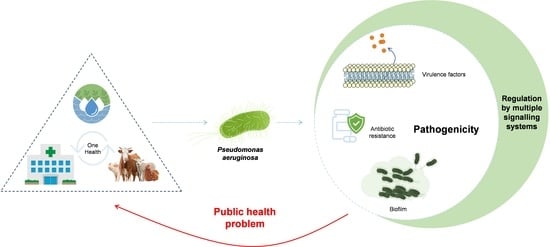
Genomic and Metabolic Characteristics of the Pathogenicity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
Share and Cite
de Sousa, T.; Hébraud, M.; Dapkevicius, M.L.N.E.; Maltez, L.; Pereira, J.E.; Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Genomic and Metabolic Characteristics of the Pathogenicity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12892. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312892
de Sousa T, Hébraud M, Dapkevicius MLNE, Maltez L, Pereira JE, Capita R, Alonso-Calleja C, Igrejas G, Poeta P. Genomic and Metabolic Characteristics of the Pathogenicity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(23):12892. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312892
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Sousa, Telma, Michel Hébraud, Maria L. N. Enes Dapkevicius, Luís Maltez, José Eduardo Pereira, Rosa Capita, Carlos Alonso-Calleja, Gilberto Igrejas, and Patricia Poeta. 2021. "Genomic and Metabolic Characteristics of the Pathogenicity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 23: 12892. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312892
APA Stylede Sousa, T., Hébraud, M., Dapkevicius, M. L. N. E., Maltez, L., Pereira, J. E., Capita, R., Alonso-Calleja, C., Igrejas, G., & Poeta, P. (2021). Genomic and Metabolic Characteristics of the Pathogenicity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(23), 12892. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312892