Identification of Spiro-Fused [3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane]oxindoles as Potential Antitumor Agents: Initial In Vitro Evaluation of Anti-Proliferative Effect and Actin Cytoskeleton Transformation in 3T3 and 3T3-SV40 Fibroblast
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Drug-Likeness and Bioactivity Scores
2.2. Cell Multiplication Study after 4a–c Compounds Treatment
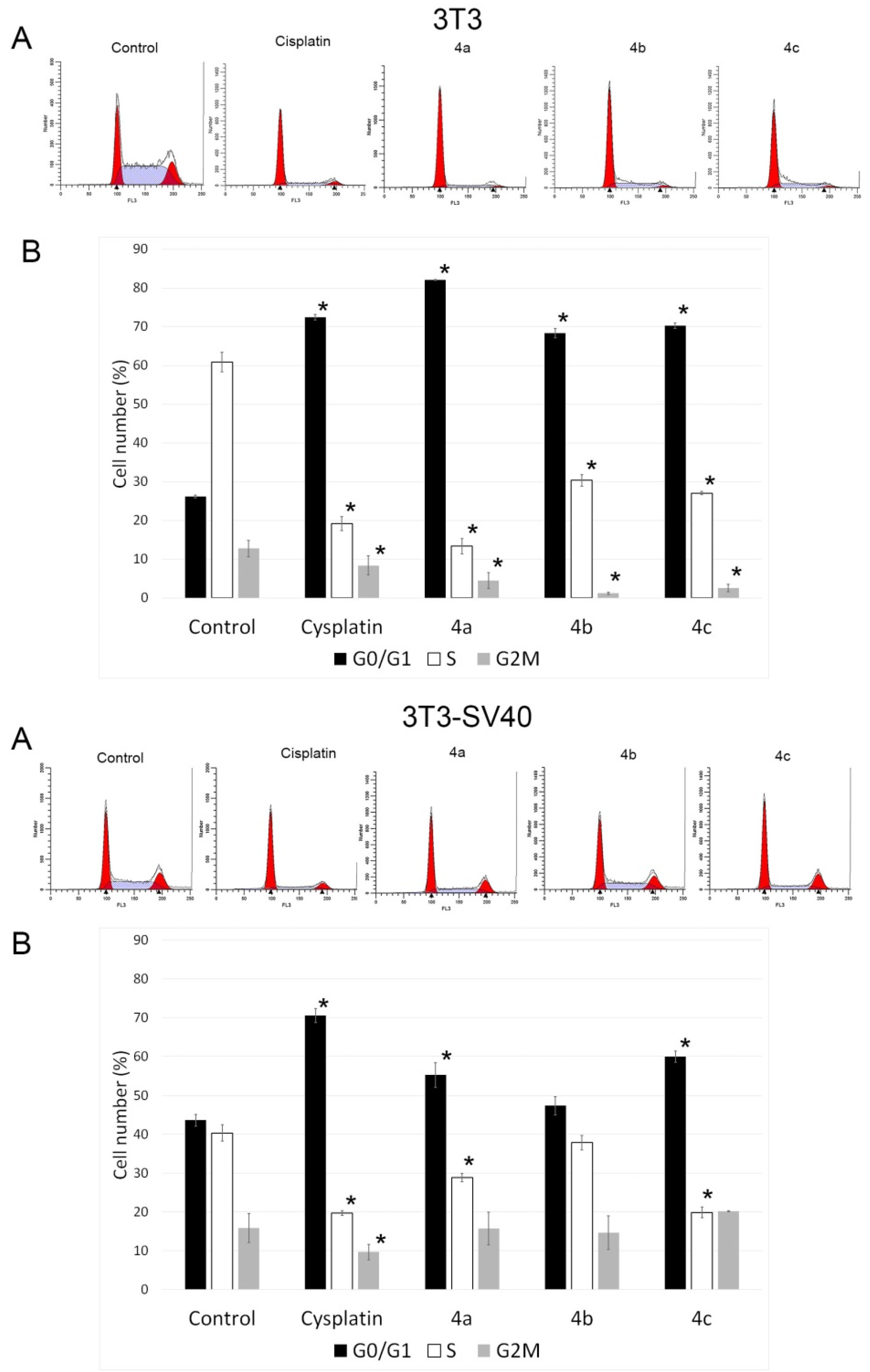
2.3. Cell Cycle Analysis
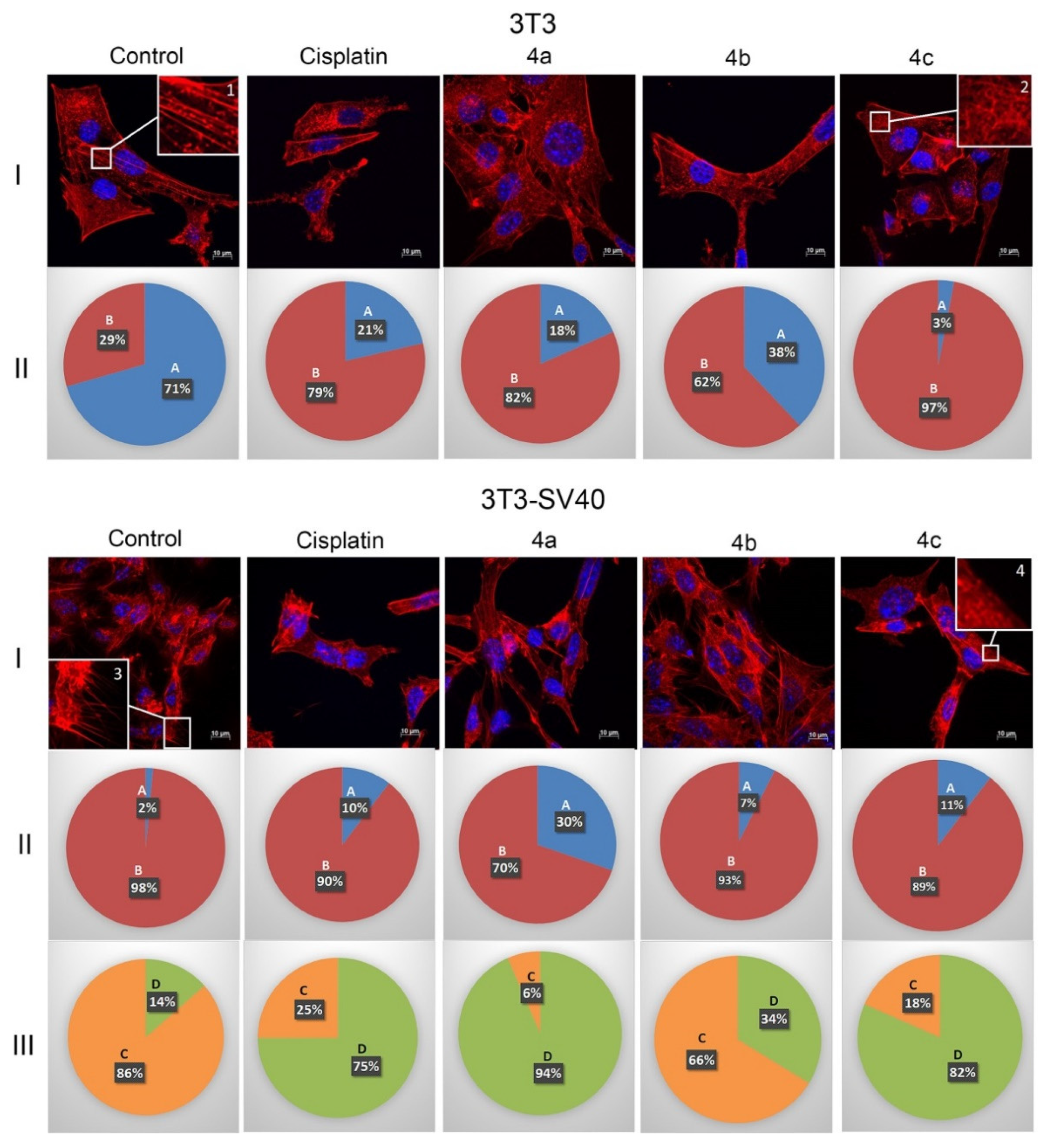
2.4. Actin Cytoskeleton
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. In Silico Study
3.2. Synthesis
3.3. Cell Culture and Culturing Conditions
3.4. Cell Treatment
3.5. Evaluation of Cell Multiplication and Cell Cycle Studies by Flow Cytometry
3.6. Actin Cytoskeleton Staining
3.7. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akgun, H.; Us Yilmaz, D.; Cetin Atalay, R.; Gozen, D. A Series of 2,4(1H,3H)-Quinazolinedione Derivatives: Synthesis and Biological Evaluation as Potential Anticancer Agents. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2016, 13, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blass, B.E. Chapter 1—Drug Discovery and Development: An Overview of Modern Methods and Principles. In Basic Principles of Drug Discovery and Development, 1st ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Vistoli, G.; Pedretti, A.; Testa, B. Assessing drug-likeness—What are we missing? Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, C.; Carreira, E.M. Construction of Spiro[pyrrolidine-3,3′-oxindoles]—Recent Applications to the Synthesis of Oxindole Alkaloids. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 12, 2209–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.-M.; Qu, R.-Y.; Yang, G.-F. An overview of spirooxindole as a promising scaffold for novel drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2020, 15, 603–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khetmalis, Y.M.; Shivani, M.; Murugesan, S.; Chandra Sekhar, K.V.G. Oxindole and its derivatives: A review on recent progress in biological activities. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, B.K.S.; Zou, B.; Rottmann, M.; Lakshminarayana, S.B.; Ang, S.H.; Leong, S.Y.; Tan, J.; Wong, J.; Keller-Maerki, S.; Fischli, C.; et al. Spirotetrahydro beta-carbolines (spiroindolones): A new class of potent and orally efficacious compounds for the treatment of malaria. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5155–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikorodov, A.V.; Ionova, V.A.; Degtyarev, O.V.; Sukhenko, L.T. Synthesis and Antimicrobial and Antifungal Activity of Carbamate-Functionized Spiro Compounds. Pharm. Chem. J. 2013, 46, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filatov, A.S.; Knyazev, N.A.; Molchanov, A.P.; Panikorovsky, T.L.; Kostikov, R.R.; Larina, A.G.; Boitsov, V.M.; Stepakov, A.V. Synthesis of Functionalized 3-Spiro[cyclopropa[a]pyrrolizine]-and 3-Spiro[3 -azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane]oxindoles from Cyclopropenes and Azomethine Ylides via [3 + 2]-Cycloaddition. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filatov, A.S.; Knyazev, N.A.; Ryazantsev, M.N.; Suslonov, V.V.; Larina, A.G.; Molchanov, A.P.; Kostikov, R.R.; Boitsov, V.M.; Stepakov, A.V. A highly diastereoselective one-pot three-component 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of cyclopropenes with azomethine ylides generated from 11H-indeno[1,2-b]-quinoxalin-11-ones. Org. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filatov, A.S.; Knyazev, N.A.; Shmakov, S.V.; Bogdanov, A.A.; Ryazantsev, M.N.; Shtyrov, A.A.; Starova, G.L.; Molchanov, A.P.; Larina, A.G.; Boitsov, V.M.; et al. Concise Synthesis of Tryptanthrin Spiro Analogues with In Vitro Antitumor Activity Based on One-Pot, Three-Component 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition of Azomethine Ylides to Cyclopropenes. Synthesis 2019, 51, 713–729. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Filatov, A.S.; Lozovskiy, S.V.; Shmakov, S.V.; Khoroshilova, O.V.; Larina, A.G.; Selivanov, S.I.; Boitsov, V.M.; Stepakov, A.V. Construction of Spiro[3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexanes] via 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition of 1,2-Diphenylcyclopropenes to Ninhydrin-Derived Azomethine Ylides. Synthesis 2021, 53, 2114–2132. [Google Scholar]
- Ivlev, A.P.; Efremova, T.N.; Khaitlina, S.Y.; Bozhokina, E.S. Difference in Susceptibility of 3T3 and 3T3-SV40 Cells to Invasion by Opportunistic Pathogens Serratia grimesii. Cell Tissue Biol. 2018, 12, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, M.; Miyoshi, H.; Miura, T.; Tanaka, H.; Tsubota, K.I.; Liu, H. Dynamics of Actin Stress Fibers and Focal Adhesions during Slow Migration in Swiss 3T3 Fibroblasts: Intracellular Mechanism of Cell Turning. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 5749749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Laney, T.V.; Cherry, R.S.; Coppinger, J.A.; Truskey, G.A. Altered distribution of mitochondria and actin fibers in 3T3 cells cultured on microcarriers. Biotechnol. Prog. 1992, 8, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamaley, I.A.; Kirpichnikova, K.M.; Vakhromova, E.A.; Filatova, N.A. N-acetylcysteine reduces susceptibility of transformed and embryonic cells to lytic activity of natural killer cells. Cell Tissue Biol. 2010, 4, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertl, P.; Rohde, B.; Selzer, P. Fast Calculation of Molecular Polar Surface Area as a Sum of Fragment-Based Contributions and Its Application to the Prediction of Drug Transport Properties. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 3714–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, D.E.; Pickett, S.D. Computational methods for the prediction of ‘drug-likeness’. Drug Discov. Today 2000, 5, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajouhesh, H.; Lenz, G.R. Medicinal chemical properties of successful central nervous system drugs. NeuroRX 2005, 2, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hitchcock, S.A.; Pennington, L.D. Structure−Brain Exposure Relationships. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 7559–7583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senwar, K.R.; Sharma, P.; Reddy, T.S.; Jeengar, M.K.; Nayak, V.L.; Naidu, V.G.M.; Kamal, A.; Shankaraiah, N. Spirooxindole-derived morpholine-fused-1,2,3-triazoles: Design, synthesis, cytotoxicity and apoptosis inducing studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 102, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Wang, S.; Jin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hua, D.; Miao, T.; Tao, X.; Wang, S. Synthesis and Evaluation of New Quinoxaline Derivatives of Dehydroabietic Acid as Potential Antitumor Agents. Molecules 2017, 22, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horibe, S.; Matsuda, A.; Tanahashi, T.; Inoue, J.; Kawauchi, S.; Mizuno, S.; Ueno, M.; Takahashi, K.; Maeda, Y.; Maegouchi, T.; et al. Cisplatin resistance in human lung cancer cells is linked with dysregulation of cell cycle associated proteins. Life Sci. 2015, 124, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Cui, J.; Wen, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X. Cisplatin induces HepG2 cell cycle arrest through targeting specific long noncoding RNAs and the p53 signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 4605–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spano, A.; Monaco, G.; Barni, S.; Sciola, L. Cisplatin treatment of NIH/3T3 cultures induces a form of autophagic death in polyploid cells. Histol. Histopathol. 2008, 23, 717–730. [Google Scholar]
- Bonello, T.T.; Stehn, J.R.; Gunning, P.W. New approaches to targeting the actin cytoskeleton for chemotherapy. Future Med. Chem. 2009, 1, 1311–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brayford, S.; Schevzov, G.; Vos, J.; Gunning, P. The Role of the Actin Cytoskeleton in Cancer and Its Potential Use as a Therapeutic Target. In The Cytoskeleton in Health and Disease; Schatten, H., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 373–391. [Google Scholar]
- Sahai, E.; Marshall, C.J. Differing modes of tumour cell invasion have distinct requirements for Rho/ROCK signalling and extracellular proteolysis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, L.; Sun, W.; Lu, J.; McEachern, D.; Li, X.; Yu, S.; Bernard, D.; Ochsenbein, P.; Ferey, V.; et al. Diastereomeric Spirooxindoles as Highly Potent and Efficacious MDM2 Inhibitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7223–7234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lo, M.M.-C.; Neumann, C.S.; Nagayama, S.; Perlstein, E.O.; Schreiber, S.L. A Library of Spirooxindoles Based on a Stereoselective Three-Component Coupling Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 16077–16086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 23, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knyazev, N.A.; Samoilova, K.A.; Abrahamse, H.; Filatova, N.A. Downregulation of tumorogenicity and changes in the actin cytoskeleton of murine hepatoma after irradiation with polychromatic visible and IR light. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2015, 33, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Compound | Mol. wt 1 | H-Bond Donors 2 | H-Bond Acceptors 3 | C Log P 4 | TPSA (Å2) 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rule | ≤500 | ≤5 | ≤10 | ≤5 | ≤140 |
| 4a | 484.64 | 2 | 3 | 6.88 | 41.14 |
| 4b | 484.64 | 2 | 3 | 6.88 | 41.12 |
| 4c | 502.68 | 2 | 3 | 5.96 | 41.12 |
| Cisplatin | 300,05 | 6 | 2 | −4.58 | 55.28 |
| Compound | Caco2 1 Permeability | HIA 2 (%) | PPB 3 (%) | BBB 4 (Cbrain/Cblood) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rule | ≥4 | ≥70 | ≥90 | ≥0.4 |
| 4a | 48.3202 | 95.542381 | 97.857647 | 8.62779 |
| 4b | 48.3128 | 95.542356 | 97.212995 | 8.82546 |
| 4c | 23.9496 | 96.734547 | 100.000000 | 0.992983 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Knyazev, N.A.; Shmakov, S.V.; Pechkovskaya, S.A.; Filatov, A.S.; Stepakov, A.V.; Boitsov, V.M.; Filatova, N.A. Identification of Spiro-Fused [3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane]oxindoles as Potential Antitumor Agents: Initial In Vitro Evaluation of Anti-Proliferative Effect and Actin Cytoskeleton Transformation in 3T3 and 3T3-SV40 Fibroblast. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158264
Knyazev NA, Shmakov SV, Pechkovskaya SA, Filatov AS, Stepakov AV, Boitsov VM, Filatova NA. Identification of Spiro-Fused [3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane]oxindoles as Potential Antitumor Agents: Initial In Vitro Evaluation of Anti-Proliferative Effect and Actin Cytoskeleton Transformation in 3T3 and 3T3-SV40 Fibroblast. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(15):8264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158264
Chicago/Turabian StyleKnyazev, Nickolay A., Stanislav V. Shmakov, Sofya A. Pechkovskaya, Alexander S. Filatov, Alexander V. Stepakov, Vitali M. Boitsov, and Natalia A. Filatova. 2021. "Identification of Spiro-Fused [3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane]oxindoles as Potential Antitumor Agents: Initial In Vitro Evaluation of Anti-Proliferative Effect and Actin Cytoskeleton Transformation in 3T3 and 3T3-SV40 Fibroblast" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 15: 8264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158264
APA StyleKnyazev, N. A., Shmakov, S. V., Pechkovskaya, S. A., Filatov, A. S., Stepakov, A. V., Boitsov, V. M., & Filatova, N. A. (2021). Identification of Spiro-Fused [3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane]oxindoles as Potential Antitumor Agents: Initial In Vitro Evaluation of Anti-Proliferative Effect and Actin Cytoskeleton Transformation in 3T3 and 3T3-SV40 Fibroblast. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(15), 8264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158264






