Expression of Connexin43 Stimulates Endothelial Angiogenesis Independently of Gap Junctional Communication In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Modulation of Cx43 Expression in HUVECs
2.2. Dye Transfer Is Modulated by Cx43 Expression and Blockage of Cx43-Dependent Coupling
2.3. Cell Proliferation Remained Unaltered by Modulation of Functional Cx43
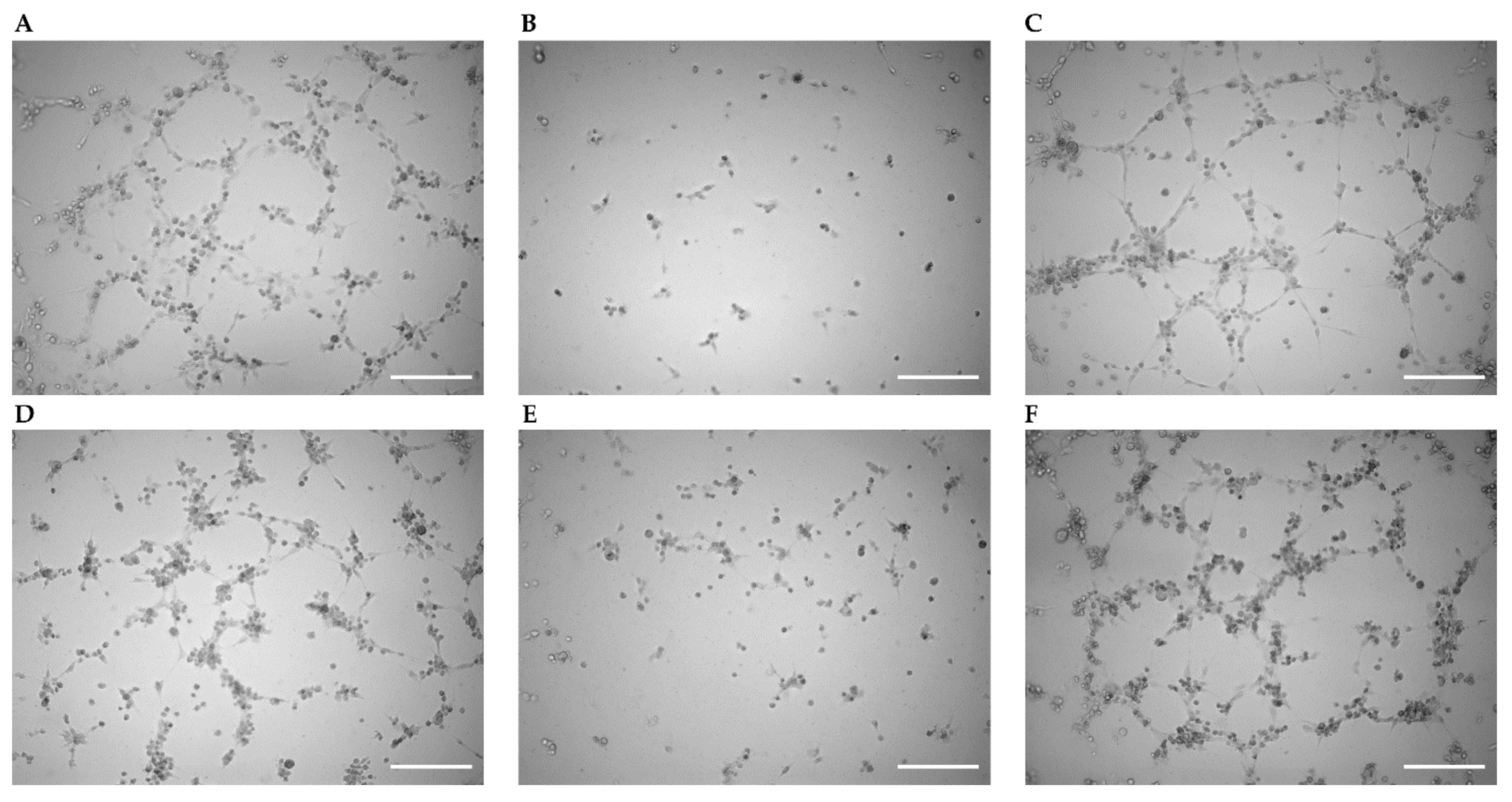
2.4. Enhancement of Tube Formation by Cx43 Expression Remained Unaffected by Gap27
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design
4.2. Preparation and Culture of HUVECs
4.3. Plasmid Constructs, Transfection of Plasmid-cDNA and SiRNA, and Treatment with Gap27
4.4. Tube Formation Assay
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
| Cx43: | forward 5′-CTGAGTGCCTGAACTTGCCT-3′ |
| reverse 5′-CCTGGGCACCACTCTTTTGC-3′ | |
| L28: | forward 5′-ATGGTCGTGCGGAACTGCT-3′ |
| reverse 5′-TTGTAGCGGAAGGAATTGCG-3′ |
4.6. Scrape Loading/Dye Transfer Assay
4.7. Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) Incorporation Assay
4.8. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pohl, U. Connexins: Key Players in the Control of Vascular Plasticity and Function. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 100, 525–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leybaert, L.; Lampe, P.D.; Dhein, S.; Kwak, B.; Ferdinandy, P.; Beyer, E.; Laird, D.W.; Naus, C.C.; Green, C.R.; Schulz, R. Connexins in Cardiovascular and Neurovascular Health and Disease: Pharmacological Implications. Pharmacol. Rev. 2017, 69, 396–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, V.J.; Wölfle, S.E.; Boettcher, M.; De Wit, C. Gap junctions synchronize vascular tone within the microcirculation. Pharmacol. Rep. 2008, 60, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Jobs, A.; Schmidt, K.; Schmidt, V.J.; Lübkemeier, I.; Van Veen, T.A.; Kurtz, A.; Willecke, K.; De Wit, C. Defective Cx40 Maintains Cx37 Expression but Intact Cx40 Is Crucial for Conducted Dilations Irrespective of Hypertension. Hypertension 2012, 60, 1422–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pogoda, K.; Kameritsch, P.; Mannell, H.; Pohl, U. Connexins in the control of vasomotor function. Acta Physiol. 2019, 225, e13108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söhl, G.; Willecke, K. Gap junctions and the connexin protein family. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 62, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, V.J.; Jobs, A.; von Maltzahn, J.; Wörsdörfer, P.; Willecke, K.; de Wit, C. Connexin45 is expressed in vascular smooth muscle but its function remains elusive. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.X.; Gu, S. Gap junction- and hemichannel-independent actions of connexins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 2005, 1711, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kameritsch, P.; Pogoda, K.; Pohl, U. Channel-independent influence of connexin 43 on cell migration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 2012, 1818, 1993–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Jiang, J.X. Gap junction and hemichannel-independent actions of connexins on cell and tissue functions—An update. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 1186–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins-Marques, T.; Ribeiro-Rodrigues, T.; Batista-Almeida, D.; Aasen, T.; Kwak, B.R.; Girao, H. Biological Functions of Connexin43 Beyond Intercellular Communication. Trends Cell Biol. 2019, 29, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuuchi, L.; Naus, C.C. Gap junction proteins on the move: Connexins, the cytoskeleton and migration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leithe, E.; Mesnil, M.; Aasen, T. The connexin 43 C-terminus: A tail of many tales. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 2018, 1860, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotini, M.; Barriga, E.H.; Leslie, J.; Gentzel, M.; Rauschenberger, V.; Schambony, A.; Mayor, R. Gap junction protein Connexin-43 is a direct transcriptional regulator of N-cadherin in vivo. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reaume, A.; De Sousa, P.; Kulkarni, S.; Langille, B.; Zhu, D.; Davies, T.; Juneja, S.; Kidder, G.; Rossant, J. Cardiac malformation in neonatal mice lacking connexin43. Science 1995, 267, 1831–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, L.A.; Kriegstein, A.R. Gap junctions: Multifaceted regulators of embryonic cortical development. Trends Neurosci. 2008, 31, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elias, L.A.B.; Wang, D.D.; Kriegstein, A.R. Gap junction adhesion is necessary for radial migration in the neocortex. Nature 2007, 448, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, L.; Torii, M.; Rakic, P. Connexin 43 controls the multipolar phase of neuronal migration to the cerebral cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8280–8285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLachlan, E.; Shao, Q.; Wang, H.-L.; Langlois, S.; Laird, D.W. Connexins Act as Tumor Suppressors in Three-dimensional Mammary Cell Organoids by Regulating Differentiation and Angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9886–9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Behrens, J.; Kameritsch, P.; Wallner, S.; Pohl, U.; Pogoda, K. The carboxyl tail of Cx43 augments p38 mediated cell migration in a gap junction-independent manner. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 89, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Kung, C.I.; Tseng, Y.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, C.H.; Tsai, C.H.; Yeh, H.I. Activation of endothelial cells to pathological status by down-regulation of connexin43. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 79, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gärtner, C.; Ziegelhöffer, B.; Kostelka, M.; Stepan, H.; Mohr, F.-W.; Dhein, S. Knockdown of endothelial connexins impairs angiogenesis. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 65, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-H.; Su, C.-H.; Wu, Y.-J.; Li, J.-Y.; Tseng, Y.-M.; Lin, Y.-C.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Tsai, C.-H.; Yeh, H.-I. Reduction of connexin43 in human endothelial progenitor cells impairs the angiogenic potential. Angiogenesis 2013, 16, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polykandriotis, E.; Tjiawi, J.; Euler, S.; Arkudas, A.; Hess, A.; Brune, K.; Greil, P.; Lametschwandtner, A.; Horch, R.E.; Kneser, U. The venous graft as an effector of early angiogenesis in a fibrin matrix. Microvasc. Res. 2008, 75, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, V.J.; Hilgert, J.G.; Covi, J.M.; Weiß, C.; Wietbrock, J.O.; De Wit, C.; Horch, R.E.; Kneser, U. High Flow Conditions Increase Connexin43 Expression in a Rat Arteriovenous and Angioinductive Loop Model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, V.J.; Hilgert, J.G.; Covi, J.M.; Leibig, N.; Wietbrock, J.O.; Arkudas, A.; Polykandriotis, E.; de Wit, C.; Horch, R.E.; Kneser, U. Flow Increase Is Decisive to Initiate Angiogenesis in Veins Exposed to Altered Hemodynamics. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henn, D.; Abu-Halima, M.; Wermke, D.; Falkner, F.; Thomas, B.; Kopple, C.; Ludwig, N.; Schulte, M.; Brockmann, M.A.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. MicroRNA-regulated pathways of flow-stimulated an-giogenesis and vascular remodeling in vivo. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babica, P.; Sovadinova, I.; Upham, B.L. Scrape Loading/Dye Transfer Assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1437, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polykandriotis, E.; Arkudas, A.; Beier, J.P.; Hess, A.; Greil, P.; Papadopoulos, T.; Kopp, J.; Bach, A.D.; Horch, R.E.; Kneser, U. Intrinsic Axial Vascularization of an Osteoconductive Bone Matrix by Means of an Arteriovenous Vascular Bundle. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2007, 120, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkudas, A.; Beier, J.P.; Heidner, K.; Tjiawi, J.; Polykandriotis, E.; Srour, S.; Sturzl, M.; Horch, R.E.; Kneser, U. Axial prevascularization of porous matrices using an arteriovenous loop promotes survival and differentiation of transplanted autologous osteoblasts. Tissue Eng. 2007, 13, 1549–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotter, M.L.; Boitano, S.; Lampe, P.D.; Solan, J.L.; Vagner, J.; Ek-Vitorin, J.F.; Burt, J.M. The lipidated connexin mimetic peptide SRPTEKT-Hdc is a potent inhibitor of Cx43 channels with specificity for the pS368 phospho-isoform. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2019, 317, C825–C842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameritsch, P.; Khandoga, N.; Nagel, W.; Hundhausen, C.; Lidington, D.; Pohl, U. Nitric oxide specifically reduces the permeability of Cx37-containing gap junctions to small molecules. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 203, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, X.; Doble, B.W.; Kardami, E. The carboxy-tail of connexin-43 localizes to the nucleus and inhibits cell growth. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 242, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorby, C.; Patel, M. Dual Functions for Connexins: Cx43 Regulates Growth Independently of Gap Junction Formation. Exp. Cell Res. 2001, 271, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olbina, G.; Eckhart, W. Mutations in the second extracellular region of connexin 43 prevent localization to the plasma membrane, but do not affect its ability to suppress cell growth. Mol. Cancer Res. 2003, 1, 690–700. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-H.; Mayo, J.N.; Gourdie, R.G.; Johnstone, S.R.; Isakson, B.E.; Bearden, S.E. The connexin 43/ZO-1 complex regulates cerebral endothelial F-actin architecture and migration. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2015, 309, C600–C607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; De Bock, M.; Decrock, E.; Bol, M.; Gadicherla, A.; Vinken, M.; Rogiers, V.; Bukauskas, F.F.; Bultynck, G.; Leybaert, L. Paracrine signaling through plasma membrane hemichannels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; De Bock, M.; Antoons, G.; Gadicherla, A.K.; Bol, M.; Decrock, E.; Evans, W.H.; Sipido, K.R.; Bukauskas, F.F.; Ley-baert, L. Connexin mimetic peptides inhibit Cx43 hemichannel opening triggered by voltage and intracellular Ca2+ elevation. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2012, 107, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Bock, M.; Culot, M.; Wang, N.; Bol, M.; Decrock, E.; De Vuyst, E.; Da Costa, A.; Dauwe, I.; Vinken, M.; Simon, A.M.; et al. Connexin Channels Provide a Target to Manipulate Brain Endothelial Calcium Dynamics and Blood—Brain Barrier Permeability. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 31, 1942–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okamoto, T.; Akita, N.; Kawamoto, E.; Hayashi, T.; Suzuki, K.; Shimaoka, M. Endothelial connexin32 enhances angiogenesis by positively regulating tube formation and cell migration. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 321, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haefliger, J.-A.; Allagnat, F.; Hamard, L.; Le Gal, L.; Meda, P.; Nardelli-Haefliger, D.; Génot, E.; Alonso, F. Targeting Cx40 (Connexin40) Expression or Function Reduces Angiogenesis in the Developing Mouse Retina. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 2136–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alonso, F.; Domingos-Pereira, S.; Le Gal, L.; Derre, L.; Meda, P.; Jichlinski, P.; Nardelli-Haefliger, D.; Haefliger, J.A. Targeting endothelial connexin40 inhibits tumor growth by reducing angiogenesis and improving vessel perfusion. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 14015–14028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, J.; Angelov, S.N.; Simon, A.M.; Burt, J.M. Cx40 Is Required for, and Cx37 Limits, Postischemic Hindlimb Perfusion, Survival and Recovery. J. Vasc. Res. 2011, 49, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buschmann, I.; Pries, A.; Styp-Rekowska, B.; Hillmeister, P.; Loufrani, L.; Henrion, D.; Shi, Y.; Duelsner, A.; Hoefer, I.; Gatzke, N.; et al. Pulsatile shear and Gja5 modulate arterial identity and remodeling events during flow-driven arteriogenesis. Development 2010, 137, 2187–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, T.K.; Sorgen, P.L.; Burt, J.M. Carboxy terminus and poreforming domain properties specific to Cx37 are necessary for Cx37-mediated suppression of insulinoma cell proliferation. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2013, 305, C1246–C1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, W.H.; Boitano, S. Connexin mimetic peptides: Specific inhibitors of gapjunctional intercellular communication. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2001, 29, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baudin, B.; Bruneel, A.; Bosselut, N.; Vaubourdolle, M. A protocol for isolation and culture of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschumperle, D.; Deriche, R. Vectorvalued image regularization with PDEs: A common framework for different applications. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carpentier, G.; Berndt, S.; Ferratge, S.; Rasband, W.; Cuendet, M.; Uzan, G.; Albanese, P. Angiogenesis Analyzer for ImageJ—A comparative morphometric analysis of “Endothelial Tube Formation Assay” and “Fibrin Bead Assay” and “Fibrin Bead Assay”. Sci. Rep 2020, 10, 11568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)). Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koepple, C.; Zhou, Z.; Huber, L.; Schulte, M.; Schmidt, K.; Gloe, T.; Kneser, U.; Schmidt, V.J.; de Wit, C. Expression of Connexin43 Stimulates Endothelial Angiogenesis Independently of Gap Junctional Communication In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147400
Koepple C, Zhou Z, Huber L, Schulte M, Schmidt K, Gloe T, Kneser U, Schmidt VJ, de Wit C. Expression of Connexin43 Stimulates Endothelial Angiogenesis Independently of Gap Junctional Communication In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(14):7400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147400
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoepple, Christoph, Zizi Zhou, Lena Huber, Matthias Schulte, Kjestine Schmidt, Torsten Gloe, Ulrich Kneser, Volker Jürgen Schmidt, and Cor de Wit. 2021. "Expression of Connexin43 Stimulates Endothelial Angiogenesis Independently of Gap Junctional Communication In Vitro" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 14: 7400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147400
APA StyleKoepple, C., Zhou, Z., Huber, L., Schulte, M., Schmidt, K., Gloe, T., Kneser, U., Schmidt, V. J., & de Wit, C. (2021). Expression of Connexin43 Stimulates Endothelial Angiogenesis Independently of Gap Junctional Communication In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(14), 7400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147400







