The Effects of Human BDH2 on the Cell Cycle, Differentiation, and Apoptosis and Associations with Leukemia Transformation in Myelodysplastic Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Characteristics
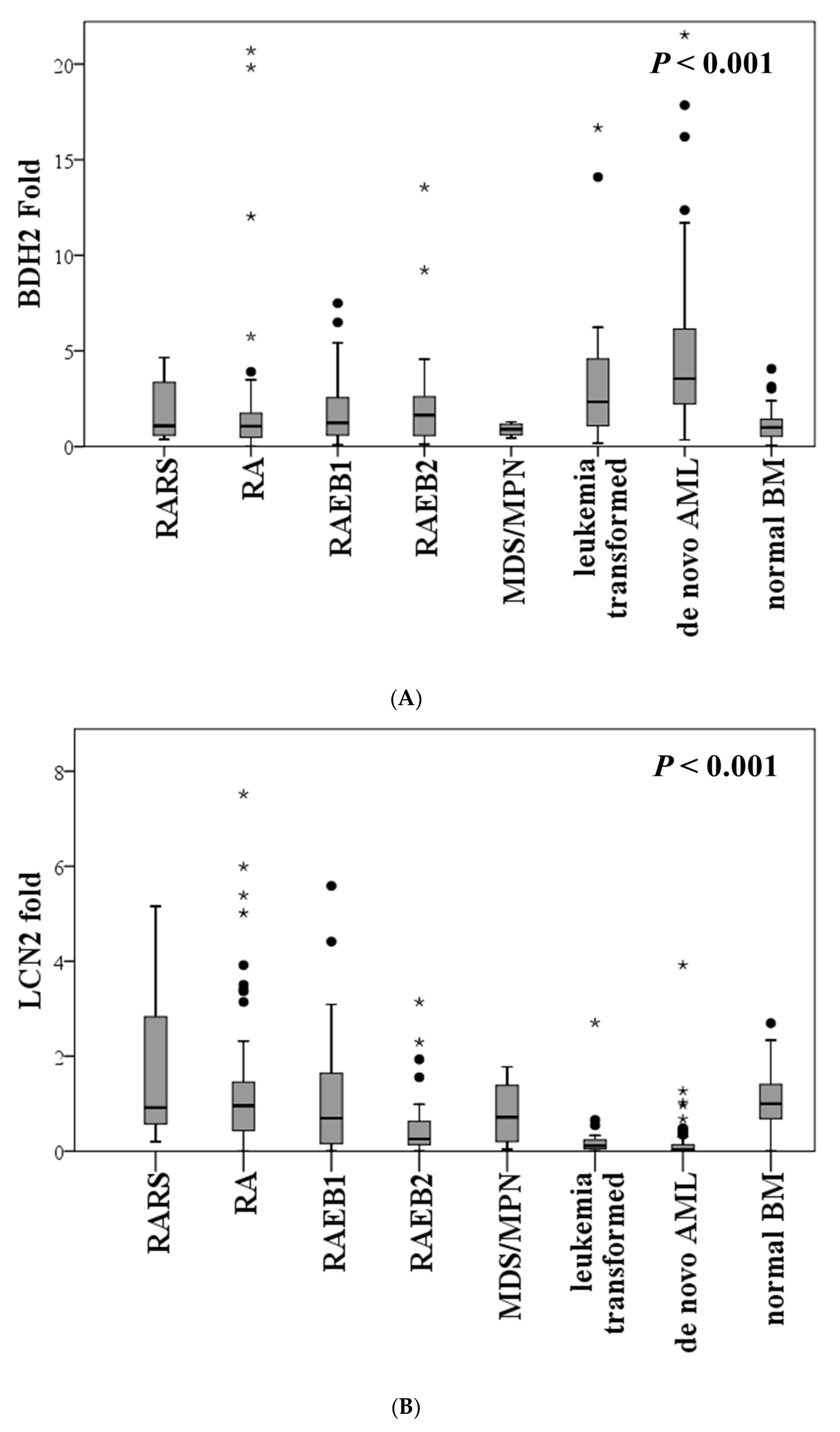
2.2. Expression of BDH2 and LCN2 in MDS and Control Patients
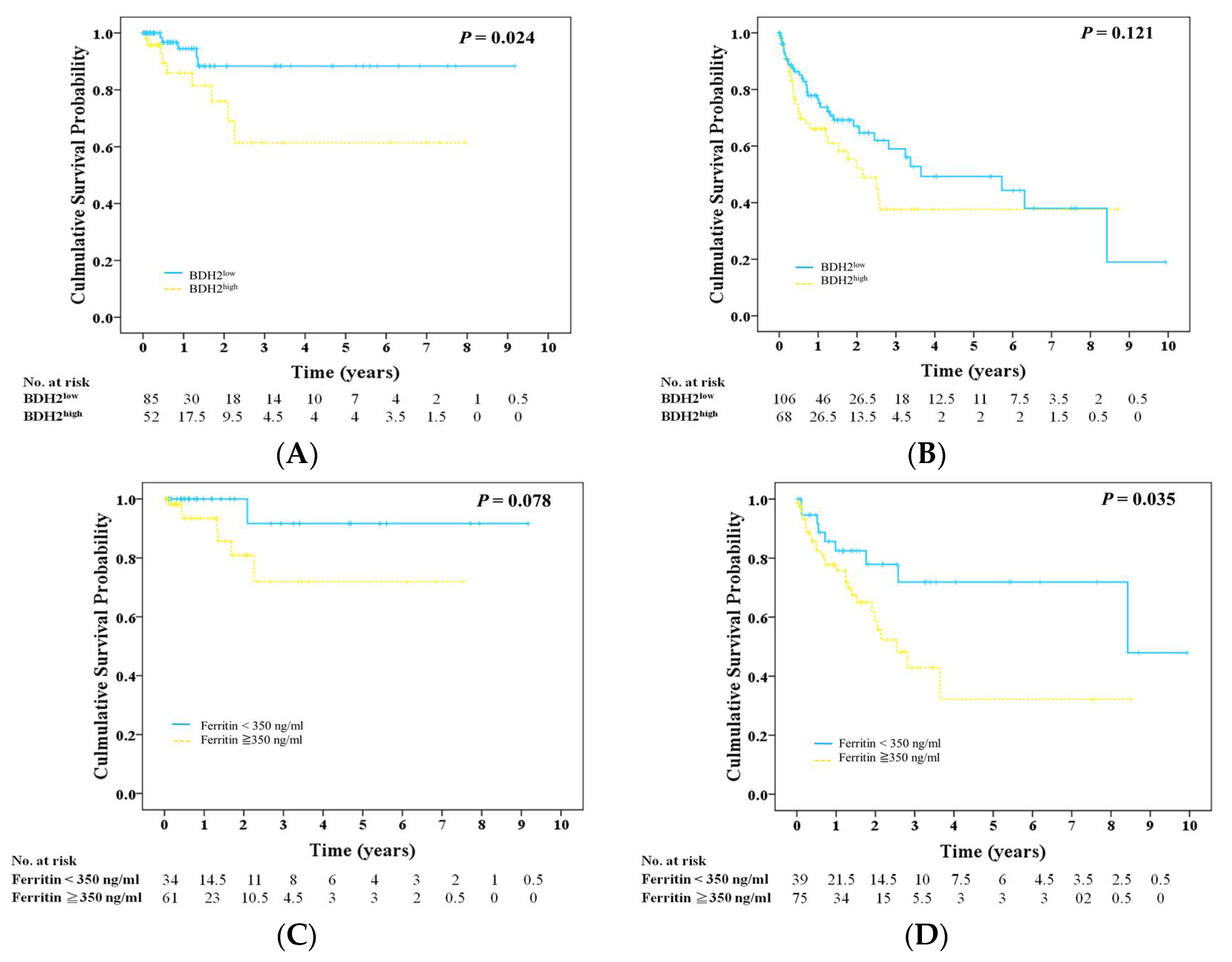
2.3. BDH2 Expression Is Related to Ferritin Levels
2.4. Prognosis, BDH2 Expression, and Ferritin
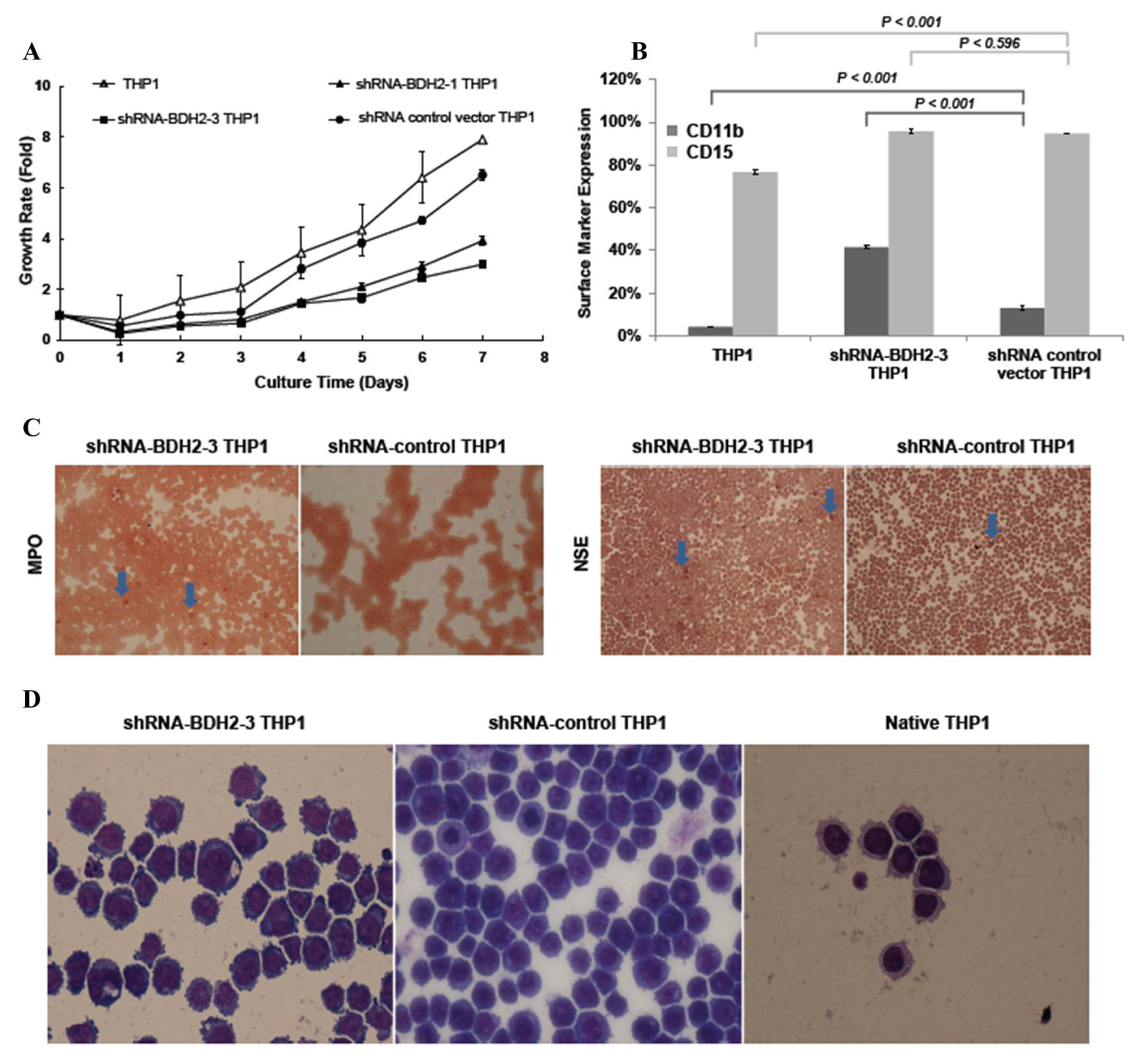
2.5. BDH2 Knockdown (KD) THP1 Showed a Slow Growth Rate Related to Cell Differentiation and Cell Cycle Retardation
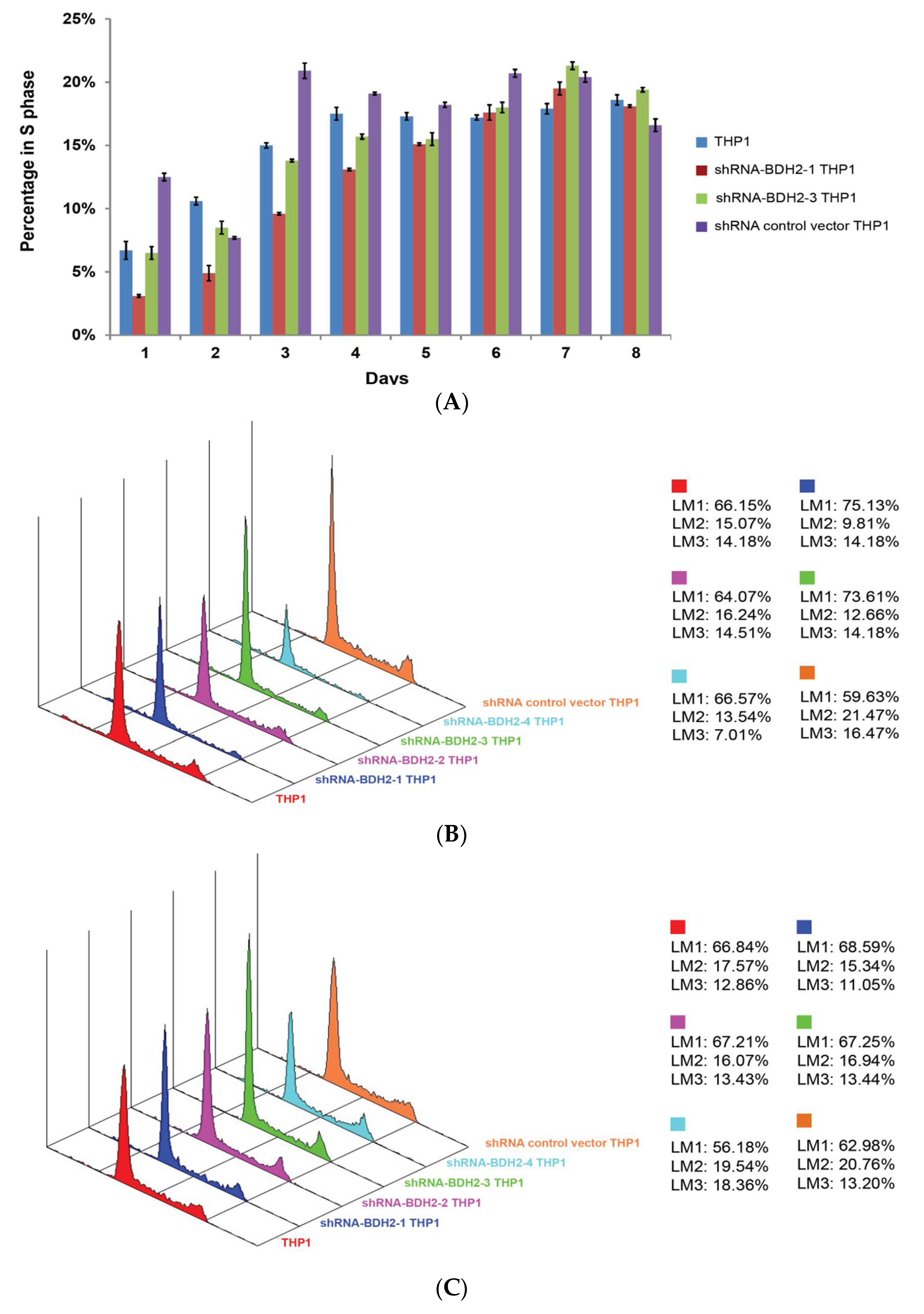
2.5.1. Cell Cycle Retardation
2.5.2. Increased Differentiation in shRNA-BDH2 THP1 Cells
2.5.3. Longer Cell Cycle Arrest in shRNA Interference BDH2-KD THP1 Cells
2.6. BDH2 in Myeloid and Erythroid Series
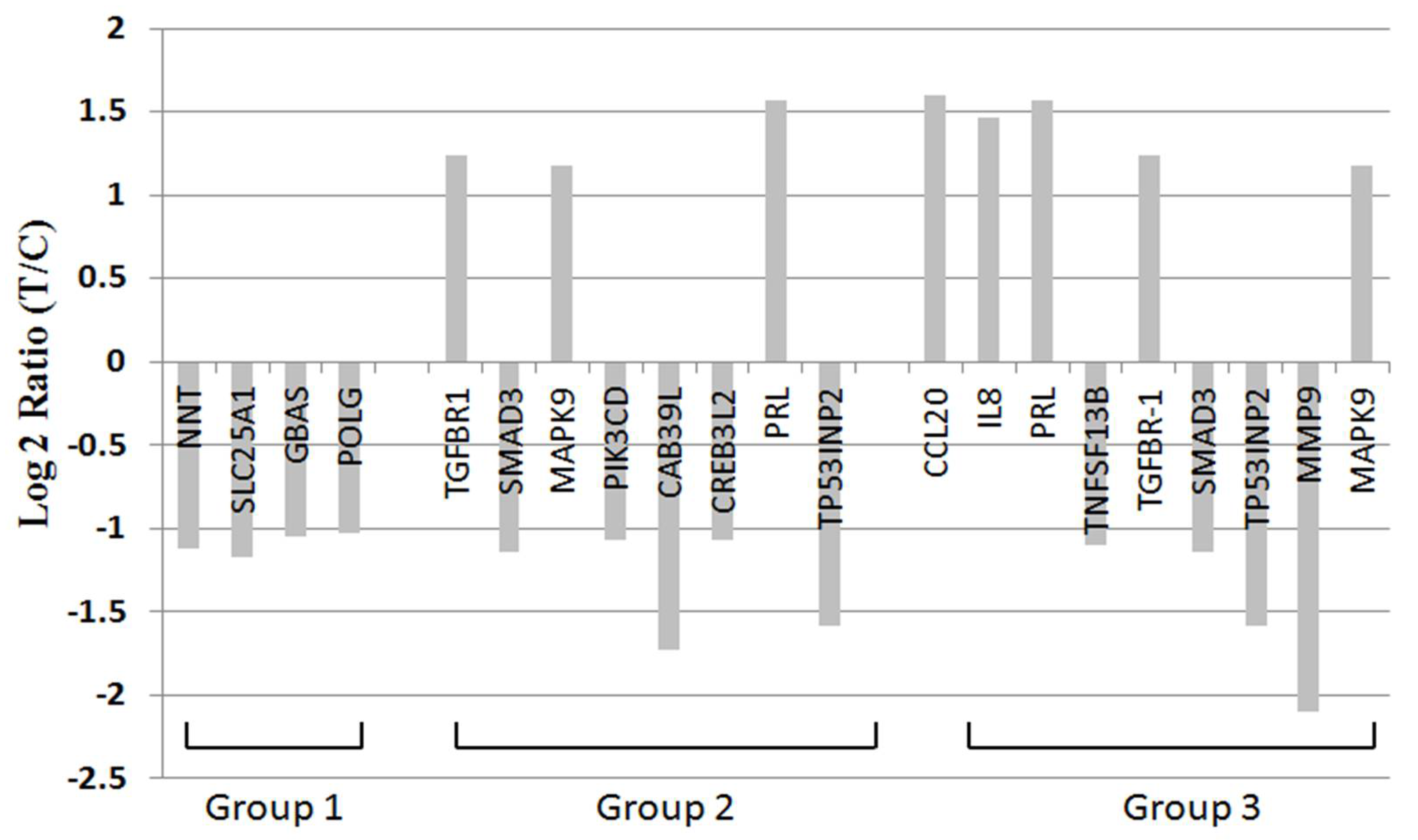
2.7. BDH2 Targets on Multiple Genes Related to Cell Proliferation, Survival, and Cancer Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Population
4.2. RNA Interference-Mediated BDH2-KD in THP1 Cells and Cell Culture
4.3. qRT-PCR for mRNA Expression of BDH2 and LCN2
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Flow Cytometry for Cell Differentiation and Cell Cycle Analysis
4.6. Special Stains
4.7. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4.8. mRNA Microarray Analysis
4.9. Clinical Endpoints
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDS | myelodysplastic syndrome |
| BDH2 | type 2-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase |
| BM | bone marrow |
| qRT-PCR | quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| BDH2-KD | BDH2 knockdown |
| AML | acute myeloid leukemia |
| RUNX1 | runt-related transcription factor 1 |
| c-CBL | c-Casitas B-lineage lymphoma |
| DNMT3A | DNA methyltransferase 3 alpha |
| TET2 | tet methylcytosine dioxygenase 2 |
| EZH2 | enhancer of zeste homolog 2 |
| U2AF1 | U2 small nuclear RNA auxiliary factor 1 |
| U2AF35 | U2 small nuclear RNA auxiliary factor 35 |
| ZRSR2 | zinc finger CCCH type, RNA binding motif, and serine/arginine-rich 2 |
| SRSF2 | serine and arginine-rich splicing factor 2 |
| SF3B | splicing factor 3b subunit 1 |
| GDF11 | growth differentiation factor-11 |
| GDF15 | growth differentiation factor-15 |
| LFS | Leukemia-free survival |
| OS | overall survival |
| LCN2 | lipocalin 24p3 |
| 2,5-DHBA | 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| IPSS-R | Revised International Prognostic Scoring System |
| RA | refractory anemia |
| RARS | refractory anemia with ring sideroblast |
| RAEB1 | refractory anemia with excess of blast 1 |
| RAEB2 | refractory anemia with excess of blast 2 |
| MDS/MPN | myelodysplasitic syndrome/myeloproliferative neoplasm |
| NNT | nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase |
| TCA | tricarboxylic acid |
| SLC25A1 | solute carrier 25 A1 |
| BBF2H7/CREB3L2 | CAMP responsive element binding protein 3 like 2 |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor-β |
| MMP-9 | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 |
| PIK3CD | Phosphoinositide-3-kinase, catalytic, delta polypeptide |
| TNFSF13B | tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 13B |
| IL | interleukin |
| CCL | Chemokine ligand |
| PRL | prolactin |
References
- Corey, S.J.; Minden, M.D.; Barber, D.L.; Kantarjian, H.; Wang, J.C.; Schimmer, A.D. Myelodysplastic syndromes: The complexity of stem-cell diseases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.M.; Catovsky, D.; Daniel, M.T.; Flandrin, G.; Galton, D.A.; Gralnick, H.R.; Sultan, C. Proposals for the classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes. Br. J. Haematol. 1982, 51, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, P.; Cox, C.; LeBeau, M.M.; Fenaux, P.; Morel, P.; Sanz, G.; Sanz, M.; Vallespi, T.; Hamblin, T.; Oscier, D.; et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1997, 89, 2079–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardiman, J.W.; Harris, N.L.; Brunning, R.D. The World Health Organization (WHO) classification of the myeloid neoplasms. Blood 2002, 100, 2292–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moukalled, N.M.; El Rassi, F.A.; Temraz, S.N.; Taher, A.T. Iron overload in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: An updated overview. Cancer 2018, 124, 3979–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Sanada, M.; Shiraishi, Y.; Nowak, D.; Nagata, Y.; Yamamoto, R.; Sato, Y.; Sato-Otsubo, A.; Kon, A.; Nagasaki, M.; et al. Frequent pathway mutations of splicing machinery in myelodysplasia. Nature 2011, 478, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejar, R.; Levine, R.; Ebert, B.L. Unraveling the molecular pathophysiology of myelodysplastic syndromes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thol, F.; Kade, S.; Schlarmann, C.; Löffeld, P.; Morgan, M.; Krauter, J.; Wlodarski, M.W.; Kölking, B.; Wichmann, M.; Görlich, K.; et al. Frequency and prognostic impact of mutations in SRSF2, U2AF1, and ZRSR2 in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2012, 119, 3578–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejar, R.; Stevenson, K.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Galili, N.; Nilsson, N.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Kantarjian, H.; Raza, A.; Levine, R.L.; Neuberg, D.; et al. Clinical effect of point mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2496–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haferlach, T. Molecular genetics in myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk. Res. 2012, 36, 1459–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Grabar, S.; Kelaidi, C.; Beyne-Rauzy, O.; Picard, F.; Bardet, V.; Coiteux, V.; Leroux, G.; Lepelley, P.; Daniel, M.T.; et al. Predictive factors of response and survival in myelodysplastic syndrome treated with erythropoietin and G-CSF: The GFM experience. Blood 2008, 111, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvedson, T.L.; Sasu, B.J. Role and regulation of iron metabolism in erythropoiesis and disease. In Erythropoietins, Erythropoietic Factors, and Erythropoiesis Milestones in Drug Therapy; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2009; Volume 4, pp. 279–298. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, R.; Gale, R.; Zhu, G.; Xu, Z.; Qin, T.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, G.; Li, B.; Fang, L.; Zhang, H.; et al. Serum iron metabolism and erythropoiesis in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome not receiving RBC transfusion. Leuk. Res. 2014, 38, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenoy, N.; Vallumsetla, N.; Rachmilewitz, E.; Verma, A.; Ginzburg, Y. Impact of iron overload and potential benefit from iron chelation in low-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2014, 124, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suragani, R.N.; Cadena, S.M.; Cawley, S.M.; Sako, D.; Mitchell, D.; Li, R.; Davies, M.V.; Alexander, M.J.; Devine, M.; Loveday, K.S.; et al. Transforming growth factor-β superfamily ligand trap ACE-536 corrects anemia by promoting late-stage erythropoiesis. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimer, S.D. Myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2008, 111, 4841–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenaux, P.; Rose, C. Impact of iron overload in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood Rev. 2009, 23, S15–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcovati, L.; Porta, M.G.; Pascutto, C.; Invernizzi, R.; Boni, M.; Travaglino, E.; Passamonti, F.; Arcaini, L.; Maffioli, M.; Bernasconi, P.; et al. Prognostic factors and life expectancy in myelodysplastic syndromes classified according to WHO criteria: A basis for clinical decision making. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 7594–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, G.; Nomdedeu, B.; Such, E.; Bernal, T.; Belkaid, M.; Ardanaz, M.T.; Marco, V.; Pedro, C.; Ramos, F.; Consuelo del Cañizo, M.; et al. Independent impact of iron overload and transfusion dependency on survival and leukemic evolution in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2008, 112, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, D.H.; Holmes, M.A.; Borregaard, N.; Bluhm, M.E.; Raymond, K.N.; Strong, R.K. The neutrophil lipocalin NGAL is a bacteriostatic agent that interferes with siderophore-mediated iron acquisition. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Goetz, D.; Li, J.Y.; Wang, W.; Mori, K.; Setlik, D.; Du, T.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Strong, R.; et al. An iron delivery pathway mediated by a lipocalin. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devireddy, L.R.; Gazin, C.; Zhu, X.; Green, M.R. A cell-surface receptor for lipocalin 24p3 selectively mediates apoptosis and iron uptake. Cell 2005, 123, 1293–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devireddy, L.R.; Hart, D.O.; Goetz, D.H.; Green, M.R. A mammalian siderophore synthesized by an enzyme with a bacterial homolog involved in enterobactin production. Cell 2010, 141, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, K.; Lukacik, P.; Papagrigoriou, E.; Meier, M.; Lee, W.H.; Adamski, J.; Oppermann, U. Characterization of human DHRS6, an orphan short chain dehydrogenase/reductase enzyme: A novel, cytosolic type 2 R-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 10291–10297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Lanford, R.; Mueller, S.; Gerhard, G.S.; Luscieti, S.; Sanchez, M.; Devireddy, L. Siderophore-mediated iron trafficking in humans is regulated by iron. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 90, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.C.; Tsai, W.C.; Lin, P.M.; Yang, M.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Chang, C.S.; Yu, W.H.; Lin, S.F. Human BDH2, an anti-apoptosis factor, is a novel poor prognostic factor for de novo cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. J. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 20, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Chen, Q.; Gu, J.; Li, S.; Zhao, G.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X. Synergistic inhibitory effects of deferasirox in combination with decitabine on leukemia cell lines SKM-1, THP-1, and K-562. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 36517–36530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fang, J.; Rhyasen, G.; Bolanos, L.; Rasch, C.; Varney, M.; Wunderlich, M.; Goyama, S.; Jansen, G.; Cloos, J.; Rigolino, C.; et al. Cytotoxic effects of bortezomib in myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myeloid leukemia depend on autophagy-mediated lysosomal degradation of TRAF6 and repression of PSMA1. Blood 2012, 120, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibes, R.; Al-Kali, A.; Oliver, G.R.; Delman, D.H.; Hansen, N.; Bhagavatula, K.; Mohan, J.; Rakhshan, F.; Wood, T.; Foran, J.M.; et al. The Hedgehog pathway as targetable vulnerability with 5-azacytidine in myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, P.; Tuechler, H.; Schanz, J.; Sanz, G.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Solé, F.; Bennett, J.M.; Bowen, D.; Fenaux, P.; Dreyfus, F.; et al. Revised International Prognostic Scoring System for Myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2012, 120, 2454–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valent, P.; Horny, H.P.; Bennett, J.M.; Fonatsch, C.; Germing, U.; Greenberg, P.; Haferlach, T.; Haase, D.; Kolb, H.J.; Krieger, O.; et al. Definitions and standards in the diagnosis and treatment of the myelodysplastic syndromes: Consensus statements and report from a working conference. Leuk. Res. 2007, 31, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.M.; Komrokji, R.S. The myelodysplastic syndromes: Diagnosis, molecular biology and risk assessment. Hematology 2005, 10, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, S.; Kobune, M.; Iyama, S.; Sato, T.; Murase, K.; Kawano, Y.; Takada, K.; Ono, K.; Hayashi, T.; Miyanishi, K.; et al. Prognostic significance of serum ferritin level at diagnosis in myelodysplastic syndrome. Int. J. Hematol. 2012, 95, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; He, X.; Cao, X.; Xu, P.; Xu, P.; Xing, Y.; Sui, S.; Wang, L.; Meng, J.; Lu, W.; et al. Iron overload impairs normal hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells through reactive oxygen species and shortens survival in myelodysplastic syndrome mice. Hematologica 2018, 103, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zughaier, S.M.; Stauffer, B.B.; McCarty, N.A. Inflammation nad ER stress downregulate BDH2 expression nad dysregulate intracellular iron in macrophages. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 140728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Raza, A.; Gezer, S.; Mundle, S.; Gao, X.Z.; Alvi, S.; Borok, R.; Rifkin, S.; Iftikhar, A.; Shetty, V.; Parcharidou, A.; et al. Apoptosis in bone marrow biopsy samples involving stromal and hematopoietic cells in 50 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1995, 86, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, H.M.; Jilani, I.; Estey, E.H.; Keating, M.J.; Dey, A.L.; Manshouri, T.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Estrov, Z.; Cortes, J.E.; Thomas, D.A.; et al. Increased apoptosis in bone marrow B lymphocytes but not T lymphocytes in myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2003, 102, 1866–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claessens, Y.E.; Bouscary, D.; Dupont, J.M.; Picard, F.; Melle, J.; Gisselbrecht, S.; Lacombe, C.; Dreyfus, F.; Mayeux, P.; Fontenay-Roupie, M. In vitro proliferation and differentiation of erythroid progenitors from patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: Evidence for Fas-dependent apoptosis. Blood 2002, 99, 1594–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehranchi, R.; Fadeel, B.; Forsblom, A.M.; Christensson, B.; Samuelsson, J.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Hellstrom-Lindberg, E. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor inhibits spontaneous cytochrome c release and mitochondria-dependent apoptosis of myelodysplastic syndrome hematopoietic progenitors. Blood 2003, 101, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, K.; Nakakuma, H.; Kawaguchi, T.; Iwamoto, N.; Nagakura, S.; Kagimoto, T.; Takatsuki, K. Apoptosis resistance of blood cells from patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, aplastic anemia, and myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 1997, 90, 2716–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloand, E.M.; Kim, S.; Fuhrer, M.; Risitano, A.M.; Nakamura, R.; Maciejewski, J.P.; Barrett, A.J.; Young, N.S. Fas-mediated apoptosis is important in regulating cell replication and death in trisomy 8 hematopoietic cells but not in cells with other cytogenetic abnormalities. Blood 2002, 100, 4427–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Simon, H.U.; Haj-Yehia, A.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction. Apoptosis 2000, 5, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapaksa, R.; Ginzton, N.; Rott, L.S.; Greenberg, P.L. Altered oncoprotein expression and apoptosis in myelodysplastic syndrome marrow cells. Blood 1996, 88, 4275–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerbauy, D.B.; Deeg, H.J. Apoptosis and antiapoptotic mechanisms in the progression of myelodysplastic syndrome. Exp. Hematol. 2007, 35, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, J.E.; Mufti, G.J.; Rasool, F.; Mijovic, A.; Devereux, S.; Pagliuca, A. The role of apoptosis, proliferation, and the Bcl-2-related proteins in the myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia secondary to MDS. Blood 2000, 96, 3932–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elghetany, M.T. Surface marker abnormalities in myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica 1998, 83, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.E.; Hoy, T.G.; Jacobs, A. Granulocyte and monocyte surface membrane markers in the myelodysplastic syndromes. J. Clin. Pathol. 1985, 38, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gameiro, P.A.; Laviolette, L.A.; Kelleher, J.K.; Iliopoulos, O.; Stephanopoulos, G. Cofactor balance by nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase (NNT) coordinates reductive carboxylation and glucose catabolism in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 12967–12977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, F. The mitochondrial transporter family SLC25: Identification, properties and physiopathylogy. Mol. Asp. Med. 2013, 34, 465–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morciano, P.; Carrisi, C.; Capobianco, L.; Mannini, L.; Burgio, G.; Cestra, G.; De Benedetto, G.E.; Corona, D.F.; Musio, A.; Cenci, G. A conserved role for the mitochondrial citrate transporter Sea/SLC25A1 in the maintenance of chromosome integrity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 4180–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.Q.; Compitello, N.; Horwitz, E.; Sramkoski, M.; Knudsen, E.S.; Renne, R. The Latency-associated nuclear antigen of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus modulates cellular gene expression and protects lymphoid cells from p16 INK4A-induced cell cycle arrest. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 3862–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, A.; Kanemoto, S.; Zhang, Y.; Asada, R.; Hino, K.; Imaizumi, K. Chondrocyte proliferation regulated by secreted luminal domain of ER stress transducer BBF2H7/CREB3L2. Mol. Cell 2014, 53, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Letterio, J. Transforming growth factor-β signaling in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Leukemia 2003, 17, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrana, J.L.; Attisano, L.; Wieser, R.; Ventura, F.; Massagué, J. Mechanism of activation of TGF-β receptor. Nature 1994, 370, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heissig, B.; Hattori, K.; Dias, S.; Friedrich, M.; Ferris, B.; Hackett, N.R.; Crystal, R.G.; Besmer, P.; Lyden, D.; Moore, M.A.; et al. Recruitment of stem and progenitor cells from the bone marrow niche requires MMP-9 mediated release of Kit-ligand. Cell 2002, 109, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Chapuis, N.; Tamburini, J.; Bardet, V.; Cornillet-Lefebvre, P.; Willems, L.; Green, A.; Mayeux, P.; Lacombe, C.; Bouscary, D. Role of the PI3K/AKT and mTOR signaling pathways in acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2010, 95, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henley, T.; Kovesdi, D.; Turner, M. B-cell responses to b-cell activation factor of the TNF family (BAFF) are impaired in the absence of PI3K delta. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 3543–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terui, Y.; Ikeda, M.; Tomizuka, H.; Kasahara, T.; Ohtsuki, T.; Uwai, M.; Mori, M.; Itoh, T.; Tanaka, M.; Yamada, M.; et al. Identification of a novel apoptosis-inducing factor derived from leukemic cells: Endothelial interleukin-8, but not monocyte-derived, induces apoptosis in leukemic cells. Biochem. Biophy. Res. Commun. 1998, 243, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieshima, K.; Imai, T.; Opdenakker, G.; Van Damme, J.; Kusuda, J.; Tei, H.; Sakaki, Y.; Takatsuki, K.; Miura, R.; Yoshie, O.; et al. Molecular cloning of a novel human CC chemokine liver and activation-regulated chemokine (LARC) expressed in liver. Chemotactic activity for lymphocytes and gene localization on chromosome 2. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 5846–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beider, K.; Abraham, M.; Begin, M.; Wald, H.; Weiss, I.D.; Wald, O.; Pikarsky, E.; Abramovitch, R.; Zeira, E.; Galun, E.; et al. Interaction between CXCR4 and CCL20 pathways regulates tumor growth. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, V.; Young, J.; Chanson, P.; Binart, N. New insights in prolactin: Pathological implications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockman, J.L.; Schroeder, M.D.; Schuler, L.A. PRL activates the cyclin D1 promoter via the Jak2/Stat pathway. Mol. Endocrinol. 2002, 16, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wick, M.; Pinggera, W.; Lehmann, P. Iron Storage—Ferritins, Isoferritins. In Clinical Aspects and Laboratory—Iron Metabolism, Anemias; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Schwende, H.; Fitzke, E.; Ambs, P.; Dieter, P. Differences in the state of differentiation of THP-1 cells induced by phorbol ester and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1996, 59, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Total (n = 186) | Low BDH2 Expression (n = 114) | High BDH2 Expression (n = 73) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex † | 0.444 | |||
| Male | 119 | 75 (65.79%) | 44 (60.27%) | |
| Female | 68 | 39 (34.21%) | 29 (39.73%) | |
| Age (years) ‡ | 65 (19–87) | 66 (35–87) | 0.976 | |
| Laboratory data ‡ | ||||
| WBC, μL−1 | 3990 (1100–56,000) | 3945 (1220–34,000) | 4100 (1100–56,000) | 0.144 |
| Hb, g/dL | 8.4 (4.3–14.7) | 8.55 (4.3–13.5) | 8.4 (5.6–14.7) | 0.720 |
| MCV, fl | 99.2 (52–122.7) | 98.5 (70–122.7) | 99.2 (52–117) | 0.812 |
| Platelets, ×1000/μL | 79,000 (8000–456,000) | 94,000 (8000–456,000) | 66,000 (12,000–346,000) | 0.051 |
| Ferritin, ng/mL || | 555.75 (62–5912) | 423.3 (8.1–5614) | 1003.6 (133.1–5916) | 0.02 ** |
| Type † | 0.003 ** | |||
| RA | 65 | 47 (35.09%) | 18 (24.66%) | 0.027 ** |
| RARS | 14 | 10 (8.77%) | 4 (5.48%) | 0.336 |
| RAEB-1 | 38 | 21 (18.42%) | 17 (23.29%) | 0.420 |
| RAEB-2 | 36 | 17 (14.91%) | 19 (26.03%) | 0.060 |
| MDS/MPN | 12 | 11 (9.65%) | 1 (1.37%) | 0.024 ** |
| Leukemia change | 22 | 8(7.02%) | 14 (19.18%) | 0.012 ** |
| IPSS-R score §† | 0.004 ** | |||
| Very low | 6 | 5 (4.39%) | 1 (1.37%) | 0.254 |
| Low | 53 | 40 (35.09%) | 13 (17.81%) | 0.011 ** |
| Int | 43 | 29(25.44%) | 14 (19.18%) | 0.321 |
| High | 32 | 13 (11.40%) | 19 (26.03%) | 0.017 ** |
| Very high | 47 | 22 (19.30%) | 25 (34.25%) | 0.022 ** |
| Leukemia progression §† | 4 (3.77%) | 9 (15.25%) | 0.017 ** |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, W.-C.; Lin, S.-F.; Wang, S.-C.; Tsai, W.-C.; Wu, C.-C.; Wu, S.-C. The Effects of Human BDH2 on the Cell Cycle, Differentiation, and Apoptosis and Associations with Leukemia Transformation in Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093033
Yang W-C, Lin S-F, Wang S-C, Tsai W-C, Wu C-C, Wu S-C. The Effects of Human BDH2 on the Cell Cycle, Differentiation, and Apoptosis and Associations with Leukemia Transformation in Myelodysplastic Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(9):3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093033
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Wen-Chi, Sheng-Fung Lin, Shu-Chen Wang, Wan-Chi Tsai, Chun-Chieh Wu, and Shih-Chi Wu. 2020. "The Effects of Human BDH2 on the Cell Cycle, Differentiation, and Apoptosis and Associations with Leukemia Transformation in Myelodysplastic Syndrome" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 9: 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093033
APA StyleYang, W.-C., Lin, S.-F., Wang, S.-C., Tsai, W.-C., Wu, C.-C., & Wu, S.-C. (2020). The Effects of Human BDH2 on the Cell Cycle, Differentiation, and Apoptosis and Associations with Leukemia Transformation in Myelodysplastic Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(9), 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093033







