Protein Adsorption onto Modified Porous Silica by Single and Binary Human Serum Protein Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
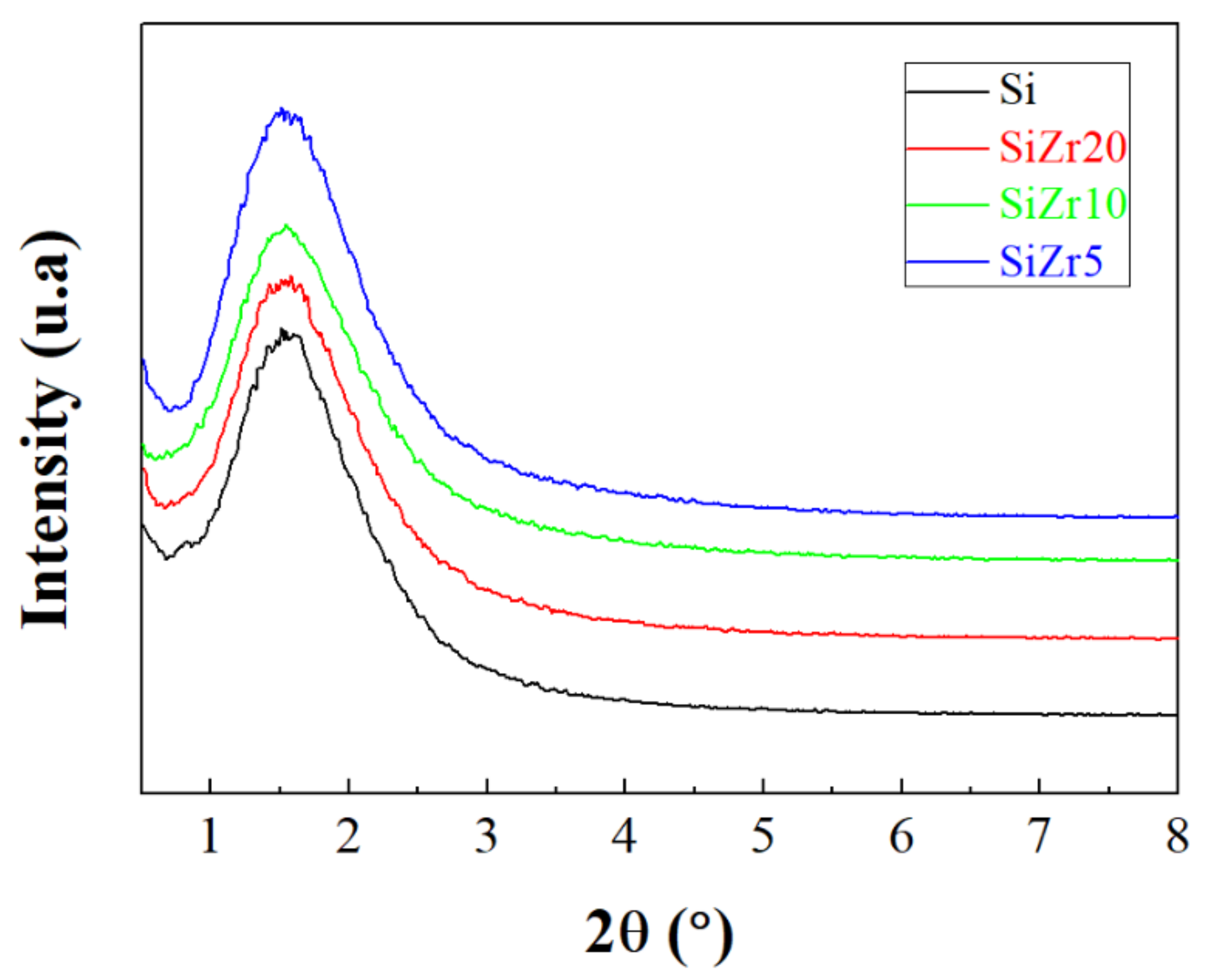
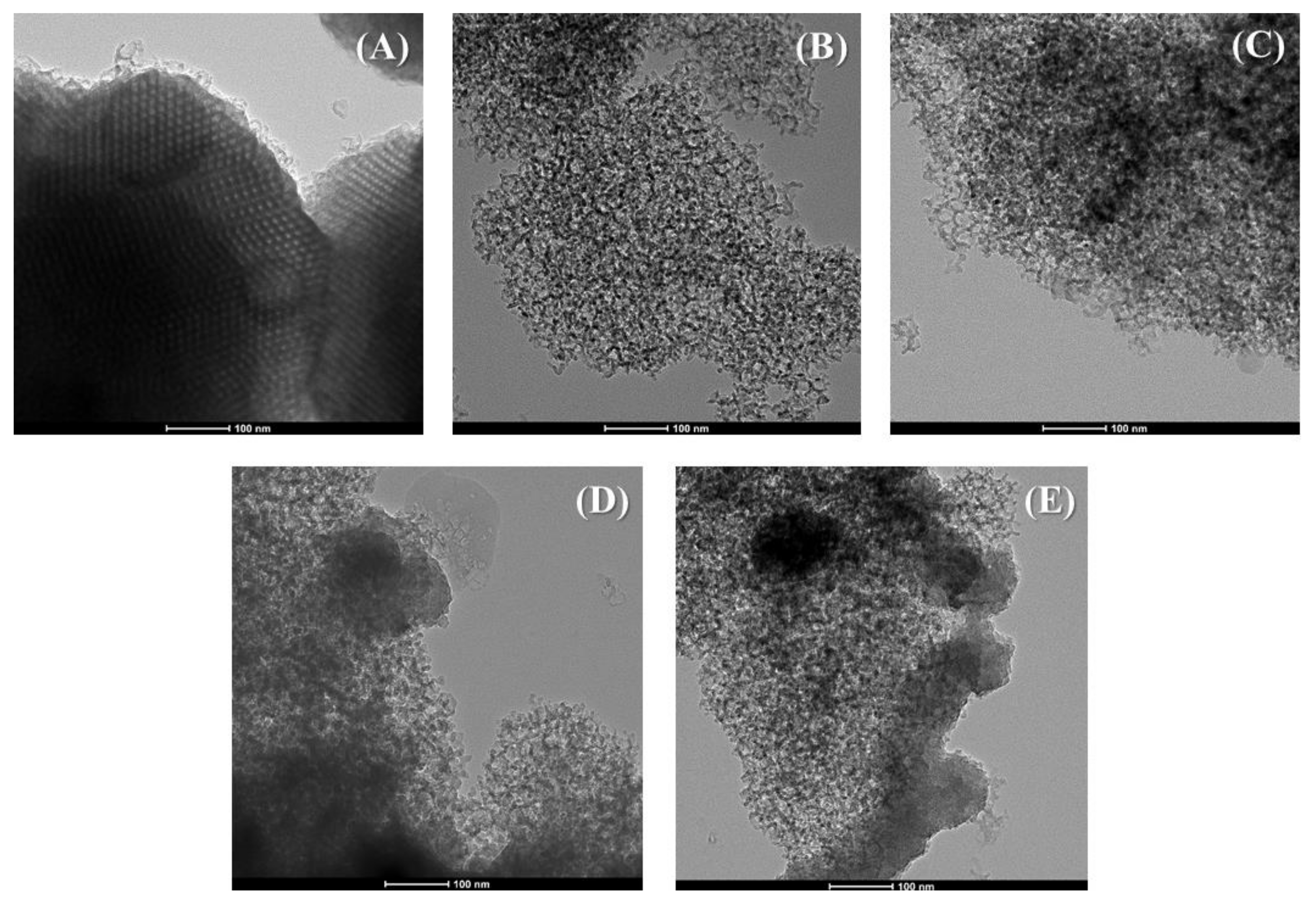
2. Characterization of the Materials
3. Batch Adsorption Tests
3.1. Effect of pH Buffers Solutions
3.2. Effect Contact Time
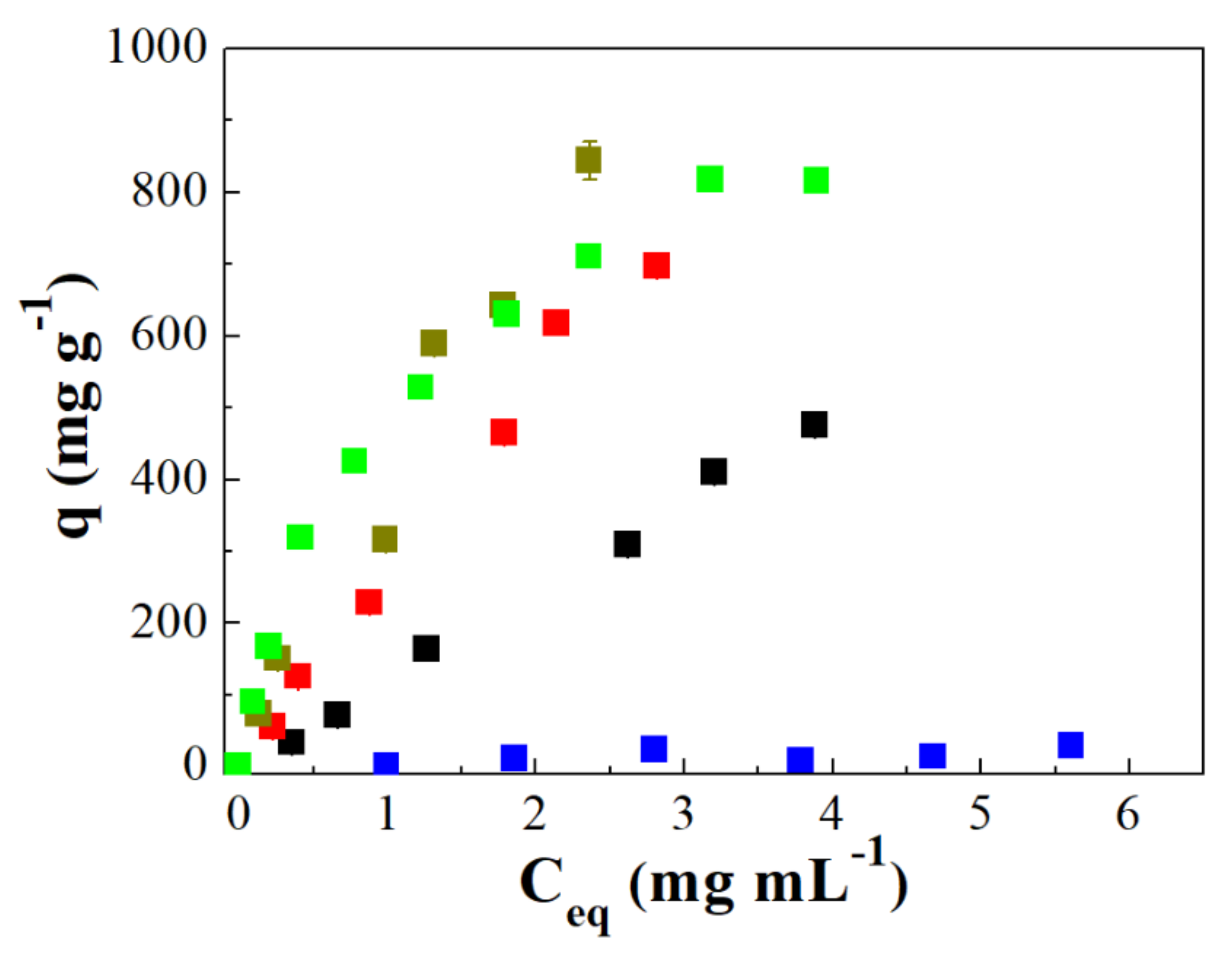
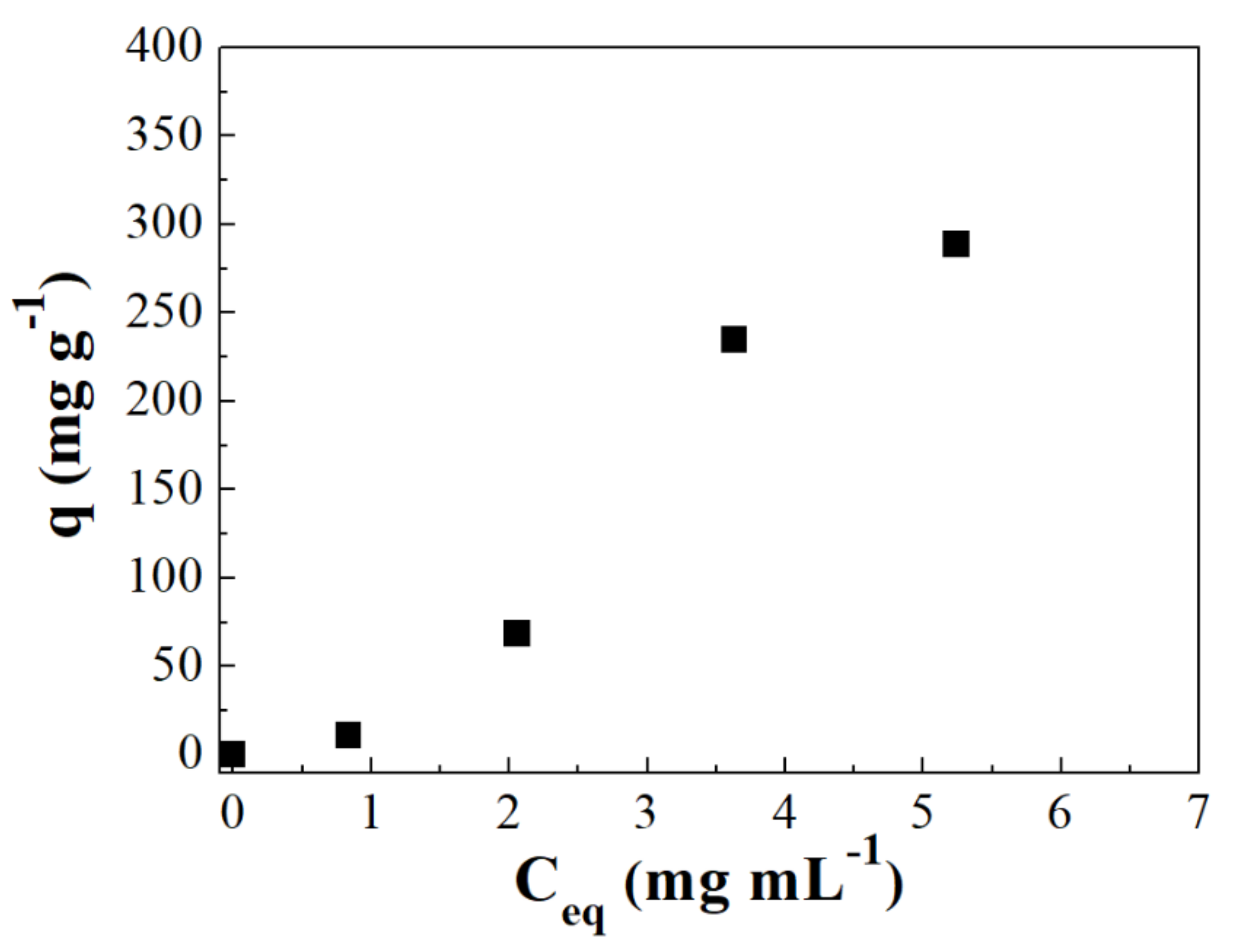
3.3. Adsorption Isotherms
3.4. Characterization of the Samples after the Adsorption Test
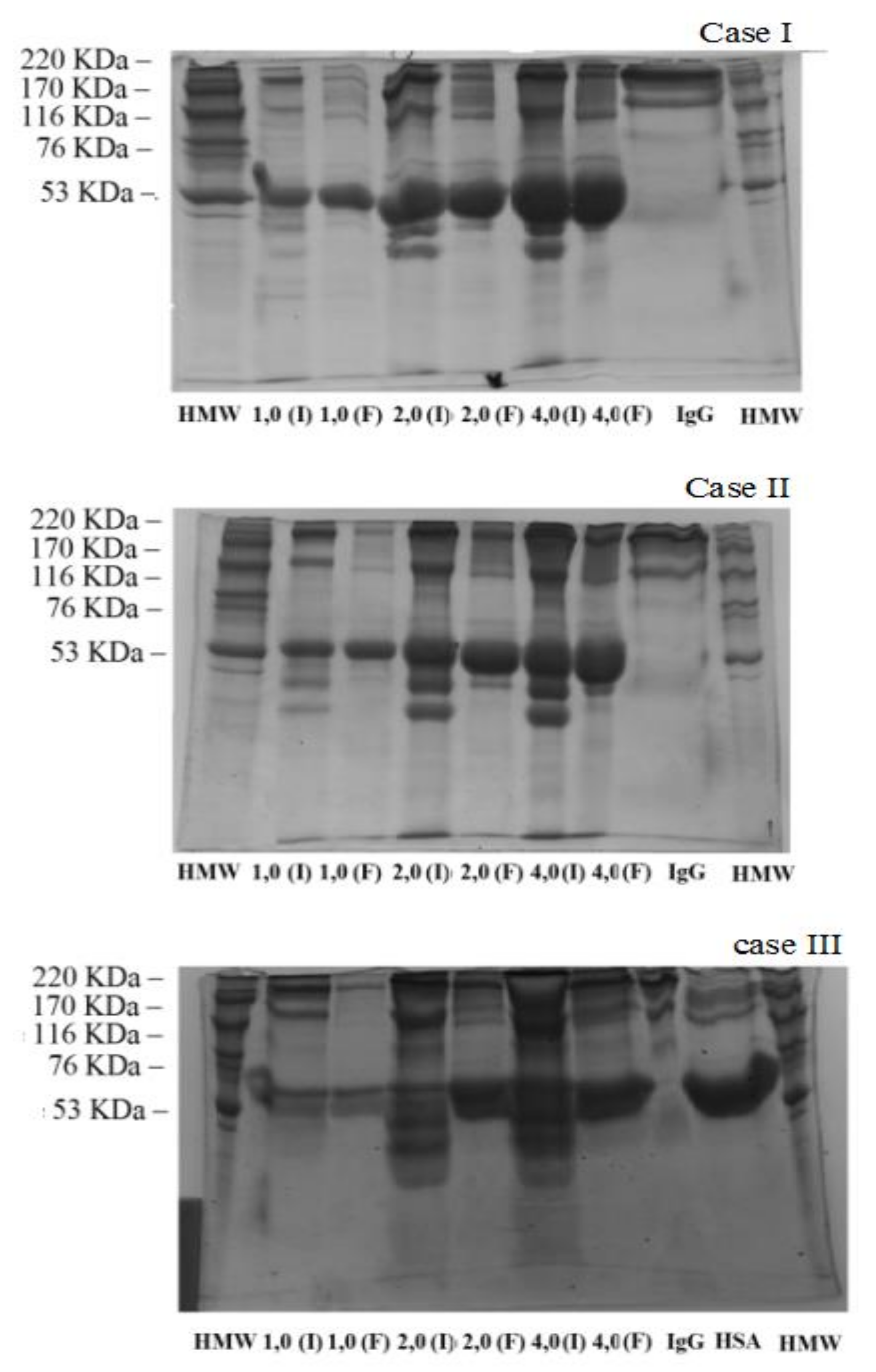
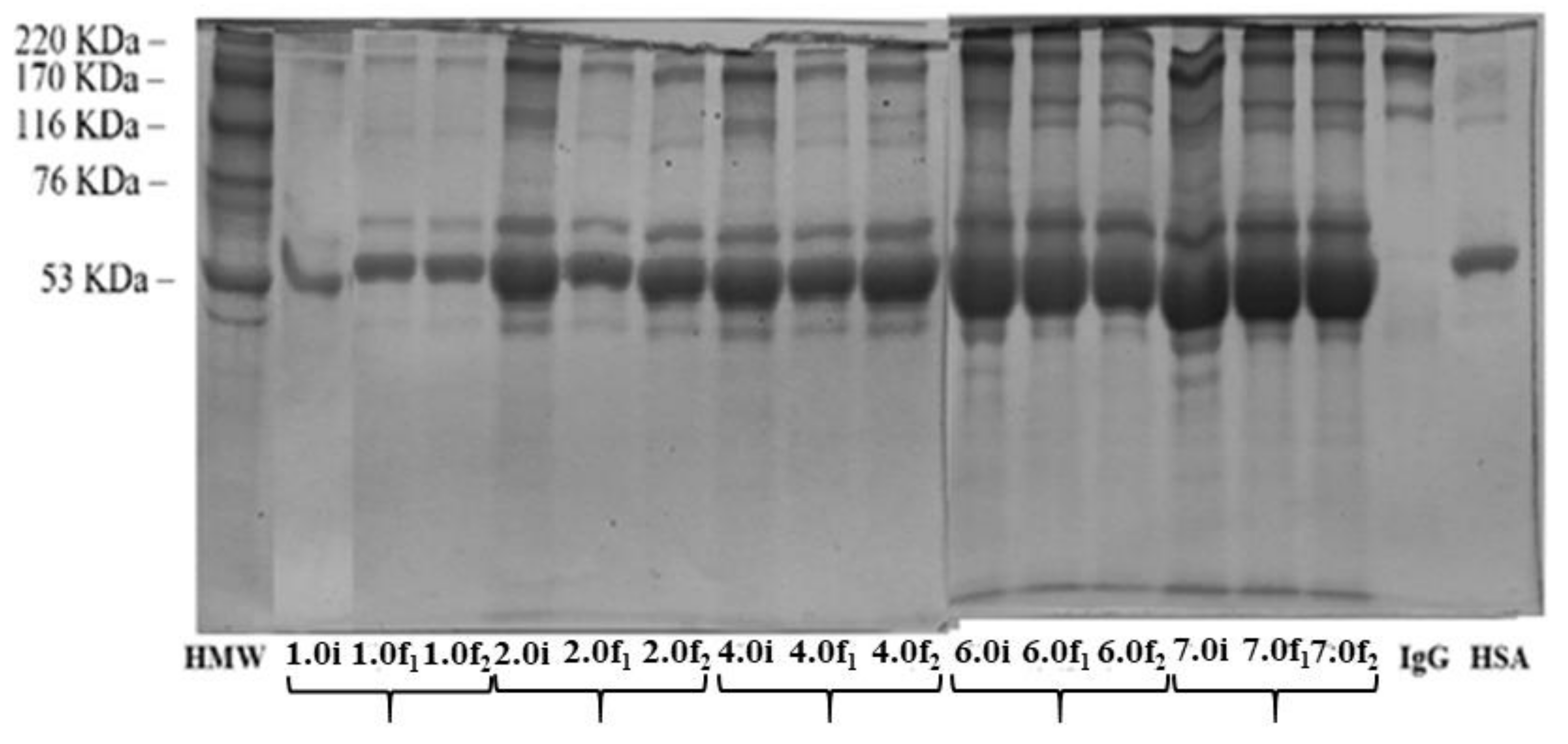
4. Protein Purification
4.1. Binary Solution Diluted in TRIS/HCl at pH 9.0
4.2. Human Serum Solution Diluted in TRIS/HCl at pH 9.0
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Reagents
5.2. Synthesis of the Porous Silicas
5.3. Characterization of the Adsorbents
5.4. Adsorption Batch Experiments
5.5. Batch Protein Purification with Binary Solution (IgG and HSA)
5.5.1. Binary Solution Preparation
5.5.2. Protein Quantification in Binary Solution
5.6. Batch Protein Purification with Human Serum Solution
5.6.1. Human Serum Samples Diluted in TRIS/HCl pH 9.0
5.6.2. Protein Quantification by Bradford Methods
5.7. Electrophoresis Analyses
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Z.; Hartmann, M. Progress in enzyme immobilization in ordered mesoporous materials and related applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3894–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Lin, T.S.; Mou, C.Y. Mesoporous materials for encapsulating enzymes. Nano Today 2009, 4, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, N.; Gustafsson, H.; Thörn, C.; Olsson, L.; Holmberg, K.; Åkerman, B. Enzymes immobilized in mesoporous silica: A physical-chemical perspective. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2014, 205, 339–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harraz, F.A. Porous silicon chemical sensors and biosensors: A review. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2014, 202, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanekar, S.; Jain, S. Porous silicon biosensor: Current status. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Gao, F.; Fu, Y.; Jin, W.; Yang, P.; Zhao, D. Biomolecule separation using large pore mesoporous SBA-15 as a substrate in high performance liquid chromatography. Chem. Commun. 2002, 7, 752–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, L.; Du, Y.; Guo, Z.; Ong, T.T.; Chen, Y.; Ng, S.C.; Yang, Y. Synthesis of large pore-diameter SBA-15 mesostructured spherical silica and its application in ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 7767–7773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasmin, T.; Müller, K. Synthesis and characterization of surface modified SBA-15 silica materials and their application in chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 6464–6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Kaskel, S.; Ikoma, T.; Hanagata, N. Magnetic SBA-15/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) composite: Preparation, characterization and temperature-responsive drug release property. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2009, 123, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriazo, D.; del Arco, M.; Martín, C.; Ramos, C.; Rives, V. Influence of the inorganic matrix nature on the sustained release of naproxen. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2010, 130, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.W.; Cao, A. Biosafety and bioapplication of nanomaterials by designing protein-nanoparticle interactions. Small 2013, 9, 1635–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellezza, F.; Alberani, A.; Posati, T.; Tarpani, L.; Latterani, L.; Cipiciani, A. Protein interactions with nanosized hydrotalcites of different composition. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 106, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belleza, F.; Cipiciani, A.; Latterini, L.; Posati, T.; Sassi, P. Structure and catalytic behavior of myoglobin adsorbed onto nanosized hydrotalcites. Langmuir 2009, 25, 10918–10924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralla, K.; Sohling, U.; Suck, K.; Sander, F.; Kasper, C.; Ruf, F.; Scheper, T. Adsorption and separation of proteins by a synthetic hydrotalcite. Colloids Surf. B 2011, 87, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, K.A.B.; Cecilia, J.A.; Santos, S.O.; Aguiar, J.E.; Vilarrasa-García, E.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Azevedo, D.C.S.; Silva, I.J. Adsorption behavior of bovine serum albumin on Zn–Al and Mg–Al layered double hydroxides. J. Sol. Gel. Sci. Technol. 2016, 80, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondim, D.R.; Cecilia, J.A.; Santos, S.O.; Rodrigues, T.N.B.; Aguiar, J.E.; Vilarrasa-García, E.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Azevedo, D.C.S.; Silva, I.J. Influence of buffer solutions in the adsorption of human serum proteins onto layered double hydroxide. Int. J. Biolog. Macromol. 2018, 106, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, S.K.; Sarkar, D. Study of BSA protein adsorption/release on hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 286, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandori, K.; Hamazaki, H.; Matsuzawa, M.; Togashi, S. Selective adsorption of acidic protein of bovine serum albumin onto sheet-like calcium hydroxyapatite particles produced by microreactor. Adv. Powder Technol. 2014, 25, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, H.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Salahi, E.; Tayebifard, A.; Keyanpour-Rad, M.; Rahimipour, M.R.; Ramakrishna, S. Protein adsorption on electrospun zinc doped hydroxyapatite containing nylon 6 membrane: Kinetics and isotherm. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2015, 443, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.; Hosseinkhani, H.; Ickowicz, D.; Hong, P.D.; Yu, D.S.; Domb, A.J. Polysaccharide gene transfections agents. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 4224–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedini, F.; Ebrahimi, M.; Roozbehani, A.H.; Domb, A.J.; Hosseinkhani, H. Overview on natural hydrophilic polysaccharide polymers in drug delivery. Polym. Adv. Techol. 2018, 29, 2564–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadiri, M.; Vasheghani-Farahani, E.; Atyabi, F.; Kobarfard, F.; Mohamadyar-Toupkanlou, F.; Hosseinkhani, H. Transferrin-conjugated magnetic dextran-spermine nanoparticles for targeted drug transport across blood-brain barrier. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2017, 105, 2851–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, W.W.Y.; Hosseinkhani, H.; Rahman, S.A.; Rozli, R.; Domb, A.J.; Abdullah, S. Safety profile of dextran-spermine gene delivery vector in mouse lungs. J. Nanosci. Nonotechol. 2014, 14, 3328–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedini, F.; Hosseinkhani, H.; Ismail, M.; Domb, A.J.; Omar, A.R.; Chong, P.P.; Hong, P.D.; Yu, D.S.; Farber, I.Y. Cationized dextran nanoparticle-encapsulated CXCR4-siRNA enhanced correlation between CXCR4 expression and serum alkaline phosphatase in a mouse model of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 4159–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.A.; Beppu, M.M.; Santana, C.C. Characterization of chemically modified chitosan microspheres as adsorbents using standard proteins (bovine serum albumin and lysozyme). Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2007, 24, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gondim, D.R.; Lima, L.P.; de Souza, M.C.M.; Bresolin, I.T.L.; Adriano, W.S.; Azevedo, D.C.S.; Silva, I.J. Dye ligand epoxide chitosan/alginate: A potential new stationary phase for human IgG purification. Ads. Sci. Technol. 2012, 30, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondim, D.R.; Dias, N.A.; Bresolin, I.T.L.; Baptistiolli, A.M.; Azevedo, D.C.S.; Silva, I.J. Human IgG adsorption using dye-ligand epoxy chitosan/alginate as adsorbent: Influence of buffer system. Adsorption 2014, 20, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Shao, Z.; Yao, J.; Huang, Y. Protein adsorption and separation with chitosan-based amphoteric membranes. Polymer 2009, 50, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, P.H.L.; Pereira, S.V.A.; Rabello, R.B.; Rodriguez-Castellón, E.; Beppu, M.M.; Chevallier, P.; Mantovani, D.; Vieira, R.S. Blood protein adsorption on sulfonated chitosan and κ-carrageenan films. Colloid Surf. B 2013, 111, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denizli, F.; Denizli, A.; Arica, M.Y. Affinity microspheres and their application to lysozyme adsorption: Cibacron Blue F3GA and Cu(II) with poly(HEMA-EGDMA). Polym. Int. 1999, 48, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayramoğlu, G.; Senel, A.U.; Arica, M.Y. Adsorption of IgG on spacer-arm and L-arginine ligand attached poly(GMA/MMA/EGDMA) beads. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 104, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayramoğlu, G.; Yalçin, E.; Arica, M.Y. Adsorption of serum albumin and γ-globulin from single and binary mixture and characterization of pHEMA-based affinity membrane surface by contact angle measurements. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 26, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayramoǧlu, G.; Şenel, A.Ü.; Yalçın, E.; Arica, M.Y. Human serum albumin adsorption on poly[(glycidyl methacrylate)-co-(methyl methacrylate)] beads modified with a spacer-arm-attached L-histidine ligand. Polym. Int. 2006, 55, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinkhain, H.; Abedini, F.; Ou, K.L.; Domb, A.J. Polymers in gene therapy technology. Polym. Adv. Techol. 2015, 26, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinkhain, H.; Domb, A.J. Biodegradable polymers in gene-silencing technology. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 2647–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, N.Y.; Campos, L.M.; Feng, Y.; Domb, A.J.; Hosseinkhain, H. Cyclopropenium nanoparticles and gene transfection in cells. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibolandi, M.; Abnous, K.; Sadeghi, F.; Hosseinkhani, H.; Ramezani, M.; Hadizadeh, F. Folate receptor-targeted multimodal polymersomes for delivery of quantum dots and doxorubicin to breast adenocarcinoma: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 500, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Hosseinkhani, H.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Roveimiab, Z.; Hueng, D.Y.; Ou, K.L.; Domb, A.J. Polymeric nanoparticles for therapy and imaging. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2014, 25, 1216–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinkhani, H.; Chen, Y.R.; He, W.; Hong, P.D.; Yu, D.S.; Dong, A.J. Engineering of magnetic DNA nanoparticles for tumor-targeted therapy. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, A.; Ji, L.; Smirniotis, P.; Pinto, N.G. Protein adsorption on the mesoporous molecular sieve silicate SBA-15: Effects of pH and pore size. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1069, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, A.; Yadav, S.; Smirniotis, P.G.; Pinto, N.G. Synthesis of ordered large pore SBA-15 spherical particles for adsorption of biomolecules. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1122, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.B.; Lee, J.W.; Shim, W.G.; Moon, H. Synthesis of functionalized SBA-15 with ordered large pore size and its adsorption properties of BSA. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2008, 110, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, S. Effect of pore-size of mesoporous SBA-15 on adsorption of bovine serum albumin and lysozyme protein. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 18, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salis, A.; Bhattacharyya, M.S.; Monduzzi, M. Specific ion effects on adsorption of lysozyme on functionalized SBA-15 mesoporous silica. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 7996–8001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, S.M.L.; Cecilia, J.A.; Vilarrasa-García, E.; Silva, I.J.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Azevedo, D.C.S. The effect of structure modifying agents in the SBA-15 for its application in the biomolecules adsorption. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2016, 232, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.M.L.; Cecilia, J.A.; Vilarrasa-García, E.; García-Sancho, C.; Silva, I.J.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Azevedo, D.C.S. Adsorption of biomolecules in porous silicas modified with zirconium. Effect of the textural properties and acidity. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2018, 260, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.S.; Vartuli, J.C.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Kresge, C.T.; Schmitt, K.D.; Chu, C.T.W.; Olson, D.H.; Sheppard, E.W.; McCullen, S.B.; et al. A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10834–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Feng, J.; Huo, Q.; Melosh, N.; Fredrickson, G.H.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Triblock copolymer syntheses of mesoporous silica with periodic 50 to 300 angstrom pores. Science 1998, 279, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meynen, V.; Cool, P.; Vansant, E.F. Verified syntheses of mesoporous materials. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2009, 125, 170–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yan, Y.; Yang, H.; Meng, Y.; Yu, C.; Tu, B.; Zhao, D. Understanding effect of wall structure on the hydrothermal stability of mesostructured silica SBA-15. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 8723–8732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, B.; Erdem, S.; Öksüzoğlu, R.M.; Çıtak, A. High-surface-area SBA-15–SO3H with enhanced catalytic activity by the addition of poly(ethylene glycol). J. Porous Mater. 2013, 20, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gea, H.; Bao, W. Synthesis and characteristics of SBA-15 with thick pore wall and high hydrothermal stability. Mater. Lett. 2015, 145, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilarrasa-García, E.; Cecilia, J.A.; Santos, S.M.L.; Cavalcante, C.L.; Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Azevedo, D.C.S.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. CO2 adsorption on APTES functionalized mesocellular foams obtained from mesoporous sílicas. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2014, 187, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilarrasa-Garcia, E.; Ortigosa Moya, E.M.; Cecilia, J.A.; Cavalcante, C.L.; Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Azevedo, D.C.S.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. CO2 adsorption on amine modified mesoporous silicas: Effect of the progressive disorder of the honeycomb arrangement. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2015, 209, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayari, A.; Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M.; Moudrakovski, I.L. New approaches to pore size engineering of mesoporous silicates. Adv. Mater. 1998, 10, 1376–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luechinger, M.; Pirngruber, G.D.; Lindlar, B.; Laggner, P.; Prins, R. The effect of the hydrophobicity of aromatic swelling agents on pore size and shape of mesoporous silicas. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2005, 79, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, J.; Ma, D.; Bao, X.; Klein-Hoffmann, A.; Weinberg, G.; Su, D.; Schlögl, R. Unusual mesoporous SBA-15 with parallel channels running along the short axis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 7440–7441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, T.; Lan, J.; Ya, W. Synthesis and characterization of sulfonic acid-functionalized SBA-15 for adsorption of biomolecules. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2011, 142, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinu, A.; Hartmann, M. Adsorption of cytochrome c on MCM-41 and SBA-15: Influence of pH. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2004, 154, 2987–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyahara, M.; Vinu, A.; Ariga, K. Adsorption myoglobin over mesoporous silica molecular sieves: Pore size effect and pore-filling model. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2007, 27, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Y.; Xian, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wu, F.; Ling, Y.; Jin, L. Encapsulation hemoglobin in ordered mesoporous silicas: Influence factors for immobilization and bioelectrochemistry. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tischer, W.; Kasche, V. Immobilized enzymes: Crystals or carriers? Trends Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogler, A. Protein adsorption in three dimensions. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1201–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.C. Non-native protein aggregation kinetics. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 98, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, H.; Magner, E.; Cooney, J.; Hodnett, B.K. Influence of pH and ionic strength on the adsorption, leaching and activity of myoglobin immobilized onto ordered mesoporous silicates. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2007, 49, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinu, A.; Murugesan, V.; Hartmann, M. Adsorption of lysozyme over mesoporous molecular sieves MCM-41 and SBA-15: influence of pH and aluminum incorporation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 7323–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinu, A.; Murugesan, V.; Tangermann, O.; Hartmann, M. Adsorption of cytochrome c on mesoporous molecular sieves: Influence of pH, pore diameter, and aluminum incorporation. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 3056–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivkovic, L.T.I.; Zivkovic, L.S.; Babic, B.M.; Kokunesoski, M.J.; Jokic, B.M.; Karadzic, I.M. Immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase by adsorption onto biosafe meso/macroporous silica and zirconia. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 93, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washmon-Kriel, L.; Jimenez, V.L.; Balkus, K.J., Jr. Cytochrome c immobilization into mesoporous molecular sieves. J. Molec. Catal. B Enzym. 2000, 10, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moerz, S.T.; Huber, P. Protein adsorption into mesopores: A combination of electrostatic interaction, counterion release, and van der Waals forces. Langmuir 2014, 30, 2729–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, T., Jr. Serum albumin. Adv. Protein Chem. 1985, 37, 161–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, D.C.; Ho, J.X. Structure of serum albumin. Adv. Protein Chem. 1994, 45, 153–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbkowska, M.; Adamczyk, Z.; Kujda, M. Mechanism of HSA adsorption on mica determined by streaming potential, AFM and XPS measurements. Colloid. Surf. B 2013, 101, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faser, W.; Chamberlain, J.C. Blood and Transport Proteins. In Medical Biochemistry; Mosby: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Indesta, T.; Laine, J.; Kleinschek, K.S.; Zemljič, L.F. Adsorption of human serum albumin (HSA) on modified PET films monitored by QCM-D, XPS and AFM. Colloid. Surf. A 2010, 360, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yue, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, X.; Liu, R.; Sun, Y.; Li, X. Study of interaction between human serum albumin and three phenanthridine derivatives: Fluorescence spectroscopy and computational approach. Spectrochim Acta A. 2007, 9, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, H.W.; Cavacini, L. Structure and function of immunoglobulins. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S41–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidarsson, G.; Dekkers, G.; Rispens, T. IgG subclasses and allotypes: From structure to effector functions. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; May, K. Disulfide bond structures of IgG molecules. mAbs 2012, 4, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irani, V.; Guy, A.J.; Andrew, D.; Beeson, J.G.; Ramsland, P.A.; Richards, J.S. Molecular properties of human IgG subclasses and their implications for designing therapeutic monoclonal antibodies against infectious diseases. Mol. Inmunol. 2015, 67, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dąbkowska, M.; Adamczyk, Z. Mechanism of immonoglobulin G adsorption on mica-AFM and electrokinetic studies. Colloid. Surf. B 2014, 118, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelliher, M.T.; Jacks, R.D.; Piraino, M.S.; Southern, C.A. The effect of sugar removal on the structure of the Fc region of an IgG antibody as observed with single molecule Förster Resonance Energy Transfer. Mol. Inmunol. 2014, 60, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofińska, K.; Adamczyk, Z.; Barbasz, J. Mechanism of immunoglobulin G adsorption on polystyrene microspheres. Colloid. Surf. B 2016, 137, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.H.; Liu, M.; Nolting, B.; Go, J.G.; Gervay-Hague, J.; Liu, G.Y. A nanoengineering approach for investigation and regulation of protein immobilization. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 2374–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuxiang, L.; Feng, Y.; Yongli, L.; Ruifeng, L.; Kechang, X. Direct synthesis of Zr-SBA-15 mesoporous molecular sieves with high zirconium loading: Characterization and catalytic performance after sulfated. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2007, 101, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zong, E.; Wan, H.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, S.; Zhu, D. Zirconia functionalized SBA-15 as effective adsorbent for phosphate removal. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2012, 155, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecilia, J.A.; Vilarrasa-García, E.; Morales-Ospino, R.; Bastos-Neto, M.; Azevedo, D.C.S.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. Insights into CO2 adsorption in amino-functionalized SBA-15 synthesized at different aging temperature. Adsorption 2020, 26, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarneau, A.; Cambon, H.; Di Renzo, F.; Fajula, F. True microporosity and surface area of mesoporous SBA-15 silicas as a function of synthesis temperature. Langmuir 2001, 17, 8328–8335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landers, J.; Gor, G.Y.; Neimark, A.V. Density functional theory methods for characterization of porous materials. Colloid. Surf. A 2013, 437, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia, M.D.; Balu, A.M.; Campelo, J.M.; Luque, R.; Marinas, J.M.; Romero, A.A. Evidences of the in situ generation of highly active Lewis acid species on Zr-SBA-15. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 371, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, J.F.; Stickle, W.F.; Sobol, P.E.; Bomben, K.D. Handbook of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; Perkin-Elmer Corporation: Waltham, MN, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Salas, P.; Wang, J.A.; Armendariz, H.; Angeles-Chavez, C.; Chen, L.F. Effect of the Si/Zr molar ratio on the synthesis of Zr-based mesoporous molecular sieves. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 114, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Regalbuto, J.R. The synthesis of highly dispersed noble and base metals on silica via strong electrostatic adsorption: II. Mesoporous silica SBA-15. J. Catal. 2008, 260, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steri, D.; Monduzzi, M.; Salis, A. Ionic strength affects lysozyme adsorption and release from SBA-15 mesoporous silica. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2013, 170, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakta, S.A.; Evans, E.; Benavidez, T.E.; García, C.D. Protein adsorption onto nanomaterials for the development of biosensors and analytical devices: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 872, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M. Ordered mesoporous materials for bioadsorption and biocatalysis. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 4577–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyahara, M.; Vinu, A.; Hossain, K.Z.; Nakanishi, T.; Ariga, K. Adsorption study of heme proteins on SBA-15 mesoporous silica with pore-filling models. Thin Solid Film. 2006, 499, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartvig, R.A.; van de Weert, M.; Østergaard, J.; Jorgensen, L.; Jensen, H. Protein adsorption at charged surfaces: The role of electrostatic interactions and interfacial charge regulation. Langmuir 2011, 27, 2634–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, A.; Ji, L.; Smirniotis, P.G.; Pinto, N.G. Adsorption of bovine serum albumin and lysozyme on siliceous MCM-41. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2005, 80, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroman, L.; Adams, A.L. Findings with the recording ellipsometer suggesting rapid exchange of specific plasma proteins at liquid/solid interfaces. Surf. Sci. 1969, 16, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobert, T.A. Mass action effects on competitive adsorption of fibrinogen from hemoglobin solutions and from plasma. Thromb. Haemost. 1984, 51, 174–181. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, V.; Schaaf, P.; Voegel, J.C. Mechanism of interfacial exchange phenomena for proteins adsorbed at solid-liquid interfaces. In Biopolymers at Interfaces, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dahman, Y.; Jayasuriya, K.E. Preliminary study of binary protein adsorption system and potential bioseparation under homogeneous field of shear in airlift biocontactor. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 710–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, J.; Ma, D.; Weinberg, G.; Su, D.S.; Xinhe, B. Engineered complex emulsion system: Toward modulating the pore length and morphological architecture of mesoporous silicas. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 25908–25915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ip, A.W.M.; Barford, J.P.; McKay, G. A comparative study on the kinetics and mechanisms of removal of reactive black 5 by adsorption onto activated carbons and bone char. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 157, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 : the error of each experiment.
: the error of each experiment.
 : the error of each experiment.
: the error of each experiment.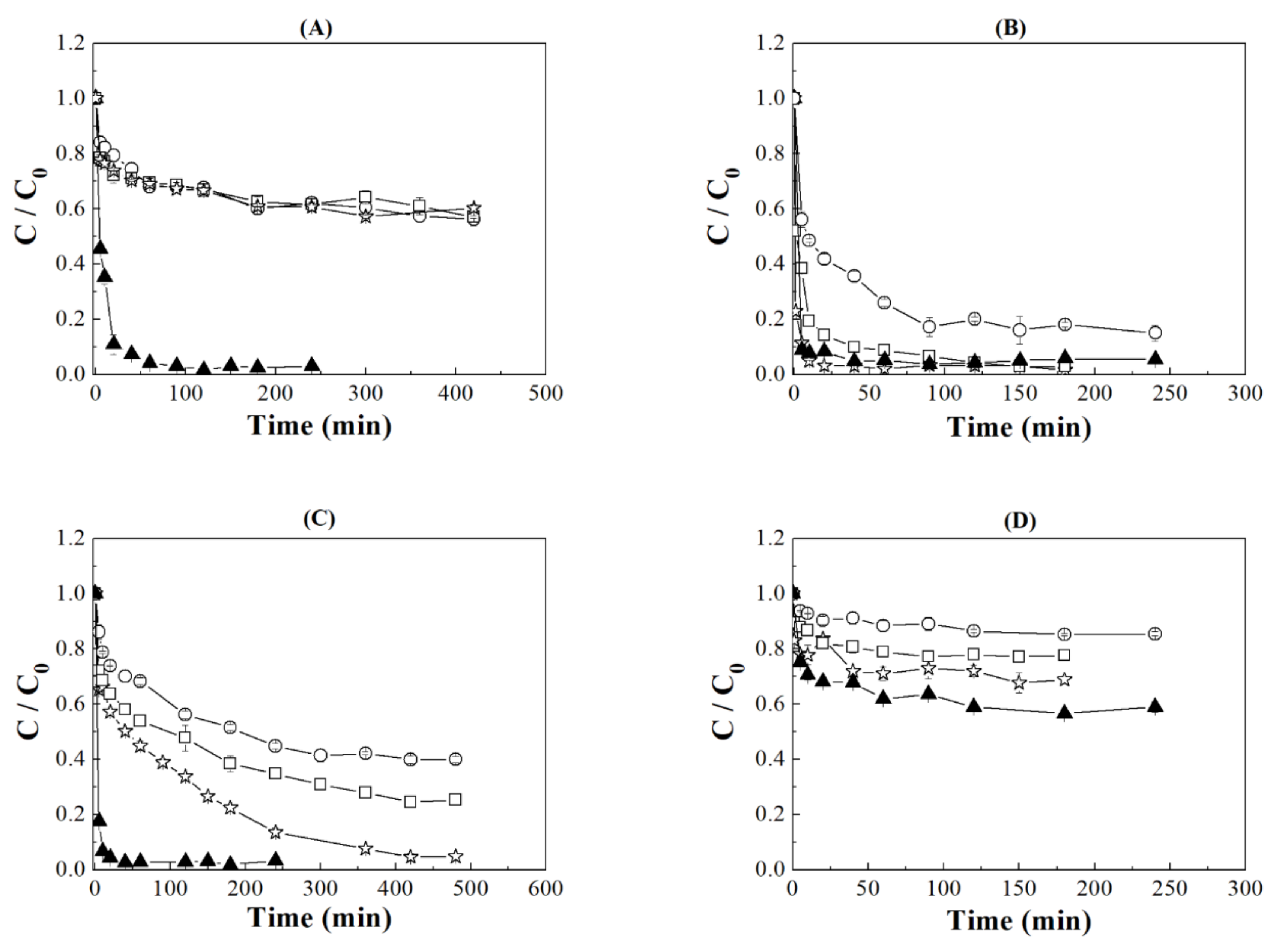
 : the error of each experiment.
: the error of each experiment.
 : the error of each experiment.
: the error of each experiment.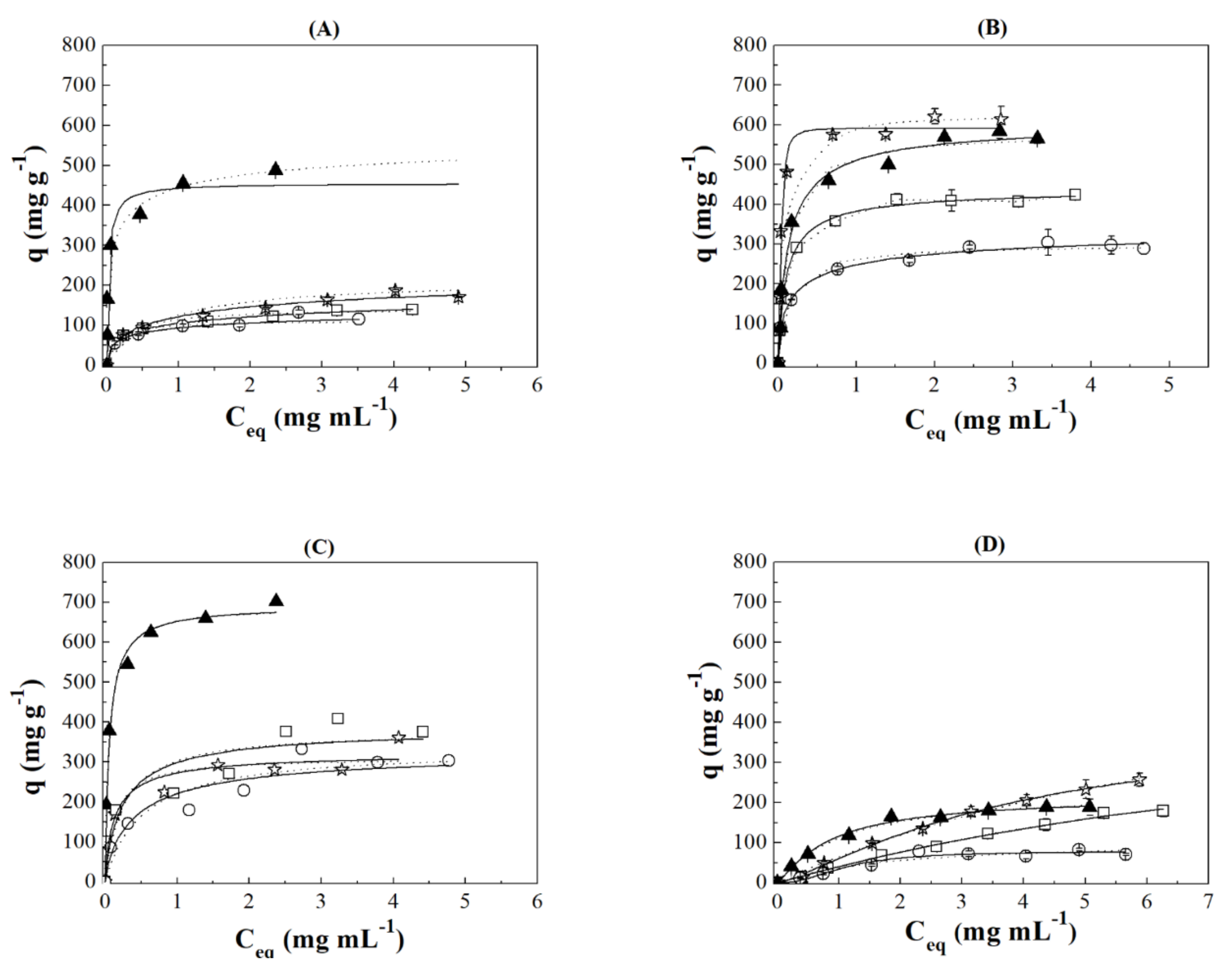
 ), case II (
), case II ( ), case III (
), case III ( ), 100% of IgG (
), 100% of IgG ( ) and 100% of HSA (
) and 100% of HSA ( ).
).
 ), case II (
), case II ( ), case III (
), case III ( ), 100% of IgG (
), 100% of IgG ( ) and 100% of HSA (
) and 100% of HSA ( ).
).
| Sample | SBET (m2 g−1) 1 | VP (cm3 g−1) 2 | DP (Å) 3 | Total Acid Sites (μmol g−1) 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | 337 | 2.54 | 30.1 | 13 |
| SiZr20 | 416 | 2.38 | 25.8 | 127 |
| SiZr10 | 432 | 1.80 | 17.4 | 342 |
| SiZr5 | 420 | 1.51 | 11.9 | 524 |
| Sample | Atomic Concentration (%) Binding Energy (eV) | Molar Ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C 1s | O 1s | Si 2p | Zr 3d | (Si+Zr)/O | Si/Zr | |
| Si | 4.87% 284.8 | 64.13% 532.8 | 31.00% 103.4 | - | 2.07 | ∞ |
| SiZr20 | 5.45% 284.8 | 60.93%/2.47% 533.2/531.2 | 30.16% 103.3 | 0.46% 182.7 | 2.07 | 65.56 |
| SiZr10 | 5.06% 284.8 | 59.71%/3.01% 533.2/531.2 | 31.63% 103.4 | 0.56% 182.8 | 1.95 | 56.48 |
| SiZr5 | 4.94% 284.8 | 57.82%/5.13% 533.2/531.2 | 30.29% 103.3 | 0.95% 182.8 | 2.04 | 31.88 |
| Sample | Atomic Concentration (%) Binding Energy (eV) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C 1s | O 1s | Si 2p | N 1s | |
| Si | 4.87% 284.8 | 64.13% 532.8 | 31.00% 103.4 | - |
| Si (HSA) | 15.21%/4.49% 284.8/287.8 | 50.18% 532.5 | 24.94% 103.3 | 5.18% 399.8 |
| Si (IgG) | 16.47%/4.59% 284.8/287.7 | 49.20% 532.6 | 24.75% 103.4 | 4.98% 399.7 |
| Sample | HSA | IgG | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | LF | L | LF | |
| qmax (mg g−1) | 50.42 ± 2.1 | - | 1.153.9 ± 70.2 | 936.02 ± 26.2 |
| kL (mL mg−1) | 0.032 ± 0.015 | - | 1.099 ± 0.15 | - |
| kLF (mL mg−1) | - | - | - | 1.53 ± 0.15 |
| R2 | 0.52 | - | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| qmax (mg g−1) | - | - | - | 1.23 ± 0.06 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gondim, D.R.; Cecilia, J.A.; Rodrigues, T.N.B.; Vilarrasa-García, E.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Azevedo, D.C.S.; Silva, I.J., Jr. Protein Adsorption onto Modified Porous Silica by Single and Binary Human Serum Protein Solutions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179164
Gondim DR, Cecilia JA, Rodrigues TNB, Vilarrasa-García E, Rodríguez-Castellón E, Azevedo DCS, Silva IJ Jr. Protein Adsorption onto Modified Porous Silica by Single and Binary Human Serum Protein Solutions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(17):9164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179164
Chicago/Turabian StyleGondim, Diego R., Juan A. Cecilia, Thaina N. B. Rodrigues, Enrique Vilarrasa-García, Enrique Rodríguez-Castellón, Diana C. S. Azevedo, and Ivanildo J. Silva, Jr. 2021. "Protein Adsorption onto Modified Porous Silica by Single and Binary Human Serum Protein Solutions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 17: 9164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179164
APA StyleGondim, D. R., Cecilia, J. A., Rodrigues, T. N. B., Vilarrasa-García, E., Rodríguez-Castellón, E., Azevedo, D. C. S., & Silva, I. J., Jr. (2021). Protein Adsorption onto Modified Porous Silica by Single and Binary Human Serum Protein Solutions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(17), 9164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179164










