Ptk7 Is Dynamically Localized at Neural Crest Cell–Cell Contact Sites and Functions in Contact Inhibition of Locomotion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
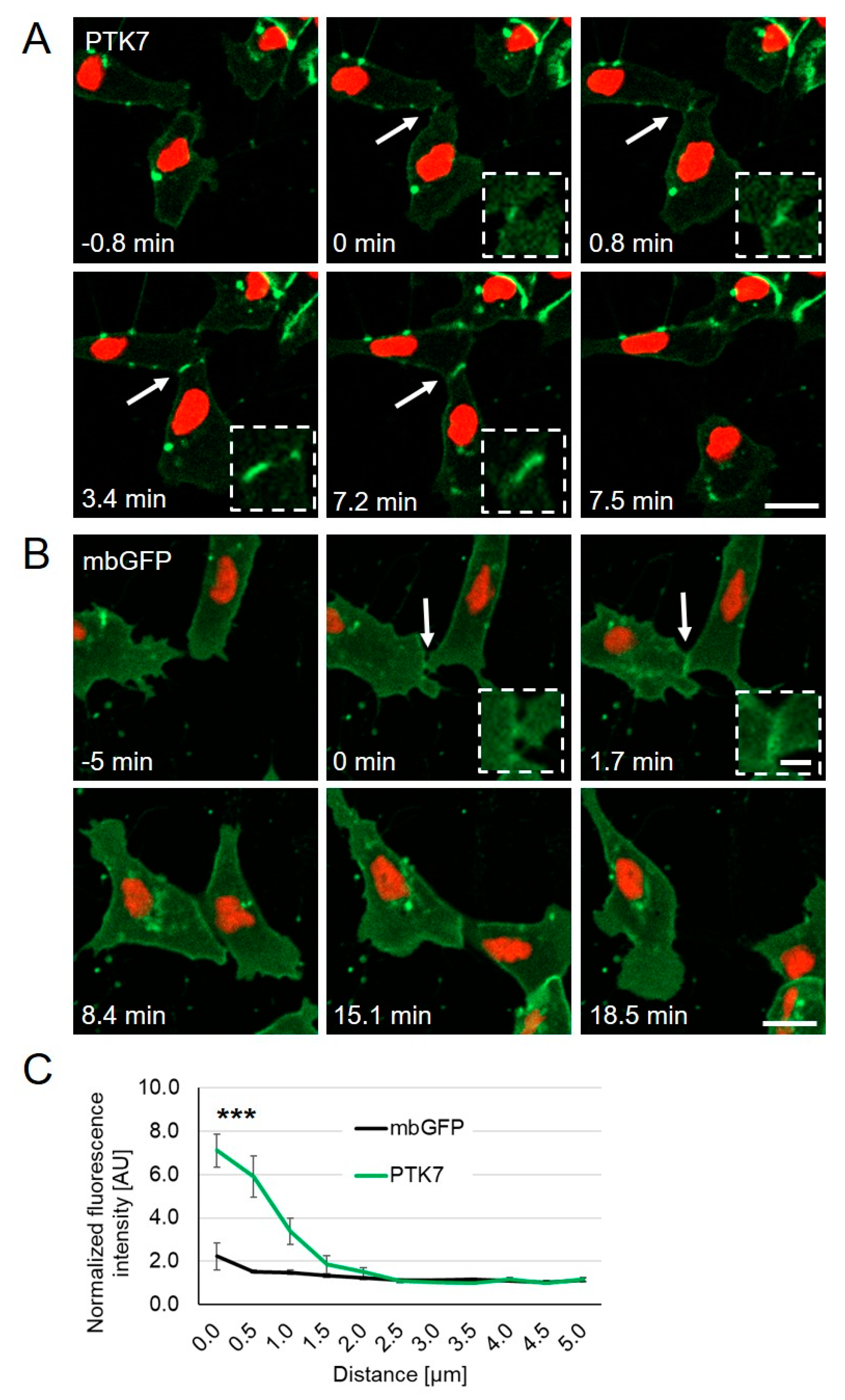
2.1. Ptk7 Is Dynamically Localized at NC Cell–Cell Contacts
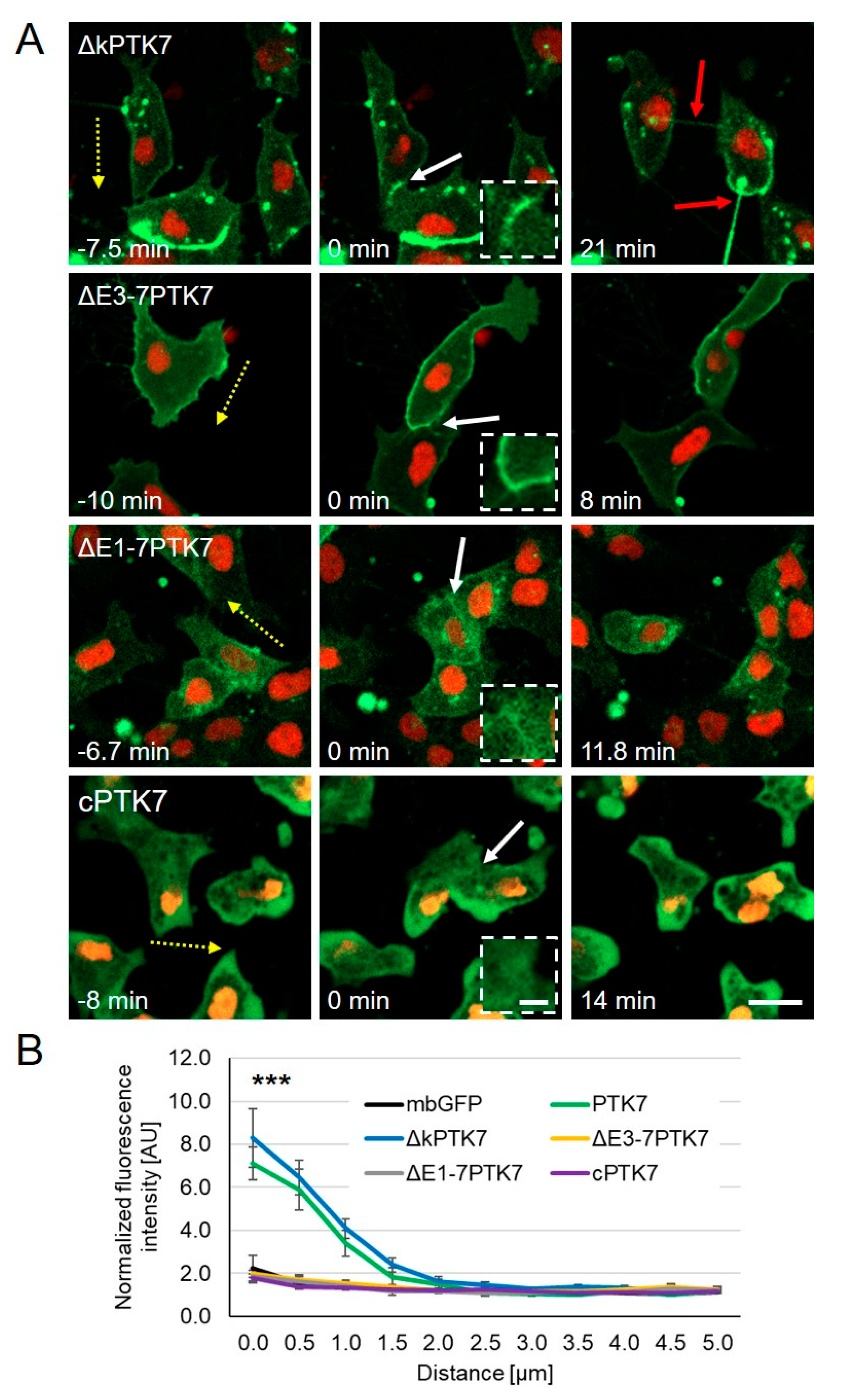
2.2. The Extracellular Domains of Ptk7 Are Essential for Its Accumulation at Cell–Cell Contacts
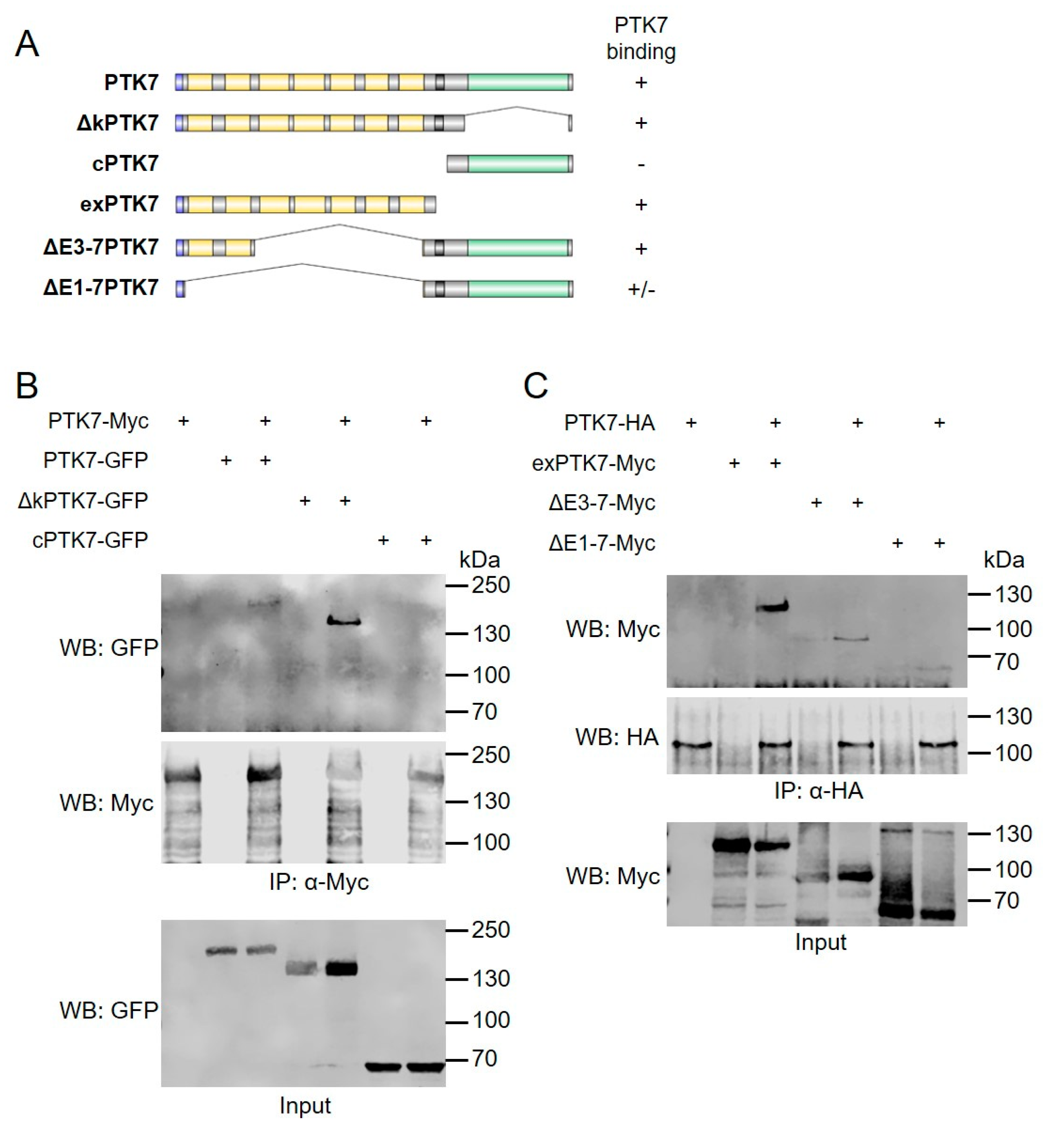
2.3. The Extracellular Domains of Ptk7 Mediate Homophilic Binding
2.4. Ptk7 Is Required for CIL of Migrating NC Cells
2.5. Ptk7 Protects Non-NC Tissue from Cell Invasion
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Constructs
4.2. Embryo Manipulation
4.3. NC Cell Explants and Analysis
4.4. Cell Transfection and Co-Immunoprecipitation
4.5. RNA Purification and RT-PCR
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szabo, A.; Mayor, R. Mechanisms of Neural Crest Migration. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2018, 52, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shellard, A.; Mayor, R. Integrating chemical and mechanical signals in neural crest cell migration. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2019, 57, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theveneau, E.; Mayor, R. Neural crest migration: Interplay between chemorepellents, chemoattractants, contact inhibition, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and collective cell migration. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2012, 1, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuriyama, S.; Mayor, R. Molecular analysis of neural crest migration. Philos Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 1349–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gallik, K.L.; Treffy, R.W.; Nacke, L.M.; Ahsan, K.; Rocha, M.; Green-Saxena, A.; Saxena, A. Neural crest and cancer: Divergent travelers on similar paths. Mech. Dev. 2017, 148, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, D.R.; Blasky, A.J.; Britt, S.G.; Artinger, K.B. Riding the crest of the wave: Parallels between the neural crest and cancer in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and migration. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2013, 5, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Theveneau, E.; Mayor, R. Neural crest delamination and migration: From epithelium-to-mesenchyme transition to collective cell migration. Dev. Biol. 2012, 366, 34–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davey, C.F.; Moens, C.B. Planar cell polarity in moving cells: Think globally, act locally. Development 2017, 144, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roycroft, A.; Mayor, R. Michael Abercrombie: Contact inhibition of locomotion and more. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2018, 62, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramer, B.; Mayor, R. Mechanisms and in vivo functions of contact inhibition of locomotion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Fontaine, C.; Matthews, H.K.; Kuriyama, S.; Moreno, M.; Dunn, G.A.; Parsons, M.; Stern, C.D.; Mayor, R. Contact inhibition of locomotion in vivo controls neural crest directional migration. Nature 2008, 456, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abercrombie, M. Contact inhibition and malignancy. Nature 1979, 281, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roycroft, A.; Mayor, R. Molecular basis of contact inhibition of locomotion. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- VanderVorst, K.; Dreyer, C.A.; Konopelski, S.E.; Lee, H.; Ho, H.H.; Carraway, K.L., 3rd. Wnt/PCP Signaling Contribution to Carcinoma Collective Cell Migration and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1719–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Menck, K.; Heinrichs, S.; Baden, C.; Bleckmann, A. The WNT/ROR Pathway in Cancer: From Signaling to Therapeutic Intervention. Cells 2021, 10, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Steele, R.E. Lemon encodes an unusual receptor protein-tyrosine kinase expressed during gametogenesis in Hydra. Dev. Biol. 2000, 224, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kroiher, M.; Miller, M.A.; Steele, R.E. Deceiving appearances: Signaling by “dead” and “fractured” receptor protein-tyrosine kinases. Bioessays 2001, 23, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossie, K.; Jallal, B.; Alves, F.; Sures, I.; Plowman, G.D.; Ullrich, A. Colon carcinoma kinase-4 defines a new subclass of the receptor tyrosine kinase family. Oncogene 1995, 11, 2179–2184. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, N.R.; Tolwinski, N.S. Ptk7 and Mcc, Unfancied Components in Non-Canonical Wnt Signaling and Cancer. Cancers 2016, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berger, H.; Wodarz, A.; Borchers, A. PTK7 Faces the Wnt in Development and Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peradziryi, H.; Tolwinski, N.S.; Borchers, A. The many roles of PTK7: A versatile regulator of cell-cell communication. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 524, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnitsar, I.; Borchers, A. PTK7 recruits dsh to regulate neural crest migration. Development 2008, 135, 4015–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Podleschny, M.; Grund, A.; Berger, H.; Rollwitz, E.; Borchers, A. A PTK7/Ror2 Co-Receptor Complex Affects Xenopus Neural Crest Migration. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Borchers, A.G.; Jolicoeur, C.; Rayburn, H.; Baker, J.C.; Tessier-Lavigne, M. PTK7/CCK-4 is a novel regulator of planar cell polarity in vertebrates. Nature 2004, 430, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peradziryi, H.; Kaplan, N.A.; Podleschny, M.; Liu, X.; Wehner, P.; Borchers, A.; Tolwinski, N.S. PTK7/Otk interacts with Wnts and inhibits canonical Wnt signalling. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3729–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wehner, P.; Shnitsar, I.; Urlaub, H.; Borchers, A. RACK1 is a novel interaction partner of PTK7 that is required for neural tube closure. Development 2011, 138, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berger, H.; Breuer, M.; Peradziryi, H.; Podleschny, M.; Jacob, R.; Borchers, A. PTK7 localization and protein stability is affected by canonical Wnt ligands. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 1890–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinez, S.; Scerbo, P.; Giordano, M.; Daulat, A.M.; Lhoumeau, A.C.; Thome, V.; Kodjabachian, L.; Borg, J.P. The PTK7 and ROR2 Protein Receptors Interact in the Vertebrate WNT/Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 30562–30572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Linnemannstons, K.; Ripp, C.; Honemann-Capito, M.; Brechtel-Curth, K.; Hedderich, M.; Wodarz, A. The PTK7-related transmembrane proteins off-track and off-track 2 are co-receptors for Drosophila Wnt2 required for male fertility. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, S.F.; Mayor, R.; Kashef, J. Cadherin-11 mediates contact inhibition of locomotion during Xenopus neural crest cell migration. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hudson, C.; Clements, D.; Friday, R.V.; Stott, D.; Woodland, H.R. Xsox17alpha and -beta mediate endoderm formation in Xenopus. Cell 1997, 91, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Souza, A.; Lee, M.; Taverner, N.; Mason, J.; Carruthers, S.; Smith, J.C.; Amaya, E.; Papalopulu, N.; Zorn, A.M. Molecular components of the endoderm specification pathway in Xenopus tropicalis. Dev. Dyn. 2003, 226, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpa, E.; Szabo, A.; Bibonne, A.; Theveneau, E.; Parsons, M.; Mayor, R. Cadherin Switch during EMT in Neural Crest Cells Leads to Contact Inhibition of Locomotion via Repolarization of Forces. Dev. Cell 2015, 34, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Theveneau, E.; Marchant, L.; Kuriyama, S.; Gull, M.; Moepps, B.; Parsons, M.; Mayor, R. Collective chemotaxis requires contact-dependent cell polarity. Dev. Cell 2010, 19, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puppo, F.; Thome, V.; Lhoumeau, A.C.; Cibois, M.; Gangar, A.; Lembo, F.; Belotti, E.; Marchetto, S.; Lecine, P.; Prebet, T.; et al. Protein tyrosine kinase 7 has a conserved role in Wnt/beta-catenin canonical signalling. EMBO Rep. 2011, 12, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bin-Nun, N.; Lichtig, H.; Malyarova, A.; Levy, M.; Elias, S.; Frank, D. PTK7 modulates Wnt signaling activity via LRP6. Development 2014, 141, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kratzer, M.C.; Becker, S.F.S.; Grund, A.; Merks, A.; Harnos, J.; Bryja, V.; Giehl, K.; Kashef, J.; Borchers, A. The Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor Trio is required for neural crest cell migration and interacts with Dishevelled. Development 2020, 147, dev186338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashef, J.; Kohler, A.; Kuriyama, S.; Alfandari, D.; Mayor, R.; Wedlich, D. Cadherin-11 regulates protrusive activity in Xenopus cranial neural crest cells upstream of Trio and the small GTPases. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, R.; Theveneau, E.; Pozzi, S.; Alexandre, P.; Richardson, J.; Merks, A.; Parsons, M.; Kashef, J.; Linker, C.; Mayor, R. Par3 controls neural crest migration by promoting microtubule catastrophe during contact inhibition of locomotion. Development 2013, 140, 4763–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lichtig, H.; Cohen, Y.; Bin-Nun, N.; Golubkov, V.; Frank, D. PTK7 proteolytic fragment proteins function during early Xenopus development. Dev. Biol 2019, 453, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubkov, V.S.; Strongin, A.Y. Insights into ectodomain shedding and processing of protein-tyrosine pseudokinase 7 (PTK7). J. Biol Chem 2012, 287, 42009–42018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golubkov, V.S.; Strongin, A.Y. Downstream signaling and genome-wide regulatory effects of PTK7 pseudokinase and its proteolytic fragments in cancer cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2014, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, W.S.; Gim, J.; Won, S.; Lee, S.T. Biphasic regulation of tumorigenesis by PTK7 expression level in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Kwon, J.; Lee, H.W.; Kang, M.C.; Yoon, H.J.; Lee, S.T.; Park, J.H. Protein tyrosine kinase 7 plays a tumor suppressor role by inhibiting ERK and AKT phosphorylation in lung cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 2708–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, Q.; Tao, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, J. Loss of expression of protein tyrosine kinase 7 in invasive ductal breast cancers. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, F.; Tang, J.; Kong, F.L.; Zou, H.W.; Ni, B.L.; Yu, J.C. Identification of PTK7 as a promising therapeutic target for thyroid cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 6809–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karvonen, H.; Perttila, R.; Niininen, W.; Barker, H.; Ungureanu, D. Targeting Wnt signaling pseudokinases in hematological cancers. Eur. J. Haematol. 2018, 101, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damelin, M.; Bankovich, A.; Bernstein, J.; Lucas, J.; Chen, L.; Williams, S.; Park, A.; Aguilar, J.; Ernstoff, E.; Charati, M.; et al. A PTK7-targeted antibody-drug conjugate reduces tumor-initiating cells and induces sustained tumor regressions. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astin, J.W.; Batson, J.; Kadir, S.; Charlet, J.; Persad, R.A.; Gillatt, D.; Oxley, J.D.; Nobes, C.D. Competition amongst Eph receptors regulates contact inhibition of locomotion and invasiveness in prostate cancer cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 1194–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batson, J.; Maccarthy-Morrogh, L.; Archer, A.; Tanton, H.; Nobes, C.D. EphA receptors regulate prostate cancer cell dissemination through Vav2-RhoA mediated cell-cell repulsion. Biol. Open 2014, 3, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moriyoshi, K.; Richards, L.J.; Akazawa, C.; O’Leary, D.D.; Nakanishi, S. Labeling neural cells using adenoviral gene transfer of membrane-targeted GFP. Neuron 1996, 16, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Megason, S.G.; Fraser, S.E. Digitizing life at the level of the cell: High-performance laser-scanning microscopy and image analysis for in toto imaging of development. Mech. Dev. 2003, 120, 1407–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwkoop, P.D.; Faber, J. Hubrecht Laboratory Utrecht. Normal Table of Xenopus laevis (Daudin): A Systematical and Chronological Survey of the Development from the Fertilized Egg till the End of Metamorphosis; North-Holland Pub. Co.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1956; p. 243. [Google Scholar]
- Borchers, A.; Epperlein, H.H.; Wedlich, D. An assay system to study migratory behavior of cranial neural crest cells in Xenopus. Dev. Genes Evol. 2000, 210, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maj, E.; Kunneke, L.; Loresch, E.; Grund, A.; Melchert, J.; Pieler, T.; Aspelmeier, T.; Borchers, A. Controlled levels of canonical Wnt signaling are required for neural crest migration. Dev. Biol. 2016, 417, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradl, D.; Kuhl, M.; Wedlich, D. The Wnt/Wg signal transducer beta-catenin controls fibronectin expression. Mol. Cell Biol. 1999, 19, 5576–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grund, A.; Till, K.; Giehl, K.; Borchers, A. Ptk7 Is Dynamically Localized at Neural Crest Cell–Cell Contact Sites and Functions in Contact Inhibition of Locomotion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179324
Grund A, Till K, Giehl K, Borchers A. Ptk7 Is Dynamically Localized at Neural Crest Cell–Cell Contact Sites and Functions in Contact Inhibition of Locomotion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(17):9324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179324
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrund, Anita, Katharina Till, Klaudia Giehl, and Annette Borchers. 2021. "Ptk7 Is Dynamically Localized at Neural Crest Cell–Cell Contact Sites and Functions in Contact Inhibition of Locomotion" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 17: 9324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179324
APA StyleGrund, A., Till, K., Giehl, K., & Borchers, A. (2021). Ptk7 Is Dynamically Localized at Neural Crest Cell–Cell Contact Sites and Functions in Contact Inhibition of Locomotion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(17), 9324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179324





