Identifying the p65-Dependent Effect of Sulforaphene on Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression via Bioinformatics Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
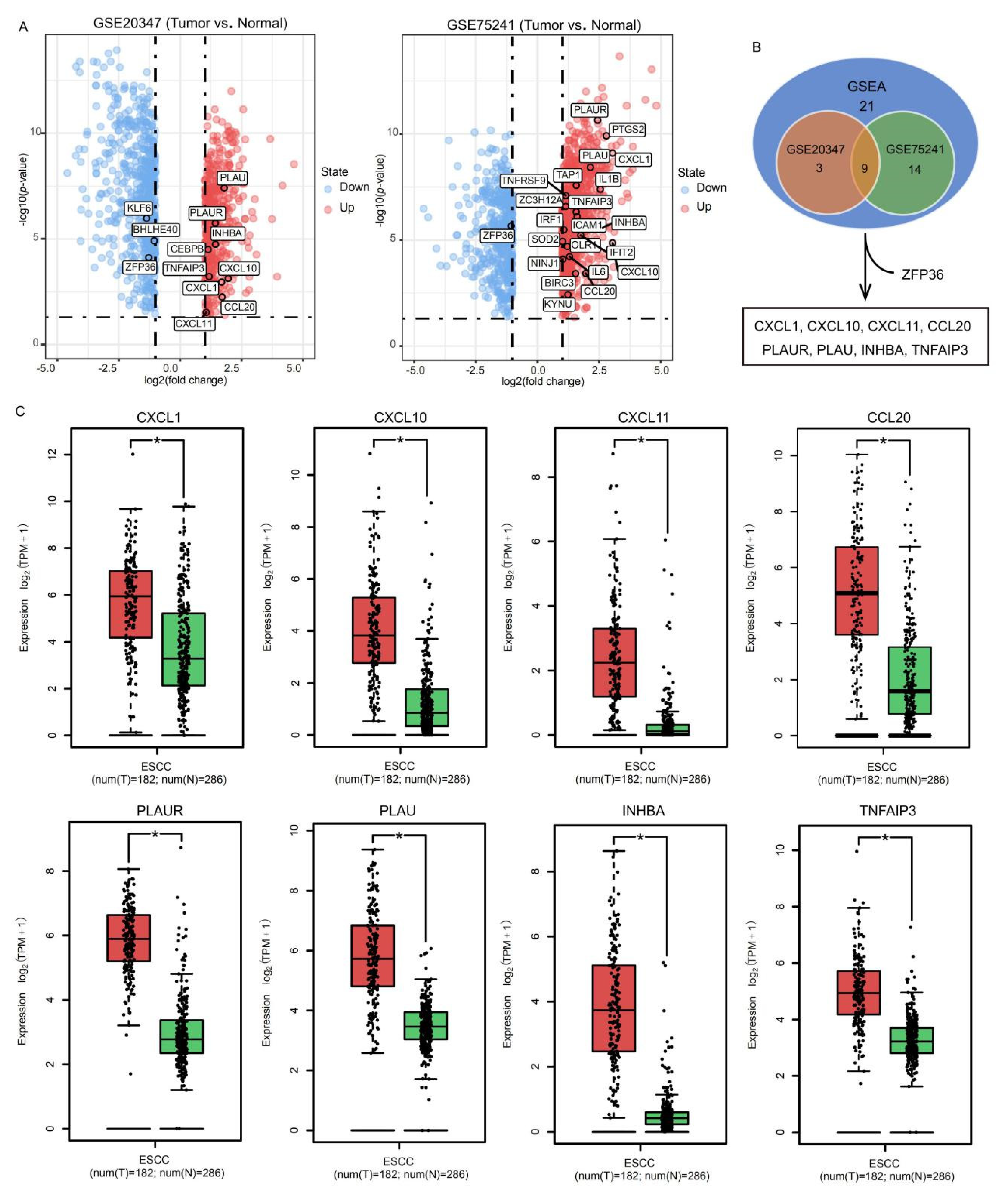
2.1. Identification of SFE-Regulated Molecular Signatures in ESCC
2.2. Evaluation of the SFE-Regulated ESCC Progression Signatures in the TCGA Samples
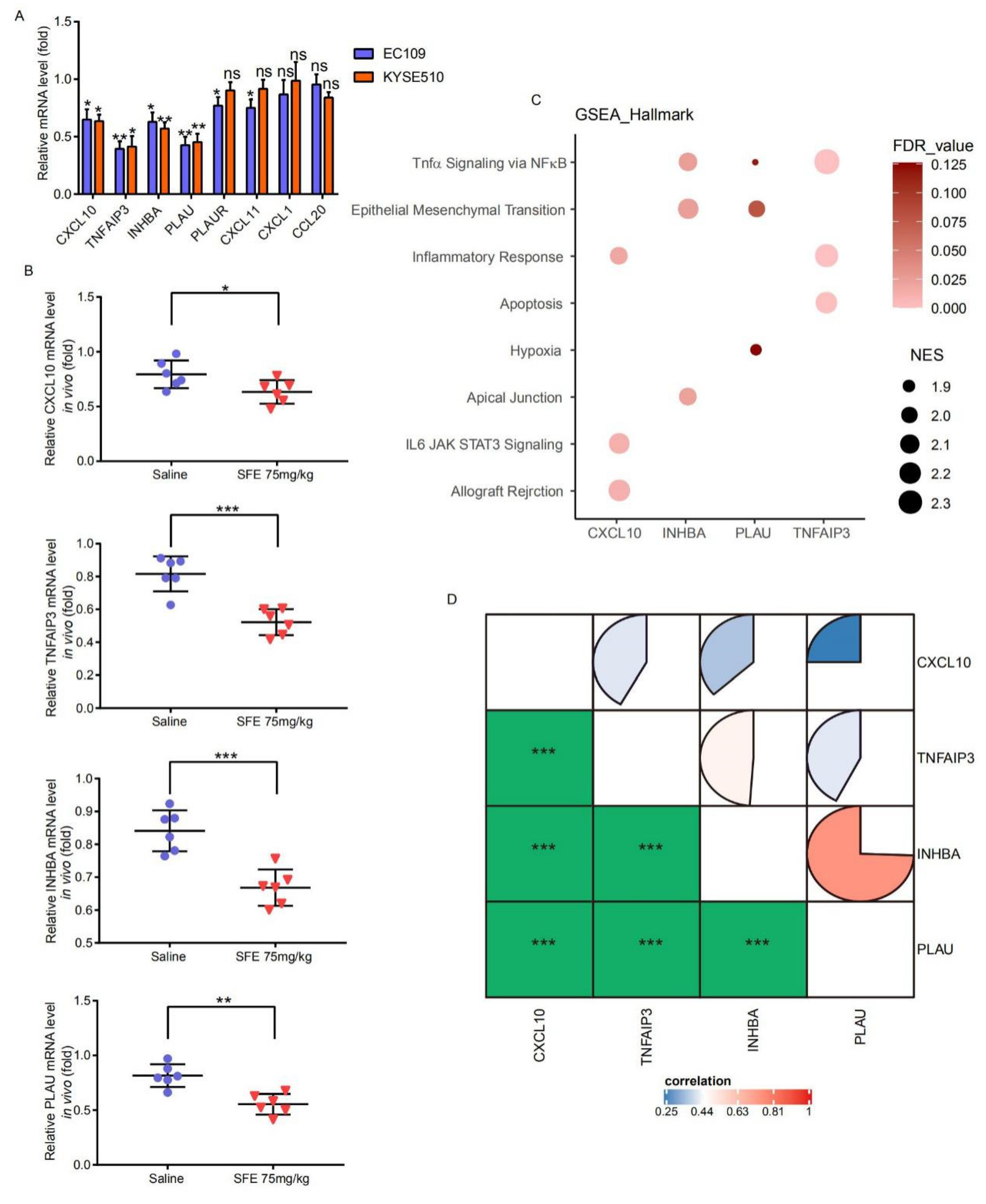
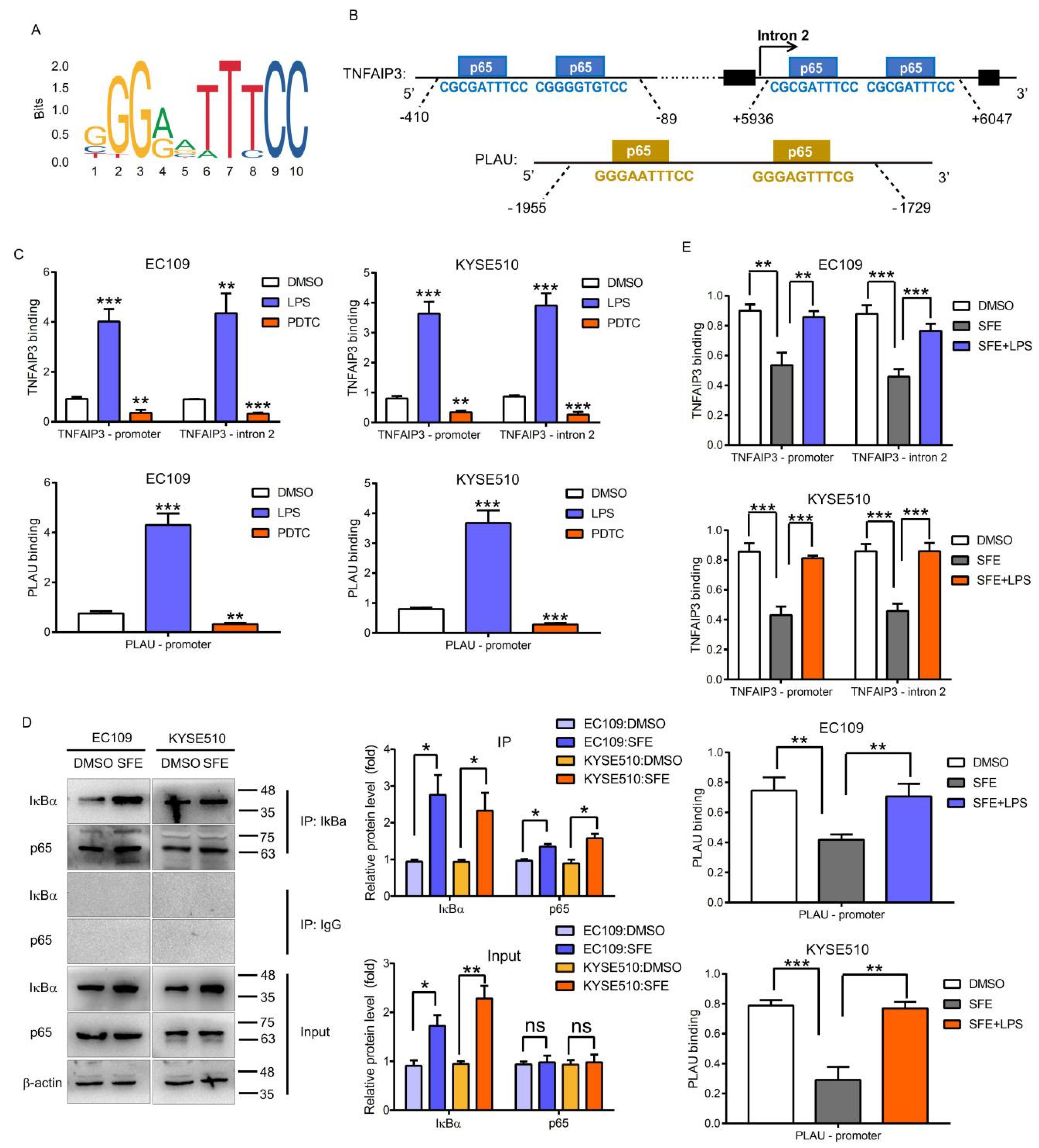
2.3. NFκB-p65 Can Induce TNFAIP3 and PLAU Expression in ESCC Cells
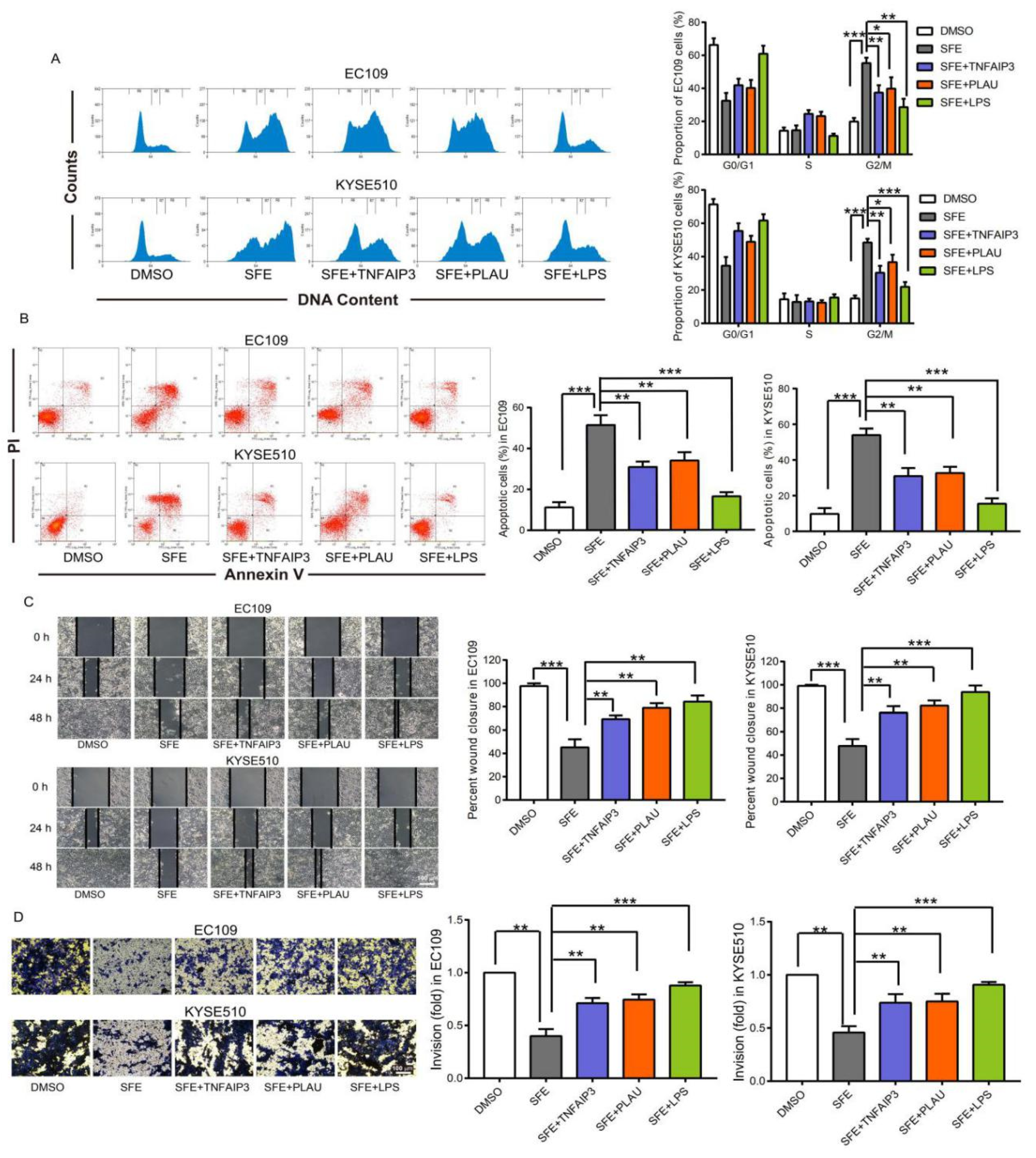
2.4. SFE Suppresses TNFAIP3 and PLAU Expression by Inactivating the NFκB Pathway to Inhibit ESCC Cell Progression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Chemicals
4.2. Plasmid Construction
4.3. Cell Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Analysis
4.4. Scrape Motility and Trans-Well Assays
4.5. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.6. Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Protein Extraction
4.7. Western Blotting Assay
4.8. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and ChIP-qPCR Assays
4.9. Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) Assay
4.10. Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.11. Statistics and Bioinformatics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prabhu, A.; Obi, K.O.; Rubenstein, J.H. The synergistic effects of alcohol and tobacco consumption on the risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, N.D.; Park, Y.; Subar, A.F.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Schatzkin, A.; Abnet, C.C. Fruit and vegetable intake and esophageal cancer in a large prospective cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 2753–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cools-Lartigue, J.; Spicer, J.; Ferri, L.E. Current status of management of malignant disease: Current management of esophageal cancer. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2015, 19, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, P.Q.; Song, D.; Yuan, Q.P.; Lv, X.H.; Zhao, D.; Liang, H. Preparative separation and purification of sulforaphene from radish seeds by high-speed countercurrent chromatography. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, P.Q.; Song, D.; Yuan, Q.P.; Yi, R.; Lv, X.H.; Liang, H. Separation and purification of sulforaphene from radish seeds using macroporous resin and preparative high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Teng, W.D.; Qu, Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Yuan, Q.P. Sulforaphene inhibits triple negative breast cancer through activating tumor suppressor Egr1. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 158, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Ren, M.; Qu, Y.; Teng, W.D.; Wang, Z.P.; Liang, H.; Yuan, Q.P. Sulforaphene inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma through repressing keratin 8 and activating anoikis. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 70326–70334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhou, M.; Liu, W.L.; Kuang, P.Q.; Liang, H.; Yuan, Q.P. The natural compound sulforaphene, as a novel anticancer reagent, targeting PI3K-AKT signaling pathway in lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 76656–76666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.C.; Wang, Y.D.; Ma, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.M.D.; Yuan, Q.P. Sulforaphene inhibits esophageal cancer progression via suppressing SCD and CDH3 expression, and activating the GADD45B-MAP2K3-p38-p53 feedback loop. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, N.D. Integrating cell-signalling pathways with nf-kappab and ikk function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Bharti, A.C.; Varghese, P.S.D.; Das, B.C. Differential expression and activation of NF-kappaB family proteins during oral carcinogenesis: Role of high risk human papillomavirus infection. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 2840–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmore, T.D. The Rel/NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway: Introduction. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6842–6844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.L.; Yang, X.P.; Yan, B.; Friedman, J.; Duggal, P.; Bagain, L.; Dong, G.; Yeh, N.T.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; et al. A novel nuclear factor-kappaB gene signature is differentially expressed in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas in association with TP53 status. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 5680–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altonsy, M.O.; Sasse, S.K.; Phang, T.L.; Gerber, A.N. Context-dependent Cooperation between Nuclear Factor B (NF-kB) and the Glucocorticoid Receptor at a TNFAIP3 Intronic Enhancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 8231–8239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.Y.; Wu, S.D.; Tsai, M.H.; Chuang, E.Y.; Chuang, L.L.; Hsu, L.C.; Lai, L.C. Transcription of Tnfaip3 kB and p38 via C/EBPb in Activated Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuning, U.; Guerrini, L.; Nishiguchi, T.; Page, S.; Seibold, H.; Magdolen, V.; Graeff, H.; Schmitt, M. Rel transcription factors contribute to elevated urokinase expression in human ovarian carcinoma cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 259, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Akita, K.; Tanida, S.; Ishida, A.; Toda, M.; Inoue, M.; Yashiro, M.; Sawada, T.; Hirakawa, K.; Nakada, H. MUC1 Protein Induces Urokinase-type Plasminogen Activator (uPA) by Forming a Complex with NF-B p65 Transcription Factor and Binding to the uPA Promoter, Leading to Enhanced Invasiveness of Cancer Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 35193–35204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opipari, A.W., Jr.; Hu, H.M.; Yabkowitz, R.; Dixit, V.M. The A20 zinc finger protein protects cells from tumor necrosis factor cytotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 12424–12427. [Google Scholar]
- Lars, V.; Rudi, B.; van Loo, G. The ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20 (TNFAIP3) is a central regulator of immunopathology. Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 383–391. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Jung, S.M.; Yang, K.M.; Bae, E.; Ahn, S.G.; Park, J.S.; Seo, D.; Kim, M.; Ha, J.; Lee, J.; et al. A20 promotes metastasis of aggressive basal-like breast cancers through multi-monoubiquitylation of Snail1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 1260–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wan, M.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, L.; Tai, S.; Cui, Y.F. The Prognostic Role of SOCS3 and A20 in Human Cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, C.G.; Studer, P.; Skroch, M.; Mahiou, J.; Minussi, D.C.; Peterson, C.R.; Wilson, S.W.; Patel, V.I.; Ma, A.; Csizmadia, E.; et al. A20 promotes liver regeneration by decreasing SOCS3 expression to enhance IL-6/STAT3 proliferative signals. Hepatology 2013, 57, 2014–2025. [Google Scholar]
- Hjelmeland, A.B.; Wu, Q.; Wickman, S.; Eyler, C.; Heddleston, J.; Shi, Q.; Lathia, J.D.; Macswords, J.; Lee, J.; McLendon, R.E.; et al. Targeting A20 decreases glioma stem cell survival and tumor growth. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, G.; Redman, J.E.; Wernisch, L.; Newton, R.; Malhotra, S.; Dawsey, S.M.; Lao-Sirieix, P.; Fitzgerald, R.C. The Discovery and Validation of Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Esophageal Squamous Dysplasia and Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Prev. Res. 2016, 9, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, P.A.; Kjøller, L.; Christensen, L.; Duffy, M.J. The urokinase-type plasminogen activator system in cancer metastasis: A review. Int. J. Cancer 1997, 72, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danø, K.; Behrendt, N.; Høyer-Hansen, G.; Johnsen, M.; Lund, L.R.; Ploug, M.; Rømer, J. Plasminogen activation and cancer. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 93, 676–681. [Google Scholar]
- Sidenius, N.; Blasi, F. The urokinase plasminogen activator system in cancer: Recent advances and implication for prognosis and therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.Y.; Wu, X.F.; Block, M.L.; Liu, Y.X.; Breese, G.R.; Hong, J.S.Y.; Knapp, D.J.; Crews, F.T. Systemic LPS Causes Chronic Neuroinflammation and Progressive Neurodegeneration. Glia 2007, 55, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Németh, Z.H.; Deitch, E.A.; Szabó, C.; Haskó, G. Pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate inhibits NF-kappaB activation and IL-8 production in intestinal epithelial cells. Immunol. Lett. 2003, 85, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Ge, G. Lysyl oxidase, extracellular matrix remodeling and cancer metastasis. Cancer Microenviron. 2012, 5, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddard, E.T.; Bozic, I.; Riddell, S.R.; Ghajar, C.M. Dormant tumour cells, their niches and the influence of immunity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Clifford, R.J.; Yang, H.H.; Wang, C.; Goldstein, A.M.; Ding, T.; Taylor, P.R.; Lee, M.P. Genome wide analysis of DNA copy number neutral loss of heterozygosity (CNNLOH) and its relation to gene expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedro, N.; Nathalia, M.D.C.; Paulo, T.d.S.S.; Isabela, M.G.; Maria, A.F.; Simone, G.; Miguel, A.M.; Hector, N.S.; Lilian, B.; Anke, B.; et al. Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma transcriptome reveals the effect of FOXM1 on patient outcome through novel PIK3R3 mediated activation of PI3K signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 16634–16647. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Q. Identifying the p65-Dependent Effect of Sulforaphene on Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression via Bioinformatics Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010060
Han S, Wang Z, Liu J, Yuan Q. Identifying the p65-Dependent Effect of Sulforaphene on Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression via Bioinformatics Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(1):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010060
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Sichong, Zhe Wang, Jining Liu, and Qipeng Yuan. 2021. "Identifying the p65-Dependent Effect of Sulforaphene on Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression via Bioinformatics Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 1: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010060
APA StyleHan, S., Wang, Z., Liu, J., & Yuan, Q. (2021). Identifying the p65-Dependent Effect of Sulforaphene on Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression via Bioinformatics Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(1), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010060






