NarL, a Novel Repressor for CYP108j1 Expression during PAHs Degradation in Rhodococcus sp. P14
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Indentified Promoter of CYP108J1
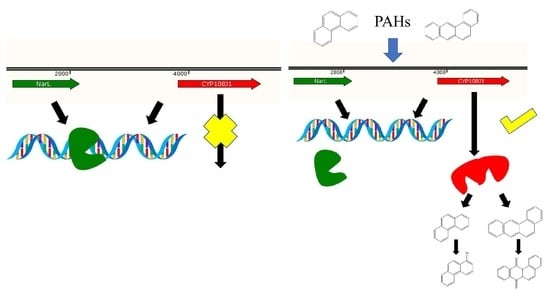
2.2. NarL as a Repressor for Expression of cyp108j1
2.3. NarL Directly Binds to the Promoter of cyp108j1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Bacteria Strains, Plasmids, and Growth Conditions
4.3. Promoter Activity Analysis
4.4. Construction of NarL Mutant
4.5. Purification of NarL
4.6. EMSA
4.7. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, L.; Kaiser, R.I.; Xu, B.; Ablikim, U.; Ahmed, M.; Evseev, M.M.; Bashkirov, E.K.; Azyazov, V.N.; Mebel, A.M. Low-temperature formation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Titan’s atmosphere. Nat. Astron. 2018, 2, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.N.; Kumari, B.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Mishra, S.; Kumar, D. Bacterial degradation of pyrene in minimal salt medium mediated by catechol dioxygenases: Enzyme purification and molecular size determination. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 133, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Jahan, S.A.; Kabir, E.; Brown, R.J. A review of airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their human health effects. Environ. Int. 2013, 60, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charis, P.M.; Cliff, P.; Jennifer, F.; Kay, F.; Olaf, H.; Wan-Mohaiza, D.; William, M.B. Effect of a complex environmental mixture from coal tar containing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) on the tumor initiation, PAH–DNA binding and metabolic activation of carcinogenic PAH in mouse epidermis. Carcinogenesis 2001, 22, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W.; Warshawsky, D. Metabolic activation of polycyclic and heterocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and DNA damage: A review. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 206, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanka, B.; Yves, G.; Pavel, R.J.; Miroslav, D.; Radim, J.S. The effect of dibenzo[a,l]pyrene and benzo[a]pyrene on human diploid lung fibroblasts: The induction of DNA adducts, expression of p53 and p21WAF1 proteins and cell cycle distribution. Mutat. Res. /Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagenes. 2000, 471, 57–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal, D.; Ghosh, S.; Dutta, T.K.; Ahn, Y. Corrigendum: Current State of Knowledge in Microbial Degradation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs): A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haritash, A.K.; Kaushik, C.P. Biodegradation aspects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T.H.; Stefani, F.O.; Abram, K.; Champagne, J.; Yergeau, E.; Hijri, M.; St-Arnaud, M. A Diverse Soil Microbiome Degrades More Crude Oil than Specialized Bacterial Assemblages Obtained in Culture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5530–5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessee, C.T.; Li, Q.X.; Parales, R.E. Effects of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Mixtures on Degradation, Gene Expression, and Metabolite Production in Four Mycobacterium Species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3357–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaly, R.A.; Bartha, R.; Watanabe, K.; Harayama, S. Rapid Mineralization of Benzo[a]pyrene by a Microbial Consortium Growing on Diesel Fuel. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4205–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Song, X.; Kong, J.; Shen, C.; Huang, T.; Hu, Z. Anaerobic biodegradation of high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by a facultative anaerobe Pseudomonas sp. JP1. Biodegradation 2014, 25, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Kweon, O.; Jones, R.C.; Freeman, J.P.; Edmondson, R.D.; Cerniglia, C.E. Complete and integrated pyrene degradation pathway in Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1 based on systems biology. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, M.J.; Kulakov, L.A.; Allen, C.C.R. Biodegradation and Rhodococcus–masters of catabolic versatility. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2005, 16, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, U.; Beyer, M.; Klein, J.; Rehm, H.J. Degradation of pyrene by Rhodococcus sp. UW1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1991, 34, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvaux, S.; Chevalier, F.; Le, D.C.; Fayolle, F.; Miras, I.; Kunst, F.; Beguin, P. Cloning of a genetically unstable cytochrome P-450 gene cluster involved in degradation of the pollutant ethyl tert-butyl ether by Rhodococcus ruber. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 6551–6557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, E.; Prieto, M.A. Bacterial promoters triggering biodegradation of aromatic pollutants. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2000, 11, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, T.; Waki, T.; Nakamura, K.; Mukouzaka, Y.; Kudo, T. The GAF-like-domain-containing transcriptional regulator DfdR is a sensor protein for dibenzofuran and several hydrophobic aromatic compounds. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, T.; Hu, Z. Isolation, characterization of Rhodococcus sp. P14 capable of degrading high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and aliphatic hydrocarbons. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2122–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Wang, H.; Kan, J.; Li, J.; Huang, T.; Xiong, G.; Hu, Z. A novel 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in Rhodococcus sp. P14 for transforming 17beta-estradiol to estrone. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 276, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Peng, T.; Feng, J.; Yang, Q.; Pratush, A.; Xiong, G.; Huang, T.; Hu, Z. A novel dehydrogenase 17beta-HSDx from Rhodococcus sp. P14 with potential application in bioremediation of steroids contaminated environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 362, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, F.; Qiao, J.; Li, G.; Shen, C.; Huang, T.; Hu, Z. Draft genome sequence of Rhodococcus sp. strain P14, a biodegrader of high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, T.; Luo, A.; Kan, J.; Liang, L.; Huang, T.; Hu, Z. Identification of A Ring-Hydroxylating Dioxygenases Capable of Anthracene and Benz[a]anthracene Oxidization from Rhodococcus sp. P14. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, A.; Wu, Y.R.; Xu, Y.; Kan, J.; Qiao, J.; Liang, L.; Huang, T.; Hu, Z. Characterization of a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase capable of high molecular weight PAHs oxidization from Rhodococcus sp. P14. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 2127–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoh, O. Substrate Recognition Sites in Cytochrome P450 Family 2 (CYPB) Proteins Inferred from Comparative Analyses of Amino Acid and Coding Nucleotide Sequences. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Nebert, D.W.; Russell, D.W. Clinical importance of the cytochromes P450. Lancet. 2002, 360, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannemann, F.; Bichet, A.; Ewen, K.M.; Bernhardt, R. Cytochrome P450 systems--biological variations of electron transport chains. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1770, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, R. Cytochromes P450 as versatile biocatalysts. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 124, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, K.J.; Sabri, M.; Marshall, K.R.; Lawson, R.J.; Lewis, D.G.; Clift, D.; Balding, P.R.; Dunford, A.J.; Warman, A.J.; McVey, J.P.; et al. Biodiversity of cytochrome P450 redox systems. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005, 33, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.G.; Yang, W.; Yorke, J.A.; Zhou, W.; Wang, H.; Harmer, J.; Copley, R.; Zhang, A.; Zhou, R.; Bartlam, M.; et al. Structure and function of CYP108D1 from Novosphingobium aromaticivorans DSM12444: An aromatic hydrocarbon-binding P450 enzyme. Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 2012, 68, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putkaradze, N.; Litzenburger, M.; Abdulmughni, A.; Milhim, M.; Brill, E.; Hannemann, F.; Bernhardt, R. CYP109E1 is a novel versatile statin and terpene oxidase from Bacillus megaterium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 8379–8393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Wu, Z.L. Construction and functional analysis of a whole-cell biocatalyst based on CYP108N7. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2017, 106, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Campbell, A.; Karlin, S. Correlations between Shine-Dalgarno Sequences and Gene Features Such as Predicted Expression Levels and Operon Structures. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 5733–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.L.; Nie, Y.; Wang, M.; Xiong, G.; Wang, Y.P.; Maser, E.; Wu, X.L. Regulation of alkane degradation pathway by a TetR family repressor via an autoregulation positive feedback mechanism in a Gram-positive Dietzia bacterium. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 99, 338–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantini, A.; Maître, A.; Lefèbvre, E.; Marques, M.; Rajhi, A.; Douki, T. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in binary mixtures modulate the efficiency of benzo[a]pyrene to form DNA adducts in human cells. Toxicology 2011, 279, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Xu, J.; Kong, D.; Li, Y. iTRAQ-based comparative proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins in Rhodococcus sp. BAP-1 induced by fluoranthene. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, D.L. Quorum sensing in vibrios: Complexity for diversification. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 296, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q. Phosphorylation of PppA at threonine 253 controls T6SS2 expression and bacterial killing capacity in the marine pathogen Vibrio alginolyticus. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 209, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, S.H.M.B.; Edwards, J.; Rosser, S.J.; Rathbone, D.A.; Bruce, N.C. The Explosive-Degrading Cytochrome P450 System Is Highly Conserved among Strains of Rhodococcus spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 4550–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, M.L. GraphPad Prism, Data Analysis, and Scientific Graphing. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1997, 37, 411–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellman, L.M.; Fried, M.G. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) for detecting protein-nucleic acid interactions. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1849–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Thomas, D.S. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kan, J.; Peng, T.; Huang, T.; Xiong, G.; Hu, Z. NarL, a Novel Repressor for CYP108j1 Expression during PAHs Degradation in Rhodococcus sp. P14. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030983
Kan J, Peng T, Huang T, Xiong G, Hu Z. NarL, a Novel Repressor for CYP108j1 Expression during PAHs Degradation in Rhodococcus sp. P14. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(3):983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030983
Chicago/Turabian StyleKan, Jie, Tao Peng, Tongwang Huang, Guangming Xiong, and Zhong Hu. 2020. "NarL, a Novel Repressor for CYP108j1 Expression during PAHs Degradation in Rhodococcus sp. P14" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 3: 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030983
APA StyleKan, J., Peng, T., Huang, T., Xiong, G., & Hu, Z. (2020). NarL, a Novel Repressor for CYP108j1 Expression during PAHs Degradation in Rhodococcus sp. P14. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030983