CD73+ CD127high Long-Term Memory CD4 T Cells Are Highly Proliferative in Response to Recall Antigens and Are Early Targets in HIV-1 Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. CD73+ Memory CD4+ T Cells in Peripheral Blood, Lymph Nodes and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
2.2. Detailed Phenotype of CD73+ Memory CD4+ T Cells
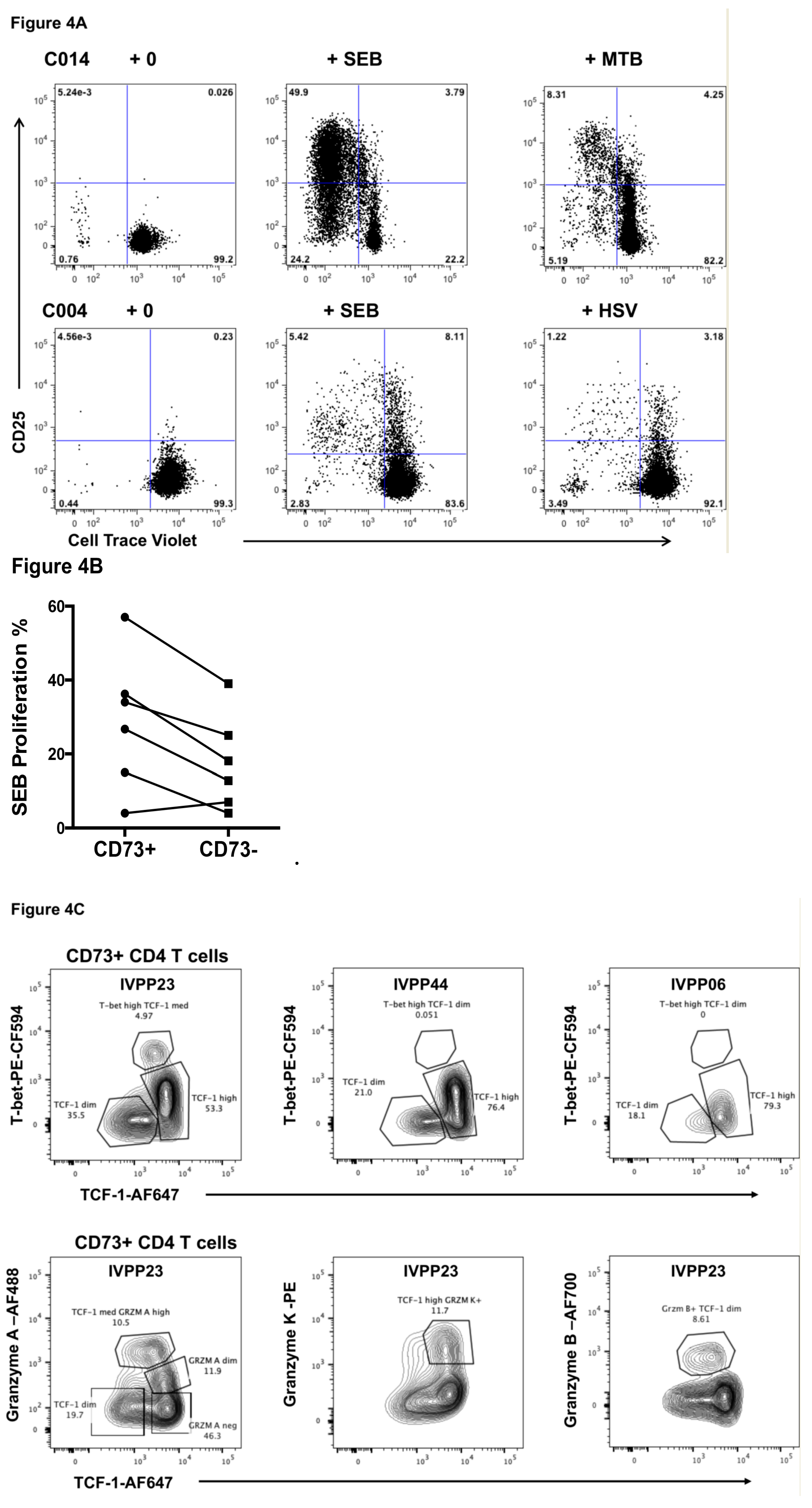
2.3. Function of CD73+ Memory CD4+ T Cells
2.4. Transcriptomics of CD73+ Memory CD4+ T Cells
2.5. Response of CD73+ Memory CD4+ T Cells to Incubation with IL-7 and IL-2
2.6. Effect of HIV-1 Infection on CD73+ Memory CD4+ T Cells
2.7. CD73+ Memory CD4+ T Cells in Gut Biopsies
2.8. HIV-Infection of CD73+ CD4+ T Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Subjects
4.2. Ethics
4.3. Immunophenotyping
4.4. CyTOF Analysis
4.5. Cell Sorting and Lymphoproliferation Assays
4.6. Antigen-Specific CD4+ T Cell Assays
4.7. Ultrasound-Guided Lymph Node Fine Needle Biopsies
4.8. Gut Biopsies
4.9. HIV DNA Quantitative PCR
4.10. Microarray Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zimmermann, H.; Zebisch, M.; Sträter, N. Cellular function and molecular structure of ecto-nucleotidases. Purinergic Signal. 2012, 8, 437–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deaglio, S.; Dwyer, K.M.; Gao, W.; Friedman, D.; Usheva, A.; Erat, A.; Chen, J.-F.; Enjyoji, K.; Linden, J.; Oukka, M.; et al. Adenosine generation catalyzed by CD39 and CD73 expressed on regulatory T cells mediates immune suppression. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seddiki, N.; Santner-Nanan, B.; Martinson, J.; Zaunders, J.; Sasson, S.; Landay, A.; Solomon, M.; Selby, W.; Alexander, S.I.; Nanan, R.; et al. Expression of interleukin (IL)-2 and IL-7 receptors discriminates between human regulatory and activated T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 1693–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, K.M.; Hanidziar, D.; Putheti, P.; Hill, P.A.; Pommey, S.; McRae, J.L.; Winterhalter, A.; Doherty, G.F.; Deaglio, S.; Koulmanda, M.; et al. Expression of CD39 by Human Peripheral Blood CD4+CD25+ T Cells Denotes a Regulatory Memory Phenotype. Am. J. Transpl. 2010, 10, 2410–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doherty, G.A.; Bai, A.; Hanidziar, D.; Longhi, M.S.; Lawlor, G.O.; Putheti, P.; Csizmadia, E.; Nowak, M.; Cheifetz, A.S.; Moss, A.C.; et al. CD73 is a phenotypic marker of effector memory Th17 cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 3062–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tóth, I.; Le, A.Q.; Hartjen, P.; Thomssen, A.; Matzat, V.; Lehmann, C.; Scheurich, C.; Beisel, C.; Busch, P.; Degen, O.; et al. Decreased frequency of CD73+CD8+T cells of HIV-infected patients correlates with immune activation and T cell exhaustion. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 94, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J.M.; Lonergan, R.; Costelloe, L.; Kinsella, K.; Moran, B.; O’Farrelly, C.; Tubridy, N.; Mills, K.H.G. CD39+Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells Suppress Pathogenic Th17 Cells and Are Impaired in Multiple Sclerosis. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 7602–7610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, L.F. Editorial: CD73 deficiency and immune dysregulation in HIV infection: Cause or effect? J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 94, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, R.S.; Thompson, H. Epstein-Barr virus infections in homosexual men with chronic persistent, generalised lymphadenopathy. J. Infect. Dis. 1985, 151, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, P.J.; Saze, Z.; Hong, C.-S.; Muller, L.; Gillespie, D.G.; Cheng, D.; Harasymczuk, M.; Mandapathil, M.; Lang, S.; Jackson, E.K.; et al. Human CD4+CD39+regulatory T cells produce adenosine upon co-expression of surface CD73 or contact with CD73+exosomes or CD73+cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 177, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-S.; Ackermann, C.; Tóth, I.; Dierks, P.; Eberhard, J.M.; Wroblewski, R.; Scherg, F.; Geyer, M.; Schmidt, R.E.; Beisel, C.; et al. Down-regulation of CD73 on B cells of patients with viremic HIV correlates with B cell activation and disease progression. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schuler, P.; Macatangay, B.; Saze, Z.; Jackson, E.; Riddler, S.; Buchanan, W.; Hildorfer, B.; Mellors, J.; Whiteside, T.; Rinaldo, C.R. CD4+CD73+ T cells are associated with lower T cell activation and CRP levels and are depleted in HIV-1 infection regardless of viral suppression. AIDS 2013, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaunders, J.J.; Carr, A.; McNally, L.; Penny, R.; Cooper, D.A. Effects of primary HIV-1 infection on subsets of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes. AIDS 1995, 9, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaunders, J.J.; Munier, C.M.L.; Kaufmann, D.E.; Ip, S.; Grey, P.; Smith, D.; Ramacciotti, T.; Quan, D.; Finlayson, R.J.; Kaldor, J.; et al. Early proliferation of CCR5+CD38+++ antigen-specific CD4+ Th1 effector cells during primary HIV-1 infection. Blood 2005, 106, 1660–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ålgars, A.; Karikoski, M.; Yegutkin, G.G.; Stoitzner, P.; Niemelä, J.; Salmi, M.; Jalkanen, S. Different role of CD73 in leukocyte trafficking via blood and lymph vessels. Blood 2011, 117, 4387–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takedachi, M.; Qu, D.; Ebisuno, Y.; Oohara, H.; Joachims, M.L.; McGee, S.T.; Maeda, E.; McEver, R.P.; Tanaka, T.; Miyasaka, M.; et al. CD73-Generated Adenosine Restricts Lymphocyte Migration into Draining Lymph Nodes. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 6288–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sallusto, F.; Geginat, J.; Lanzavecchia, A. Central Memory and Effector MemoryT Cell Subsets: Function, Generation, and Maintenance. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 22, 745–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Andrian, U.H.; Mackay, C.R. T-cell function and migration. Two sides of the same coin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1020–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, J.H.; Thompson, L.F.; Mueller, C.; Waickman, A.T.; Jalkanen, S.; Niemela, J.; Airas, L.; Bynoe, M.S. CD73 is required for efficient entry of lymphocytes into the central nervous system during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9325–9330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Resta, R.; Yamashita, Y.; Thompson, L.F. Ecto-enzyme and signaling functions of lymphocyte CD 7 3. Immunol. Rev. 1998, 161, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Hooker, S.W.; Jiang, H.; Laurent, A.B.; Resta, R.; Khare, K.; Coe, A.; Kincade, P.W.; Thompson, L.F. CD73 expression and fyn-dependent signaling on murine lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 1998, 28, 2981–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsellino, G.; Kleinewietfeld, M.; Di Mitri, D.; Sternjak, A.; Diamantini, A.; Giometto, R.; Höpner, S.; Centonze, D.; Bernardi, G.; Dell’Acqua, M.L.; et al. Expression of ectonucleotidase CD39 by Foxp3+ Treg cells: Hydrolysis of extracellular ATP and immune suppression. Blood 2007, 110, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hey-Nguyen, W.J.; Xu, Y.; Pearson, C.F.; Bailey, M.; Suzuki, K.; Tantau, R.; Obeid, S.; Milner, B.; Field, A.; Carr, A.; et al. Quantification of Residual Germinal Center Activity and HIV-1 DNA and RNA Levels Using Fine Needle Biopsies of Lymph Nodes During Antiretroviral Therapy. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2017, 33, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.P.; Kameoka, J.; Hegen, M.; Tanaka, T.; Xu, Y.; Schlossman, S.F.; Morimoto, C. Characterization of adenosine deaminase binding to human CD26 on T cells and its biologic role in immune response. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Appay, V.; Zaunders, J.J.; Papagno, L.; Sutton, J.; Jaramillo, A.; Waters, A.; Easterbrook, P.; Grey, P.; Smith, D.; McMichael, A.J.; et al. Characterization of CD4+CTLs Ex Vivo. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 5954–5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaunders, J.J.; Dyer, W.B.; Wang, B.; Munier, M.L.; Saksena, M.M.; Newton, R.; Moore, J.; Mackay, C.R.; Cooper, D.A.; Saksena, N.K.; et al. Identification of circulating antigen-specific CD4+ T lymphocytes with a CCR5+, cytotoxic phenotype in an HIV-1 long-term nonprogressor and in CMV infection. Blood 2004, 103, 2238–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munier, C.M.L.; Van Bockel, D.; Bailey, M.; Ip, S.; Xu, Y.; Alcantara, S.; Liu, S.M.; Denyer, G.; Kaplan, W.; Suzuki, K.; et al. The primary immune response to Vaccinia virus vaccination includes cells with a distinct cytotoxic effector CD4 T-cell phenotype. Vaccine 2016, 34, 5251–5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaunders, J.; Munier, C.M.L.; McGuire, H.M.; Law, H.; Howe, A.; Xu, Y.; Groth, B.F.D.S.; Schofield, P.; Christ, D.; Milner, B.; et al. Mapping the extent of heterogeneity of human CCR5+ CD4+ T cells in peripheral blood and lymph nodes. AIDS 2020, 34, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-H.W.; Nish, S.A.; Yen, B.; Chen, Y.-H.; Adams, W.C.; Kratchmarov, R.; Rothman, N.J.; Bhandoola, A.; Xue, H.-H.; Reiner, S.L. CD8+ T Lymphocyte Self-Renewal during Effector Cell Determination. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchholz, V.R.; Busch, D.H. Back to the Future: Effector Fate during T Cell Exhaustion. Immunity 2019, 51, 970–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spychala, J.; Kitajewski, J. Wnt and beta; cateninsignalingtargettheexpressionofecto−5beta;-cateninsignalingtargettheexpressionofecto-5prime;-nucleotidase and increase extracellular adenosine generation. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 296, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harjunpää, H.; Guillerey, C. TIGIT as an emerging immune checkpoint. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 200, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaunders, J.J.; Munier, C.M.L.; Seddiki, N.; Pett, S.; Ip, S.; Bailey, M.; Xu, Y.; Brown, K.; Dyer, W.B.; Kim, M.; et al. High Levels of Human Antigen-Specific CD4+ T Cells in Peripheral Blood Revealed by Stimulated Coexpression of CD25 and CD134 (OX40). J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2827–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaunders, J.; van Bockel, D. Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Long-Term Non-Progression in HIV Disease. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koelsch, K.K.; Boesecke, C.; McBride, K.; Gelgor, L.; Fahey, P.; Natarajan, V.; Baker, D.; Bloch, M.; Murray, J.M.; Zaunders, J.; et al. Impact of treatment with raltegravir during primary or chronic HIV infection on RNA decay characteristics and the HIV viral reservoir. AIDS 2011, 25, 2069–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seddiki, N.; Sasson, S.C.; Santner-Nanan, B.; Munier, C.M.L.; Van Bockel, D.; Ip, S.; Marriott, D.; Pett, S.; Nanan, R.; Cooper, D.A.; et al. Proliferation of weakly suppressive regulatory CD4+ T cells is associated with over-active CD4+ T-cell responses in HIV-positive patients with mycobacterial immune restoration disease. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.; Chuah, J.; Hudson, J.; French, M.; Hoy, J.; Law, M.; Sayer, D.; Emery, S.; Cooper, D.A. A randomised, open-label comparison of three highly active antiretroviral therapy regimens including two nucleoside analogues and indinavir for previously untreated HIV-1 infection: The OzCombo1 study. AIDS 2000, 14, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandapathil, M.; Szczepanski, M.J.; Szajnik, M.; Ren, J.; Lenzner, D.E.; Jackson, E.K.; Gorelik, E.; Lang, S.; Johnson, J.T.; Whiteside, T.L. Increased Ectonucleotidase Expression and Activity in Regulatory T Cells of Patients with Head and Neck Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6348–6357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaunders, J.J.; Dyer, W.B.; Munier, C.M.L.; Ip, S.; Liu, J.; Amyes, E.; Rawlinson, W.; De Rose, R.; Kent, S.J.; Sullivan, J.S.; et al. CD127+CCR5+CD38+++CD4+ Th1 Effector Cells Are an Early Component of the Primary Immune Response to Vaccinia Virus and Precede Development of Interleukin-2+ Memory CD4+ T Cells. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 10151–10161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaunders, J.; Danta, M.; Bailey, M.; Mak, G.; Marks, K.; Seddiki, N.; Xu, Y.; Templeton, D.J.; Cooper, D.A.; Boyd, M.A.; et al. CD4+ T Follicular Helper and IgA+ B Cell Numbers in Gut Biopsies from HIV-Infected Subjects on Antiretroviral Therapy Are Similar to HIV-Uninfected Individuals. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McBride, K.; Xu, Y.; Bailey, M.; Seddiki, N.; Suzuki, K.; Murray, J.M.; Gao, Y.; Yan, C.; Cooper, D.A.; Kelleher, A.D.; et al. The Majority of HIV Type 1 DNA in Circulating CD4+T Lymphocytes Is Present in Non-Gut-Homing Resting Memory CD4+T Cells. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2013, 29, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hey-Nguyen, W.J.; Bailey, M.; Xu, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Van Bockel, D.; Finlayson, R.; Brown, A.J.L.; Carr, A.; Cooper, D.A.; Kelleher, A.D.; et al. HIV-1 DNA Is Maintained in Antigen-Specific CD4+ T Cell Subsets in Patients on Long-Term Antiretroviral Therapy Regardless of Recurrent Antigen Exposure. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2019, 35, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, L.F.; Eltzschig, H.K.; Ibla, J.C.; Van De Wiele, C.J.; Resta, R.; Morote-Garcia, J.C.; Colgan, S.P. Crucial Role for Ecto-5′-Nucleotidase (CD73) in Vascular Leakage during Hypoxia. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sakaguchi, S. Cell-autonomous and -non-autonomous roles of CTLA-4 in immune regulation. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joolharzadeh, P.; Hilaire, C.S. CD73 (Cluster of Differentiation 73) and the Differences between Mice and Humans. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kelleher, A.D.; Carr, A.; Zaunders, J.; Cooper, D.A. Alterations in the Immune Response of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)-Infected Subjects Treated with an HIV-Specific Protease Inhibitor, Ritonavir. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 173, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaunders, J.J.; Cunningham, P.; Kelleher, A.; Kaufmann, G.R.; Jaramillo, A.B.; Wright, R.; Smith, D.; Grey, P.; Vizzard, J.; Carr, A.; et al. Potent Antiretroviral Therapy of Primary Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1) Infection: Partial Normalization of T Lymphocyte Subsets and Limited Reduction of HIV-1 DNA Despite Clearance of Plasma Viremia. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 180, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brenchley, J.M.; Schacker, T.W.; Ruff, L.E.; Price, D.A.; Taylor, J.H.; Beilman, G.J.; Nguyen, P.L.; Khoruts, A.; Larson, M.; Haase, A.T.; et al. CD4+ T Cell Depletion during all Stages of HIV Disease Occurs Predominantly in the Gastrointestinal Tract. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, M.; Ueno, Y.; Yajima, T.; Iwao, Y.; Tsuchiya, M.; Ishikawa, H.; Aiso, S.; Hibi, T.; Ishii, H. Interleukin 7 is produced by human intestinal epithelial cells and regulates the proliferation of intestinal mucosal lymphocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 2945–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaunders, J.J.; Ip, S.; Munier, C.M.L.; Kaufmann, D.E.; Suzuki, K.; Brereton, C.; Sasson, S.C.; Seddiki, N.; Koelsch, K.; Landay, A.; et al. Infection of CD127+ (Interleukin-7 Receptor+) CD4+ Cells and Overexpression of CTLA-4 Are Linked to Loss of Antigen-Specific CD4 T Cells during Primary Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 10162–10172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, J.M.; McBride, K.; Boesecke, C.; Bailey, M.; Amin, J.; Suzuki, K.; Baker, D.; Zaunders, J.J.; Emery, S.; Cooper, D.A.; et al. Integrated HIV DNA accumulates prior to treatment while episomal HIV DNA records ongoing transmission afterwards. AIDS 2012, 26, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murray, J.M.; Zaunders, J.J.; McBride, K.L.; Xu, Y.; Bailey, M.; Suzuki, K.; Cooper, D.A.; Emery, S.; Kelleher, A.D.; Koelsch, K.K. HIV DNA subspecies persist in both activated and resting memory CD4+ T cells during ART. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 3516–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seddiki, N.; Cook, L.; Hsu, D.C.; Phetsouphanh, C.; Brown, K.; Xu, Y.; Kerr, S.J.; Cooper, D.A.; Munier, C.M.L.; Pett, S.; et al. Human antigen-specific CD4+CD25+CD134+CD39+ T cells are enriched for regulatory T cells and comprise a substantial proportion of recall responses. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 1644–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesch, J.S.Z.; Thomssen, A.; Hartjen, P.; Tóth, I.; Lehmann, C.; Meyer-Olson, D.; Colberg, K.; Frerk, S.; Babikir, D.; Schmiedel, S.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Frequency and Phenotype of T Regulatory Cells in HIV Infection: CD39 Expression of FoxP3+ T Regulatory Cells Correlates with Progressive Disease. J. Virol. 2010, 85, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prlic, M.; Bevan, M.J. Cutting edge: Beta-catenin is dispensable for T cell effector differentiation, memory formation, and recall responses. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 1542–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ljungberg, J.K.; Kling, J.C.; Tran, T.T.; Blumenthal, A. Functions of the WNT Signaling Network in Shaping Host Responses to Infection. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, R.R.; Nigam, P.; Sharma, S.; Liu, J.; Bostik, V. Long-lived poxvirus immunity, robust CD4 help, and better persistence of CD4 than CD8 T cells. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 3811–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puissant-Lubrano, B.; Combadière, B.; Duffy, D.; Wincker, N.; Frachette, M.-J.; Aït-Mohand, H.; Verrier, B.; Katlama, C.; Autran, B. Influence of antigen exposure on the loss of long-term memory to childhood vaccines in HIV-infected patients. Vaccine 2009, 27, 3576–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaunders, J.J.; Lévy, Y.; Seddiki, N. Exploiting differential expression of the IL-7 receptor on memory T cells to modulate immune responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014, 25, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, Y.; Sereti, I.; Tambussi, G.; Routy, J.P.; Lelièvre, J.D.; Delfraissy, J.F.; Molina, J.M.; Fischl, M.; Goujard, C.; Rodriguez, B.G.; et al. Effects of Recombinant Human Interleukin 7 on T-Cell Recovery and Thymic Output in HIV-Infected Patients Receiving Antiretroviral Therapy: Results of a Phase I/IIa Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Multicenter Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, S.K.; Gallinger, S.; Roder, J.; Frey, J.; Young, H.A.; Ortaldo, J.R. A cyclophilin-related protein involved in the function of natural killer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alkhatib, G.; Murata, K.; Roder, J.C. Cellular distribution of a natural killer cell tumour recognition-related surface antigen in purified human lymphocytes. Immunology 1997, 92, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iyasere, C.; Tilton, J.C.; Johnson, A.J.; Younes, S.; Yassine-Diab, B.; Sekaly, R.P.; Kwok, W.W.; Migueles, S.A.; Laborico, A.C.; Shupert, W.L.; et al. Diminished proliferation of human immunodeficiency virus-specific CD4+ T cells is associated with diminished interleukin-2 (IL-2) production and is recovered by exogenous IL-2. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 10900–10909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keoshkerian, E.; Helbig, K.; Beard, M.; Zaunders, J.; Seddiki, N.; Kelleher, A.; Hampartzoumian, T.; Zekry, A.; Lloyd, A.R. A novel assay for detection of hepatitis C virus-specific effector CD4+ T cells via co-expression of CD25 and CD134. J. Immunol. Methods 2012, 375, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, B.; Bharadwaj, M.; Burrows, J.; Fazou, C.; Wakefield, D.; Hickie, I.; Ffrench, R.; Khanna, R.; Lloyd, A. Dubbo Infection Outcomes Study Prolonged Illness after Infectious Mononucleosis Is Associated with Altered Immunity but Not with Increased Viral Load. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 193, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stern, L.; McGuire, H.; Avdic, S.; Rizzetto, S.; Groth, B.F.D.S.; Luciani, F.; Slobedman, B.; Blyth, E. Mass Cytometry for the Assessment of Immune Reconstitution After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, L.; Munier, C.M.L.; Seddiki, N.; Van Bockel, D.; Ontiveros, N.; Hardy, M.Y.; Gillies, J.K.; Levings, M.K.; Reid, H.H.; Petersen, J.; et al. Circulating gluten-specific FOXP3+CD39+ regulatory T cells have impaired suppressive function in patients with celiac disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1592–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phetsouphanh, C.; Xu, Y.; Amin, J.; Seddiki, N.; Procopio, F.; Sekaly, R.P.; Zaunders, J.J.; Kelleher, A.D. Characterization of Transcription Factor Phenotypes within Antigen-Specific CD4+ T Cells Using Qualitative Multiplex Single-Cell RT-PCR. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, N.; Thatte, J.; Braciale, T.; Ley, K.; O’Connell, M.; Lee, J.K. Local-pooled-error test for identifying differentially expressed genes with a small number of replicated microarrays. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seddiki, N.; Zaunders, J.; Phetsouphanh, C.; Brezar, V.; Xu, Y.; McGuire, H.M.; Bailey, M.; McBride, K.; Hey-Cunningham, W.; Munier, C.M.L.; et al. CD73+ CD127high Long-Term Memory CD4 T Cells Are Highly Proliferative in Response to Recall Antigens and Are Early Targets in HIV-1 Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020912
Seddiki N, Zaunders J, Phetsouphanh C, Brezar V, Xu Y, McGuire HM, Bailey M, McBride K, Hey-Cunningham W, Munier CML, et al. CD73+ CD127high Long-Term Memory CD4 T Cells Are Highly Proliferative in Response to Recall Antigens and Are Early Targets in HIV-1 Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(2):912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020912
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeddiki, Nabila, John Zaunders, Chan Phetsouphanh, Vedran Brezar, Yin Xu, Helen M. McGuire, Michelle Bailey, Kristin McBride, Will Hey-Cunningham, Cynthia Mee Ling Munier, and et al. 2021. "CD73+ CD127high Long-Term Memory CD4 T Cells Are Highly Proliferative in Response to Recall Antigens and Are Early Targets in HIV-1 Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 2: 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020912
APA StyleSeddiki, N., Zaunders, J., Phetsouphanh, C., Brezar, V., Xu, Y., McGuire, H. M., Bailey, M., McBride, K., Hey-Cunningham, W., Munier, C. M. L., Cook, L., Kent, S., Lloyd, A., Cameron, B., Fazekas de St Groth, B., Koelsch, K., Danta, M., Hocini, H., Levy, Y., & Kelleher, A. D. (2021). CD73+ CD127high Long-Term Memory CD4 T Cells Are Highly Proliferative in Response to Recall Antigens and Are Early Targets in HIV-1 Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(2), 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020912






