BMAL1 Knockdown Leans Epithelial–Mesenchymal Balance toward Epithelial Properties and Decreases the Chemoresistance of Colon Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Transcriptome of CRC Patients Shows BMAL1 Correlation to EMT and Cancer Invasiveness
2.2. BMAL1-KD Increases E-Cadherin Expression and E-Cadherin/β-Catenin Co-Localization at the Plasma Membrane of CRC Cells
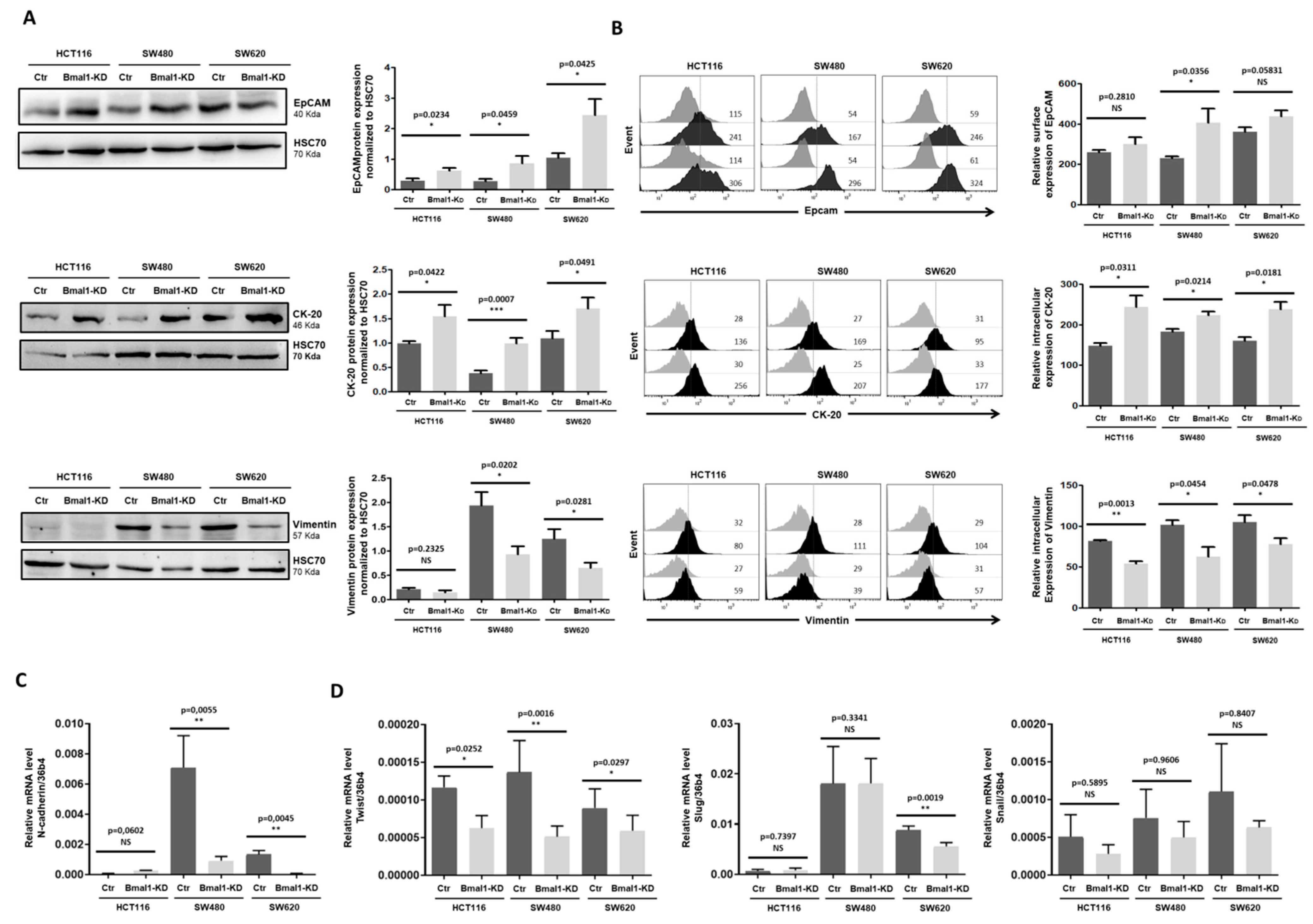
2.3. BMAL1-KD Leans Epithelial–Mesenchymal Balance of CRC Cells toward Epithelial Properties
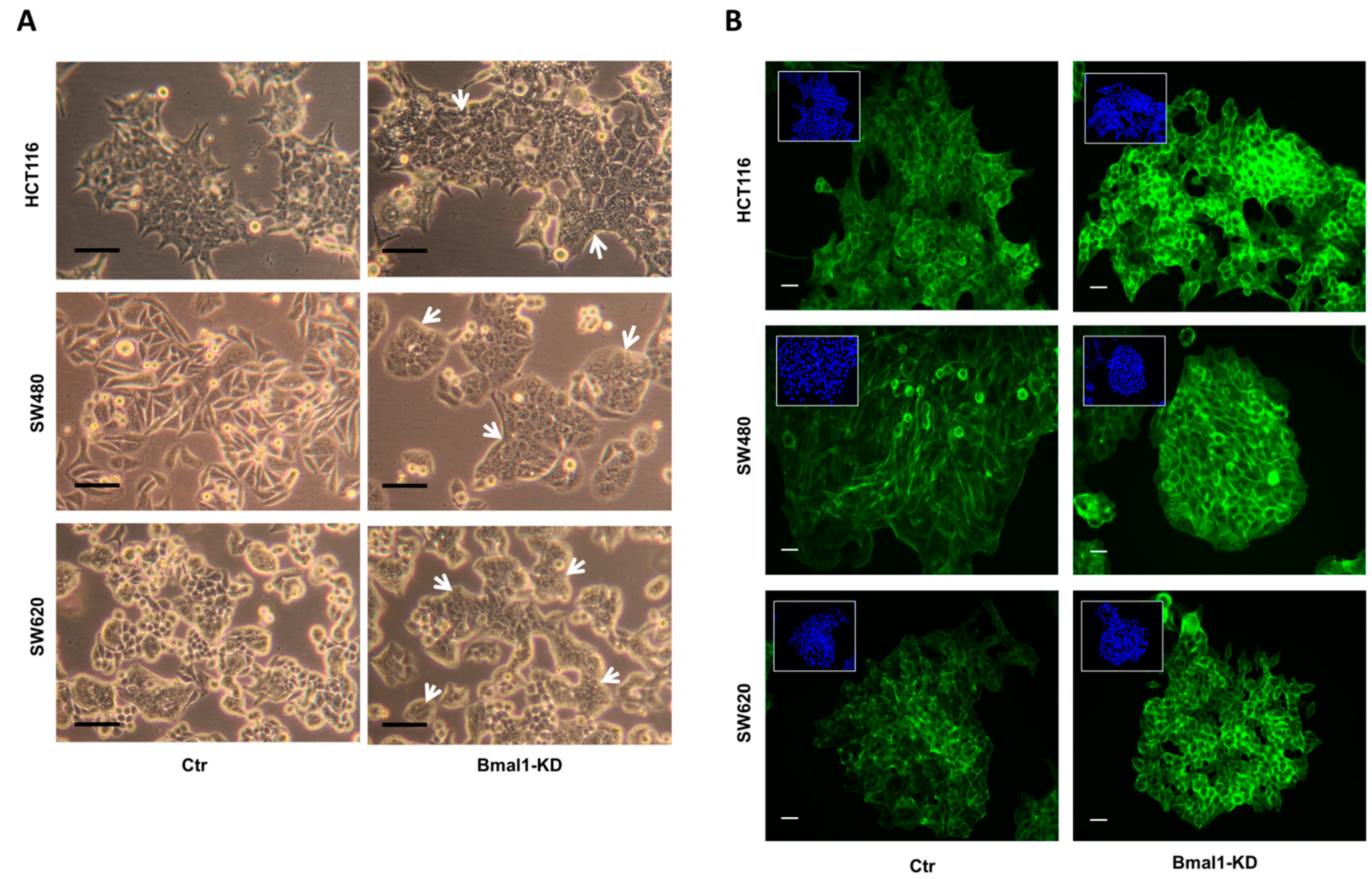
2.4. BMAL1-KD Induces Morphological Changes in CRC Cell Lines
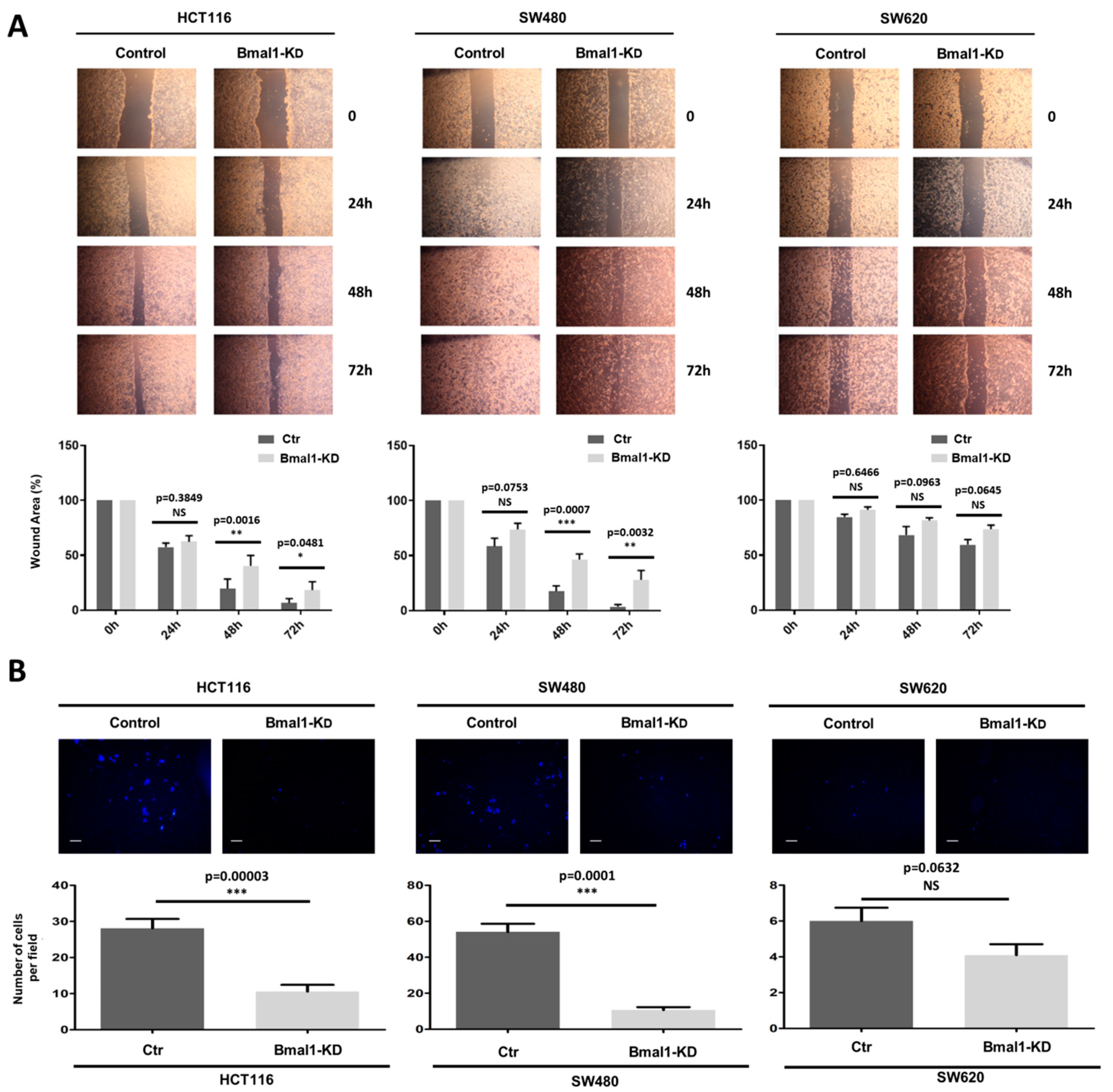
2.5. BMAL1-KD Reduces Cell Migration and the Invasive Potential of CRC Cell Lines
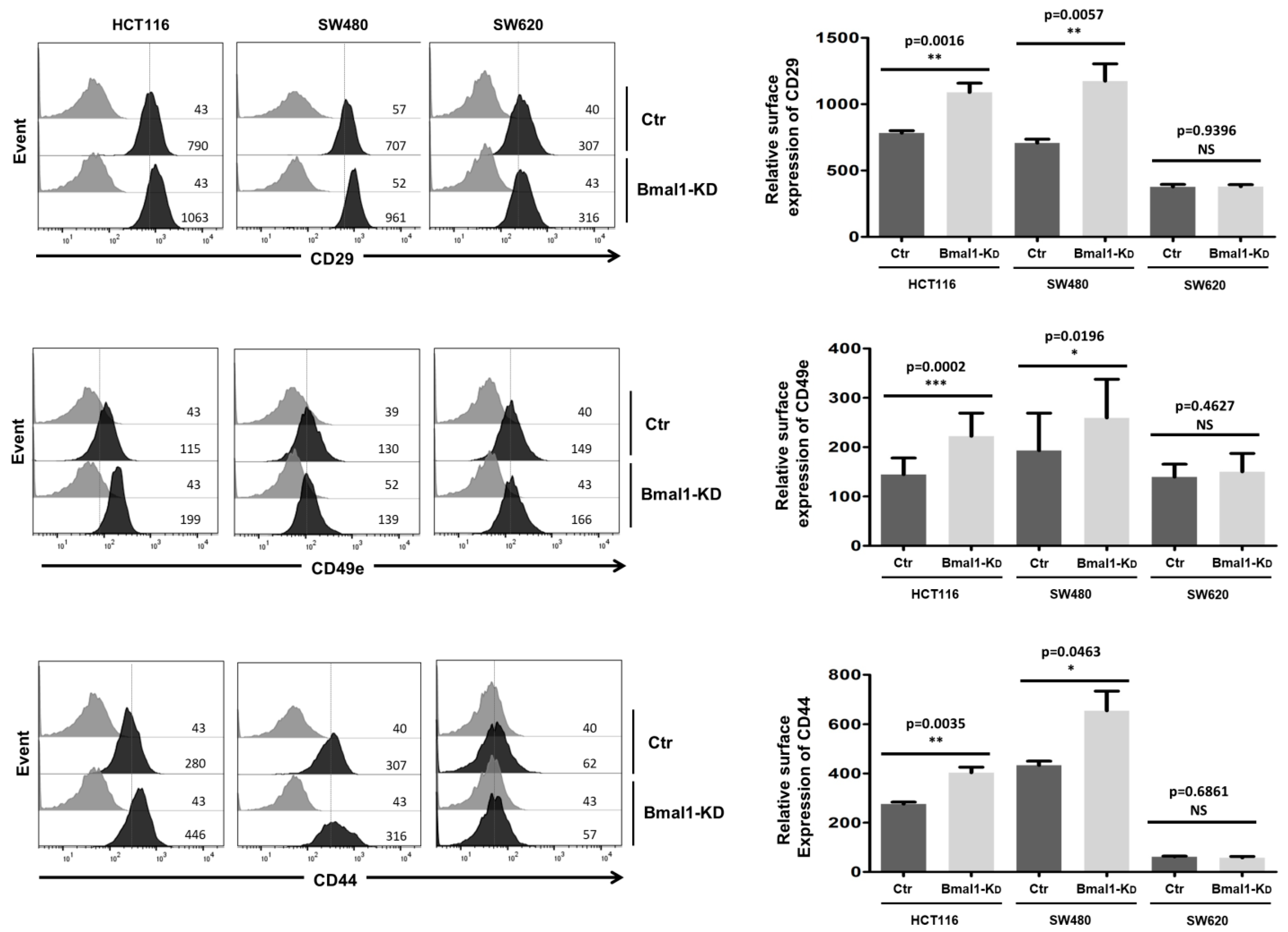
2.6. BMAL1-KD Increases the Expression of Cell Adhesion Molecules in CRC Cell Lines
2.7. Response to Standard Therapy Is Increased in BMAL1-KD CRC Cell Lines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. RNAseq Analysis
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. The shRNA Cloning in Lentiviral Vector
4.4. Lentivirus Production and Cell Transduction
4.5. Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Extracts Preparation
4.6. Western-Blot Analysis
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.8. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.9. Immunofluorescence and Confocal Microscopy
4.10. Migration and Invasion Assays
4.11. Drug Sensitivity Assay
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Medhanie, G.A.; Fedewa, S.A.; Jemal, A. State Variation in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer in the United States, 1995–2015. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 111, 1104–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, S.; Deng, G.; Wu, X.; He, J.; Pei, H.; Shen, H.; Zeng, S. A prognostic analysis of 895 cases of stage III colon cancer in different colon subsites. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2015, 30, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.J.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions in Development and Disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tian, X.-J.; Xing, J. Signal Transduction Pathways of EMT Induced by TGF-β, SHH, and WNT and Their Crosstalks. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeanes, A.; Gottardi, C.J.; Yap, A.S. Cadherins and cancer: How does cadherin dysfunction promote tumor progression? Oncogene 2008, 27, 6920–6929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, J.S. Transcriptional architecture of the mammalian circadian clock. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Kettner, N.M. The Circadian Clock in Cancer Development and Therapy. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2013, 119, 221–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallmann, R.; Okyar, A.; Lévi, F. Dosing-Time Makes the Poison: Circadian Regulation and Pharmacotherapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 430–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lévi, F.; Okyar, A.; Dulong, S.; Innominato, P.F.; Clairambault, J. Circadian Timing in Cancer Treatments. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 50, 377–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulli, G.; Lam, M.T.Y.; Panda, S. Interplay between Circadian Clock and Cancer: New Frontiers for Cancer Treatment. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 475–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straif, K.; Baan, R.; Grosse, Y.; Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Altieri, A.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Cogliano, V. Carcinogenicity of shift-work, painting, and fire-fighting. Lancet Oncol. 2007, 8, 1065–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacchetti, S. Chronotherapy of colorectal cancer. Chronobiol. Int. 2002, 19, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Focan, C.; Kreutz, F.; Graas, M.-P.; Longrée, L.; Focan-Henrard, D.; Demolin, G.; Moeneclaey, N. Phase I–II study to assess the feasibility and activity of the triple combination of 5-fluorouracil/folinic acid, carboplatin and irinotecan (CPT-11) administered by chronomodulated infusion for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer. Final report of the BE-1603 study. Pathol. Biol. 2013, 61, e27–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunger, M.K.; Wilsbacher, L.D.; Moran, S.M.; Clendenin, C.; Radcliffe, L.A.; HogenEsch, J.B.; Simon, M.C.; Takahashi, J.S.; Bradfield, C.A. Mop3 is an essential component of the master circadian pacemaker in mammals. Cell 2000, 103, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhao, S.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, E.; Hu, G.; Hu, B.; Zheng, P.; Xiao, J.; Lu, Z.; Lu, Y.; et al. The circadian clock gene Bmal1 acts as a potential anti-oncogene in pancreatic cancer by activating the p53 tumor suppressor pathway. Cancer Lett. 2016, 371, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Cheng, B.; Xie, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L. Circadian Clock Gene Bmal1 Inhibits Tumorigenesis and Increases Paclitaxel Sensitivity in Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Lee, C.C. The circadian clock: Pacemaker and tumour suppressor. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.A.; Ouyang, C.; Qi, Y.; Chung, Y.; Cheng, C.-T.; LaBarge, M.A.; Seewaldt, V.L.; Ann, D.K. A Non-canonical Function of BMAL1 Metabolically Limits Obesity-Promoted Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. iScience 2020, 23, 100839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, T.; Takenoshita, S.; Akaike, M.; Kunisaki, C.; Fujii, S.; Nozaki, A.; Numata, K.; Shiozawa, M.; Rino, Y.; Tanaka, K.; et al. Expression of circadian genes correlates with liver metastasis and outcomes in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 25, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgermeister, E.; Battaglin, F.; Eladly, F.; Wu, W.; Herweck, F.; Schulte, N.; Betge, J.; Härtel, N.; Kather, J.N.; Weis, C.-A.; et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like (ARNTL/BMAL1) is associated with bevacizumab resistance in colorectal cancer via regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor A. EBioMedicine 2019, 45, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Devocelle, A.; Souza, L.; Foudi, A.; Bento, S.T.; Desterke, C.; Sherrard, R.; Ballesta, A.; Adam, R.; Giron-Michel, J.; et al. BMAL1 knockdown triggers different colon carcinoma cell fates by altering the delicate equilibrium between AKT/mTOR and P53/P21 pathways. Aging 2020, 10, 8067–8083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frixen, U.H.; Behrens, J.; Sachs, M.; Eberle, G.; Voss, B.; Warda, A.; Löchner, D.; Birchmeier, W. E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion prevents invasiveness of human carcinoma cells. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 113, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsella, A.R.; Lepts, G.C.; Hill, C.L.; Jones, M. Reduced E-cadherin expression correlates with increased invasiveness in colorectal carcinoma cell lines. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 1994, 12, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ye, J.; Wu, D.; Shen, J.; Wu, P.; Ni, C.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X. Enrichment of colorectal cancer stem cells through epithelial-mesenchymal transition via CDH1 knockdown. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 6, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Liu, Z.; Niu, B.; Zhang, J.; Tan, T.K.; Lee, S.R.; Zhao, Y.; Harris, D.C.H.; Zheng, G. E-Cadherin/β-Catenin Complex and the Epithelial Barrier. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 567305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Hua, F.; Hu, Z.-W. The regulation of β-catenin activity and function in cancer: Therapeutic opportunities. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33972–33989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilles, C.; Polette, M.; Mestdagt, M.; Nawrocki-Raby, B.; Ruggeri, P.; Birembaut, P.; Foidart, J.-M. Transactivation of vimentin by beta-catenin in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 2658–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Becker, B.N.; Hoffmann, F.M.; Mertz, J.E. Complete reversal of epithelial to mesenchymal transition requires inhibition of both ZEB expression and the Rho pathway. BMC Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavadil, J.; Bitzer, M.; Liang, D.; Yang, Y.-C.; Massimi, A.; Kneitz, S.; Piek, E.; Böttinger, E.P. Genetic programs of epithelial cell plasticity directed by transforming growth factor-beta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6686–6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Tilló, E.; Liu, Y.; De Barrios, O.; Siles, L.; Fanlo, L.; Cuatrecasas, M.; Darling, D.S.; Dean, D.C.; Castells, A.; Postigo, A. EMT-activating transcription factors in cancer: Beyond EMT and tumor invasiveness. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 3429–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tang, H. miR-10a suppresses colorectal cancer metastasis by modulating the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and anoikis. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlobec, I.; Lugli, A.; Baker, K.; Roth, S.; Minoo, P.; Hayashi, S.; Terracciano, L.; Jass, J.R. Role of APAF-1, E-cadherin and peritumoural lymphocytic infiltration in tumour budding in colorectal cancer. J. Pathol. 2007, 212, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starchenko, A.; Graves-Deal, R.; Yang, Y.-P.; Li, C.; Zent, R.; Singh, B.; Coffey, R.J. Clustering of integrin α5 at the lateral membrane restores epithelial polarity in invasive colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2017, 28, 1288–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuang, A.D.; Fan, F.; Camp, E.R.; Van Buren, G.; Liu, W.; Somcio, R.; Gray, M.J.; Cheng, H.; Hoff, P.M.; Ellis, L.M. Chronic Oxaliplatin Resistance Induces Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 4147–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, M.A.; Valdecanas, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhan, Y.; Bhardwaj, V.; Calin, G.A.; Komaki, R.; Giri, D.K.; Quini, C.C.; Wolfe, T.; et al. Therapeutic Delivery of miR-200c Enhances Radiosensitivity in Lung Cancer. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2014, 22, 1494–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Yang, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhai, Z. Transforming growth factor-β1 contributes to oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer via epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mårtensson, A.; Oberg, A.; Jung, A.; Cederquist, K.; Stenling, R.; Palmqvist, R. Beta-catenin expression in relation to genetic instability and prognosis in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 17, 447–452. [Google Scholar]
- Lugli, A.; Zlobec, I.; Minoo, P.; Baker, K.; Tornillo, L.; Terracciano, L.; Jass, J.R. Prognostic significance of the wnt signalling pathway molecules APC, beta-catenin and E-cadherin in colorectal cancer: A tissue microarray-based analysis. Histopathology 2007, 50, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munemitsu, S.; Albert, I.; Souza, B.; Rubinfeld, B.; Polakis, P. Regulation of intracellular beta-catenin levels by the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) tumor-suppressor protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 3046–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, B.R. Nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of APC regulates β-catenin subcellular localization and turnover. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, N.; Lu, C.; Bei, Y.; Qian, R.; Hua, L. Upregulation of circadian gene ’hClock’ contribution to metastasis of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, R.; Price, L.S.; Koffer, A. Rho Controls Cortical F-actin Disassembly in Addition to, but Independently of, Secretion in Mast Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 38140–38146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relógio, A.; Thomas, P.; Medina-Pérez, P.; Reischl, S.; Bervoets, S.; Gloc, E.; Riemer, P.; Mang-Fatehi, S.; Maier, B.; Schäfer, R.; et al. Ras-Mediated Deregulation of the Circadian Clock in Cancer. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Athman, R.; Fuhr, L.; Relógio, A. A Systems-Level Analysis Reveals Circadian Regulation of Splicing in Colorectal Cancer. EBioMedicine 2018, 33, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhr, L.; El-Athman, R.; Scrima, R.; Cela, O.; Carbone, A.; Knoop, H.; Li, Y.; Hoffmann, K.; Laukkanen, M.O.; Corcione, F.; et al. The Circadian Clock Regulates Metabolic Phenotype Rewiring Via HKDC1 and Modulates Tumor Progression and Drug Response in Colorectal Cancer. EBioMedicine 2018, 33, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Du, X. KRAS mutation testing in metastatic colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 5171–5180. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Yang, Z.; Lu, N. A new role for the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2015, 9, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Xiao, Y.; Song, Y.; Yuan, H.; Luo, J.; Xu, W. FAT4 regulates the EMT and autophagy in colorectal cancer cells in part via the PI3K-AKT signaling axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Jeught, K.; Xu, H.-C.; Li, Y.-J.; Lu, X.-B.; Ji, G. Drug resistance and new therapies in colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3834–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederroth, C.R.; Albrecht, U.; Bass, J.; Brown, S.A.; Dyhrfjeld-Johnsen, J.; Gachon, F.; Green, C.B.; Hastings, M.H.; Helfrich-Förster, C.; Hogenesch, J.B.; et al. Medicine in the Fourth Dimension. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, T.; Aygenli, F.; Emisoglu, H.; Ozcelik, G.; Canturk, A.; Yilmaz, S.; Ozturk, N. Opposite Carcinogenic Effects of Circadian Clock Gene BMAL1. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, W.; Takenoshita, S. Overexpression of both CLOCK and BMAL1 inhibits entry to S phase in human colon cancer cells. Fukushima J. Med. Sci. 2015, 61, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.-L.; Luo, H.-Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, W.-J.; Chen, D.-L.; Huang, P.; Xu, R.-H. Overexpression of the Circadian Clock Gene Bmal1 Increases Sensitivity to Oxaliplatin in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Balibrea, E.; Martínez-Cardús, A.; Ginés, A.; De Porras, V.R.; Moutinho, C.; Layos, L.; Manzano, J.L.; Bugés, C.; Bystrup, S.; Esteller, M.; et al. Tumor-Related Molecular Mechanisms of Oxaliplatin Resistance. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.-J.; Zhang, W.; Xu, X.-M.; Zhang, F.; Tao, W.-P.; Ye, J.-J.; Ge, W. Twist mediates an aggressive phenotype in human colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Fan, J.; Zhi, F.; Li, A.; Li, C.; Berger, A.E.; Boorgula, M.P.; Barkataki, S.; Courneya, J.-P.; Chen, Y.; et al. Mobilization of epithelial mesenchymal transition genes distinguishes active from inactive lesional tissue in patients with ulcerative colitis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 4615–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang-Verslues, W.W.; Chang, P.-H.; Jeng, Y.-M.; Kuo, W.-H.; Chiang, P.-H.; Chang, Y.-C.; Hsieh, T.-H.; Su, F.-Y.; Lin, L.-C.; Abbondante, S.; et al. Loss of corepressor PER2 under hypoxia up-regulates OCT1-mediated EMT gene expression and enhances tumor malignancy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12331–12336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, A.; Beligala, D.H.; Sharma, V.P.; Burgos, C.A.; Lee, A.M.; Geusz, M.E. Cancer stem cell generation during epithelial-mesenchymal transition is temporally gated by intrinsic circadian clocks. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2020, 37, 617–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.; Beligala, D.H.; Sharma, V.P.; Fry, B.R.; Geusz, M.E. Abstract 858: The circadian clock of glioma cells undergoing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Y. BMAL1 but not CLOCK is associated with monochromatic green light-induced circadian rhythm of melatonin in chick pinealocytes. Endocr. Connect. 2019, 8, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 2012, 487, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Complex Cancer Genomics and Clinical Profiles Using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) Hallmark Gene Set Collection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lê, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: An R Package for Multivariate Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordier, L.; Bluteau, D.; Jalil, A.; Legrand, C.; Pan, J.; Rameau, P.; Jouni, D.; Bluteau, O.; Mercher, T.; Leon, C.; et al. RUNX1-induced silencing of non-muscle myosin heavy chain IIB contributes to megakaryocyte polyploidization. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Giacchetti, S.; Parouchev, A.; Hadadi, E.; Li, X.; Dallmann, R.; Xandri-Monje, H.; Portier, L.; Adam, R.; Lévi, F.; et al. Dosing time dependent in vitro pharmacodynamics of Everolimus despite a defective circadian clock. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Devocelle, A.; Desterke, C.; de Souza, L.E.B.; Hadadi, É.; Acloque, H.; Foudi, A.; Xiang, Y.; Ballesta, A.; Chang, Y.; et al. BMAL1 Knockdown Leans Epithelial–Mesenchymal Balance toward Epithelial Properties and Decreases the Chemoresistance of Colon Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105247
Zhang Y, Devocelle A, Desterke C, de Souza LEB, Hadadi É, Acloque H, Foudi A, Xiang Y, Ballesta A, Chang Y, et al. BMAL1 Knockdown Leans Epithelial–Mesenchymal Balance toward Epithelial Properties and Decreases the Chemoresistance of Colon Carcinoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(10):5247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105247
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuan, Aurore Devocelle, Christophe Desterke, Lucas Eduardo Botelho de Souza, Éva Hadadi, Hervé Acloque, Adlen Foudi, Yao Xiang, Annabelle Ballesta, Yunhua Chang, and et al. 2021. "BMAL1 Knockdown Leans Epithelial–Mesenchymal Balance toward Epithelial Properties and Decreases the Chemoresistance of Colon Carcinoma Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 10: 5247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105247
APA StyleZhang, Y., Devocelle, A., Desterke, C., de Souza, L. E. B., Hadadi, É., Acloque, H., Foudi, A., Xiang, Y., Ballesta, A., Chang, Y., & Giron-Michel, J. (2021). BMAL1 Knockdown Leans Epithelial–Mesenchymal Balance toward Epithelial Properties and Decreases the Chemoresistance of Colon Carcinoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(10), 5247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105247





