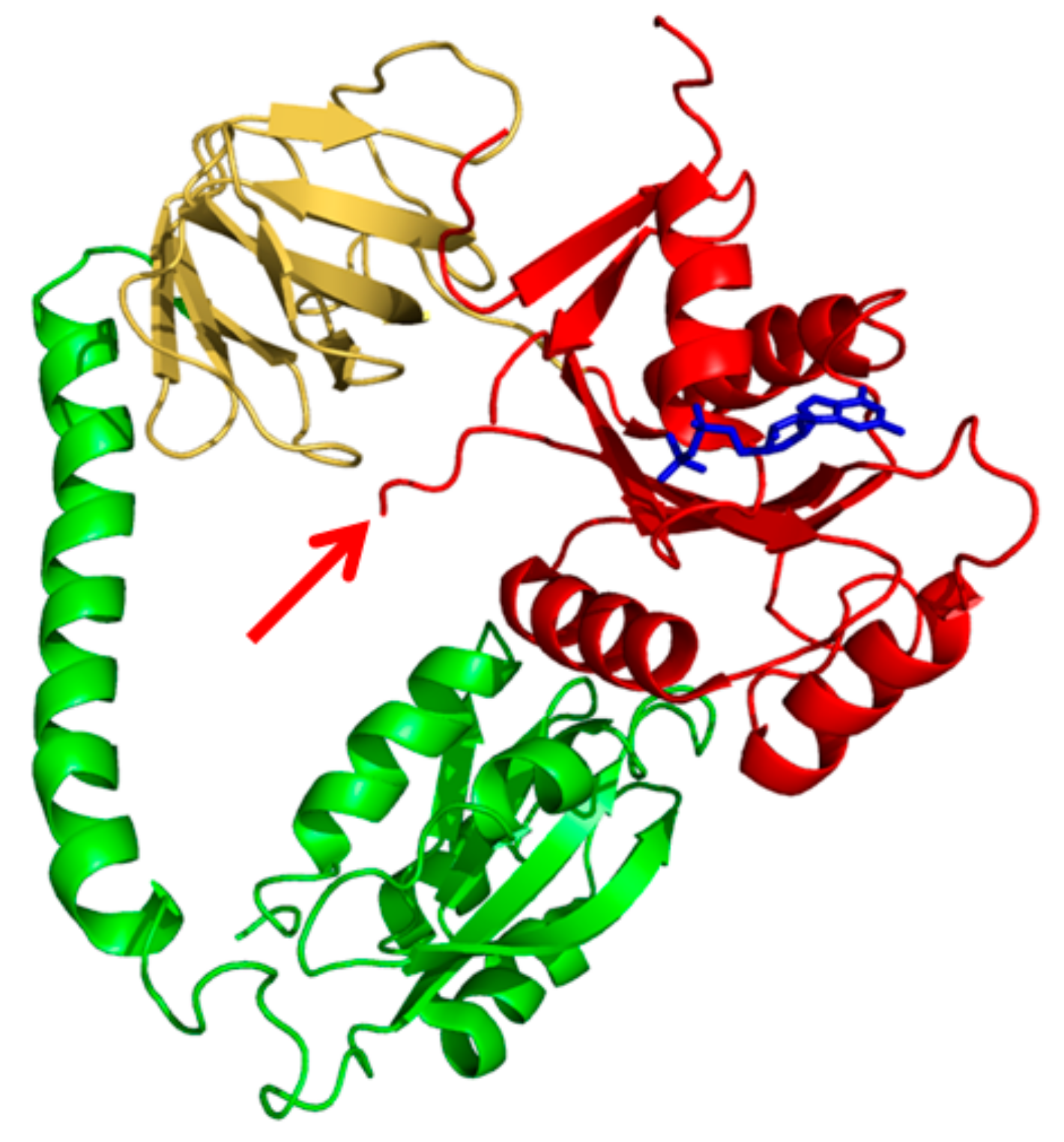
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of the In Vivo Expression of IF2H301 Substitution Mutants
2.2. Ribosome-dependent GTPase Activity of the IF2 Mutants
2.3. The Reason for Loss of GTPase Activity Is Different in Different IF2His301 Mutants
2.3.1. GTP Binding to the IF2H301 mutants
2.3.2. Ribosome-Independent GTPase Activity of IF2
2.3.3. Binding of IF2H301 Mutants to 50S Subunits
2.4. Activity of the IF2 Mutants in Supporting Single Steps of the Translation Initiation Pathway
2.4.1. Binding of fMet-tRNAfMet to Ribosomes
2.4.2. Puromycin Reaction of Ribosome-Bound fMet-tRNA
2.4.3. Initiation Dipeptide Formation
2.5. Dissociation of IF2 from the Ribosome
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Preparations
4.2. Overexpression of the IF2 Variants
4.3. Ribosome Dependent GTPase Activity of IF2
4.4. Ribosome-Independent GTPase Activity of IF2
4.5. Mant-GTP Binding to wtIF2 and IF2 Mutants
4.6. Binding of IF2 to 50S Ribosomal Subunits
4.7. IF2-dependent fMet-tRNA Binding to 30S Subunits (30S IC Formation)
4.8. fMet-puromycin and Initiation Dipeptide Formation
4.9. Dissociation of IF2 from the Ribosome
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IF | (translation) initiation factor |
| GDP | guanosine diphosphate |
| GTP | guanosine triphosphate |
| ppGpp | guanosine tetraphosphate |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| PAGE | polyacrylamide electrophoresis |
| 30S IC | 30S initiation complex |
| 70S IC | 70S initiation complex |
| DTT | dithiothreitol |
| PMSF | phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride |
References
- Gualerzi, C.O.; Brandi, L.; Caserta, E.; La Teana, A.; Spurio, R.; Tomšic, J.; Pon, C.L. Translation initiation in bacteria. In The Ribosome; Garrett, R.A., Douthwaite, S.R., Liljas, A., Matheson, A.T., Moore, P.B., Noller, H.F., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; pp. 475–494. [Google Scholar]
- Gualerzi, C.O.; Brandi, L.; Caserta, E.; Garofalo, C.; Lammi, M.; La Teana, A.; Petrelli, D.; Spurio, R.; Tomsic, J.; Pon, C.L. Role of the initiation factors in the early events of mRNA translation in bacteria. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 2001, 66, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marintchev, A.; Wagner, G. Translation initiation: Structures, mechanisms and evolution. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2004, 37, 197–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, B.S.; Sorensen, H.P.; Mortensen, K.K.; Sperling-Petersen, H.U. Initiation of protein synthesis in bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myasnikov, A.G.; Simonetti, A.; Marzi, S.; Klaholz, B.P. Structure-function insights into prokaryotic and eukaryotic translation initiation. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2009, 19, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualerzi, C.O.; Fabbretti, A.; Brandi, L.; Milon, P.; Pon, C.L. Role of the initiation factors in mRNA start site selection and fMet-tRNA recruitment by bacterial ribosomes. Isr. J. Chem. 2010, 50, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milon, P.; Maracci, C.; Filonava, L.; Gualerzi, C.O.; Rodnina, M.V. Kinetic landscape of the 30S translation initiation complex formation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 609–615. [Google Scholar]
- Gualerzi, C.O.; Pon, C.L. Initiation of mRNA translation in bacteria—Structural and dynamic aspects. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 4341–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaledhonkar, S.; Fu, Z.; Caban, K.; Li, W.; Chen, B.; Sun, M.; Gonzalez, R.L., Jr.; Frank, J. Late steps in bacterial translation initiation visualized using time-resolved cryo-EM. Nature 2019, 570, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, J.M.; Kildsgaard, J.; Siwanowicz, I.; Mortensen, K.K.; Sperling Petersen, H.U. Binding of Escherichia coli initiation factor IF2 to 30S ribosomal subunits: A functional role for the N-terminus of the factor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 252, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.M.; Drskjotersen, L.; Kristensen, J.E.; Mortensen, K.K.; Sperling-Petersen, H.U. Characterization of the domains of E. coli initiation factor IF2 responsible for recognition of the ribosome. FEBS Lett. 1999, 455, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caserta, E.; Tomsic, J.; Spurio, R.; La Teana, A.; Pon, C.L.; Gualerzi, C.O. Translation initiation factor IF2 interacts with the 30S ribosomal subunit via two separate binding sites. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 362, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caserta, E.; Ferrara, C.; Milon, P.; Fabbretti, A.; Rocchetti, A.; Tomsic, J.; Pon, C.L.; Gualerzi, C.O.; La Teana, A. Ribosomal interaction of Bacillus stearothermophilus translation initiation factor IF2: Characterization of the active sites. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 396, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonetti, A.; Marzi, S.; Billas, I.M.; Tsai, A.; Fabbretti, A.; Myasnikov, A.G.; Roblin, P.; Vaiana, A.C.; Hazemann, I.; Eiler, D.; et al. Involvement of protein IF2 N domain in ribosomal subunit joining revealed from architecture and function of the full-length initiation factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 15656–15661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- La Teana, A.; Gualerzi, C.O.; Dahlberg, A.E. Initiation factor IF 2 binds to the α-sarcin loop and helix 89 of Escherichia coli 23S ribosomal RNA. RNA 2001, 7, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzi, S.; Knight, W.; Brandi, L.; Caserta, E.; Soboleva, N.; Hill, W.; Gualerzi, C.O.; Lodmell, S. Ribosomal localization of translation initiation factor IF2. RNA 2003, 9, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gualerzi, C.O.; Severini, M.; Spurio, R.; La Teana, A.; Pon, C.L. Molecular dissection of translation initiation factor IF2. Evidence for two structural and functional domains. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 16356–16362. [Google Scholar]
- Myasnikov, A.G.; Marzi, S.; Simonetti, A.; Giuliodori, A.M.; Gualerzi, C.O.; Yusupova, G.; Yusupov, M.; Klaholz, B.P. Conformational transition of initiation factor 2 from the GTP- to GDP-state visualized on the ribosome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.S.; Zavialov, A.; Gursky, R.; Ehrenberg, M.; Frank, J. The cryo-EM structure of a translation initiation complex from Escherichia coli. Cell 2005, 121, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simonetti, A.; Marzi, S.; Myasnikov, A.G.; Yusupov, M.; Gualerzi, C.O.; Klaholz, B.P. Structure of a 30S ribosomal initiation complex. Nature 2008, 455, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprink, T.; Ramrath, D.J.; Yamamoto, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Loerke, J.; Ismer, J.; Hildebrand, P.W.; Scheerer, P.; Bürger, J.; Mielke, T.; et al. Structures of ribosome-bound initiation factor 2 reveal the mechanism of subunit association. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dongre, R.; Folkers, G.E.; Gualerzi, C.O.; Boelens, R.; Wienk, H. A model for the interaction of the G3-subdomain of Geobacillus stearothermophilus IF2 with the 30S ribosomal subunit. Protein Sci. 2016, 25, 1722–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milon, P.; Carotti, M.; Konevega, A.L.; Wintermeyer, W.; Rodnina, M.V.; Gualerzi, C.O. The ribosome- bound initiation factor 2 recruits initiator tRNA to the 30S initiation complex. EMBO Rep. 2010, 11, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spurio, R.; Brandi, L.; Caserta, E.; Pon, C.L.; Gualerzi, C.O.; Misselwitz, R.; Krafft, C.; Welfle, K.; Welfle, H. The C-terminal sub-domain (IF2 C-2) contains the entire fMet-tRNA binding site of initiation factor IF2. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 2447–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meunier, S.; Spurio, R.; Czisch, M.; Wechselberger, R.; Guenneugues, M.; Gualerzi, C.O.; Boelens, R. Solution structure of the fMet-tRNA binding domain of B. stearothermophilus initiation factor IF2. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 1918–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guenneugues, M.; Meunier, S.; Boelens, R.; Caserta, E.; Brandi, L.; Spurio, R.; Pon, C.L.; Gualerzi, C.O. Mapping the fMet-tRNA binding site of initiation factor IF2. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 5233–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Alonso, J.P.; Fabbretti, A.; Kaminishi, T.; Iturrioz, I.; Brandi, L.; Gil-Carton, D.; Gualerzi, C.O.; Fucini, P.; Connell, S.R. Structure of a 30S pre-initiation complex stalled by GE81112 reveals structural parallels in bacterial and eukaryotic protein synthesis initiation pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 2179–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pon, C.L.; Paci, M.; Pawlik, R.T.; Gualerzi, C.O. Structure-function relationship in Escherichia coli initiation factors. Biochemical and biophysical characterization of the interaction between IF-2 and guanosine nucleotides. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 8918–8924. [Google Scholar]
- Wienk, H.; Tishchenko, E.; Belardinelli, R.; Tomaselli, S.; Dongre, R.; Spurio, R.; Folkers, G.E.; Gualerzi, C.O.; Boelens, R. Structural dynamics of bacterial translation initiation factor IF2. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 10922–10932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simonetti, A.; Marzi, S.; Fabbretti, A.; Hazemann, I.; Jenner, L.; Urzhumtsev, A.; Gualerzi, C.O.; Klaholz, B.P. Structure of the protein core of translation initiation factor 2 in apo, GTP-bound and GDP-bound forms. Acta Crystall. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2013, 69, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eiler, D.; Lin, J.; Simonetti, A.; Klaholz, B.P.; Steitz, T.A. Initiation factor 2 crystal structure reveals a different domain organization from eukaryotic initiation factor 5B and mechanism among translational GTPases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 15662–15667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lockwood, A.H.; Chakraborty, P.R.; Maitra, U. A complex between initiation factor IF2, guanosine triphosphate, and fMet-tRNA: An intermediate in initiation complex formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1971, 68, 3122–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milón, P.; Tischenko, E.; Tomšič, J.; Caserta, E.; Folkers, G.; La Teana, A.; Rodnina, M.V.; Pon, C.L.; Boelens, R.; Gualerzi, C.O. The nucleotide binding site of bacterial translation initiation factor IF2 as a metabolic sensor. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13962–13967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fabbretti, A.; Brandi, L.; Milon, P.; Spurio, R.; Pon, C.L.; Gualerzi, C.O. Translation initiation without IF2-dependent GTP hydrolysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 7946–7955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antoun, A.; Pavlov, M.Y.; Andersson, K.; Tenson, T.; Ehrenberg, M. The roles of initiation factor 2 and guanosine triphosphate in initiation of protein synthesis. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 5593–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antoun, A.; Pavlov, M.Y.; Tenson, T.; Ehrenberg, M. Ribosome formation from subunits studied by stopped-flow Rayleigh light scattering. Biol. Proced. Online 2004, 6, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomsic, J.; Vitali, L.A.; Daviter, T.; Savelsbergh, A.; Spurio, R.; Striebeck, P.; Wintermeyer, W.; Rodnina, M.V.; Gualerzi, C.O. Late events of translation initiation in bacteria: A kinetic analysis. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 2127–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grigoriadou, C.; Marzi, S.; Kirillov, S.; Gualerzi, C.O.; Cooperman, B.S. A qualitative kinetic scheme for 70S initiation complex formation. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 373, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- La Teana, A.; Pon, C.L.; Gualerzi, C.O. Late events in translation initiation. Adjustment of fMet-tRNA in the ribosomal P-site. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 256, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, A.H.; Sarkar, P.; Maitra, U. Release of polypeptide chain initiation factor IF2 during initiation complex formation. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1972, 69, 3602–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fakunding, J.L.; Hershey, J.W. The interaction of radioactive initiation factor IF-2 with ribosomes during initiation of protein synthesis. J. Mol. Biol. 1973, 248, 4206–4212. [Google Scholar]
- Luchin, S.; Putzer, H.; Cenatiempo, Y.; Grunberg-Manago, M.; Laalami, S. In Vitro study of two dominant inhibitory GTPase mutants of Escherichia coli translation initiation factor IF2. Direct evidence that GTP hydrolysis is necessary for factor recycling. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 6074–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dever, T.E.; Glynias, M.J.; Merrick, W.C. GTP-binding domain: Three consensus sequence elements with distinct spacing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 1814–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourne, H.R.; Sanders, D.A.; McCormick, F. The GTPase superfamily: Conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature 1991, 349, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cool, R.H.; Parmeggiani, A. Substitution of histidine-84 and the GTPase mechanism of elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savelsbergh, A.; Matassova, N.B.; Rodnina, M.V.; Wintermeyer, W. Role of domains 4 and 5 in elongation factor G functions on the ribosome. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 300, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severini, M.; Spurio, R.; La Teana, A.; Pon, C.L.; Gualerzi, C.O. Ribosome-independent GTPase activity of translation initiation factor IF2 and of its G-domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 22800–22802. [Google Scholar]
- Mitkevich, V.A.; Ermakov, A.; Kulikova, A.A.; Tankov, S.; Shyp, V.; Soosaar, A.; Tenson, T.; Makarov, A.A.; Ehrenberg, M.; Hauryliuk, V. Thermodynamic characterization of ppGpp binding to EF-G or IF2 and of initiator tRNA binding to free IF2 in the presence of GDP, GTP, or ppGpp. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 402, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Belardinelli, R.; Maracci, C.; Milon, P.; Rodnina, M.V. Directional transition from initiation to elongation in bacterial translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 10700–10712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubnoff, J.S.; Maitra, U. Protein factors involved in polypeptide chain initiation in Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1969, 34, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakunding, J.L.; Traugh, J.A.; Traut, R.R.; Hershey, J.W. Purification and phosphorylation of initiation factor IF2. Meth. Enzymol. 1974, 30, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Dubnoff, J.S.; Lockwood, A.H.; Maitra, U. Studies on the role of guanosine triphosphate in polypeptide chain initiation in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1972, 247, 2884–2894. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brandi, A.; Piersimoni, L.; Feto, N.A.; Spurio, R.; Alix, J.H.; Schmidt, F.; Gualerzi, C.O. Translation initiation factor IF2 contributes to ribosome assembly and maturation during cold adaptation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 4652–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roll-Mecak, A.; Cao, C.; Dever, T.E.; Burley, S.K. X-ray structures of the universal translation initiation factor IF2/eIF5B: Conformational changes on GDP and GTP binding. Cell 2000, 103, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dever, T.E.; Roll-Mecak, A.; Choi, S.K.; Lee, J.H.; Cao, C.; Shin, B.S.; Burley, S.K. Universal translation initiation factor IF2/eIF5B. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2001, 66, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandi, L.; Marzi, S.; Fabbretti, A.; Fleischer, C.; Hill, W.E.; Gualerzi, C.O.; Lodmell, J.S. The translation initiation functions of IF2: Targets for thiostrepton inhibition. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 335, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Grigoriadou, C.; Cooperman, B.S. Interaction of IF2 with the ribosomal GTPase-associated center during 70S initiation complex formation. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 4699–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlson, M.A.; Haddad, B.G.; Weis, A.J.; Blackwood, C.S.; Shelton, C.D.; Wuerth, M.E.; Walter, J.D.; Spiegel, P.C., Jr. Ribosomal protein L7/L12 is required for GTPase translation factors EF-G, RF3, and IF2 to bind in their GTP state to 70S ribosomes. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 1631–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milon, P.; Konevega, A.L.; Peske, F.; Fabbretti, A.; Gualerzi, C.O.; Rodnina, M.V. Transient kinetics, fluorescence, and FRET in studies of initiation of translation in bacteria. Meth. Enzymol. 2007, 430, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Brandi, L.; Fabbretti, A.; Milon, P.; Carotti, M.; Pon, C.L.; Gualerzi, C.O. Methods for identifying compounds that specifically target translation. Meth. Enzymol. 2007, 431, 229–267. [Google Scholar]
- Rodnina, M.V.; Savelsbergh, A.; Matassova, N.B.; Katunin, V.I.; Semenkov, Y.P.; Wintermeyer, W. Thiostrepton inhibits the turnover but not the GTPase of elongation factor G on the ribosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9586–9590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sambrook, J.; Maniatis, T.; Fritsh, E.F. Molecular Cloning; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
 ); IF2H301Y(
); IF2H301Y(  ); IF2H301Q(
); IF2H301Q(  ); IF2H301L(
); IF2H301L(  ); IF2H301R (
); IF2H301R (  ) and IF2H301S(
) and IF2H301S(  ) expression. Further details are given in Materials and Methods.
) expression. Further details are given in Materials and Methods.
 ); IF2H301Y(
); IF2H301Y(  ); IF2H301Q(
); IF2H301Q(  ); IF2H301L(
); IF2H301L(  ); IF2H301R (
); IF2H301R (  ) and IF2H301S(
) and IF2H301S(  ) expression. Further details are given in Materials and Methods.
) expression. Further details are given in Materials and Methods.
 ); IF2H301Y(
); IF2H301Y(  ); IF2H301Q(
); IF2H301Q(  ); IF2H301L(
); IF2H301L(  ); IF2H301R (
); IF2H301R (  ) and IF2H301S(
) and IF2H301S(  ).
).
 ); IF2H301Y(
); IF2H301Y(  ); IF2H301Q(
); IF2H301Q(  ); IF2H301L(
); IF2H301L(  ); IF2H301R (
); IF2H301R (  ) and IF2H301S(
) and IF2H301S(  ).
).
 ); IF2H301Y(
); IF2H301Y(  ); IF2H301Q(
); IF2H301Q(  ); IF2H301L(
); IF2H301L(  ); IF2H301R (
); IF2H301R (  ) and IF2H301S(
) and IF2H301S(  ).
).
 ); IF2H301Y(
); IF2H301Y(  ); IF2H301Q(
); IF2H301Q(  ); IF2H301L(
); IF2H301L(  ); IF2H301R (
); IF2H301R (  ) and IF2H301S(
) and IF2H301S(  ).
).
 ); IF2H301Y(
); IF2H301Y(  ); IF2H301Q(
); IF2H301Q(  ); IF2H301L(
); IF2H301L(  ); IF2H301R (
); IF2H301R (  ) and IF2H301S(
) and IF2H301S(  ). Further details are given in Materials and Methods.
). Further details are given in Materials and Methods.
 ); IF2H301Y(
); IF2H301Y(  ); IF2H301Q(
); IF2H301Q(  ); IF2H301L(
); IF2H301L(  ); IF2H301R (
); IF2H301R (  ) and IF2H301S(
) and IF2H301S(  ). Further details are given in Materials and Methods.
). Further details are given in Materials and Methods.


| Type of IF2 | Kd, µM |
|---|---|
| wild-type | 10 ± 0.7 |
| H301S | 19.1 ± 0.8 |
| H301Q | 18 ± 0.9 |
| H301R | 24.7 ± 1 |
| H301L | 23.4 ± 1 |
| H301Y | 22 ± 0.9 |
| Activity | IF2wt | H301Y | H301Q | H301R | H301S | H301L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTP binding | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| GTP hydrolysis | +++ | − | +++ | − | − | − |
| 30S IC formation | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| fMet-puromycin formation | +++ | + | +++ | ++ | + | + |
| Initiation dipeptide (fMet-Phe) formation | +++ | − | + | − | − | − |
| Affinity for 70S | + | +++ | +++ | + | ++ | ++ |
| Affinity for 30S IC | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ |
| Dissociation from 70S IC | + | − | − | − | − | − |
| Dominant lethal phenotype | − | + | − | − | + | + |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomsic, J.; Smorlesi, A.; Caserta, E.; Giuliodori, A.M.; Pon, C.L.; Gualerzi, C.O. Disparate Phenotypes Resulting from Mutations of a Single Histidine in Switch II of Geobacillus stearothermophilus Translation Initiation Factor IF2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030735
Tomsic J, Smorlesi A, Caserta E, Giuliodori AM, Pon CL, Gualerzi CO. Disparate Phenotypes Resulting from Mutations of a Single Histidine in Switch II of Geobacillus stearothermophilus Translation Initiation Factor IF2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(3):735. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030735
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomsic, Jerneja, Arianna Smorlesi, Enrico Caserta, Anna Maria Giuliodori, Cynthia L. Pon, and Claudio O. Gualerzi. 2020. "Disparate Phenotypes Resulting from Mutations of a Single Histidine in Switch II of Geobacillus stearothermophilus Translation Initiation Factor IF2" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 3: 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030735
APA StyleTomsic, J., Smorlesi, A., Caserta, E., Giuliodori, A. M., Pon, C. L., & Gualerzi, C. O. (2020). Disparate Phenotypes Resulting from Mutations of a Single Histidine in Switch II of Geobacillus stearothermophilus Translation Initiation Factor IF2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030735





