Role of Immune Cells in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cells of the Innate Immune Response in HBV-Related HCC
2.1. Natural Killer and Natural Killer T Cells
2.2. Kupffer Cells and Monocytes
2.3. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell
3. Cells in the Adaptive Immune Response in HBV-Related HCC
3.1. CD8+ T Cells
3.1.1. Effector HBV-Specific CD8+ T Cells
3.1.2. Exhausted HBV-Specific CD8+ T Cells
3.2. CD4+ T Cells
3.2.1. Th1 and Th17 Cells
3.2.2. CD4+ Cytotoxic T Cells
3.3. Regulatory T Cells
3.4. B Cells
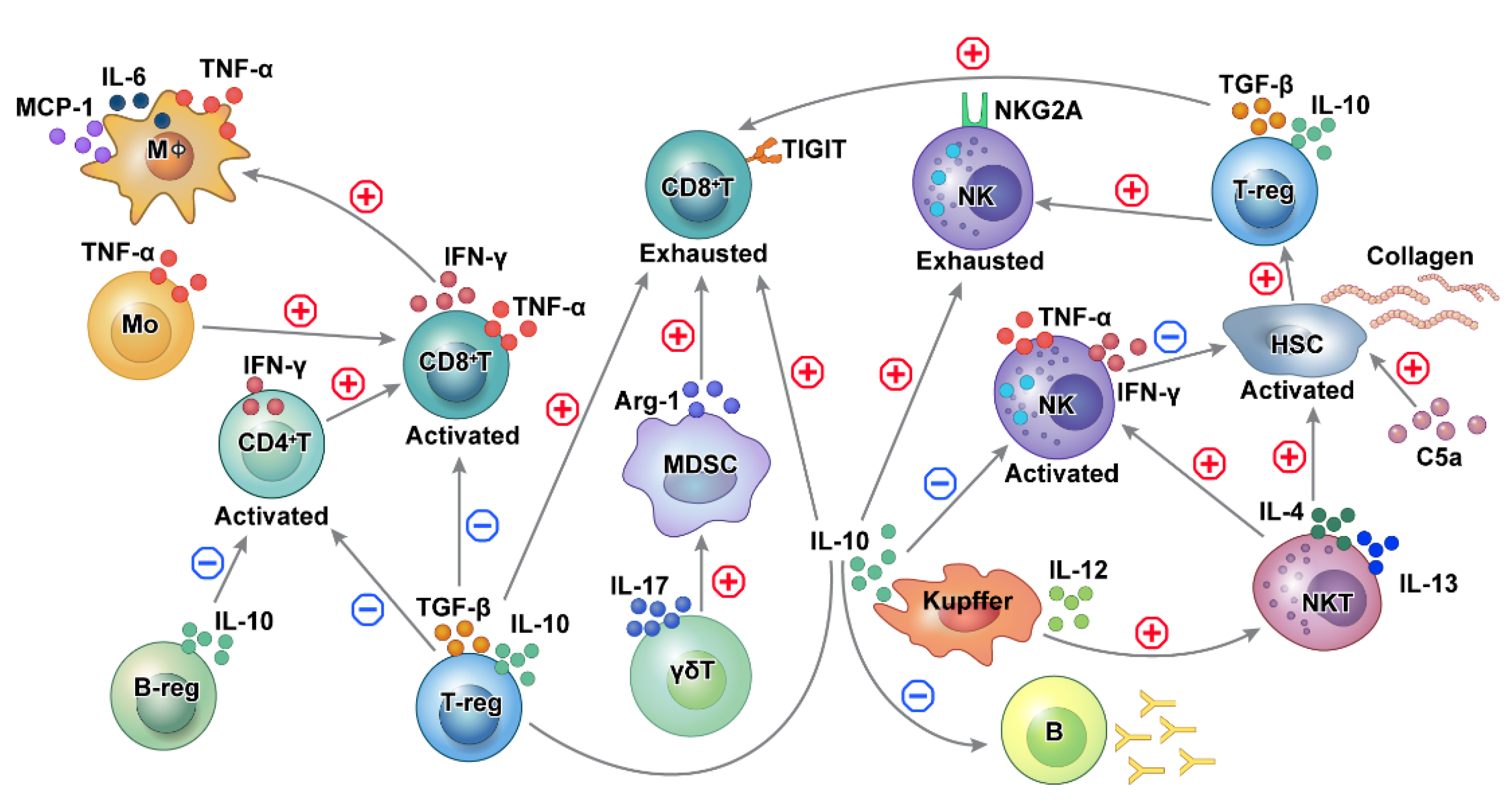
4. Regulation among Different Immune Cells in HBV-Related HCC
5. Sex-Related Differences in the Immune System
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nguyen, V.T.; Law, M.G.; Dore, G.J. Hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiological characteristics and disease burden. J. Viral. Hepat. 2009, 16, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.H.; Park, J.W. Epidemiology of liver cancer in South Korea. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2018, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Tang, A.; Lee, J.M. Comparison of international guidelines for noninvasive diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2018 update. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2019, 25, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Tian, Z. HBV-Induced Immune Imbalance in the Development of HCC. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, C.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Pan, L.; Lai, L.; Chua, C.; Wasser, M.; Lim, T.K.H.; Yeong, J.; Toh, H.C.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Multidimensional analyses reveal distinct immune microenvironment in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2019, 68, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doherty, D.G.; Norris, S.; Madrigal-Estebas, L.; McEntee, G.; Traynor, O.; Hegarty, J.E.; O’Farrelly, C. The human liver contains multiple populations of NK cells, T cells, and CD3+CD56+ natural T cells with distinct cytotoxic activities and Th1, Th2, and Th0 cytokine secretion patterns. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 2314–2321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gao, B. Natural killer cells in liver disease. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Tian, Z. NK cell education via nonclassical MHC and non-MHC ligands. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chemin, I.; Zoulim, F. Hepatitis B virus induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. Lett. 2009, 286, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppa, D.; Micco, L.; Javaid, A.; Kennedy, P.T.; Schurich, A.; Dunn, C.; Pallant, C.; Ellis, G.; Khanna, P.; Dusheiko, G.; et al. Blockade of immunosuppressive cytokines restores NK cell antiviral function in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Han, Q.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, J. Exosomes mediate hepatitis B virus (HBV) transmission and NK-cell dysfunction. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Han, Q.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J. miR−146a negatively regulates NK cell functions via STAT1 signaling. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maini, M.K.; Peppa, D. NK cells: A double-edged sword in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zenewicz, L.A.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Valenzuela, D.M.; Murphy, A.J.; Karow, M.; Flavell, R.A. Interleukin−22 but not interleukin−17 provides protection to hepatocytes during acute liver inflammation. Immunity 2007, 27, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Hao, X.; Sun, R.; Wei, H.; Tian, Z. Natural Killer Cell-Derived Interferon-Gamma Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Through the Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Axis in Hepatitis B Virus Transgenic Mice. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1735–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Sun, R.; Wei, H.; Gao, X.; Chen, Y.; Tian, Z. Accelerated liver fibrosis in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice: Involvement of natural killer T cells. Hepatology 2011, 53, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Su, Y.; Hua, X.; Xie, C.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Gao, Z. Levels of hepatic Th17 cells and regulatory T cells upregulated by hepatic stellate cells in advanced HBV-related liver fibrosis. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jenne, C.N.; Kubes, P. Immune surveillance by the liver. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Hao, X.; Zheng, M.; Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, R.; Tian, Z. CD205-TLR9-IL−12 axis contributes to CpG-induced oversensitive liver injury in HBsAg transgenic mice by promoting the interaction of NKT cells with Kupffer cells. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Cheng, L.; Guo, M.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Tan, Y.; Ma, S.; Li, S.; Yang, Y.; et al. CD137-mediated pathogenesis from chronic hepatitis to hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B virus-transgenic mice. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 7654–7662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Yin, W.; Sun, R.; Wei, H.; Tian, Z. Kupffer cell-derived IL−10 plays a key role in maintaining humoral immune tolerance in hepatitis B virus-persistent mice. Hepatology 2014, 59, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Sun, R.; Xu, L.; Yin, W.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Lian, Z.; Wei, H.; Tian, Z. Kupffer Cells Support Hepatitis B Virus-Mediated CD8+ T Cell Exhaustion via Hepatitis B Core Antigen-TLR2 Interactions in Mice. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 3100–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Akbar, S.M.; Abe, M.; Hiasa, Y.; Onji, M. Immunosuppressive functions of hepatic myeloid-derived suppressor cells of normal mice and in a murine model of chronic hepatitis B virus. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 166, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoechst, B.; Ormandy, L.A.; Ballmaier, M.; Lehner, F.; Kruger, C.; Manns, M.P.; Greten, T.F.; Korangy, F. A new population of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma patients induces CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) T cells. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Sun, R.; Chen, Y.; Wei, H.; Tian, Z. gammadeltaT cells drive myeloid-derived suppressor cell-mediated CD8+ T cell exhaustion in hepatitis B virus-induced immunotolerance. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, K.M.; Traum, D.; Park, J.J.; Ho, S.; Ojiro, K.; Wong, D.K.; Wahed, A.S.; Terrault, N.A.; Khalili, M.; Sterling, R.K.; et al. Distinct phenotype and function of circulating Vdelta1+ and Vdelta2+ gammadeltaT-cells in acute and chronic hepatitis B. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoletti, A.; Ferrari, C. Adaptive immunity in HBV infection. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S71–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, S.; Chokshi, S.; Riva, A.; Evans, A.; Williams, R.; Naoumov, N.V. CD8(+) T cell control of hepatitis B virus replication: Direct comparison between cytolytic and noncytolytic functions. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuch, A.; Salimi, A.E.; Heim, K.; Wieland, D.; Kiraithe, M.M.; Kemming, J.; Llewellyn-Lacey, S.; Sogukpinar, Ö.; Ni, Y.; Urban, S.; et al. Phenotypic and functional differences of HBV core-specific versus HBV polymerase-specific CD8+ T cells in chronically HBV-infected patients with low viral load. Gut 2019, 68, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamoto, Y.; Guidotti, L.G.; Kuhlen, C.V.; Fowler, P.; Chisari, F.V. Immune pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, Y.; Kaneko, S.; Fan, H.; Momoi, T.; Tsutsui, H.; Nakanishi, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Suda, T. Prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma development associated with chronic hepatitis by anti-fas ligand antibody therapy. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, X.; Chen, Y.; Bai, L.; Wei, H.; Sun, R.; Tian, Z. HBsAg-specific CD8(+) T cells as an indispensable trigger to induce murine hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringelhan, M.; McKeating, J.A.; Protzer, U. Viral hepatitis and liver cancer. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B. Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y. Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1018, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zong, L.; Peng, H.; Sun, C.; Li, F.; Zheng, M.; Chen, Y.; Wei, H.; Sun, R.; Tian, Z. Breakdown of adaptive immunotolerance induces hepatocellular carcinoma in HBsAg-tg mice. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wherry, E.J. T cell exhaustion. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benechet, A.P.; Iannacone, M. Determinants of hepatic effector CD8(+) T cell dynamics. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisicaro, P.; Barili, V.; Rossi, M.; Montali, I.; Vecchi, A.; Acerbi, G.; Laccabue, D.; Zecca, A.; Penna, A.; Missale, G.; et al. Pathogenetic Mechanisms of T Cell Dysfunction in Chronic HBV Infection and Related Therapeutic Approaches. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, C.; Lampertico, P.; Talamona, L.; Giuberti, T.; Invernizzi, F.; Barili, V.; Fisicaro, P.; Rossi, M.; Cavallo, M.C.; Vecchi, A.; et al. Natural killer cell phenotype modulation and natural killer/T-cell interplay in nucleos(t)ide analogue-treated hepatitis e antigen-negative patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2015, 62, 1697–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppa, D.; Gill, U.S.; Reynolds, G.; Easom, N.J.; Pallett, L.J.; Schurich, A.; Micco, L.; Nebbia, G.; Singh, H.D.; Adams, D.H.; et al. Up-regulation of a death receptor renders antiviral T cells susceptible to NK cell-mediated deletion. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, K.; Binder, B.; Sagar, W.D.; Hensel, N.; Llewellyn-Lacey, S.; Gostick, E.; Price, D.A.; Emmerich, F.; Vingerhoet, H.; Kraft, A.R.M.; et al. TOX defines the degree of CD8+ T cell dysfunction in distinct phases of chronic HBV infection. Gut 2020, 70, 1550–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, B.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Kong, H.; Tian, L.; Chen, Y. T-cell exhaustion in chronic hepatitis B infection: Current knowledge and clinical significance. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schurich, A.; Khanna, P.; Lopes, A.R.; Han, K.J.; Peppa, D.; Micco, L.; Nebbia, G.; Kennedy, P.T.; Geretti, A.M.; Dusheiko, G.; et al. Role of the coinhibitory receptor cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen−4 on apoptosis-Prone CD8 T cells in persistent hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1494–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebbia, G.; Peppa, D.; Schurich, A.; Khanna, P.; Singh, H.D.; Cheng, Y.; Rosenberg, W.; Dusheiko, G.; Gilson, R.; ChinAleong, J.; et al. Upregulation of the Tim−3/galectin−9 pathway of T cell exhaustion in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.D.; Song, G.W.; Park, S.; Jung, M.K.; Kim, M.H.; Kang, H.J.; Yoo, C.; Yi, K.; Kim, K.H.; Eo, S.; et al. Association Between Expression Level of PD1 by Tumor-Infiltrating CD8(+) T Cells and Features of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1936–1950.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Dang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Kong, Y.; Yang, Z. PD−1+ TIGIT+ CD8+ T cells are associated with pathogenesis and progression of patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 2041–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P.T.; Sandalova, E.; Jo, J.; Gill, U.; Ushiro–Lumb, I.; Tan, A.T.; Naik, S.; Foster, G.R.; Bertoletti, A. Preserved T-cell function in children and young adults with immune-tolerant chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.; Celis, E. Multiple roles for CD4+ T cells in anti-tumor immune responses. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 222, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Liu, X.-L.; Xiao, G.; Li, N.-L.; Deng, Y.-N.; Han, L.-Z.; Yin, L.-C.; Ling, L.-J.; Liu, L.-X. Prevalence and clinical relevance of T-helper cells, Th17 and Th1, in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Wang, K.; Meng, Q.H.; Qi, Z.X.; Meng, F.L.; Fan, Y.C. Implication of Th17 and Th1 cells in patients with chronic active hepatitis B. J. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 30, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, S.; Komita, H.; Sagawa, Y.; Ohno, T.; Toda, G. Antitumour activity mediated by CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes against MHC class II-negative mouse hepatocellular carcinoma induced by dendritic cell vaccine and interleukin−12. Immunology 2005, 115, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.I.; Kim, H.J.; Oh, S.T.; Kim, T.G. In vitro induction of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes by dendritic cells transduced with recombinant adenoviruses. Vaccine 2003, 22, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porakishvili, N.; Roschupkina, T.; Kalber, T.; Jewell, A.P.; Patterson, K.; Yong, K.; Lydyard, P.M. Expansion of CD4+ T cells with a cytotoxic phenotype in patients with B-chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (B-CLL). Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2001, 126, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Qi, Z.; Xing, S.; Lv, J.; Shi, J.; Fu, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.Y.; et al. Impairment of CD4+ cytotoxic T cells predicts poor survival and high recurrence rates in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2013, 58, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, J.B.; Tanaka, A.; Sakaguchi, S. Human FOXP3(+) Regulatory T Cell Heterogeneity and Function in Autoimmunity and Cancer. Immunity 2019, 50, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanamori, M.; Nakatsukasa, H.; Okada, M.; Lu, Q.; Yoshimura, A. Induced Regulatory T Cells: Their Development, Stability, and Applications. Trends. Immunol. 2016, 37, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvas, S.; Azkur, A.K.; Kim, B.S.; Kumaraguru, U.; Rouse, B.T. CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells control the severity of viral immunoinflammatory lesions. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 4123–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suvas, S.; Kumaraguru, U.; Pack, C.D.; Lee, S.; Rouse, B.T. CD4+CD25+ T cells regulate virus-specific primary and memory CD8+ T cell responses. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.W.; Chang, D.Y.; Sung, P.S.; Jung, M.K.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, J.I.; Park, H.; et al. Liver injury in acute hepatitis A is associated with decreased frequency of regulatory T cells caused by Fas-mediated apoptosis. Gut 2015, 64, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluestone, J.A.; Abbas, A.K. Natural versus adaptive regulatory T cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretschmer, K.; Apostolou, I.; Hawiger, D.; Khazaie, K.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; von Boehmer, H. Inducing and expanding regulatory T cell populations by foreign antigen. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanthakumar, A.; Liao, Y.; Teh, P.; Pascutti, M.F.; Oja, A.E.; Garnham, A.L.; Gloury, R.; Tempany, J.C.; Sidwell, T.; Cuadrado, E.; et al. The TNF Receptor Superfamily-NF-κB Axis Is Critical to Maintain Effector Regulatory T Cells in Lymphoid and Non-lymphoid Tissues. Cell. Rep. 2017, 20, 2906–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, H.; Grinberg-Bleyer, Y.; Liao, W.; Maloney, D.; Wang, P.; Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Bhatt, D.M.; Heise, N.; Schmid, R.M.; et al. An NF-κB Transcription-Factor-Dependent Lineage-Specific Transcriptional Program Promotes Regulatory T Cell Identity and Function. Immunity 2017, 47, 450–465.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- TrehanPati, N.; Kotillil, S.; Hissar, S.S.; Shrivastava, S.; Khanam, A.; Sukriti, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Sarin, S.K. Circulating Tregs correlate with viral load reduction in chronic HBV-treated patients with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoop, J.N.; van der Molen, R.G.; Baan, C.C.; van der Laan, L.J.; Kuipers, E.J.; Kusters, J.G.; Janssen, H.L. Regulatory T cells contribute to the impaired immune response in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2005, 41, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Fu, J.; Jin, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, C.; Zou, Z.; Zhao, J.M.; Zhang, B.; Shi, M.; Ding, X.; et al. Circulating and liver resident CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells actively influence the antiviral immune response and disease progression in patients with hepatitis B. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoop, J.N.; van der Molen, R.G.; Kuipers, E.J.; Kusters, J.G.; Janssen, H.L. Inhibition of viral replication reduces regulatory T cells and enhances the antiviral immune response in chronic hepatitis B. Virology 2007, 361, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pal, S.; Nandi, M.; Dey, D.; Chakraborty, B.C.; Shil, A.; Ghosh, S.; Banerjee, S.; Santra, A.; Ahammed, S.K.M.; Chowdhury, A.; et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells induce regulatory T cells in chronically HBV infected patients with high levels of hepatitis B surface antigen and persist after antiviral therapy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 1346–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Liu, A.; Xie, Q.; Guo, T.B.; Wan, B.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, J.Z. Association of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells with chronic activity and viral clearance in patients with hepatitis B. Int. Immunol. 2007, 19, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fantini, M.C.; Becker, C.; Monteleone, G.; Pallone, F.; Galle, P.R.; Neurath, M.F. Cutting edge: TGF-beta induces a regulatory phenotype in CD4+CD25- T cells through Foxp3 induction and down-regulation of Smad7. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 5149–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ichikawa, S.; Mucida, D.; Tyznik, A.J.; Kronenberg, M.; Cheroutre, H. Hepatic stellate cells function as regulatory bystanders. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 5549–5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trehanpati, N.; Vyas, A.K. Immune Regulation by T Regulatory Cells in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Inflammation and Cancer. Scand. J. Immunol. 2017, 85, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Jiang, P.; Wei, S.; Xu, X.; Wang, J. Regulatory T cells in tumor microenvironment: New mechanisms, potential therapeutic strategies and future prospects. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Mei, M.H.; Fei, R.; Liu, F.; Wang, J.H.; Liao, W.J.; Qin, L.L.; Wei, L.; Chen, H.S. Regulatory T cells in chronic hepatitis B patients affect the immunopathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma by suppressing the anti-tumour immune responses. J. Viral. Hepat. 2010, 17 (Suppl. S1), 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Li, Q.J.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Markowitz, G.J.; Ning, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, Y.; et al. TGF-β-miR−34a-CCL22 signaling-induced Treg cell recruitment promotes venous metastases of HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2012, 22, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, Q.; Qiu, S.J.; Fan, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.Y.; Xiao, Y.S.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.W.; Tang, Z.Y. Intratumoral balance of regulatory and cytotoxic T cells is associated with prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 2586–2593. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Song, D.; Min, Z.; Wang, X.; Gu, Y.; Wei, B.; Yao, J.; Chen, K.; Jiang, Z.; Xie, H.; et al. Perioperative dynamic alterations in peripheral regulatory T and B cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.; Khosla, R.; David, P.; Rastogi, A.; Vyas, A.; Singh, D.; Bhardwaj, A.; Sahney, A.; Maiwall, R.; Sarin, S.K.; et al. CD4+CD25+CD127(low) Regulatory T Cells Play Predominant Anti-Tumor Suppressive Role in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathai, A.M.; Kapadia, M.J.; Alexander, J.; Kernochan, L.E.; Swanson, P.E.; Yeh, M.M. Role of Foxp3-positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in the histologic features and clinical outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, A.; Tanaka, F.; Mimori, K.; Inoue, H.; Kai, S.; Shibata, K.; Ohta, M.; Kitano, S.; Mori, M. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 34, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milich, D.R.; Chen, M.; Schödel, F.; Peterson, D.L.; Jones, J.E.; Hughes, J.L. Role of B cells in antigen presentation of the hepatitis B core. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 14648–14653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.; Yin, W. The Multiple Functions of B Cells in Chronic HBV Infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 582292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, A.R.; Pallett, L.J.; McCoy, L.E.; Suveizdyte, K.; Amin, O.E.; Swadling, L.; Alberts, E.; Davidson, B.R.; Kennedy, P.T.; Gill, U.S.; et al. Circulating and intrahepatic antiviral B cells are defective in hepatitis B. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4588–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, X.; Lao, X.-M.; Chen, M.-M.; Liu, R.-X.; Wei, Y.; Ouyang, F.-Z.; Chen, D.-P.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, X.-F. PD−1hi identifies a novel regulatory B-cell population in human hepatoma that promotes disease progression. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarvaria, A.; Madrigal, J.A.; Saudemont, A. B cell regulation in cancer and anti-tumor immunity. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michaud, D.; Steward, C.R.; Mirlekar, B.; Pylayeva-Gupta, Y. Regulatory B cells in cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2021, 299, 74–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, D.; Mansilla, M.A.; Ferrier, A.; Soto, L.; Oleinika, K.; Aguillón, J.C.; Aravena, O. Immunosuppressive Mechanisms of Regulatory B Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 611795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Lin, F.; Tan, H.; Zhu, Z.-Q.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Zhao, L. Overrepresentation of IL−10-Expressing B Cells Suppresses Cytotoxic CD4+ T Cell Activity in HBV-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Lo, C.M.; Ling, C.C.; Liu, X.B.; Ng, K.T.; Chu, A.C.; Ma, Y.Y.; Li, C.X.; Fan, S.T.; Man, K. Regulatory B cells accelerate hepatocellular carcinoma progression via CD40/CD154 signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2014, 355, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, K.; Sarris, M.; Talianidis, I. Molecular pathways: The complex roles of inflammation pathways in the development and treatment of liver cancer. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2013, 19, 2810–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.Q.; Li, W.M.; Lu, Z.Q.; Yao, Y.M. Roles of Tregs in development of hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7971–7978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonejima, A.; Mizukoshi, E.; Tamai, T.; Nakagawa, H.; Kitahara, M.; Yamashita, T.; Arai, K.; Terashima, T.; Iida, N.; Fushimi, K.; et al. Characteristics of Impaired Dendritic Cell Function in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Hepatology 2019, 70, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pasquale, C.; Campana, S.; Barberi, C.; Sidoti Migliore, G.; Oliveri, D.; Lanza, M.; Musolino, C.; Raimondo, G.; Ferrone, S.; Pollicino, T.; et al. Human Hepatitis B Virus Negatively Impacts the Protective Immune Crosstalk Between Natural Killer and Dendritic Cells. Hepatology 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Chen, P.J.; Yeh, S.H. Gender disparity in chronic hepatitis B: Mechanisms of sex hormones. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, H.-J.; Cheong, J.-Y. Role of Immune Cells in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158011
Cho H-J, Cheong J-Y. Role of Immune Cells in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(15):8011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158011
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Hyo-Jung, and Jae-Youn Cheong. 2021. "Role of Immune Cells in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 15: 8011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158011
APA StyleCho, H.-J., & Cheong, J.-Y. (2021). Role of Immune Cells in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(15), 8011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158011





