CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein ε27 Antagonism of GATA-1 Transcriptional Activity in the Eosinophil Is Mediated by a Unique N-Terminal Repression Domain, Is Independent of Sumoylation and Does Not Require DNA Binding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. C/EBPε and GATA-1 Bind In Vivo in Eosinophil Myelocytes to Their Functional Sites in the MBP1-P2 Promoter
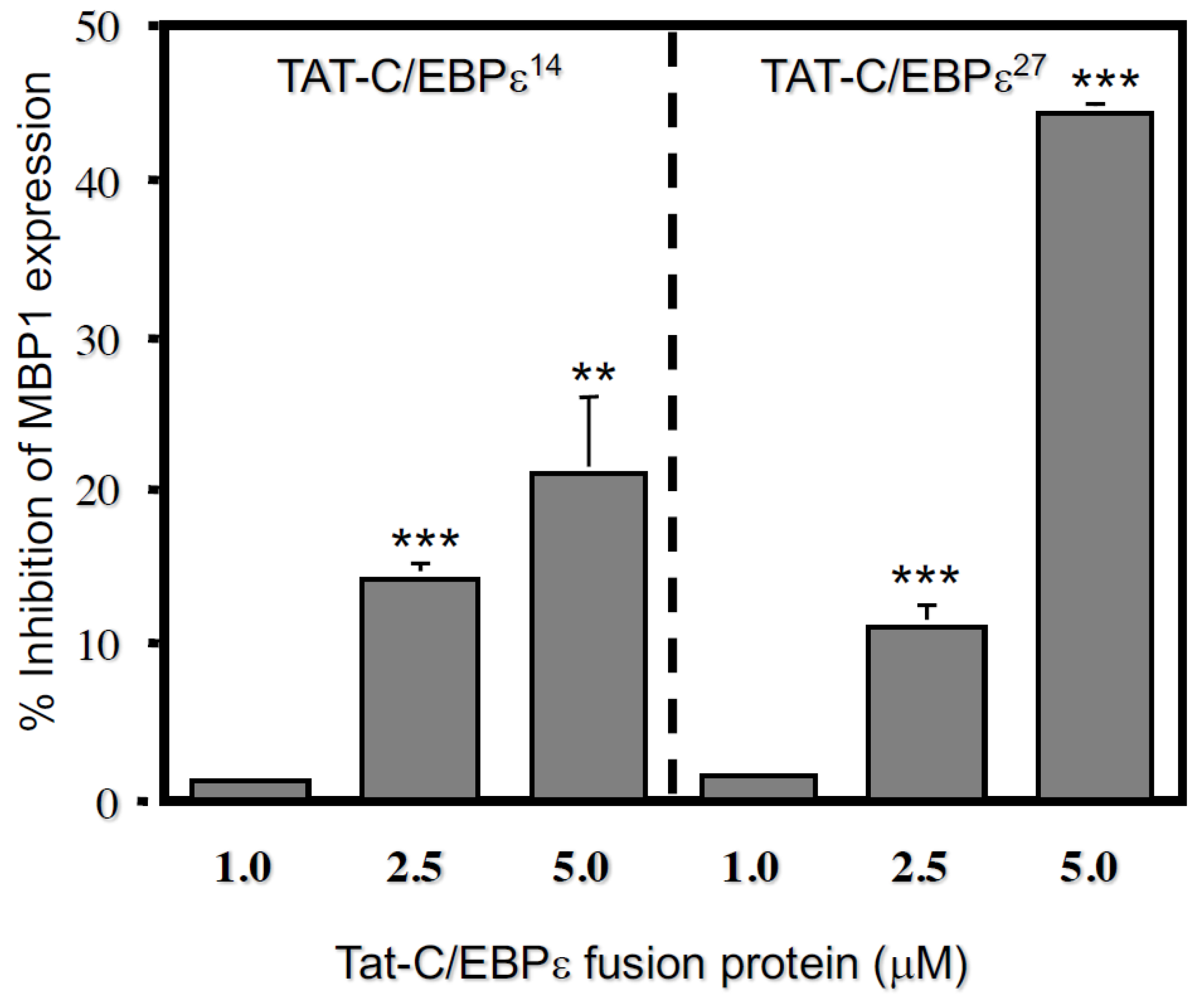
2.2. Transduction with a TAT-C/EBPε27 Fusion Protein Inhibits GATA-1 Transactivation of the MBP1-P2 Promoter in CV-1 Cells and Expression of the Endogenous MBP1 Gene in AML14.3D10 Eosinophils
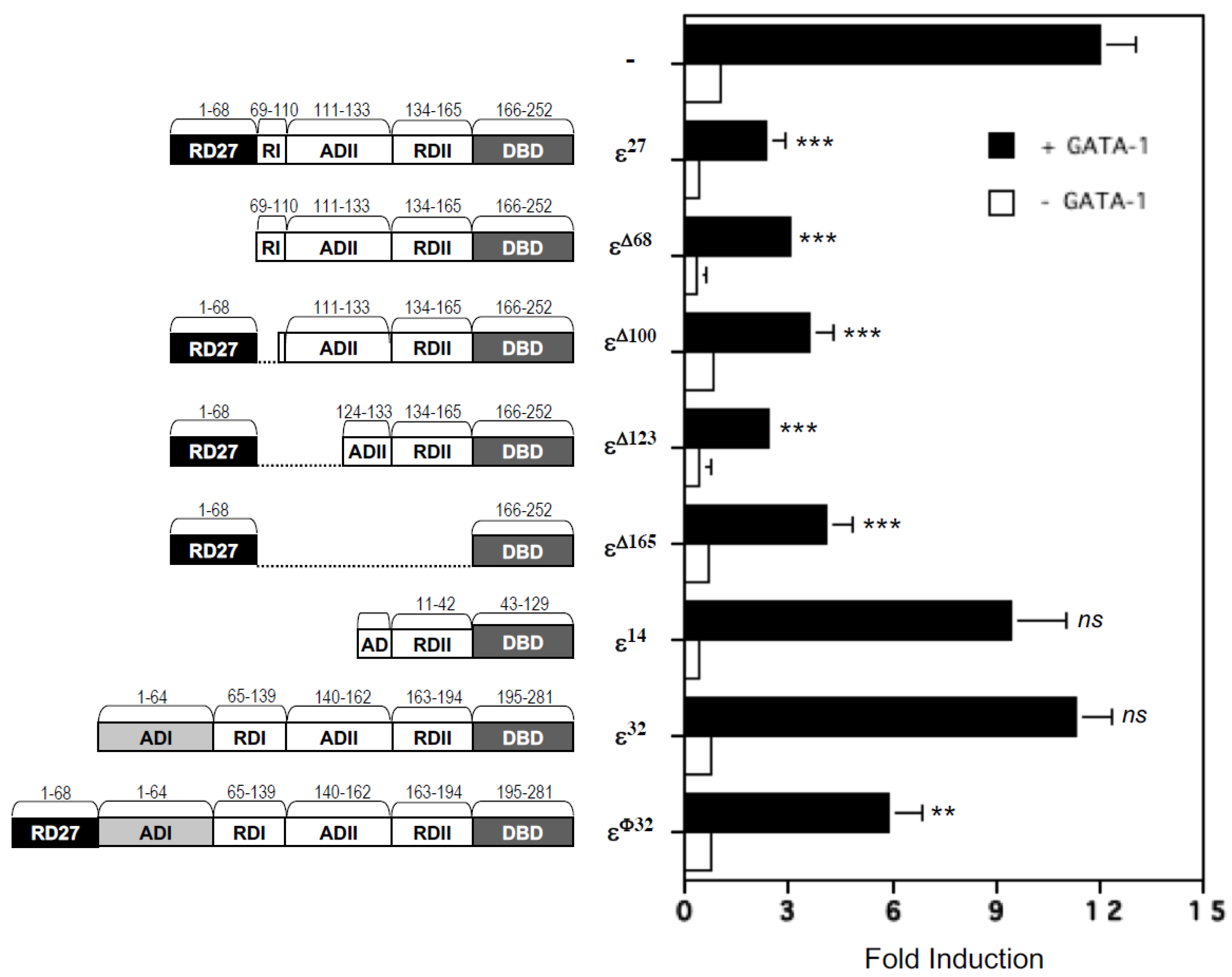
2.3. Repression Domains of C/EBPε27 Attenuate GATA-1 Transcriptional Activity: Both the Unique C/EBPε27 N-Terminus (RD27) and RDI Domains Inhibit GATA-1 Activity
2.4. C/EBPε Is Constitutively Sumoylated in Eosinophilic Myelocytes and in Heterologous Cells Transfected with a SUMO-1 Expression Vector
2.5. Over-Expression of SUMO-1 Has No Effect on C/EBPε27 Inhibition of GATA-1 Transactivation of the MBP1-P2 Promoter
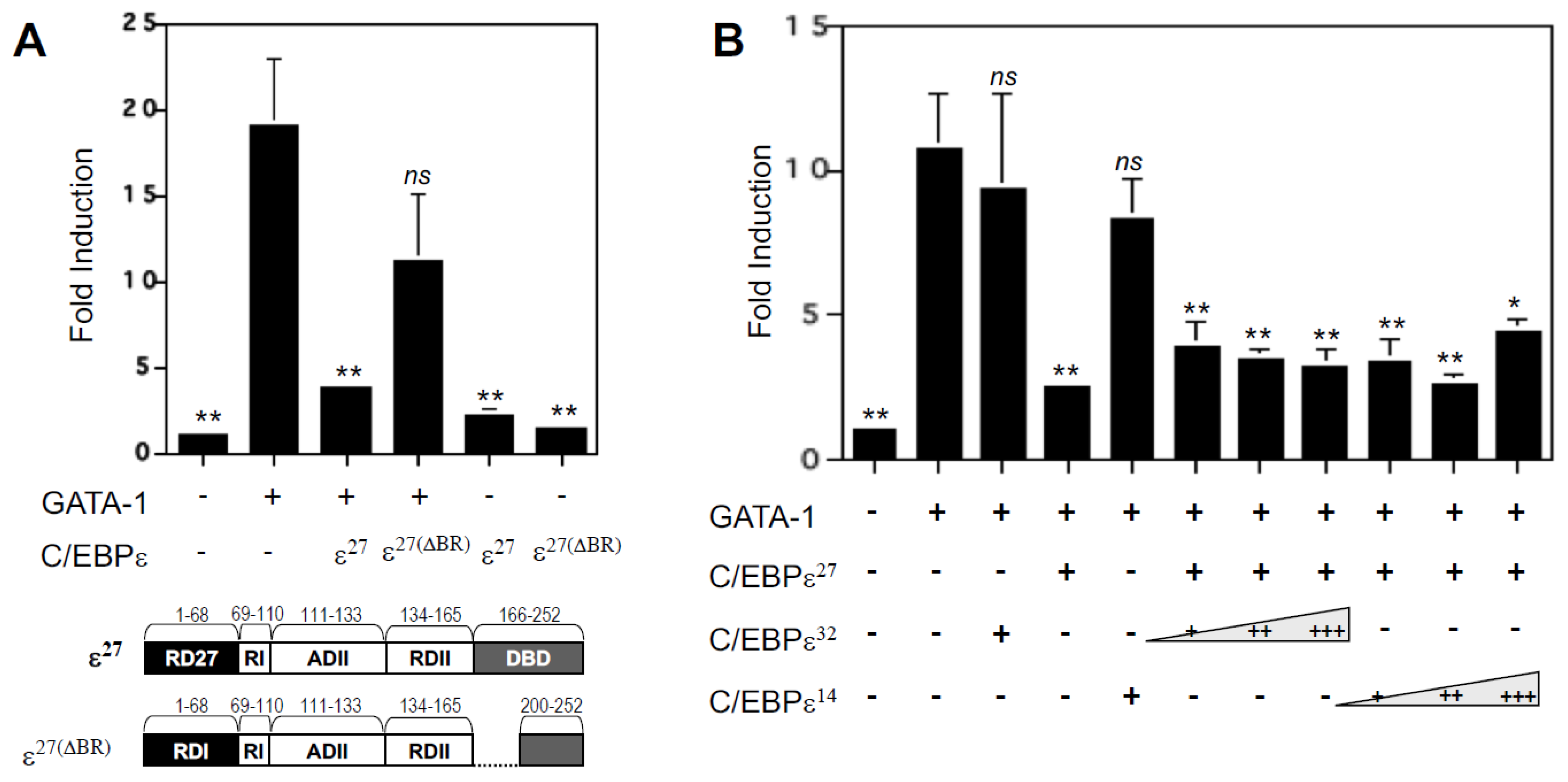
2.6. Deletion of the DNA Binding Domain of C/EBPε27 Only Partially Relieves Repressor Activity for GATA-1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Transfections
4.2. Plasmid Constructs
4.3. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
4.4. Tat-C/EBPε Fusion Proteins and Cell Transductions
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Yamanaka, R.; Kim, G.D.; Radomska, H.S.; Lekstrom-Himes, J.; Smith, L.T.; Antonson, P.; Tenen, D.G.; Xanthopoulos, K.G. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein epsilon is preferentially up-regulated during granulocytic differentiation and its functional versatility is determined by alternative use of promoters and differential splicing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 6462–6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williamson, E.A.; Xu, H.N.; Gombart, A.F.; Verbeek, W.; Chumakov, A.M.; Friedman, A.D.; Koeffler, H.P. Identification of transcriptional activation and repression domains in human CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein epsilon. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 14796–14804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morosetti, R.; Park, D.J.; Chumakov, A.M.; Grillier, I.; Shiohara, M.; Gombart, A.F.; Nakamaki, T.; Weinberg, K.; Koeffler, H.P. A novel, myeloid transcription factor, C/EBP epsilon, is upregulated during granulocytic, but not monocytic, differentiation. Blood 1997, 90, 2591–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.C.; Du, Y.; Schwartz, R.C.; Weiler, S.R.; Ortiz, M.; Keller, J.R.; Johnson, P.F. C/EBPepsilon is a myeloid-specific activator of cytokine, chemokine, and macrophage-colony-stimulating factor receptor genes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 13493–13501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamanaka, R.; Barlow, C.; Lekstrom-Himes, J.; Castilla, L.H.; Liu, P.P.; Eckhaus, M.; Decker, T.; Wynshaw-Boris, A.; Xanthopoulos, K.G. Impaired granulopoiesis, myelodysplasia, and early lethality in CCAAT/enhancer binding protein epsilon-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13187–13192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verbeek, W.; Wachter, M.; Lekstrom-Himes, J.; Koeffler, H.P. C/EBPε−/− mice: Increased rate of myeloid proliferation and apoptosis. Leukemia 2001, 15, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lekstrom-Himes, J.A.; Dorman, S.E.; Kopar, P.; Holland, S.M.; Gallin, J.I. Neutrophil-specific granule deficiency results from a novel mutation with loss of function of the transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein epsilon. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 1847–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gombart, A.F.; Shiohara, M.; Kwok, S.H.; Agematsu, K.; Komiyama, A.; Koeffler, H.P. Neutrophil-specific granule deficiency: Homozygous recessive inheritance of a frameshift mutation in the gene encoding transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein–epsilon. Blood 2001, 97, 2561–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, H.F.; Gallin, J.I. Neutrophil-specific granule deficiency includes eosinophils. Blood 1993, 82, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lekstrom-Himes, J.A. The role of C/EBP(epsilon) in the terminal stages of granulocyte differentiation. Stem. Cells 2001, 19, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Stankiewicz, M.J.; Liu, Y.; Xi, Q.; Schmitz, J.E.; Lekstrom-Himes, J.A.; Ackerman, S.J. Novel combinatorial interactions of GATA-1, PU.1, and C/EBPepsilon isoforms regulate transcription of the gene encoding eosinophil granule major basic protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 43481–43494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bedi, R.; Du, J.; Sharma, A.K.; Gomes, I.; Ackerman, S.J. Human C/EBP-epsilon activator and repressor isoforms differentially reprogram myeloid lineage commitment and differentiation. Blood 2009, 113, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirasawa, R.; Shimizu, R.; Takahashi, S.; Osawa, M.; Takayanagi, S.; Kato, Y.; Onodera, M.; Minegishi, N.; Yamamoto, M.; Fukao, K.; et al. Essential and instructive roles of GATA factors in eosinophil development. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Cantor, A.B.; Yang, H.; Browne, C.; Wells, R.A.; Fujiwara, Y.; Orkin, S.H. Targeted deletion of a high-affinity GATA-binding site in the GATA-1 promoter leads to selective loss of the eosinophil lineage in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Humbles, A.A.; Lloyd, C.M.; McMillan, S.J.; Friend, D.S.; Xanthou, G.; McKenna, E.E.; Ghiran, S.; Gerard, N.P.; Yu, C.; Orkin, S.H.; et al. A critical role for eosinophils in allergic airways remodeling. Science 2004, 305, 1776–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Ackerman, S.J.; Minegishi, N.; Takiguchi, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Suda, T. Mechanisms of transcription in eosinophils: GATA-1, but not GATA-2, transactivates the promoter of the eosinophil granule major basic protein gene. Blood 1998, 91, 3447–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Nishio, H.; Kishi, K.; Ackerman, S.J.; Suda, T. C/EBPbeta and GATA-1 synergistically regulate activity of the eosinophil granule major basic protein promoter: Implication for C/EBPbeta activity in eosinophil gene expression. Blood 1999, 94, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNagny, K.; Graf, T. Making eosinophils through subtle shifts in transcription factor expression. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, F43–F47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Cantwell, C.A.; Johnson, P.F.; Pfarr, C.M.; Williams, S.C. Transcriptional activity of CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins is controlled by a conserved inhibitory domain that is a target for sumoylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 38037–38044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanian, L.; Benson, M.D.; Iniguez-Lluhi, J.A. A synergy control motif within the attenuator domain of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha inhibits transcriptional synergy through its PIASy-enhanced modification by SUMO-1 or SUMO-3. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9134–9141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eaton, E.M.; Sealy, L. Modification of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-beta by the small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) family members, SUMO-2 and SUMO-3. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 33416–33421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verger, A.; Perdomo, J.; Crossley, M. Modification with SUMO. A role in transcriptional regulation. EMBO Rep. 2003, 4, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, C.C.; Mahrer, S.; Tolbert, M.; Elbert, B.L.; Wong, I.; Ackerman, S.J.; Baumann, M.A. Changing the differentiation program of hematopoietic cells: Retinoic acid-induced shift of eosinophil-committed cells to neutrophils. Blood 1995, 86, 3737–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumann, M.A.; Paul, C.C. The AML14 and AML14.3D10 cell lines: A long-overdue model for the study of eosinophils and more. Stem Cells 1998, 16, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakansson, S.; Jacobs, A.; Caffrey, M. Heparin binding by the HIV-1 tat protein transduction domain. Protein Sci. 2001, 10, 2138–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekstrom-Himes, J.; Xanthopoulos, K.G. Biological role of the CCAAT/Enhancer-binding protein family of transcription factors. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 28545–28548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angerer, N.D.; Du, Y.; Nalbant, D.; Williams, S.C. A short conserved motif is required for repressor domain function in the myeloid-specific transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein epsilon. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 4147–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ross, S.; Best, J.L.; Zon, L.I.; Gill, G. SUMO-1 modification represses Sp3 transcriptional activation and modulates its subnuclear localization. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadia, J.S.; Dowdy, S.F. Protein transduction technology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.J.; Cui, J.; Bates, M.E.; Stout, B.A.; Koenderman, L.; Coffer, P.J.; Bertics, P.J. Transduction of a dominant-negative H-Ras into human eosinophils attenuates extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation and interleukin-5-mediated cell viability. Blood 2001, 98, 2014–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagahara, H.; Vocero-Akbani, A.M.; Snyder, E.L.; Ho, A.; Latham, D.G.; Lissy, N.A.; Becker-Hapak, M.; Ezhevsky, S.A.; Dowdy, S.F. Transduction of full-length TAT fusion proteins into mammalian cells: TAT-p27Kip1 induces cell migration. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1449–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patruno, M.; Melotti, L.; Gomiero, C.; Sacchetto, R.; Topel, O.; Martinello, T. A mini-review of TAT-MyoD fused proteins: State of the art and problems to solve. Eur. J. Transl. Myol. 2017, 27, 6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Sharma, S.; Li, Y.; Cobos, E.; Palvimo, J.J.; Williams, S.C. Repression and coactivation of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein epsilon by sumoylation and protein inhibitor of activated STATx proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 12246–12254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gruart, V.; Truong, M.J.; Plumas, J.; Zandecki, M.; Kusnierz, J.P.; Prin, L.; Vinatier, D.; Capron, A.; Capron, M. Decreased expression of eosinophil peroxidase and major basic protein messenger RNAs during eosinophil maturation. Blood 1992, 79, 2592–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, J.G.; Koeffler, H.P. Structural and functional studies of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein epsilon. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 17739–17746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walkley, C.R.; Purton, L.E.; Snelling, H.J.; Yuan, Y.D.; Nakajima, H.; Chambon, P.; Chandraratna, R.A.; McArthur, G.A. Identification of the molecular requirements for an RAR alpha-mediated cell cycle arrest during granulocytic differentiation. Blood 2004, 103, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mack, E.A.; Stein, S.J.; Rome, K.S.; Xu, L.; Wertheim, G.B.; Melo, R.C.N.; Pear, W.S. Trib1 regulates eosinophil lineage commitment and identity by restraining the neutrophil program. Blood 2019, 133, 2413–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyamsunder, P.; Shanmugasundaram, M.; Mayakonda, A.; Dakle, P.; Teoh, W.W.; Han, L.; Kanojia, D.; Lim, M.C.; Fullwood, M.; An, O.; et al. Identification of a novel enhancer of CEBPE essential for granulocytic differentiation. Blood 2019, 133, 2507–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, H.; Watanabe, N.; Shibata, F.; Kitamura, T.; Ikeda, Y.; Handa, M. N-terminal Region of CCAAT/Enhancer-binding Protein epsilon is critical for cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and functional maturation during myeloid differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 14494–14502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wells, J.; Boyd, K.E.; Fry, C.J.; Bartley, S.M.; Farnham, P.J. Target gene specificity of E2F and pocket protein family members in living cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 5797–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, Y.; Rayman, J.B.; Dynlacht, B.D. Analysis of promoter binding by the E2F and pRB families in vivo: Distinct E2F proteins mediate activation and repression. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 804–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker-Hapak, M.; McAllister, S.S.; Dowdy, S.F. TAT-mediated protein transduction into mammalian cells. Methods 2001, 24, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stankiewicz, M.J.; Du, J.; Martinico, D.; Ackerman, S.J. CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein ε27 Antagonism of GATA-1 Transcriptional Activity in the Eosinophil Is Mediated by a Unique N-Terminal Repression Domain, Is Independent of Sumoylation and Does Not Require DNA Binding. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312689
Stankiewicz MJ, Du J, Martinico D, Ackerman SJ. CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein ε27 Antagonism of GATA-1 Transcriptional Activity in the Eosinophil Is Mediated by a Unique N-Terminal Repression Domain, Is Independent of Sumoylation and Does Not Require DNA Binding. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(23):12689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312689
Chicago/Turabian StyleStankiewicz, Monika J., Jian Du, Dominick Martinico, and Steven J. Ackerman. 2021. "CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein ε27 Antagonism of GATA-1 Transcriptional Activity in the Eosinophil Is Mediated by a Unique N-Terminal Repression Domain, Is Independent of Sumoylation and Does Not Require DNA Binding" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 23: 12689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312689
APA StyleStankiewicz, M. J., Du, J., Martinico, D., & Ackerman, S. J. (2021). CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein ε27 Antagonism of GATA-1 Transcriptional Activity in the Eosinophil Is Mediated by a Unique N-Terminal Repression Domain, Is Independent of Sumoylation and Does Not Require DNA Binding. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(23), 12689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312689




