Regulation of AQP4 in the Central Nervous System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Translational Regulation of AQP4
3. Phosphorylation Driven Regulation of AQP4
4. Metal Ion Mediated Regulation of AQP4
5. Regulation of AQP4 via Small Molecule Inhibitors
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIA | Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis |
| AQP | Aquaporin |
| AQP4 | Aquaporin-4 |
| ASA | Acetylsulfanilamide |
| AZA | Acetazolamide |
| CaMKII | Calcium dependent protein kinase II |
| CII | Cerebral Ischemic Injury |
| CKII | Casein Kinase II |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| COII | Type-II Collagen |
| Cu2+ | Copper |
| CuCl2 | Copper Chloride |
| Cx43 | Connexin 43 |
| 1,2-DCE | 1,2-dichloroethane |
| DFO | Deferoxamine |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-Related Kinase |
| EZA | 6-Ethoxybenzothiazole-2-sulfonamide |
| Fe2+ | Ferrous Iron |
| FRT | Fischer Rat Thyroid |
| GFAP | Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein |
| GFP | Green Fluorescent Protein |
| hAQP4 | Human Aquaporin 4 |
| Hg2+ | Mercury |
| IC50 | Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration |
| ICH | Intracerebral Hemorrhage |
| kg | Kilogram |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| mAQP4 | Mouse Aquaporin 4 |
| MeHg | Methylmercury |
| mg | Milligram |
| miRNA | Micro Ribonucleic Acid |
| mM | Millimolar |
| mRNA | Messenger Ribonucleic Acid |
| NF- κB | Nuclear Factor κB |
| NMO | Neuromyelitis Optica |
| Pf | Osmotic Water Permeability |
| PKA | Protein Kinase A |
| PKC | Protein Kinase C |
| rAQP4 | Rat Aquaporin 4 |
| siRNA | Small Interfering Ribonucleic Acid |
| TBI | Traumatic Brain Injury |
| TEA | Tetraethylammonium |
| TGN-020 | 2-(Nicotinamide)-1,3,4-thiadiazole |
| TLE | Temporal Lobe Epilepsy |
| ZnCl2 | Zinc Chloride |
| μM | Micromolar |
References
- Verkman, A.S.; Anderson, M.O.; Papadopoulos, M.C. Aquaporins: Important but elusive drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abir-Awan, M.; Kitchen, P.; Salman, M.; Conner, M.; Conner, A.; Bill, R. Inhibitors of Mammalian Aquaporin Water Channels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assentoft, M.; Larsen, B.R.; MacAulay, N. Regulation and Function of AQP4 in the Central Nervous System. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 2615–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, H.; Ma, T.; Skach, W.; Matthay, M.A.; Verkman, A.S. Molecular cloning of a mercurial-insensitive water channel expressed in selected water-transporting tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 5497–5500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verkman, A.S.; Smith, A.J.; Phuan, P.; Tradtrantip, L.; Anderson, M.O. The aquaporin-4 water channel as a potential drug target in neurological disorders. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 21, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.; Nagelhus, E.A.; Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Bourque, C.; Agre, P.; Ottersen, O.P. Specialized membrane domains for water transport in glial cells: High-resolution immunogold cytochemistry of aquaporin-4 in rat brain. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manley, G.T.; Fujimura, M.; Ma, T.; Noshita, N.; Filiz, F.; Bollen, A.W.; Chan, P.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces brain edema after acute water intoxication and ischemic stroke. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.C.; Zhang, H.; Zador, Z.; Verkman, A.S. Impaired olfaction in mice lacking aquaporin-4 water channels. FAESB J. 2008, 22, 3216–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Patil, R.V.; Verkman, A.S. Mildly Abnormal Retinal Function in Transgenic Mice without Müller Cell Aquaporin-4 Water Channels. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 573–579. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Verkman, A.S. Impaired Hearing in Mice Lacking Aquaporin-4 Water Channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 31233–31237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagelhus, E.A.; Mathiisen, T.M.; Ottersen, O.P. Aquaporin-4 in the central nervous system: Cellular and subcellular distribution and coexpression with KIR4.1. Neuroscience 2004, 129, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warth, A.; Mittelbronn, M.; Wolburg, H. Redistribution of the water channel protein aquaporin-4 and the K+ channel protein Kir4.1 differs in low- and high-grade human brain tumors. Acta Neuropathol. 2005, 109, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-4 independent Kir4.1 K+ channel function in brain glial cells. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2008, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, D.K.; Yao, X.; Zador, Z.; Sick, T.J.; Verkman, A.S.; Manley, G.T. Increased seizure duration and slowed potassium kinetics in mice lacking aquaporin-4 water channels. Glia 2006, 53, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, M.C.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-4 and brain edema. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2007, 22, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Yang, G.-Y. Aquaporin-4: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Cerebral Edema. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, H.; Huber, V.J.; Tsujita, M.; Nakada, T. Pretreatment with a novel aquaporin 4 inhibitor, TGN-020, significantly reduces ischemic cerebral edema. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 32, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Nishigami, C.; Irie, K.; Shigemori, Y.; Sano, K.; Yamashita, Y.; Myose, T.; Tominaga, K.; Matsuo, K.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. Goreisan Prevents Brain Edema after Cerebral Ischemic Stroke by Inhibiting Aquaporin 4 Upregulation in Mice. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tradtrantip, L.; Jin, B.-J.; Yao, X.; Anderson, M.O.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-Targeted Therapeutics: State-of-the-Field. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 969, 239–250. [Google Scholar]
- Maugeri, R.; Schiera, G.; Di Liegro, C.M.; Fricano, A.; Iacopino, D.G.; Di Liegro, I. Aquaporins and Brain Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadoun, S.; Papadopoulos, M.; Davies, D.; Krishna, S.; Bell, B. Aquaporin-4 expression is increased in oedematous human brain tumours. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 72, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolburg, H.; Noell, S.; Fallier-Becker, P.; Mack, A.F.; Wolburg-Buchholz, K. The disturbed blood–brain barrier in human glioblastoma. Mol. Asp. Med. 2012, 33, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, T.; Ma, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Ying, G.; Fu, L.; Gu, F. Role of aquaporin-4 in the regulation of migration and invasion of human glioma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 38, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ding, T.; Gu, F.; Fu, L.; Ma, Y.-J. Aquaporin-4 in glioma invasion and an analysis of molecular mechanisms. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2010, 17, 1359–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, L.; Pisani, F.; Mola, M.G.; De Bellis, M.; Merla, G.; Micale, L.; Frigeri, A.; Vescovi, A.L.; Svelto, M.; Nicchia, G.P. AQP4 Aggregation State Is a Determinant for Glioma Cell Fate. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 2182–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, K.; Jiang, W.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Tian, C.; Li, Z.; Ying, G.; Fu, L.; et al. Knockdown a Water Channel Protein, Aquaporin-4, Induced Glioblastoma Cell Apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.J.; Jin, B.-J.; Ratelade, J.; Verkman, A.S. Aggregation state determines the localization and function of M1– and M23–aquaporin-4 in astrocytes. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 204, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, J.W.; Asher, R.A. The glial scar and central nervous system repair. Brain Res. Bull. 1999, 49, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.M.; Sheilabi, M.A.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Kitchen, P.; Conner, A.C.; Bill, R.M.; Woodroofe, M.N.; Conner, M.T.; Princivalle, A.P. Transcriptome analysis suggests a role for the differential expression of cerebral aquaporins and the MAPK signalling pathway in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2017, 46, 2121–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvestad, S.; Hammer, J.; Hoddevik, E.H.; Skare, Ø.; Sonnewald, U.; Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Ottersen, O.P. Mislocalization of AQP4 precedes chronic seizures in the kainate model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2013, 105, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, T.; Lee, T.-S.W.; Thomas, M.J.; Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Bjørnsen, L.P.; Spencer, D.D.; Agre, P.; Ottersen, O.P.; de Lanerolle, N.C. Loss of perivascular aquaporin 4 may underlie deficient water and K+ homeostasis in the human epileptogenic hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarius, S.; Wildemann, B. AQP4 antibodies in neuromyelitis optica: Diagnostic and pathogenetic relevance. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mader, S.; Lutterotti, A.; Pauli, F.D.; Kuenz, B.; Schanda, K.; Aboul-Enein, F.; Khalil, M.; Storch, M.K.; Jarius, S.; Kristoferitsch, W.; et al. Patterns of Antibody Binding to Aquaporin-4 Isoforms in Neuromyelitis Optica. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, M.C.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin 4 and neuromyelitis optica. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingerchuk, D.; Banwell, B.; Bennett, J.; Cabre, P.; Carroll, W.; Chitnis, T.; Seze, J.D.; Fujihara, K.; Greenberg, B.; Jacob, A.; et al. Revised Diagnostic Criteria for Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders (S63.001). Neurology 2014, 82, S63.001. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Shimizu, K.; Ugawa, Y.; Nishizawa, M.; Takahashi, H.; Kakita, A. Characteristics of aquaporin expression surrounding senile plaques and cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Alzheimer disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 71, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Y.-L.; Zhao, J.; Ma, T.; Li, S. The Potential Roles of Aquaporin 4 in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 5300–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Kwee, I.L.; Nakada, T. Water influx into cerebrospinal fluid is significantly reduced in senile plaque bearing transgenic mice, supporting beta-amyloid clearance hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol. Res. 2014, 36, 1094–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, L.; Lill, C.M.; Tanzi, R.E. The genetics of Alzheimer disease: Back to the future. Neuron 2010, 68, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohschein, S.; Hüttmann, K.; Gabriel, S.; Binder, D.K.; Heinemann, U.; Steinhäuser, C. Impact of aquaporin-4 channels on K+ buffering and gap junction coupling in the hippocampus. Glia 2011, 59, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitvitsky, V.M.; Garg, S.K.; Keep, R.F.; Albin, R.L.; Banerjee, R. Na+ and K+ ion imbalances in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2012, 1822, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-K.; Wang, F.; Wang, W.; Luo, Y.; Wu, P.-F.; Xiao, J.-L.; Hu, Z.-L.; Jin, Y.; Hu, G.; Chen, J.-G. Aquaporin-4 Deficiency Impairs Synaptic Plasticity and Associative Fear Memory in the Lateral Amygdala: Involvement of Downregulation of Glutamate Transporter-1 Expression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1867–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.-N.; Sun, X.-L.; Gao, L.; Fan, Y.; Ding, J.-H.; Hu, G. Aquaporin-4 deficiency down-regulates glutamate uptake and GLT-1 expression in astrocytes. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2007, 34, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.; da Silva, I.V.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Castro, R.E.; Soveral, G. The Emerging Role of microRNAs in Aquaporin Regulation. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushati, N.; Cohen, S.M. microRNA Functions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007, 23, 175–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Hagedorn, C.H.; Cullen, B.R. Human microRNAs are processed from capped, polyadenylated transcripts that can also function as mRNAs. RNA 2004, 10, 1957–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-K.; Kim, V.N. Processing of intronic microRNAs. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jullienne, A.; Fukuda, A.M.; Ichkova, A.; Nishiyama, N.; Aussudre, J.; Obenaus, A.; Badaut, J. Modulating the water channel AQP4 alters miRNA expression, astrocyte connectivity and water diffusion in the rodent brain. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Ma, Y.; Tang, G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, L.; Wang, Y.; Ouyang, Y.-B.; et al. MicroRNA-29b is a therapeutic target in cerebral ischemia associated with aquaporin 4. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Liang, B.; Hu, M.; Liu, J.; Lin, L.; Jiang, J.; Lin, X.; Huang, Y.; Lu, L.; Jiang, L.; et al. MicroRNA-29b-3p aggravates 1,2-dichloroethane-induced brain edema by targeting aquaporin 4 in Sprague-Dawley rats and CD-1 mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 319, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Cheng, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Pan, C. Overexpression of MicroRNA-145 Ameliorates Astrocyte Injury by Targeting Aquaporin 4 in Cerebral Ischemic Stroke. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepramaniam, S.; Armugam, A.; Lim, K.Y.; Karolina, D.S.; Swaminathan, P.; Tan, J.R.; Jeyaseelan, K. MicroRNA 320a Functions as a Novel Endogenous Modulator of Aquaporins 1 and 4 as Well as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Cerebral Ischemia. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 29223–29230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Ran, J.; Jiang, R.; Guo, P.; Shi, X.; Li, H.; Lv, X.; Li, J.; Chen, D. miRNA-320a inhibits glioma cell invasion and migration by directly targeting aquaporin 4. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 1939–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepramaniam, S.; Ying, L.K.; Armugam, A.; Wintour, E.M.; Jeyaseelan, K. MicroRNA-130a Represses Transcriptional Activity of Aquaporin 4 M1 Promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 12006–12015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, M.; Pei, A.; Xie, L.; Zhu, S. Upregulation of miR-130b protects against cerebral ischemic injury by targeting water channel protein aquaporin 4 (AQP4). Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 3452–3461. [Google Scholar]
- Nesverova, V.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S. Phosphorylation-Dependent Regulation of Mammalian Aquaporins. Cells 2019, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P. The origins of protein phosphorylation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, E127–E130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmosino, M.; Procino, G.; Tamma, G.; Mannucci, R.; Svelto, M.; Valenti, G. Trafficking and phosphorylation dynamics of AQP4 in histamine-treated human gastric cells. Biol. Cell 2007, 99, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadohira, I.; Abe, Y.; Nuriya, M.; Sano, K.; Tsuji, S.; Arimitsu, T.; Yoshimura, Y.; Yasui, M. Phosphorylation in the C-terminal domain of Aquaporin-4 is required for Golgi transition in primary cultured astrocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 377, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Wax, M.B.; Patil, R.V. Regulation of Aquaporin-4 Water Channels by Phorbol Ester-dependent Protein Phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 6001–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assentoft, M.; Kaptan, S.; Fenton, R.A.; Hua, S.Z.; de Groot, B.L.; MacAulay, N. Phosphorylation of rat aquaporin-4 at Ser 111 is not required for channel gating: No Phosphorylation-Dependent Gating of AQP4. Glia 2013, 61, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundby, A.; Secher, A.; Lage, K.; Nordsborg, N.B.; Dmytriyev, A.; Lundby, C.; Olsen, J.V. Quantitative maps of protein phosphorylation sites across 14 different rat organs and tissues. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazzina, G.; Amorini, A.M.; Marmarou, C.R.; Fukui, S.; Okuno, K.; Dunbar, J.G.; Glisson, R.; Marmarou, A.; Kleindienst, A. The Protein Kinase C Activator Phorbol Myristate Acetate Decreases Brain Edema by Aquaporin 4 Downregulation after Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in the Rat. J. Neurotrauma 2009, 27, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, H.B.; Fenton, R.A.; Zeuthen, T.; MacAulay, N. Vasopressin-dependent short-term regulation of aquaporin 4 expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Neuroscience 2009, 164, 1674–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, E.S.; Haas, B.R.; Sontheimer, H. Water permeability through aquaporin-4 is regulated by protein kinase C and becomes rate-limiting for glioma invasion. Neuroscience 2010, 168, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchen, P.; Day, R.E.; Taylor, L.H.J.; Salman, M.M.; Bill, R.M.; Conner, M.T.; Conner, A.C. Identification and Molecular Mechanisms of the Rapid Tonicity-induced Relocalization of the Aquaporin 4 Channel. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 16873–16881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnarson, E.; Zelenina, M.; Axehult, G.; Song, Y.; Bondar, A.; Krieger, P.; Brismar, H.; Zelenin, S.; Aperia, A. Identification of a molecular target for glutamate regulation of astrocyte water permeability. Glia 2008, 56, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Gunnarson, E. Potassium Dependent Regulation of Astrocyte Water Permeability Is Mediated by cAMP Signaling. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarson, E.; Axehult, G.; Baturina, G.; Zelenin, S.; Zelenina, M.; Aperia, A. Lead induces increased water permeability in astrocytes expressing aquaporin 4. Neuroscience 2005, 136, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelenina, M.; Zelenin, S.; Bondar, A.A.; Brismar, H.; Aperia, A. Water permeability of aquaporin-4 is decreased by protein kinase C and dopamine. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2002, 283, F309–F318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, T.L.; Brooks, H.L.; Boassa, D.; Leonov, S.; Yanochko, G.M.; Regan, J.W.; Yool, A.J. Cloned Human Aquaporin-1 Is a Cyclic GMP-Gated Ion Channel. Mol. Pharm. 2000, 57, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichow, S.L.; Clemens, D.M.; Freites, J.A.; Németh-Cahalan, K.L.; Heyden, M.; Tobias, D.J.; Hall, J.E.; Gonen, T. Allosteric mechanism of water-channel gating by Ca 2+ —calmodulin. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaptan, S.; Assentoft, M.; Schneider, H.P.; Fenton, R.A.; Deitmer, J.W.; MacAulay, N.; de Groot, B.L. H95 Is a pH-Dependent Gate in Aquaporin 4. Structure 2015, 23, 2309–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.D.; Yeh, R.; Sandstrom, A.; Chorny, I.; Harries, W.E.C.; Robbins, R.A.; Miercke, L.J.W.; Stroud, R.M. Crystal structure of human aquaporin 4 at 1.8 Å and its mechanism of conductance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7437–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assentoft, M.; Larsen, B.R.; Olesen, E.T.B.; Fenton, R.A.; MacAulay, N. AQP4 plasma membrane trafficking or channel gating is not significantly modulated by phosphorylation at COOH-terminal serine residues. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2014, 307, C957–C965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ximenes-da-Silva, A. Metal Ion Toxins and Brain Aquaporin-4 Expression: An Overview. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Ottersen, O.P. The molecular basis of water transport in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, M.; Hazama, A.; Kwon, T.-H.; Nielsen, S.; Guggino, W.B.; Agre, P. Rapid gating and anion permeability of an intracellular aquaporin. Nature 1999, 402, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukutake, Y.; Tsuji, S.; Hirano, Y.; Adachi, T.; Takahashi, T.; Fujihara, K.; Agre, P.; Yasui, M.; Suematsu, M. Mercury chloride decreases the water permeability of aquaporin-4-reconstituted proteoliposomes. Biol. Cell 2008, 100, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukutake, Y.; Yasui, M. Regulation of water permeability through aquaporin-4. Neuroscience 2010, 168, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Takeya, M.; Ikeshima-Kataoka, H.; Yasui, M.; Kawasaki, Y.; Shiraishi, M.; Majima, E.; Shiraishi, S.; Uezono, Y.; Sasaki, M.; et al. Increased expression of aquaporin-4 with methylmercury exposure in the brain of the common marmoset. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 37, 749–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yukutake, Y.; Hirano, Y.; Suematsu, M.; Yasui, M. Rapid and Reversible Inhibition of Aquaporin-4 by Zinc. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 12059–12061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, J.; Hayashi, M.K.; Aizu, S.; Yukutake, Y.; Takeda, J.; Yasui, M. A general anaesthetic propofol inhibits aquaporin-4 in the presence of Zn2+. Biochem. J. 2013, 454, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelenina, M.; Tritto, S.; Bondar, A.A.; Zelenin, S.; Aperia, A. Copper Inhibits the Water and Glycerol Permeability of Aquaporin-3. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 51939–51943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, K.V.R.; Jayakumar, A.R.; Reddy, P.V.B.; Tong, X.; Curtis, K.M.; Norenberg, M.D. Aquaporin-4 in manganese-treated cultured astrocytes. Glia 2010, 58, 1490–1499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, B.; Sun, Q.; Yang, G.; Bian, L. Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in ferrous iron-induced aquaporin-4 expression in cultured astrocytes. NeuroToxicology 2019, 73, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, G.; Keep, R.F.; Hoff, J.T. Erythrocytes and delayed brain edema formation following intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 89, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Keep, R.F.; Hoff, J.T.; Xi, G. Thrombin Preconditioning Attenuates Brain Edema Induced by Erythrocytes and Iron. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2003, 23, 1448–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, W.G.; Dong, Y.Q.; Ping, T.Q.; Lai, L.G.; Fang, L.D.; Min, H.W.; Xia, L.; Heng, P.Y. Brain edema after intracerebral hemorrhage in rats: The role of iron overload and aquaporin 4: Laboratory investigation. J. Neurosurg. 2009, 110, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Cui, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Q.; Yang, G.; Bian, L. Curcumin attenuates brain edema in mice with intracerebral hemorrhage through inhibition of AQP4 and AQP9 expression. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2015, 36, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, L.; De Wilde, G.; Van Damme, P.; Vanden Berghe, W.; Haegeman, G. Transcriptional activation of the NF-κB p65 subunit by mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase-1 (MSK1). EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Sun, S.Q.; Lu, W.T.; Xu, J.; Gan, S.W.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, G.P.; Huang, S.Q.; Zhuo, F.; Liu, Q.; et al. The internalization and lysosomal degradation of brain AQP4 after ischemic injury. Brain Res. 2013, 1539, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Mesquita, S.; Louveau, A.; Vaccari, A.; Smirnov, I.; Cornelison, R.C.; Kingsmore, K.M.; Contarino, C.; Onengut-Gumuscu, S.; Farber, E.; Raper, D.; et al. Functional aspects of meningeal lymphatics in ageing and Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2018, 560, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, V.J.; Tsujita, M.; Yamazaki, M.; Sakimura, K.; Nakada, T. Identification of arylsulfonamides as Aquaporin 4 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 1270–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, V.J.; Tsujita, M.; Kwee, I.L.; Nakada, T. Inhibition of Aquaporin 4 by antiepileptic drugs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, V.J.; Tsujita, M.; Nakada, T. Identification of Aquaporin 4 inhibitors using in vitro and in silico methods. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanimura, Y.; Hiroaki, Y.; Fujiyoshi, Y. Acetazolamide reversibly inhibits water conduction by aquaporin-4. J. Struct. Biol. 2009, 166, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, H.; Verkman, A.S. Lack of aquaporin-4 water transport inhibition by antiepileptics and arylsulfonamides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 7489–7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamegawa, A.; Hiroaki, Y.; Tani, K.; Fujiyoshi, Y. Two-dimensional crystal structure of aquaporin-4 bound to the inhibitor acetazolamide. Microscopy 2016, 65, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Glober, N.K.; Sprague, S.; Ahmad, S.; Mayfield, K.G.; Fletcher, L.M.; Digicaylioglu, M.H.; Sayre, N.L. Acetazolamide Treatment Prevents Redistribution of Astrocyte Aquaporin 4 after Murine Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurosci. J. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturdivant, N.M.; Smith, S.G.; Ali, S.F.; Wolchok, J.C.; Balachandran, K. Acetazolamide Mitigates Astrocyte Cellular Edema Following Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Lei, C.; Li, R.; Chen, W.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Li, C. Overexpression of aquaporin 4 in articular chondrocytes exacerbates the severity of adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats: An in vivo and in vitro study. J. Inflamm. 2017, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanotto, C.; Abib, R.T.; Batassini, C.; Tortorelli, L.S.; Biasibetti, R.; Rodrigues, L.; Nardin, P.; Hansen, F.; Gottfried, C.; Leite, M.C.; et al. Non-specific inhibitors of aquaporin-4 stimulate S100B secretion in acute hippocampal slices of rats. Brain Res. 2013, 1491, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, G.; Imitola, J.; Lu, J.; De Filippis, D.; Scuderi, C.; Ganesh, V.S.; Folkerth, R.; Hecht, J.; Shin, S.; Iuvone, T.; et al. Genomic and functional profiling of human Down syndrome neural progenitors implicates S100B and aquaporin 4 in cell injury. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 440–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, H.; Tsujita, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Kwee, I.L.; Nakada, T. Inhibition of aquaporin-4 significantly increases regional cerebral blood flow. NeuroReport 2013, 24, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirici, I.; Balsanu, T.A.; Bogdan, C.; Margaritescu, C.; Divan, T.; Vitalie, V.; Mogoanta, L.; Pirici, D.; Carare, R.O.; Muresanu, D.F. Inhibition of Aquaporin-4 Improves the Outcome of Ischaemic Stroke and Modulates Brain Paravascular Drainage Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| MicroRNA | AQP4 Species | Effect | Role | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-224/miR-19a | Mouse, Rat | Downregulates AQP4 and Cx43 | Astrocyte connectivity and water permeability. | [48] |
| miR-29b | Mouse | Downregulates AQP4 | Reaction to ischemia, reduces infarct volume edema and BBB disruption. Upregulated in response to 1,2-DCE exposure, leading to an induction of brain edema. | [49,50] |
| miRNA-145 | Rat | Downregulates AQP4 | Reaction to ischemia, Attenuates AQP4 induced astrocyte injury. | [51] |
| miRNA-320a | Mouse, Human, Rat | Downregulates AQP4 and AQP1 | Increases infarct volume in ischemic cerebral edema, inhibits glioma cell invasion and migration. | [52,53] |
| miRNA-130a | Human, Rat | Downregulates AQP4 M1 | Increases infarct volume in ischemic cerebral edema. | [54] |
| miRNA-130b | Rat | Downregulates AQP4 | Reaction to ischemia, Attenuates AQP4 induced astrocyte injury. | [55] |
| Compound | Species | In Vitro Effect | In Vivo Effect | Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mercury(Hg2+, MeHg) | Rat, Marmoset | Inhibition of water permeability through AQP4 in proteoliposomes. No effect in oocyte model. | Upregulation of AQP4 expression in reactive astrocytes. | Inhibition mediated via binding at C178 and C253 | [76,79,81] |
| Zinc (ZnCl2) | Rat, Human | Inhibition of water permeability through AQP4 in proteoliposomes, increased in presence of propofol and diamide. | Not applicable. | Inhibition mediated via binding at C178 and C253 | [82,83] |
| Copper (CuCl2) | Rat | Inhibition of water permeability through AQP4 in proteoliposomes. No effect in BEAS-2b cell model. | Not applicable. | Inhibition mediated via binding at C178 | [82] |
| Lead (Pb2+) | Rat | Increase in water permeability through AQP4. | No increase in AQP4 expression. | CaMKII induced phosphorylation of S111 | [69] |
| Manganese (Mn2+) | Rat | Increase in AQP4 expression on plasma membrane without increase in overall protein expression. | Not applicable. | Activation of ERK1/2 and p38-MAPK. | [85] |
| Ferrous Iron (Fe2+) | Mouse, Rat | Increase in AQP4 protein expression. | Increase in AQP4 expression in ICH models. | Both activation of the MAPK pathway and the NF-κB pathway likely contribute to the increased AQP4. | [86,87,88,89,90,91] |
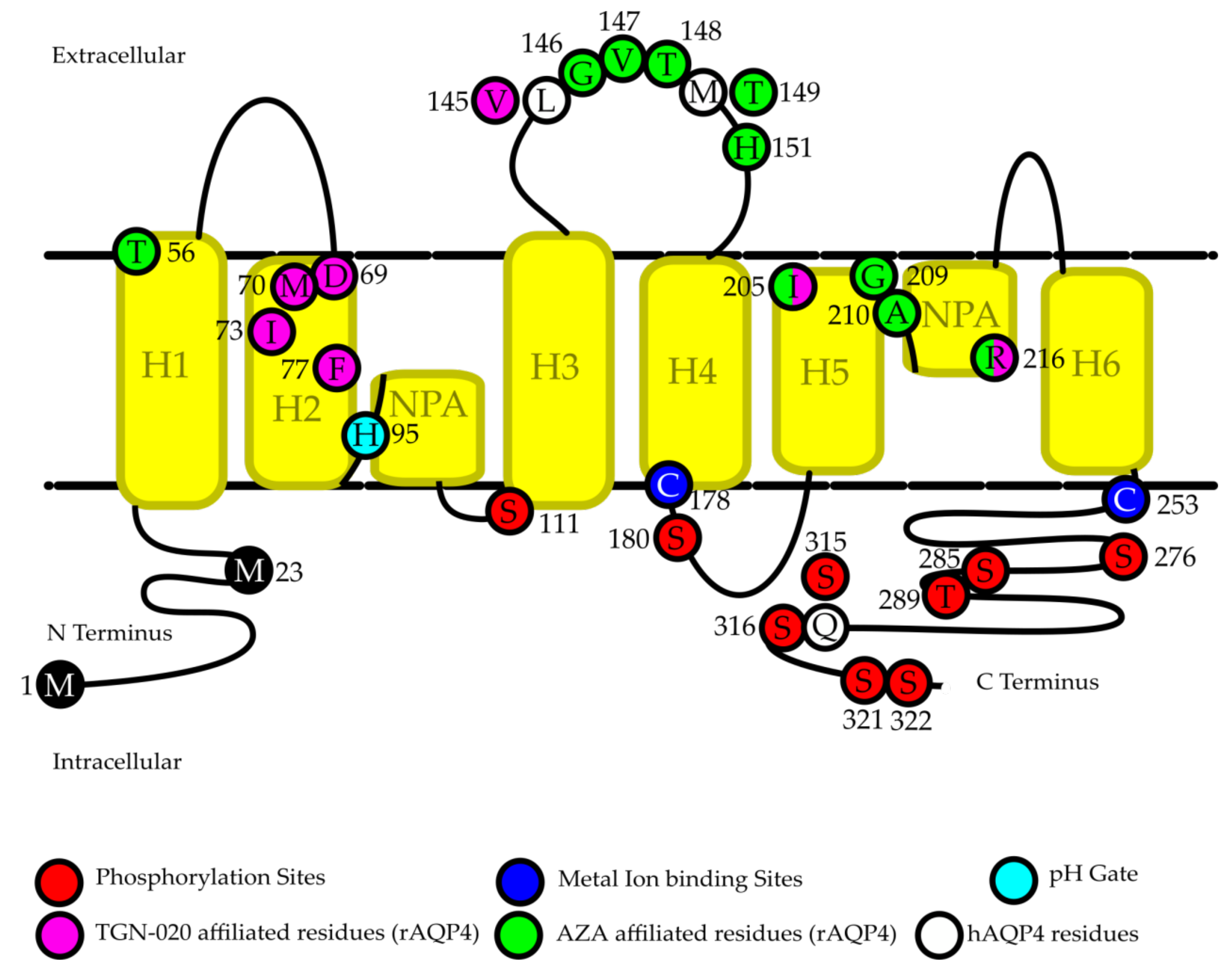
| Acetazolamide | Mouse, Rat, Human | Potent inhibition of hAQP4 in oocytes. Weak inhibition of rAQP4 in proteoliposomes. No inhibition in FRT cell vesicles, mouse glial cells, and mouse erythrocytes. | Protects against edema during TBI. Alleviates AIA symptoms via suppression of AQP4 expression. | Direct binding inhibition likely mediated by binding to T56, G146, V147, T148, T149 (rat)/M149 (human), H151, I205, G209, A210, and R216. Indirect mechanism unidentified. | [94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101] |
| Valporic acid | Rat, Human | Potent inhibition of hAQP4 in oocytes. No inhibition of rAQP4 in proteoliposomes. | Not applicable. | Mechanism unidentified. | [96,97] |
| EZA, Topiramate, Zonisamide, Phenytoin, Lamotrigine, Sumatriptan | Mouse, Rat, Human | Potent inhibition of hAQP4 in oocytes. No inhibition in FRT cell vesicles, mouse glial cells, and mouse erythrocytes. | Not applicable. | Mechanism unidentified. | [94,95,96,98] |
| TGN-020 | Mouse, Rat, Human | Potent inhibition of hAQP4 in oocytes. | AQP4 specific inhibition leading to improved outcomes of ischemic stroke and increased regional blood flow. | Direct binding inhibition likely mediated by binding to D69, M70, I73, F77, V145 (rat)/L145 (human), I205, and R216. | [17,96,105,106] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vandebroek, A.; Yasui, M. Regulation of AQP4 in the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051603
Vandebroek A, Yasui M. Regulation of AQP4 in the Central Nervous System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(5):1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051603
Chicago/Turabian StyleVandebroek, Arno, and Masato Yasui. 2020. "Regulation of AQP4 in the Central Nervous System" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 5: 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051603
APA StyleVandebroek, A., & Yasui, M. (2020). Regulation of AQP4 in the Central Nervous System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(5), 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051603





