Cannabidiol Modulates the Motivational and Anxiety-Like Effects of 3,4-Methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Drugs
2.3. Conditioned Place Preference
2.4. Self-Administration
2.4.1. Surgery
2.4.2. Acquisition of MDPV Self-Administration
2.4.3. Progressive Ratio Test
2.5. Elevated Plus Maze (EPM)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
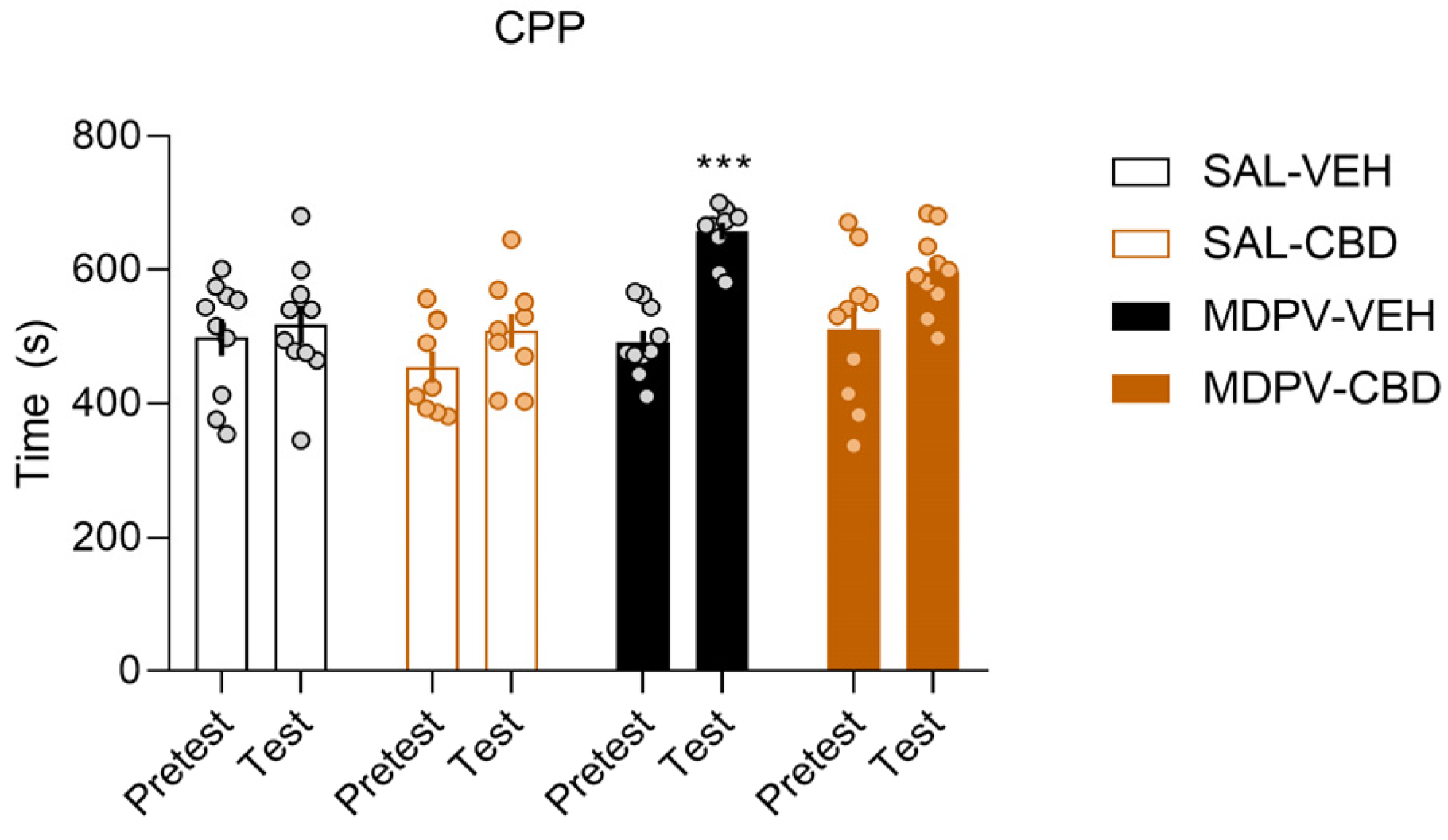
3.1. CBD Treatment Partially Prevents MDPV-Induced CPP
3.2. CBD Does Not Modify MDPV (0.05 mg/kg)-Induced Self-Administration
3.3. CBD Increases MDPV (0.075 mg/kg) Reinforcing Effects Only in High-Responders
3.4. Mice Modulate Their Drug-Seeking Behaviour to Maintain MDPV Consumption
3.5. CBD Increases the Anxiolytic Effects of MDPV in the EPM
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CBD | cannabidiol |
| CPP | conditioned place preference |
| DAT | dopamine transporter |
| EPM | elevated plus maze |
| FR1 | fixed ratio 1 |
| MDMA | 3:4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine |
| MDPV | 3:4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone |
| NET | norepinephrine transporter |
| NPS | new psychoactive substances |
| PR | progressive ratio |
| SERT | serotonin transporter |
References
- United Nations Publication. World Drug Report; United Nations Publication: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- EMCDDA. European Drug Report 2020: Trends and Developments; EMCDDA: Lisbon, Portugal, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Karch, S. Cathinone Neurotoxicity (“The “3Ms”). Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2014, 13, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baumann, M.H.; Bukhari, M.O.; Lehner, K.R.; Anizan, S.; Rice, K.C.; Concheiro, M.; Huestis, M.A. Neuropharmacology of 3,4–Methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV), Its metabolites, and related analogs HHS Public Access. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 32, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karila, L.; Lafaye, G.; Scocard, A.; Cottencin, O.; Benyamina, A. MDPV and α-PVP use in humans: The twisted sisters. Neuropharmacol 2018, 134, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, E.A.; Reisfield, G.M.; Watson, M.C.; Chronister, C.W.; Goldberger, B.A. Psychoactive “bath salts” intoxication with methylenedioxypyrovalerone. Am. J. Med. 2012, 125, 854–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmler, L.D.; Buser, T.A.; Donzelli, M.; Schramm, Y.; Dieu, L.-H.; Huwyler, J.; Chaboz, S.; Hoener, M.C.; Liechti, M.E.; Liechti, M.E. Pharmacological characterization of designer cathinones in vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 168, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumann, M.H.; Partilla, J.S.; Lehner, K.R.; Thorndike, E.B.; Hoffman, A.F.; Holy, M.; Rothman, R.B.; Goldberg, S.R.; Lupica, C.R.; Sitte, H.H.; et al. Powerful cocaine–like actions of 3,4–methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV), a principal constituent of psychoactive ‘bath salts’ products. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simmons, S.J.; Gregg, R.A.; Tran, F.H.; Mo, L.; Von Weltin, E.; Barker, D.J.; Gentile, T.A.; Watterson, L.R.; Rawls, S.M.; Muschamp, J.W. Comparing rewarding and reinforcing properties between “bath salt” 3,4–methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) and cocaine using ultrasonic vocalizations in rats HHS Public Access. Addict. Biol. 2018, 23, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, S.J.; Martorana, R.; Philogene-Khalid, H.; Tran, F.H.; Gentile, T.A.; Xu, X.; Su, S.; Rawls, S.M.; Muschamp, J.W. Role of hypocretin/orexin receptor blockade on drug-taking and ultrasonic vocalizations (USVs) associated with low-effort self-administration of cathinone-derived 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) in rats. Psychopharmacology 2017, 234, 3207–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duart-Castells, L.; Carmen Blanco-Gandía, M.; Ferrer-Pérez, C.; Puster, B.; Pubill, D.; Miñarro, J.; Escubedo, E.; Rodríguez-Arias, M. Cross–reinstatement between 3,4–methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) and cocaine using conditioned place preference. Prog. Neuro–Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 100, 109876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, C.; Huang, P.; Ramos, L.; Nayak, S.U.; Caro, Y.; Reitz, A.B.; Smith, G.R.; Lee, D.Y.-W.; Rawls, S.M.; Liu-Chen, L.Y. Dopamine D1–like receptor agonist and D2–like receptor antagonist (−)–stepholidine reduces reinstatement of drug–seeking behavior for 3,4–methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) in rats. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risca, H.I.; Zuarth-Gonzalez, J.D.; Baker, L.E. Conditioned place preference following concurrent treatment with 3, 4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) and methamphetamine in male and female Sprague-Dawley rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2020, 198, 173032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewalia, K.; Watterson, L.R.; Hryciw, A.; Belloc, A.; Ortiz, J.B. Neurocognitive dysfunction following repeated binge-like self-administration of the synthetic cathinone 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV). Neuropharmacology 2018, 134, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, C.W.; Thorndike, E.B.; Goldberg, S.R.; Lehner, K.R.; Cozzi, N.V.; Brandt, S.D.; Baumann, M.H. Reinforcing and neurochemical effects of the “bath salts” constituents 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) and 3,4-methylenedioxy–N–methylcathinone (methylone) in male rats. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geste, J.R.; Pompilus, M.; Febo, M.; Bruijnzeel, A.W. Self–administration of the synthetic cathinone MDPV enhances reward function via a nicotinic receptor dependent mechanism. Neuropharmacology 2018, 137, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarde, S.M.; Huang, P.K.; Dickerson, T.J.; Taffe, M.A. Binge–like acquisition of 3,4−methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) self–administration and wheel activity in rats. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 1867–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aarde, S.M.; Huang, P.K.; Creehan, K.M.; Dickerson, T.J.; Taffe, M.A. The novel recreational drug 3,4–methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) is a potent psychomotor stimulant: Self-administration and locomotor activity in rats. Neuropharmacology 2013, 71, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aarde, S.M.; Creehan, K.M.; Vandewater, S.A.; Dickerson, T.J.; Taffe, M.A. In vivo potency and efficacy of the novel cathinone α – pyrrolidinopentiophenone and 3,4–methylenedioxypyrovalerone: Self–administration and locomotor stimulation in male rats. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 3045–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watterson, L.R.; Kufahl, P.R.; Nemirovsky, N.E.; Sewalia, K.; Grabenauer, M.; Thomas, B.F.; Marusich, J.A.; Wegner, S.; Olive, M.F. Potent rewarding and reinforcing effects of the synthetic cathinone 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV). Addict. Biol. 2014, 19, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannon, B.M.; Galindo, K.I.; Rice, K.C.; Collins, G.T. Individual differences in the relative reinforcing effects of 3,4–methylenedioxypyrovalerone under fixed and progressive ratio schedules of reinforcement in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 361, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fantegrossi, W.E.; Gannon, B.M.; Zimmerman, S.M.; Rice, K.C. In vivo effects of abused “bath salt” constituent 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) in mice: Drug discrimination, thermoregulation, and locomotor activity. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 38, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gannon, B.M.; Russell, L.N.; Modi, M.S.; Rice, K.C.; Fantegrossi, W.E. Effects of orally self-administered bath salt constituent 3,4–methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) in mice. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017, 179, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsaid, S.; Kloiber, S.; Le Foll, B. Effects of cannabidiol (CBD) in neuropsychiatric disorders: A review of pre–clinical and clinical findings. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2019, 167, 25–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R de Mello Schier, A.R.; de Oliveira Ribeiro, N.P.; Coutinho, D.S.; Machado, S.; Arias-Carrión, O.; Crippa, J.A.; Zuardi, A.W.; Nardi, A.E.; Silva, A.C. Antidepressant–like and anxiolytic–like effects of cannabidiol: A chemical compound of Cannabis sativa. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 13, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Navarrete, F.; Gasparyan, A.; Austrich-Olivares, A.; Sala, F.; Manzanares, J. Cannabidiol: A potential new alternative for the treatment of anxiety, depression, and psychotic disorders. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chye, Y.; Christensen, E.; Solowij, N.; Yücel, M. The Endocannabinoid System and Cannabidiol’s Promise for the Treatment of Substance Use Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, A.A.; Borrelli, F.; Capasso, R.; Di Marzo, V.; Mechoulam, R. Non-psychotropic plant cannabinoids: New therapeutic opportunities from an ancient herb. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laprairie, R.B.; Bagher, A.M.; Kelly, M.E.M.; Denovan-Wright, E.M. Cannabidiol is a negative allosteric modulator of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 4790–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Pinilla, E.; Varani, K.; Reyes-Resina, I.; Angelats, E.; Vincenzi, F.; Ferreiro-Vera, C.; Oyarzabal, J.; Canela, E.I.; Lanciego, J.L.; Nadal, X.; et al. Binding and signaling studies disclose a potential allosteric site for cannabidiol in cannabinoid CB2 receptors. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calpe-López, C.; Pilar García-Pardo, M.; Aguilar, M.A. Cannabidiol treatment might promote resilience to cocaine and methamphetamine use disorders: A review of possible mechanisms. Molecules 2019, 24, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, L.A.; Caroba, M.E.S.; Taba, F.K.; Filev, R.; Gallassi, A.D. Evaluation of the potential use of cannabidiol in the treatment of cocaine use disorder: A systematic review. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2020, 196, 172982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luján, M.Á.; Castro-Zavala, A.; Alegre-Zurano, L.; Valverde, O. Repeated Cannabidiol treatment reduces cocaine intake and modulates neural proliferation and CB1R expression in the mouse hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 2018, 143, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luján, M.Á.; Cantacorps, L.; Valverde, O. The pharmacological reduction of hippocampal neurogenesis attenuates the protective effects of cannabidiol on cocaine voluntary intake. Addict. Biol. 2019, 25, e12778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegre-Zurano, L.; Luján, M.Á.; Cantacorps, L.; Martín-Sánchez, A.; García-Baos, A.; Valverde, O. Cannabidiol effects on cocaine–seeking behaviour and incubation of craving in mice. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, L.A.; Burton, P.; Sorge, R.E.; Yakiwchuk, C.; Mechoulam, R. Effect of low doses of 9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol on the extinction of cocaine-induced and amphetamine-induced conditioned place preference learning in rats. Psychopharmacology 2004, 175, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, G.L.; Baracz, S.J.; Everett, N.A.; Roberts, J.; Costa, P.A.; Arnold, J.C.; McGregor, I.S.; Cornish, J.L. Cannabidiol treatment reduces the motivation to self-administer methamphetamine and methamphetamine-primed relapse in rats. J. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 32, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegre-Zurano, L.; Martín-Sánchez, A.; Valverde, O. Behavioural and molecular effects of cannabidiolic acid in mice. Life Sci. 2020, 259, 118271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, G.; Mendizábal, V.; Touriño, C.; Robledo, P.; Ledent, C.; Parmentier, M.; Maldonado, R.; Valverde, O. Lack of CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Impairs Cocaine Self-Administration. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 30, 1670–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, G.; Barbano, M.F.; Maldonado, R.; Valverde, O.; Soria, G.; Barbano, M.F.; Maldonado, R.; Valverde, O. A reliable method to study cue-, priming-, and stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine self-administration in mice. Psychopharmacology 2008, 199, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lujan, M.A.; Alegre-Zurano, L.; Martin-Sanchez, A.; Valverde, O. The effects of cannabidiol on cue- and stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking behavior in mice are reverted by the CB1 receptor antagonist AM4113. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, H.E.; Wakeford, A.; Taylor, W.; Wetzell, B.; Rice, K.C.; Riley, A.L. Sex differences in 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV)-induced taste avoidance and place preferences. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 137, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chesworth, R.; Karl, T. Cannabidiol (CBD) reduces cocaine-environment memory in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2020, 199, 173065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledesma, J.C.; Manzanedo, C.; Aguilar, M.A. Cannabidiol prevents several of the behavioral alterations related to cocaine addiction in mice. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 111, 110390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duart-Castells, L.; López-Arnau, R.; Vizcaíno, S.; Camarasa, J.; Pubill, D.; Escubedo, E. 7,8–Dihydroxyflavone blocks the development of behavioral sensitization to MDPV, but not to cocaine: Differential role of the BDNF–TrkB pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 163, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duart-Castells, L.; López-Arnau, R.; Buenrostro-Jáuregui, M.; Muñoz-Villegas, P.; Valverde, O.; Camarasa, J.; Pubill, D.; Escubedo, E. Neuroadaptive changes and behavioral effects after a sensitization regime of MDPV. Neuropharmacology 2019, 144, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watterson, L.R.; Olive, M.F. Synthetic cathinones and their rewarding and reinforcing effects in rodents. The Rise of Synthetic Cathinone Use and Abuse. Adv. Neurosci. 2014, 2014, 209875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Touriño, C.; Ledent, C.; Maldonado, R.; Valverde, O. CB1Cannabinoid Receptor Modulates 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine Acute Responses and Reinforcement. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gannon, B.M.; Baumann, M.H.; Walther, D.; Jimenez-Morigosa, C.; Sulima, A.; Rice, K.C.; Collins, G.T. The abuse–related effects of pyrrolidine-containing cathinones are related to their potency and selectivity to inhibit the dopamine transporter. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 2399–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, G.T.; Sulima, A.; Rice, K.C.; France, C.P. Self–administration of the synthetic cathinones 3,4–methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) and α–pyrrolidinopentiophenone (α–PVP) in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 3677–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannon, B.M.; Rice, K.C.; Murnane, K.S. MDPV “high–responder” rats also self-administer more oxycodone than their “low-responder” counterparts under a fixed ratio schedule of reinforcement. Psychopharmacology 2021, 238, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, G.-H.; Galaj, E.; He, Y.; Xi, Z.-X. Cannabidiol inhibits sucrose self-administration by CB1 and CB2 receptor mechanisms in rodents. Addict. Biol. 2019, 25, e12783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaj, E.; Bi, G.-H.; Yang, H.-J.; Xi, Z.-X. Cannabidiol attenuates the rewarding effects of cocaine in rats by CB2, 5–TH1A and TRPV1 receptor mechanisms. Neuropharmacology 2019, 167, 107740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Arnau, R.; Duart-Castells, L.; Aster, B.; Camarasa, J.; Escubedo, E.; Pubill, D. Effects of MDPV on dopamine transporter regulation in male rats. Comparison with cocaine. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, H.E.; Wetzell, B.; Rice, K.C.; Riley, A.L. 3,4-Methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV)-induced conditioned taste avoidance in the F344/N and LEW rat strains. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 126, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merluzzi, A.P.; Hurwitz, Z.E.; Briscione, M.A.; Cobuzzi, J.L.; Wetzell, B.; Rice, K.C.; Riley, A.L. Age-dependent MDPV-induced taste aversions and thermoregulation in adolescent and adult rats. Dev. Psychobiol. 2014, 56, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campos, A.C.; Ortega, Z.; Palazuelos, J.; Fogaça, M.V.; Aguiar, D.C.; Díaz-Alonso, J.; Ortega-Gutiérrez, S.; Vázquez-Villa, H.; Moreira, F.A.; Guzmán, M.; et al. The anxiolytic effect of cannabidiol on chronically stressed mice depends on hippocampal neurogenesis: Involvement of the endocannabinoid system. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 16, 1407–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guimarães, F.S.; Chiaretti, T.M.; Graeff, F.G.; Zuardi, A.W. Antianxiety effect of cannabidiol in the elevated plus–maze. Psychopharmacology 1990, 100, 558–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaivi, S.; Green, M.R. Pharmacological characterization of cannabinoids in the elevated plus maze. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1990, 253, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alegre-Zurano, L.; López-Arnau, R.; Luján, M.Á.; Camarasa, J.; Valverde, O. Cannabidiol Modulates the Motivational and Anxiety-Like Effects of 3,4-Methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158304
Alegre-Zurano L, López-Arnau R, Luján MÁ, Camarasa J, Valverde O. Cannabidiol Modulates the Motivational and Anxiety-Like Effects of 3,4-Methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(15):8304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158304
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlegre-Zurano, Laia, Raúl López-Arnau, Miguel Á. Luján, Jordi Camarasa, and Olga Valverde. 2021. "Cannabidiol Modulates the Motivational and Anxiety-Like Effects of 3,4-Methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 15: 8304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158304
APA StyleAlegre-Zurano, L., López-Arnau, R., Luján, M. Á., Camarasa, J., & Valverde, O. (2021). Cannabidiol Modulates the Motivational and Anxiety-Like Effects of 3,4-Methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(15), 8304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158304






