Lamin A/C Is Dispensable to Mechanical Repression of Adipogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
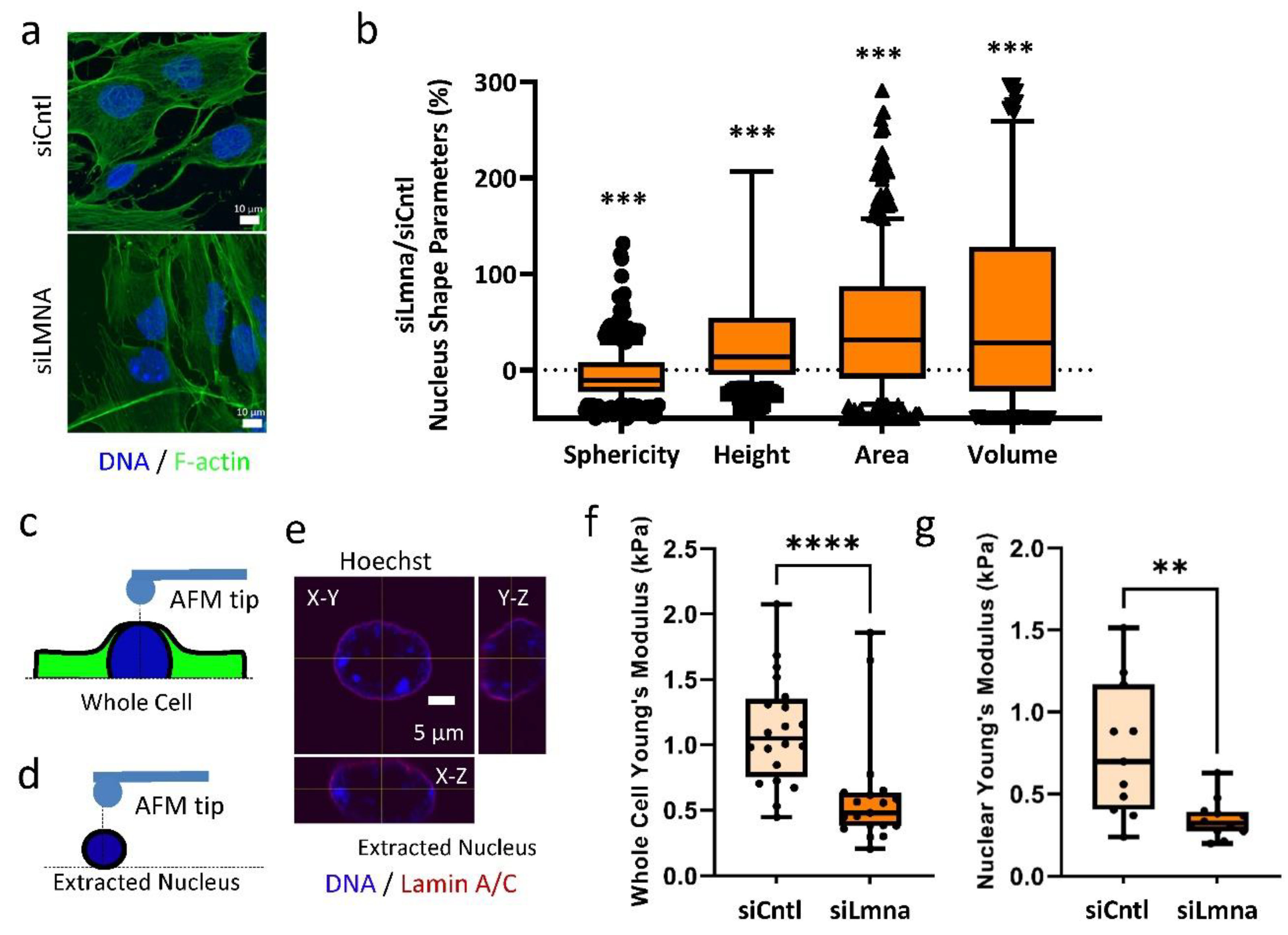
2.1. siRNA Depletion of Lamin A/C Weakens the Nuclear Elastic Modulus in MSCs
2.2. siRNA Depletion of Lamin A/C Increases SUN2 Nuclear Levels and Focal Adhesion Proteins
2.3. Focal Adhesions Maintain Response to Mechanical Stimulus in Lamin-A/C-Depleted MSCs
2.4. Application of Daily LIV Treatment Decreases Adipogenic Differentiation in MSCs
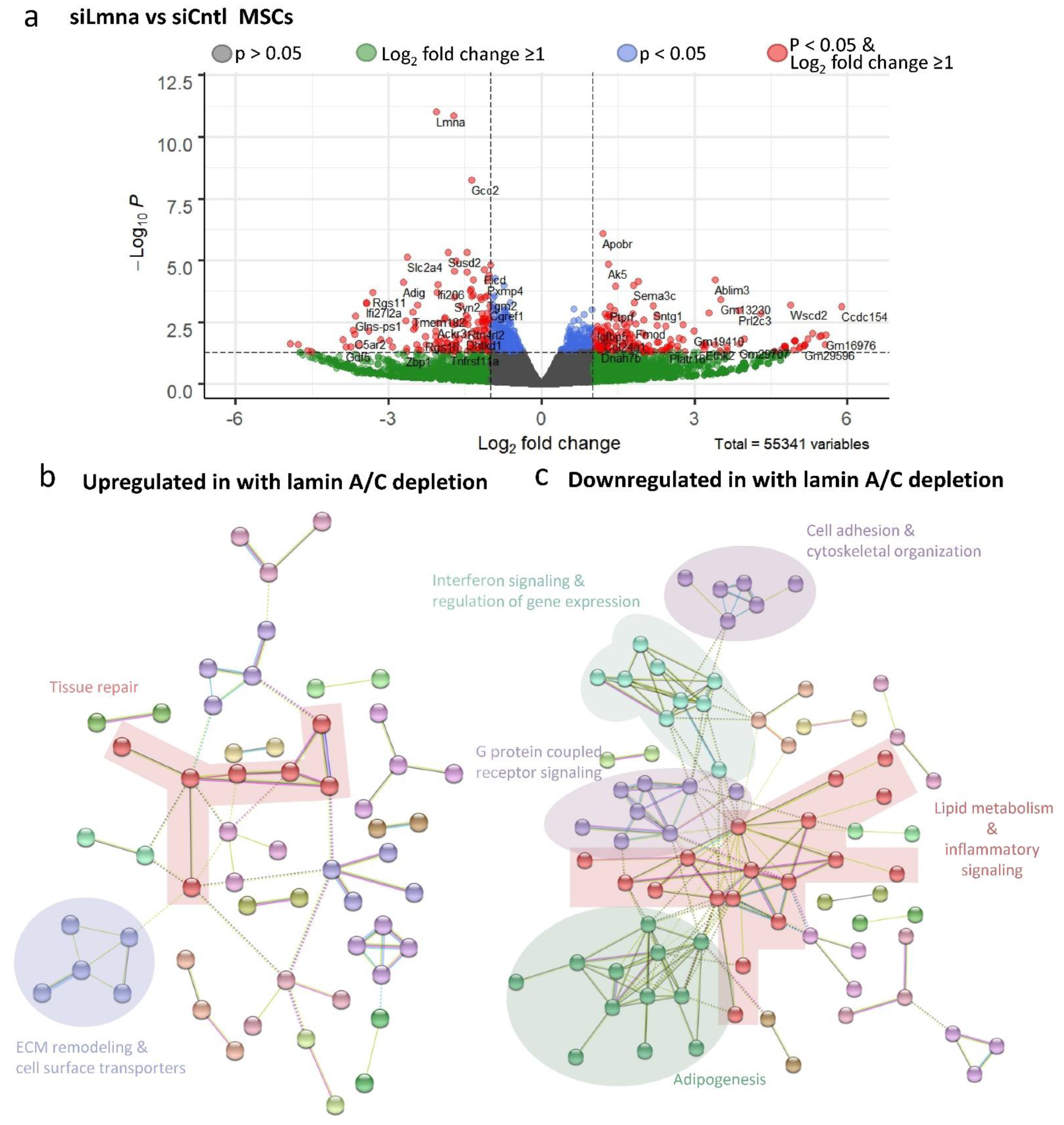
2.5. Differential Effect of Lamin A/C Depletion and LIV on mRNA Transcription during Adipogenic Differentiation
2.6. Lamin A/C Depletion Impedes Adipogenic Transcription in MSCs
2.7. Low-Intensity Vibration (LIV) Decreases Interferon Signaling Pathway Gene Expression
3. Discussion and Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. MSC Isolation
4.2. Cell Culture, Pharmacological Reagents, and Antibodies
4.3. LIV and Strain
4.4. Isolation of Focal Adhesions
4.5. siRNA-Silencing Sequences
4.6. Isolation of Nuclei for Young’s Modulus
4.7. RNA-Seq
4.8. Immunofluorescence
4.9. Lipid Droplet Analysis
4.10. Nuclear Morphology
4.11. Western Blotting
4.12. Statistical Analysis and Reproducibility
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shumaker, D.K.; Dechat, T.; Kohlmaier, A.; Adam, S.A.; Bozovsky, M.R.; Erdos, M.R.; Eriksson, M.; Goldman, A.E.; Khuon, S.; Collins, F.S.; et al. Mutant nuclear lamin A leads to progressive alterations of epigenetic control in premature aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8703–8708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, K.H.; Kennedy, B.K. When lamins go bad: Nuclear structure and disease. Cell 2013, 152, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sandre-Giovannoli, A.; Bernard, R.; Cau, P.; Navarro, C.; Amiel, J.; Boccaccio, I.; Lyonnet, S.; Stewart, C.L.; Munnich, A.; Le Merrer, M.; et al. Lamin a truncation in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria. Science 2003, 300, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinescu, D.; Gray, H.L.; Sammak, P.J.; Schatten, G.P.; Csoka, A.B. Lamin A/C expression is a marker of mouse and human embryonic stem cell differentiation. Stem Cells 2006, 24, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chojnowski, A.; Ong, P.F.; Foo, M.X.R.; Liebl, D.; Hor, L.P.; Stewart, C.L.; Dreesen, O. Heterochromatin loss as a determinant of progerin-induced DNA damage in Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilton, B.A.; Liu, J.; Cartwright, B.M.; Liu, Y.; Breitman, M.; Wang, Y.; Jones, R.; Tang, H.; Rusinol, A.; Musich, P.R.; et al. Progerin sequestration of PCNA promotes replication fork collapse and mislocalization of XPA in laminopathy-related progeroid syndromes. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 3882–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, T.; Escalante-Alcalde, D.; Bhatt, H.; Anver, M.; Bhat, N.; Nagashima, K.; Stewart, C.L.; Burke, B. Loss of A-type lamin expression compromises nuclear envelope integrity leading to muscular dystrophy. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 147, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatelli, P.; Lattanzi, G.; Ognibene, A.; Columbaro, M.; Capanni, C.; Merlini, L.; Maraldi, N.M.; Squarzoni, S. Nuclear alterations in autosomal-dominant Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve 2001, 24, 826–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraeten, V.L.; Ji, J.Y.; Cummings, K.S.; Lee, R.T.; Lammerding, J. Increased mechanosensitivity and nuclear stiffness in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria cells: Effects of farnesyltransferase inhibitors. Aging Cell 2008, 7, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Hale, C.M.; Panorchan, P.; Khatau, S.B.; George, J.P.; Tseng, Y.; Stewart, C.L.; Hodzic, D.; Wirtz, D. Nuclear lamin A/C deficiency induces defects in cell mechanics, polarization, and migration. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 2542–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammerding, J.; Schulze, P.C.; Takahashi, T.; Kozlov, S.; Sullivan, T.; Kamm, R.D.; Stewart, C.L.; Lee, R.T. Lamin A/C deficiency causes defective nuclear mechanics and mechanotransduction. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, F.H.; Tayebi, T.; Dehghan, M.; Eslami, G.; Nadri, H.; Moradi, A.; Vahedian-Ardakani, H.; Barzegar, K. Differentiation ofC bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into chondrocytes after short term culture in alkaline medium. Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Res. 2014, 8, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akter, R.; Rivas, D.; Geneau, G.; Drissi, H.; Duque, G. Effect of lamin A/C knockdown on osteoblast differentiation and function. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2009, 24, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yeo, L.S.; Vidal, C.; McCorquodale, T.; Herrmann, M.; Fatkin, D.; Duque, G. Decreased bone formation and osteopenia in lamin a/c-deficient mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermeo, S.; Vidal, C.; Zhou, H.; Duque, G. Lamin A/C Acts as an Essential Factor in Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation Through the Regulation of the Dynamics of the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 2344–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patni, N.; Li, X.; Adams-Huet, B.; Vasandani, C.; Gomez-Diaz, R.A.; Garg, A. Regional Body Fat Changes and Metabolic Complications in Children with Dunnigan Lipodystrophy-Causing LMNA Variants. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldenburg, A.; Briand, N.; Sørensen, A.L.; Cahyani, I.; Shah, A.; Moskaug, J.Ø.; Collas, P. A lipodystrophy-causing lamin A mutant alters conformation and epigenetic regulation of the anti-adipogenic MIR335 locus. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 2731–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift, J.; Ivanovska, I.L.; Buxboim, A.; Harada, T.; Dingal, P.C.D.P.; Pinter, J.; Pajerowski, J.D.; Spinler, K.R.; Shin, J.-W.; Tewari, M.; et al. Nuclear Lamin-A Scales with Tissue Stiffness and Enhances Matrix-Directed Differentiation. Science 2013, 341, 6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, B.; Xie, Z.; Case, N.; Styner, M.; Rubin, C.T.; Rubin, J. Mechanical signal influence on mesenchymal stem cell fate is enhanced by incorporation of refractory periods into the loading regimen. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, B.; Xie, Z.; Case, N.; Ma, M.; Rubin, C.; Rubin, J. Mechanical strain inhibits adipogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells by stimulating a durable beta-catenin signal. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 6065–6075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, B.; Guilluy, C.; Xie, Z.; Case, N.; Styner, M.; Thomas, J.; Oguz, I.; Rubin, C.; Burridge, K.; Rubin, J. Mechanically induced focal adhesion assembly amplifies anti-adipogenic pathways in mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 2011, 29, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzer, G.; Pongkitwitoon, S.; Ete Chan, M.; Judex, S. Vibration induced osteogenic commitment of mesenchymal stem cells is enhanced by cytoskeletal remodeling but not fluid shear. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 2296–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, G.; Loisate, S.; Hudon, S.F.; Woods, K.; Hayden, E.J.; Pu, X.; Beard, R.; Oxford, J.T.; Uzer, G. Low Intensity Vibrations Augment Mesenchymal Stem Cell Proliferation and Differentiation Capacity during in vitro Expansion. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, B.; Spatz, J.P.; Bershadsky, A.D. Environmental sensing through focal adhesions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamadi, A.; Bouali, M.; Dontenwill, M.; Stoeckel, H.; Takeda, K.; Rondé, P. Regulation of focal adhesion dynamics and disassembly by phosphorylation of FAK at tyrosine 397. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 4415–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzer, G.; Thompson, W.R.; Sen, B.; Xie, Z.; Yen, S.S.; Miller, S.; Bas, G.; Styner, M.; Rubin, C.T.; Judex, S.; et al. Cell Mechanosensitivity to Extremely Low-Magnitude Signals Is Enabled by a LINCed Nucleus. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 2063–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzer, G.; Fuchs, R.K.; Rubin, J.; Thompson, W.R. Concise Review: Plasma and Nuclear Membranes Convey Mechanical Information to Regulate Mesenchymal Stem Cell Lineage. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, B.; Xie, Z.; Case, N.; Thompson, W.R.; Uzer, G.; Styner, M.; Rubin, J. mTORC2 regulates mechanically induced cytoskeletal reorganization and lineage selection in marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, W.R.; Yen, S.S.; Uzer, G.; Xie, Z.; Sen, B.; Styner, M.; Burridge, K.; Rubin, J. LARG GEF and ARHGAP18 orchestrate RhoA activity to control mesenchymal stem cell lineage. Bone 2018, 107, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tontonoz, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Fat and Beyond: The Diverse Biology of PPARγ. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008, 77, 289–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnotti, G.M.; Styner, M.; Uzer, G.; Patel, V.S.; Wright, L.E.; Ness, K.K.; Guise, T.A.; Rubin, J.; Rubin, C.T. Combating osteoporosis and obesity with exercise: Leveraging cell mechanosensitivity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzer, G.; Bas, G.; Sen, B.; Xie, Z.; Birks, S.; Olcum, M.; McGrath, C.; Styner, M.; Rubin, J. Sun-mediated mechanical LINC between nucleus and cytoskeleton regulates βcatenin nuclear access. J. Biomech. 2018, 74, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskan, O.; Mese, G.; Ozcivici, E. Low-intensity vibrations normalize adipogenesis-induced morphological and molecular changes of adult mesenchymal stem cells. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2017, 231, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Mering, C.; Huynen, M.; Jaeggi, D.; Schmidt, S.; Bork, P.; Snel, B. STRING: A database of predicted functional associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammerding, J.; Fong, L.G.; Ji, J.Y.; Reue, K.; Stewart, C.L.; Young, S.G.; Lee, R.T. Lamins A and C but not lamin B1 regulate nuclear mechanics. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 25768–25780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raharjo, W.H.; Enarson, P.; Sullivan, T.; Stewart, C.L.; Burke, B. Nuclear envelope defects associated with LMNA mutations cause dilated cardiomyopathy and Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 4447–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-K.; Louhghalam, A.; Lee, G.; Schafer, B.W.; Wirtz, D.; Kim, D.-H. Nuclear lamin A/C harnesses the perinuclear apical actin cables to protect nuclear morphology. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corne, T.D.J.; Sieprath, T.; Vandenbussche, J.; Mohammed, D.; Te Lindert, M.; Gevaert, K.; Gabriele, S.; Wolf, K.; De Vos, W.H. Deregulation of focal adhesion formation and cytoskeletal tension due to loss of A-type lamins. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2017, 11, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chancellor, T.J.; Lee, J.; Thodeti, C.K.; Lele, T. Actomyosin tension exerted on the nucleus through nesprin-1 connections influences endothelial cell adhesion, migration, and cyclic strain-induced reorientation. Biophys. J. 2010, 99, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Abrahamsen, G.; Mills, R.; Calderón, C.C.; Tee, J.Y.; Leyton, L.; Murrell, W.; Cooper-White, J.; McGrath, J.J.; Mackay-Sim, A. Focal Adhesion Dynamics Are Altered in Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shi, Z.; Jiao, S.; Chen, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Greene, M.I.; Zhou, Z. Structural insights into SUN-KASH complexes across the nuclear envelope. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 1440–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, F.; Lloyd, D.J.; Smallwood, D.T.; Dent, C.L.; Shanahan, C.M.; Fry, A.M.; Trembath, R.C.; Shackleton, S. SUN1 Interacts with Nuclear Lamin A and Cytoplasmic Nesprins to Provide a Physical Connection between the Nuclear Lamina and the Cytoskeleton. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 3738–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Chiu, P.H.; Yip, K.Y.; Chan, S.Y. Subcellular Localization of SUN2 Is Regulated by Lamin A and Rab5. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartwright, T.; Senussi, O.; Grady, M.D. The Mechanism of the Inactivation of Human Fibroblast Interferon by Mechanical Stress. J. Gen. Virol. 1977, 36, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruijter, J.M.; Ruiz-Villalba, A.; van den Hoff, A.J.J.; Gunst, Q.D.; Wittwer, C.T.; van den Hoff, M.J.B. Removal of artifact bias from qPCR results using DNA melting curve analysis. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 14542–14555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaby, J.C.; Buckley, D.H. The Use of Degenerate Primers in qPCR Analysis of Functional Genes Can Cause Dramatic Quantification Bias as Revealed by Investigation of nifH Primer Performance. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 74, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmann, Y.W.; Klee, E.W.; Thompson, E.A.; Perez, E.A.; Middha, S.; Oberg, A.L.; Therneau, T.M.; Smith, D.I.; Poland, G.A.; Wieben, E.D.; et al. 3′ tag digital gene expression profiling of human brain and universal reference RNA using Illumina Genome Analyzer. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.R.; Neff, N.F.; Kalisky, T.; Dalerba, P.; Treutlein, B.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Mburu, F.M.; Mantalas, G.L.; Sim, S.; Clarke, M.F.; et al. Quantitative assessment of single-cell RNA-sequencing methods. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; He, M. Differential gene expression identified by RNA-Seq and qPCR in two sizes of pearl oyster (Pinctada fucata). Gene 2014, 538, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: A revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, M.; Griffith, O.L.; Mwenifumbo, J.; Goya, R.; Morrissy, A.S.; Morin, R.D.; Corbett, R.; Tang, M.J.; Hou, Y.C.; Pugh, T.J.; et al. Alternative expression analysis by RNA sequencing. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peister, A.; Mellad, J.A.; Larson, B.L.; Hall, B.M.; Gibson, L.F.; Prockop, D.J. Adult stem cells from bone marrow (MSCs) isolated from different strains of inbred mice vary in surface epitopes, rates of proliferation, and differentiation potential. Blood 2004, 103, 1662–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudakovic, A.; Camilleri, E.; Riester, S.M.; Lewallen, E.A.; Kvasha, S.; Chen, X.; Radel, D.J.; Anderson, J.M.; Nair, A.A.; Evans, J.M.; et al. High-resolution molecular validation of self-renewal and spontaneous differentiation in clinical-grade adipose-tissue derived human mesenchymal stem cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 115, 1816–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Rodríguez, A. Identifying pediatric cancer clusters in Florida using loglinear models and generalized lasso penalties. Stat. Public Policy 2014, 1, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudakovic, A.; Camilleri, E.T.; Paradise, C.R.; Samsonraj, R.M.; Gluscevic, M.; Paggi, C.A.; Begun, D.L.; Khani, F.; Pichurin, O.; Ahmed, F.S.; et al. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (Ezh2) controls bone formation and cell cycle progression during osteogenesis in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 12894–12907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennison, E.; Cooper, C. Epidemiology of osteoporotic fractures. Horm. Res. 2000, 54, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalari, K.R.; Nair, A.A.; Bhavsar, J.D.; O’Brien, D.R.; Davila, J.I.; Bockol, M.A.; Nie, J.; Tang, X.; Baheti, S.; Doughty, J.B.; et al. MAP-RSeq: Mayo Analysis Pipeline for RNA sequencing. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—A Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metsalu, T.; Vilo, J. ClustVis: A web tool for visualizing clustering of multivariate data using Principal Component Analysis and heatmap. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W566–W570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.; Woods, K.; Newberg, J.; Oxford, J.T.; Uzer, G. Low-intensity vibration restores nuclear YAP levels and acute YAP nuclear shuttling in mesenchymal stem cells subjected to simulated microgravity. NPJ Microgravity 2020, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goelzer, M.; Dudakovic, A.; Olcum, M.; Sen, B.; Ozcivici, E.; Rubin, J.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Uzer, G. Lamin A/C Is Dispensable to Mechanical Repression of Adipogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126580
Goelzer M, Dudakovic A, Olcum M, Sen B, Ozcivici E, Rubin J, van Wijnen AJ, Uzer G. Lamin A/C Is Dispensable to Mechanical Repression of Adipogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(12):6580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126580
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoelzer, Matthew, Amel Dudakovic, Melis Olcum, Buer Sen, Engin Ozcivici, Janet Rubin, Andre J. van Wijnen, and Gunes Uzer. 2021. "Lamin A/C Is Dispensable to Mechanical Repression of Adipogenesis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 12: 6580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126580
APA StyleGoelzer, M., Dudakovic, A., Olcum, M., Sen, B., Ozcivici, E., Rubin, J., van Wijnen, A. J., & Uzer, G. (2021). Lamin A/C Is Dispensable to Mechanical Repression of Adipogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(12), 6580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126580





