NPA-Cu2+ Complex as a Fluorescent Sensing Platform for the Selective and Sensitive Detection of Glyphosate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Spectral Characteristics of Probe NPA upon Coordination with Cu2+
2.2. Sensing Assay for Glyphosate by NPA-Cu2+
2.3. Applications in Real Samples
3. Discussion
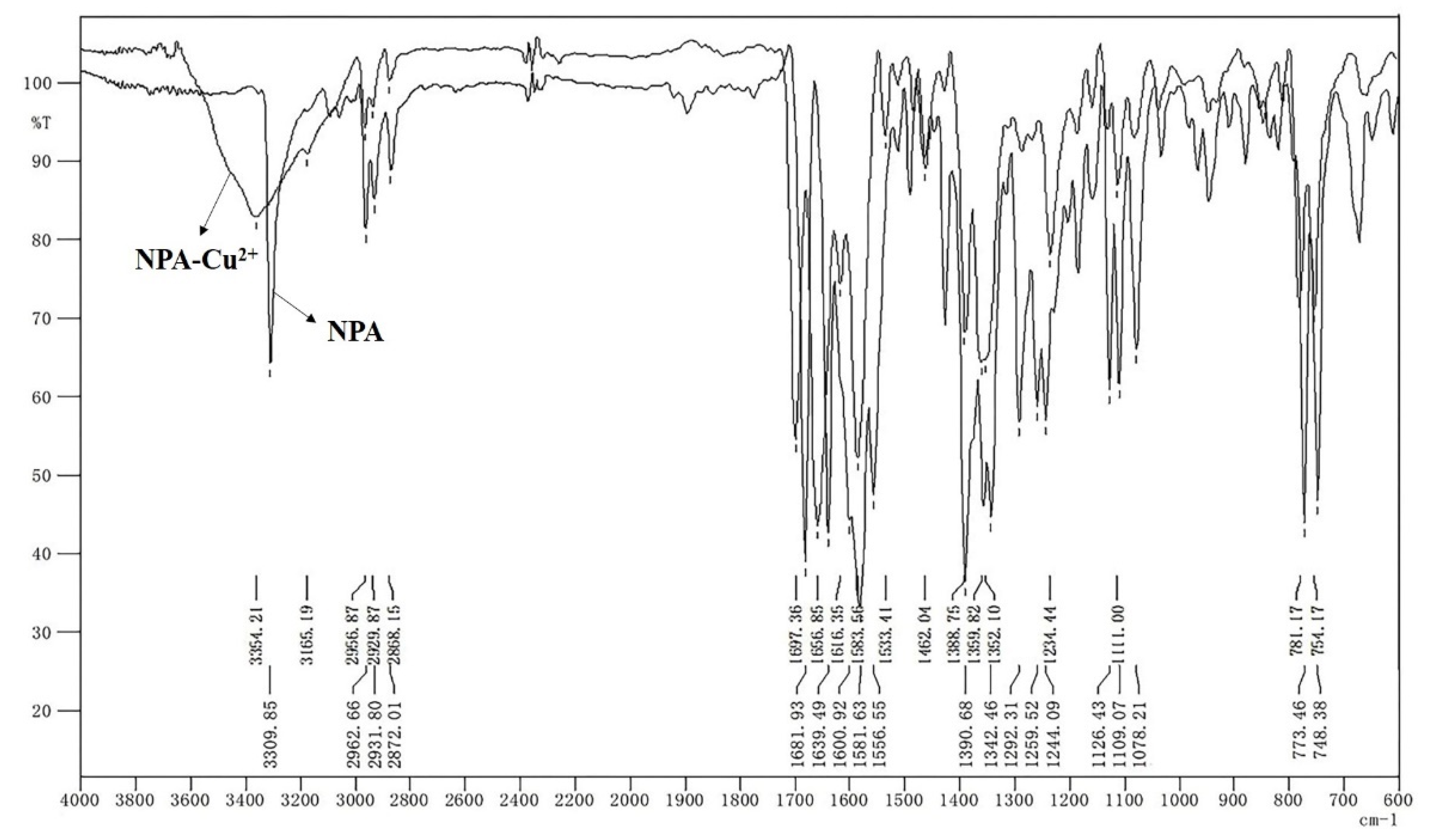
3.1. Sensing Mechanism of Cu2+ by NPA
3.2. Sensing Mechanism of Glyphosate by NPA-Cu2+
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Physical Instruments
4.2. Synthesis of the Probe NPA
4.3. General Procedures for Spectrophotometric Studies
4.4. Theoretical Calculation Methods
4.5. Measurement of Glyphosate Using the NPA-Cu2+ System
4.6. Applications in Real Samples
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiao, C.K.; Wang, C.X.; Pang, R.L.; Tian, F.J.; Han, L.J.; Guo, L.L.; Fang, J.B. Environmental behavior and influencing factors of glyphosate in peach orchard ecosystem. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2020, 206, 11209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbrook, C.M. Trends in glyphosate herbicide use in the United States and globally. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conrad, A.; Schroter-Kermani, C.; Hoppe, H.W.; Ruther, M.; Pieper, S.; Kolossa-Gehring, M. Glyphosate in German adults-time trend (2001 to 2015) of human exposure to a widely used herbicide. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duke, S.O. The history and current status of glyphosate. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, L.; Sharma, A.S.; Chen, M.; Chen, Q. A system composed of polyethylenimine-capped upconversion nanoparticles, copper (II), hydrogen peroxide and 3,3’,5,5’-tetramethylbenzidine for colorimetric and fluorometric determination of glyphosate. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasnier, C.; Dumont, C.; Benachour, N.; Clair, E.; Chagnon, M.C.; Seralini, G.E. Glyphosate-based herbicides are toxic and endocrine disruptors in human cell lines. Toxicology 2009, 262, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, E.; Reszka, E.; Jablonska, E.; Balcerczyk, A.; Broncel, M.; Bukowska, B. Glyphosate affects methylation in the promoter regions of selected tumor suppressors as well as expression of major cell cycle and apoptosis drivers in PBMCs (in vitro study). Toxicol. In Vitro 2020, 63, 104736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyton, K.Z.; Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; Grosse, F.E.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Scoccianti, C.; Mattock, H.; Straif, K. Carcinogenicity of tetrachlorvinphos, parathion, malathion, diazinon, and glyphosate. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 490–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Edition of the Drinking Water Standards and Health Advisories; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Health Canada. Guidelines for canadian drinking water quality-supporting documents-glyphosate. In Health Canada Guidelines; Health Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, E.; Coggan, T.; Anumol, T.; Clarke, B.; Allinson, G. A simple and rapid direct injection method for the determination of glyphosate and AMPA in environmental water samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islas, G.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Mendoza-Huizar, L.H.; Perez-Moreno, F.; Carrillo, E.G. Determination of glyphosate and aminomethyl phosphonic acid in soils byhplc with precolumn derivatization using 1,2-naphthoquinone-4-sulfonate. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2014, 37, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortl, M.; Nemeth, G.; Juracsek, J.; Darvas, B.; Kamp, L.; Rubio, F.; Szekacs, A. Determination of glyphosate residues in Hungarian water samples by immunoassay. Microchem. J. 2013, 107, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbera, M.; Hidalgo, A.; Salvado, V.; Wieczorek, P. Determination of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in natural water using the capillary electrophoresis combined with enrichment step. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 54, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Bayo, F.; Hyne, R.V.; Hyne, K.L. An amperometric method for the detection of amitrole, glyphosate and its aminomethyl-phosphonic acid metabolite in environmental waters using passive samplers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 675, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.A.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.H.; Pang, J.; Lin, T.R.; Guo, L.Q.; Fu, F.F. Colorimetric sensing of glyphosate in environmental water based on peroxidase mimetic activity of MoS2 nanosheets. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 5730–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, A.L.; Tibaldo, G.; Sanchez, G.H.; Siano, G.G.; Marsili, N.R.; Schenone, A.V. A novel fluorimetric method for glyphosate and AMPA determination with NBD-Cl and MCR-ALS. Spectrochim. Acta A 2019, 214, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, M.D.; Aguirre, S.E.; Gomez, C.G. A Cu2+–Cu/glassy carbon system for glyphosate determination. Sensor. Actuat. B—Chem. 2019, 284, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.Y.; Ye, S.S.; Dai, C.Y.; Wu, C.Y.; Chen, L.L.; Huang, Z.Y. Sensitive and on-site detection of glyphosate based on papain-stabilized fluorescent gold nanoclusters. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 8177–8184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.D.; Chen, C.; He, J.B.; Zhang, H.Y.; Xu, Z.X. Fluorescence assay for three organophosphorus pesticides in agricultural products based on Magnetic-Assisted fluorescence labeling aptamer probe. Food Chem. 2020, 307, 125534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Yang, Y.X.; Huo, D.Q.; Ji, Z.; Ma, Y.; Yang, M.; Luo, H.B.; Luo, X.G.; Hou, C.J.; Lv, J.Y. A turn-on fluorescent nanoprobe based on N-doped silicon quantum dots for rapid determination of glyphosate. Microchimica. Acta 2020, 187, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.Z.; Wang, X.F.; Wang, S.Y.; Zhang, C.; Hou, C.J.; He, Q.; Huo, D.Q. A turn-on fluorescent sensor based on carbon dots from Sophora japonica leaves for the detection of glyphosate. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 4130–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, M.K.; Mohapatra, S. Ultrasensitive detection of glyphosate through effective photoelectron transfer between CdTe and chitosan derived carbon dot. Colloid Surface A 2020, 596, 124710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Jiang, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Hu, X. Fluorescent carbon dots for glyphosate determination based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer and logic gate operation. Sens. Actuat. B—Chem. 2020, 242, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Li, G.D.; Liu, H.; Leung, C.H.; Ma, D.L. G-quadruplex-based detection of glyphosate in complex biological systems by a time-resolved luminescent assay. Sens. Actuat. B—Chem. 2020, 320, 128393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, X.F.; Ma, C.B. Sensitive Fluorescence Assay for the Detection of Alkaline Phosphatase Based on a Cu2+-Thiamine System. Sensors 2021, 21, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padnya, P.; Shibaeva, K.; Arsenyev, M.; Baryshnikova, S.; Terenteva, O.; Shiabiev, I.; Khannanov, A.; Boldyrev, A.; Boldyrev, A.; Gerasimov, A.; et al. Catechol-containing schiff bases on thiacalixarene: Synthesis, copper (II) recognition, and formation of organic-inorganic copper-based materials. Molecules 2021, 26, 2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, H.; Zhao, C.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, X.J. Evaluation of fluorescent Cu2+ probes: Instant sensing, cell permeable recognition and quantitative detection. Molecules 2021, 26, 512. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.F.; Sakinati, M.; Yang, Y.X.; Ma, Y.; Yang, M.; Luo, H.B.; Hou, C.J.; Huo, D. The construction of a CND/Cu2+ fluorescence sensing system for the ultrasensitive detection of glyphosate. Anal. Methods-UK 2020, 12, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Y.L.; Liu, C.G.; Ye, F.; Fu, Y. Two luminescent dye@MOFs systems as dual-emitting platforms for efficient pesticides detection. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Gao, S.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.L.; Li, P.; Ye, F.; Fu, Y. Cobalt (II) complex as a fluorescent sensing platform for the selective and sensitive detection of triketone HPPD inhibitors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.W.; Zhao, L.X.; Ma, P.; Ye, T.; Fu, Y.; Ye, F. Fragments Recombination, Design, Synthesis, Safener Activity and CoMFA Model of Novel Substituted Dichloroacetylphenyl Sulfonamide Derivatives. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 1724–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Zhai, Y.; Guo, K.L.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, N.; Gao, S.; Zhao, L.X.; Fu, Y. Safeners improve maize tolerance under herbicide toxicity stress by increasing the activity of enzyme in vivo. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 11568–11576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, L.X.; Zhang, S.Q.; Liu, Y.X.; Guo, Y.Y.; Zhang, D.; Gao, S.; Ye, F. Design, synthesis, herbicidal activity and CoMFA of novel aryl-formyl piperidinone HPPD inhibitors. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 174, 104811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampes, R.; Tepper, R.; Gorls, H.; Bellstedt, P.; Jager, M.; Schubert, U.S. Facile and Reliable Emission-Based Nanomolar Anion Sensing by Luminescent Iridium Receptors Featuring Chelating Halogen-Bonding Sites. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 14679–14687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, F.; Liang, X.M.; Xu, K.X.; Pang, X.X.; Chai, Q.; Fu, Y. A novel dithiourea-appended naphthalimide “on−off” fluorescent probe for detecting Hg2+ and Ag+ and its application in cell imaging. Talanta 2019, 200, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Wang, Y. A new fluorescent sensor containing glutamic acid for Fe3+ and its resulting complex as a secondary sensor for PPi in purely aqueous solution. New. J. Chem. 2017, 41, 4234–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Han, X.T.; Mao, S.S.; Aderinto, S.O.; Shi, X.K.; Shen, K.S.; Wu, H.L. A new, highly potent 1,8-naphthalimide-based fluorescence turn-off chemosensor capable of detecting Cu (II) ions in real-world water samples. Color Technol. 2018, 134, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, Y.R.; Niu, N.; Chen, L.G. Synthesis of molecularly imprinted fluorescent probe based on biomass-derived carbon quantum dots for detection of mesotrione. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 5519–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bi, Y.D.; Gao, J.; Li, Y.J.; Ding, H.; Ding, L. Carbon dots based turn-on fluorescent probes for the sensitive deter-mination of glyphosate in environmental water samples. RSC Adv. 2016, 89, 85820–85828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheals, J.; Persson, P.; Hedman, B. IR and EXAFS spectroscopic studies of glyphosate protonation and copper (II) complexes of glyphosate in aqueous solution. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2001, 40, 4302–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, J.S.; Dimaki, M.; Mortensen, J.; Svendsen, W.E. Detection of glyphosate in drinking water: A fast and direct detection method without sample pretreatment. Sensors—Basel 2018, 18, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, T.; Namera, A.; Tsuji, T.; Noguchi, W.; Inokuchi, S. Determination of glyphosate and glufosinate in human serum by monospin TiO extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Acta Chromatogr. 2020, 32, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbokana, J.G.Y.; Dedzo, G.K.; Ngameni, E. Grafting of organophilic silane in the interlayer space of acid-treated smectite: Application to the direct electrochemical. Apple Clay Sci. 2020, 188, 105513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, M.P.; Goncalves, L.M.; Pereira, E.A. Determination of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid by capillary electrophoresis with indirect detection using pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid or 3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.M.; Qin, C.X.; Wang, J.J.; Sun, J.; Dai, L.X.; Chen, G.Q.; Mei, F. Sensitive and selective probe for visual detection of Cu2+ based on 1, 8-naphthalimidederivative. Sens. Actuat. B—Chem. 2018, 265, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.J.; Huang, P.C.; Zhou, X.; Wu, F.Y. A highly selective and sensitive “turn-on” fluorescent probe of Cu2+ by p-dimethylaminobenzamide-based derivative and its bioimaging in living cells. Sens. Actuat. B—Chem. 2016, 232, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.L.; Tomiyasu, H.; Wu, C.; Cong, H.; Zeng, X.; Rahman, S. Synthesis, crystal structure and complexation behaviour study of an efficient Cu2+ ratiometric fluorescent chemosensor based on thiacalix[4]arene. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 8521–8527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Pang, X.X.; Wang, Z.Q.; Chai, Q.; Ye, F. A highly sensitive and selective fluorescent probe for determination of Cu (II) and application in live cell imaging. Spectrochim. Acta A 2019, 208, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhorge, Y.R.; Tsai, H.T.; Huang, K.F.; Pape, A.J.; Janaki, S.N.; Yen, Y.P. A new pyrene-based Schiff-base: A selective colorimetric and fluorescent chemosensor for detection of Cu(II) and Fe(III). Spectrochim. Acta A 2014, 130, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.J.; Huang, P.C.; Zhang, C.Y.; Wu, F.Y. Colorimetric detection of Cu2+ in aqueous solution and on the test kit by 4-aminoantipyrine derivatives. Sens. Actuat. B—Chem. 2016, 226, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Zhao, L.X.; Jiang, C.Y.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.L.; Fu, Y.; Ye, F. A naked-eye visible colorimetric and fluorescent chemosensor for rapid detection of fluoride anions: Implication for toxic fluorine-containing pesticides detection. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 302, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Wang, F.; You, J. Dual lanthanide-probe based on coordination polymer networks for ratiometric detection of glyphosate in food samples. Food Chem. 2020, 323, 5519–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Samples | Added (μM) | Found (n = 3) (μM) | Recovery (n = 3) (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | - 30 | 0.0 ± 0.0 34.5 ± 0.1 | - 115.0 ± 1.7 | - 1.9 |
| 60 | 62.9 ± 0.2 | 104.8 ± 0.4 | 1.2 | |
| 90 | 93.6 ± 0.1 | 104.0 ± 0.1 | 2.0 | |
| - | 0.0 ± 0.0 | - | - | |
| Songhua River | 30 | 35.2 ± 0.3 | 116.7 ± 0.2 | 2.5 |
| 60 | 66.0 ± 0.1 | 110.3 ± 0.1 | 1.5 | |
| 90 | 94.1 ± 0.6 | 104.4 ± 1.1 | 0.9 | |
| - | 0.0 ± 0.0 | - | - | |
| Tap Water | 30 | 33.2 ± 0.2 | 109.6 ± 1.1 | 1.6 |
| 60 | 65.4 ± 0.4 | 105.6 ± 0.1 | 1.4 | |
| 90 | 89.3 ± 0.5 | 98.8 ± 0.1 | 2.1 | |
| - | 0.0 ± 0.0 | - | - | |
| 30 | 32.5 ± 0.1 | 108.3 ± 0.8 | 1.5 | |
| Rice | 60 | 62.8 ± 0.3 | 104.6 ± 0.3 | 2.3 |
| 90 | 89.5 ± 0.5 | 99.4 ± 0.5 | 1.8 | |
| - | 0.0 ± 0.0 | - | - | |
| 30 | 31.9 ± 0.3 | 106.3 ± 1.3 | 1.6 | |
| Milk | 60 | 61.7 ± 0.5 | 102.8 ± 1.5 | 1.1 |
| 90 | 89.8 ± 0.6 | 99.7 ± 0.8 | 2.3 | |
| - | 0.0 ± 0.0 | - | - | |
| 30 | 31.5 ± 0.9 | 105.0 ± 0.3 | 0.9 | |
| Millet | 60 | 61.4 ± 0.7 | 102.5 ± 0.1 | 0.5 |
| 90 | 90.6 ± 0.9 | 100.7 ± 0.1 | 0.7 | |
| - | 0.0 ± 0.0 | - | - | |
| 30 | 30.7 ± 0.3 | 102.3 ± 0.3 | 0.7 | |
| Maize | 60 | 60.7 ± 0.2 | 101.2 ± 0.1 | 0.5 |
| 90 | 90.5 ± 0.3 | 105.5 ± 0.1 | 0.7 | |
| - | 0.0 ± 0.0 | - | - | |
| 30 | 30.6 ± 0.2 | 102.3 ± 0.3 | 0.9 | |
| Soybean | 60 | 60.8 ± 0.4 | 101.5 ± 0.5 | 1.0 |
| 90 | 90.2 ± 0.3 | 100.5 ± 0.6 | 1.8 | |
| - | 0.0 ± 0.0 | - | - | |
| 30 | 29.0 ± 0.4 | 96.6 ± 0.1 | 0.4 | |
| Mung bean | 60 | 59.2 ± 0.3 | 98.6 ± 0.6 | 0.5 |
| 90 | 89.4 ± 0.2 | 99.3 ± 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Sensing System | Range (μg/mL) | LOD (μg/mL) | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDs–Fe3+ | 0.1–16 | 8.75 | Potatoes Water Serum Soil Water | [22] |
| Gold Electrode | 50–300 | 2.0 | [42] | |
| LC-MS/MS | 1–250 | 0.5 | [43] | |
| Electrochemical sensor | 1.7–16.9 | 0.98 | [44] | |
| Capillary electrophoretic methodologies | 1.0–8.0 | 0.5 | [45] | |
| NPA-Cu2+ | 0–18.6 | 0.32 | Water Soil | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, F.; Ye, X.-L.; Wang, Y.-B.; Yue, M.-L.; Li, P.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.-L.; Fu, Y. NPA-Cu2+ Complex as a Fluorescent Sensing Platform for the Selective and Sensitive Detection of Glyphosate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9816. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189816
Sun F, Ye X-L, Wang Y-B, Yue M-L, Li P, Yang L, Liu Y-L, Fu Y. NPA-Cu2+ Complex as a Fluorescent Sensing Platform for the Selective and Sensitive Detection of Glyphosate. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(18):9816. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189816
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Fang, Xin-Lu Ye, Yu-Bo Wang, Ming-Li Yue, Ping Li, Liu Yang, Yu-Long Liu, and Ying Fu. 2021. "NPA-Cu2+ Complex as a Fluorescent Sensing Platform for the Selective and Sensitive Detection of Glyphosate" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 18: 9816. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189816
APA StyleSun, F., Ye, X.-L., Wang, Y.-B., Yue, M.-L., Li, P., Yang, L., Liu, Y.-L., & Fu, Y. (2021). NPA-Cu2+ Complex as a Fluorescent Sensing Platform for the Selective and Sensitive Detection of Glyphosate. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(18), 9816. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189816







