Identification and Analysis of Genes Involved in Double Fertilization in Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
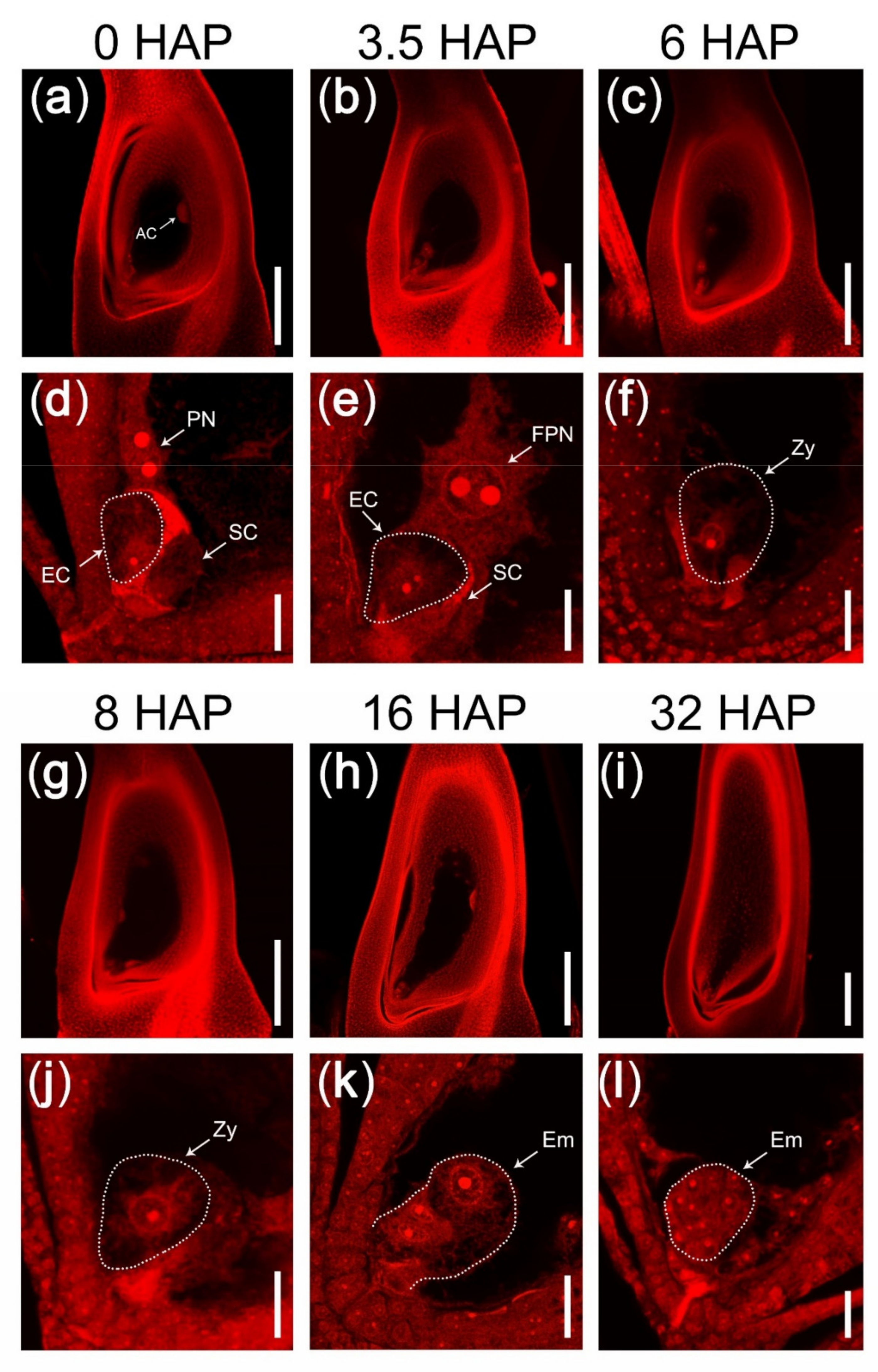
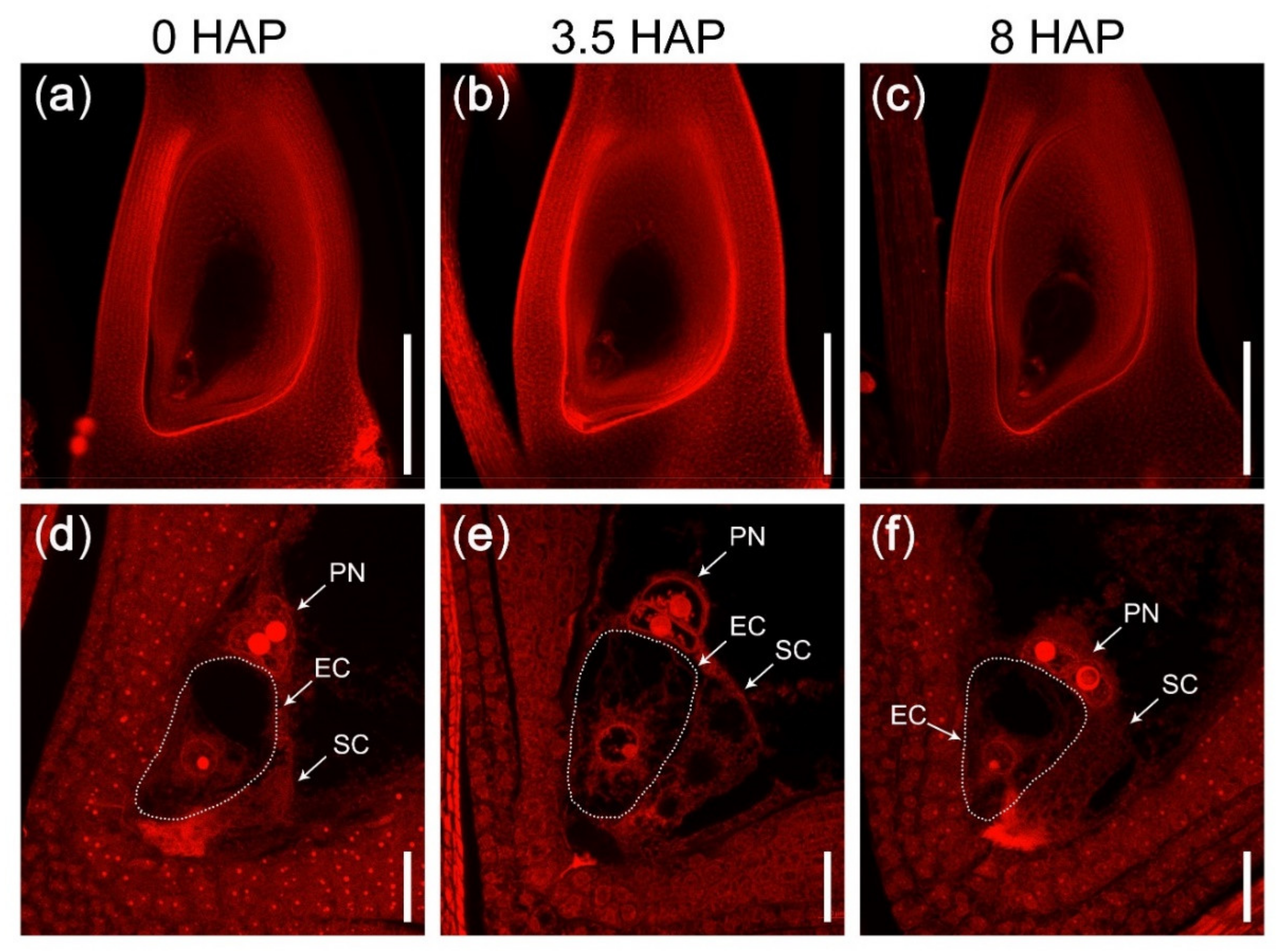
2.1. A Rice Mutant with Fertilization Barrier
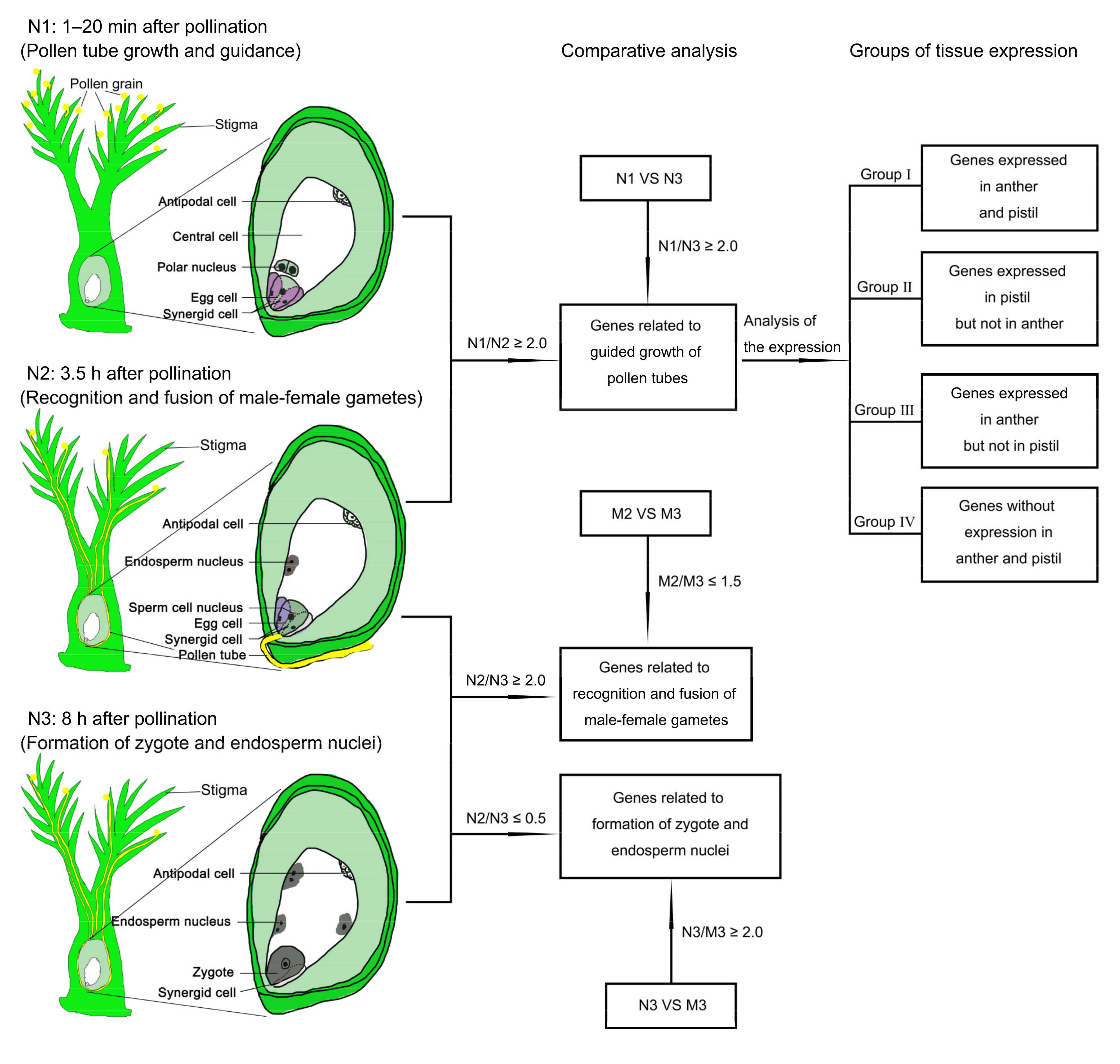
2.2. Strategy to Identify Genes Related to Rice Double Fertilization Process
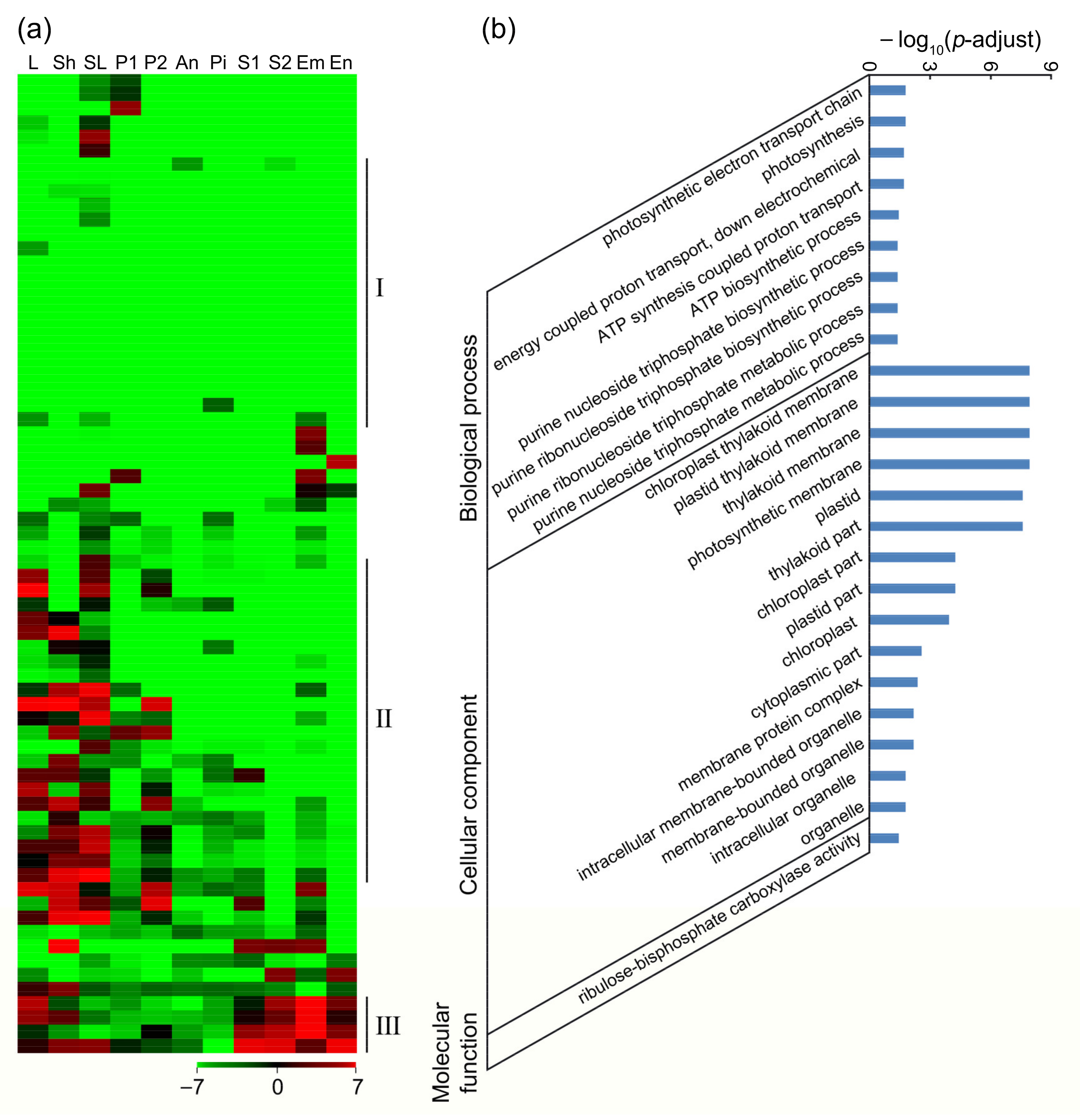
2.3. Global Analysis of the RNA-seq Data
2.4. Identification of Pollen Tube-Related Genes
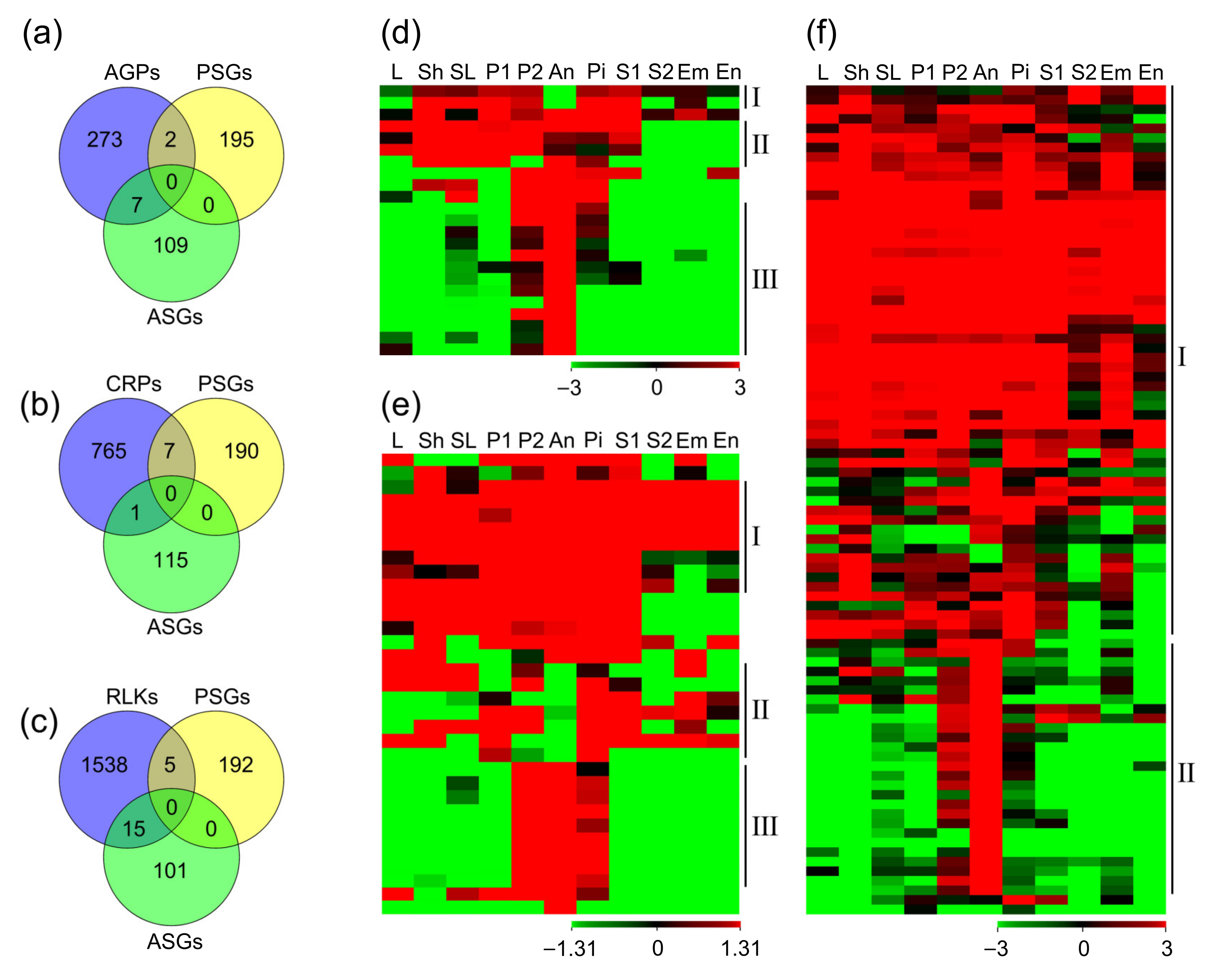
2.5. Distribution of AGP, CRP, and RLK Genes during the Guided Growth of Pollen Tubes
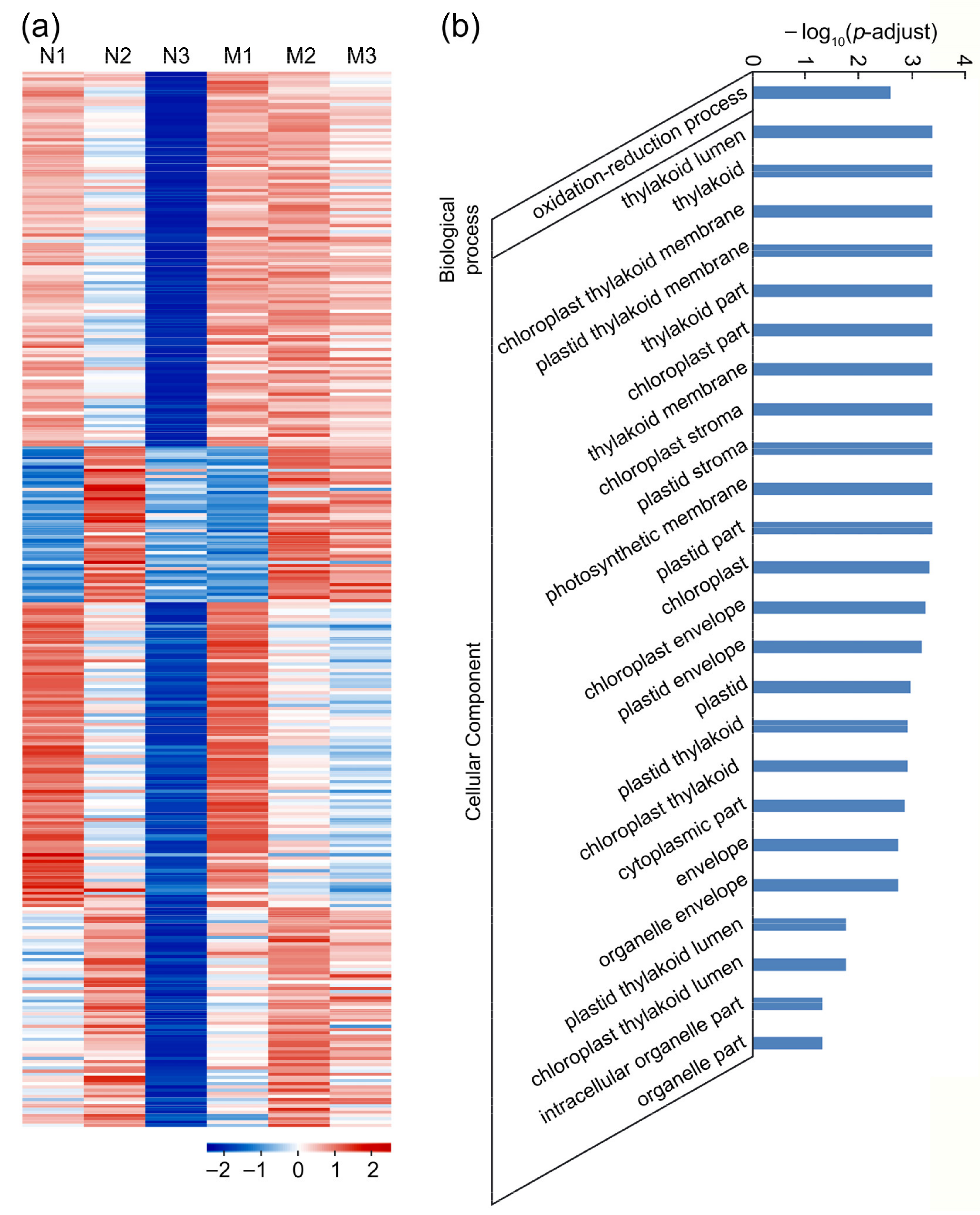
2.6. Identification of Genes Involved in the Recognition and Fusion of the Male–Female Gametes
2.7. Identification of Genes Involved in Zygote Formation and Endosperm Nuclear Division
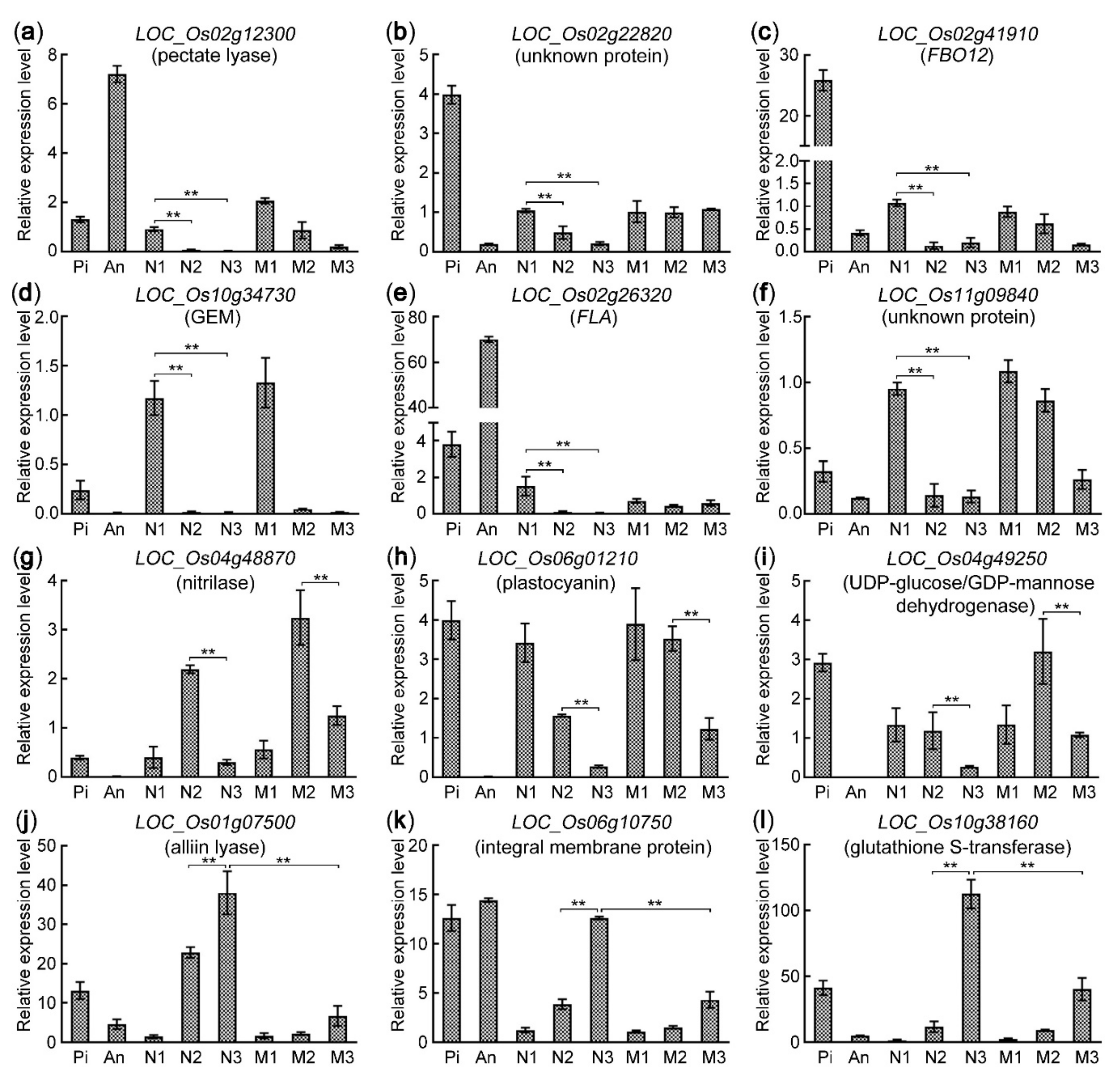
2.8. Validation of Gene Expression Patterns via qRT-PCR
3. Discussion
3.1. The Mutant Feb Could Help to Investigate the Mechanism about the Recognition and Fusion of Male–Female Gametes
3.2. Photosynthetic Pathway Was Activated in Rice Pistil during the Guided Growth of Pollen Tubes
3.3. Pistil Communicated with Pollen Tube in Different Species
3.4. AGPs Played Different Roles in Dry and Wet Stigmas
3.5. This Study Laid Solid Foundation for Investigating Fertilization Mechanism in Rice
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Ovary Clearing and Microscopy Observation
4.3. RNA Extraction and Sequencing
4.4. Reads Optimization and Transcriptome Assembly
4.5. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes and Cluster Analysis
4.6. Venn Analysis and Heat Map Construction
4.7. Functional Annotation and Enrichment Analyses
4.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Zhong, S.; Qu, L.J. Peptide/receptor-like kinase-mediated signaling involved in male-female interactions. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2019, 51, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; de Graaf, B.; Mariani, C.; Cheung, A.Y. Hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins in plant reproductive tissues: Structure, functions and regulation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 1418–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, C.N.; Kent, L.; McClure, B.A. The stylar 120 kDa glycoprotein is required for S-specific pollen rejection in Nicotiana. Plant J. 2005, 43, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.B.; Swatek, K.N.; McClure, B. Pollen proteins bind to the C-terminal domain of Nicotiana alata pistil arabinogalactan proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 26965–26973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, A.Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.M. A floral transmitting tissue-specific glycoprotein attracts pollen tubes and stimulates their growth. Cell 1995, 82, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.M.; Wang, H.; Cheung, A.Y. A pollen tube growth stimulatory glycoprotein is deglycosylated by pollen tubes and displays a glycosylation gradient in the flower. Cell 1995, 82, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, S.; Costa, M.; Jones, B.; Mendes, M.A.; Pereira, L.G. Pollen grain development is compromised in Arabidopsis agp6 agp11 null mutants. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 3133–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coimbra, S.; Costa, M.; Mendes, M.A.; Pereira, A.M.; Pinto, J.; Pereira, L.G. Early germination of Arabidopsis pollen in a double null mutant for the arabinogalactan protein genes AGP6 and AGP11. Sex. Plant Reprod. 2010, 23, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizukami, A.G.; Inatsugi, R.; Jiao, J.; Kotake, T.; Kuwata, K.; Ootani, K.; Okuda, S.; Sankaranarayanan, S.; Sato, Y.; Maruyama, D.; et al. The AMOR arabinogalactan sugar chain induces pollen-tube competency to respond to ovular guidance. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamport, D.T.; Varnai, P.; Seal, C.E. Back to the future with the AGP-Ca2+ flux capacitor. Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 1069–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamport, D.T.; Tan, L.; Held, M.A.; Kieliszewski, M.J. Pollen tube growth and guidance: Occam’s razor sharpened on a molecular arabinogalactan glycoprotein Rosetta Stone. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.; An, S.; An, G. OsMLO12, encoding seven transmembrane proteins, is involved with pollen hydration in rice. Plant Reprod. 2014, 27, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Long, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ren, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. OsCNGC13 promotes seed-setting rate by facilitating pollen tube growth in stylar tissues. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwano, M.; Ito, K.; Shimosato-Asano, H.; Lai, K.S.; Takayama, S. Self-incompatibility in the Brassicaceae. In Sexual Reproduction in Animals and Plants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 245–254. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, M.; Suwabe, K.; Suzuki, G. Molecular genetics, physiology and biology of self-incompatibility in Brassicaceae. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2012, 88, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, S.L.; Anderson, E.M.; Mullen, R.T.; Goring, D.R. ARC1 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase and promotes the ubiquitination of proteins during the rejection of self-incompatible Brassica pollen. Plant Cell. 2003, 15, 885–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Lian, X.; Converse, R.; Zhu, L. Identification of interacting motifs between armadillo repeat containing 1 (ARC1) and exocyst 70 A1 (Exo70A1) proteins in Brassica oleracea. Protein J. 2016, 35, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Bergonci, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zou, Y.; Du, S.; Liu, M.C.; Luo, X.; Ruan, H.; García-Valencia, L.E.; Zhong, S.; et al. Arabidopsis pollen tube integrity and sperm release are regulated by RALF-mediated signaling. Science 2017, 358, 1596–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, M.C.; Zhou, L.Z.; Wang, L.; Zhong, S.; Hou, S.; Jiang, J.; Liu, T.; Huang, Q.; et al. LLG2/3 are co-receptors in BUPS/ANX-RALF signaling to regulate Arabidopsis pollen tube integrity. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 3256–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecchia, M.A.; Santos-Fernandez, G.; Duss, N.N.; Somoza, S.C.; Boisson-Dernier, A.; Gagliardini, V.; Martínez-Bernardini, A.; Fabrice, T.N.; Ringli, C.; Muschietti, J.P.; et al. RALF4/19 peptides interact with LRX proteins to control pollen tube growth in Arabidopsis. Science 2017, 358, 1600–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, S.; Tsutsui, H.; Shiina, K.; Sprunck, S.; Takeuchi, H.; Yui, R.; Kasahara, R.D.; Hamamura, Y.; Mizukami, A.; Susaki, D.; et al. Defensin-like polypeptide LUREs are pollen tube attractants secreted from synergid cells. Nature 2009, 458, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H.; Higashiyama, T. Tip-localized receptors control pollen tube growth and LURE sensing in Arabidopsis. Nature 2016, 531, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Márton, M.L.; Cordts, S.; Broadhvest, J.; Dresselhaus, T. Micropylar pollen tube guidance by egg apparatus 1 of maize. Science 2005, 307, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márton, M.L.; Fastner, A.; Uebler, S.; Dresselhaus, T. Overcoming hybridization barriers by the secretion of the maize pollen tube attractant ZmEA1 from Arabidopsis ovules. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Hou, S.; Xu, Y.C.; Ge, Z.; Song, Z.; Huang, J.; Qiu, X.; et al. Cysteine-rich peptides promote interspecific genetic isolation in Arabidopsis. Science 2019, 364, eaau9564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Liang, L.; Xue, Y.; Jia, P.F.; Chen, W.; Zhang, M.X.; Wang, Y.C.; Li, H.J.; Yang, W.C. A receptor heteromer mediates the male perception of female attractants in plants. Nature 2016, 531, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amien, S.; Kliwer, I.; Márton, M.L.; Debener, T.; Geiger, D.; Becker, D.; Dresselhaus, T. Defensin-like ZmES4 mediates pollen tube burst in maize via opening of the potassium channel KZM1. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Restrepo, J.M.; Huck, N.; Kessler, S.; Gagliardini, V.; Gheyselinck, J.; Yang, W.C.; Grossniklaus, U. The FERONIA receptor-like kinase mediates male-female interactions during pollen tube reception. Science 2007, 317, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capron, A.; Gourgues, M.; Neiva, L.S.; Faure, J.E.; Berger, F.; Pagnussat, G.; Krishnan, A.; Alvarez-Mejia, C.; Vielle-Calzada, J.P.; Lee, Y.R.; et al. Maternal control of male-gamete delivery in Arabidopsis involves a putative GPI-anchored protein encoded by the LORELEI gene. Plant Cell. 2008, 20, 3038–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Kuroiwa, H.; Higashiyama, T.; Kuroiwa, T. GENERATIVE CELL SPECIFIC 1 is essential for angiosperm fertilization. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2006, 8, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprunck, S.; Rademacher, S.; Vogler, F.; Gheyselinck, J.; Grossniklaus, U.; Dresselhaus, T. Egg cell-secreted EC1 triggers sperm cell activation during double fertilization. Science 2012, 338, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.S.; Yu, Y.M.; Xu, C.G.; Li, G.W.; Ouyang, Y.D. Prezygotic reproductive isolation and fertility in crosses between indica and japonica subspecies. Sci. Sin. Vitae 2014, 44, 815–821. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, W.; Huang, B.; Cao, X.; Zhou, X.; Ye, S.; Li, C.; Gao, F.; Zou, T.; Xie, K.; et al. Natural variation in PTB1 regulates rice seed setting rate by controlling pollen tube growth. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhao, J. Genome-wide identification, classification, and expression analysis of the arabinogalactan protein gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 2647–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Ma, H.; Zhao, H.; Qi, H.; Zhao, J. Identification, characterization, and transcription analysis of xylogen-like arabinogalactan proteins in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Yan, C.; Li, H.; Wu, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ma, H. Bioinformatics prediction and evolution analysis of arabinogalactan proteins in the plant kingdom. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverstein, K.A.; Moskal, W.A., Jr.; Wu, H.C.; Underwood, B.A.; Graham, M.A.; Town, C.D.; VandenBosch, K.A. Small cysteine-rich peptides resembling antimicrobial peptides have been under-predicted in plants. Plant J. 2007, 51, 262–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenton, M.R.; Ohyanagi, H.; Wang, Z.X.; Toyoda, A.; Fujiyama, A.; Nagata, T.; Feng, Q.; Han, B.; Kurata, N. Rapid turnover of antimicrobial-type cysteine-rich protein genes in closely related Oryza genomes. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2015, 290, 1753–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.Y.; Lin, X.J.; Liang, H.M.; Wang, F.F.; Chen, L.Y. The long journey of pollen tube in the pistil. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, L.; Christoff, A.P.; de Lima, J.C.; de Ross, B.; Sachetto-Martins, G.; Margis-Pinheiro, M.; Margis, R. The wall-associated kinase gene family in rice genomes. Plant Sci. 2014, 229, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.G.; Kim, D.S.; Jang, C.S. Comparative analysis of evolutionary dynamics of genes encoding leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase between rice and Arabidopsis. Genetica 2011, 139, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaid, N.; Pandey, P.K.; Tuteja, N. Genome-wide analysis of lectin receptor-like kinase family from Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2012, 80, 365–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vij, S.; Giri, J.; Dansana, P.K.; Kapoor, S.; Tyagi, A.K. The receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase (OsRLCK) gene family in rice: Organization, phylogenetic relationship, and expression during development and stress. Mol. Plant 2008, 1, 732–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiu, S.H.; Karlowski, W.M.; Pan, R.; Tzeng, Y.H.; Mayer, K.F.; Li, W.H. Comparative analysis of the receptor-like kinase family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Cell. 2004, 16, 1220–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Shi, J.; Zhou, J.; Gu, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Cheng, W.; Mao, D.; Tian, L.; Buchanan, B.B.; et al. ANK6, a mitochondrial ankyrin repeat protein, is required for male-female gamete recognition in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22332–22337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisson-Dernier, A.; Frietsch, S.; Kim, T.H.; Dizon, M.B.; Schroeder, J.I. The peroxin loss-of-function mutation abstinence by mutual consent disrupts male-female gametophyte recognition. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.Z.; Song, L.F.; Zou, J.J.; Su, Z.; Wu, W.H. Transcriptome analyses show changes in gene expression to accompany pollen germination and tube growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conze, L.L.; Berlin, S.; Le Bail, A.; Kost, B. Transcriptome profiling of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) pollen and pollen tubes. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Zou, W.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Zhao, J. Functional divergence of chloroplast Cpn60α subunits during Arabidopsis embryo development. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1007036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Zhang, D.; Jung, K.H. Molecular basis of pollen germination in cereals. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shen, L.; Xiao, Y.; Vyshedsky, D.; Peng, C.; Sun, X.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, H.; Han, Z.; et al. Pollen PCP-B peptides unlock a stigma peptide-receptor kinase gating mechanism for pollination. Science 2021, 372, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.J.; Li, L.; Lan, Z.; Dresselhaus, T. Peptide signalling during the pollen tube journey and double fertilization. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 5139–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, M.J.; de Graaf, B.H.; Hadjiosif, N.; Perry, R.M.; Poulter, N.S.; Osman, K.; Vatovec, S.; Harper, A.; Franklin, F.C.; Franklin-Tong, V.E. Identification of the pollen self-incompatibility determinant in Papaver Rhoeas. Nature 2009, 459, 992–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Guo, X.; Cyprys, P.; Zhang, Y.; Bleckmann, A.; Cai, L.; Huang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Gu, H.; Dresselhaus, T. Maternal ENODLs are required for pollen tube reception in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 2343–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, M.; Geng, L.L.; Zhao, J. The fasciclin-like arabinogalactan protein gene, FLA3, is involved in microspore development of Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2010, 64, 482–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitin, B.; Richter, D.; Markovich, I.; Zik, M. Arabinogalactan proteins 6 and 11 are required for stamen and pollen function in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2008, 56, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Ma, T.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yu, K.; Chen, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhao, J. Identification and analysis of the stigma and embryo sac-preferential/specific genes in rice pistils. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.X.; Hu, C.Y.; Lu, Y.G.; Li, J.Q.; Liu, X.D. Abnormalities occurring during female gametophyte development result in the diversity of abnormal embryo sacs and leads to abnormal fertilization in indica/japonica hybrids in rice. J. Integr. Plant. Biol. 2009, 51, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Nie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, J. OsMre11 is required for mitosis during rice growth and development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, L.; Yu, L.; Liang, R.; Sun, R.; Hu, F.; Lu, X.; Zhao, J. Identification and Analysis of Genes Involved in Double Fertilization in Rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312850
You L, Yu L, Liang R, Sun R, Hu F, Lu X, Zhao J. Identification and Analysis of Genes Involved in Double Fertilization in Rice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(23):12850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312850
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Li, Li Yu, Ronghong Liang, Ruhao Sun, Fan Hu, Xiaoyun Lu, and Jie Zhao. 2021. "Identification and Analysis of Genes Involved in Double Fertilization in Rice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 23: 12850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312850
APA StyleYou, L., Yu, L., Liang, R., Sun, R., Hu, F., Lu, X., & Zhao, J. (2021). Identification and Analysis of Genes Involved in Double Fertilization in Rice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(23), 12850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312850





