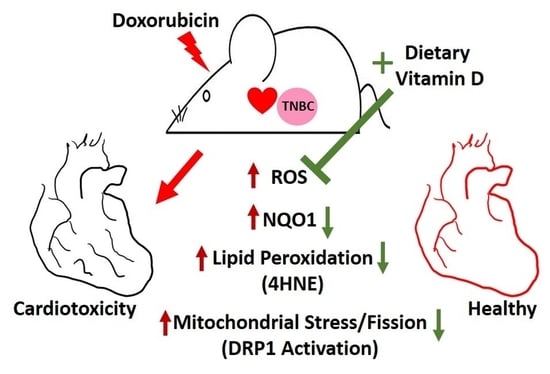
Cytoprotective Effect of Vitamin D on Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiac Toxicity in Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
Share and Cite
Lee, K.J.; Wright, G.; Bryant, H.; Wiggins, L.A.; Dal Zotto, V.L.; Schuler, M.; Malozzi, C.; Cohen, M.V.; Gassman, N.R. Cytoprotective Effect of Vitamin D on Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiac Toxicity in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147439
Lee KJ, Wright G, Bryant H, Wiggins LA, Dal Zotto VL, Schuler M, Malozzi C, Cohen MV, Gassman NR. Cytoprotective Effect of Vitamin D on Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiac Toxicity in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(14):7439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147439
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Kevin J, Griffin Wright, Hannah Bryant, Leigh Ann Wiggins, Valeria L. Dal Zotto, Michele Schuler, Christopher Malozzi, Michael V Cohen, and Natalie R Gassman. 2021. "Cytoprotective Effect of Vitamin D on Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiac Toxicity in Triple Negative Breast Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 14: 7439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147439
APA StyleLee, K. J., Wright, G., Bryant, H., Wiggins, L. A., Dal Zotto, V. L., Schuler, M., Malozzi, C., Cohen, M. V., & Gassman, N. R. (2021). Cytoprotective Effect of Vitamin D on Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiac Toxicity in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(14), 7439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147439