Myelin Defects in Niemann–Pick Type C Disease: Mechanisms and Possible Therapeutic Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cholesterol in Myelination
| Main Events in Cholesterol Metabolism | Defective Protein | Impairment | Hypomyelinating Diseases | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthesis | 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase | abnormality in cholesterol production | Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome | [26,27] |
| acyl-CoA oxidase 1 (ACOX1) | very-long-chain fatty acid (VLCFA) accumulation | Peroxisome biogenesis disorder | [28,29] | |
| 3 b-Hydroxysteroid 8, 7-sterol isomerase | 8,9-unsaturated sterols accumulation | Greenberg dysplasia, Conradi–Hunermann syndrome | [30] | |
| Transport | ABCA1 transporter, HDL | No transport out cell | Tangier disease | [31] |
| ABCA1, Lrp1 | disrupts cholesterol homeostasis | Peroxisome biogenesis disorder | [16,29] | |
| NPC1, NPC2 | defective cellular cholesterol transportation | Niemann–Pick disease C | [26,32] | |
| Accumulation | sterol 27-hydroxylase (CYP27A1) | abnormal cholesterol accumulation | Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis, | [33,34] |
| CYP27A1, Lecithin–cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) enzyme, vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein B (VapB), and OxySterol Binding Proteins (OSBP) | higher total cholesterol and HDL and LDL levels | Sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | [35] | |
| beta-galactosylceramidase | galactosyl-sphingolipids accumulation | Globoid cell leukodystrophy or Krabbe disease | [36] | |
| arylsulfatase A (ARSA) and Prosaposin precursor (PSAP) | Sulfatides accumulation | Metachromatic leukodystrophy | [37,38] | |
| PLP1 | co-accumulation of PLP and cholesterol | Pelizaeus–Merzbacher disease | [39,40] | |
| peripheral myelin protein 22 (PMP22) | co-accumulation of apoE, LRP1, and ABCA1 | Charcot–Marie–Tooth, Dejerine–Sottas syndrome | [41,42,43] |
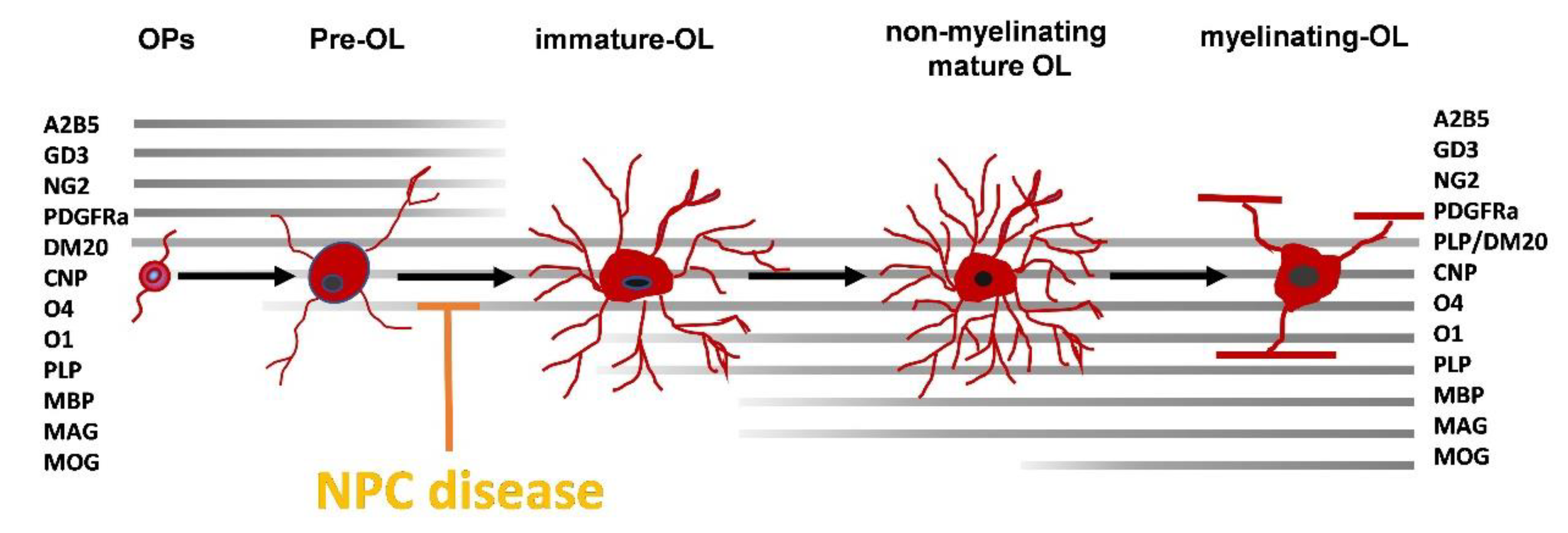
3. Myelin Defects in NPC1
4. NPC Cellular Defects Potentially Affecting OLs Differentiation
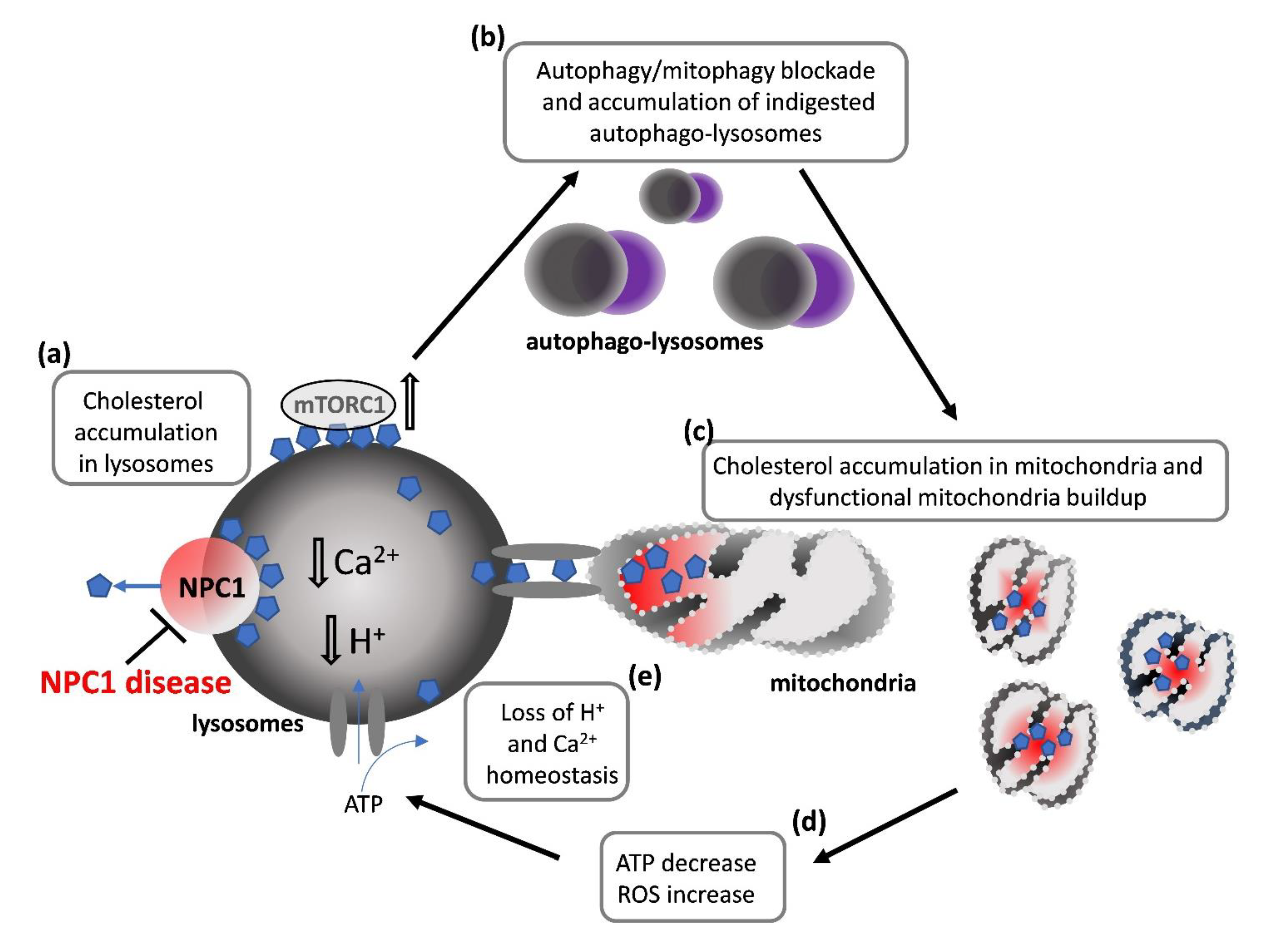
4.1. How Lysosomal Impairment Affects Mitochondria and OLs Differentiation
4.2. How Impairment in Lysosomal Functions Affects Autophagy and OLs Differentiation
5. Therapy Perspectives: The State of the Art
5.1. Miglustat
5.2. Cyclodextrins
6. Pharmacological Advance in the Development of New Targets: Preclinical Studies
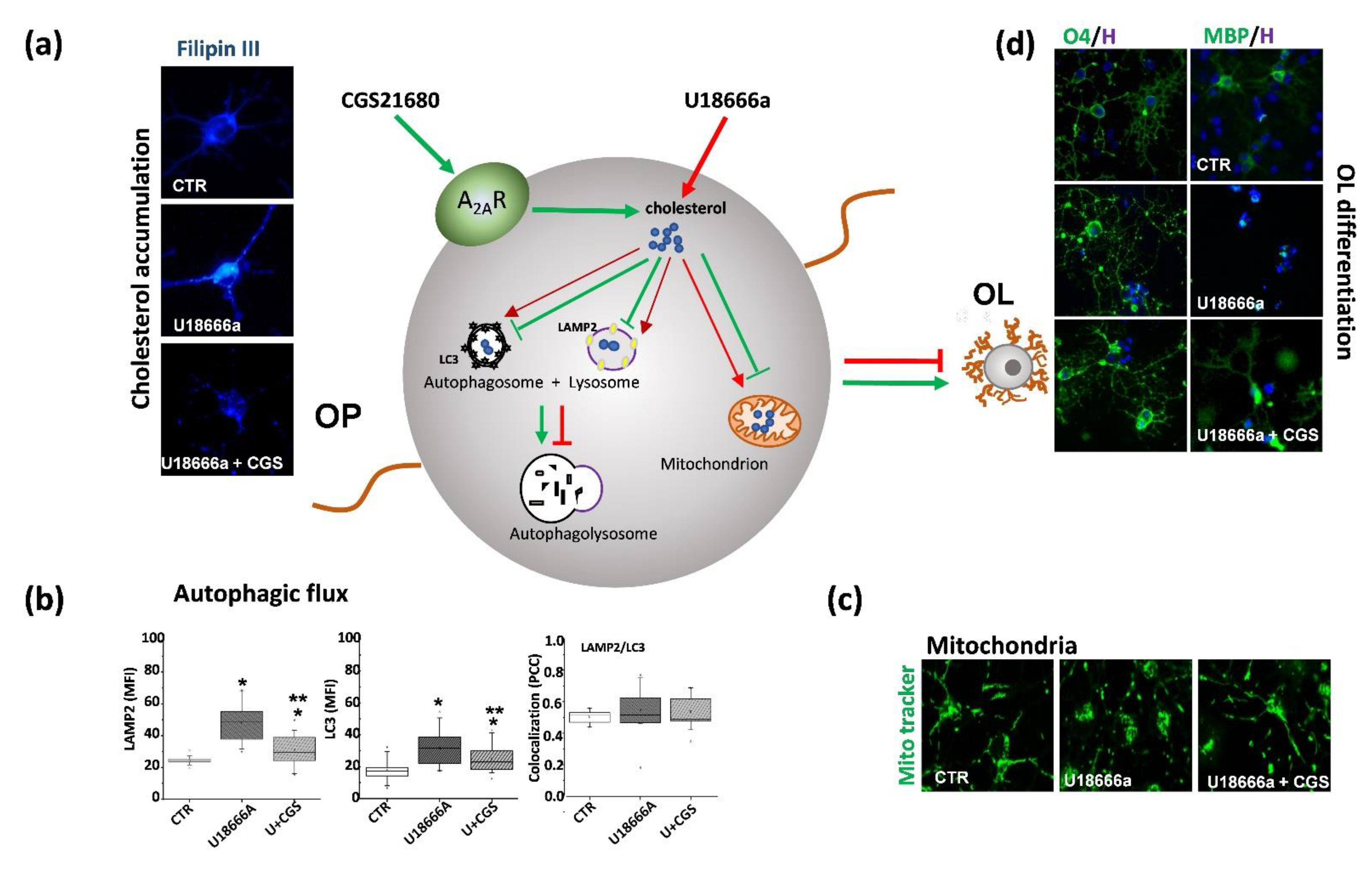
7. Role of Adenosine and Adenosine A2A Receptors in NPC
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | ATP-binding cassette |
| ACOX1 | acyl-CoA oxidase 1 |
| ApoE | Apolipoprotein E |
| ARSA | Arylsulfatase A |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CY27A1 | Sterol 27-hydroxylase |
| DHC | Dehydrocholesterol |
| DHCR | Dehydrocholesterol reductase |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| HMG CoA | Hydroxymethyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase |
| HSP70 | Heat Shock Protein 70 |
| LCAT | Lecithin–cholesterol acyltransferase |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| LRP1 | Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 |
| MAG | Myelin-associated glycoprotein |
| MBP | Myelin basic protein |
| mTORC1 | Mammalian Target of Rapamycin complex 1 |
| NPC1 | Niemann-Pick C1 Protein |
| NPC2 | Niemann-Pick C2 Protein |
| OL | Oligodendrocyte |
| OP | Oligodendrocyte precursor cell |
| OSBP | OxySterol Binding Proteins |
| PLP | Proteolipid protein |
| PM | Plasma membrane |
| PMP22 | Peripheral myelin protein 22 |
| PNS | Peripheral nervous system |
| PSAP | Prosaposin precursor |
| RE | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| VapB | Vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein B |
| VLCFA | Very-long-chain fatty acid |
References
- Toledano-Zaragoza, A.; Ledesma, M.D. Addressing Neurodegeneration in Lysosomal Storage Disorders: Advances in Niemann Pick Diseases. Neuropharmacology 2020, 171, 107851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuchman, E.H.; Wasserstein, M.P. Types A and B Niemann-Pick Disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vanier, M.T. Niemann-Pick Disease Type, C. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2010, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pallottini, V.; Pfrieger, F.W. Understanding and Treating Niemann–Pick Type C Disease: Models Matter. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Evans, E.; Morgan, A.J.; He, X.; Smith, D.A.; Elliot-Smith, E.; Sillence, D.J.; Churchill, G.C.; Schuchman, E.H.; Galione, A.; Platt, F.M. Niemann-Pick Disease Type C1 Is a Sphingosine Storage Disease That Causes Deregulation of Lysosomal Calcium. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, S.; Sillence, D.J. Niemann–Pick Type C Disease: Cellular Pathology and Pharmacotherapy. J. Neurochem. 2020, 153, 674–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torres, S.; García-Ruiz, C.M.; Fernandez-Checa, J.C. Mitochondrial Cholesterol in Alzheimer’s Disease and Niemann-Pick Type C Disease. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, B.E.; LeBlanc, V.G.; Mailman, T.M.; Fice, D.; Burton, I.; Karakach, T.K.; Karten, B. Pre-Symptomatic Activation of Antioxidant Responses and Alterations in Glucose and Pyruvate Metabolism in Niemann-Pick Type C1-Deficient Murine Brain. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, T.; Lieberman, A.P. Npc1 Acting in Neurons and Glia Is Essential for the Formation and Maintenance of CNS Myelin. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrov, A.M.; Kasimov, M.R.; Zefirov, A.L. Brain Cholesterol Metabolism and Its Defects:Linkage to Neurodegenerative Diseases and Synaptic Dysfunction. Acta Nat. 2016, 8, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, G.; Wang, J.; Rasul, A.; Anwar, H.; Imran, A.; Qasim, M.; Zafar, S.; Kamran, S.K.S.; Razzaq, A.; Aziz, N.; et al. Role of Cholesterol and Sphingolipids in Brain Development and Neurological Diseases. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathews, E.S.; Appel, B. Cholesterol Biosynthesis Supports Myelin Gene Expression and Axon Ensheathment through Modulation of P13K/Akt/MTor Signaling. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 7628–7639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saher, G.; Brügger, B.; Lappe-Siefke, C.; Möbius, W.; Tozawa, R.; Wehr, M.C.; Wieland, F.; Ishibashi, S.; Nave, K.-A. High Cholesterol Level Is Essential for Myelin Membrane Growth. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterham, H.R. Defects of Cholesterol Biosynthesis. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 5442–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montani, L. Lipids in Regulating Oligodendrocyte Structure and Function. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 112, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-P.; Mironova, Y.A.; Shrager, P.; Giger, R.J. LRP1 Regulates Peroxisome Biogenesis and Cholesterol Homeostasis in Oligodendrocytes and Is Required for Proper CNS Myelin Development and Repair. Elife 2017, 6, e30498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auderset, L.; Pitman, K.A.; Cullen, C.L.; Pepper, R.E.; Taylor, B.V.; Foa, L.; Young, K.M. Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1 (LRP1) Is a Negative Regulator of Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cell Differentiation in the Adult Mouse Brain. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 564351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer-Albers, E.-M.; Gehrig-Burger, K.; Thiele, C.; Trotter, J.; Nave, K.-A. Perturbed Interactions of Mutant Proteolipid Protein/DM20 with Cholesterol and Lipid Rafts in Oligodendroglia:Implications for Dysmyelination in Spastic Paraplegia. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 11743–11752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castello-Serrano, I.; Lorent, J.H.; Ippolito, R.; Levental, K.R.; Levental, I. Myelin-Associated MAL and PLP Are Unusual among Multipass Transmembrane Proteins in Preferring Ordered Membrane Domains. J. Phys. Chem. 2020, 124, 5930–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanier, M.T. Complex Lipid Trafficking in Niemann-Pick Disease Type, C. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2015, 38, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, F.; Garcia-Ruiz, C.; Fernandez-Checa, J.C. Intracellular Cholesterol Trafficking and Impact in Neurodegeneration. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hammond, N.; Munkacsi, A.B.; Sturley, S.L. The Complexity of a Monogenic Neurodegenerative Disease:More than Two Decades of Therapeutic Driven Research into Niemann-Pick Type C Disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infante, R.E.; Wang, M.L.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Kwon, H.J.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. NPC2 Facilitates Bidirectional Transfer of Cholesterol between NPC1 and Lipid Bilayers, a Step in Cholesterol Egress from Lysosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15287–15292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vance, J.E.; Karten, B. Niemann-Pick C Disease and Mobilization of Lysosomal Cholesterol by Cyclodextrin. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1609–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hawes, C.M.; Wiemer, H.; Krueger, S.R.; Karten, B. Pre-Synaptic Defects of NPC1-Deficient Hippocampal Neurons Are Not Directly Related to Plasma Membrane Cholesterol. J. Neurochem. 2010, 114, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saher, G.; Stumpf, S.K. Cholesterol in Myelin Biogenesis and Hypomyelinating Disorders. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2015, 1851, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslan, A.; Borcek, A.O.; Pamukcuoglu, S.; Baykaner, M.K. Intracranial Undifferentiated Malign Neuroglial Tumor in Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome:A Theory of a Possible Predisposing Factor for Primary Brain Tumors via a Case Report. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2017, 33, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyriou, C.; D’Agostino, M.D.; Braverman, N. Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders. TRD 2016, 1, 111–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jo, D.S.; Park, N.Y.; Cho, D.-H. Peroxisome Quality Control and Dysregulated Lipid Metabolism in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1486–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.; Hassan, A.; Thompson, B.M.; McDonald, J.G.; Wang, J.; Li, X. Structural Basis for Human Sterol Isomerase in Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Multidrug Recognition. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagappa, M.; Taly, A.B.; Mahadevan, A.; Pooja, M.; Bindu, P.S.; Chickabasaviah, Y.T.; Gayathri, N.; Sinha, S. Tangier’s Disease:An Uncommon Cause of Facial Weakness and Non-Length Dependent Demyelinating Neuropathy. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2016, 19, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodachi, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Mizuguchi, M.; Osaka, H.; Kanai, N.; Nanba, E.; Ohno, K.; Yamagata, T. Severe Demyelination in a Patient with a Late Infantile Form of Niemann-Pick Disease Type, C. Neuropathology 2017, 37, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.Y.; Kim, M.-W.; Do, H.J.; Jang, D.-H.; Lee, H.W. Sonographic Findings of Polyneuropathy Associated With Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis:A Case Report. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 41, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patni, N.; Wilson, D.P. Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Grossman, A., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Vejux, A.; Namsi, A.; Nury, T.; Moreau, T.; Lizard, G. Biomarkers of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis:Current Status and Interest of Oxysterols and Phytosterols. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, A.B.; Givogri, M.I.; Lopez-Rosas, A.; Cao, H.; van Breemen, R.; Thinakaran, G.; Bongarzone, E.R. Psychosine Accumulates in Membrane Microdomains in the Brain of Krabbe Patients, Disrupting the Raft Architecture. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 6068–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beerepoot, S.; Nierkens, S.; Boelens, J.J.; Lindemans, C.; Bugiani, M.; Wolf, N.I. Peripheral Neuropathy in Metachromatic Leukodystrophy:Current Status and Future Perspective. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cesani, M.; Lorioli, L.; Grossi, S.; Amico, G.; Fumagalli, F.; Spiga, I.; Filocamo, M.; Biffi, A. Mutation Update of ARSA and PSAP Genes Causing Metachromatic Leukodystrophy. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saher, G.; Rudolphi, F.; Corthals, K.; Ruhwedel, T.; Schmidt, K.-F.; Löwel, S.; Dibaj, P.; Barrette, B.; Möbius, W.; Nave, K.-A. Therapy of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Disease in Mice by Feeding a Cholesterol-Enriched Diet. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, K.J. The Molecular and Cellular Defects Underlying Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Disease. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2008, 10, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Bazick, H.; Miles, J.R.; Fethiere, A.I.; Salihi, M.O.A.; Fazio, S.; Tavori, H.; Notterpek, L. A Neutral Lipid-Enriched Diet Improves Myelination and Alleviates Peripheral Nerve Pathology in Neuropathic Mice. Exp. Neurol. 2019, 321, 113031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Miles, J.R.; Tavori, H.; Lin, M.; Khoshbouei, H.; Borchelt, D.R.; Bazick, H.; Landreth, G.E.; Lee, S.; Fazio, S.; et al. PMP22 Regulates Cholesterol Trafficking and ABCA1-Mediated Cholesterol Efflux. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 5404–5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Borchelt, D.; Bauson, J.C.; Fazio, S.; Miles, J.R.; Tavori, H.; Notterpek, L. Subcellular Diversion of Cholesterol by Gain- and Loss-of-function Mutations in PMP22. Glia 2020, 68, 2300–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walterfang, M. White and Gray Matter Alterations in Adults with Niemann-Pick Disease Type C. Neurology 2010, 75, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies-Thompson, J.; Vavasour, I.; Scheel, M.; Rauscher, A.; Barton, J.J.S. Reduced Myelin Water in the White Matter Tracts of Patients with Niemann-Pick Disease Type C. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1487–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weintraub, H.; Abramovici, A.; Sandbank, U.; Booth, A.D.; Pentchev, P.G.; Sela, B. Dysmyelination in NCTR-Balb/C mouse mutant with a lysosomal storage disorder. Acta Neuropathol. 1987, 74, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takikita, S.; Fukuda, T.; Mohri, I.; Yagi, T.; Suzuki, K. Perturbed Myelination Process of Premyelinating Oligodendrocyte in Niemann-Pick Type C Mouse. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 63, 660–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, X.; Lukas, J.; Witt, M.; Wree, A.; Hübner, R.; Frech, M.; Köhling, R.; Rolfs, A.; Luo, J. Decreased Expression of Myelin Gene Regulatory Factor in Niemann-Pick Type C 1 Mouse. Metab. Brain Dis. 2011, 26, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Feng, X.; Rolfs, A.; Luo, J. Lovastatin Promotes Myelin Formation in NPC1 Mutant Oligodendrocytes. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 386, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Guan, Y.; Feng, X.; Rolfs, A.; Schlüter, H.; Luo, J. Proteomics of the Corpus Callosum to Identify Novel Factors Involved in Hypomyelinated Niemann-Pick Type C Disease Mice. Mol. Brain 2019, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporali, P.; Bruno, F.; Palladino, G.; Dragotto, J.; Petrosini, L.; Mangia, F.; Erickson, R.P.; Canterini, S.; Fiorenza, M.T. Developmental Delay in Motor Skill Acquisition in Niemann-Pick C1 Mice Reveals Abnormal Cerebellar Morphogenesis. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2016, 4, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagel, J.H.; Sikora, T.U.; Prociuk, M.; Pesayco, J.P.; Mizisin, A.P.; Shelton, G.D.; Vite, C.H. Electrodiagnostic Testing and Histopathologic Changes Confirm Peripheral Nervous System Myelin Abnormalities in the Feline Model of Niemann-Pick Disease Type C. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 72, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishibashi, T.; Dakin, K.A.; Stevens, B.; Lee, P.R.; Kozlov, S.V.; Stewart, C.L.; Fields, R.D. Astrocytes Promote Myelination in Response to Electrical Impulses. Neuron 2006, 49, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Domingues, H.S.; Portugal, C.C.; Socodato, R.; Relvas, J.B. Oligodendrocyte, Astrocyte, and Microglia Crosstalk in Myelin Development, Damage, and Repair. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, V.E. Microglia-Driven Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Lineage Cells, Myelination, and Remyelination. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, A.; Dinkel, L.; Müller, S.A.; Monasor, L.S.; Schifferer, M.; Cantuti-castelvetri, L.; König, J.; Vidatic, L.; Bremova-ertl, T.; Lieberman, A.P.; et al. Impairs Lipid Trafficking in Microglia. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabandé-Rodríguez, E.; Pérez-Cañamás, A.; Soto-Huelin, B.; Mitroi, D.N.; Sánchez-Redondo, S.; Martínez-Sáez, E.; Venero, C.; Peinado, H.; Ledesma, M.D. Lipid-induced Lysosomal Damage after Demyelination Corrupts Microglia Protective Function in Lysosomal Storage Disorders. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e99553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreher, C.; Favret, J.; Maulik, M.; Shin, D. Lysosomal Functions in Glia Associated with Neurodegeneration. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, R.; Wong, A.; Silva, J.; Li, M.; Itoh, A.; Horiuchi, M.; Itoh, T.; Pleasure, D.; Cortopassi, G. Oligodendroglial Differentiation Induces Mitochondrial Genes and Inhibition of Mitochondrial Function Represses Oligodendroglial Differentiation. Mitochondrion 2010, 10, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres, S.; Matías, N.; Baulies, A.; Nuñez, S.; Alarcon-Vila, C.; Martinez, L.; Nuño, N.; Fernandez, A.; Caballeria, J.; Levade, T.; et al. Mitochondrial GSH Replenishment as a Potential Therapeutic Approach for Niemann Pick Type C Disease. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, B.E.; Madreiter, C.T.; Vishnu, N.; Malli, R.; Graier, W.F.; Karten, B. Adaptations of Energy Metabolism Associated with Increased Levels of Mitochondrial Cholesterol in Niemann-Pick Type C1-Deficient Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 16278–16289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, W.; Gong, J.-S.; Ko, M.; Garver, W.S.; Yanagisawa, K.; Michikawa, M. Altered Cholesterol Metabolism in Niemann-Pick Type C1 Mouse Brains Affects Mitochondrial Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 11731–11739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visentin, S.; De Nuccio, C.; Bernardo, A.; Pepponi, R.; Ferrante, A.; Minghetti, L.; Popoli, P. The Stimulation of Adenosine A2A Receptors Ameliorates the Pathological Phenotype of Fibroblasts from Niemann-Pick Type C Patients. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 15388–15393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Nuccio, C.; Bernardo, A.; Ferrante, A.; Pepponi, R.; Martire, A.; Falchi, M.; Visentin, S.; Popoli, P.; Minghetti, L. Adenosine A2A Receptor Stimulation Restores Cell Functions and Differentiation in Niemann-Pick Type C-like Oligodendrocytes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colacurcio, D.J.; Nixon, R.A. Disorders of Lysosomal Acidification-The Emerging Role of v-ATPase in Aging and Neurodegenerative Disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiselyov, K.K.; Ahuja, M.; Rybalchenko, V.; Patel, S.; Muallem, S. The Intracellular Ca2+ Channels of Membrane Traffic. Channels 2012, 6, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buratta, S.; Tancini, B.; Sagini, K.; Delo, F.; Chiaradia, E.; Urbanelli, L.; Emiliani, C. Lysosomal Exocytosis, Exosome Release and Secretory Autophagy:The Autophagic- and Endo-Lysosomal Systems Go Extracellular. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, O.B.; Shin, H.R.; Lim, C.-Y.; Wu, E.Y.; Kukurugya, M.; Maher, C.F.; Perera, R.M.; Ordonez, M.P.; Zoncu, R. NPC1-MTORC1 Signaling Couples Cholesterol Sensing to Organelle Homeostasis and Is a Targetable Pathway in Niemann-Pick Type C. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 260–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, B.M.; Thelen, A.M.; Moldavski, O.; Feltes, M.; van der Welle, R.E.N.; Mydock-McGrane, L.; Jiang, X.; van Eijkeren, R.J.; Davis, O.B.; Louie, S.M.; et al. Lysosomal Cholesterol Activates MTORC1 via an SLC38A9–Niemann-Pick C1 Signaling Complex. Science 2017, 355, 1306–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bankston, A.N.; Forston, M.D.; Howard, R.M.; Andres, K.R.; Smith, A.E.; Ohri, S.S.; Bates, M.L.; Bunge, M.B.; Whittemore, S.R. Autophagy Is Essential for Oligodendrocyte Differentiation, Survival, and Proper Myelination. Glia 2019, 67, 1745–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun-Julien, F.; Bachmann, L.; Norrmén, C.; Trötzmüller, M.; Köfeler, H.; Rüegg, M.A.; Hall, M.N.; Suter, U. Balanced MTORC1 Activity in Oligodendrocytes Is Required for Accurate CNS Myelination. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 8432–8448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Figlia, G.; Gerber, D.; Suter, U. Myelination and MTOR. Glia 2018, 66, 693–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Platt, F.M.; Neises, G.R.; Karlsson, G.B.; Dwek, R.A.; Butters, T.D. N-Butyldeoxygalactonojirimycin Inhibits Glycolipid Biosynthesis but Does Not Affect N-Linked Oligosaccharide Processing. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 27108–27114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkegaard, T.; Gray, J.; Priestman, D.A.; Wallom, K.L.; Atkins, J.; Olsen, O.D.; Klein, A.; Drndarski, S.; Petersen, N.H.; Ingemann, L.; et al. Heat Shock Protein-Based Therapy as a Potential Candidate for Treating the Sphingolipidoses. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 355ra118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pipalia, N.H.; Cosner, C.C.; Huang, A.; Chatterjee, A.; Bourbon, P.; Farley, N.; Helquist, P.; Wiest, O.; Maxfield, F.R. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Treatment Dramatically Reduces Cholesterol Accumulation in Niemann-Pick Type C1 Mutant Human Fibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5620–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pineda, M.; Wraith, J.E.; Mengel, E.; Sedel, F.; Hwu, W.-L.; Rohrbach, M.; Bembi, B.; Walterfang, M.; Korenke, G.C.; Marquardt, T. Miglustat in Patients with Niemann-Pick Disease Type C (NP-C):A Multicenter Observational Retrospective Cohort Study. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2009, 98, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, F.M. Emptying the Stores:Lysosomal Diseases and Therapeutic Strategies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, M.C.; Vecchio, D.; Prady, H.; Abel, L.; Wraith, J.E. Miglustat for Treatment of Niemann-Pick C Disease:A Randomised Controlled Study. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmatoug, N.; Burlina, A.; Giraldo, P.; Hendriksz, C.J.; Kuter, D.J.; Mengel, E.; Pastores, G.M. Gastrointestinal Disturbances and Their Management in Miglustat-Treated Patients. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2011, 34, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, M.C.; Mengel, E.; Vanier, M.T.; Moneuse, P.; Rosenberg, D.; Pineda, M. Treatment Outcomes Following Continuous Miglustat Therapy in Patients with Niemann-Pick Disease Type C:A Final Report of the NPC Registry. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheel, M.; Abegg, M.; Lanyon, L.J.; Mattman, A.; Barton, J.J. Eye Movement and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Analysis of Treatment Effects in a Niemann—Pick Type C Patient. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2010, 99, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, M.; Walterfang, M.; Patterson, M.C. Miglustat in Niemann-Pick Disease Type C Patients:A Review. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, F.; Vossio, S.; Mercier, V.; Moreau, D.; Johnson, S.; Scott, C.C.; Montoya, J.P.; Moniatte, M.; Gruenberg, J. Cyclodextrin Triggers MCOLN1-Dependent Endo-Lysosome Secretion in Niemann-Pick Type C Cells. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Li, H.; Repa, J.J.; Turley, S.D.; Dietschy, J.M. Genetic Variations and Treatments That Affect the Lifespan of the NPC1 Mouse. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feltes, M.; Gale, S.E.; Moores, S.; Ory, D.S.; Schaffer, J.E. Monitoring the Itinerary of Lysosomal Cholesterol in Niemann-Pick Type C1-Deficient Cells after Cyclodextrin Treatment. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hastings, C.; Vieira, C.; Liu, B.; Bascon, C.; Gao, C.; Wang, R.Y.; Casey, A.; Hrynkow, S. Expanded Access with Intravenous Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin to Treat Children and Young Adults with Niemann-Pick Disease Type C1:A Case Report Analysis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Moya-Ortega, M.D.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Concheiro, A. Pharmacokinetics of Cyclodextrins and Drugs after Oral and Parenteral Administration of Drug/Cyclodextrin Complexes. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calias, P. 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrins and the Blood-Brain Barrier:Considerations for Niemann-Pick Disease Type C1. CPD 2018, 23, 6231–6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lope-Piedrafita, S.; Totenhagen, J.W.; Hicks, C.M.; Erickson, R.P.; Trouard, T.P. MRI Detects Therapeutic Effects in Weanling Niemann-Pick Type C Mice. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 2802–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, R.J.; Williams, I.M.; Gibson, A.L.; Davidson, C.D.; Incao, A.A.; Hubbard, B.T.; Porter, F.D.; Pavan, W.J.; Venditti, C.P. Systemic AAV9 Gene Therapy Improves the Lifespan of Mice with Niemann-Pick Disease, Type C1. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Gong, X.M.; Luo, J.; Li, B.L.; Song, B.L. AAV9-NPC1 Significantly Ameliorates Purkinje Cell Death and Behavioral Abnormalities in Mouse NPC Disease. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hughes, D.A.; Smith, L.; Morris, C.; Fletcher, A.; Colaco, M.; Huebecker, J.; Tordo, N.; Palomar, G.; Massaro, E.; Henckaerts, S.N.; et al. Rahim AAV9 Intracerebroventricular Gene Therapy Improves Lifespan, Locomotor Function and Pathology in a Mouse Model of Niemann-Pick Type C1 Disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 3079–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, E.; Smith, D.A.; Smith, C.; Morris, L.; Bremova-Ertl, T.; Cortina-Borja, M.; Fineran, P.; Morten, K.J.; Poulton, J.; Boland, B.; et al. Acetyl-Leucine Slows Disease Progression in Lysosomal Storage Disorders. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcaa148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Shin, K.; Choi, E.-K.; Choi, Y.; Jang, J.-Y.; Kim, J.; Jeong, H.-S.; Lee, W.; Lee, Y.-B.; Kim, S.U.; et al. Protective Effects of N -Acetyl-L-Cysteine in Human Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells and Restoration of Motor Function in Neonatal Rats with Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 764251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Griffin, L.D.; Gong, W.; Verot, L.; Mellon, S.H. Niemann—Pick Type C Disease Involves Disrupted Neurosteroidogenesis and Responds to Allopregnanolone. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellon, S.H.; Gong, W.; Schonemann, M.D. Endogenous and Synthetic Neurosteroids in Treatment of Niemann–Pick Type C Disease. Brain Res. Rev. 2008, 57, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holzmann, C.; Witt, M.; Rolfs, A.; Antipova, V.; Wree, A. Gender-Specific Effects of Two Treatment Strategies in a Mouse Model of Niemann-Pick Disease Type C1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I.; Lope-Piedrafita, S.; Bi, X.; Hicks, C.; Yao, Y.; Yu, C.; Chaitkin, E.; Howison, C.M.; Weberg, L.; Trouard, T.P.; et al. Allopregnanolone Treatment, Both as a Single Injection or Repetitively, Delays Demyelination and Enhances Survival of Niemann-Pick C Mice. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 82, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, C.D.; Ali, N.F.; Micsenyi, M.C.; Stephney, G.; Renault, S.; Dobrenis, K.; Ory, D.S.; Vanier, M.T.; Walkley, S.U. Chronic Cyclodextrin Treatment of Murine Niemann-Pick C Disease Ameliorates Neuronal Cholesterol and Glycosphingolipid Storage and Disease Progression. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomes, C.V.; Kaster, M.P.; Tomé, A.R.; Agostinho, P.M.; Cunha, R.A. Adenosine Receptors and Brain Diseases:Neuroprotection and Neurodegeneration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2011, 1808, 1380–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sachdeva, S.; Gupta, M. Adenosine and Its Receptors as Therapeutic Targets:An Overview. Saudi Pharm. J. 2013, 21, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klinger, M.; Freissmuth, M.; Nanoff, C. Adenosine Receptors:G Protein-Mediated Signalling and the Role of Accessory Proteins. Cell. Signal. 2002, 14, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, B.; Lebon, G. Human Adenosine A2A Receptor:Molecular Mechanism of Ligand Binding and Activation. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.-F.; Sonsalla, P.K.; Pedata, F.; Melani, A.; Domenici, M.R.; Popoli, P.; Geiger, J.; Lopes, L.V.; de Mendonça, A. Adenosine A2A Receptors and Brain Injury:Broad Spectrum of Neuroprotection, Multifaceted Actions and “Fine Tuning” Modulation. Prog. Neurobiol. 2007, 83, 310–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoli, P.; Pintor, A.; Domenici, M.R.; Frank, C.; Tebano, M.T.; Pèzzola, A.; Scarchilli, L.; Quarta, D.; Reggio, R.; Malchiodi-Albedi, F.; et al. Blockade of Striatal Adenosine A2A Receptor Reduces, through a Presynaptic Mechanism, Quinolinic Acid-Induced Excitotoxicity:Possible Relevance to Neuroprotective Interventions in Neurodegenerative Diseases of the Striatum. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 1967–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Popoli, P.; Blum, D.; Martire, A.; Ledent, C.; Ceruti, S.; Abbracchio, M. Functions, Dysfunctions and Possible Therapeutic Relevance of Adenosine A2A Receptors in Huntington’s Disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2007, 81, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popoli, P.; Blum, D.; Domenici, M.R.; Burnouf, S.; Chern, Y. A Critical Evaluation of Adenosine A2A Receptors as Potentially “Druggable” Targets in Huntington’s Disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 1500–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, J.; Jakova, E.; Cayabyab, F.S. Adenosine A1 and A2A Receptors in the Brain:Current Research and Their Role in Neurodegeneration. Molecules 2017, 22, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.-C.; Chang, C.-P.; Lin, C.-J.; Lai, H.-L.; Kao, Y.-H.; Cheng, S.-J.; Chen, H.-M.; Liao, Y.-P.; Faivre, E.; Buée, L.; et al. Adenosine Augmentation Evoked by an ENT1 Inhibitor Improves Memory Impairment and Neuronal Plasticity in the APP/PS1 Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 8936–8952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.-H.; Lin, M.-S.; Chen, C.-M.; Wu, Y.-R.; Chen, H.-M.; Lai, H.-L.; Chern, Y.; Lin, C.-J. Targeting ENT1 and Adenosine Tone for the Treatment of Huntington’s Disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, ddw402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherchi, F.; Pugliese, A.; Coppi, E. Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cell Maturation:Role of Adenosine Receptors. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 1686–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppi, E.; Cellai, L.; Maraula, G.; Pugliese, A.M.; Pedata, F. Adenosine A2A Receptors Inhibit Delayed Rectifier Potassium Currents and Cell Differentiation in Primary Purified Oligodendrocyte Cultures. Neuropharmacology 2013, 73, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontenas, L.; Welsh, T.G.; Piller, M.; Coughenour, P.; Gandhi, A.V.; Prober, D.A.; Kucenas, S. The Neuromodulator Adenosine Regulates Oligodendrocyte Migration at Motor Exit Point Transition Zones. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 115–128.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, S.; Xu, S.; Yan, Y.; Yu, H.; Ling, S.; Luo, J. Decreased Purinergic Inhibition of Synaptic Activity in a Mouse Model of Niemann-Pick Disease Type C. Hippocampus 2011, 21, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, A.; De Nuccio, C.; Pepponi, R.; Visentin, S.; Martire, A.; Bernardo, A.; Minghetti, L.; Popoli, P. Stimulation of Adenosine A2A Receptors Reduces Intracellular Cholesterol Accumulation and Rescues Mitochondrial Abnormalities in Human Neural Cell Models of Niemann-Pick C1. Neuropharmacology 2016, 103, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrante, A.; Pezzola, A.; Matteucci, A.; Di Biase, A.; Attorri, L.; Armida, M.; Martire, A.; Chern, Y.; Popoli, P. The Adenosine A2A Receptor Agonist T1–11 Ameliorates Neurovisceral Symptoms and Extends the Lifespan of a Mouse Model of Niemann-Pick Type C Disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 110, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtanik, K.M.; Liscum, L. The Transport of Low Density Lipoprotein-Derived Cholesterol to the Plasma Membrane Is Defective in NPC1 Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 14850–14856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGraw, C.; Yang, L.; Levental, I.; Lyman, E.; Robinson, A.S. Membrane Cholesterol Depletion Reduces Downstream Signaling Activity of the Adenosine A2A Receptor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martire, A.; Calamandrei, G.; Felici, F.; Scattoni, M.L.; Lastoria, G.; Domenici, M.R.; Tebano, M.T.; Popoli, P. Opposite Effects of the A2A Receptor Agonist CGS21680 in the Striatum of Huntington’s Disease versus Wild-Type Mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 417, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fog, C.K.; Kirkegaard, T. Animal Models for Niemann-Pick Type C:Implications for Drug Discovery & Development. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Drug | Main Mechanism of Action | Phase (or Clinical Use if Applicable) | Effect on Dysmyelination (Preclinical) | Effect on Dysmyelination (Clinical) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Miglustat | Glycosphingolipid synthesis inhibition | Approved by the EMA for clinical use in NPC Prescribed off-label in the US | no data available | Improvement of fractional anisotropy (FA) | [81,82] |
| Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβCD) | Cholesterol chelation and redistribution | phase III, ongoing | Increased myelination, rescued lipid droplet formation, restored homeostasis of microglia | Improvement in fine and gross motor functions, and swallowing | [56,85,88] |
| N-Acetyl-L-Leucine | Neuroinflammation Reduction | phase II, ongoing | Protective towards oligodendrocyte progenitor cells in models of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) | no data available | [93] |
| Lovastatin | Inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzime A (HMG-CoA) reductase | none | Reduced cholesterol accumulation and increased the maturation of NPC OLs | no data available | [49] |
| Allopregnanolone | Neurosteroid deficient in NPC mice | none | In NPC mice, allopregnanolone solubilized in HPβCD delayed clinical onset, extended lifespan, reduced ganglioside accumulation, normalized myelin content | no data available | [88,94,95,96,97] |
| CGS21680 | Adenosine A2A receptor agonist | none | Overcame the OP maturation arrest, restored the morphology of cells, reduced cholesterol accumulation, mitochondria abnormalities, and protected OP from the unbalanced autophagic flux | no data available | [64] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernardo, A.; De Nuccio, C.; Visentin, S.; Martire, A.; Minghetti, L.; Popoli, P.; Ferrante, A. Myelin Defects in Niemann–Pick Type C Disease: Mechanisms and Possible Therapeutic Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168858
Bernardo A, De Nuccio C, Visentin S, Martire A, Minghetti L, Popoli P, Ferrante A. Myelin Defects in Niemann–Pick Type C Disease: Mechanisms and Possible Therapeutic Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(16):8858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168858
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernardo, Antonietta, Chiara De Nuccio, Sergio Visentin, Alberto Martire, Luisa Minghetti, Patrizia Popoli, and Antonella Ferrante. 2021. "Myelin Defects in Niemann–Pick Type C Disease: Mechanisms and Possible Therapeutic Perspectives" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 16: 8858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168858
APA StyleBernardo, A., De Nuccio, C., Visentin, S., Martire, A., Minghetti, L., Popoli, P., & Ferrante, A. (2021). Myelin Defects in Niemann–Pick Type C Disease: Mechanisms and Possible Therapeutic Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(16), 8858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168858






