The Keratinocyte as a Crucial Cell in the Predisposition, Onset, Progression, Therapy and Study of the Atopic Dermatitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
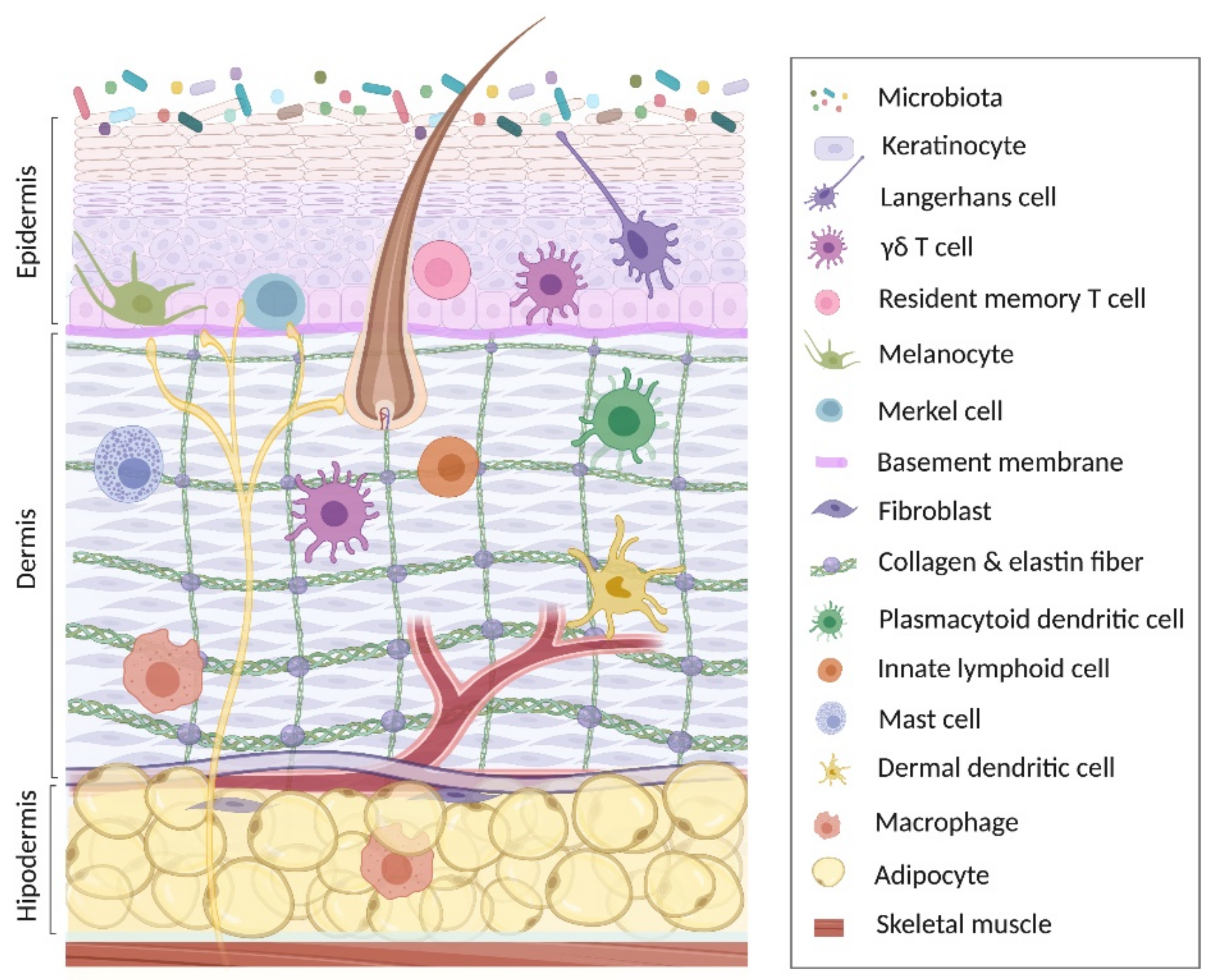
2. Keratinocyte in Skin Homeostasis
2.1. Proliferation Phase
2.2. Maturation Phase
2.3. Cornification Phase
3. Participation of Keratinocyte in Predisposition, Onset and Progression of the Atopic Dermatitis
3.1. Genetic Background of the Keratinocyte Predisposing to Atopic Dermatitis
| Structural Genes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | Polymorphism/ Mutations | Mechanism | Prevalent Populations | OR | Reference |
| FLG | P478S | Prevents the protease cleavage through serine phosphorylation, and then affects the FLG aggregation to keratin filaments | Asian (Taiwan) Asian (Korean) | 5.67 1.877 | [115,116] |
| 3321delA | Premature termination codon 41 bases downstream that stops protein translation in filaggrin repeat domain 2 | Asian | 3.54 | [112,117] | |
| S2554X, S2889X, S3296X, K4022X, R501X | Nonsense mutations | Asian | 3.54 | [112,117] | |
| 2282del4 | Deletion of four base pairs that results in a premature stop codon and complete loss of FLG production | Northern European European American African American | NR 5.6 2.5 | [118,119] | |
| Innate immune response | |||||
| TLR2 | R753Q | Alteration of the function of the intracellular signaling portion homologous to the IL-1 receptor designated as Toll/IL-1 receptor (TIR) domain. | German Italian | NR NR | [120] |
| R677W | Associated with reduced NF-κB activation and to increase the risk of bacterial infection | [121] | |||
| TLR4 | D299G | Impaired dimerization of TLR4 and MD-2 in presence of ligand | Italian | 2.46 | [122,123] |
| DEFB1 | A692G | Generates an NF-kB transcription factor-binding sequence in the position -20 of the 5′ untranslated region (5′ UTR) with a plausible effect on the expression of hBD2 | Mexican | 3.21 | [124] |
| G1654A | In exon 2, meaning a changed Val37Ile next to six conserved cysteine residues that could affect its folding | Mexican | 17.37 | [124] | |
| TSLP | rs11466749 | Means a change 813A/G | European American | 0.6 | [125,126] |
| rs10043985 | Means a change 597T/C | African American | 0.5 | [125,127] | |
| rs2289276 | Means a change 1350C/T | American African | 1.8 | [125,127] | |
3.2. The Keratinocyte in the Primary Origin of Atopic Dermatitis
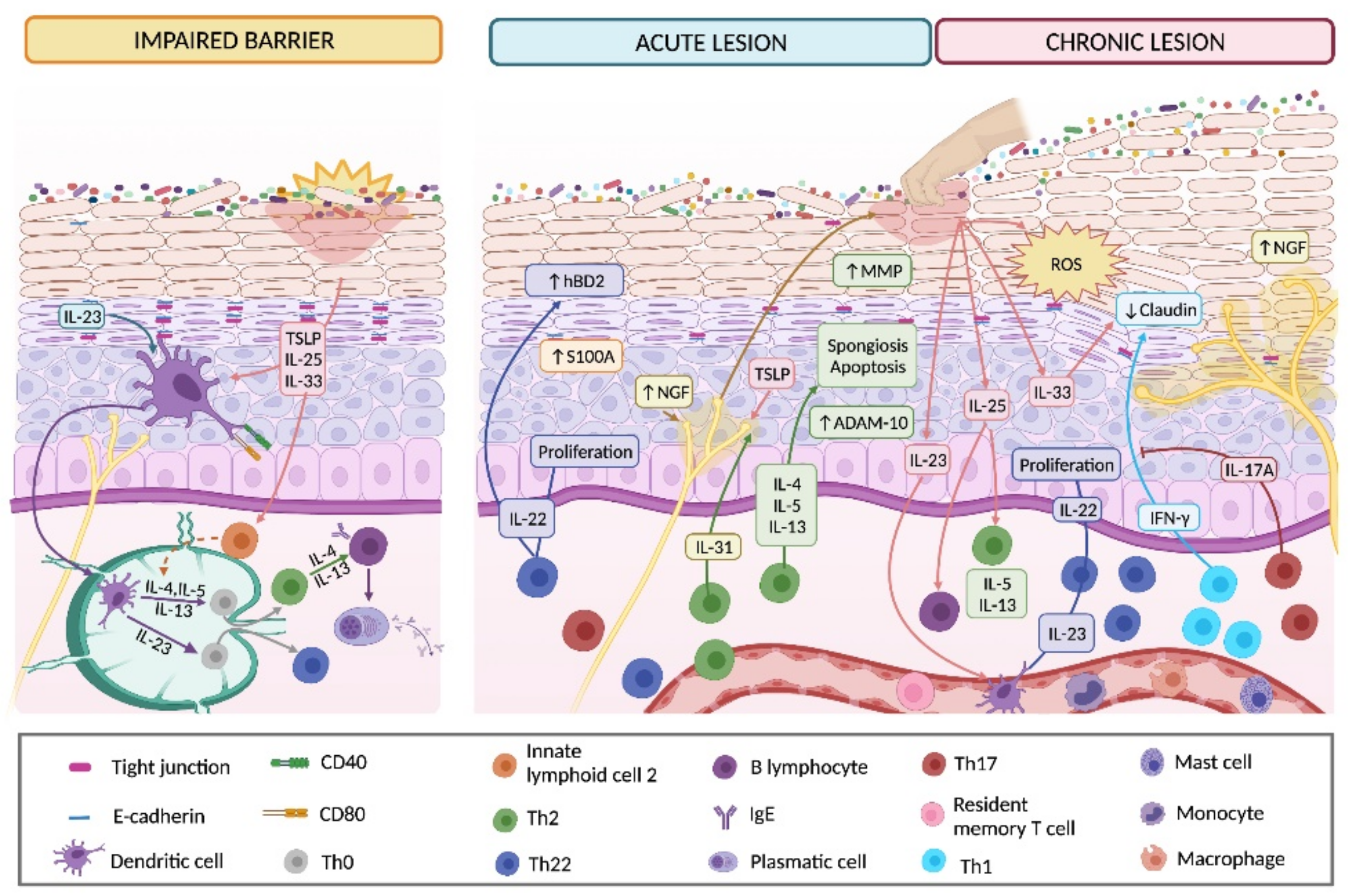
3.3. Involvement of Keratinocytes in Acute Lesions
3.4. Chronic Lesions and KC Participation
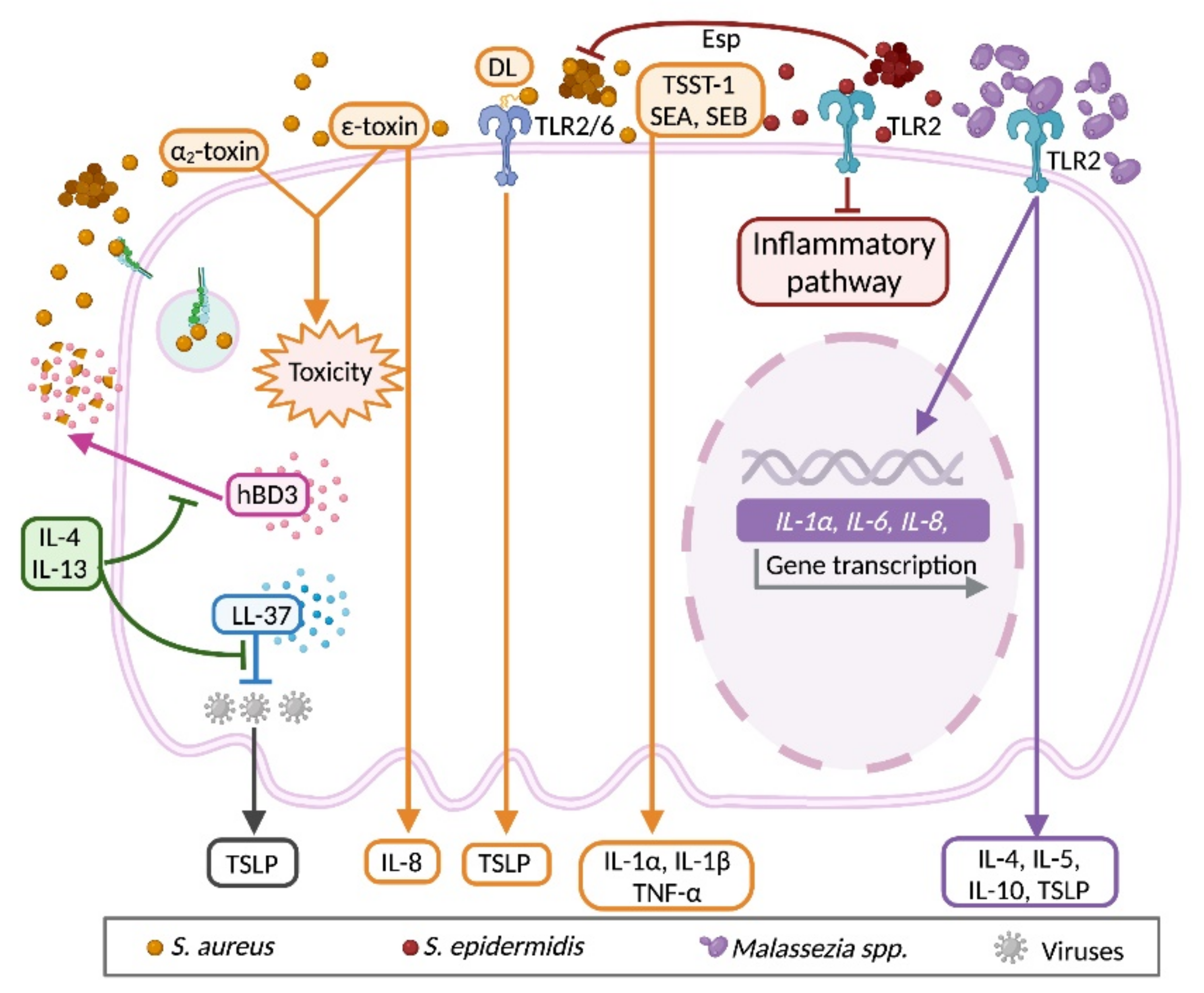
3.5. Bidirectional Communication between Keratinocyte and Microbiota
4. The Use of the Keratinocyte as an In Vitro Model of Atopic Dermatitis
5. Pharmacological Therapy to Restore Keratinocytes
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boniol, M.; Verriest, J.-P.; Pedeux, R.; Doré, J.-F. Proportion of Skin Surface Area of Children and Young Adults from 2 to 18 Years Old. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, R.L. Human Skin Is the Largest Epithelial Surface for Interaction with Microbes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1213–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.; Geyer, S.; Weninger, W.J.; Guimberteau, J.-C.; Wong, J.K. The dynamic anatomy and patterning of skin. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 25, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancerotto, L.; Stecco, C.; Macchi, V.; Porzionato, A.; Stecco, A.; De Caro, R. Layers of the abdominal wall: Anatomical investigation of subcutaneous tissue and superficial fascia. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2011, 33, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroni, A.; Buommino, E.; De Gregorio, V.; Ruocco, E.; Ruocco, V.; Wolf, R. Structure and function of the epidermis related to barrier properties. Clin. Dermatol. 2012, 30, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventre, M.; Mollica, F.; Netti, P.A. The effect of composition and microstructure on the viscoelastic properties of dermis. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittet, J.-C.; Freis, O.; Vazquez-Duchêne, M.-D.; Périé, G.; Pauly, G. Evaluation of Elastin/Collagen Content in Human Dermis in-Vivo by Multiphoton Tomography—Variation with Depth and Correlation with Aging. Cosmetics 2014, 1, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, J.D.; Teunissen, M.B.; Cairo, I.; Krieg, S.R.; Kapsenberg, M.L.; Das, P.K.; Borst, J. T-Cell Receptor γδ Bearing Cells in Normal Human Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1990, 94, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narbutt, J.; Lesiak, A.; Sysa-Jedrzejowska, A.; Smolewski, P.; Robak, T.; Zalewska, A. The number and distribution of blood dendritic cells in the epidermis and dermis of healthy human subjects. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2006, 44, 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- Toulon, A.; Breton, L.; Taylor, K.R.; Tenenhaus, M.; Bhavsar, D.; Lanigan, C.; Rudolph, R.; Jameson, J.; Havran, W.L. A role for human skin—resident T cells in wound healing. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, P.L.; Roediger, B.; Kolesnikoff, N.; Biro, M.; Tay, S.S.; Jain, R.; Shaw, L.E.; Grimbaldeston, M.A.; Weninger, W. The Skin Immune Atlas: Three-Dimensional Analysis of Cutaneous Leukocyte Subsets by Multiphoton Microscopy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkington, S.; Barron, M.; Watson, R.; Griffiths, C.; Bulfone-Paus, S. Aged human skin accumulates mast cells with altered functionality that localize to macrophages and vasoactive intestinal peptide-positive nerve fibres. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 180, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabashima, K.; Honda, T.; Ginhoux, F.; Egawa, G. The immunological anatomy of the skin. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 19, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.M.; Xu, H.; Wang, C.C.; Elmets, C.A. Proteomic characterization of skin and epidermis in response to environmental agents. Expert Rev. Proteomics 2005, 2, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartschuh, W.; Reinecke, M.; Weihe, E.; Yanaihara, N. VIP-immunoreactivity in the skin of various mammals: Immunohistochemical, radioimmunological and experimental evidence for a dual localization in cutaneous nerves and Merkel cells. Peptides 1984, 5, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga-Kalabis, M.; Martinez, G.; Liu, Z.-J.; Kalabis, J.; Mrass, P.; Weninger, W.; Firth, S.M.; Planque, N.; Perbal, B.; Herlyn, M. CCN3 controls 3D spatial localization of melanocytes in the human skin through DDR1. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 175, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, T.; Wakim, L.M.; Eidsmo, L.; Reading, P.; Heath, W.; Carbone, F.R. Memory T cells in nonlymphoid tissue that provide enhanced local immunity during infection with herpes simplex virus. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, P.A.; Miron, M.; Farber, D.L. Location, location, location: Tissue resident memory T cells in mice and humans. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4, eaas9673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edslev, S.; Olesen, C.; Nørreslet, L.; Ingham, A.; Iversen, S.; Lilje, B.; Clausen, M.-L.; Jensen, J.; Stegger, M.; Agner, T.; et al. Staphylococcal Communities on Skin Are Associated with Atopic Dermatitis and Disease Severity. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiger, M.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Neumann, A.U. The skin microbiome as a clinical biomarker in atopic eczema: Promises, navigation, and pitfalls. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; di Nardo, A.; Nakatsuji, T.; Leichtle, A.; Yang, Y.; Cogen, A.L.; Wu, Z.; Hooper, L.V.; von Aulock, S.; Radek, K.A.; et al. Commensal Bacteria Regulate TLR3-Dependent Inflammation Following Skin Injury. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemter, A.M.; Nagler, C.R. Influences on allergic mechanisms through gut, lung, and skin microbiome exposures. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, E.; Kong, H.; Conlan, S.; Deming, C.B.; Davis, J.; Young, A.C.; Bouffard, G.G.; Blakesley, R.W.; Murray, P.R.; Green, E.D.; et al. Topographical and Temporal Diversity of the Human Skin Microbiome. Science 2009, 324, 1190–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findley, K.; Program, N.I.S.C.C.S.; Oh, J.; Yang, J.; Conlan, S.; Deming, C.; Meyer, J.A.; Schoenfeld, D.; Nomicos, E.; Park, M.; et al. Topographic diversity of fungal and bacterial communities in human skin. Nature 2013, 498, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamimi, A.H.; Maxwell, S.; Edmonds, S.L.; Gerba, C.P. Impact of the use of an alcohol-based hand sanitizer in the home on reduction in probability of infection by respiratory and enteric viruses. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 3335–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldust, M.; Abdelmaksoud, A.; Navarini, A. Hand disinfection in the combat against COVID-19. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, e454–e455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foulongne, V.; Sauvage, V.; Hebert, C.; Dereure, O.; Cheval, J.; Gouilh, M.A.; Pariente, K.; Segondy, M.; Burguière, A.; Manuguerra, J.-C.; et al. Human Skin Microbiota: High Diversity of DNA Viruses Identified on the Human Skin by High Throughput Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.C.-H.; McMillan, N.; Antonsson, A. Human papillomavirus type spectrum in normal skin of individuals with or without a history of frequent sun exposure. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 2891–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechler, T.; Fuchs, E. Asymmetric cell divisions promote stratification and differentiation of mammalian skin. Nature 2005, 437, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, E.; De Paepe, K.; Rogiers, V. A Keratinocyte’s Course of Life. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 20, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiringer, P.; Eyerich, S.; Eyerich, K.; Dittlein, D.; Pilz, A.; Scala, E.; Ring, J.; Behrendt, H.; Cavani, A.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C. Keratinocytes Regulate the Threshold of Inflammation by Inhibiting T Cell Effector Functions. Cells 2021, 10, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-N.; Li, M. The Immune Function of Keratinocytes in Anti-Pathogen Infection in the Skin. Int. J. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 3, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebholz, B.; Haase, I.; Eckelt, B.; Paxian, S.; Flaig, M.J.; Ghoreschi, K.; Nedospasov, S.A.; Mailhammer, R.; Debey-Pascher, S.; Schultze, J.; et al. Crosstalk between Keratinocytes and Adaptive Immune Cells in an IκBα Protein-Mediated Inflammatory Disease of the Skin. Immunity 2007, 27, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Pawar, M.; Bothra, A.; Choudhary, N. Overzealous hand hygiene during the COVID 19 pandemic causing an increased incidence of hand eczema among general population. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, e37–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, M.; Fullard, N.; Costello, L.; Bradbury, S.; Markiewicz, E.; O’Reilly, S.; Darling, N.; Ritchie, P.; Määttä, A.; Karakesisoglou, I.; et al. Bioengineering the microanatomy of human skin. J. Anat. 2019, 234, 438–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leinonen, P.T.; Hägg, P.M.; Peltonen, S.; Jouhilahti, E.-M.; Melkko, J.; Korkiamäki, T.; Oikarinen, A.; Peltonen, J. Reevaluation of the Normal Epidermal Calcium Gradient, and Analysis of Calcium Levels and ATP Receptors in Hailey–Hailey and Darier Epidermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumamoto, J.; Goto, M.; Nagayama, M.; Denda, M. Real-time imaging of human epidermal calcium dynamics in response to point laser stimulation. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 86, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- In, M.K.; Richardson, K.C.; Loewa, A.; Hedtrich, S.; Kaessmeyer, S.; Plendl, J. Histological and functional comparisons of four anatomical regions of porcine skin with human abdominal skin. Anatomia Histologia Embryologia 2019, 48, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulais, N.; Misery, L. Merkel cells. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 57, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheuk, S.H.; Schlums, H.; Sérézal, I.G.; Martini, E.; Chiang, S.; Marquardt, N.; Gibbs, A.; Detlofsson, E.; Introini, A.; Forkel, M.; et al. CD49a Expression Defines Tissue-Resident CD8 + T Cells Poised for Cytotoxic Function in Human Skin. Immunity 2017, 46, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, A.; Mackay, L.; Rahimpour, A.; Braun, A.; Veldhoen, M.; Carbone, F.R.; Manton, J.H.; Heath, W.; Mueller, S.N. Persistence of skin-resident memory T cells within an epidermal niche. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5307–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, W.G.; Wayner, E.A.; Bouchard, T.S.; Kaur, P. The role of integrins alpha 2 beta 1 and alpha 3 beta 1 in cell-cell and cell-substrate adhesion of human epidermal cells. J. Cell Biol. 1990, 110, 1387–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennenbaum, T.; Li, L.; Belanger, A.J.; de Luca, L.M.; Yuspa, S.H. Selective Changes in Laminin Adhesion and A6β4 Integrin Regulation Are Associated with the Initial Steps in Keratinocyte Maturation. Cell Growth Differ. 1996, 7, 615–628. [Google Scholar]
- Purkis, P.; Steel, J.; Mackenzie, I.; Nathrath, W.; Leigh, I.; Lane, E. Antibody markers of basal cells in complex epithelia. J. Cell Sci. 1990, 97, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, A.; Kedeshian, P.A.; Dans, M.; Curatola, A.M.; Gagnoux-Palacios, L.; Giancotti, F.G. EGF-R signaling through Fyn kinase disrupts the function of integrin α6β4 at hemidesmosomes. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geuijen, C.A.W.; Sonnenberg, A. Dynamics of the α6β4 Integrin in Keratinocytes. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 3845–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margadant, C.; Charafeddine, R.A.; Sonnenberg, A. Unique and redundant functions of integrins in the epidermis. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 4133–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltmann, K.; Roth, W.; Kröger, C.; Loschke, F.; Lederer, M.; Hüttelmaier, S.; Magin, T.M. Keratins Mediate Localization of Hemidesmosomes and Repress Cell Motility. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, H.; Sehgal, L.; Kundu, S.; Dalal, S.N.; Vaidya, M.M. Novel function of keratins 5 and 14 in proliferation and differentiation of stratified epithelial cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 4068–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miroshnikova, Y.A.; Le, H.; Schneider, D.; Thalheim, T.; Rübsam, M.; Bremicker, N.; Polleux, J.; Kamprad, N.; Tarantola, M.; Wang, I.; et al. Adhesion forces and cortical tension couple cell proliferation and differentiation to drive epidermal stratification. Nature 2017, 20, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttagomol, J.; Ahmad, U.S.; Rehman, A.; Huang, Y.; Laly, A.C.; Kang, A.; Soetaert, J.; Chance, R.; Teh, M.-T.; Connelly, J.T.; et al. Evidence for the Desmosomal Cadherin Desmoglein-3 in Regulating YAP and Phospho-YAP in Keratinocyte Responses to Mechanical Forces. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.A.; Nelson, W.J.; Chavez, N. Cell—Cell Junctions Organize Structural and Signaling Networks. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 10, a029181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandner, J.M.; Haftek, M.; Niessen, C.M. Adherens Junctions, Desmosomes and Tight Junctions in Epidermal Barrier Function. Open Dermatol. J. 2010, 4, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan-Crispi, D.M.; Overmiller, A.M.; Tamayo-Orrego, L.; Marous, M.R.; Sahu, J.; McGuinn, K.P.; Cooper, F.; Georgiou, I.C.; Frankfurter, M.; Salas-Alanis, J.C.; et al. Overexpression of Desmoglein 2 in a Mouse Model of Gorlin Syndrome Enhances Spontaneous Basal Cell Carcinoma Formation through STAT3-Mediated Gli1 Expression. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deo, P.N.; Deshmukh, R. Pathophysiology of keratinization. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2018, 22, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroyasu, S.; Colburn, Z.T.; Jones, J.C.R. A hemidesmosomal protein regulates actin dynamics and traction forces in motile keratinocytes. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 2298–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pora, A.; Yoon, S.; Windoffer, R.; Leube, R.E. Hemidesmosomes and Focal Adhesions Treadmill as Separate but Linked Entities during Keratinocyte Migration. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1876–1888.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odland, G.F. A Submicroscopic Granular Component in Human Epidermis**From the Department of Anatomy, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1960, 34, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiszniewski, L.; Limat, A.; Saurat, J.-H.; Meda, P.; Salomon, D. Differential Expression of Connexins during Stratification of Human Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 115, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vela-Romera, A.; Carriel, V.; Martín-Piedra, M.A.; Aneiros-Fernández, J.; Campos, F.; Chato-Astrain, J.; Prados-Olleta, N.; Campos, A.; Alaminos, M.; Garzón, I. Characterization of the human ridged and non-ridged skin: A comprehensive histological, histochemical and immunohistochemical analysis. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 151, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandner, J.M.; Kief, S.; Grund, C.; Rendl, M.; Houdek, P.; Kuhn, C.; Tschachler, E.; Franke, W.W.; Moll, I. Organization and formation of the tight junction system in human epidermis and cultured keratinocytes. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 81, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Yokouchi, M.; Nagao, K.; Ishii, K.; Amagai, M.; Kubo, A. Functional tight junction barrier localizes in the second layer of the stratum granulosum of human epidermis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 71, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matter, K.; Balda, M.S. Functional analysis of tight junctions. Methods 2003, 30, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, L.; Roberts-Thompson, L.; Reichelt, J. Deletion of K1/K10 does not impair epidermal stratification but affects desmosomal structure and nuclear integrity. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillan, J.R.; Akiyama, M.; Shimizu, H.; Haftek, M.; South, A.P.; Perrot, H.; McGrath, J.; Eady, R.A. Alterations in Desmosome Size and Number Coincide with the Loss of Keratinocyte Cohesion in Skin with Homozygous and Heterozygous Defects in the Desmosomal Protein Plakophilin 1. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 121, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, O.J.; Brasch, J.; Lasso, G.; Katsamba, P.; Ahlsen, G.; Honig, B.; Shapiro, L. Structural basis of adhesive binding by desmocollins and desmogleins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7160–7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowndes, M.; Rakshit, S.; Shafraz, O.; Borghi, N.; Harmon, R.M.; Green, K.J.; Sivasankar, S.; Nelson, W.J. Different roles of cadherins in the assembly and structural integrity of the desmosome complex. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 2339–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rübsam, M.; Mertz, A.F.; Kubo, A.; Marg, S.; Jüngst, C.; Goranci-Buzhala, G.; Schauss, A.C.; Horsley, V.; Dufresne, E.R.; Moser, M.; et al. E-cadherin integrates mechanotransduction and EGFR signaling to control junctional tissue polarization and tight junction positioning. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, L.J.; Pei, X.F.; Watt, F.M.; Pie, X.F. Expression of E-cadherin, P-cadherin and involucrin by normal and neoplastic keratinocytes in culture. Carcinogenesis 1991, 12, 1345–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunggal, J.A.; Helfrich, I.; Schmitz, A.; Schwarz, H.; Günzel, D.; Fromm, M.; Kemler, R.; Krieg, T.; Niessen, C.M. E-cadherin is essential for in vivo epidermal barrier function by regulating tight junctions. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo-Orta, E.; Hoy, T.; Evans, W.H. Intercellular communication in the immune system: Differential expression of connexin 40 and 43, and perturbation of gap junction channel functions in peripheral blood and tonsil human lymphocyte subpopulations. Immunology 2000, 99, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, A.; Shao, Q.; White, K.K.; Lucaciu, S.A.; Esseltine, J.L.; Barr, K.; Laird, D.W. Comparative Analysis of Cx31 and Cx43 in Differentiation-Competent Rodent Keratinocytes. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanapathy, M.; Simpson, R.; Madden, L.; Thrasivoulou, C.; Mosahebi, A.; Becker, D.L.; Richards, T. Upregulation of epidermal gap junctional proteins in patients with venous disease. BJS 2017, 105, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, S.; Schmidt, R.; Shroot, B.; Reichert, U. Morphological and Biochemical Characterization of the Cornified Envelopes from Human Epidermal Keratinocytes of Different Origin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1988, 91, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steven, A.; Bisher, M.; Roop, D.; Steinert, P. Biosynthetic pathways of filaggrin and loricrin—two major proteins expressed by terminally differentiated epidermal keratinocytes. J. Struct. Biol. 1990, 104, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steven, A.; Steinert, P. Protein composition of cornified cell envelopes of epidermal keratinocytes. J. Cell Sci. 1994, 107, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida-Yamamoto, A.; Igawa, S.; Kishibe, M. Molecular basis of the skin barrier structures revealed by electron microscopy. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida-Yamamoto, A.; Kishibe, M.; Murakami, M.; Honma, M.; Takahashi, H.; Iizuka, H. Lamellar Granule Secretion Starts before the Establishment of Tight Junction Barrier for Paracellular Tracers in Mammalian Epidermis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida-Yamamoto, A.; Simon, M.; Kishibe, M.; Miyauchi, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Yoshida, S.; O’Brien, T.J.; Serre, G.; Iizuka, H. Epidermal Lamellar Granules Transport Different Cargoes as Distinct Aggregates. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A.; Ganz, T.; Liu, L.; Meerloo, T. In human epidermis, β-defensin 2 is packaged in lamellar bodies. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2003, 74, 180–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braff, M.H.; Di Nardo, A.; Gallo, R.L. Keratinocytes Store the Antimicrobial Peptide Cathelicidin in Lamellar Bodies. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, M.-L.; Slotved, H.-C.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Agner, T. Measurements of AMPs in stratum corneum of atopic dermatitis and healthy skin—tape stripping technique. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drislane, C.; Irvine, A. The role of filaggrin in atopic dermatitis and allergic disease. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 124, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, G.T.; Lim, S.E.; Jang, S.-I.; Morasso, M.I. Suprabasin, a Novel Epidermal Differentiation Marker and Potential Cornified Envelope Precursor. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 45195–45202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoshima, M.; Phadungsaksawasdi, P.; Nakazawa, S.; Iwasaki, M.; Sakabe, J.-I.; Umayahara, T.; Yatagai, T.; Ikeya, S.; Shimauchi, T.; Tokura, Y. Decreased expression of suprabasin induces aberrant differentiation and apoptosis of epidermal keratinocytes: Possible role for atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2019, 95, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haftek, M.; Teillon, M.-H.; Schmitt, D. Stratum corneum, corneodesmosomes and ex vivo percutaneous penetration. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1998, 43, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyai, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Yamanishi, H.; Yamamoto-Tanaka, M.; Tsuboi, R.; Hibino, T. Keratinocyte-Specific Mesotrypsin Contributes to the Desquamation Process via Kallikrein Activation and LEKTI Degradation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1665–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sextius, P.; Marionnet, C.; Bon, F.-X.; De La Chapelle, A.L.; Tacheau, C.; Lahfa, M.; Mauviel, A.; Bernard, B.A.; LeClaire, J.; Bernerd, F.; et al. Large scale study of epidermal recovery after stratum corneum removal: Dynamics of genomic response. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoste, E.; Kemperman, P.; Devos, M.; Denecker, G.; Kezic, S.; Yau, N.; Gilbert, B.; Lippens, S.; De Groote, P.; Roelandt, R.; et al. Caspase-14 Is Required for Filaggrin Degradation to Natural Moisturizing Factors in the Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 2233–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabanillas, B.; Novak, N. Atopic dermatitis and filaggrin. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 42, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, E.; Jensen, J.-M.; Elias, P.M. Skin lipids and epidermal differentiation in atopic dermatitis. Clin. Dermatol. 2003, 21, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caussin, J.; Gooris, G.S.; Janssens, M.; Bouwstra, J.A. Lipid organization in human and porcine stratum corneum differs widely, while lipid mixtures with porcine ceramides model human stratum corneum lipid organization very closely. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2008, 1778, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambers, H.; Piessens, S.; Bloem, A.; Pronk, H.; Finkel, P. Natural skin surface pH is on average below 5, which is beneficial for its resident flora. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2006, 28, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nodake, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; Miura, R.; Honda, H.; Ishibashi, G.; Matsumoto, S.; Dekio, I.; Sakakibara, R. Pilot study on novel skin care method by augmentation with Staphylococcus epidermidis, an autologous skin microbe—A blinded randomized clinical trial. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 79, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proksch, E. pH in nature, humans and skin. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vessey, D.A.; Lee, K.-H.; Boyer, T.D. Differentiation-Induced Enhancement of the Ability of Cultured Human Keratinocytes to Suppress Oxidative Stress. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1995, 104, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeij, W.; Alia, A.; Backendorf, C. ROS Quenching Potential of the Epidermal Cornified Cell Envelope. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindo, Y.; Witt, E.; Han, D.; Epstein, W.; Packer, L. Enzymic and Non-Enzymic Antioxidants in Epidermis and Dermis of Human Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1994, 102, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.T.; Chew, F.T. A systematic review and meta-analysis of risk factors associated with atopic dermatitis in Asia. World Allergy Organ. J. 2020, 13, 100477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meylan, P.; Lang, C.; Mermoud, S.; Johannsen, A.; Norrenberg, S.; Hohl, D.; Vial, Y.; Prod’Hom, G.; Greub, G.; Kypriotou, M.; et al. Skin Colonization by Staphylococcus aureus Precedes the Clinical Diagnosis of Atopic Dermatitis in Infancy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; Nakatsuji, T.; Sanford, J.; Vrbanac, A.F.; Gallo, R.L. Staphylococcus aureus Induces Increased Serine Protease Activity in Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 137, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin, L.; Leung, D.Y.M. Genetic and epigenetic studies of atopic dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2016, 12, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez-Fariñas, M.; N Dhingra, B.; Gittler, J.; Shemer, A.; Cardinale, I.; de Strong, C.G.; Krueger, J.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Intrinsic Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Shows Similar Th2 and Higher Th17 Immune Activation Compared to Extrinsic AD. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 132, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittler, J.K.; Shemer, A.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Gulewicz, K.J.; Wang, C.Q.; Mitsui, H.; Cardinale, I.; Strong, C.D.G.; Krueger, J.G.; et al. Progressive activation of TH2/TH22 cytokines and selective epidermal proteins characterizes acute and chronic atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esaki, H.; Brunner, P.; Renert-Yuval, Y.; Czarnowicki, T.; Huynh, T.; Tran, G.; Lyon, S.; Rodriguez, G.; Immaneni, S.; Johnson, D.B.; et al. Early-onset pediatric atopic dermatitis is T H 2 but also T H 17 polarized in skin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1639–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, P.M.; Steinhoff, M. “Outside-to-Inside” (and Now Back to “Outside”) Pathogenic Mechanisms in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1067–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdyshev, E.; Goleva, E.; Bronova, I.; Dyjack, N.; Rios, C.; Jung, J.; Taylor, P.; Jeong, M.; Hall, C.F.; Richers, B.N.; et al. Lipid abnormalities in atopic skin are driven by type 2 cytokines. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e98006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamsteeg, M.; Bergers, M.; de Boer, R.; Zeeuwen, P.; Hato, S.V.; Schalkwijk, J.; Tjabringa, G.S. Type 2 Helper T-Cell Cytokines Induce Morphologic and Molecular Characteristics of Atopic Dermatitis in Human Skin Equivalent. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 2091–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, G.J.; Archer, N.K.; Miller, L.S. Which Way Do We Go? Complex Interactions in Atopic Dermatitis Pathogenesis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 141, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebok, B.; Schneider, I.; Harangi, F.; Countys, P.C.P.I.B. Familiar and environmental factors influencing atopic dermatitis in the childhood. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2006, 20, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhme, M.; Wickman, M.; Nordvall, S.L.; Svartengren, M.; Wahlgren, C.F. Family history and risk of atopic dermatitis in children up to 4 years. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2003, 33, 1226–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseki, R.; Morii, W.; Noguchi, E.; Ishikawa, M.; Yang, L.; Yamamoto-Hanada, K.; Narita, M.; Saito, H.; Ohya, Y. Effect of filaggrin loss-of-function mutations on atopic dermatitis in young age: A longitudinal birth cohort study. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 64, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toncic, R.J.; Kezic, S.; Jakasa, I.; Hadzavdic, S.L.; Balic, A.; Petkovic, M.; Pavicic, B.; Zuzul, K.; Marinovic, B. Filaggrin loss-of-function mutations and levels of filaggrin degradation products in adult patients with atopic dermatitis in Croatia. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 1789–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, M.D.; Kim, B.E.; Gao, P.; Grant, A.V.; Boguniewicz, M.; DeBenedetto, A.; Schneider, L.; Beck, L.A.; Barnes, K.C.; Leung, D.Y. Cytokine modulation of atopic dermatitis filaggrin skin expression. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Yang, S.W.; Kim, H.-L.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, S.J.; Park, S.-M.; Son, M.; Ryu, S.; Pyo, Y.-S.; Lee, J.-S.; et al. Association between P478S polymorphism of the filaggrin gene & atopic dermatitis. Indian J. Med. Res. 2013, 138, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, I.; Lin, T.; Kuo, C.; Lin, S.; Lee, Y.; Chen, P.-C. Filaggrin polymorphism P478S, IgE level, and atopic phenotypes. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 164, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, T.; Sandilands, A.; Akiyama, M.; Liao, H.; Evans, A.T.; Sakai, K.; Ota, M.; Sugiura, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Sato, H.; et al. Unique mutations in the filaggrin gene in Japanese patients with ichthyosis vulgaris and atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, C.; Irvine, A.; Terron-Kwiatkowski, A.; Zhao, Y.; Liao, H.; Lee, S.P.; Goudie, D.R.; Sandilands, A.; Campbell, L.E.; Smith, F.J.D.; et al. Common loss-of-function variants of the epidermal barrier protein filaggrin are a major predisposing factor for atopic dermatitis. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.-S.; Rafaels, N.M.; Hand, T.; Murray, T.; Boguniewicz, M.; Hata, T.; Schneider, L.; Hanifin, J.M.; Gallo, R.; Gao, L.; et al. Filaggrin mutations that confer risk of atopic dermatitis confer greater risk for eczema herpeticum. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 507–513.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad-Nejad, P.; Mrabet-Dahbi, S.; Breuer, K.; Klotz, M.; Werfel, T.; Herz, U.; Heeg, K.; Neumaier, M.; Renz, H. The Toll-like receptor 2 R753Q polymorphism defines a subgroup of patients with atopic dermatitis having severe phenotype. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 565–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, M.A.; Ramadan, M.M.; Arram, E.O. Toll-like Receptor-2 Arg753Gln and Arg677Trp Polymorphisms and Susceptibility to Pulmonary and Peritoneal Tuberculosis. APMIS 2017, 125, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakawa, N.; Ohto, U.; Akashi-Takamura, S.; Takahashi, K.; Saitoh, S.-I.; Tanimura, N.; Suganami, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Shibata, T.; Shimizu, T.; et al. Human TLR4 polymorphism D299G/T399I alters TLR4/MD-2 conformation and response to a weak ligand monophosphoryl lipid A. Int. Immunol. 2012, 25, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salpietro, C.; Rigoli, L.; Del Giudice, M.M.; Cuppari, C.; Di Bella, C.; Maiello, N.; La Rosa, M.; Marseglia, G.; Leonardi, S.; Briuglia, S.; et al. TLR2 and TLR4 Gene Polymorphisms and Atopic Dermatitis in Italian Children: A Multicenter Study. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2011, 24, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oca, E.P.-M.; García-Vargas, A.; Lozano-Inocencio, R.; Gallegos-Arreola, M.P.; Sandoval-Ramírez, L.; Dávalos-Rodríguez, N.O.; Figuera, L.E. Association of β-Defensin 1 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms with Atopic Dermatitis. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2006, 142, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.-S.; Rafaels, N.M.; Mu, D.; Hand, T.; Murray, T.; Boguniewicz, M.; Hata, T.; Schneider, L.; Hanifin, J.M.; Gallo, R.; et al. Genetic variants in thymic stromal lymphopoietin are associated with atopic dermatitis and eczema herpeticum. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 1403–1407.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, W.I.; Park, K.Y.; Lee, M.-K.; Moon, N.J.; Seo, S.J. TSLP Polymorphisms in Atopic Dermatitis and Atopic March in Koreans. Ann. Dermatol. 2018, 30, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semlali, A.; Almutairi, M.; Azzi, A.; Parine, N.R.; Alamri, A.; Alsulami, S.; Alumri, T.M.; Alanazi, M.S.; Rouabhia, M. TSLP and TSLP receptors variants are associated with smoking. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, K.; Torres, V. Staphylococcus aureus Secreted Toxins and Extracellular Enzymes. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, A.T.; Baba, T.; Chen, X.; Le, T.A.; Kinoshita, H.; Xie, Y.; Kamijo, S.; Hiramatsu, K.; Ikeda, S.; Ogawa, H.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus membrane and diacylated lipopeptide induce thymic stromal lymphopoietin in keratinocytes through the Toll-like receptor 2–Toll-like receptor 6 pathway. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 985–993.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.; Mira, J.P.; Cornish, K.L.; Arbour, N.C.; Schwartz, D.A. A Novel Polymorphism in the Toll-Like Receptor 2 Gene and Its Potential Association with Staphylococcal Infection. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 6398–6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.-J. Detection of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) mutation in the lepromatous leprosy patients. FEMS Immunol. Med Microbiol. 2001, 31, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.; Mira, J.P.; Frees, K.L.; Schwartz, D.A. Relevance of Mutations in the TLR4 Receptor in Patients With Gram-Negative Septic Shock. Arch. Intern. Med. 2002, 162, 1028–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwase, T.; Uehara, Y.; Shinji, H.; Tajima, A.; Seo, H.; Takada, K.; Agata, T.; Mizunoe, Y. Staphylococcus epidermidis Esp inhibits Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation and nasal colonization. Nature 2010, 465, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurevic, R.; Chrisman, P.; Mancl, L.; Livingston, R.; Dale, B. Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Haplotype Analysis inβ-Defensin Genes in Different Ethnic Populations. Genet. Test. 2002, 6, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurevic, R.J.; Bai, M.; Chadwick, R.B.; White, T.C.; Dale, B.A. Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Human β-Defensin 1: High-Throughput SNP Assays and Association with Candida Carriage in Type I Diabetics and Nondiabetic Controls. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demehri, S.; Morimoto, M.; Holtzman, M.J.; Kopan, R. Skin-Derived TSLP Triggers Progression from Epidermal-Barrier Defects to Asthma. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e1000067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidinger, S.; Beck, L.A.; Bieber, T.; Kabashima, K.; Irvine, A.D. Atopic dermatitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Tintle, S.J.; Shemer, A.; Chiricozzi, A.; Nograles, K.; Cardinale, I.; Duan, S.; Bowcock, A.; Krueger, J.G.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Nonlesional atopic dermatitis skin is characterized by broad terminal differentiation defects and variable immune abnormalities. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 954–964.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokura, Y.; Hayano, S. Subtypes of atopic dermatitis: From phenotype to endotype. Allergol. Int. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Linse, F.; Heller, R.; Moths, C.; Goebel, R.; Neumann, C. Adhesion molecules in atopic dermatitis: VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression is increased in healthy-appearing skin. Allergy 1996, 51, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwingen, J.; Kaplan, M.; Kurschus, F.C. Review—Current Concepts in Inflammatory Skin Diseases Evolved by Transcriptome Analysis: In-Depth Analysis of Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, D.; Ding, L.; Sivaprasad, U.; Geh, E.; Myers, J.B.; Bernstein, J.A.; Hershey, G.K.K.; Mersha, T.B. Multiple Transcriptome Data Analysis Reveals Biologically Relevant Atopic Dermatitis Signature Genes and Pathways. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.E.; Leung, D.Y.; Boguniewicz, M.; Howell, M.D. Loricrin and involucrin expression is down-regulated by Th2 cytokines through STAT-6. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 126, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaisin, Y.; Ratanachamnong, P.; Wongsawattkul, O.; Watthammawut, A.; Malaniyom, K.; Natewong, S. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of piperine on UV-B-irradiated human HaCaT keratinocyte cells. Life Sci. 2020, 263, 118607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-B.; Kang, O.-H.; Joung, D.-K.; Mun, S.-H.; Seo, Y.-S.; Cha, M.-R.; Ryu, S.-Y.; Shin, D.-W.; Kwon, D.-Y. Anti-inflammatory effects of tectroside on UVB-induced HaCaT cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, X.; Zhong, F. Nickel Induces Interleukin-1β Secretion via the NLRP3-ASC—Caspase-1 Pathway. Inflammation 2013, 37, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, Y.; Jeong, S.H.; Park, Y.-H.; Bae, H.C.; Lee, H.; Ryu, W.-I.; Park, G.H.; Son, S.W. UVB Induces HIF-1α-Dependent TSLP Expression via the JNK and ERK Pathways. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 2601–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, L.T.N.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.; Lee, Y.C. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Human Skin Diseases Due to Particulate Matter. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.-P.; Li, Z.; Choi, E.K.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.K.; Seo, E.Y.; Chung, J.H.; Cho, S. Urban particulate matter in air pollution penetrates into the barrier-disrupted skin and produces ROS-dependent cutaneous inflammatory response in vivo. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 91, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidaka, T.; Ogawa, E.; Kobayashi, E.H.; Suzuki, T.; Funayama, R.; Nagashima, T.; Fujimura, T.; Aiba, S.; Nakayama, K.; Okuyama, R.; et al. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor AhR links atopic dermatitis and air pollution via induction of the neurotrophic factor artemin. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 18, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onami, K.; Kimura, Y.; Ito, Y.; Yamauchi, T.; Yamasaki, K.; Aiba, S. Nonmetal Haptens Induce ATP Release from Keratinocytes through Opening of Pannexin Hemichannels by Reactive Oxygen Species. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1951–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, P.R.; Wölfle, U.; Dürr, C.; Von Loewenich, F.D.; Schempp, C.M.; Freudenberg, M.A.; Jakob, T.; Martin, S.F. Contact Sensitizers Induce Skin Inflammation via ROS Production and Hyaluronic Acid Degradation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Leyva-Castillo, J.M.; Wang, G.; Galand, C.; Oyoshi, M.K.; Kumar, L.; Hoff, S.; He, R.; Chervonsky, A.; Oppenheim, J.J.; et al. IL-23 induced in keratinocytes by endogenous TLR4 ligands polarizes dendritic cells to drive IL-22 responses to skin immunization. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 2147–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Sayama, K.; Tohyama, M.; Shirakata, Y.; Hanakawa, Y.; Tokumaru, S.; Yang, L.; Hirakawa, S.; Hashimoto, K. Mite allergen is a danger signal for the skin via activation of inflammasome in keratinocytes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 806–814.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.H.; Choi, J.K.; Jin, M.; Choi, Y.-A.; Ryoo, Z.Y.; Lee, H.-S.; Park, P.-H.; Kim, S.-U.; Kwon, T.K.; Jang, M.H.; et al. House Dust Mite Increases pro-Th2 Cytokines IL-25 and IL-33 via the Activation of TLR1/6 Signaling. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 2354–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, A.; Kubo, T.; Kawata, K.; Kamekura, R.; Yamashita, K.; Jitsukawa, S.; Nagaya, T.; Sumikawa, Y.; Himi, T.; Yamashita, T.; et al. Keratinocytes in atopic dermatitis express abundant ΔNp73 regulating thymic stromal lymphopoietin production via NF-κB. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 88, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.M.L.; Hener, P.; Jiang, H.; Li, M. TSLP Produced by Keratinocytes Promotes Allergen Sensitization through Skin and Thereby Triggers Atopic March in Mice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soumelis, V.; Reche, P.; Kanzler, H.; Yuan, W.; Edward, G.; Homey, B.; Gilliet, M.; Ho, S.; Antonenko, S.; Lauerma, A.; et al. Human epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell—mediated allergic inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Castillo, J.M.; Galand, C.; Mashiko, S.; Bissonnette, R.; McGurk, A.; Ziegler, S.F.; Dong, C.; McKenzie, A.N.; Sarfati, M.; Geha, R.S. ILC2 activation by keratinocyte-derived IL-25 drives IL-13 production at sites of allergic skin inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 1606–1614.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimi, M.; Barlow, J.L.; Saunders, S.; Xue, L.; Gutowska-Owsiak, D.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.-C.; Johnson, D.; Scanlon, S.T.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; et al. A role for IL-25 and IL-33—driven type-2 innate lymphoid cells in atopic dermatitis. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 2939–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savinko, T.; Matikainen, S.; Saarialho-Kere, U.; Lehto, M.; Wang, G.; Lehtimäki, S.; Karisola, P.; Reunala, T.; Wolff, H.; Lauerma, A.; et al. IL-33 and ST2 in Atopic Dermatitis: Expression Profiles and Modulation by Triggering Factors. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1392–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, P.; Avcil, S.; Neşelioğlu, S.; Biçer, C.; Çatal, F. Association of oxidative stress and dynamic thiol-disulphide homeostasis with atopic dermatitis severity and chronicity in children: A prospective study. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 43, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, H.; Takai, T.; Le, T.A.; Kamijo, S.; Wang, X.L.; Ushio, H.; Hara, M.; Kawasaki, J.; Vu, A.T.; Ogawa, T.; et al. Cytokine milieu modulates release of thymic stromal lymphopoietin from human keratinocytes stimulated with double-stranded RNA. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.A.; Takai, T.; Vu, A.T.; Kinoshita, H.; Chen, X.; Ikeda, S.; Ogawa, H.; Okumura, K. Flagellin Induces the Expression of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin in Human Keratinocytes via Toll-Like Receptor 5. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 155, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogiatzi, S.I.; Fernandez, I.; Bichet, J.-C.; Marloie-Provost, M.-A.; Volpe, E.; Sastre, X.; Soumelis, V. Cutting Edge: Proinflammatory and Th2 Cytokines Synergize to Induce Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Production by Human Skin Keratinocytes. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 3373–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Siracusa, M.C.; Saenz, S.A.; Noti, M.; Monticelli, L.A.; Sonnenberg, G.F.; Hepworth, M.; Van Voorhees, A.S.; Comeau, M.R.; Artis, D. TSLP Elicits IL-33-Independent Innate Lymphoid Cell Responses to Promote Skin Inflammation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 170ra16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, Y.; Yasuda, K.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Haneda, T.; Mizutani, H.; Yoshimoto, T.; Nakanishi, K.; Yamanishi, K. Skin-specific expression of IL-33 activates group 2 innate lymphoid cells and elicits atopic dermatitis-like inflammation in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13921–13926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.Y.M.; Boguniewicz, M.; Howell, M.D.; Nomura, I.; Hamid, Q.A. New Insights into Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, N.; Peters, A.T. Atopic dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2019, 40, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivry, T.; Mayhew, D.; Paps, J.S.; Linder, K.E.; Peredo, C.; Rajpal, D.; Hofland, H.; Cote-Sierra, J. Early Activation of Th2/Th22 Inflammatory and Pruritogenic Pathways in Acute Canine Atopic Dermatitis Skin Lesions. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Ma, W.; Yan, J.; Zhong, H. Evaluation of the effects of IL-22 on the proliferation and differentiation of keratinocytes in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 2715–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, T.; Memezawa, A.; Okuyama, R.; Sayo, T.; Sugiyama, Y.; Inoue, S.; Aiba, S. Increased Hyaluronan Production and Decreased E-Cadherin Expression by Cytokine-Stimulated Keratinocytes Lead to Spongiosis Formation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 1412–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maretzky, T.; Scholz, F.; Köten, B.; Proksch, E.; Saftig, P.; Reiss, K. ADAM10-Mediated E-Cadherin Release Is Regulated by Proinflammatory Cytokines and Modulates Keratinocyte Cohesion in Eczematous Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1737–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, J.; Godwin, H.; Green, A.; Wilkes, L.; Holden, N.; Moffatt, M.; Cookson, W.; Layton, G.; Chandler, S. A study of matrix metalloproteinase expression and activity in atopic dermatitis using a novel skin wash sampling assay for functional biomarker analysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 162, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhrl, J.; Yang, D.; Oppenheim, J.J.; Hehlgans, T. Human β-Defensin 2 and 3 and Their Mouse Orthologs Induce Chemotaxis through Interaction with CCR2. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 6688–6694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soruri, A.; Grigat, J.; Forssmann, U.; Riggert, J.; Zwirner, J. β-Defensins chemoattract macrophages and mast cells but not lymphocytes and dendritic cells: CCR6 is not involved. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 2474–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.-G.; Bai, X.; Huang, X.F.; Yao, C.; Chen, S.Y. Phenotypic knockout of HIV type 1 chemokine coreceptor CCR-5 by intrakines as potential therapeutic approach for HIV-1 infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 11567–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DaSilva-Arnold, S.C.; Thyagarajan, A.; Seymour, L.J.; Yi, Q.; Bradish, J.R.; Al-Hassani, M.; Zhou, H.; Perdue, N.J.; Nemeth, V.; Krbanjevic, A.; et al. Phenotyping acute and chronic atopic dermatitis-like lesions in Stat6VT mice identifies a role for IL-33 in disease pathogenesis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2018, 310, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, W.-I.; Lee, H.; Bae, H.C.; Jeon, J.; Ryu, H.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; Son, J.W.; Imai, Y.; Yamanishi, K.; et al. IL-33 down-regulates CLDN1 expression through the ERK/STAT3 pathway in keratinocytes. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 90, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, E.; Mittermeir, M.; Ess, S.; Neuper, T.; Schmiedlechner, A.; Duschl, A.; Horejs-Hoeck, J. Prerequisites for Functional Interleukin 31 Signaling and Its Feedback Regulation by Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 3 (SOCS3). J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 24747–24759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevikbas, F.; Wang, X.; Akiyama, T.; Kempkes, C.; Savinko, T.; Antal, A.; Kukova, G.; Buhl, T.; Ikoma, A.; Buddenkotte, J.; et al. A sensory neuron-expressed IL-31 receptor mediates T helper cell-dependent itch: Involvement of TRPV1 and TRPA1. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 133, 448–460.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.R.; Thé, L.; Batia, L.M.; Beattie, K.; Katibah, G.E.; McClain, S.P.; Pellegrino, M.; Estandian, D.M.; Bautista, D.M. The Epithelial Cell-Derived Atopic Dermatitis Cytokine TSLP Activates Neurons to Induce Itch. Cell 2013, 155, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikoma, A.; Steinhoff, M.; Ständer, S.; Yosipovitch, G.; Schmelz, M. The neurobiology of itch. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groneberg, D.; Bester, C.; Grützkau, A.; Serowka, F.; Fischer, A.; Henz, B.M.; Welker, P. Mast cells and vasculature in atopic dermatitis—Potential stimulus of neoangiogenesis. Allergy 2005, 60, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verge, V.M.; Richardson, P.M.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z.; Hokfelt, T. Differential influence of nerve growth factor on neuropeptide expression in vivo: A novel role in peptide suppression in adult sensory neurons. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 2081–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, M.; Nakamura, M.; Makino, T.; Hino, T.; Kagoura, M.; Morohashi, M. Nerve growth factor and substance P are useful plasma markers of disease activity in atopic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2002, 147, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallrapp, A.; Burkett, P.R.; Riesenfeld, S.; Kim, S.-J.; Christian, E.; Abdulnour, R.-E.E.; Thakore, P.I.; Schnell, A.; Lambden, C.; Herbst, R.H.; et al. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Negatively Regulates Alarmin-Driven Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell Responses. Immunity 2019, 51, 709–723.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Ishida, A.; Kubo, A.; Kawasaki, H.; Ochiai, S.; Nakayama, M.; Koseki, H.; Amagai, M.; Okada, T. Homeostatic pruning and activity of epidermal nerves are dysregulated in barrier-impaired skin during chronic itch development. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, D.M.; Wilson, S.R.; Hoon, M.A. Why we scratch an itch: The molecules, cells and circuits of itch. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainichi, T.; Kitoh, A.; Otsuka, A.; Nakajima, S.; Nomura, T.; Kaplan, D.H.; Kabashima, K. The epithelial immune microenvironment (EIME) in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, Y.; Takagi, N.; Nagata, H.; Inoue, S. Interferon-γ downregulates tight junction function, which is rescued by interleukin-17A. Exp. Dermatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoi, L.C.; Rodriguez, E.; Stölzl, D.; Wehkamp, U.; Sun, J.; Gerdes, S.; Sarkar, M.; Hübenthal, M.; Zeng, C.; Uppala, R.; et al. Progression of acute-to-chronic atopic dermatitis is associated with quantitative rather than qualitative changes in cytokine responses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brøgger, P.; Blom, L.H.; Simonsen, S.; Thyssen, J.P.; Skov, L. Antagonism of the interleukin 4 receptor α promotes T H 1-signalling among T cells from patients with atopic dermatitis after stimulation. Scand. J. Immunol. 2019, 91, e12835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyerich, K.; Huss-Marp, J.; Darsow, U.; Wollenberg, A.; Foerster, S.; Ring, J.; Behrendt, H.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C. Pollen Grains Induce a Rapid and Biphasic Eczematous Immune Response in Atopic Eczema Patients. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2007, 145, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, M.; Tengara, S.; Kamo, A.; Ogawa, H.; Takamori, K. Psoralen-ultraviolet A therapy alters epidermal Sema3A and NGF levels and modulates epidermal innervation in atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2009, 55, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tominaga, M.; Takamori, K. Itch and nerve fibers with special reference to atopic dermatitis: Therapeutic implications. J. Dermatol. 2014, 41, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, Y.; Sumi, H.; Kawahira, K.; Terashima, T.; Nakamura, T.; Akamatsu, H. Protein oxidative damage in the stratum corneum: Evidence for a link between environmental oxidants and the changing prevalence and nature of atopic dermatitis in Japan. Br. J. Dermatol. 2003, 149, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, T. Atopic Dermatitis. Ann. Dermatol. 2010, 22, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totté, J.; Van Der Feltz, W.; Hennekam, M.; Van Belkum, A.; Van Zuuren, E.; Pasmans, S. Prevalence and odds of Staphylococcus aureuscarriage in atopic dermatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 175, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeck, D.; Mempel, M. Staphylococcus aureuscolonization in atopic dermatitis and its therapeutic implications. Br. J. Dermatol. 1998, 139, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisich, K.O.; Carspecken, C.W.; Fiéve, S.; Boguniewicz, M.; Leung, D.Y. Defective killing of Staphylococcus aureus in atopic dermatitis is associated with reduced mobilization of human β-defensin-3. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Oscherwitz, J.; Cease, K.B.; Chan, S.M.; Muñoz-Planillo, R.; Hasegawa, M.; Villaruz, A.E.; Cheung, G.Y.C.; McGavin, M.; Travers, J.; et al. Staphylococcus δ-toxin induces allergic skin disease by activating mast cells. Nature 2013, 503, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merriman, J.A.; Klingelhutz, A.J.; Diekema, D.J.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Schlievert, P.M. Novel Staphylococcus aureus Secreted Protein Alters Keratinocyte Proliferation and Elicits a Proinflammatory Response In Vitro and In Vivo. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 4855–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Han, J.H.; Chung, J.H.; Cho, K.H.; Eun, H.C. Role of Staphylococcal Superantigen in Atopic Dermatitis: Influence on Keratinocytes. J. Korean Med Sci. 2006, 21, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.A.; Nair, S.P. Interaction of staphylococci with bone. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 300, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bur, S.; Preissner, K.T.; Herrmann, M.; Bischoff, M. The Staphylococcus aureus Extracellular Adherence Protein Promotes Bacterial Internalization by Keratinocytes Independent of Fibronectin-Binding Proteins. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 2004–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis—The ‘accidental’ pathogen. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 7, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, A.L.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A. The human skin microbiome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 16, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argemi, X.; Hansmann, Y.; Prola, K.; Prévost, G. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Pathogenomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méric, G.; Mageiros, L.; Pensar, J.; Laabei, M.; Yahara, K.; Pascoe, B.; Kittiwan, N.; Tadee, P.; Post, V.; Lamble, S.; et al. Disease-associated genotypes of the commensal skin bacterium Staphylococcus epidermidis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widerström, M.; Wiström, J.; Sjöstedt, A.; Monsen, T. Coagulase-negative staphylococci: Update on the molecular epidemiology and clinical presentation, with a focus on Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus saprophyticus. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 31, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, A.L.; Deming, C.; Cassidy, S.K.B.; Harrison, O.J.; Ng, W.-I.; Conlan, S.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A.; Kong, H.H.; Program, N.C.S. Staphylococcus aureusandStaphylococcus epidermidisstrain diversity underlying pediatric atopic dermatitis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaal4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Iwase, T.; Liu, G.Y. Intranasal Application of S. epidermidis Prevents Colonization by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatz, M.; Bosshard, P.P.; Hoetzenecker, W.; Schmid-Grendelmeier, P. The Role of Malassezia spp. in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 4, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thammahong, A.; Kiatsurayanon, C.; Edwards, S.W.; Rerknimitr, P.; Chiewchengchol, D. The clinical significance of fungi in atopic dermatitis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2020, 59, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, K.; Saito, M.; Sugita, T.; Tsuboi, R. Malasseziaspecies and their associated skin diseases. J. Dermatol. 2015, 42, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prohic, A.; Sadikovic, T.J.; Krupalija-Fazlic, M.; Kuskunovic-Vlahovljak, S. Malasseziaspecies in healthy skin and in dermatological conditions. Int. J. Dermatol. 2015, 55, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, T.; Suto, H.; Unno, T.; Tsuboi, R.; Ogawa, H.; Shinoda, T.; Nishikawa, A. Molecular analysis of malassezia microflora on the skin of atopic dermatitis patients and healthy subjects. Nippon Ishinkin Gakkai Zasshi 2001, 42, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowicka, D.; Nawrot, U. Contribution of Malassezia spp. to the development of atopic dermatitis. Mycoses 2019, 62, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnarumma, G.; Perfetto, B.; Paoletti, I.; Oliviero, G.; Clavaud, C.; Del Bufalo, A.; Guéniche, A.; Jourdain, R.; Tufano, M.A.; Breton, L. Analysis of the response of human keratinocytes to Malassezia globosa and restricta strains. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2014, 306, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, Y.; Sugita, T.; Nishikawa, A. Cytokine secretion profile of human keratinocytes exposed toMalasseziayeasts. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 48, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, Y.; Sugawara, K.; Sugita, T.; Nishikawa, A. Secretion of thymic stromal lymphopoietin from human keratinocytes in response to Malassezia yeasts. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2011, 62, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollenberg, A.; Wetzel, S.; Burgdorf, W.H.C.; Haas, J. Viral infections in atopic dermatitis: Pathogenic aspects and clinical management. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopfnagel, V.; Harder, J.; Werfel, T. Expression of antimicrobial peptides in atopic dermatitis and possible immunoregulatory functions. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 13, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, M.D.; Gallo, R.L.; Boguniewicz, M.; Jones, J.F.; Wong, C.; Streib, J.E.; Leung, D.Y. Cytokine Milieu of Atopic Dermatitis Skin Subverts the Innate Immune Response to Vaccinia Virus. Immunity 2006, 24, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyoshi, M.K.; Venturelli, N.; Geha, R.S. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin and IL-33 promote skin inflammation and vaccinia virus replication in a mouse model of atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.Y.; Gao, P.-S.; Grigoryev, D.N.; Rafaels, N.M.; Streib, J.E.; Howell, M.D.; Taylor, P.A.; Boguniewicz, M.; Canniff, J.; Armstrong, B.; et al. Human atopic dermatitis complicated by eczema herpeticum is associated with abnormalities in IFN-γ response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 965–973.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, M.D.; Wollenberg, A.; Gallo, R.L.; Flaig, M.; Streib, J.E.; Wong, C.; Pavicic, T.; Boguniewicz, M.; Leung, D.Y.M. Cathelicidin deficiency predisposes to eczema herpeticum. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 117, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin, L.; Kim, B.E.; Hall, C.F.; Leach, S.M.; Leung, D.Y. Inhibition of Transcription Factor Specificity Protein 1 Alters the Gene Expression Profile of Keratinocytes Leading to Upregulation of Kallikrein-Related Peptidases and Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 2213–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, L.; Howell, M.D.; Kim, B.E.; Streib, J.E.; Hall, C.F.; Leung, N.Y. Specificity protein 1 is pivotal in the skin’s antiviral response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 430–438.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, T.K.; Hanifin, J.; Mahmood, M.; Larson, B.; Baig-Lewis, S.; Long, T.; Lim, J.Y.; Berlin, M.; Weese, K. Atopic Dermatitis Is Associated With Cervical High Risk Human Papillomavirus Infection. J. Low. Genit. Tract Dis. 2015, 19, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergot, A.-S.; Monnet, N.; Tran, L.S.; Mittal, D.; Al-Kouba, J.; Steptoe, R.; Grimbaldeston, M.A.; Frazer, I.; Wells, J.W. HPV16 E7 expression in skin induces TSLP secretion, type 2 ILC infiltration and atopic dermatitis-like lesions. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2015, 93, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, A.B.; Juul, S.; Thestrup-Pedersen, K. Atopic Dermatitis Is Increased Following Vaccination for Measles, Mumps and Rubella or Measles Infection. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2003, 83, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, S.; Barker, D.; Heyes, C.; Shiell, A.; Aaby, P.; Hall, A.; Goudiaby, A. Measles and atopy in Guinea-Bissau. Lancet 1996, 347, 1792–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, N.; Fukutomi, O.; Ozawa, T.; Agata, H.; Kameyama, T.; Kuwabara, N.; Shinoda, S.; Orii, T. Improvement of food-sensitive atopic dermatitis accompanied by reduced lymphocyte responses to food antigen following natural measles virus infection. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1993, 23, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennino, A.; Cornu, C.; Rozieres, A.; Augey, F.; Villard-Truc, F.; Payot, F.; Lachaux, A.; Nicolas, J.F.; Horvat, B. Influence of measles vaccination on the progression of atopic dermatitis in infants. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2007, 18, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourru-Lesimple, G.; Mathieu, C.; Thevenet, T.; Guillaume-Vasselin, V.; Jégou, J.-F.; Boer, C.; Tomczak, K.; Bloyet, L.-M.; Giraud, C.; Grande, S.; et al. Measles virus infection of human keratinocytes: Possible link between measles and atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 86, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duval, K.; Grover, H.; Han, L.-H.; Mou, Y.; Pegoraro, A.F.; Fredberg, J.; Chen, Z. Modeling Physiological Events in 2D vs. 3D Cell Culture. Physiology 2017, 32, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymanski, L.; Cios, A.; Lewicki, S.; Szymanski, P.; Stankiewicz, W. Fas/FasL pathway and cytokines in keratinocytes in atopic dermatitis—Manipulation by the electromagnetic field. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poumay, Y.; Pittelkow, M.R. Cell Density and Culture Factors Regulate Keratinocyte Commitment to Differentiation and Expression of Suprabasal K1/K10 Keratins. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1995, 104, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deyrieux, A.F.; Wilson, V.G. In vitro culture conditions to study keratinocyte differentiation using the HaCaT cell line. Cytotechnology 2007, 54, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehman, T.A.; Modali, R.; Boukamp, P.; Stanek, J.; Bennett, W.P.; Welsh, J.A.; Metcalf, R.A.; Stampfer, M.R.; Fusenig, N.; Rogan, E.M.; et al. p53 Mutations in human immortalized epithelial cell lines. Carcinogenesis 1993, 14, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukamp, P.; Petrussevska, R.T.; Breitkreutz, D.; Hornung, J.; Markham, A.; Fusenig, N.E. Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 106, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori-Miyake, M.; Yamashita, M.; Tsunemi, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Yagi, J. In Vitro Assessment of IL-4- or IL-13-Mediated Changes in the Structural Components of Keratinocytes in Mice and Humans. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, N.; Pang, S.; Song, H.; An, L.; Ma, X. Filaggrin silencing by shRNA directly impairs the skin barrier function of normal human epidermal keratinocytes and then induces an immune response. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, M.; Yeo, H.; Ko, J.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, C.-H. MAP17 is associated with the T-helper cell cytokine-induced down-regulation of filaggrin transcription in human keratinocytes. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, M.-D.; Kang, T.-J.; Lee, C.-H.; Lee, A.-Y.; Noh, M. HaCaT Keratinocytes and Primary Epidermal Keratinocytes Have Different Transcriptional Profiles of Cornified Envelope-Associated Genes to T Helper Cell Cytokines. Biomol. Ther. 2012, 20, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.K.; Jang, Y.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.-R.; Choi, Y.-A.; Jin, M.; Choi, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Park, P.-H.; Choi, H.; et al. Chrysin attenuates atopic dermatitis by suppressing inflammation of keratinocytes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 110, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Baek, J.; Lee, J.R.; Roh, J.Y.; Jung, Y. Optimization of Cytokine Milieu to Reproduce Atopic Dermatitis-related Gene Expression in HaCaT Keratinocyte Cell Line. Immune Netw. 2018, 18, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosdy, M.; Clauss, L.-C. Terminal Epidermal Differentiation of Human Keratinocytes Grown in Chemically Defined Medium on Inert Filter Substrates at the Air-Liquid Interface. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1990, 95, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batheja, P.; Song, Y.; Wertz, P.; Michniak-Kohn, B. Effects of Growth Conditions on the Barrier Properties of a Human Skin Equivalent. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouaud-Tinguely, P.; Boudier, D.; Marchand, L.; Barruche, V.; Bordes, S.; Coppin, H.; Roth, M.; Closs, B. From the morphological to the transcriptomic characterization of a compromised three-dimensional in vitro model mimicking atopic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danso, M.O.; van Drongelen, V.; Mulder, A.; van Esch, J.; Scott, H.; van Smeden, J.; El Ghalbzouri, A.; Bouwstra, J.A. TNF-α and Th2 Cytokines Induce Atopic Dermatitis—Like Features on Epidermal Differentiation Proteins and Stratum Corneum Lipids in Human Skin Equivalents. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, N.A.; Morrell, D.S. Systemic therapy of childhood atopic dermatitis. Clin. Dermatol. 2015, 33, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berke, R.; Singh, A.; Guralnick, M. Atopic dermatitis: An overview. Am. Fam. Physician 2012, 86, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Katoh, N.; Ohya, Y.; Ikeda, M.; Ebihara, T.; Katayama, I.; Saeki, H.; Shimojo, N.; Tanaka, A.; Nakahara, T.; Nagao, M.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of atopic dermatitis 2018. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, 1053–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimalt, R.; Mengeaud, V.; Cambazard, F. The Steroid-Sparing Effect of an Emollient Therapy in Infants with Atopic Dermatitis: A Randomized Controlled Study. Dermatology 2006, 214, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchiyama, N.; Yamamoto, A.; Kameda, K.; Yamaguchi, H.; Ito, M. The activity of fatty acid synthase of epidermal keratinocytes is regulated in the lower stratum spinousum and the stratum basale by local inflammation rather than by circulating hormones. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2000, 24, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.-M.; Pfeiffer, S.; Witt, M.; Bräutigam, M.; Neumann, C.; Weichenthal, M.; Schwarz, T.; Fölster-Holst, R.; Proksch, E. Different effects of pimecrolimus and betamethasone on the skin barrier in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xhauflaire-Uhoda, E.; Thirion, L.; Piérard-Franchimont, C.; Piérard, G. Comparative Effect of Tacrolimus and Betamethasone Valerate on the Passive Sustainable Hydration of the Stratum Corneum in Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatology 2007, 214, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.-J.; Gallo, R.L. Antimicrobial peptides. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R14–R19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Zhao, J.; Tegtmeyer, K.; Shah, P.; Lio, P.A. US Prescription trends of antihistamines for atopic dermatitis, 2011–2016. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2020, 38, 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Nishihira, J.; Watanabe, H.; Abe, R.; Ishibashi, T.; Shimizu, H. Cetirizine, an H1-receptor antagonist, suppresses the expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor: Its potential anti-inflammatory action. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2004, 34, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matterne, U.; Böhmer, M.M.; Weisshaar, E.; Jupiter, A.; Carter, B.; Apfelbacher, C.J. Oral H1 antihistamines as ‘add-on’ therapy to topical treatment for eczema. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 2019, CD012167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, J.; AlOmar, A.; Bieber, T.; Deleuran, M.; Fink-Wagner, A.; Gelmetti, C.; Gieler, U.; Lipozencic, J.; Luger, T.; Oranje, A.; et al. Guidelines for treatment of atopic eczema (atopic dermatitis) Part I. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 26, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rancan, F.; Volkmann, H.; Giulbudagian, M.; Schumacher, F.; Stanko, J.I.; Kleuser, B.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Calderón, M.; Vogt, A. Dermal Delivery of the High-Molecular-Weight Drug Tacrolimus by Means of Polyglycerol-Based Nanogels. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; Chow, M. Pimecrolimus: A review. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2003, 17, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, N.J.; Al-Daraji, W.I. Calcineurin inhibitors and sirolimus: Mechanisms of action and applications in dermatology. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2002, 27, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, A.W.; Bonham, C.A.; Zeevi, A. Mode of Action of Tacrolimus (FK506): Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms. Ther. Drug Monit. 1995, 17, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, L.; Harvima, I.T. Mast cells of psoriatic and atopic dermatitis skin are positive for TNF-α and their degranulation is associated with expression of ICAM-1 in the epidermis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1998, 290, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.-C.; Yu, H.-S.; Wu, C.-S.; Kuo, H.-Y.; Chai, C.-Y.; Chen, G.-S. FK506 inhibits tumour necrosis factor-alpha secretion in human keratinocytes via regulation of nuclear factor-kappaB. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 153, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.-C.; Kao, Y.-H.; Huang, S.-M.; Yu, H.-S.; Chen, G.-S. FK506 independently upregulates transforming growth factor beta and downregulates inducible nitric oxide synthase in cultured human keratinocytes: Possible mechanisms of how tacrolimus ointment interacts with atopic skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 2004, 151, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, E.; Kameyoshi, Y.; Hiragun, T.; Mihara, S.; Yamamoto, S. The C-C chemokines, RANTES and eotaxin, in atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2001, 56, 194–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.; Lee, B.; Han, H.; Lee, C.; Ahn, H. Tacrolimus decreases the expression of eotaxin, CCR3, RANTES and interleukin-5 in atopic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 152, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakugawa, M.; Nakamura, K.; Akatsuka, M.; Nakagawa, H.; Tamaki, K. Interferon-Gamma-Induced RANTES Production by Human Keratinocytes Is Enhanced by IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-4 and IL-13 and Is Inhibited by Dexamethasone and Tacrolimus. Dermatology 2001, 202, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, J.M.; Kang, H.J.; Cho, S.H.; Chang, S.E. Epidermal Growth Factor Relieves Inflammatory Signals in Staphylococcus aureus-Treated Human Epidermal Keratinocytes and Atopic Dermatitis-Like Skin Lesions in Nc/Nga Mice. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9439182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, T. TSLP Expression: Cellular Sources, Triggers, and Regulatory Mechanisms. Allergol. Int. 2012, 61, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, D.; Chen, R.; Stewart, D.; Brown, K.; Sundram, U. The direct cellular target of topically applied pimecrolimus may not be infiltrating lymphocytes. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 164, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zuo, J.; Tang, W. Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paller, A.S.; Tom, W.L.; Lebwohl, M.G.; Blumenthal, R.L.; Boguniewicz, M.; Call, R.S.; Eichenfield, L.F.; Forsha, D.W.; Rees, W.C.; Simpson, E.L.; et al. Efficacy and safety of crisaborole ointment, a novel, nonsteroidal phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor for the topical treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD) in children and adults. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 75, 494–503.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.L.; Imafuku, S.; Poulin, Y.; Ungar, B.; Zhou, L.; Malik, K.; Wen, H.-C.; Xu, H.; Estrada, Y.D.; Peng, X.; et al. A Phase 2 Randomized Trial of Apremilast in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanifin, J.M.; Lloyd, R.; Okubo, K.; Guerin, L.L.; Fancher, L.; Chan, S.C. Relationship Between Increased Cyclic AMP-Phosphodiesterase Activity and Abnormal Adenylyl Cyclase Regulation in Leukocytes From Patients With Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1992, 98, S100–S105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, D.W.; Ivanova, I.A.; Dagnino, L. DRM02, a novel phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor with cutaneous anti-inflammatory activity. Tissue Barriers 2020, 8, 1765633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, S.; Takaishi, M.; Nakajima, K.; Sano, S. Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors reduce the expression of proinflammatory mediators by human epidermal keratinocytes independent of intracellular cAMP elevation. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2020, 100, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, P.H.; Adams, M.; Horan, G.; Truzzi, F.; Marconi, A.; Pincelli, C. Apremilast Normalizes Gene Expression of Inflammatory Mediators in Human Keratinocytes and Reduces Antigen-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in Mice. Drugs R D 2019, 19, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gallegos-Alcalá, P.; Jiménez, M.; Cervantes-García, D.; Salinas, E. The Keratinocyte as a Crucial Cell in the Predisposition, Onset, Progression, Therapy and Study of the Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910661
Gallegos-Alcalá P, Jiménez M, Cervantes-García D, Salinas E. The Keratinocyte as a Crucial Cell in the Predisposition, Onset, Progression, Therapy and Study of the Atopic Dermatitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(19):10661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910661
Chicago/Turabian StyleGallegos-Alcalá, Pamela, Mariela Jiménez, Daniel Cervantes-García, and Eva Salinas. 2021. "The Keratinocyte as a Crucial Cell in the Predisposition, Onset, Progression, Therapy and Study of the Atopic Dermatitis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 19: 10661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910661
APA StyleGallegos-Alcalá, P., Jiménez, M., Cervantes-García, D., & Salinas, E. (2021). The Keratinocyte as a Crucial Cell in the Predisposition, Onset, Progression, Therapy and Study of the Atopic Dermatitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(19), 10661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910661








