Treatment with Edoxaban Attenuates Acute Stroke Severity in Mice by Reducing Blood–Brain Barrier Damage and Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
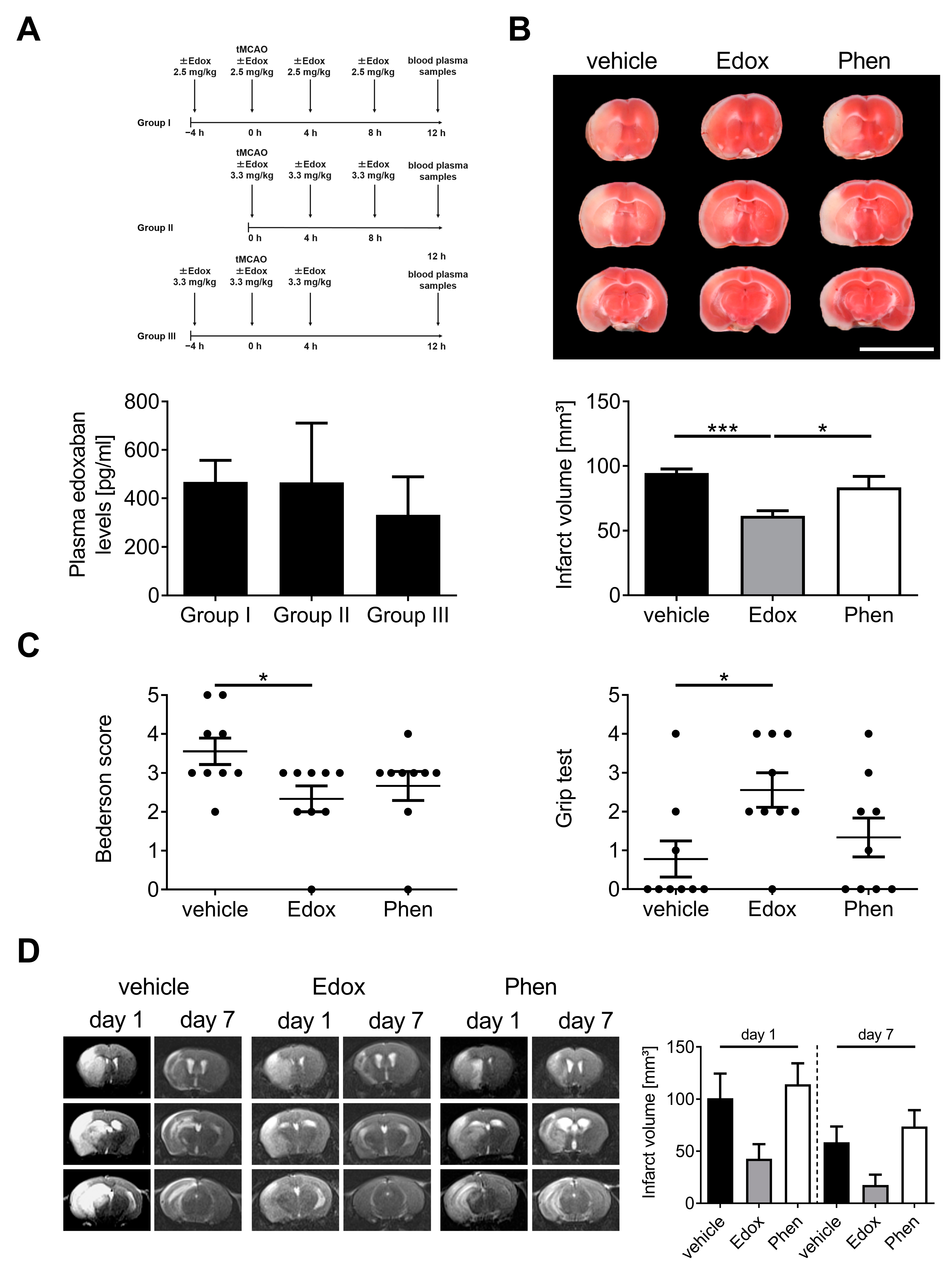
2.1. Treatment with Edoxaban Improves Outcome after Stroke in Mice
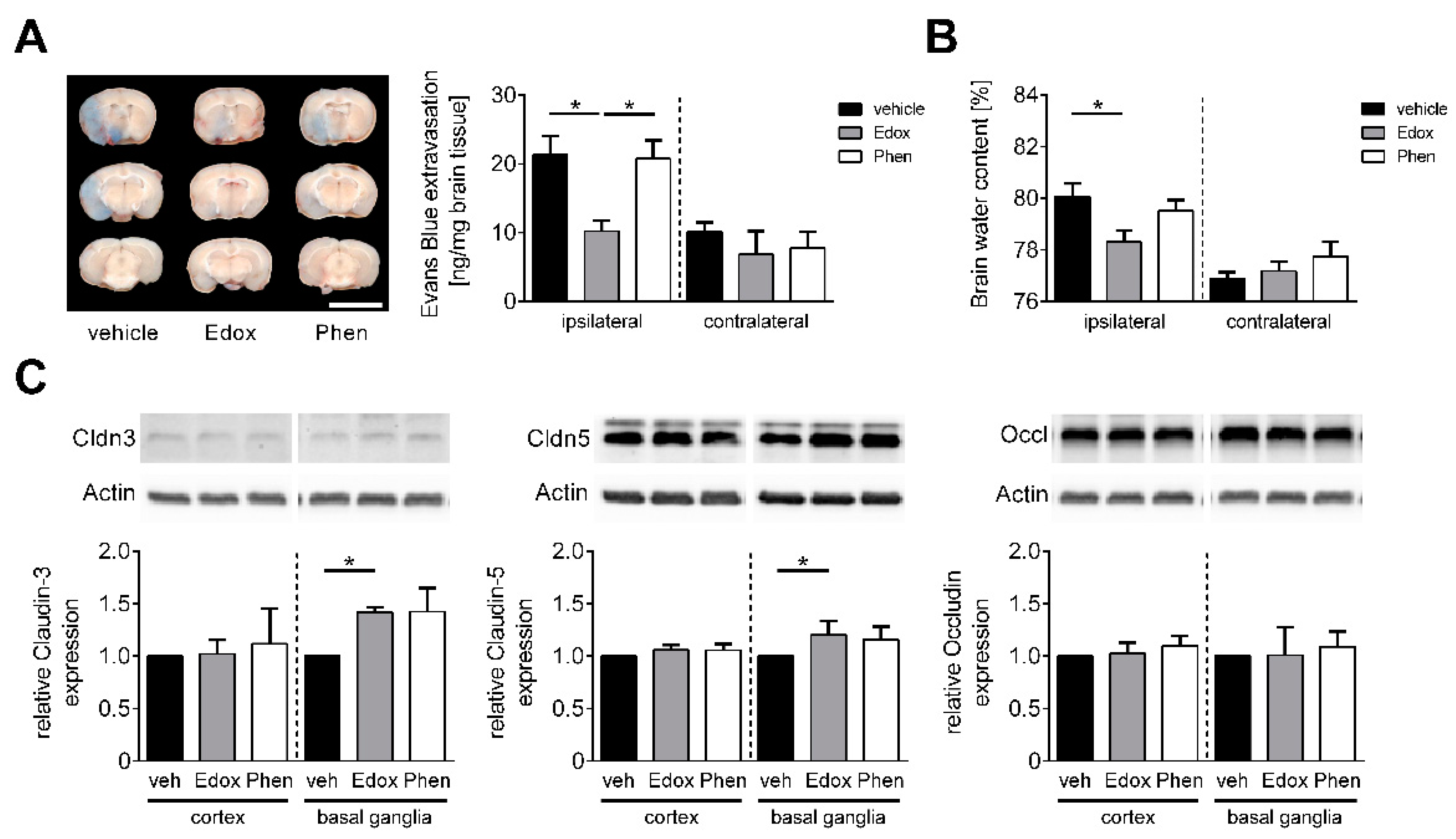
2.2. Edoxaban Stabilizes the BBB after Stroke
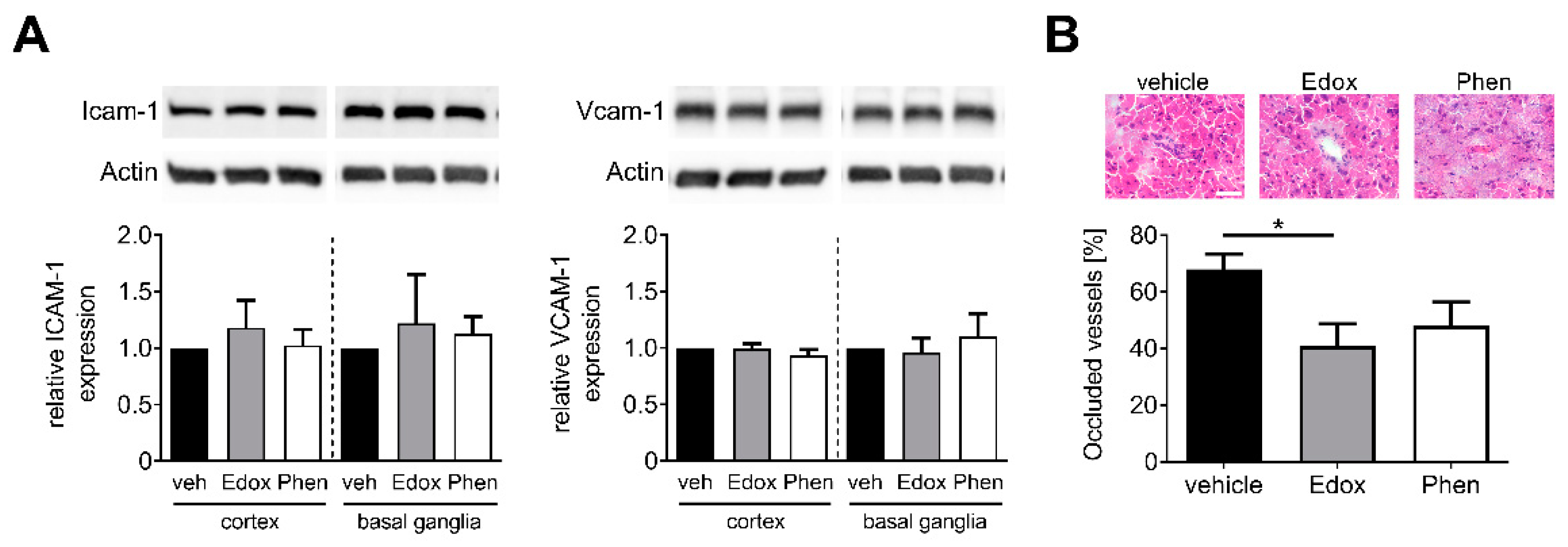
2.3. Treatment with Edoxaban Reduces Cerebral Inflammation after tMCAO
2.4. Treatment with Edoxaban Does Not Alter Cellular Adhesion but Reduces Intracerebral Thrombosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Animal Treatment
4.3. Measurement of Edoxaban Plasma Concentrations
4.4. Ischemia Model
4.5. Exclusion Criteria
4.6. Assessment of Functional Outcome
4.7. Triphenyltetrazolium Chloride (TTC) Staining
4.8. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
4.9. Determination of BBB Leakage and Brain Edema Formation
4.10. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
4.11. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.12. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolf, P.A.; Abbott, R.D.; Kannel, W.B. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: The Framingham Study. Stroke 1991, 22, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hart, R.G.; Pearce, L.A.; Aguilar, M.I. Meta-analysis: Antithrombotic therapy to prevent stroke in patients who have nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2007, 146, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, R.P.; Ruff, C.T.; Braunwald, E.; Murphy, S.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Halperin, J.L.; Waldo, A.L.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Weitz, J.I.; Spinar, J.; et al. Edoxaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2093–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Connolly, S.J.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Yusuf, S.; Eikelboom, J.; Oldgren, J.; Parekh, A.; Pogue, J.; Reilly, P.A.; Themeles, E.; Varrone, J.; et al. Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granger, C.B.; Alexander, J.H.; McMurray, J.J.; Lopes, R.D.; Hylek, E.M.; Hanna, M.; Al-Khalidi, H.R.; Ansell, J.; Atar, D.; Avezum, A.; et al. Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.R.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Garg, J.; Pan, G.; Singer, D.E.; Hacke, W.; Breithardt, G.; Halperin, J.L.; Hankey, G.J.; Piccini, J.P.; et al. Rivaroxaban versus warfarin in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dittmeier, M.; Wassmuth, K.; Schuhmann, M.K.; Kraft, P.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Fluri, F. Dabigatran Etexilate Reduces Thrombin-Induced Inflammation and Thrombus Formation in Experimental Ischemic Stroke. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2016, 13, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovic, M.; Smiljanic, K.; Dobutovic, B.; Syrovets, T.; Simmet, T.; Isenovic, E.R. Thrombin and vascular inflammation. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2012, 359, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojta, J. Macrophages and Thrombin-Another Link between Inflammation and Coagulation. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suo, Z.; Wu, M.; Citron, B.A.; Gao, C.; Festoff, B.W. Persistent protease-activated receptor 4 signaling mediates thrombin-induced microglial activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 31177–31183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Mulholland, M. Thrombin and PAR-1-AP increase proinflammatory cytokine expression in C6 cells. J. Surg. Res. 2005, 129, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, T.; Dohgu, S.; Takata, F.; Matsumoto, J.; Kimura, I.; Koga, M.; Nakamoto, K.; Yamauchi, A.; Kataoka, Y. Role of thrombin-PAR1-PKCtheta/delta axis in brain pericytes in thrombin-induced MMP-9 production and blood-brain barrier dysfunction in vitro. Neuroscience 2017, 350, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, M.L.; Kissela, B.; Woo, D.; Kleindorfer, D.; Alwell, K.; Sekar, P.; Moomaw, C.J.; Haverbusch, M.; Broderick, J.P. The increasing incidence of anticoagulant-associated intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 2007, 68, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, W.; Tripathi, D.; Ronaldson, P.T. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in ischemic stroke: Targeting tight junctions and transporters for vascular protection. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2018, 315, C343–C356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnus, T.; Wiendl, H.; Kleinschnitz, C. Immune mechanisms of stroke. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2012, 25, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmeier, M.; Kraft, P.; Schuhmann, M.K.; Fluri, F.; Kleinschnitz, C. Pretreatment with rivaroxaban attenuates stroke severity in rats by a dual antithrombotic and anti-inflammatory mechanism. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 115, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, L.B.; Bertels, C.; Davis, J.N. Interrater reliability of the NIH stroke scale. Arch. Neurol. 1989, 46, 660–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, H.; Hagii, J.; Metoki, N.; Saito, S.; Shiroto, H.; Hitomi, H.; Kamada, T.; Seino, S.; Takahashi, K.; Sasaki, S.; et al. Severity and Functional Outcome of Patients with Cardioembolic Stroke Occurring during Non-vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulant Treatment. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 24, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, P.; Gob, E.; Schuhmann, M.K.; Gobel, K.; Deppermann, C.; Thielmann, I.; Herrmann, A.M.; Lorenz, K.; Brede, M.; Stoll, G.; et al. FTY720 ameliorates acute ischemic stroke in mice by reducing thrombo-inflammation but not by direct neuroprotection. Stroke 2013, 44, 3202–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nieswandt, B.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Stoll, G. Ischaemic stroke: A thrombo-inflammatory disease? J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 4115–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, G.; Nieswandt, B. Thrombo-inflammation in acute ischaemic stroke-implications for treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploen, R.; Sun, L.; Zhou, W.; Heitmeier, S.; Zorn, M.; Jenetzky, E.; Veltkamp, R. Rivaroxaban does not increase hemorrhage after thrombolysis in experimental ischemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krekels, E.H.; Niebecker, R.; Karlsson, M.O.; Miller, R.; Shimizu, T.; Karlsson, K.E.; Ruff, C.T.; Simonsson, U.S.; Jonsson, S. Population Pharmacokinetics of Edoxaban in Patients with Non-Valvular Atrial Fibrillation in the ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 Study, a Phase III Clinical Trial. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2016, 55, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, S.; Yamashita, T.; Deguchi, K.; Omote, Y.; Yunoki, T.; Sato, K.; Kurata, T.; Hishikawa, N.; Abe, K. Rivaroxaban and apixaban reduce hemorrhagic transformation after thrombolysis by protection of neurovascular unit in rat. Stroke 2014, 45, 2404–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bohmann, F.; Mirceska, A.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Lindhoff-Last, E.; Steinmetz, H.; Foerch, C.; Pfeilschifter, W. No influence of dabigatran anticoagulation on hemorrhagic transformation in an experimental model of ischemic stroke. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.D.; Zhao, R.; Feng, X.Y.; Shi, Y.H.; Wu, Y.L.; Shen, X.L.; Li, G.F.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhao, Y.; He, X.W.; et al. Rivaroxaban does not influence hemorrhagic transformation in a diabetes ischemic stroke and endovascular thrombectomy model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, J.; Yamashita, T.; Kono, S.; Morihara, R.; Nakano, Y.; Fukui, Y.; Li, X.; Hishikawa, N.; Ohta, Y.; Abe, K. Effects of Pretreatment with Warfarin or Rivaroxaban on Neurovascular Unit Dissociation after Tissue Plasminogen Activator Thrombolysis in Ischemic Rat Brain. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 1997–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, V.H.; Conners, J.J.; Prabhakaran, S. Intravenous thrombolysis in a stroke patient taking dabigatran. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2012, 21, 916.e11–916.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornkamm, K.; Harloff, A. Safe intravenous thrombolysis in acute stroke despite treatment with rivaroxaban. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 2012–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.T.; Hellkamp, A.S.; Becker, R.C.; Berkowitz, S.D.; Breithardt, G.; Fox, K.A.A.; Hacke, W.; Halperin, J.L.; Hankey, G.J.; Mahaffey, K.W.; et al. Outcome of Patients Receiving Thrombolytic Therapy While on Rivaroxaban for Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation (from Rivaroxaban Once Daily Oral Direct Factor Xa Inhibition Compared With Vitamin K Antagonism for Prevention of Stroke and Embolism Trial in Atrial Fibrillation). Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 120, 1837–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehaj, F.; Sokol, J.; Ivankova, J.; Mokan, M.; Mokan, M.; Stasko, J. Edoxaban affects TRAP-dependent platelet aggregation. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2020, 49, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, J.; Nehaj, F.; Ivankova, J.; Mokan, M.; Lisa, L.; Zolkova, J.; Vadelova, L.; Mokan, M.; Stasko, J. Impact of Edoxaban on Thrombin-Dependent Platelet Aggregation. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2020, 26, 1076029620948585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tuma, R.F.; Kunapuli, S.P. Deficiency of PAR4 attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieber, M.; Schuhmann, M.K.; Volz, J.; Kumar, G.J.; Vaidya, J.R.; Nieswandt, B.; Pham, M.; Stoll, G.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Kraft, P. Description of a Novel Phosphodiesterase (PDE)-3 Inhibitor Protecting Mice from Ischemic Stroke Independent from Platelet Function. Stroke 2019, 50, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving bioscience research reporting: The ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foerster, K.I.; Huppertz, A.; Muller, O.J.; Rizos, T.; Tilemann, L.; Haefeli, W.E.; Burhenne, J. Simultaneous quantification of direct oral anticoagulants currently used in anticoagulation therapy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 148, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration. Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance for Industry; US Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- European Medicines Agency. Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschnitz, C.; Pozgajova, M.; Pham, M.; Bendszus, M.; Nieswandt, B.; Stoll, G. Targeting platelets in acute experimental stroke: Impact of glycoprotein Ib, VI, and IIb/IIIa blockade on infarct size, functional outcome, and intracranial bleeding. Circulation 2007, 115, 2323–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuhmann, M.K.; Kraft, P.; Bieber, M.; Kollikowski, A.M.; Schulze, H.; Nieswandt, B.; Pham, M.; Stegner, D.; Stoll, G. Targeting Platelet GPVI Plus rt-PA Administration but Not alpha2beta1-Mediated Collagen Binding Protects against Ischemic Brain Damage in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bieber, M.; Gronewold, J.; Scharf, A.C.; Schuhmann, M.K.; Langhauser, F.; Hopp, S.; Mencl, S.; Geuss, E.; Leinweber, J.; Guthmann, J.; et al. Validity and Reliability of Neurological Scores in Mice Exposed to Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion. Stroke 2019, 50, 2875–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P.M.; Higgins, L.S.; Cordell, B.; Moser, P.C. Age-related learning deficits in transgenic mice expressing the 751-amino acid isoform of human beta-amyloid precursor protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 5341–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bieber, M.; Werner, R.A.; Tanai, E.; Hofmann, U.; Higuchi, T.; Schuh, K.; Heuschmann, P.U.; Frantz, S.; Ritter, O.; Kraft, P.; et al. Stroke-induced chronic systolic dysfunction driven by sympathetic overactivity. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuhmann, M.K.; Guthmann, J.; Stoll, G.; Nieswandt, B.; Kraft, P.; Kleinschnitz, C. Blocking of platelet glycoprotein receptor Ib reduces “thrombo-inflammation” in mice with acute ischemic stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bieber, M.; Foerster, K.I.; Haefeli, W.E.; Pham, M.; Schuhmann, M.K.; Kraft, P. Treatment with Edoxaban Attenuates Acute Stroke Severity in Mice by Reducing Blood–Brain Barrier Damage and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9893. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189893
Bieber M, Foerster KI, Haefeli WE, Pham M, Schuhmann MK, Kraft P. Treatment with Edoxaban Attenuates Acute Stroke Severity in Mice by Reducing Blood–Brain Barrier Damage and Inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(18):9893. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189893
Chicago/Turabian StyleBieber, Michael, Kathrin I. Foerster, Walter E. Haefeli, Mirko Pham, Michael K. Schuhmann, and Peter Kraft. 2021. "Treatment with Edoxaban Attenuates Acute Stroke Severity in Mice by Reducing Blood–Brain Barrier Damage and Inflammation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 18: 9893. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189893
APA StyleBieber, M., Foerster, K. I., Haefeli, W. E., Pham, M., Schuhmann, M. K., & Kraft, P. (2021). Treatment with Edoxaban Attenuates Acute Stroke Severity in Mice by Reducing Blood–Brain Barrier Damage and Inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(18), 9893. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189893





