On Top of the Alveolar Epithelium: Surfactant and the Glycocalyx
Abstract
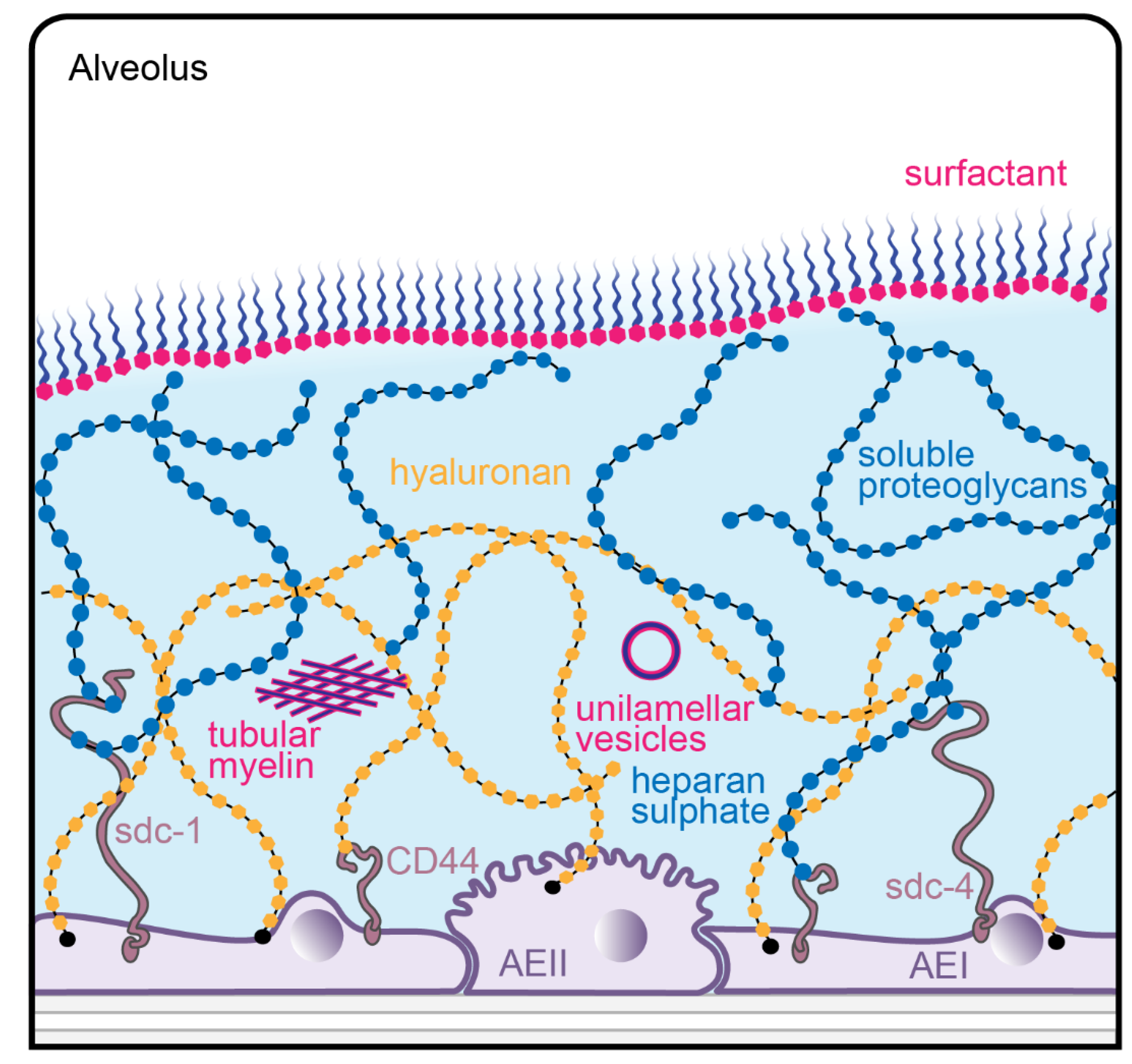
:1. The Alveolar Epithelium of the Lung and its Surfactant Lining
2. The Glycocalyx of the Alveolar Epithelium
3. Interactions Between Surfactant and the Glycocalyx
4. Visualizing the Glycocalyx by Electron Microscopy
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schneider, J.P.; Wrede, C.; Hegermann, J.; Weibel, E.R.; Mühlfeld, C.; Ochs, M. On the topological complexity of human alveolar epithelial type 1 cells. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 1153–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochs, M.; Weibel, E.R. Functional design of the human lung for gas exchange. In Fishman´s Pulmonary Diseases and Disorders, 5th ed.; Grippi, M.A., Elias, J.A., Fishman, J.A., Kotloff, R.M., Pack, A.I., Senior, R.M., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 20–62. [Google Scholar]
- Hsia, C.C.W.; Hyde, D.M.; Weibel, E.R. Lung structure and the intrinsic challenges of gas exchange. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 827–895. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Low, F.N. Electron microscopy of the rat lung. Anat. Rec. 1952, 113, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, F.N. The pulmonary alveolar epithelium of laboratory animals and man. Anat. Rec. 1953, 117, 241–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weibel, E.R.; Gil, J. Electron microscopic demonstration of an extracellular duplex lining layer of alveoli. Respir. Physiol. 1968, 4, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J.; Weibel, E.R. Improvements in demonstration of lining layer of lung alveoli by electron microscopy. Respir. Physiol. 1969, 8, 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastacky, J.; Lee, C.Y.C.; Goerke, J.; Koushafar, H.; Yager, D.; Kenaga, L.; Speed, T.P.; Chen, Y.; Clements, J.A. Alveolar lining layer is thin and continuous: Low-temperature scanning electron microscopy of rat lung. J. Appl. Physiol. 1995, 79, 1615–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Gil, J. Structure of pulmonary surfactant membranes and films: The role of proteins and lipid-protein interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1778, 1676–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ochs, M. The closer we look the more we see? Quantitative microscopic analysis of the pulmonary surfactant system. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 25, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgeig, S.; Morrison, J.L.; Daniels, C.B. Evolution, development and function of the pulmonary surfactant system in normal and perturbed environments. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 363–432. [Google Scholar]
- Olmeda, B.; Martinez-Calle, M.; Perez-Gil, J. Pulmonary surfactant metabolism in the alveolar airspace: Biogenesis, extracellular conversions, recycling. Ann. Anat. 2017, 209, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudsen, L.; Ochs, M. The micromechanics of lung alveoli: Structure and function of surfactant and tissue components. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 150, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bennett, H.S. Morphological aspects of extracellular polysaccharides. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1963, 11, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reitsma, S.; Slaaf, D.W.; Vink, H.; van Zandvoort, M.A.M.J.; oude Egbrink, M.G.A. The endothelial glycocalyx: Composition, functions, and visualization. Pfluegers Arch. 2007, 454, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarbell, J.M.; Cancel, L.M. The glycocalyx and its significance in human medicine. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 280, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LaRiviere, W.B.; Schmidt, E.P. The pulmonary endothelial glycocalyx in ARDS: A critical role of heparan sulphate. Curr. Top. Membr. 2018, 82, 33–52. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, E.P.; Yang, Y.; Janssen, W.J.; Gandjeva, A.; Perez, M.J.; Barthel, L.; Zemans, R.L.; Bowman, J.C.; Konayagi, D.E.; Yunt, Z.X.; et al. The pulmonary endothelial glycocalyx regulates neutrophil adhesion and lung injury during experimental sepsis. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inagawa, R.; Okada, H.; Takemura, G.; Suzuki, K.; Takada, C.; Yano, H.; Ando, Y.; Usui, T.; Hotta, Y.; Miyazaki, N.; et al. Ultrastructural alteration of pulmonary capillary endothelial glycocalyx during endotoxemia. Chest 2018, 154, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biasin, V.; Wygrecka, M.; Bärnthaler, T.; Jandl, K.; Jain, P.P.; Balint, Z.; Kovacs, G.; Leitinger, G.; Kolb-Lenz, D.; Kornmueller, K.; et al. Docking of meprin α to heparan sulphate protects the endothelium from inflammatory cell extravasation. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 1790–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Park, P.W.; Wilson, C.L.; Parks, W.C. Matrilysin shedding of syndecan-1 regulates chemokine mobilization and transepithelial efflux of neutrophils in acute lung injury. Cell 2002, 111, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pruessmeyer, J.; Martin, C.; Hess, F.M.; Schwarz, N.; Schmidt, S.; Kogel, T.; Hoettecke, N.; Schmidt, B.; Secht, A.; Uhlig, S.; et al. A disintegrin and metalloproteinase 17 (ADAM17) mediates inflammation-induced shedding of syndecan-1 and -4 by lung epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haeger, S.M.; Liu, X.; Han, X.; McNeil, J.B.; Oshima, K.; McMurty, S.A.; Yang, Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Nozik-Grayck, E.; et al. Epithelial heparan sulfate contributes to alveolar barrier function and is shed during lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 59, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidenfeld, S.; Kuebler, W.M. Shedding first light on the alveolar epithelial glycocalyx. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 59, 283–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegra, L.; Patrona, S.D.; Petrigni, G. Hyaluronic acid: Perspectives in lung disease. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2012, 207, 385–401. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, D.V. Lung lining liquid—The hidden depths. Biol. Neonate 2002, 81 (Suppl. 1), 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.C.; Tanswell, A.K.; Lynn, W.S. Isolation and characterization of glycosaminoglycans secreted by human foetal lung type II pneumocytes in culture. J. Cell Sci. 1980, 42, 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, S.J.M.; Post, M.; Torday, J.S.; Stiles, A.D.; Smith, B.T. Characterization of proteoglycans synthesized by fetal rat lung type II pneumonocytes in vitro and the effects of cortisol. Exp. Lung Res. 1987, 12, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.W.; Goerke, J.; Clements, J.A.; Taeusch, H.W. Hyaluronan decreases surfactant inactivation in vitro. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 57, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taeusch, H.W.; de la Bernardino Serra, J.; Perez-Gil, J.; Alonso, C.; Zasadzinski, J.A. Inactivation of pulmonary surfactant due to serum-inhibited adsorption and reversal by hydrophilic polymers: Experimental. Biophys. J. 2005, 89, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Sun, Z.; Qian, L.; Guo, C.; Yu, W.; Wang, W.; Lu, K.W.; Taeusch, H.W.; Sun, B. Effects of hyaluronan-fortified surfactant in ventilated premature piglets with respiratory distress. Biol. Neonate 2006, 89, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Rodriguez, E.; Cruz, A.; Richter, R.; Taeusch, H.W.; Perez-Gil, J. Transient exposure of pulmonary surfactant to hyaluronan promotes structural and compositional transformations into a highly active state. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 29872–29881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lutz, D.; Gazdhar, A.; Lopez-Rodriguez, E.; Ruppert, C.; Mahavadi, P.; Günther, A.; Klepetko, W.; Bates, J.H.; Smith, B.; Geiser, T.; et al. Alveolar derecruitment and collapse induration as crucial mechanisms in lung injury and fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 52, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffen, L.; Ruppert, C.; Hoymann, H.G.; Funke, M.; Ebener, S.; Kloth, C.; Mühlfeld, C.; Ochs, M.; Knudsen, L.; Lopez-Rodriguez, E. Surfactant replacement therapy reduces acute lung injury and collapse induration related lung remodeling in the bleomycin model. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 313, L313–L327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Yu, Z.; Jian, M.Y.; Ahmad, I.; Trempus, C.; Wagener, B.M.; Pittet, J.F.; Aggarwal, S.; Garantziotis, S.; Song, W.; et al. Instillation of hyaluronan reverses acid instillation injury to the mammalian blood gas barrier. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2018, 314, L808–L821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, N.W.; Atamas, S.P.; Luzina, I.G.; Galvin, J.R. Permanent alveolar collapse is the predominant mechanism in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2015, 9, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, L.; Ruppert, C.; Ochs, M. Tissue remodelling in pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 367, 607–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, T.; Liu, N.; Chen, H.; Geng, Y.; Kurkciyan, A.; Stripp, B.R.; Jiang, D.; Noble, P.W.; et al. Hyaluronan and TLR4 promote surfactant-protein-C-positive alveolar progenitor cell renewal and prevent severe pulmonary fibrosis. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawgood, S.; Clements, J. Pulmonary surfactant and its apoproteins. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hawgood, S.; Poulain, F.R. The pulmonary collectins and surfactant metabolism. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2001, 63, 495–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, E.; Wright, J.R. Surfactant proteins A and D and pulmonary host defense. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2001, 63, 521–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, F.X.; Whitsett, J.A. The pulmonary collectins, SP-A and SP-D, orchestrate innate immunity in the lung. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.R. Immunoregulatory functions of surfactant proteins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingma, P.S.; Whitsett, J.A. In defense of the lung: Surfactant protein A and surfactant protein B. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2006, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, T.E.; Conkright, J.J. Functions of surfactant proteins B and C. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2001, 63, 555–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitsett, J.A.; Weaver, T.E. Hydrophobic surfactant proteins in lung function and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, B.A. The role of hyaluronan in the pulmonary alveolus. J. Theor. Biol. 2001, 210, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibel, E.R.; Gil, J. Structure-Function Relationships at the Alveolar Level. In Bioengineering Aspects of the Lung; Lung Biology in Health and Disease; West, J.B., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1977; Volume 3, pp. 1–81. [Google Scholar]
- Rühl, N.; Lopez-Rodriguez, E.; Albert, K.; Smith, B.J.; Waever, T.E.; Ochs, M.; Knudsen, L. Surfactant protein B deficiency induced high surface tension: Relationship between alveolar micromechanics, alveolar fluid properties and alveolar epithelial cell injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Y.; Poon, G.F.T.; Arif, A.A.; Lee-Sayer, S.S.M.; Dosanjh, M.; Johnson, P. The survival of fetal and bone-marrow monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages is promoted by CD44 and its interaction with hyaluronan. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Y.; Arif, A.A.; Guo, J.; Ha, Z.; Lee-Sayer, S.S.M.; Poon, G.F.T.; Dosanjh, M.; Roskelley, C.D.; Huan, T.; Johnson, P. CD44 loss disrupts lung lipid surfactant homeostasis and exacerbates oxidized lipid-induced lung inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ochs, M.; Knudsen, L.; Hegermann, J.; Wrede, C.; Grothausmann, R.; Mühlfeld, C. Using electron microscopes to look into the lung. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 146, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J. Histological preservation and ultrastructure of alveolar surfactant. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1985, 47, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Amoudi, A.; Chang, J.J.; Leforestier, A.; McDowall, A.; Salamin, L.M.; Norlen, L.P.O.; Richter, K.; Blanc, N.S.; Studer, D.; Dubochet, J. Cryo-electron microscopy of vitreous sections. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 3583–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dubochet, J. Cryo-EM—The first 30 years. J. Microsc. 2011, 245, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studer, D.; Humbel, B.; Chiquet, M. Electron microscopy of high pressure frozen samples: Bridging the gap between cellular ultrastructure and atomic resolution. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 130, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vanhecke, D.; Herrmann, G.; Graber, W.; Hillmann-Marti, T.; Mühlfeld, C.; Studer, D.; Ochs, M. Lamellar body ultrastructure revisited: High-pressure freezing and cryo-electron microscopy of vitreous sections. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 134, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebong, E.E.; Macaluso, F.P.; Spray, D.C.; Tarbell, J.M. Imaging the endothelial glycocalyx in vitro by rapid freezing/freeze substitution transmission electron microscopy. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 1908–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsia, C.C.W.; Hyde, D.M.; Ochs, M.; Weibel, E.R. An official research policy statement of the American Thoracic Society / European Respiratory Society: Standards for quantitative assessment of lung structure. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 394–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weibel, E.R. Morphometric and stereological methods in respiratory physiology, including fixation techniques. In Techniques in the Life Sciences. Techniques in Respiratory Physiology; Part 1; Otis, A.B., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, S. The enteric surface coat on cat intestinal microvilli. J. Cell Biol. 1956, 27, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luft, J.H. Electron microscopy of cell extraneous coats as revealed by ruthenium red staining. J. Cell Biol. 1964, 23, 54A–55A. [Google Scholar]
- Rambourg, A.; Leblond, C.P. Electron microscope observations on the carbohydrate-rich cell coat present at the surface of cells in the rat. J. Cell Biol. 1967, 32, 27–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, M.A. Stains and Cytochemical Methods; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Groniowski, J.; Biczyskowa, W. Structure of the alveolar lining film of the lungs. Nature 1964, 21, 745–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, C., III. Cytochemistry of pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells. Am. J. Pathol. 1968, 53, 809–833. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brooks, R.E. Ruthenium red stainable surface layer on lung alveolar cells; electron microscopic interpretation. Stain Technol. 1969, 44, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bignon, J.; Faubert, F.; Jaurand, M.C. Plasma protein immunocytochemistry and polysaccharide cytochemistry at the surface of alveolar and endothelial cells in the rat lung. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1976, 24, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adamson, I.Y.R.; Bowden, D.H. The surface complexes of the lung. Am. J. Pathol. 1970, 61, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roth, J. Ultrahistochemical demonstration of saccharide components of complex carbohydrates at the alveolar cell surface and at the mesothelial cell surface of the pleura visceralis of mice by means of concanavalin A. Exp. Pathol. 1973, 8, 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Nir, I.; Pease, D.C. Polysaccharides in lung alveoli. Am. J. Anat. 1976, 147, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meban, C. Ultrastructural visualisation of carbohydrate groups in the surface coating of hamster alveolar macrophages and pneumonocytes. J. Anat. 1986, 146, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Taatjes, D.J.; Barcomb, L.; Leslie, K.O.; Low, R.B. Lectin binding patterns to terminal sugars of rat lung alveolar epithelial cells. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1990, 38, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwatsuki, H.; Sasaki, K.; Suda, M.; Itano, C. Cell differentiation of alveolar epithelium in the developing rat lung: Ultrahistochemical studies of glycoconjugates on the epithelial cell surface. Histochemistry 1993, 100, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.F.; Bairos, V.A. Glycocalyx of lung epithelial cells. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2002, 216, 131–173. [Google Scholar]
- Groot, C.G. Positive colloidal thorium dioxide as an electron microscopical contrasting agent for glycosaminoglycans, compared with ruthenium red and positive colloidal iron. Histochemistry 1981, 71, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lünsdorf, H.; Kristen, I.; Barth, E. Cationic hydrous thorium dioxide colloids—A useful tool for staining negatively charged surface matrices of bacteria for use in energy-filtered transmission electron microscopy. BMC Microbiol. 2006, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hegermann, J.; Lünsdorf, H.; Ochs, M.; Haller, H. Visualization of the glomerular endothelial glycocalyx by electron microscopy using cationic colloidal thorium dioxide. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 145, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mühlfeld, C.; Rothen-Rutishauer, B.; Vanhecke, D.; Blank, F.; Gehr, P.; Ochs, M. Visualization and quantitative analysis of nanoparticles in the respiratory tract by transmission electron microscopy. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2007, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ochs, M.; Johnen, G.; Müller, K.M.; Wahlers, T.; Hawgood, S.; Richter, J.; Brasch, F. Intracellular and intraalveolar localization of surfactant protein A (SP-A) in the parenchymal region of the human lung. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2002, 26, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorhout, W.F.; Veenendaal, T.; Haagsman, H.P.; Verkleij, A.J.; Van Golde, L.M.G.; Geuze, H.J. Surfactant protein A is localized at the corners of the pulmonary tubular myelin lattice. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1991, 39, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macklin, C.C. The pulmonary alveolar mucoid film and the pneumonocytes. Lancet 1954, 6822, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, J.A. Surface tension of lung extracts. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1957, 95, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolande, R.P.; Klaus, M.H. The morphologic demonstration of an alveolar lining layer and its relationship to pulmonary surfactant. Am. J. Pathol. 1964, 45, 449–463. [Google Scholar]
- Purcell, S.C.; Godula, K. Synthetic glycoscapes: Addressing the structural and functional complexity of the glycocalyx. Interface Focus 2019, 9, 20180080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, T.; Lu, X.; Berger, D.; Gmeiner, C.; Cho, J.; Schalek, R.; Ploegh, H.; Lichtman, J. Nanobody immunostaining for correlated light and electron microscopy with preservation of ultrastructure. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 1029–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegermann, J.; Wrede, C.; Fassbender, S.; Schliep, R.; Ochs, M.; Knudsen, L.; Mühlfeld, C. Volume-CLEM: A method for correlative light and electron microscopy in three dimensions. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2019, 317, L778–L784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ochs, M.; Hegermann, J.; Lopez-Rodriguez, E.; Timm, S.; Nouailles, G.; Matuszak, J.; Simmons, S.; Witzenrath, M.; Kuebler, W.M. On Top of the Alveolar Epithelium: Surfactant and the Glycocalyx. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093075
Ochs M, Hegermann J, Lopez-Rodriguez E, Timm S, Nouailles G, Matuszak J, Simmons S, Witzenrath M, Kuebler WM. On Top of the Alveolar Epithelium: Surfactant and the Glycocalyx. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(9):3075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093075
Chicago/Turabian StyleOchs, Matthias, Jan Hegermann, Elena Lopez-Rodriguez, Sara Timm, Geraldine Nouailles, Jasmin Matuszak, Szandor Simmons, Martin Witzenrath, and Wolfgang M. Kuebler. 2020. "On Top of the Alveolar Epithelium: Surfactant and the Glycocalyx" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 9: 3075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093075
APA StyleOchs, M., Hegermann, J., Lopez-Rodriguez, E., Timm, S., Nouailles, G., Matuszak, J., Simmons, S., Witzenrath, M., & Kuebler, W. M. (2020). On Top of the Alveolar Epithelium: Surfactant and the Glycocalyx. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(9), 3075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093075




