The Impact of Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites in Autism Spectrum Disorders
Abstract
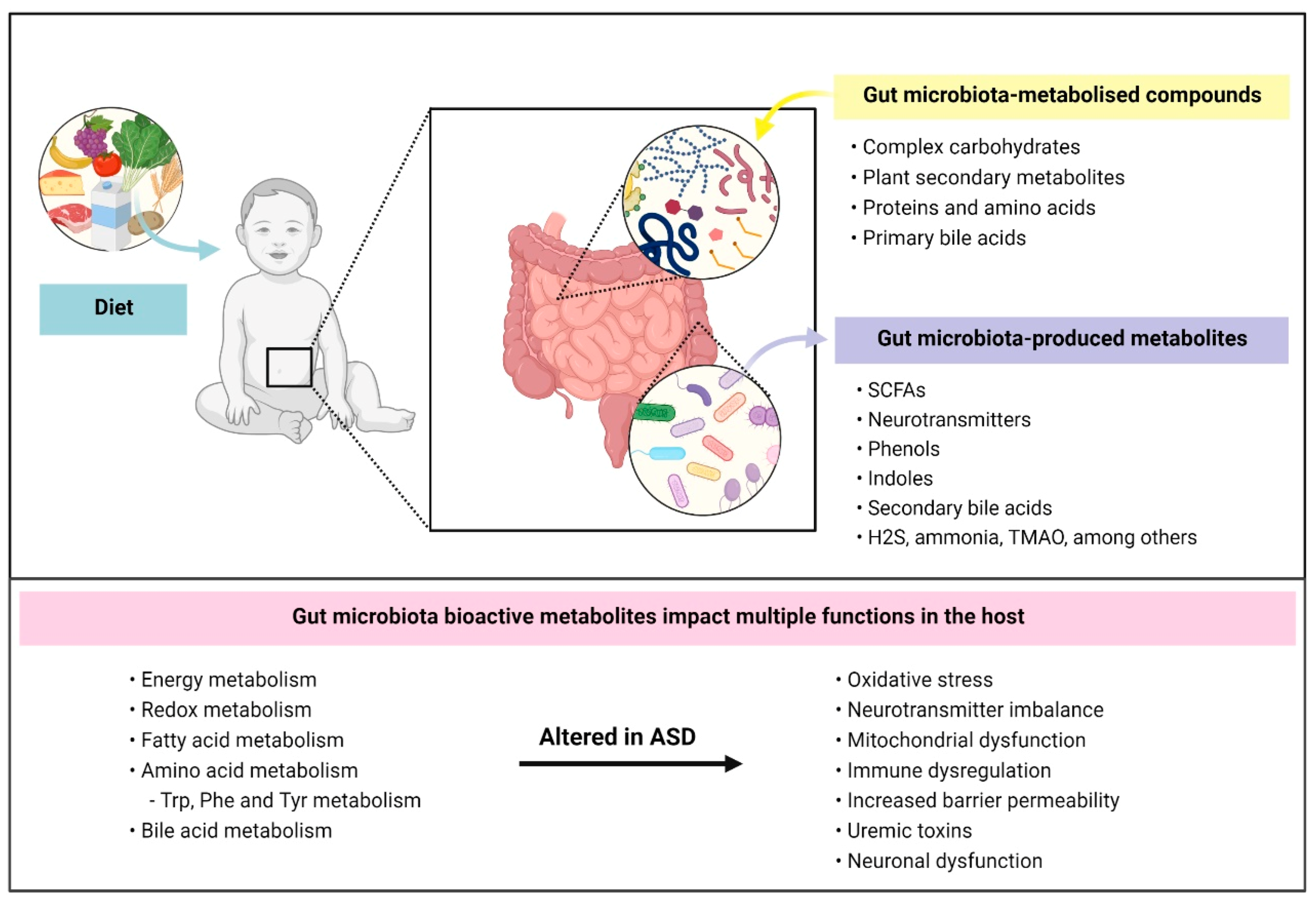
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Interplay between Microbiota, Gut and Brain
4. ASD-Associated Differences in Faecal Bacterial Composition
| ASD | ||
|---|---|---|
| Increased | Decreased | |
| α-diversity | [47,48,49] | [40,41,42,43,44,45,46] |
| Bacteroidetes/Firmicutes | [53] | [43,51,52] |
| Firmicutes | [54,55,58] | [44,47,48] |
| Blautia | - | [44,49,59] |
| Clostridium | [42,47,48,56,58,59,60] | [47] |
| Coprococcus | - | [40,44,48,49] |
| Dorea | [45,48,52] | [59] |
| Enterococcus | [45] | [17,55] |
| Faecalibacterium | [49] | [41,45,48] |
| Lactobacillus | [17,51,52,55] | - |
| Roseburia | [49,60] | - |
| Ruminococcus | [49] | [43,47,48,60] |
| Streptococcus | - | [47,49,53] |
| Bacteroidetes | [44,47,49,53,54] | [52,58] |
| Bacteroides | [44,47,48,49] | [42,43,46] |
| Prevotella | [54,60] | [40,41,43,45,48,55] |
| Proteobacteria | [47,49] | [54] |
| Desulfovibrio | [45,47] | [43,44,55] |
| Escherichia | [43] | [48,53] |
| Klebsiella | [42] | [17] |
| Parasutterella | [48] | [58] |
| Shigella | [43] | [48] |
| Sutterella | - | [43,59] |
| Actinobacteria | - | [47,49,54] |
| Bifidobacterium | [43,55] | [17,44,47,48,49,57] |
| Verrucomicrobia | - | [54] |
| Akkermansia | [40,44,48,54] | [57] |
5. ASD-Associated Differences in Gut Microbial Metabolites
| Study Group | Metabolic Assessment | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | Country | Sample Size | Male:Female | Mean Age | Associated Symptoms | Sample Type | Method | Results | Molecular Pathways |
| [64] | USA | 20 ASD patients 33 control individuals | Unspecified | Unspecified | - | Plasma | HPLC | ASD patients vs. Controls ↓ totalGSH, totalGSH/GSSG, SAM/SAH | Oxidative stress and methylation dysfunction |
| [65] | USA | 262 ASD patients 60 control individuals | 211:51 30:30 | 2–13 yo 2–13 yo | - | Urine | GC+MS | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ HPHPA | Altered gut bacterial metabolism (AAA) |
| [66] | Australia | 39 ASD patients 28 neurotypical siblings 34 control individuals | 35:4 14:14 17:17 | 3–9 yo | - | Urine | MRS | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ Taurine, succinate, acetate, dimethyl amine, N-methyl nicotinic acid and N-methyl nicotinamide ↓ Glutamate, hippurate, phenylacetylglutamine | Oxidative stress, altered AA, nicotinic and gut bacterial metabolism (AAA) |
| [17] | USA | 58 ASD patients 39 control individuals | 50:8 18:21 | 6.91 ± 3.4 yo | Gastrointestinal problems | Faeces | GC+FID | ASD patients vs. Controls ↓ Acetate, valerate, propionate and butyrate | Altered gut bacterial metabolism (SCFAs) |
| [67] | Italy | 59 ASD individuals 59 control individuals | 44:15 44:15 | 8.29 ± 0.56 yo 8.46 ± 0.59 yo | - | Urine | HPLC+UV | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ p-cresol | Altered gut bacterial metabolism (AAA) |
| [68] | USA | 48 ASD patients 53 control individuals | 36:12 34:19 | 10.7 ± 4.0 yo 10.2 ± 3.8 yo | Gastrointestinal problems | Urine | LC/GC+MS | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl) propionate and taurocholonate sulfate ↓ free AA and carnosine | Oxidative stress, altered gut bacterial metabolism (AA) |
| [69] | USA | 27 ASD patients 27 control individuals | Unspecified | Unspecified | Oxidative stress | Cerebellum Temporal cortex | HPLC+MS | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ 3-nitrotyrosine, 3-chlorotyrosine and 8-oxo-deoxyguanosine ↓ GSH and GSH/GSSG | Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction |
| [70] | China | 23 ASD individuals 31 control individuals | 21:2 15:16 | 123 ± 9 mo 136 ± 9 mo | - | Faeces | HPLC GC+MS | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ total SCFAs, acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid, isobutyric acid, valeric acid ammonia | Altered gut bacterial metabolism (SCFAs) |
| [71] | France | 26 ASD individuals 24 control individuals | 22:4 16:8 | 6–9 yo 6–9 yo | - | Urine | GC+MS | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ Succinate, Glycolate ↓ Hippurate, 3-hydroxyhippurate, 3-hydroxyphenylacetate, indole-3-acetate, phosphate | Altered gut bacterial metabolism (AA) |
| [72] | USA | 18 ASD + MD + patients 18 ASD + MD – patients 54 control individuals | 14:4 15:3 Unspecified | 8.5 ± 3 yo 7.9 ± 3.2 yo Unspecified | Mitochondrial disease (MD) | Plasma | HPLC | ASD + MD + patients vs. ASD + MD- ↑ GSSG and freeGSH/GSSG Both ASD groups vs. Controls ↓ freeGSH and freeGSH/GSSG ↑ 3-clorotyrosine | Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction |
| [73] | France | 33 ASD patients 33 control individuals | 29:4 29:4 | 7.9 ± 0.57 yo 7.6 ± 0.61 yo | - | Urine | HPLC | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ p-cresol, p-cresylsulfate, p-cresylglucuronate | Altered gut bacterial metabolism (AAA) |
| [74] | USA | 52 ASD individuals 30 control individuals | 41:11 26:4 | 5.37 ± 0.81 yo 5.6 ± 0.95 yo | - | Plasma | LC/GC+MS LC+HMRS+MS | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ Aspartic acid, serine, glutamic acid, glutaric acid, succinic acid, 3-aminoisobutyric acid ↓ Homocitrulline, 2-hydroxyvaleric acid, cystine, isoleucine, creatinine, 4-hydroxyphenyllactic acid, citric acid, lactic acid, heptadecanoic acid, myristic acid | Altered energy metabolism, mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress |
| [75] | Australia | 15 ASD individuals 12 control individuals | 10:5 10:2 | 8.47 ± 2.36 yo 9.61 ± 2.9 yo | - | Serum | UPLC+FLD GC+MS | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ Kynurenine/tryptophan, kynurenine, quinolinic acid ↓ picolinic acid | Altered kynurenine pathway |
| [76] | China | 73 ASD individuals 63 control individuals | 59:14 51:12 | 4.6 ± 0.8 yo 4.1 ± 0.7 yo | - | Serum | UPLC+ Q-TOF+MS | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ Phytosphingosine, pregnanetriol, lysophosphatidylcholines, lysophosphatidylethanolamines, sphingosine 1-phosphate ↓ L-acetylcarnitine, uric acid, decanoylcarnitine, arachidonic acid, docosahexaenoic acid, adrenic acid, docosapentaenoic acid | Altered fatty acid metabolism, mitochondrial dysfunction and immune dysregulation |
| [77] | China | 62 ASD individuals 62 control individuals | 48:14 48:14 | 3.69 ± 1.62 yo 3.45 ± 1.62 yo | - | Urine | GC+MS | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ HPHPA, 3-hydroxyphenylacetic acid and 3-hydroxyhippuric acid | Altered gut bacterial metabolism (AAA) |
| [49] | Italy | 11 ASD patients 14 control individuals | 9:2 8:6 | 35 ± 5.7 mo 35 ± 8.4 mo | Gastrointestinal problems | Faeces | GC+MS | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ Butyrate | Altered gut bacterial metabolism (SCFAs) |
| [41] | USA | 21 ASD patients 23 control individuals | 15:6 22:1 | 10.1 ± 4.1 yo 8.4 ± 3.4 yo | Gastrointestinal problems | Faeces | (H) MRS | ASD patients vs. Controls ↓ GABA, lactate, butyrate, acetate, propionate, formate, nicotinate, glutamate, aspartate ↑ tyrosine, p-cresol and isopropanol | Altered neurotransmitter and gut bacterial metabolism (AAA, SCFAs) |
| [78] | China | 60 ASD individuals 30 control individuals | 49:11 25:5 | 42.86 ± 11 mo 39.3 ± 12.9 mo | - | Serum | MS/MS | ASD patients vs. Controls ↓ free carnitine, glutaryl carnitine, octyl carnitine, 24 carbonyl carnitine, carnosyl carnitine | Altered fatty acid metabolism, mitochondrial dysfunction |
| [79] | Russia | 32 ASD patients 40 control individuals | 23:9 27:13 | 2–60 yo 1–62 yo | - | Prefrontal cortex | LC+MS | ASD patients vs. Controls the concentrations of 205 out of 1366 analysed metabolites showed significant differences | Altered metabolisms: glutathione, purine, pyruvate, propanoate, TCA cycle, galactose, starch and sucrose, nicotinate and nicotinamide, cysteine and methionine, and arginine and proline |
| [42] | China | 43 ASD individuals 31 control individuals | 36:7 17:14 | 4.51 ± 2.23 yo 3.14 ± 1.73 yo | Gastrointestinal problems | Faeces | LC+MS | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ Taurocholic acid ↓ 2-keto-glutaramic acid, L-aspartic acid, L-phenylalanine, L-tyrosine, epinephrine, cortisol | Altered neurotransmitter and gut bacterial metabolism (AA: glutamate and tyrosine) |
| [43] | China | 143 ASD patients 143 control individuals | 130:13 127:16 | 4.9 ± 0.16 yo 5.2 ± 0.17 yo | Gastrointestinal problems | Faeces | LC+MS | ASD patients vs. Controls 37 metabolites showed significant differences | Altered fatty acid, purine and pyrimidine, neurotransmitter and gut bacterial metabolism (AA) |
| [80] | Italy and Northern Europe | 40 ASD patients 40 control individuals | 31:9 29:11 | 4.95 ± 0.45 yo 4.35 ± 0.55 yo | - | Urine | UHPLC+MS | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ p-cresol, ascorbate, dopamine, homovanillic aid, glutamate ↓ norafrenaline, adrenaline, vanillylmanelic acid, GABA, pyridoxal phosphate | Altered neurotransmitter and gut bacterial metabolism (AA) |
| [81] | Japan | 98 ASD individuals 77 control individuals | 73:25 39:38 | 7.08 ± 2.87 yo 8.49 ± 3.75 yo | Insomnia, depression and anxiety | Plasma | d-ROMs test BAP test | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ dROM ↓ BAP/dROM | Oxidative stress and compromised antioxidant capacity |
| [82] | Slovakia | 24 ASD individuals 13 control individuals | 24:0 13:0 | 7.7 ± 0.9 yo 8.2 ± 1.2 yo | - | Urine | UHPLC+MS | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ Indoxyl sulfate | Altered gut bacterial metabolism (AAA) |
| [83] | China | 164 ASD patients 164 control individuals | 129:35 129:35 | 5 ± 1.0 yo 5 ± 1.0 yo | - | Plasma | HPLC+MS | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ TMAO, choline | Altered gut bacterial metabolism (choline) |
| [84] | Japan | 30 ASD patients 30 control individuals | 25:5 17:13 | 8.27 ± 1.21 yo 7.96 ± 1.44 yo | - | Plasma | CE+MS | ASD patients vs. Controls ↑ 48 significant metabolites showed significant differences | Altered lipid biosynthesis and metabolism, oxidative stress and synaptic function |
5.1. Bacterial-Derived Metabolites from Complex Polysaccharide Metabolism
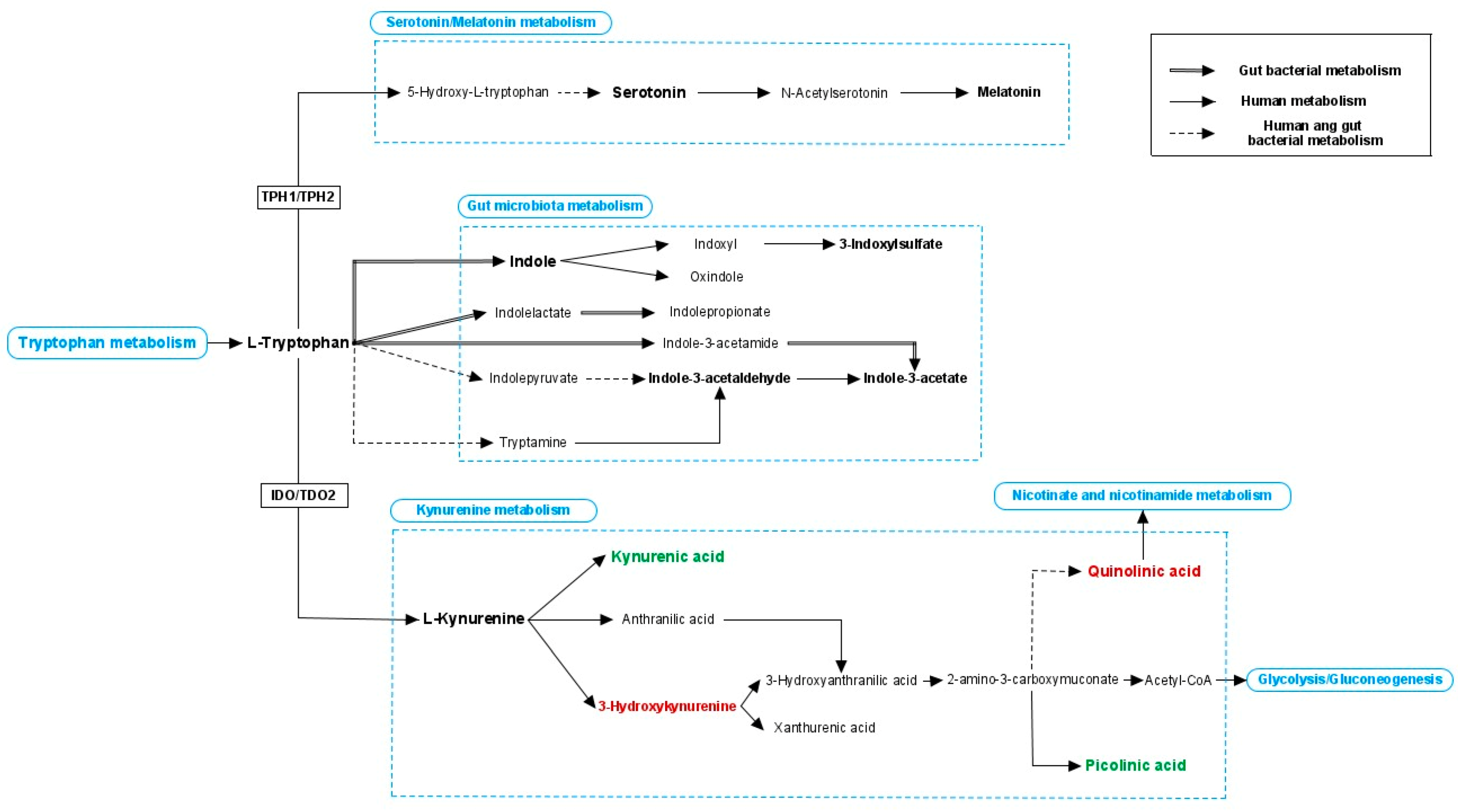
5.2. Bacterial Metabolites from (Aromatic) Amino Acid Metabolism and Neurotransmitters
5.3. Other Bacterial Metabolites
6. Future Perspectives and Conclusions—Shaping the Gut Microbiota
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lloyd-Price, J.; Abu-Ali, G.; Huttenhower, C. The healthy human microbiome. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreiro, A.; Crook, N.; Gasparrini, A.J.; Dantas, G. Multiscale Evolutionary Dynamics of Host-Associated Microbiomes. Cell 2018, 172, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Stombaugh, J.I.; Gordon, J.I.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, F.J.; Ahern, A.M.; Fitzgerald, R.S.; Laserna-Mendieta, E.J.; Power, E.M.; Clooney, A.G.; O’Donoghue, K.W.; McMurdie, P.J.; Iwai, S.; Crits-Christoph, A.; et al. Colonic microbiota is associated with inflammation and host epigenomic alterations in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Microbiota and diabetes: An evolving relationship. Gut 2014, 63, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiBaise, J.K.; Zhang, H.; Crowell, M.D.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R.; Decker, G.A.; Rittmann, B.E. Gut microbiota and its possible relationship with obesity. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, G.; Sampson, T.R.; Geschwind, D.H.; Mazmanian, S.K. The Central Nervous System and the Gut Microbiome. Cell 2016, 167, 915–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Xing, C.; Long, W.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, R.F. Impact of microbiota on central nervous system and neurological diseases: The gut-brain axis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, K.; Maljaars, J.; Carrington, S.J.; Carter, A.S.; Happé, F.; Steyaert, J.; Leekam, S.R.; Noens, I. How well are DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for ASD represented in standardized diagnostic instruments? Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2021, 30, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geschwind, D.H.; Levitt, P. Autism spectrum disorders: Developmental disconnection syndromes. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2007, 17, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarotti, F.; Venerosi, A. Epidemiology of Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Review of Worldwide Prevalence Estimates Since 2014. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, L.Y. Impact of DSM-5 on epidemiology of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2014, 8, 1454–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Treatment and Intervention Services for Autism Spectrum Disorder; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/treatment.html (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Li, Q.; Zhou, J.M. The microbiota-gut-brain axis and its potential therapeutic role in autism spectrum disorder. Neuroscience 2016, 324, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, F.; Liu, Y.; Rhoads, J.M. Can probiotics benefit children with autism spectrum disorders? World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 10093–10102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolov, R.N.; Bearss, K.E.; Lettinga, J.; Erickson, C.; Rodowski, M.; Aman, M.G.; McCracken, J.T.; McDougle, C.J.; Tierney, E.; Vitiello, B.; et al. Gastrointestinal symptoms in a sample of children with pervasive developmental disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2009, 39, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.B.; Johansen, L.J.; Powell, L.D.; Quig, D.; Rubin, R.A. Gastrointestinal flora and gastrointestinal status in children with autism—Comparisons to typical children and correlation with autism severity. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, H.K.; Rose, D.; Ashwood, P. The Gut Microbiota and Dysbiosis in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2018, 18, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwin, E.; Bordenstein, S.R.; Quinn, J.L.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Microbiota and the social brain. Science 2019, 366, eaar2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.M.; Surette, M.; Bercik, P. The interplay between the intestinal microbiota and the brain. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Heijtz, R.; Wang, S.; Anuar, F.; Qian, Y.; Bjorkholm, B.; Samuelsson, A.; Hibberd, M.L.; Forssberg, H.; Pettersson, S. Normal gut microbiota modulates brain development and behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3047–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Mahony, S.M. The microbiome-gut-brain axis: From bowel to behavior. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulle, J.G.; Sharp, W.G.; Cubells, J.F. The gut microbiome: A new frontier in autism research. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2013, 15, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajmalnik-Brown, R.; Lozupone, C.; Kang, D.W.; Adams, J.B. Gut bacteria in children with autism spectrum disorders: Challenges and promise of studying how a complex community influences a complex disease. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 26914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borre, Y.E.; O’Keeffe, G.W.; Clarke, G.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Microbiota and neurodevelopmental windows: Implications for brain disorders. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, S.H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraneveld, A.D.; Szklany, K.; de Theije, C.G.; Garssen, J. Gut-to-Brain Axis in Autism Spectrum Disorders: Central Role for the Microbiome. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2016, 131, 263–287. [Google Scholar]
- Tremlett, H.; Bauer, K.C.; Appel-Cresswell, S.; Finlay, B.B.; Waubant, E. The gut microbiome in human neurological disease: A review. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cox, L.M.; Weiner, H.L. Microbiota Signaling Pathways that Influence Neurologic Disease. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appleton, J. The Gut-Brain Axis: Influence of Microbiota on Mood and Mental Health. Integr. Med. 2018, 17, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Roussin, L.; Prince, N.; Perez-Pardo, P.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Rabot, S.; Naudon, L. Role of the Gut Microbiota in the Pathophysiology of Autism Spectrum Disorder: Clinical and Preclinical Evidence. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemarajata, P.; Versalovic, J. Effects of probiotics on gut microbiota: Mechanisms of intestinal immunomodulation and neuromodulation. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2013, 6, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, C.A.; Diaz-Arteche, C.; Eliby, D.; Schwartz, O.S.; Simmons, J.G.; Cowan, C.S.M. The gut microbiota in anxiety and depression—A systematic review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2021, 83, 101943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremaroli, V.; Backhed, F. Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature 2012, 489, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; Knight, R.; Abubucker, S.; Badger, J.H.; Chinwalla, A.T.; Creasy, H.H.; Earl, A.M.; FitzGerald, M.G.; Fulton, R.S.; et al. The Human Microbiome Project, C., Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Prehn-Kristensen, A.; Zimmermann, A.; Tittmann, L.; Lieb, W.; Schreiber, S.; Baving, L.; Fischer, A. Reduced microbiome alpha diversity in young patients with ADHD. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critchfield, J.W.; van Hemert, S.; Ash, M.; Mulder, L.; Ashwood, P. The potential role of probiotics in the management of childhood autism spectrum disorders. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2011, 2011, 161358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.W.; Park, J.G.; Ilhan, Z.E.; Wallstrom, G.; Labaer, J.; Adams, J.B.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R. Reduced incidence of Prevotella and other fermenters in intestinal microflora of autistic children. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.W.; Ilhan, Z.E.; Isern, N.G.; Hoyt, D.W.; Howsmon, D.P.; Shaffer, M.; Lozupone, C.A.; Hahn, J.; Adams, J.B.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R. Differences in fecal microbial metabolites and microbiota of children with autism spectrum disorders. Anaerobe 2018, 49, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wan, J.; Rong, H.; He, F.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Cai, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, R.; Yin, Z.; et al. Alterations in Gut Glutamate Metabolism Associated with Changes in Gut Microbiota Composition in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. mSystems 2019, 4, e00321-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, Z.; Mao, X.; Liu, Q.; Guo, M.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, K.; Chen, J.; Xu, R.; Tang, J.; et al. Altered gut microbial profile is associated with abnormal metabolism activity of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 1246–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubeva, A.V.; Joyce, S.A.; Moloney, G.; Burokas, A.; Sherwin, E.; Arboleya, S.; Flynn, I.; Khochanskiy, D.; Moya-Perez, A.; Peterson, V.; et al. Microbiota-related Changes in Bile Acid & Tryptophan Metabolism are Associated with Gastrointestinal Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Autism. EBioMedicine 2017, 24, 166–178. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.S.; Lim, M.Y.; Choi, Y.; Ko, G. Modeling environmental risk factors of autism in mice induces IBD-related gut microbial dysbiosis and hyperserotonemia. Mol. Brain 2017, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, G.; Cruz, N.J.; Kang, D.W.; Gandal, M.J.; Wang, B.; Kim, Y.M.; Zink, E.M.; Casey, C.P.; Taylor, B.C.; Lane, C.J.; et al. Human Gut Microbiota from Autism Spectrum Disorder Promote Behavioral Symptoms in Mice. Cell 2019, 177, 1600–1618.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finegold, S.M.; Dowd, S.E.; Gontcharova, V.; Liu, C.; Henley, K.E.; Wolcott, R.D.; Youn, E.; Summanen, P.H.; Granpeesheh, D.; Dixon, D.; et al. Pyrosequencing study of fecal microflora of autistic and control children. Anaerobe 2010, 16, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Angelis, M.; Piccolo, M.; Vannini, L.; Siragusa, S.; De Giacomo, A.; Serrazzanetti, D.I.; Cristofori, F.; Guerzoni, M.E.; Gobbetti, M.; Francavilla, R. Fecal microbiota and metabolome of children with autism and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76993. [Google Scholar]
- Coretti, L.; Paparo, L.; Riccio, M.P.; Amato, F.; Cuomo, M.; Natale, A.; Borrelli, L.; Corrado, G.; Comegna, M.; Buommino, E.; et al. Gut Microbiota Features in Young Children With Autism Spectrum Disorders. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magne, F.; Gotteland, M.; Gauthier, L.; Zazueta, A.; Pesoa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Balamurugan, R. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio: A Relevant Marker of Gut Dysbiosis in Obese Patients? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomova, A.; Husarova, V.; Lakatosova, S.; Bakos, J.; Vlkova, B.; Babinska, K.; Ostatnikova, D. Gastrointestinal microbiota in children with autism in Slovakia. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 138, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strati, F.; Cavalieri, D.; Albanese, D.; De Felice, C.; Donati, C.; Hayek, J.; Jousson, O.; Leoncini, S.; Renzi, D.; Calabro, A.; et al. New evidences on the altered gut microbiota in autism spectrum disorders. Microbiome 2017, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, W.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Wang, J. Analysis of gut microbiota profiles and microbe-disease associations in children with autism spectrum disorders in China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwala, S.; Naik, B.; Ramachandra, N.B. Diversity of Gut Microbiota in Autism Reveals Differential Abundance of Prevotella and Akkermansia Species. Preprints 2018, 2018050375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulikkan, J.; Maji, A.; Dhakan, D.B.; Saxena, R.; Mohan, B.; Anto, M.M.; Agarwal, N.; Grace, T.; Sharma, V.K. Gut Microbial Dysbiosis in Indian Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 76, 1102–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parracho, H.M.; Bingham, M.O.; Gibson, G.R.; McCartney, A.L. Differences between the gut microflora of children with autistic spectrum disorders and that of healthy children. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 54 Pt 10, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Christophersen, C.T.; Sorich, M.J.; Gerber, J.P.; Angley, M.T.; Conlon, M.A. Low relative abundances of the mucolytic bacterium Akkermansia muciniphila and Bifidobacterium spp. in feces of children with autism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6718–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Theije, C.G.; Wopereis, H.; Ramadan, M.; van Eijndthoven, T.; Lambert, J.; Knol, J.; Garssen, J.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Oozeer, R. Altered gut microbiota and activity in a murine model of autism spectrum disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 37, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, R.A.; Oezguen, N.; Balderas, M.; Venkatachalam, A.; Runge, J.K.; Versalovic, J.; Veenstra-VanderWeele, J.; Anderson, G.M.; Savidge, T.; Williams, K.C. Distinct Microbiome-Neuroimmune Signatures Correlate With Functional Abdominal Pain in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 3, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, E.Y.; McBride, S.W.; Hsien, S.; Sharon, G.; Hyde, E.R.; McCue, T.; Codelli, J.A.; Chow, J.; Reisman, S.E.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell 2013, 155, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.; Burcelin, R.; Gibson, G.; Jia, W.; Pettersson, S. Host-Gut Microbiota Metabolic Interactions. Science 2012, 336, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooks, M.G.; Garrett, W.S. Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, K.B.; Leone, V.; Chang, E.B. Microbial metabolites in health and disease: Navigating the unknown in search of function. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 8553–8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, S.J.; Cutler, P.; Melnyk, S.; Jernigan, S.; Janak, L.; Gaylor, D.W.; Neubrander, J.A. Metabolic biomarkers of increased oxidative stress and impaired methylation capacity in children with autism. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1611–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, W. Increased urinary excretion of a 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-3-hydroxypropionic acid (HPHPA), an abnormal phenylalanine metabolite of Clostridia spp. in the gastrointestinal tract, in urine samples from patients with autism and schizophrenia. Nutr. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, I.K.; Angley, M.; Veselkov, K.A.; Holmes, E.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. Urinary metabolic phenotyping differentiates children with autism from their unaffected siblings and age-matched controls. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 2996–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altieri, L.; Neri, C.; Sacco, R.; Curatolo, P.; Benvenuto, A.; Muratori, F.; Santocchi, E.; Bravaccio, C.; Lenti, C.; Saccani, M.; et al. Urinary p-cresol is elevated in small children with severe autism spectrum disorder. Biomarkers 2011, 16, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, X.; Stein, T.P.; Barnes, V.; Rhodes, N.; Guo, L. Metabolic perturbance in autism spectrum disorders: A metabolomics study. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 5856–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, S.; Melnyk, S.; Pavliv, O.; Bai, S.; Nick, T.G.; Frye, R.E.; James, S.J. Evidence of oxidative damage and inflammation associated with low glutathione redox status in the autism brain. Transl. Psychiatry 2012, 2, e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Christophersen, C.T.; Sorich, M.J.; Gerber, J.P.; Angley, M.T.; Conlon, M.A. Elevated fecal short chain fatty acid and ammonia concentrations in children with autism spectrum disorder. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 2096–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emond, P.; Mavel, S.; Aidoud, N.; Nadal-Desbarats, L.; Montigny, F.; Bonnet-Brilhault, F.; Barthelemy, C.; Merten, M.; Sarda, P.; Laumonnier, F.; et al. GC-MS-based urine metabolic profiling of autism spectrum disorders. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 5291–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, R.E.; Delatorre, R.; Taylor, H.; Slattery, J.; Melnyk, S.; Chowdhury, N.; James, S.J. Redox metabolism abnormalities in autistic children associated with mitochondrial disease. Transl. Psychiatry 2013, 3, e273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriele, S.; Sacco, R.; Cerullo, S.; Neri, C.; Urbani, A.; Tripi, G.; Malvy, J.; Barthelemy, C.; Bonnet-Brihault, F.; Persico, A.M. Urinary p-cresol is elevated in young French children with autism spectrum disorder: A replication study. Biomarkers 2014, 19, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, P.R.; Amaral, D.G.; Bais, P.; Smith, A.M.; Egnash, L.A.; Ross, M.E.; Palmer, J.A.; Fontaine, B.R.; Conard, K.R.; Corbett, B.A.; et al. Metabolomics as a tool for discovery of biomarkers of autism spectrum disorder in the blood plasma of children. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112445. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, C.K.; Essa, M.M.; de Paula Martins, R.; Lovejoy, D.B.; Bilgin, A.A.; Waly, M.I.; Al-Farsi, Y.M.; Al-Sharbati, M.; Al-Shaffae, M.A.; Guillemin, G.J. Altered kynurenine pathway metabolism in autism: Implication for immune-induced glutamatergic activity. Autism Res. 2016, 9, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liang, S.; Wang, M.; Gao, J.; Sun, C.; Wang, J.; Xia, W.; Wu, S.; Sumner, S.J.; Zhang, F.; et al. Potential serum biomarkers from a metabolomics study of autism. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2016, 41, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, T.; Peng, Y. Urinary 3-(3-Hydroxyphenyl)-3-hydroxypropionic Acid, 3-Hydroxyphenylacetic Acid, and 3-Hydroxyhippuric Acid Are Elevated in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 9485412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Q.Q.; You, C.; Zou, X.B.; Deng, H.Z. Acyl-carnitine, C5DC, and C26 as potential biomarkers for diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder in children. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 267, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurochkin, I.; Khrameeva, E.; Tkachev, A.; Stepanova, V.; Vanyushkina, A.; Stekolshchikova, E.; Li, Q.; Zubkov, D.; Shichkova, P.; Halene, T.; et al. Metabolome signature of autism in the human prefrontal cortex. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevi, F.; Belardo, A.; Zolla, L. A metabolomics approach to investigate urine levels of neurotransmitters and related metabolites in autistic children. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Tsuda, Y.; Nakatsu, T.; Kitaoka, T.; Kyotani, S. Assessment of oxidative stress in autism spectrum disorder using reactive oxygen metabolites and biological antioxidant potential. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesova, D.; Galba, J.; Piestansky, J.; Celusakova, H.; Repiska, G.; Babinska, K.; Ostatnikova, D.; Katina, S.; Kovac, A. A Novel UHPLC-MS Method Targeting Urinary Metabolomic Markers for Autism Spectrum Disorder. Metabolites 2020, 10, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.; Yi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Shi, X.T.; Feng, Z.; Miller, H.L. Plasma trimethylamine N-oxide, a gut microbe-generated phosphatidylcholine metabolite, is associated with autism spectrum disorders. Neurotoxicology 2020, 76, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usui, N.; Iwata, K.; Miyachi, T.; Takagai, S.; Wakusawa, K.; Nara, T.; Tsuchiya, K.J.; Matsumoto, K.; Kurita, D.; Kameno, Y.; et al. VLDL-specific increases of fatty acids in autism spectrum disorder correlate with social interaction. EBioMedicine 2020, 58, 102917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansma, J.; El Aidy, S. Understanding the host-microbe interactions using metabolic modeling. Microbiome 2021, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoek, S.A.; Verstege, M.I.; Boeckxstaens, G.E.; van den Wijngaard, R.M.; de Jonge, W.J. The enteric nervous system as a regulator of intestinal epithelial barrier function in health and disease. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 4, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braniste, V.; Al-Asmakh, M.; Kowal, C.; Anuar, F.; Abbaspour, A.; Tóth, M.; Korecka, A.; Bakocevic, N.; Ng, L.G.; Kundu, P.; et al. The gut microbiota influences blood-brain barrier permeability in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 263ra158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, H.J. Gut microbial metabolites in health and disease. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 187–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshchina, V.V. Evolutionary Considerations of Neurotransmitters in Microbial, Plant, and Animal Cells. In Microbial Endocrinology: Interkingdom Signaling in Infectious Disease and Health; Lyte, M., Freestone, P.P.E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 17–52. [Google Scholar]
- Grider, J.R.; Piland, B.E. The peristaltic reflex induced by short-chain fatty acids is mediated by sequential release of 5-HT and neuronal CGRP but not BDNF. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G429–G437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, B.S.; Shaito, A.; Motoike, T.; Rey, F.E.; Backhed, F.; Manchester, J.K.; Hammer, R.E.; Williams, S.C.; Crowley, J.; Yanagisawa, M.; et al. Effects of the gut microbiota on host adiposity are modulated by the short-chain fatty-acid binding G protein-coupled receptor, Gpr41. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16767–16772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFabe, D.F.; Cain, N.E.; Boon, F.; Ossenkopp, K.P.; Cain, D.P. Effects of the enteric bacterial metabolic product propionic acid on object-directed behavior, social behavior, cognition, and neuroinflammation in adolescent rats: Relevance to autism spectrum disorder. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 217, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, G.; Gambino, R.; Cassader, M. Interactions between gut microbiota and host metabolism predisposing to obesity and diabetes. Annu. Rev. Med. 2011, 62, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Formation of propionate and butyrate by the human colonic microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaak, E.E.; Canfora, E.E.; Theis, S.; Frost, G.; Groen, A.K.; Mithieux, G.; Nauta, A.; Scott, K.; Stahl, B.; van Harsselaar, J.; et al. Short chain fatty acids in human gut and metabolic health. Benef. Microbes 2020, 11, 411–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vázquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0: The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From Dietary Fiber to Host Physiology: Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Key Bacterial Metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Kang, S.G.; Park, J.H.; Yanagisawa, M.; Kim, C.H. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Activate GPR41 and GPR43 on Intestinal Epithelial Cells to Promote Inflammatory Responses in Mice. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 396–406.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, G.; Sleeth, M.L.; Sahuri-Arisoylu, M.; Lizarbe, B.; Cerdan, S.; Brody, L.; Anastasovska, J.; Ghourab, S.; Hankir, M.; Zhang, S.; et al. The short-chain fatty acid acetate reduces appetite via a central homeostatic mechanism. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.H.; Meeking, M.M.; Mepham, J.R.; Tichenoff, L.; Possmayer, F.; Liu, S.; MacFabe, D.F. The enteric bacterial metabolite propionic acid alters brain and plasma phospholipid molecular species: Further development of a rodent model of autism spectrum disorders. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, P.; Hold, G.L.; Flint, H.J. The gut microbiota, bacterial metabolites and colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nankova, B.B.; Agarwal, R.; MacFabe, D.F.; La Gamma, E.F. Enteric bacterial metabolites propionic and butyric acid modulate gene expression, including CREB-dependent catecholaminergic neurotransmission, in PC12 cells—Possible relevance to autism spectrum disorders. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Lahham, S.H.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Roelofsen, H.; Vonk, R.J.; Venema, K. Biological effects of propionic acid in humans; metabolism, potential applications and underlying mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macfabe, D.F. Short-chain fatty acid fermentation products of the gut microbiome: Implications in autism spectrum disorders. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2012, 23, 19260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, S.; Haghikia, A.; Wilck, N.; Muller, D.N.; Linker, R.A. Impacts of microbiome metabolites on immune regulation and autoimmunity. Immunology 2018, 154, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilling, R.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Microbial genes, brain & behaviour—Epigenetic regulation of the gut-brain axis. Genes Brain Behav. 2014, 13, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- MacFabe, D.F. Enteric short-chain fatty acids: Microbial messengers of metabolism, mitochondria, and mind: Implications in autism spectrum disorders. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 28177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavelle, A.; Sokol, H. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites as key actors in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, E.L.; Kelly, B.; Logan, A.; Costa, A.S.H.; Varma, M.; Bryant, C.E.; Tourlomousis, P.; Däbritz, J.H.M.; Gottlieb, E.; Latorre, I.; et al. Succinate Dehydrogenase Supports Metabolic Repurposing of Mitochondria to Drive Inflammatory Macrophages. Cell 2016, 167, 457–470.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, K.P.; Gratz, S.W.; Sheridan, P.O.; Flint, H.J.; Duncan, S.H. The influence of diet on the gut microbiota. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 69, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neis, E.P.; Dejong, C.H.; Rensen, S.S. The role of microbial amino acid metabolism in host metabolism. Nutrients 2015, 7, 2930–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, W.; Duthie, G. Plant secondary metabolites and gut health: The case for phenolic acids. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2011, 70, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, D.; Spitzer, M.H.; Van Treuren, W.; Merrill, B.D.; Hryckowian, A.J.; Higginbottom, S.K.; Le, A.; Cowan, T.M.; Nolan, G.P.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. A gut bacterial pathway metabolizes aromatic amino acids into nine circulating metabolites. Nature 2017, 551, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windey, K.; De Preter, V.; Verbeke, K. Relevance of protein fermentation to gut health. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, Y.; Sato, T.; Nomoto, K.; Tsuji, H. Identification of phenol- and p-cresol-producing intestinal bacteria by using media supplemented with tyrosine and its metabolites. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.S.; Davies, S.S. Microbial metabolism of dietary components to bioactive metabolites: Opportunities for new therapeutic interventions. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero, F.; Carmona, A.; Obrero, T.; Jiménez, M.J.; Soriano, S.; Moreno, J.A.; Martín-Malo, A.; Aljama, P. Role of endothelial microvesicles released by p-cresol on endothelial dysfunction. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankowski, B.; Ksiezarczyk, K.; Rackowska, E.; Szlufik, S.; Koziorowski, D.; Giebultowicz, J. Higher cerebrospinal fluid to plasma ratio of p-cresol sulfate and indoxyl sulfate in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 501, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persico, A.M.; Napolioni, V. Urinary p-cresol in autism spectrum disorder. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2013, 36, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, A.; Pirrone, P.; Elia, M.; Waring, R.H.; Romano, C. Sulphation deficit in “low-functioning” autistic children: A pilot study. Biol. Psychiatry 1999, 46, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, T.A.; Baker, D.; Lindon, J.C.; Everett, J.R.; Nicholson, J.K. Pharmacometabonomic identification of a significant host-microbiome metabolic interaction affecting human drug metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14728–14733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez-Martin, P.; Becker, J.A.J.; Caramello, N.; Fernandez, S.P.; Costa-Campos, R.; Canaguier, J.; Barbosa, S.; Martinez-Gili, L.; Myridakis, A.; Dumas, M.-E.; et al. The microbial metabolite p-Cresol induces autistic-like behaviors in mice by remodeling the gut microbiota. bioRxiv 2021, 9, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Pascucci, T.; Colamartino, M.; Fiori, E.; Sacco, R.; Coviello, A.; Ventura, R.; Puglisi-Allegra, S.; Turriziani, L.; Persico, A.M. P-cresol Alters Brain Dopamine Metabolism and Exacerbates Autism-Like Behaviors in the BTBR Mouse. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Theije, C.G.; Wu, J.; Koelink, P.J.; Korte-Bouws, G.A.; Borre, Y.; Kas, M.J.; Lopes da Silva, S.; Korte, S.M.; Olivier, B.; Garssen, J.; et al. Autistic-like behavioural and neurochemical changes in a mouse model of food allergy. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 261, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.E.; Moghaddam, B. Amygdala Regulation of Nucleus Accumbens Dopamine Output is Governed by the Prefrontal Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seamans, J.K.; Yang, C.R. The principal features and mechanisms of dopamine modulation in the prefrontal cortex. Prog. Neurobiol. 2004, 74, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavăl, D. A Dopamine Hypothesis of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Dev. Neurosci. 2017, 39, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Arancibia, C.; Urrutia-Piñones, J.; Illanes-González, J.; Martinez-Pinto, J.; Sotomayor-Zárate, R.; Julio-Pieper, M.; Bravo, J.A. Do your gut microbes affect your brain dopamine? Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 1611–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhala, A.; Bennett, M.J.; McGowan, K.L.; Hale, D.E. Limitations of 3-phenylpropionylglycine in early screening for medium-chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency. J. Pediatr. 1993, 122, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, R.; Risoleo, M.C.; Messina, G.; Parisi, L.; Carotenuto, M.; Vetri, L.; Roccella, M. The Neurochemistry of Autism. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tordjman, S.; Anderson, G.M.; McBride, P.A.; Hertzig, M.E.; Snow, M.E.; Hall, L.M.; Thompson, S.M.; Ferrari, P.; Cohen, D.J. Plasma beta-endorphin, adrenocorticotropin hormone, and cortisol in autism. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 1997, 38, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayneris-Perxachs, J.; Amaral, W.; Lubach, G.R.; Lyte, M.; Phillips, G.J.; Posma, J.M.; Coe, C.L.; Swann, J.R. Gut Microbial and Metabolic Profiling Reveal the Lingering Effects of Infantile Iron Deficiency Unless Treated with Iron. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, 2001018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, N.M.; Sharp, T. A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology 1999, 38, 1083–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Saito, D.N.; Hirosawa, T.; Takahashi, T.; Munesue, T.; Kosaka, H.; Naito, N.; Ouchi, Y.; Minabe, Y. Markers for the central serotonin system correlate to verbal ability and paralinguistic social voice processing in autism spectrum disorder. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatani, Y.; Sato-Suzuki, I.; Tsujino, N.; Nakasato, A.; Seki, Y.; Fumoto, M.; Arita, H. Augmented brain 5-HT crosses the blood–brain barrier through the 5-HT transporter in rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 27, 2466–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, J.M.; Yu, K.; Donaldson, G.P.; Shastri, G.G.; Ann, P.; Ma, L.; Nagler, C.R.; Ismagilov, R.F.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Hsiao, E.Y. Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis. Cell 2015, 161, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vadder, F.; Grasset, E.; Mannerås Holm, L.; Karsenty, G.; Macpherson, A.J.; Olofsson, L.E.; Bäckhed, F. Gut microbiota regulates maturation of the adult enteric nervous system via enteric serotonin networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6458–6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriele, S.; Sacco, R.; Persico, A.M. Blood serotonin levels in autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, C.L.; Anacker, A.M.J.; Veenstra-VanderWeele, J. The serotonin system in autism spectrum disorder: From biomarker to animal models. Neuroscience 2016, 321, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veenstra-VanderWeele, J.; Muller, C.L.; Iwamoto, H.; Sauer, J.E.; Owens, W.A.; Shah, C.R.; Cohen, J.; Mannangatti, P.; Jessen, T.; Thompson, B.J.; et al. Autism gene variant causes hyperserotonemia, serotonin receptor hypersensitivity, social impairment and repetitive behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5469–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reigstad, C.S.; Salmonson, C.E.; Rainey, J.F., III; Szurszewski, J.H.; Linden, D.R.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Farrugia, G.; Kashyap, P.C. Gut microbes promote colonic serotonin production through an effect of short-chain fatty acids on enterochromaffin cells. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Theije, C.G.; Koelink, P.J.; Korte-Bouws, G.A.; Lopes da Silva, S.; Korte, S.M.; Olivier, B.; Garssen, J.; Kraneveld, A.D. Intestinal inflammation in a murine model of autism spectrum disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 37, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P.J.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Clarke, G. Kynurenine pathway metabolism and the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, S.M.; Clarke, G.; Borre, Y.E.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Serotonin, tryptophan metabolism and the brain-gut-microbiome axis. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrott, J.M.; Redus, L.; O’Connor, J.C. Kynurenine metabolic balance is disrupted in the hippocampus following peripheral lipopolysaccharide challenge. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Pardo, P.; Grobben, Y.; Willemsen-Seegers, N.; Hartog, M.; Tutone, M.; Muller, M.; Adolfs, Y.; Pasterkamp, R.J.; Vu-Pham, D.; van Doornmalen, A.M.; et al. Pharmacological validation of TDO as a target for Parkinson’s disease. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 4311–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Imamura, Y.; Saito, K.; Sakai, D.; Motoyama, J. Altered kynurenine pathway metabolites in a mouse model of human attention-deficit hyperactivity/autism spectrum disorders: A potential new biological diagnostic marker. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erny, D.; Hrabě de Angelis, A.L.; Jaitin, D.; Wieghofer, P.; Staszewski, O.; David, E.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Mahlakoiv, T.; Jakobshagen, K.; Buch, T.; et al. Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-J.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, E. NMDA receptor dysfunction in autism spectrum disorders. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 20, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsood, R.; Stone, T.W. The Gut-Brain Axis, BDNF, NMDA and CNS Disorders. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 2819–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agus, A.; Planchais, J.; Sokol, H. Gut Microbiota Regulation of Tryptophan Metabolism in Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, N.; Zhang, L.; Gao, W.; Huang, C.; Huber, P.E.; Zhou, X.; Li, C.; Shen, G.; Zou, B. NAD + metabolism: Pathophysiologic mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braidy, N.; Grant, R. Kynurenine pathway metabolism and neuroinflammatory disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccuto, L.; Chen, C.-F.; Pittman, A.R.; Skinner, C.D.; McCartney, H.J.; Jones, K.; Bochner, B.R.; Stevenson, R.E.; Schwartz, C.E. Decreased tryptophan metabolism in patients with autism spectrum disorders. Mol. Autism 2013, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.A.-B. Tryptophan Metabolism: A Versatile Area Providing Multiple Targets for Pharmacological Intervention. Egypt J. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 101415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelante, T.; Iannitti, R.G.; Cunha, C.; De Luca, A.; Giovannini, G.; Pieraccini, G.; Zecchi, R.; D’Angelo, C.; Massi-Benedetti, C.; Fallarino, F.; et al. Tryptophan Catabolites from Microbiota Engage Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor and Balance Mucosal Reactivity via Interleukin-22. Immunity 2013, 39, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Sun, K.; Benechet, A.P.; Qiu, Z.; Maher, L.; Redinbo, M.R.; Phillips, R.S.; et al. Symbiotic bacterial metabolites regulate gastrointestinal barrier function via the xenobiotic sensor PXR and Toll-like receptor 4. Immunity 2014, 41, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rydzewska-Rosołowska, A.; Sroka, N.; Kakareko, K.; Rosołowski, M.; Zbroch, E.; Hryszko, T. The Links between Microbiome and Uremic Toxins in Acute Kidney Injury: Beyond Gut Feeling-A Systematic Review. Toxins 2020, 12, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assem, M.; Lando, M.; Grissi, M.; Kamel, S.; Massy, Z.A.; Chillon, J.-M.; Hénaut, L. The Impact of Uremic Toxins on Cerebrovascular and Cognitive Disorders. Toxins 2018, 10, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaglin, M.; Rhimi, M.; Philippe, C.; Pons, N.; Bruneau, A.; Goustard, B.; Daugé, V.; Maguin, E.; Naudon, L.; Rabot, S. Indole, a Signaling Molecule Produced by the Gut Microbiota, Negatively Impacts Emotional Behaviors in Rats. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J. Indole as an intercellular signal in microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 426–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.-C.; Huang, M.-F.; Liang, S.-S.; Hwang, S.-J.; Tsai, J.-C.; Liu, T.-L.; Wu, P.-H.; Yang, Y.-H.; Kuo, K.-C.; Kuo, M.-C.; et al. Indoxyl sulfate, not p-cresyl sulfate, is associated with cognitive impairment in early-stage chronic kidney disease. Neurotoxicology 2016, 53, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, S.; Xiong, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, T.; Li, Y.; He, T.; Li, Y.; et al. Indoxyl sulfate induces intestinal barrier injury through IRF1-DRP1 axis-mediated mitophagy impairment. Theranostics 2020, 10, 7384–7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannaioni, G.; Carpenedo, R.; Maria Pugliese, A.; Corradetti, R.; Moroni, F. Electrophysiological studies on oxindole, a neurodepressant tryptophan metabolite. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 125, 1751–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, S.M.S.; Hewett, S.J. Influence of glutamate and GABA transport on brain excitatory/inhibitory balance. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 1069–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baj, A.; Moro, E.; Bistoletti, M.; Orlandi, V.; Crema, F.; Giaroni, C. Glutamatergic Signaling Along The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimmura, C.; Suzuki, K.; Iwata, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.J.; Ohno, K.; Matsuzaki, H.; Iwata, K.; Kameno, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Wakuda, T.; et al. Enzymes in the glutamate-glutamine cycle in the anterior cingulate cortex in postmortem brain of subjects with autism. Mol. Autism 2013, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dringen, R.; Hirrlinger, J. Glutathione Pathways in the Brain. Biol. Chem. 2003, 384, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, F.; Chauhan, V.; Chauhan, A. Glutathione redox imbalance in brain disorders. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, A.T.; Cho, E.H.; Klitzman, B.; Nichols, S.P.; Wisniewski, N.A.; Villa, M.M.; Durand, H.K.; Jiang, S.; Midani, F.S.; Nimmagadda, S.N.; et al. Antibiotic-induced changes in the microbiota disrupt redox dynamics in the gut. eLife 2018, 7, e35987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridlon, J.M.; Kang, D.-J.; Hylemon, P.B. Bile salt biotransformations by human intestinal bacteria. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, B.D.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R.; Mazmanian, S.K. Gut microbial molecules in behavioural and neurodegenerative conditions. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 21, 717–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaap, F.G.; Trauner, M.; Jansen, P.L.M. Bile acid receptors as targets for drug development. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brestoff, J.R.; Artis, D. Commensal bacteria at the interface of host metabolism and the immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyangale, E.P.; Mottram, D.S.; Gibson, G.R. Gut microbial activity, implications for health and disease: The potential role of metabolite analysis. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 5573–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, D.; Hornig, M.; Lozupone, C.; Debelius, J.; Gilbert, J.A.; Knight, R. Towards large-cohort comparative studies to define the factors influencing the gut microbial community structure of ASD patients. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 26555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Degnan, P.H.; Taga, M.E.; Goodman, A.L. Vitamin B12 as a modulator of gut microbial ecology. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, E.A.; Jørgensen, T.N. Relationships Between Vitamin D, Gut Microbiome, and Systemic Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 10, 3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fu, X.; Liao, X.; Li, Y. Effects of gut microbial-based treatments on gut microbiota, behavioral symptoms, and gastrointestinal symptoms in children with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 293, 113471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.-W.; Adams, J.B.; Gregory, A.C.; Borody, T.; Chittick, L.; Fasano, A.; Khoruts, A.; Geis, E.; Maldonado, J.; McDonough-Means, S.; et al. Microbiota Transfer Therapy alters gut ecosystem and improves gastrointestinal and autism symptoms: An open-label study. Microbiome 2017, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.W.; Adams, J.B.; Coleman, D.M.; Pollard, E.L.; Maldonado, J.; McDonough-Means, S.; Caporaso, J.G.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R. Long-term benefit of Microbiota Transfer Therapy on autism symptoms and gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.-W.; Adams, J.B.; Vargason, T.; Santiago, M.; Hahn, J.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R. Distinct Fecal and Plasma Metabolites in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders and Their Modulation after Microbiota Transfer Therapy. mSphere 2020, 5, e00314-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.W.; Liong, M.T.; Chung, Y.E.; Huang, H.Y.; Peng, W.S.; Cheng, Y.F.; Lin, Y.S.; Wu, Y.Y.; Tsai, Y.C. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 on Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder in Taiwan: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, R.; Gibson, G.R.; Vulevic, J.; Giallourou, N.; Castro-Mejia, J.L.; Hansen, L.H.; Leigh Gibson, E.; Nielsen, D.S.; Costabile, A. A prebiotic intervention study in children with autism spectrum disorders (ASDs). Microbiome 2018, 6, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrela, S.; Vila, J.C.C.; Lu, N.; Bajic, D.; Rebolleda-Gomez, M.; Chang, C.-Y.; Sanchez, A. Metabolic rules of microbial community assembly. bioRxiv 2020, 984278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Polz, M.F.; Mazel, F.; Albright, M.B.N.; Huber, J.A.; O’Connor, M.I.; Ackermann, M.; Hahn, A.S.; Srivastava, D.S.; Crowe, S.A.; et al. Function and functional redundancy in microbial systems. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldford, J.E.; Lu, N.; Bajić, D.; Estrela, S.; Tikhonov, M.; Sanchez-Gorostiaga, A.; Segrè, D.; Mehta, P.; Sanchez, A. Emergent simplicity in microbial community assembly. Science 2018, 361, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widder, S.; Allen, R.J.; Pfeiffer, T.; Curtis, T.P.; Wiuf, C.; Sloan, W.T.; Cordero, O.X.; Brown, S.P.; Momeni, B.; Shou, W.; et al. Challenges in microbial ecology: Building predictive understanding of community function and dynamics. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2557–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, E.J.; Monk, J.M.; Palsson, B.O. Using Genome-scale Models to Predict Biological Capabilities. Cell 2015, 161, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senne de Oliveira Lino, F.; Bajic, D.; Vila, J.C.C.; Sánchez, A.; Sommer, M.O.A. Complex yeast–bacteria interactions affect the yield of industrial ethanol fermentation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukovski, I.; Bajić, D.; Chacón, J.M.; Quintin, M.; Vila, J.C.; Sulheim, S.; Pacheco, A.R.; Bernstein, D.B.; Rieh, W.J.; Korolev, K.S. Computation Of Microbial Ecosystems in Time and Space (COMETS): An open source collaborative platform for modeling ecosystems metabolism. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.01734. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peralta-Marzal, L.N.; Prince, N.; Bajic, D.; Roussin, L.; Naudon, L.; Rabot, S.; Garssen, J.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Perez-Pardo, P. The Impact of Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810052
Peralta-Marzal LN, Prince N, Bajic D, Roussin L, Naudon L, Rabot S, Garssen J, Kraneveld AD, Perez-Pardo P. The Impact of Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites in Autism Spectrum Disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(18):10052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810052
Chicago/Turabian StylePeralta-Marzal, Lucía N., Naika Prince, Djordje Bajic, Léa Roussin, Laurent Naudon, Sylvie Rabot, Johan Garssen, Aletta D. Kraneveld, and Paula Perez-Pardo. 2021. "The Impact of Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites in Autism Spectrum Disorders" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 18: 10052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810052
APA StylePeralta-Marzal, L. N., Prince, N., Bajic, D., Roussin, L., Naudon, L., Rabot, S., Garssen, J., Kraneveld, A. D., & Perez-Pardo, P. (2021). The Impact of Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites in Autism Spectrum Disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(18), 10052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810052






