Passive Transfer of Blood Sera from ALS Patients with Identified Mutations Results in Elevated Motoneuronal Calcium Level and Loss of Motor Neurons in the Spinal Cord of Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
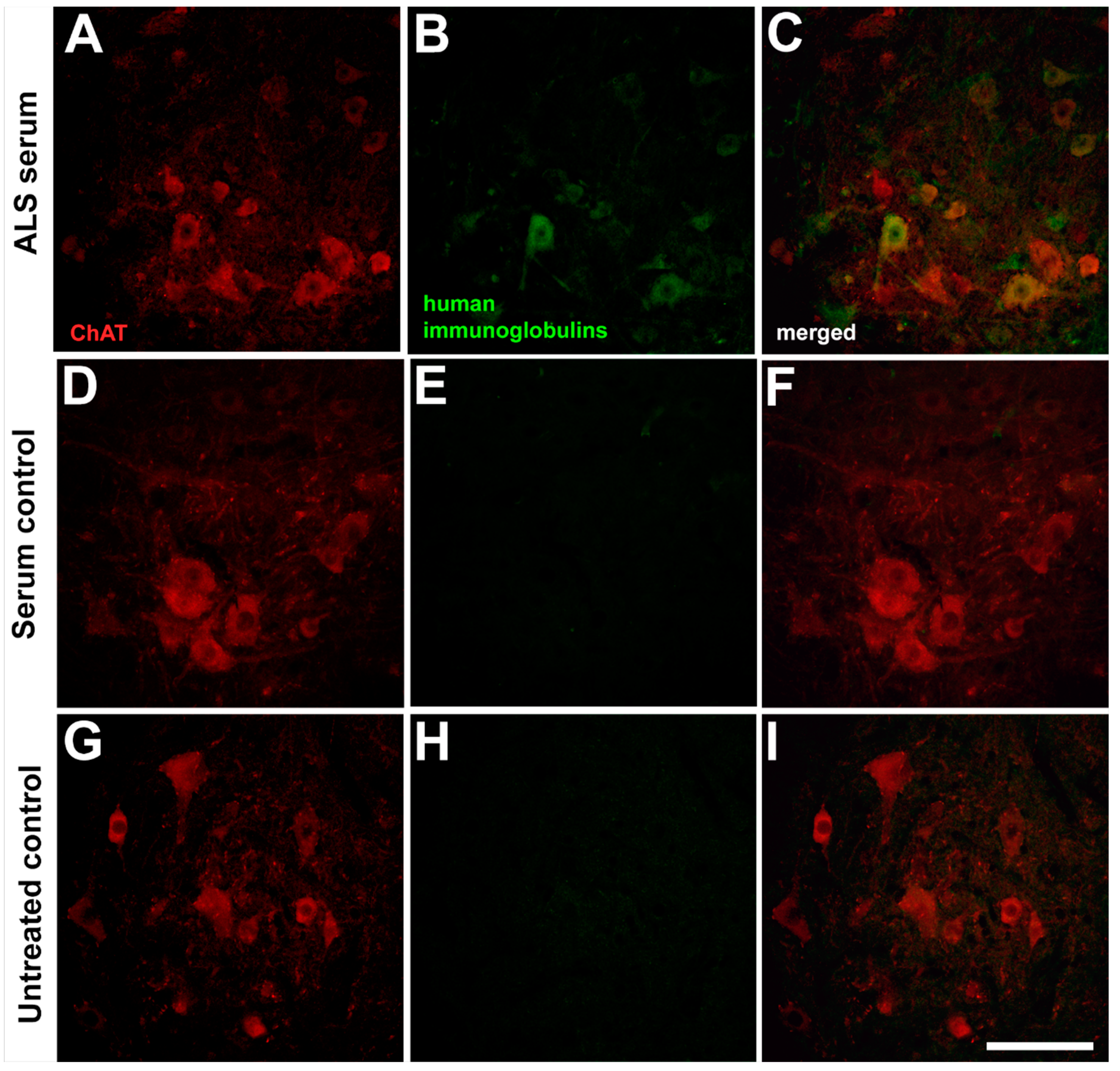
2.1. Presence of the Human Immunoglobulins in the Spinal Motor Neurons after Passive Transfer of the Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Sera
2.2. Qualitative Morphological Changes of the Lumbar Motor Neurons and Their Calcium Content after Injection of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Sera
2.3. Calcium Level Is Elevated in the Perikarya of Lumbar Motor Neurons after Injection of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Sera into Mice
2.4. Number of Lumbar Motor Neurons Is Reduced after Injection of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Sera into Mice
2.5. Correlation of Intracellular Calcium Increase in Motor Neurons and Loss of Spinal Motor Neurons of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Serum-Treated Mice
2.6. Correlation of Intracellular Calcium Increase in Motor Neurons and Motor Axon Terminals of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Serum-Treated Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Approvals and Consent to Participate
4.2. Patients
4.3. Passive Transfer of the Human Sera and Tissue Preparation for Electron Microscopy
4.4. Immunohistochemical Demonstration of Human Immunoglobulins in the Lumbar Neurons
4.5. Counting the Lumbar Motor Neurons on Histological Sections
4.6. Quantification of the Intracellular Calcium Level in the Spinal Motor Neurons
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALS | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| C9ORF72 | Chromosome 9 open reading frame 72 |
| CCNF | G2/mitotic-specific cyclin F |
| EDDs | Electron-dense deposits |
| HNRs | Hexanucleotide repeat expansions |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| MN | Motor neuron |
| NEK1 | Never in a mitosis A-related kinase 1 |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| SOD1 | Superoxide dismutase 1 |
| SQSTM1 | Sequestosome 1 |
| TBK1 | TANK-binding kinase 1 |
| TPBS | Phosphate-buffered saline with 0.2% Triton X-100 |
| UBQLN2 | Ubiquilin 2 |
References
- Hardiman, O.; van den Berg, L.H.; Kiernan, M.C. Clinical Diagnosis and Management of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinnen, B.; Robberecht, W. The Phenotypic Variability of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Chalabi, A.; van den Berg, L.H.; Veldink, J. Gene Discovery in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Implications for Clinical Management. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 13, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cunha-Oliveira, T.; Montezinho, L.; Mendes, C.; Firuzi, O.; Saso, L.; Oliveira, P.J.; Silva, F.S.G. Oxidative Stress in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Pathophysiology and Opportunities for Pharmacological Intervention. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gall, L.; Anakor, E.; Connolly, O.; Vijayakumar, U.; Duddy, W.; Duguez, S. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Affected in ALS. JPM 2020, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudman, J.; Qi, X. Stress Granule Dysregulation in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 598517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafinca, R.; Barbagallo, P.; Talbot, K. The Role of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and ER Stress in TDP-43 and C9ORF72 ALS. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 653688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beers, D.R.; Appel, S.H. Immune dysregulation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Mechanisms and emerging therapies. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béland, L.-C.; Markovinovic, A.; Jakovac, H.; de Marchi, F.; Bilic, E.; Mazzini, L.; Kriz, J.; Munitic, I. Immunity in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Blurred Lines between Excessive Inflammation and Inefficient Immune Responses. Brain Commun. 2020, 2, fcaa124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, V.; Petrozziello, T.; Secondo, A. Calcium Dyshomeostasis and Lysosomal Ca2+ Dysfunction in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Cells 2019, 8, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapeli, K.; Martinez, F.J.; Yeo, G.W. Genetic Mutations in RNA-Binding Proteins and Their Roles in ALS. Hum. Genet. 2017, 136, 1193–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burk, K.; Pasterkamp, R.J. Disrupted Neuronal Trafficking in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 137, 859–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jellinger, K.A. Basic Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration: A Critical Update. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 457–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, L.P.; Shneider, N.A. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1688–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, D.W.; Rothstein, J.D. From Charcot to Lou Gehrig: Deciphering selective motor neuron death in ALS. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.P.; Brown, R.H., Jr.; Cleveland, D.W. Decoding ALS: From genes to mechanism. Nature 2016, 539, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siklós, L.; Engelhardt, J.; Harati, Y.; Smith, R.G.; Joó, F.; Appel, S.H. Ultrastructural evidence for altered calcium in motor nerve terminals in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 1996, 39, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siklós, L.; Engelhardt, J.I.; Alexianu, M.E.; Gurney, M.E.; Siddique, T.; Appel, S.H. Intracellular calcium parallels motoneuron degeneration in SOD-1 mutant mice. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1998, 57, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engelhardt, J.I.; Siklós, L.; Kömüves, L.; Smith, R.G.; Appel, S.H. Antibodies to calcium channels from ALS patients passively transferred to mice selectively increase intracellular calcium and induce ultrastructural changes in motoneurons. Synapse 1995, 20, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obál, I.; Nógrádi, B.; Meszlényi, V.; Patai, R.; Ricken, G.; Kovacs, G.G.; Tripolszki, K.; Széll, M.; Siklós, L.; Engelhardt, J.I. Experimental Motor Neuron Disease Induced in Mice with Long-Term Repeated Intraperitoneal Injections of Serum from ALS Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meszlényi, V.; Patai, R.; Polgár, T.F.; Nógrádi, B.; Körmöczy, L.; Kristóf, R.; Spisák, K.; Tripolszki, K.; Széll, M.; Obál, I.; et al. Passive Transfer of Sera from ALS Patients with Identified Mutations Evokes an Increased Synaptic Vesicle Number and Elevation of Calcium Levels in Motor Axon Terminals, Similar to Sera from Sporadic Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, J.I.; Siklos, L.; Appel, S.H. Altered calcium homeostasis and ultrastructure in motoneurons of mice caused by passively transferred anti-motoneuronal IgG. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neur. 1997, 56, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patai, R.; Nógrádi, B.; Engelhardt, J.I.; Siklós, L. Calcium in the pathomechanism of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis—Taking center stage? Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 483, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfgram, F.; Myers, L. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Effect of Serum on Anterior Horn Cells in Tissue Culture. Science 1973, 179, 579–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng Kee Kwong, K.C.; Harbham, P.K.; Selvaraj, B.T.; Gregory, J.M.; Pal, S.; Hardingham, G.E.; Chandran, S.; Mehta, A.R. 40 Years of CSF Toxicity Studies in ALS: What Have We Learnt About ALS Pathophysiology? Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 647895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Nalini, A.; Laxmi, T.R.; Raju, T.R. ALS-CSF-induced structural changes in spinal motor neurons of rat pups cause deficits in motor behaviour. Exp. Brain Res. 2021, 239, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.G.; Hamilton, S.; Hofmann, F.; Schneider, T.; Nastainczyk, W.; Birnbaumer, L.; Stefani, E.; Appel, S.H. Serum antibodies to L-type calcium channels in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 327, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, J.I.; Appel, S.H. IgG reactivity in the spinal cord and motor cortex in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arch. Neurol. 1990, 47, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexianu, M.E.; Mohamed, A.H.; Smith, R.G.; Colom, L.V.; Appel, S.H. Apoptotic cell death of a hybrid motoneuron cell line induced by immunoglobulins from patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurochem. 1994, 63, 2365–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier, D.R.; Baldelli, P.; Delbono, O.; Smith, R.G.; Alexianu, M.E.; Appel, S.H.; Stefani, E. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis immunoglobulins increase Ca2+ currents in a motoneuron cell line. Ann. Neurol. 1995, 37, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colom, L.V.; Alexianu, M.E.; Mosier, D.R.; Smith, R.G.; Appel, S.H. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis immunoglobulins increase intracellular calcium in a motoneuron cell line. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 146, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.C.; Hernandez-Ontiveros, D.G.; Louis, M.K.; Willing, A.E.; Borlongan, C.V.; Sanberg, P.R.; Voltarelli, J.C.; Garbuzova-Davis, S. Neurovascular aspects of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2012, 102, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bataveljic, D.; Milosevic, M.; Radenovic, L.; Andjus, P. Novel molecular biomarkers at the blood-brain barrier in ALS. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 907545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palmer, A.M. The role of the blood brain barrier in neurodegenerative disorders and their treatment. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2011, 24, 643–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.N.; Pizzo, M.E.; Nehra, G.; Wilken-Resman, B.; Boroumand, S.; Thorne, R.G. Passive Immunotherapies for Central Nervous System Disorders: Current Delivery Challenges and New Approaches. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 3937–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbuzova-Davis, S.; Saporta, S.; Haller, E.; Kolomey, I.; Bennett, S.P.; Potter, H.; Sanberg, P.R. Evidence of compromised blood-spinal cord barrier in early and late symptomatic SOD1 mice modeling ALS. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, Z.; Deane, R.; Ali, Z.; Parisi, M.; Shapovalov, Y.; O’Banion, M.K.; Stojanovic, K.; Sagare, A.; Boillee, S.; Cleveland, D.W.; et al. ALS-causing SOD1 mutants generate vascular changes prior to motor neuron degeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicaise, C.; Mitrecic, D.; Demetter, P.; de Decker, R.; Authelet, M.; Boom, A.; Pochet, R. Impaired blood-brain and blood-spinal cord barriers in mutant SOD1-linked ALS rat. Brain Res. 2009, 1301, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garbuzova-Davis, S.; Hernandez-Ontiveros, D.G.; Rodrigues, M.C.; Haller, E.; Frisina-Deyo, A.; Mirtyl, S.; Sallot, S.; Saporta, S.; Borlongan, C.V.; Sanberg, P.R. Impaired blood-brain/spinal cord barrier in ALS patients. Brain Res. 2012, 1469, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, A.P.; Lebos, A.L.; Yao, Y.; Stice, S.L. Immune Response in Neurological Pathology: Emerging Role of Central and Peripheral Immune Crosstalk. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 676621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, C.; Nordhoff, E.; Casjens, S.; Turewicz, M.; Eisenacher, M.; Gold, R.; Brüning, T.; Pesch, B.; Stephan, C.; Woitalla, D.; et al. Highly immunoreactive IgG antibodies directed against a set of twenty human proteins in the sera of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis identified by protein array. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pullen, A.H.; Humphreys, P. Ultrastructural analysis of spinal motoneurones from mice treated with IgG from ALS patients, healthy individuals, or disease controls. J. Neurol. Sci. 2000, 180, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullen, A.H.; Demestre, M.; Howard, R.S.; Orrell, R.W. Passive transfer of purified IgG from patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis to mice results in degeneration of motor neurons accompanied by Ca2+ enhancement. Acta Neuropathol. 2004, 107, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milošević, M.; Milićević, K.; Božić, I.; Lavrnja, I.; Stevanović, I.; Bijelić, D.; Dubaić, M.; Živković, I.; Stević, Z.; Giniatullin, R.; et al. Immunoglobulins G from Sera of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients Induce Oxidative Stress and Upregulation of Antioxidative System in BV-2 Microglial Cell Line. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delbono, O.; García, J.; Appel, S.H.; Stefani, E. IgG from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis affects tubular calcium channels of skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 1991, 260, C1347–C1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnelli, V.; Sawada, T.; Delbono, O.; Smith, R.G.; Appel, S.H.; Stefani, E. The action of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis immunoglobulins on mammalian single skeletal muscle Ca2+ channels. J. Physiol. 1993, 461, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llinás, R.; Sugimori, M.; Cherksey, B.D.; Smith, R.G.; Delbono, O.; Stefani, E.; Appel, S. IgG from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients increases current through P-type calcium channels in mammalian cerebellar Purkinje cells and in isolated channel protein in lipid bilayer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 11743–11747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Obál, I.; Klausz, G.; Mándi, Y.; Deli, M.; Siklós, L.; Engelhardt, J.I. Intraperitoneally administered IgG from patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or from an immune-mediated goat model increase the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 in the spinal cord and serum of mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nijssen, J.; Comley, L.H.; Hedlund, E. Motor neuron vulnerability and resistance in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 133, 863–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paizs, M.; Patai, R.; Engelhardt, J.I.; Katarova, Z.; Obal, I.; Siklos, L. Axotomy Leads to Reduced Calcium Increase and Earlier Termination of CCL2 Release in Spinal Motoneurons with Upregulated Parvalbumin Followed by Decreased Neighboring Microglial Activation. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2017, 16, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beers, D.R.; Ho, B.K.; Siklós, L.; Alexianu, M.E.; Mosier, D.R.; Mohamed, A.H.; Otsuka, Y.; Kozovska, M.E.; McAlhany, R.E.; Smith, R.G.; et al. Parvalbumin overexpression alters immune-mediated increases in intracellular calcium, and delays disease onset in a transgenic model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurochem. 2001, 79, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.L.; George, K.J.; Ibba, V.; Liu, M.C.; Averill, S.; Quartu, M.; Hamlyn, P.J.; Priestley, J.V. The characteristics of neuronal injury in a static compression model of spinal cord injury in adult rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusart, I.; Schwab, M.E. Secondary cell death and the inflammatory reaction after dorsal hemisection of the rat spinal cord. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1994, 6, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidelberg, E.; Nguyen, L.H.; Polich, R.; Walden, J.G. Transsynaptic degeneration of motoneurones caudal to spinal cord lesions. Brain Res. Bull. 1989, 22, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, S.D.; Rosenberg, L.J.; Wrathall, J.R. Temporal-spatial pattern of acute neuronal and glial loss after spinal cord contusion. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 168, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fifield, K.E.; Vanderluit, J.L. Rapid degeneration of neurons in the penumbra region following a small, focal ischemic stroke. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2020, 52, 3196–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balendra, R.; Isaacs, A.M. C9orf72-mediated ALS and FTD: Multiple pathways to disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, D.; Baloh, R.H. Microglia and C9orf72 in neuroinflammation and ALS and frontotemporal dementia. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3250–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudria-Lopez, E.; Koppers, M.; de Wit, M.; van der Meer, C.; Westeneng, H.J.; Zundel, C.A.; Youssef, S.A.; Harkema, L.; de Bruin, A.; Veldink, J.H. Full ablation of C9orf72 in mice causes immune system-related pathology and neoplastic events but no motor neuron defects. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 132, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, J.; Xu, Z. Massive mitochondrial degeneration in motor neurons triggers the onset of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in mice expressing a mutant SOD1. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 3241–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Polgár, T.F.; Meszlényi, V.; Nógrádi, B.; Körmöczy, L.; Spisák, K.; Tripolszki, K.; Széll, M.; Obál, I.; Engelhardt, J.I.; Siklós, L.; et al. Passive Transfer of Blood Sera from ALS Patients with Identified Mutations Results in Elevated Motoneuronal Calcium Level and Loss of Motor Neurons in the Spinal Cord of Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189994
Polgár TF, Meszlényi V, Nógrádi B, Körmöczy L, Spisák K, Tripolszki K, Széll M, Obál I, Engelhardt JI, Siklós L, et al. Passive Transfer of Blood Sera from ALS Patients with Identified Mutations Results in Elevated Motoneuronal Calcium Level and Loss of Motor Neurons in the Spinal Cord of Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(18):9994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189994
Chicago/Turabian StylePolgár, Tamás F., Valéria Meszlényi, Bernát Nógrádi, Laura Körmöczy, Krisztina Spisák, Kornélia Tripolszki, Márta Széll, Izabella Obál, József I. Engelhardt, László Siklós, and et al. 2021. "Passive Transfer of Blood Sera from ALS Patients with Identified Mutations Results in Elevated Motoneuronal Calcium Level and Loss of Motor Neurons in the Spinal Cord of Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 18: 9994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189994
APA StylePolgár, T. F., Meszlényi, V., Nógrádi, B., Körmöczy, L., Spisák, K., Tripolszki, K., Széll, M., Obál, I., Engelhardt, J. I., Siklós, L., & Patai, R. (2021). Passive Transfer of Blood Sera from ALS Patients with Identified Mutations Results in Elevated Motoneuronal Calcium Level and Loss of Motor Neurons in the Spinal Cord of Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(18), 9994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189994





