No Intercellular Regulation of the Cell Cycle among Human Cervical Carcinoma HeLa Cells Expressing Fluorescent Ubiquitination-Based Cell-Cycle Indicators in Modulated Radiation Fields
Abstract
:1. Introduction
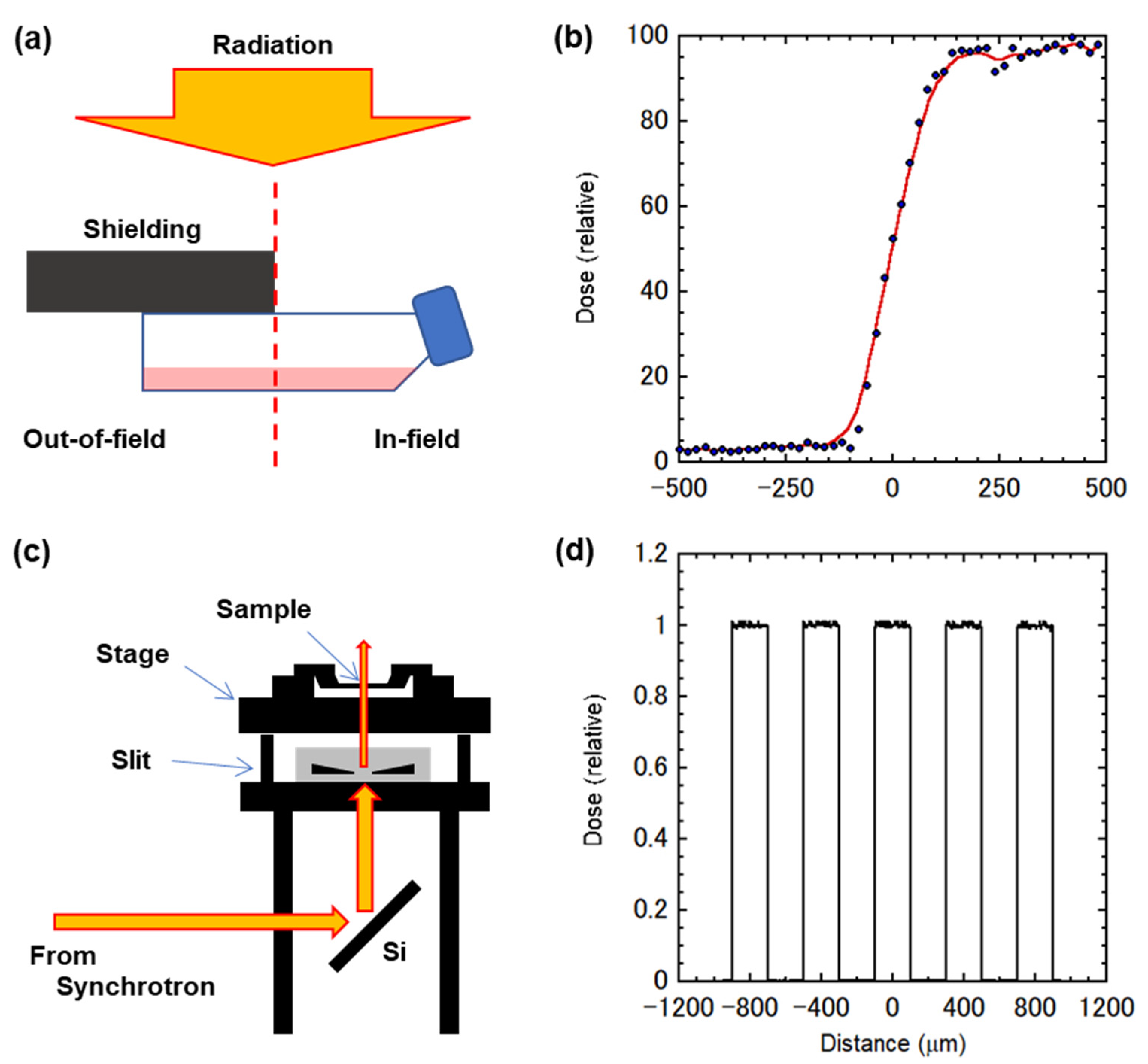
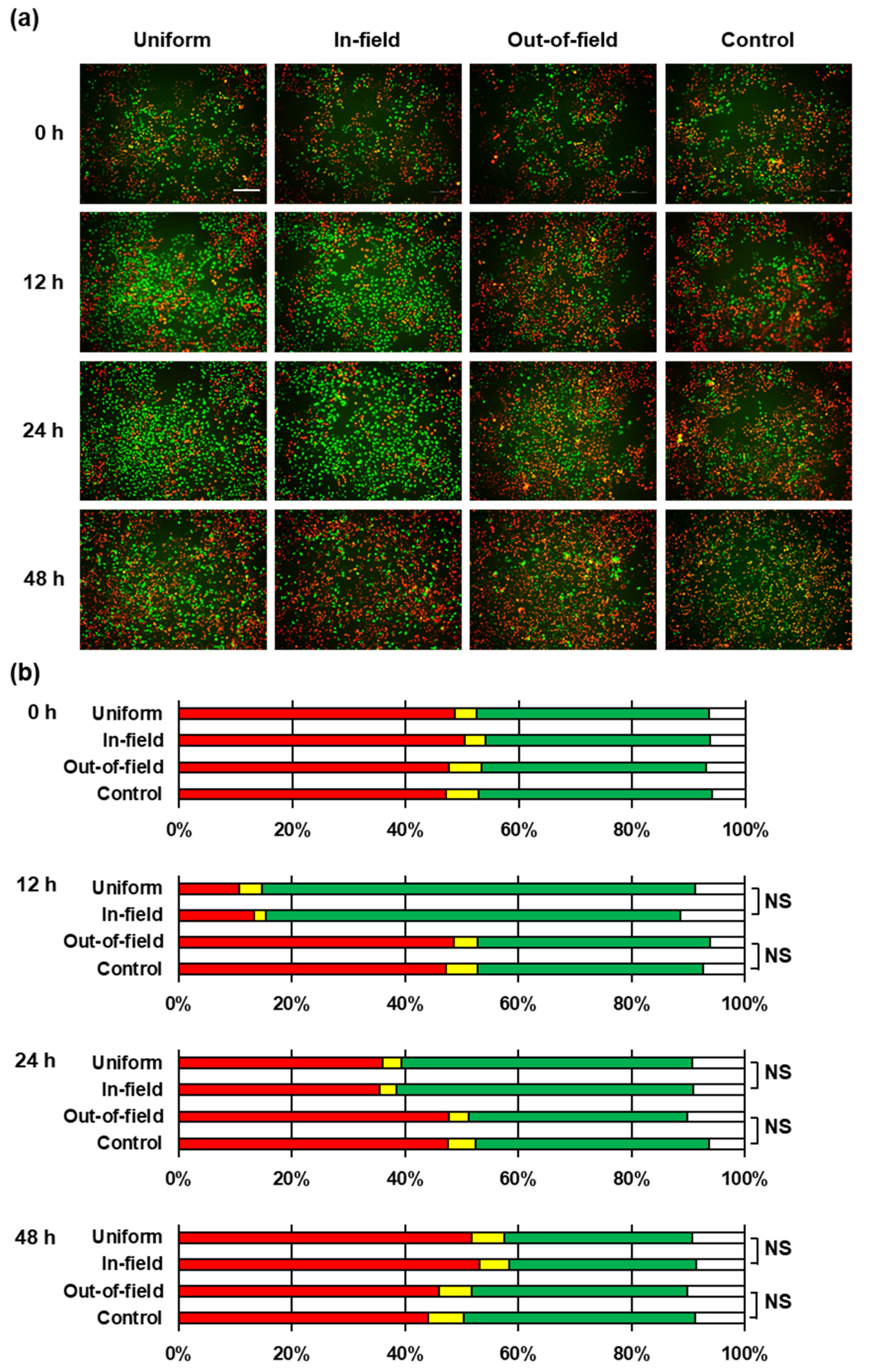
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cell Culture
3.2. Conventional X-ray Settings and Modulated Fields
3.3. Synchrotron X-ray Microbeam Settings and Micro-Slit Fields
3.4. FUCCI Imaging
3.5. Immunochemical Staining
3.6. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heeran, A.B.; Berrigan, H.P.; O’Sullivan, J.N. The Radiation-Induced Bystander Effect (RIBE) and its Connections with the Hallmarks of Cancer. Radiat. Res. 2019, 192, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, K.T.; McGarry, C.; Trainor, C.; O’Sullivan, J.M.; Hounsell, A.R.; Prise, K. Out-of-Field Cell Survival Following Exposure to Intensity-Modulated Radiation Fields. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 79, 1516–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shields, L.; Vega-Carrascal, I.; Singleton, S.; Lyng, F.L.; McClean, B. Cell Survival and DNA Damage in Normal Prostate Cells Irradiated Out-of-Field. Radiat. Res. 2014, 182, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, H.F.; Butterworth, K.; McMahon, S.; Ghita, M.; Hounsell, A.R.; Prise, K. The Impact of Hypoxia on Out-of-Field Cell Survival after Exposure to Modulated Radiation Fields. Radiat. Res. 2017, 188, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, S.J.; Butterworth, K.T.; McGarry, C.K.; Trainor, C.; O’Sullivan, J.M.; Hounsell, A.R.; Prise, K.M. A Computational Model of Cellular Response to Modulated Radiation Fields. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 84, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Funayama, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yokoya, A.; Watanabe, R. A mathematical model of radiation-induced responses in a cellular population including cell-to-cell communications. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2015, 166, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, Y.; Yokoya, A.; Watanabe, R. Cellular automaton-based model for radiation-induced bystander effects. BMC Syst. Biol. 2015, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hei, T.K.; Zhou, H.; Ivanov, V.N.; Hong, M.; Lieberman, H.B.; Brenner, D.J.; Amundson, S.A.; Geard, C.R. Mechanism of radiation-induced bystander effects: A unifying model. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 60, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prise, K.M.; O’Sullivan, J.M. Radiation-induced bystander signalling in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blyth, B.J.; Sykes, P.J. Radiation-induced bystander effects: What are they, and how relevant are they to human radiation exposures? Radiat. Res. 2011, 176, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, H.; Prise, K.M. Non-uniform radiation-induced biological responses at the tissue level involved in the health risk of environmental radiation: A radiobiological hypothesis. Environ. Health 2018, 17, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakaue-Sawano, A.; Kurokawa, H.; Morimura, T.; Hanyu, A.; Hama, H.; Osawa, H.; Kashiwagi, S.; Fukami, K.; Miyata, T.; Miyoshi, H.; et al. Visualizing Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Multicellular Cell-Cycle Progression. Cell 2008, 132, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakaue-Sawano, A.; Miyawaki, A. Visualizing Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Multicellular Cell-Cycle Progressions with Fucci Technology. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2014, 2014, pdb.prot080408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaue-Sawano, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Ohtawa, K.; Miyawaki, A. Drug-induced cell cycle modulation leading to cell-cycle arrest, nuclear mis-segregation, or endoreplication. BMC Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaida, A.; Sawai, N.; Sakaguchi, K.; Miura, M. Fluorescence kinetics in HeLa cells after treatment with cell cycle arrest inducers visualized with Fucci (fluorescent ubiquitination-based cell cycle indicator). Cell Biol. Int. 2011, 35, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yano, S.; Takehara, K.; Zhao, M.; Tan, Y.; Han, Q.; Li, S.; Bouvet, M.; Fujiwara, T.; Hoffman, R.M. Tumor-specific cell-cycle decoy by Salmonella typhimurium A1-R combined with tumor-selective cell-cycle trap by methioninase overcome tumor intrinsic chemoresistance as visualized by FUCCI imaging. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yano, S.; Takehara, K.; Tazawa, H.; Kishimoto, H.; Urata, Y.; Kagawa, S.; Fujiwara, T.; Hoffman, R.M. Efficacy of a Cell-Cycle Decoying Killer Adenovirus on 3-D Gelfoam®-Histoculture and Tumor-Sphere Models of Chemo-Resistant Stomach Carcinomatosis Visualized by FUCCI Imaging. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, S.; Takehara, K.; Tazawa, H.; Kishimoto, H.; Urata, Y.; Kagawa, S.; Fujiwara, T.; Hoffman, R.M. Cell-cycle-dependent drug-resistant quiescent cancer cells induce tumor angiogenesis after chemotherapy as visualized by real-time FUCCI imaging. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, S.; Yano, S.; Kimura, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Toneri, M.; Murakami, T.; Hayashi, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Fujiwara, T.; Tsuchiya, H.; et al. Heterogeneous cell-cycle behavior in response to UVB irradiation by a population of single cancer cells visualized by time-lapse FUCCI imaging. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 1932–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghita, M.; Fernandez-Palomo, C.; Fukunaga, H.; Fredericia, P.M.; Schettino, G.; Bräuer-Krisch, E.; Butterworth, K.T.; McMahon, S.; Prise, K.M. Microbeam evolution: From single cell irradiation to pre-clinical studies. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2018, 94, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, H.; Kaminaga, K.; Sato, T.; Butterworth, K.T.; Watanabe, R.; Usami, N.; Ogawa, T.; Yokoya, A.; Prise, K.M. High-precision microbeam radiotherapy reveals testicular tissue-sparing effects for male fertility preservation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Iwamoto, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Ogawa, T.; Furuta, T.; Abe, S.-I.; Kai, T.; Tsai, P.-E.; Matsuda, N.; Iwase, H.; et al. Features of Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) version 3.02. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaminaga, K.; Noguchi, M.; Narita, A.; Sakamoto, Y.; Kanari, Y.; Yokoya, A. Visualisation of cell cycle modifications by X-ray irradiation of single HeLa cells using fluorescent ubiquitination-based cell cycle indicators. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2015, 166, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, A.; Kaminaga, K.; Yokoya, A.; Noguchi, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Usami, N.; Fujii, K. Real-time observation of irradiated HeLa-cell modified by fluorescent ubiquitination-based cell-cycle indicator using synchrotron X-ray microbeam. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2015, 166, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminaga, K.; Noguchi, M.; Narita, A.; Hattori, Y.; Usami, N.; Yokoya, A. Cell cycle tracking for irradiated and unirradiated bystander cells in a single colony with exposure to a soft X-ray microbeam. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2016, 92, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, B.; Girard, L.; Hollestelle, A.; Minna, J.D.; Gazdar, A.F.; Soussi, T. Analysis of TP53 Mutation Status in Human Cancer Cell Lines: A Reassessment. Hum. Mutat. 2014, 35, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirao, A.; Kong, Y.-Y.; Matsuoka, S.; Wakeham, A.; Ruland, J.; Yoshida, H.; Liu, D.; Elledge, S.J.; Mak, T.W. DNA Damage-Induced Activation of p53 by the Checkpoint Kinase Chk2. Science 2000, 287, 1824–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Guntuku, S.; Cui, X.S.; Matsuoka, S.; Cortez, D.; Tamai, K.; Luo, G.; Carattini-Rivera, S.; DeMayo, F.; Bradley, A.; et al. Chk1 is an essential kinase that is regulated by Atr and required for the G2/M DNA damage checkpoint. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 1448–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, Y.; Wong, C.; Thoma, R.S.; Richman, R.; Wu, Z.; Piwnica-Worms, H.; Elledge, S.J. Conservation of the Chk1 Checkpoint Pathway in Mammals: Linkage of DNA Damage to Cdk Regulation Through Cdc25. Science 1997, 277, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lara, C.M.; Hill, M.A.; Jenner, T.J.; Papworth, D.; O’Neill, P. Dependence of the Yield of DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Chinese Hamster V79-4 Cells on the Photon Energy of Ultrasoft X Rays. Radiat. Res. 2001, 155, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S.; Mrksich, M.; Huang, S.; Whitesides, G.M.; Ingber, D.E. Geometric Control of Cell Life and Death. Science 1997, 276, 1425–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Streichan, S.J.; Hoerner, C.; Schneidt, T.; Holzer, D.; Hufnagel, L. Spatial constraints control cell proliferation in tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5586–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, K.; Hieda, K.; Maezawa, H.; Ando, M.; Ito, T. Monochromatic X-ray irradiation system (0.08-0.4 nm) for radiation biology studies using synchrotron radiation at the photon factory. J. Radiat. Res. 1987, 28, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yokoya, A.; Usami, N. Targeting Specific Sites in Biological Systems with Synchrotron X-Ray Microbeams for Radiobiological Studies at the Photon Factory. Quantum Beam Sci. 2020, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fukunaga, H.; Kaminaga, K.; Hirose, E.; Watanabe, R.; Usami, N.; Prise, K.M.; Yokoya, A. No Intercellular Regulation of the Cell Cycle among Human Cervical Carcinoma HeLa Cells Expressing Fluorescent Ubiquitination-Based Cell-Cycle Indicators in Modulated Radiation Fields. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312785
Fukunaga H, Kaminaga K, Hirose E, Watanabe R, Usami N, Prise KM, Yokoya A. No Intercellular Regulation of the Cell Cycle among Human Cervical Carcinoma HeLa Cells Expressing Fluorescent Ubiquitination-Based Cell-Cycle Indicators in Modulated Radiation Fields. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(23):12785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312785
Chicago/Turabian StyleFukunaga, Hisanori, Kiichi Kaminaga, Eri Hirose, Ritsuko Watanabe, Noriko Usami, Kevin M. Prise, and Akinari Yokoya. 2021. "No Intercellular Regulation of the Cell Cycle among Human Cervical Carcinoma HeLa Cells Expressing Fluorescent Ubiquitination-Based Cell-Cycle Indicators in Modulated Radiation Fields" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 23: 12785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312785
APA StyleFukunaga, H., Kaminaga, K., Hirose, E., Watanabe, R., Usami, N., Prise, K. M., & Yokoya, A. (2021). No Intercellular Regulation of the Cell Cycle among Human Cervical Carcinoma HeLa Cells Expressing Fluorescent Ubiquitination-Based Cell-Cycle Indicators in Modulated Radiation Fields. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(23), 12785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312785





