Transcriptional Regulation of the Human IL5RA Gene through Alternative Promoter Usage during Eosinophil Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
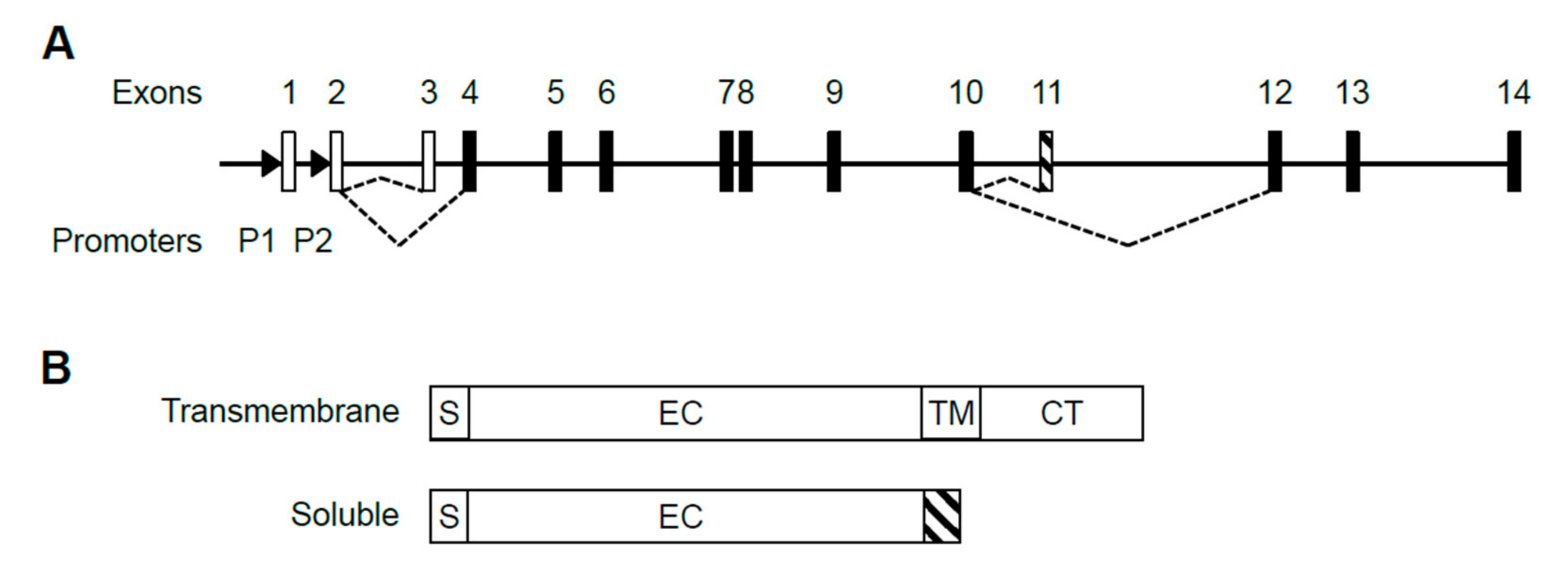
2.1. Structure of the Human IL5RA Genetic Locus and Its Transcripts
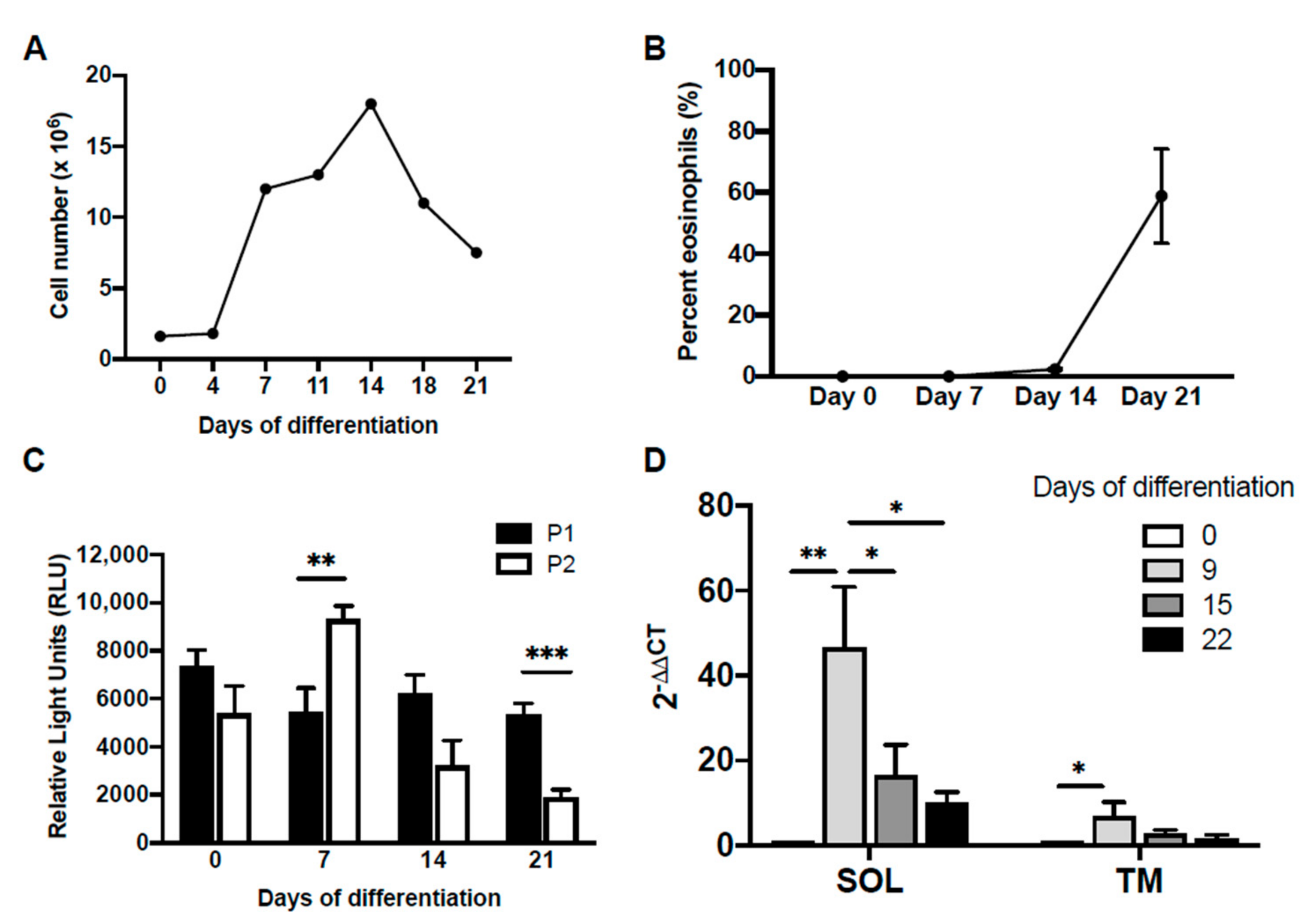
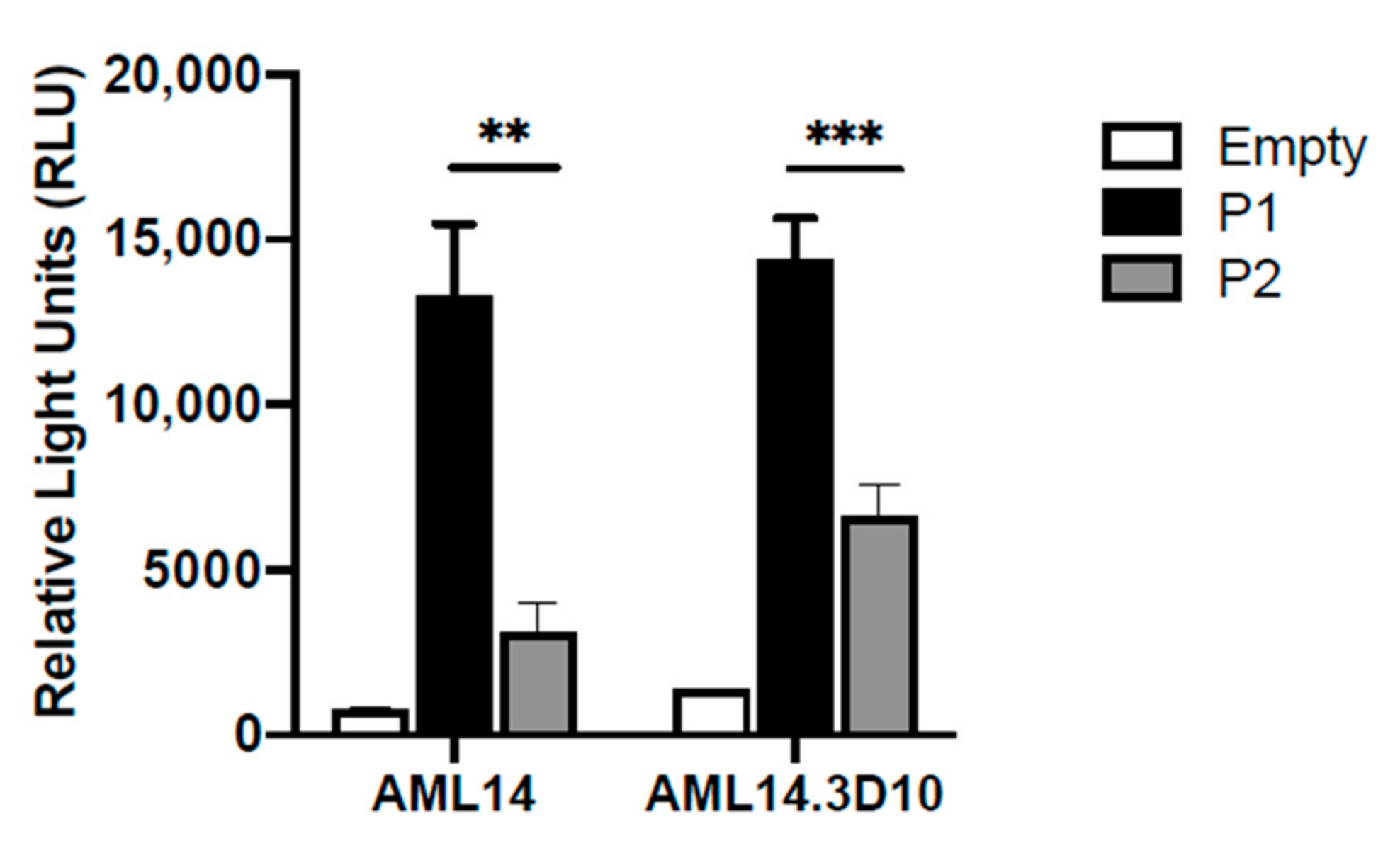
2.2. Differential Usage of P1 and P2 Promoters
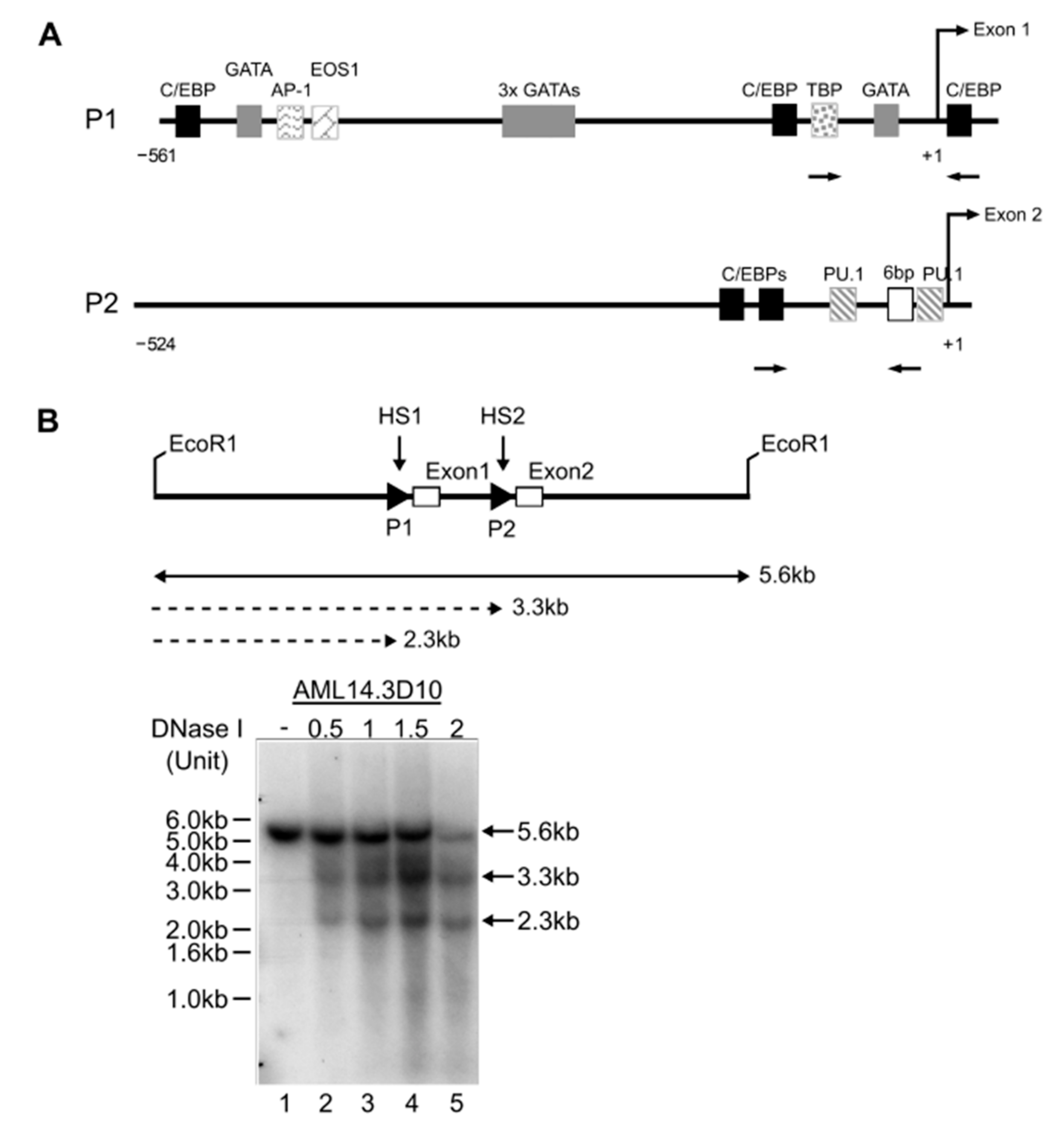
2.3. Promoter Regulation by Differential Occupancies of Transcription Factors
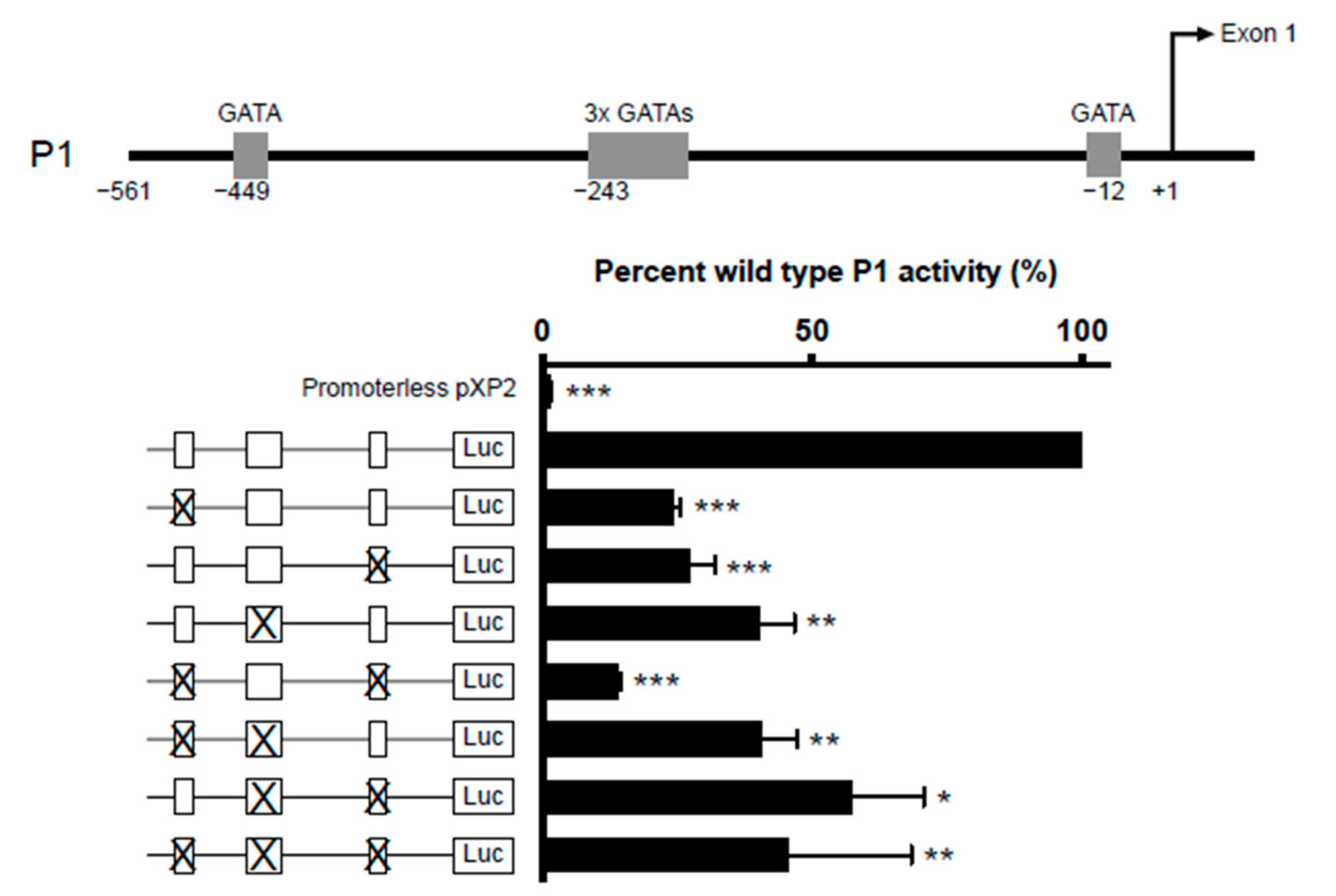
2.3.1. GATA-1 Binding Sites
2.3.2. C/EBP Binding Site
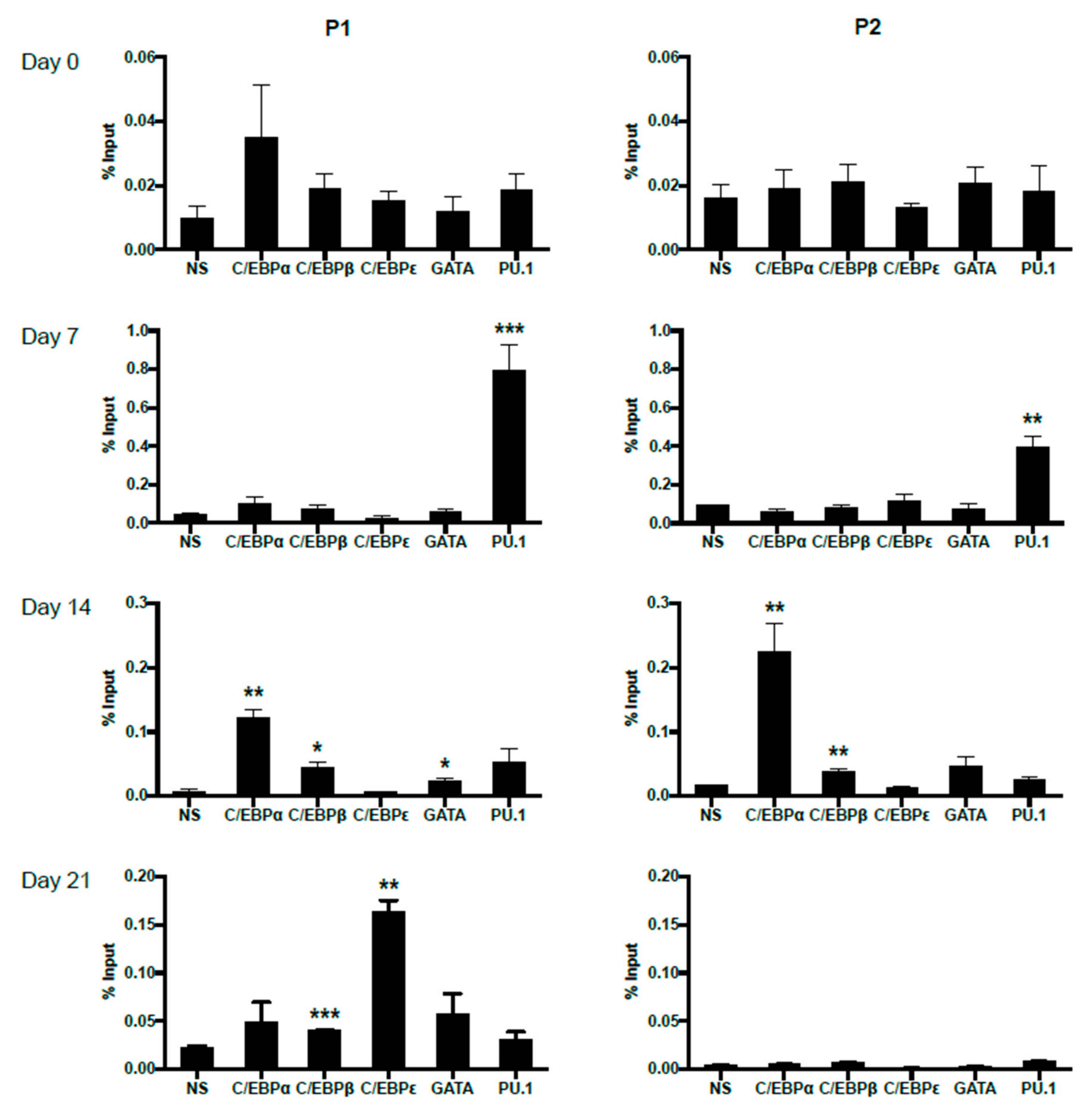
2.4. Dynamic Occupancy of Transcription Factors during Eosinophil Differentiation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Differentiation of CD34+ Progenitors
4.3. Reporter Constructs and Expression Vectors
4.4. Site-Directed Mutagenesis
4.4.1. C/EBP Site Mutagenesis
4.4.2. GATA Site Mutagenesis
4.5. Transient Transfections and Transactivations
4.6. Whole Cell Lysates and Nuclear Extracts
4.7. EMSA
4.8. ChIP Analysis
4.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.10. In Silico Prediction of Transcription Factor Binding Sites
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tavernier, J.; Devos, R.; Cornelis, S.; Tuypens, T.; Van der Heyden, J.; Fiers, W.; Plaetinck, G. A human high affinity interleukin-5 receptor (IL5R) is composed of an IL5-specific α chain and a β chain shared with the receptor for GM-CSF. Cell 1991, 66, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, Y.; Takaki, S.; Migita, M.; Kikuchi, Y.; Tominaga, A.; Takatsu, K. Molecular cloning and expression of the human inter-leukin 5 receptor. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 175, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, P.S.; Mould, A.W.; Yang, M.; Mackenzie, J.; Mattes, J.; Hogan, S.P.; Mahalingam, S.; Mckenzie, A.N.J.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Young, I.G.; et al. Elemental signals regulating eosinophil accumulation in the lung. Immunol. Rev. 2001, 179, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roboz, G.J.; Rafii, S. Interleukin-5 and the regulation of eosinophil production. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 1999, 6, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, W.W.; Lemanske, R.F. Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemanske, R.F.; Busse, W.W. Asthma: Clinical expression and molecular mechanisms. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S95–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedi, B.; Raap, U.; Lewrick, H.; Kapp, A. Delayed eosinophil programmed cell death in vitro: A common feature of inhalant allergy and extrinsic and intrinsic atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1997, 100, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H.U.; Yousefi, S.; Schranz, C.; Schapowal, A.; Bachert, C.; Blaser, K. Direct demonstration of delayed eosinophil apoptosis as a mechanism causing tissue eosinophilia. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 3902–3908. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, E.R.; Stokes, K.; August, A. The role of eosinophils in allergic airway inflammation. Discov. Med. 2010, 9, 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- A Farne, H.; Wilson, A.; Powell, C.; Bax, L.; Milan, S.J. Anti-IL5 therapies for asthma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 9, CD010834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, M.; Koenderman, L. Immunological and hematological effects of IL-5(Rα)-targeted therapy: An overview. Allergy 2018, 73, 1979–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavernier, J.; Tuypens, T.; Plaetinck, G.; Verhee, A.; Fiers, W.; Devos, R. Molecular basis of the membrane-anchored and two soluble isoforms of the human interleukin 5 receptor alpha subunit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 7041–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuypens, T.; Plaetinck, G.; Baker, E.; Sutherland, G.; Brusselle, G.; Fiers, W.; Devos, R.; Tavernier, J. Organization and chromo-somal localization of the human interleukin 5 receptor alpha-chain gene. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 1992, 3, 451–459. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, L.; Christodoulopoulos, P.; Lavigne, F.; Nakamura, Y.; Eidelman, D.; McEuen, A.; Walls, A.; Tavernier, J.; Minshall, E.; Moqbel, R.; et al. Evidence for Local Eosinophil Differentiation Within Allergic Nasal Mucosa: Inhibition with Soluble IL-5 Receptor. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 1538–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mita, S.; Takaki, S.; Hitoshi, Y.; Rolink, A.G.; Tominaga, A.; Yamaguchi, N.; Takatsu, K. Molecular characterization of the beta chain of the murine interleukin 5 receptor. Int. Immunol. 1991, 3, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaki, S.; Mita, S.; Kitamura, T.; Yonehara, S.; Yamaguchi, N.; Tominaga, A.; Miyajima, A.; Takatsu, K. Identification of the second subunit of the murine interleukin-5 receptor: Interleukin-3 receptor-like protein, AIC2B is a component of the high affinity interleukin-5 receptor. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 2833–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wu, P.; Cheewatrakoolpong, B.; Myers, J.G.; Egan, R.W.; Billah, M.M. Selective inhibition of IL-5 receptor alpha-chain gene transcription by IL-5, IL-3, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in human blood eosinophils. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 4427–4432. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gounni, A.S.; Gregory, B.; Nutku, E.; Aris, F.; Latifa, K.; Minshall, E.; North, J.; Tavernier, J.; Levit, R.; Nicolaides, N.; et al. Interleukin-9 enhances interleukin-5 receptor expression, differentiation, and survival of human eosinophils. Blood 2000, 96, 2163–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellman, C.; Halldén, G.; Hylander, B.; Lundahl, J. Regulation of the interleukin-5 receptor alpha-subunit on peripheral blood eosinophils from healthy subjects. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 131, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavernier, J.; Van Der Heyden, J.; Verhee, A.; Brusselle, G.; Van Ostade, X.; Vandekerckhove, J.; North, J.; Rankin, S.M.; Kay, A.B.; Robinson, D.S. Interleukin 5 regulates the isoform expression of its own receptor α-subunit. Blood 2000, 95, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, B.; Kirchem, A.; Phipps, S.; Gevaert, P.; Pridgeon, C.; Rankin, S.M.; Robinson, D.S. Differential regulation of human eosinophil IL-3, IL-5, and GM-CSF receptor alpha-chain expression by cytokines: IL-3, IL-5, and GM-CSF down-regulate IL-5 re-ceptor alpha expression with loss of IL-5 responsiveness, but up-regulate IL-3 receptor alpha expression. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 5359–5366. [Google Scholar]
- Nerlov, C.; Graf, T.P. 1 induces myeloid lineage commitment in multipotent hematopoietic progenitors. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 2403–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Querfurth, E.; Schuster, M.; Kulessa, H.; Crispino, J.; Döderlein, G.; Orkin, S.H.; Graf, T.; Nerlov, C. Antagonism between C/EBPbeta and FOG in eosinophil lineage commitment of multipotent hematopoietic progenitors. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 2515–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McNagny, K.M.; Sieweke, M.H.; Doderlein, G.; Graf, T.; Nerlov, C. Regulation of eosinophil-specific gene expression by a C/EBP-Ets complex and GATA-1. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 3669–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McNagny, K.; Graf, T. Making Eosinophils through Subtle Shifts in Transcription Factor Expression. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, F43–F47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamanaka, R.; Lekstrom-Himes, J.; Barlow, C.; Wynshaw-Boris, A.; Xanthopoulos, K.G. CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins are critical components of the transcriptional regulation of hematopoiesis (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 1998, 1, 213–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Stankiewicz, M.J.; Liu, Y.; Xi, Q.; Schmitz, J.E.; Lekstrom-Himes, J.A.; Ackerman, S.J. Novel combinatorial interactions of GATA-1, PU.1, and C/EBPepsilon isoforms regulate transcription of the gene encoding eosinophil granule major basic protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 43481–43494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Z.; Yergeau, D.A.; Tuypens, T.; Tavernier, J.; Paul, C.C.; Baumann, M.A.; Tenen, D.G.; Ackerman, S.J. Identification and Characterization of a Functional Promoter Region in the Human Eosinophil IL-5 Receptor α Subunit Gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Kuvelkar, R.; Cheewatrakoolpong, B.; Williams, S.; Egan, R.W.; Billah, M.M. Evidence for multiple promoters of the human IL-5 receptor alpha subunit gene: A novel 6-base pair element determines cell-specific promoter function. J. Immunol. 1997, 159, 5412–5421. [Google Scholar]
- Baltus, B.; van Dijk, T.B.; Caldenhoven, E.; Zanders, E.; Raaijmakers, J.A.; Lammers, J.W.; Koenderman, L.; de Groot, R.P. An AP-1 site in the promoter of the human IL-5R alpha gene is necessary for promoter activity in eosinophilic HL60 cells. FEBS Lett. 1998, 434, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwama, A.; Pan, J.; Zhang, P.; Reith, W.; Mach, B.; Tenen, D.; Sun, Z. Dimeric RFX Proteins Contribute to the Activity and Lineage Specificity of the Interleukin-5 Receptor α Promoter through Activation and Repression Domains. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 3940–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baumann, M.A.; Paul, C.C. The Aml14 and Aml14.3D10 Cell Lines: A Long‐Overdue Model for the Study of Eosinophils and More. Stem Cells 1998, 16, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Davuluri, R.V.; Suzuki, Y.; Sugano, S.; Plass, C.; Huang, T.H.-M. The functional consequences of alternative promoter use in mammalian genomes. Trends Genet. 2008, 24, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, R.; Du, J.; Sharma, A.K.; Gomes, I.; Ackerman, S.J. Human C/EBP-epsilon activator and repressor isoforms differentially reprogram myeloid lineage commitment and differentiation. Blood 2009, 113, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gächter, T.; Werenskiold, A.K.; Klemenz, R. Transcription of the Interleukin-1 Receptor-related T1 Gene Is Initiated at Different Promoters in Mast Cells and Fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwahana, H.; Yanagisawa, K.; Ito-Kosaka, A.; Kuroiwa, K.; Tago, K.; Komatsu, N.; Katashima, R.; Itakura, M.; Tominaga, S.-I. Different promoter usage and multiple transcription initiation sites of the interleukin-1 receptor-related human ST2 gene in UT-7 and TM12 cells. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1999, 264, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Sedgwick, J.B.; Bates, M.E.; Vrtis, R.F.; Gern, J.E.; Kita, H.; Jarjour, N.N.; Busse, W.W.; Kelly, E. Decreased Expression of Membrane IL-5 Receptor α on Human Eosinophils: II. IL-5 Down-Modulates Its Receptor Via a Proteinase-Mediated Process. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 6459–6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mack, E.; Pear, W.S. Transcription factor and cytokine regulation of eosinophil lineage commitment. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2020, 27, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulkerson, P.C. Transcription Factors in Eosinophil Development and As Therapeutic Targets. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uhm, T.G.; Kim, B.S.; Chung, I.Y. Eosinophil Development, Regulation of Eosinophil-Specific Genes, and Role of Eosinophils in the Pathogenesis of Asthma. Allergy, Asthma Immunol. Res. 2012, 4, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ackerman, S.J.; Du, J. Transcriptional Regulation of Eosinophil Lineage Commitment and Differentiation. In Eosinophils in Health and Disease; Rosenberg, H.F., Lee, J.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 76–89. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtinger, M.; Ingram, R.; Hornef, M.; Bonifer, C.; Rehli, M. Transcription Factor PU.1 Controls Transcription Start Site Positioning and Alternative TLR4 Promoter Usage. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 26874–26883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gevaert, P.; Hellman, C.; Lundblad, L.; Lundahl, J.; Holtappels, G.; Van Cauwenberge, P.; Tavernier, J.; Bachert, C. Differential expression of the interleukin 5 receptor α isoforms in blood and tissue eosinophils of nasal polyp patients. Allergy 2009, 64, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, T.M.; Maric, I.; Shukla, J.; Brown, M.; Santos, C.; Simakova, O.; Khoury, P.; Fay, M.P.; Kozhich, A.; Kolbeck, R.; et al. IL-5 receptor α levels in patients with marked eosinophilia or mastocytosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 1086–1092.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haldar, P.; Brightling, C.; Hargadon, B.; Gupta, S.; Monteiro, W.; Sousa, A.; Marshall, R.P.; Bradding, P.; Green, R.H.; Wardlaw, A.; et al. Mepolizumab and Exacerbations of Refractory Eosinophilic Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavord, I.D.; Korn, S.; Howarth, P.; Bleecker, E.R.; Buhl, R.; Keene, O.; Ortega, H.; Chanez, P. Mepolizumab for severe eosinophilic asthma (DREAM): A multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conus, S.; Straumann, A.; Bettler, E.; Simon, H.-U. Mepolizumab does not alter levels of eosinophils, T cells, and mast cells in the duodenal mucosa in eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesnil, C.; Raulier, S.; Paulissen, G.; Xiao, X.; Birrell, M.A.; Pirottin, D.; Janss, T.; Starkl, P.; Ramery, E.; Henket, M.; et al. Lung-resident eosinophils represent a distinct regulatory eosinophil subset. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3279–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Z.; Yergeau, D.A.; Wong, I.C.; Tuypens, T.; Tavernier, J.; Paul, C.C.; Baumann, M.A.; Auron, P.E.; Tenen, D.G.; Ackerman, S.J. Interleukin-5 receptor alpha subunit gene regulation in human eosinophil development: Identification of a unique cis-element that acts lie an enhancer in regulating activity of the IL-5R alpha promoter. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1996, 211, 173–187. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Alsayed, Y.M.; Xin, F.; Ackerman, S.J.; Platanias, L.C. Engagement of the CrkL Adapter in Interleukin-5 Signaling in Eosinophils. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 33167–33175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dahl, J.A.; Collas, P. Q2ChIP, a Quick and Quantitative Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay, Unravels Epigenetic Dynamics of Developmentally Regulated Genes in Human Carcinoma Cells. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikes, M.L.; Bradshaw, J.M.; Ivory, W.T.; Lunsford, J.L.; McMillan, R.E.; Morrison, C.R. A streamlined method for rapid and sensitive chromatin immunoprecipitation. J. Immunol. Methods 2009, 344, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, K.; Hayashi, N.; Kaminogawa, S.; Ra, C. Molecular mechanisms for transcriptional regulation of human high-affinity IgE receptor beta-chain gene induced by GM-CSF. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 4605–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Messeguer, X.; Escudero, R.; Farre, D.; Núñez, O.; Martínez, J.; Albà, M. PROMO: Detection of known transcription regulatory elements using species-tailored searches. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 333–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farré, D.; Roset, R.; Huerta, M.; Adsuara, J.E.; Roselló, L.; Albà, M.M.; Messeguer, X. Identification of patterns in biological sequences at the ALGGEN server: PROMO and MALGEN. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3651–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wingender, E.; Chen, X.; Fricke, E.; Geffers, R.; Hehl, R.; Liebich, I.; Krull, M.; Matys, V.; Michael, H.; Ohnhäuser, R.; et al. The TRANSFAC system on gene expression regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Primer Sequence | Mutations | |
|---|---|---|
| Primer 1 | 5′-GGTACCAGACCTGCTCACAAAGC-3′ | |
| Primer 2 | 5′-GTTCTTCACTCTTTCATCCGCAC-3′ | Δ1,2 |
| Primer 3 | 5′-GTTCTTCACTCGGTCATCATCAC-3′ | Δ8,9 |
| Primer 4 | 5′-CCGCTCGAGAAATGCGGTGGCCAT-3′ | |
| Primer 5 | 5′-GTGCGGATGAAAGAGTGAAGAAC-3′ | |
| Primer 6 | 5′-GTGATGATGACCGAGTGAAGAAC-3′ |
| Position of Mutation | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|
| −12 | Forward: 5′-AAAAAGTGCACCCAGACTTAAGGTTCGTTCTCAATGCTCTGCCG-3′ Reverse: 5′-CGGCAGAGCATTGAGAACGAACCTTAAGTCTGGGTGCACTTTTT-3′ |
| −243 | Forward: 5′-GCAGACAAGACAGTTACCACTGGCGCTCTGACGAGAGATTC-3′ Reverse: 5′-GAATCTCTCGTCCAGAGCGCCAGTGGTAACTGTCTTGTCTGC-3′ |
| −449 | Forward: 5′-CCTCAGGCCTTACTTCCCAAGAAATCATGTGTCAGTGTTGC-3′ Reverse: 5′-GCAACACTGACACATGATTTCTTGGGAAGTAAGGCCTGAGG-3′ |
| Promoter | Sequence |
|---|---|
| IL5RA P1 | Forward: 5′-CCGTGATGATGAAAGAGTGAAG-3′ Reverse: 5′-GCAGAGCATTGAGAACGAAC-3′ |
| IL5RA P2 | Forward: 5′-AGGCAAAATACCAAAATGGGC-3′ Reverse: 5′-GCAATGTGCGGTGAAACCTA-3′ |
| ACTB | Forward: 5′-TGCCTAGGTCACCCACTAACG-3′ Reverse: 5′-GTGGCCCGTGATGAAGGCTA-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laffey, K.G.; Du, J.; Schrum, A.G.; Ackerman, S.J. Transcriptional Regulation of the Human IL5RA Gene through Alternative Promoter Usage during Eosinophil Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910245
Laffey KG, Du J, Schrum AG, Ackerman SJ. Transcriptional Regulation of the Human IL5RA Gene through Alternative Promoter Usage during Eosinophil Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(19):10245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910245
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaffey, Kimberly G., Jian Du, Adam G. Schrum, and Steven J. Ackerman. 2021. "Transcriptional Regulation of the Human IL5RA Gene through Alternative Promoter Usage during Eosinophil Development" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 19: 10245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910245
APA StyleLaffey, K. G., Du, J., Schrum, A. G., & Ackerman, S. J. (2021). Transcriptional Regulation of the Human IL5RA Gene through Alternative Promoter Usage during Eosinophil Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(19), 10245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910245








