Insulin: The Friend and the Foe in the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Insulin and Insulin Signaling
3. Insulin Secretion and Signaling in β-Cells
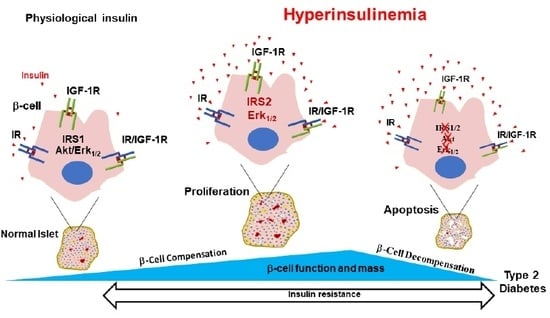
4. Insulin as a Friend: Positive Autocrine Actions
4.1. Positive Actions of Insulin on Insulin Gene Expression and Insulin Secretion
4.2. Positive Actions of Insulin on β-Cell Mass and Survival
5. Insulin as a Foe: Negative Autocrine Actions
5.1. Negative Actions of Insulin on Insulin Gene Expression and Insulin Secretion
5.2. Negative Actions of Insulin on β-Cell Mass and Survival
5.3. Insulin and the Islet Microenvironment
6. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Diabetes, A. Economic Costs of Diabetes in the U.S. in 2017. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kharroubi, A.T.; Darwish, H.M. Diabetes mellitus: The epidemic of the century. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 850–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, A.S. The epidemic of obesity and diabetes: Trends and treatments. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 2011, 38, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ganz, M.L.; Wintfeld, N.; Li, Q.; Alas, V.; Langer, J.; Hammer, M. The association of body mass index with the risk of type 2 diabetes: A case-control study nested in an electronic health records system in the United States. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choquet, H.; Meyre, D. Genetics of Obesity: What have we Learned? Curr. Genom. 2011, 12, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hruby, A.; Hu, F.B. The Epidemiology of Obesity: A Big Picture. Pharmacoeconomics 2015, 33, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, C.H.; Stender-Petersen, K.L.; Mogensen, M.S.; Torekov, S.S.; Wegner, L.; Andersen, G.; Nielsen, A.L.; Albrechtsen, A.; Borch-Johnsen, K.; Rasmussen, S.S.; et al. Low physical activity accentuates the effect of the FTO rs9939609 polymorphism on body fat accumulation. Diabetes 2008, 57, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cleland, S.J.; Fisher, B.M.; Colhoun, H.M.; Sattar, N.; Petrie, J.R. Insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes: What is ’double diabetes’ and what are the risks? Diabetologia 2013, 56, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiasson, J.L.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R. Prevention of type 2 diabetes: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function. Diabetes 2004, 53, S34–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shanik, M.H.; Xu, Y.; Skrha, J.; Dankner, R.; Zick, Y.; Roth, J. Insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia: Is hyperinsulinemia the cart or the horse? Diabetes Care 2008, 31, S262–S268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gherzi, R.; Briata, P. Insulin receptors, mechanism of signal transduction. Examples of abnormalities in states of insulin resistance. Journ Annu. Diabetol Hotel Dieu. 1993, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Treadway, J.L.; Whittaker, J.; Pessin, J.E. Regulation of the insulin receptor kinase by hyperinsulinism. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 15136–15143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rui, L.; Fisher, T.L.; Thomas, J.; White, M.F. Regulation of insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling by proteasome-mediated degradation of insulin receptor substrate-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 40362–40367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pederson, T.M.; Kramer, D.L.; Rondinone, C.M. Serine/threonine phosphorylation of IRS-1 triggers its degradation: Possible regulation by tyrosine phosphorylation. Diabetes 2001, 50, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mothe, I.; Van Obberghen, E. Phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 on multiple serine residues, 612, 632, 662, and 731, modulates insulin action. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 11222–11227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scioscia, M.; Gumaa, K.; Kunjara, S.; Paine, M.A.; Selvaggi, L.E.; Rodeck, C.H.; Rademacher, T.W. Insulin resistance in human preeclamptic placenta is mediated by serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 and -2. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, M.J.; Longacre, M.J.; Langberg, E.C.; Tibell, A.; Kendrick, M.A.; Fukao, T.; Ostenson, C.G. Decreased levels of metabolic enzymes in pancreatic islets of patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, E.; Mohammed Al-Amily, I.; Mohammed, S.; Luan, C.; Asplund, O.; Ahmed, M.; Ye, Y.; Ben-Hail, D.; Soni, A.; Vishnu, N.; et al. Preserving Insulin Secretion in Diabetes by Inhibiting VDAC1 Overexpression and Surface Translocation in beta Cells. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T.; Liew, C.W.; Hu, J.; Hinault, C.; Michael, M.D.; Krtzfeldt, J.; Yin, C.; Holzenberger, M.; Stoffel, M.; Kulkarni, R.N. Insulin receptors in beta-cells are critical for islet compensatory growth response to insulin resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8977–8982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitamura, T.; Nakae, J.; Kitamura, Y.; Kido, Y.; Biggs, W.H., 3rd; Wright, C.V.; White, M.F.; Arden, K.C.; Accili, D. The forkhead transcription factor Foxo1 links insulin signaling to Pdx1 regulation of pancreatic beta cell growth. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Movassat, J.; Saulnier, C.; Portha, B. Insulin administration enhances growth of the beta-cell mass in streptozotocin-treated newborn rats. Diabetes 1997, 46, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillen, C.; Bartolome, A.; Nevado, C.; Benito, M. Biphasic effect of insulin on beta cell apoptosis depending on glucose deprivation. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 3855–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bucris, E.; Beck, A.; Boura-Halfon, S.; Isaac, R.; Vinik, Y.; Rosenzweig, T.; Sampson, S.R.; Zick, Y. Prolonged insulin treatment sensitizes apoptosis pathways in pancreatic beta cells. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 230, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachdaoui, N.; Polo-Parada, L.; Ismail-Beigi, F. Prolonged Exposure to Insulin Inactivates Akt and Erk1/2 and Increases Pancreatic Islet and INS1E beta-Cell Apoptosis. J. Endocr. Soc. 2019, 3, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schroder, D.; Zuhlke, H. Gene technology, characterization of insulin gene and the relationship to diabetes research. Endokrinologie 1982, 79, 197–209. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Weiss, M.A.; Arunagiri, A.; Yong, J.; Rege, N.; Sun, J.; Haataja, L.; Kaufman, R.J.; Arvan, P. Biosynthesis, structure, and folding of the insulin precursor protein. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 28–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, G.; Steiner, D. The role of assembly in insulin’s biosynthesis. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1998, 8, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combettes-Souverain, M.; Issad, T. Molecular basis of insulin action. Diabetes Metab. 1998, 24, 477–489. [Google Scholar]
- De Meyts, P. Insulin and its receptor: Structure, function and evolution. Bioessays 2004, 26, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 2010, 141, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seino, S.; Seino, M.; Nishi, S.; Bell, G.I. Structure of the human insulin receptor gene and characterization of its promoter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ebina, Y.; Ellis, L.; Jarnagin, K.; Edery, M.; Graf, L.; Clauser, E.; Ou, J.H.; Masiarz, F.; Kan, Y.W.; Goldfine, I.D.; et al. The human insulin receptor cDNA: The structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell 1985, 40, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullrich, A.; Bell, J.R.; Chen, E.Y.; Herrera, R.; Petruzzelli, L.M.; Dull, T.J.; Gray, A.; Coussens, L.; Liao, Y.C.; Tsubokawa, M.; et al. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. Nature 1985, 313, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denley, A.; Cosgrove, L.J.; Booker, G.W.; Wallace, J.C.; Forbes, B.E. Molecular interactions of the IGF system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005, 16, 421–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belfiore, A.; Frasca, F.; Pandini, G.; Sciacca, L.; Vigneri, R. Insulin receptor isoforms and insulin receptor/insulin-like growth factor receptor hybrids in physiology and disease. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 586–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Meyts, P.; Wallach, B.; Christoffersen, C.T.; Urso, B.; Gronskov, K.; Latus, L.J.; Yakushiji, F.; Ilondo, M.M.; Shymko, R.M. The insulin-like growth factor-I receptor. Structure, ligand-binding mechanism and signal transduction. Horm. Res. 1994, 42, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyoucef, S.; Surinya, K.H.; Hadaschik, D.; Siddle, K. Characterization of insulin/IGF hybrid receptors: Contributions of the insulin receptor L2 and Fn1 domains and the alternatively spliced exon 11 sequence to ligand binding and receptor activation. Biochem. J. 2007, 403, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blakesley, V.A.; Scrimgeour, A.; Esposito, D.; Le Roith, D. Signaling via the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor: Does it differ from insulin receptor signaling? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1996, 7, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soos, M.A.; Field, C.E.; Siddle, K. Purified hybrid insulin/insulin-like growth factor-I receptors bind insulin-like growth factor-I, but not insulin, with high affinity. Biochem. J. 1993, 290, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boucher, J.; Softic, S.; El Ouaamari, A.; Krumpoch, M.T.; Kleinridders, A.; Kulkarni, R.N.; O’Neill, B.T.; Kahn, C.R. Differential Roles of Insulin and IGF-1 Receptors in Adipose Tissue Development and Function. Diabetes 2016, 65, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Federici, M.; Porzio, O.; Zucaro, L.; Fusco, A.; Borboni, P.; Lauro, D.; Sesti, G. Distribution of insulin/insulin-like growth factor-I hybrid receptors in human tissues. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1997, 129, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, H.A.; Edwall, D.; Lowenadler, B.; Norstedt, G.; Paleus, S.; Kottner, A. Somatomedin C in the pancreas of young and adult, normal and obese, hyperinsulinemic mice. Cell Tissue Res. 1989, 255, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, J.L.; Porte, D., Jr.; Stahl, W.L.; Baskin, D.G. Localization of insulin receptor mRNA in rat brain by in situ hybridization. Endocrinology 1990, 127, 3234–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinridders, A. Deciphering Brain Insulin Receptor and Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Receptor Signalling. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2016, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyts, P. The insulin receptor: A prototype for dimeric, allosteric membrane receptors? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008, 33, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyts, P.; Roth, J.; Neville, D.M., Jr.; Gavin, J.R., 3rd; Lesniak, M.A. Insulin interactions with its receptors: Experimental evidence for negative cooperativity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1973, 55, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyts, P. The structural basis of insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I receptor binding and negative co-operativity, and its relevance to mitogenic versus metabolic signalling. Diabetologia 1994, 37, S135–S148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Whittaker, L.; Whittaker, J. Characterization of a second ligand binding site of the insulin receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 347, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyts, P.; Whittaker, J. Structural biology of insulin and IGF1 receptors: Implications for drug design. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2002, 1, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, S.R. The insulin receptor: Both a prototypical and atypical receptor tyrosine kinase. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Kleinridders, A.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shepherd, P.R.; Withers, D.J.; Siddle, K. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase: The key switch mechanism in insulin signalling. Biochem. J. 1998, 333, 471–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taniguchi, C.M.; Emanuelli, B.; Kahn, C.R. Critical nodes in signalling pathways: Insights into insulin action. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matschinsky, F.M. Regulation of pancreatic beta-cell glucokinase: From basics to therapeutics. Diabetes 2002, 51, S394–S404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matschinsky, F.M. Glucokinase as glucose sensor and metabolic signal generator in pancreatic beta-cells and hepatocytes. Diabetes 1990, 39, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meglasson, M.D.; Matschinsky, F.M. Pancreatic islet glucose metabolism and regulation of insulin secretion. Diabetes Metab. Rev. 1986, 2, 163–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newgard, C.B.; McGarry, J.D. Metabolic coupling factors in pancreatic beta-cell signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1995, 64, 689–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poitout, V.; Hagman, D.; Stein, R.; Artner, I.; Robertson, R.P.; Harmon, J.S. Regulation of the insulin gene by glucose and fatty acids. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Gilbert, E.R.; Liu, D. Regulation of insulin synthesis and secretion and pancreatic Beta-cell dysfunction in diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2013, 9, 25–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efrat, S.; Surana, M.; Fleischer, N. Glucose induces insulin gene transcription in a murine pancreatic beta-cell line. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 11141–11143. [Google Scholar]
- Leibiger, B.; Moede, T.; Schwarz, T.; Brown, G.R.; Kohler, M.; Leibiger, I.B.; Berggren, P.O. Short-term regulation of insulin gene transcription by glucose. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9307–9312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leibiger, B.; Wahlander, K.; Berggren, P.O.; Leibiger, I.B. Glucose-stimulated insulin biosynthesis depends on insulin-stimulated insulin gene transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 30153–30156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gavin, J.R., 3rd; Roth, J.; Neville, D.M., Jr.; de Meyts, P.; Buell, D.N. Insulin-dependent regulation of insulin receptor concentrations: A direct demonstration in cell culture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blackard, W.G.; Guzelian, P.S.; Small, M.E. Down regulation of insulin receptors in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes in monolayer. Endocrinology 1978, 103, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasuga, M.; Kahn, C.R.; Hedo, J.A.; Van Obberghen, E.; Yamada, K.M. Insulin-induced receptor loss in cultured human lymphocytes is due to accelerated receptor degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 6917–6921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, Y.C.; Amherdt, M.; Orci, L. Quantitative electron microscopic autoradiography of insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin binding sites on islets. Science 1982, 217, 1155–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verspohl, E.J.; Ammon, H.P. Evidence for presence of insulin receptors in rat islets of Langerhans. J. Clin. Investig. 1980, 65, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbeck, M.C.; Louie, D.C.; Howland, J.; Wolf, B.A.; Rothenberg, P.L. Expression of insulin receptor mRNA and insulin receptor substrate 1 in pancreatic islet beta-cells. Diabetes 1996, 45, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, D.; Huang, G.C.; Amiel, S.; Jones, P.M.; Persaud, S.J. Identification of insulin signaling elements in human beta-cells: Autocrine regulation of insulin gene expression. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2835–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernal-Mizrachi, E.; Fatrai, S.; Johnson, J.D.; Ohsugi, M.; Otani, K.; Han, Z.; Polonsky, K.S.; Permutt, M.A. Defective insulin secretion and increased susceptibility to experimental diabetes are induced by reduced Akt activity in pancreatic islet beta cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rothenberg, P.L.; Willison, L.D.; Simon, J.; Wolf, B.A. Glucose-induced insulin receptor tyrosine phosphorylation in insulin-secreting beta-cells. Diabetes 1995, 44, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velloso, L.A.; Carneiro, E.M.; Crepaldi, S.C.; Boschero, A.C.; Saad, M.J. Glucose- and insulin-induced phosphorylation of the insulin receptor and its primary substrates IRS-1 and IRS-2 in rat pancreatic islets. FEBS Lett. 1995, 377, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, G.G.; Rothenberg, P.L. Insulin receptor signaling in the beta-cell influences insulin gene expression and insulin content: Evidence for autocrine beta-cell regulation. Diabetes 1998, 47, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, R.N. New insights into the roles of insulin/IGF-I in the development and maintenance of beta-cell mass. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2005, 6, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, R.N.; Bruning, J.C.; Winnay, J.N.; Postic, C.; Magnuson, M.A.; Kahn, C.R. Tissue-specific knockout of the insulin receptor in pancreatic beta cells creates an insulin secretory defect similar to that in type 2 diabetes. Cell 1999, 96, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulkarni, R.N.; Roper, M.G.; Dahlgren, G.; Shih, D.Q.; Kauri, L.M.; Peters, J.L.; Stoffel, M.; Kennedy, R.T. Islet secretory defect in insulin receptor substrate 1 null mice is linked with reduced calcium signaling and expression of sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA)-2b and -3. Diabetes 2004, 53, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Withers, D.J.; Gutierrez, J.S.; Towery, H.; Burks, D.J.; Ren, J.M.; Previs, S.; Zhang, Y.; Bernal, D.; Pons, S.; Shulman, G.I.; et al. Disruption of IRS-2 causes type 2 diabetes in mice. Nature 1998, 391, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, N.; Tobe, K.; Terauchi, Y.; Eto, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Suzuki, R.; Tsubamoto, Y.; Komeda, K.; Nakano, R.; Miki, H.; et al. Disruption of insulin receptor substrate 2 causes type 2 diabetes because of liver insulin resistance and lack of compensatory beta-cell hyperplasia. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1880–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, M.F. Regulating insulin signaling and beta-cell function through IRS proteins. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2006, 84, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibiger, B.; Leibiger, I.B.; Moede, T.; Kemper, S.; Kulkarni, R.N.; Kahn, C.R.; de Vargas, L.M.; Berggren, P.O. Selective insulin signaling through A and B insulin receptors regulates transcription of insulin and glucokinase genes in pancreatic beta cells. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibiger, B.; Moede, T.; Uhles, S.; Berggren, P.O.; Leibiger, I.B. Short-term regulation of insulin gene transcription. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2002, 30, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva Xavier, G.; Varadi, A.; Ainscow, E.K.; Rutter, G.A. Regulation of gene expression by glucose in pancreatic beta -cells (MIN6) via insulin secretion and activation of phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 36269–36277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leibiger, I.B.; Leibiger, B.; Moede, T.; Berggren, P.O. Exocytosis of insulin promotes insulin gene transcription via the insulin receptor/PI-3 kinase/p70 s6 kinase and CaM kinase pathways. Mol. Cell. 1998, 1, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibiger, I.B.; Leibiger, B.; Berggren, P.O. Insulin signaling in the pancreatic beta-cell. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2008, 28, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; MacFarlane, W.M.; Tadayyon, M.; Arch, J.R.; James, R.F.; Docherty, K. Insulin stimulates pancreatic-duodenal homoeobox factor-1 (PDX1) DNA-binding activity and insulin promoter activity in pancreatic beta cells. Biochem. J. 1999, 344, 813–818. [Google Scholar]
- Melloul, D. Transcription factors in islet development and physiology: Role of PDX-1 in beta-cell function. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 2004, 1014, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlgren, U.; Jonsson, J.; Jonsson, L.; Simu, K.; Edlund, H. beta-cell-specific inactivation of the mouse Ipf1/Pdx1 gene results in loss of the beta-cell phenotype and maturity onset diabetes. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frerichs, H.; Reich, U.; Creutzfeldt, W. Insulin Secretion in Vitro. I. Inhibition of Glucose-Induced Insulin Release by Insulin. Klin. Wochenschr. 1965, 43, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodoyez, J.C.; Sodoyez-Goffaux, F.; Foa, P.P. Evidence for an insulin-induced inhibition of insulin release by isolated islets of Langerhans. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1969, 130, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, J.; Miles, D.W. Evidence for a feedback inhibition of insulin on insulin secretion in the isolated, perfused canine pancreas. Diabetes 1971, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammon, H.P.; Reiber, C.; Verspohl, E.J. Indirect evidence for short-loop negative feedback of insulin secretion in the rat. J. Endocrinol. 1991, 128, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elahi, D.; Nagulesparan, M.; Hershcopf, R.J.; Muller, D.C.; Tobin, J.D.; Blix, P.M.; Rubenstein, A.H.; Unger, R.H.; Andres, R. Feedback inhibition of insulin secretion by insulin: Relation to the hyperinsulinemia of obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 1982, 306, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persaud, S.J.; Asare-Anane, H.; Jones, P.M. Insulin receptor activation inhibits insulin secretion from human islets of Langerhans. FEBS Lett. 2002, 510, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, J.D.; Misler, S. Nicotinic acid-adenine dinucleotide phosphate-sensitive calcium stores initiate insulin signaling in human beta cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 14566–14571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schatz, H.; Pfeiffer, E.F. Release of immunoreactive and radioactively prelabelled endogenous (pro)-insulin from isolated islets of rat pancreas in the presence of exogenous insulin. J. Endocrinol. 1977, 74, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaisse, W.J.; Malaisse-Lagae, F.; Lacy, P.E.; Wright, P.H. Insulin secretion by isolated islets in presence of glucose, insulin and anti-insulin serum. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1967, 124, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagner, J.; Samols, E.; Polonsky, K.; Pugh, W. Lack of direct inhibition of insulin secretion by exogenous insulin in the canine pancreas. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 78, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zawalich, W.S.; Zawalich, K.C. A link between insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia: Inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase augment glucose-induced insulin secretion from islets of lean, but not obese, rats. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 3287–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspinwall, C.A.; Lakey, J.R.; Kennedy, R.T. Insulin-stimulated insulin secretion in single pancreatic beta cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 6360–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aspinwall, C.A.; Qian, W.J.; Roper, M.G.; Kulkarni, R.N.; Kahn, C.R.; Kennedy, R.T. Roles of insulin receptor substrate-1, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and release of intracellular Ca2+ stores in insulin-stimulated insulin secretion in beta -cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 22331–22338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otani, K.; Kulkarni, R.N.; Baldwin, A.C.; Krutzfeldt, J.; Ueki, K.; Stoffel, M.; Kahn, C.R.; Polonsky, K.S. Reduced beta-cell mass and altered glucose sensing impair insulin-secretory function in betaIRKO mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 286, E41–E49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roper, M.G.; Qian, W.J.; Zhang, B.B.; Kulkarni, R.N.; Kahn, C.R.; Kennedy, R.T. Effect of the insulin mimetic L-783,281 on intracellular Ca2+ and insulin secretion from pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 2002, 51, S43–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, S.; Goren, H.J. Insulin constitutively secreted by beta-cells is necessary for glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2049–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouche, C.; Lopez, X.; Fleischman, A.; Cypess, A.M.; O’Shea, S.; Stefanovski, D.; Bergman, R.N.; Rogatsky, E.; Stein, D.T.; Kahn, C.R.; et al. Insulin enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in healthy humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4770–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aspinwall, C.A.; Huang, L.; Lakey, J.R.; Kennedy, R.T. Comparison of amperometric methods for detection of exocytosis from single pancreatic beta-cells of different species. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 5551–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, R.N.; Winnay, J.N.; Daniels, M.; Bruning, J.C.; Flier, S.N.; Hanahan, D.; Kahn, C.R. Altered function of insulin receptor substrate-1-deficient mouse islets and cultured beta-cell lines. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, R69–R75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cantley, J.; Choudhury, A.I.; Asare-Anane, H.; Selman, C.; Lingard, S.; Heffron, H.; Herrera, P.; Persaud, S.J.; Withers, D.J. Pancreatic deletion of insulin receptor substrate 2 reduces beta and alpha cell mass and impairs glucose homeostasis in mice. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, I.C.; Taylor, K.W. Effects of pregnancy in the rat on the size and insulin secretory response of the islets of Langerhans. J. Endocrinol. 1972, 54, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner-Weir, S. Life and death of the pancreatic beta cells. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 11, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dor, Y.; Brown, J.; Martinez, O.I.; Melton, D.A. Adult pancreatic beta-cells are formed by self-duplication rather than stem-cell differentiation. Nature 2004, 429, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgia, S.; Bhushan, A. Beta cell replication is the primary mechanism for maintaining postnatal beta cell mass. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teta, M.; Rankin, M.M.; Long, S.Y.; Stein, G.M.; Kushner, J.A. Growth and regeneration of adult beta cells does not involve specialized progenitors. Dev. Cell. 2007, 12, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ackermann, A.M.; Gannon, M. Molecular regulation of pancreatic beta-cell mass development, maintenance, and expansion. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 38, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, A.E.; Janson, J.; Bonner-Weir, S.; Ritzel, R.; Rizza, R.A.; Butler, P.C. Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003, 52, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leahy, J.L. Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch. Med. Res. 2005, 36, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner-Weir, S.; Deery, D.; Leahy, J.L.; Weir, G.C. Compensatory growth of pancreatic beta-cells in adult rats after short-term glucose infusion. Diabetes 1989, 38, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoorens, A.; Van de Casteele, M.; Kloppel, G.; Pipeleers, D. Glucose promotes survival of rat pancreatic beta cells by activating synthesis of proteins which suppress a constitutive apoptotic program. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freemark, M.; Avril, I.; Fleenor, D.; Driscoll, P.; Petro, A.; Opara, E.; Kendall, W.; Oden, J.; Bridges, S.; Binart, N.; et al. Targeted deletion of the PRL receptor: Effects on islet development, insulin production, and glucose tolerance. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulotta, A.; Farilla, L.; Hui, H.; Perfetti, R. The role of GLP-1 in the regulation of islet cell mass. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 40, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chang, Y. Regulation of pancreatic islet beta-cell mass by growth factor and hormone signaling. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2014, 121, 321–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assmann, A.; Hinault, C.; Kulkarni, R.N. Growth factor control of pancreatic islet regeneration and function. Pediatric Diabetes 2009, 10, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Modi, H.; Jacovetti, C.; Tarussio, D.; Metref, S.; Madsen, O.D.; Zhang, F.P.; Rantakari, P.; Poutanen, M.; Nef, S.; Gorman, T.; et al. Autocrine Action of IGF2 Regulates Adult beta-Cell Mass and Function. Diabetes 2015, 64, 4148–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernard, C.; Berthault, M.F.; Saulnier, C.; Ktorza, A. Neogenesis vs. apoptosis As main components of pancreatic beta cell ass changes in glucose-infused normal and mildly diabetic adult rats. FASEB J. 1999, 13, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, J.C.; Bensellam, M.; Duprez, J.; Elouil, H.; Guiot, Y.; Pascal, S.M. Glucose regulation of islet stress responses and beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2009, 11, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topp, B.G.; McArthur, M.D.; Finegood, D.T. Metabolic adaptations to chronic glucose infusion in rats. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwon, G.; Marshall, C.A.; Pappan, K.L.; Remedi, M.S.; McDaniel, M.L. Signaling elements involved in the metabolic regulation of mTOR by nutrients, incretins, and growth factors in islets. Diabetes 2004, 53, S225–S232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briaud, I.; Lingohr, M.K.; Dickson, L.M.; Wrede, C.E.; Rhodes, C.J. Differential activation mechanisms of Erk-1/2 and p70(S6K) by glucose in pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 2003, 52, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, J.D.; Bernal-Mizrachi, E.; Alejandro, E.U.; Han, Z.; Kalynyak, T.B.; Li, H.; Beith, J.L.; Gross, J.; Warnock, G.L.; Townsend, R.R.; et al. Insulin protects islets from apoptosis via Pdx1 and specific changes in the human islet proteome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19575–19580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folli, F.; Okada, T.; Perego, C.; Gunton, J.; Liew, C.W.; Akiyama, M.; D’Amico, A.; La Rosa, S.; Placidi, C.; Lupi, R.; et al. Altered insulin receptor signalling and beta-cell cycle dynamics in type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beith, J.L.; Alejandro, E.U.; Johnson, J.D. Insulin stimulates primary beta-cell proliferation via Raf-1 kinase. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 2251–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H.; Nakae, J.; Kitamura, T.; Park, B.C.; Dragatsis, I.; Accili, D. Transgenic rescue of insulin receptor-deficient mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alejandro, E.U.; Kalynyak, T.B.; Taghizadeh, F.; Gwiazda, K.S.; Rawstron, E.K.; Jacob, K.J.; Johnson, J.D. Acute insulin signaling in pancreatic beta-cells is mediated by multiple Raf-1 dependent pathways. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hennige, A.M.; Burks, D.J.; Ozcan, U.; Kulkarni, R.N.; Ye, J.; Park, S.; Schubert, M.; Fisher, T.L.; Dow, M.A.; Leshan, R.; et al. Upregulation of insulin receptor substrate-2 in pancreatic beta cells prevents diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1521–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, D.; Sun, J.; Mao, L.; Ye, H.; Polonsky, K.S. BH3-only molecule Bim mediates beta-cell death in IRS2 deficiency. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3378–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Withers, D.J.; Burks, D.J.; Towery, H.H.; Altamuro, S.L.; Flint, C.L.; White, M.F. Irs-2 coordinates Igf-1 receptor-mediated beta-cell development and peripheral insulin signalling. Nat. Genet. 1999, 23, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoukakis, N.; Mi, Z.; Rudert, W.A.; Gambotto, A.; Trucco, M.; Robbins, P. Prevention of beta cell dysfunction and apoptosis activation in human islets by adenoviral gene transfer of the insulin-like growth factor I. Gene Ther. 2000, 7, 2015–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Salojin, K.V.; Mi, Q.S.; Grattan, M.; Meagher, T.C.; Zucker, P.; Delovitch, T.L. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I/IGF-binding protein-3 complex: Therapeutic efficacy and mechanism of protection against type 1 diabetes. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, D.J.; Petrik, J.; Arany, E.; McDonald, T.J.; Delovitch, T.L. Insulin-like growth factors prevent cytokine-mediated cell death in isolated islets of Langerhans from pre-diabetic non-obese diabetic mice. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 161, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, L.M.; Rhodes, C.J. Pancreatic beta-cell growth and survival in the onset of type 2 diabetes: A role for protein kinase B in the Akt? Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 287, E192–E198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, K.; Okada, T.; Hu, J.; Liew, C.W.; Assmann, A.; Dahlgren, G.M.; Peters, J.L.; Shackman, J.G.; Zhang, M.; Artner, I.; et al. Total insulin and IGF-I resistance in pancreatic beta cells causes overt diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Feltstrom, J.; Lundquist, I.; Obermuller, S.; Salehi, A. Insulin feedback actions: Complex effects involving isoforms of islet nitric oxide synthase. Regul. Pept. 2004, 122, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poitout, V.; Amyot, J.; Semache, M.; Zarrouki, B.; Hagman, D.; Fontes, G. Glucolipotoxicity of the pancreatic beta cell. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robertson, R.P.; Harmon, J.; Tran, P.O.; Poitout, V. Beta-cell glucose toxicity, lipotoxicity, and chronic oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53, S119–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berchtold, L.A.; Prause, M.; Storling, J.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Cytokines and Pancreatic beta-Cell Apoptosis. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2016, 75, 99–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechler, M.M.; Nissley, S.P. The nature and regulation of the receptors for insulin-like growth factors. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1985, 47, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, J.H.; Krett, N.L.; Alvarez, J.M.; Gelehrter, T.D.; Romanus, J.A.; Rechler, M.M. Insulin regulation of insulin-like growth factor action in rat hepatoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 2396–2402. [Google Scholar]
- Conover, C.A.; Clarkson, J.T.; Bale, L.K. Physiological concentrations of insulin induce cellular desensitization to the mitogenic effects of insulin-like growth factor I. Diabetes 1994, 43, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grodsky, G.M.; Fanska, R.; Schmid, F.G. Evaluation of the role of exogenous insulin on phasic insulin secretion. Diabetes 1973, 22, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, P.; Scharp, D.W.; McLear, M.; Finke, E.H.; Olack, B.; Swanson, C.; Giannarelli, R.; Navalesi, R.; Lacy, P.E. Insulin inhibits its own secretion from isolated, perifused human pancreatic islets. Acta Diabetol. 1995, 32, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.A.; Goforth, P.B.; Zhang, M.; Satin, L.S. Insulin activates ATP-sensitive K(+) channels in pancreatic beta-cells through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent pathway. Diabetes 2001, 50, 2192–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barker, C.J.; Leibiger, I.B.; Leibiger, B.; Berggren, P.O. Phosphorylated inositol compounds in beta -cell stimulus-response coupling. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 283, E1113–E1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, O.; Barker, C.J.; Berggren, P.O. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and ATP-sensitive potassium channel regulation: A word of caution. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1409–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagren, O.I.; Tengholm, A. Glucose and insulin synergistically activate phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to trigger oscillations of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate in beta-cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 39121–39127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Argoud, G.M.; Schade, D.S.; Eaton, R.P. Insulin suppresses its own secretion in vivo. Diabetes 1987, 36, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, H.P.; Schmid, C.; Zapf, J.; Froesch, E.R. Effects of recombinant insulin-like growth factor I on insulin secretion and renal function in normal human subjects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 2868–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Schravendijk, C.F.; Heylen, L.; Van den Brande, J.L.; Pipeleers, D.G. Direct effect of insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I on the secretory activity of rat pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 1990, 33, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, A.Z.; Zhao, H.; Teague, J.; Fujimoto, W.; Beavo, J.A. Attenuation of insulin secretion by insulin-like growth factor 1 is mediated through activation of phosphodiesterase 3B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3223–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Komiya, I.; Inman, L.; O’Neil, J.; Appel, M.; Alam, T.; Unger, R.H. Effects of hypoglycemia and prolonged fasting on insulin and glucagon gene expression. Studies with in situ hybridization. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 84, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koranyi, L.; James, D.E.; Kraegen, E.W.; Permutt, M.A. Feedback inhibition of insulin gene expression by insulin. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 89, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Petersen, B.; Obertson, R.P. Variable regulation by insulin of insulin gene expression in HIT-T15 cells. Diabetologia 1994, 37, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Taguchi, A.; Park, S.; Kushner, J.A.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; White, M.F. Dysregulation of insulin receptor substrate 2 in beta cells and brain causes obesity and diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elghazi, L.; Balcazar, N.; Bernal-Mizrachi, E. Emerging role of protein kinase B/Akt signaling in pancreatic beta-cell mass and function. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2006, 38, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flatt, P.R.; Tan, K.S.; Bailey, C.J.; Powell, C.J.; Swanston-Flatt, S.K.; Marks, V. Effects of transplantation and resection of a radiation-induced rat insulinoma on glucose homeostasis and the endocrine pancreas. Br. J. Cancer 1986, 54, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blume, N.; Skouv, J.; Larsson, L.I.; Holst, J.J.; Madsen, O.D. Potent inhibitory effects of transplantable rat glucagonomas and insulinomas on the respective endogenous islet cells are associated with pancreatic apoptosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilon, P.; Chae, H.Y.; Rutter, G.A.; Ravier, M.A. Calcium signaling in pancreatic beta-cells in health and in Type 2 diabetes. Cell Calcium 2014, 56, 340–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatini, P.V.; Speckmann, T.; Lynn, F.C. Friend and foe: Beta-cell Ca(2+) signaling and the development of diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2019, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, L.C.; Yokoe, T.; Zhang, P.; Scott, D.K.; Kim, S.K.; O’Donnell, C.P.; Garcia-Ocana, A. Glucose infusion in mice: A new model to induce beta-cell replication. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1792–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levitt, H.E.; Cyphert, T.J.; Pascoe, J.L.; Hollern, D.A.; Abraham, N.; Lundell, R.J.; Rosa, T.; Romano, L.C.; Zou, B.; O’Donnell, C.P.; et al. Glucose stimulates human beta cell replication in vivo in islets transplanted into NOD-severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardozo, A.K.; Ortis, F.; Storling, J.; Feng, Y.M.; Rasschaert, J.; Tonnesen, M.; Van Eylen, F.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T.; Herchuelz, A.; Eizirik, D.L. Cytokines downregulate the sarcoendoplasmic reticulum pump Ca2+ ATPase 2b and deplete endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+, leading to induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress in pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 2005, 54, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gwiazda, K.S.; Yang, T.L.; Lin, Y.; Johnson, J.D. Effects of palmitate on ER and cytosolic Ca2+ homeostasis in beta-cells. Am, J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 296, E690–E701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Horta, O.; Van Eylen, F.; Herchuelz, A. Na/Ca exchanger overexpression induces endoplasmic reticulum stress, caspase-12 release, and apoptosis. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 2003, 1010, 430–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.J.; Gurlo, T.; Haataja, L.; Costes, S.; Daval, M.; Ryazantsev, S.; Wu, X.; Butler, A.E.; Butler, P.C. Calcium-activated calpain-2 is a mediator of beta cell dysfunction and apoptosis in type 2 diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dybala, M.P.; Hara, M. Heterogeneity of the Human Pancreatic Islet. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qader, S.S.; Hakanson, R.; Rehfeld, J.F.; Lundquist, I.; Salehi, A. Proghrelin-derived peptides influence the secretion of insulin, glucagon, pancreatic polypeptide and somatostatin: A study on isolated islets from mouse and rat pancreas. Regul. Pept. 2008, 146, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yukawa, M.; Takeuchi, T.; Watanabe, T.; Kitamura, S. Proportions of various endocrine cells in the pancreatic islets of wood mice (Apodemus speciosus). Anat. Histol. Embryol. 1999, 28, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Miller, K.; Jo, J.; Kilimnik, G.; Wojcik, P.; Hara, M. Islet architecture: A comparative study. Islets 2009, 1, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.R.; Moss, M.C. A morphometric study of the endocrine and exocrine capillaries of the pancreas. Q. J. Exp. Physiol. 1985, 70, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyman, L.R.; Wells, K.S.; Head, W.S.; McCaughey, M.; Ford, E.; Brissova, M.; Piston, D.W.; Powers, A.C. Real-time, multidimensional in vivo imaging used to investigate blood flow in mouse pancreatic islets. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3790–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanone, M.M.; Favaro, E.; Camussi, G. From endothelial to beta cells: Insights into pancreatic islet microendothelium. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2008, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner-Weir, S.; Orci, L. New perspectives on the microvasculature of the islets of Langerhans in the rat. Diabetes 1982, 31, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Miyake, T.; Tsubouchi, M.; Tsubouchi, Y.; Ohtsuka, A.; Fujita, T. Blood flow patterns in the rat pancreas: A simulative demonstration by injection replication and scanning electron microscopy. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1997, 37, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammert, E.; Cleaver, O.; Melton, D. Induction of pancreatic differentiation by signals from blood vessels. Science 2001, 294, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammert, E.; Gu, G.; McLaughlin, M.; Brown, D.; Brekken, R.; Murtaugh, L.C.; Gerber, H.P.; Ferrara, N.; Melton, D.A. Role of VEGF-A in vascularization of pancreatic islets. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 1070–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansson, M.; Mattsson, G.; Andersson, A.; Jansson, L.; Carlsson, P.O. Islet endothelial cells and pancreatic beta-cell proliferation: Studies in vitro and during pregnancy in adult rats. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 2315–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jansson, L.; Hellerstrom, C. Stimulation by glucose of the blood flow to the pancreatic islets of the rat. Diabetologia 1983, 25, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jansson, L.; Andersson, A.; Bodin, B.; Kallskog, O. Pancreatic islet blood flow during euglycaemic, hyperinsulinaemic clamp in anaesthetized rats. Acta Physiol. (Oxf.) 2007, 189, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhail, N.; Tuck, M.L. Insulin and the vasculature. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2000, 2, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, R.W. Insulin and atheroma. 20-yr perspective. Diabetes Care 1990, 13, 631–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubota, T.; Kubota, N.; Kumagai, H.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kozono, H.; Takahashi, T.; Inoue, M.; Itoh, S.; Takamoto, I.; Sasako, T.; et al. Impaired insulin signaling in endothelial cells reduces insulin-induced glucose uptake by skeletal muscle. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Meshinchi, S.; Dias-Leme, C.; Raffin, D.; Johnson, J.D.; Treutelaar, M.K.; Burant, C.F. Islet microvasculature in islet hyperplasia and failure in a model of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2965–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duvillie, B.; Currie, C.; Chrones, T.; Bucchini, D.; Jami, J.; Joshi, R.L.; Hill, D.J. Increased islet cell proliferation, decreased apoptosis, and greater vascularization leading to beta-cell hyperplasia in mutant mice lacking insulin. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 1530–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneghini, L. Why and how to use insulin therapy earlier in the management of type 2 diabetes. South. Med. J. 2007, 100, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, E.A.; Imes, S.; Wallace, C. Short-term intensive insulin therapy in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1028–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anderwald, C.; Bernroider, E.; Krssak, M.; Stingl, H.; Brehm, A.; Bischof, M.G.; Nowotny, P.; Roden, M.; Waldhausl, W. Effects of insulin treatment in type 2 diabetic patients on intracellular lipid content in liver and skeletal muscle. Diabetes 2002, 51, 3025–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McFarlane, S.I. Insulin therapy and type 2 diabetes: Management of weight gain. J. Clin. Hypertens. (Greenwich) 2009, 11, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rachdaoui, N. Insulin: The Friend and the Foe in the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051770
Rachdaoui N. Insulin: The Friend and the Foe in the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(5):1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051770
Chicago/Turabian StyleRachdaoui, Nadia. 2020. "Insulin: The Friend and the Foe in the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 5: 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051770
APA StyleRachdaoui, N. (2020). Insulin: The Friend and the Foe in the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(5), 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051770