Malondialdehyde-Acetaldehyde Modified (MAA) Proteins Differentially Effect the Inflammatory Response in Macrophage, Endothelial Cells and Animal Models of Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
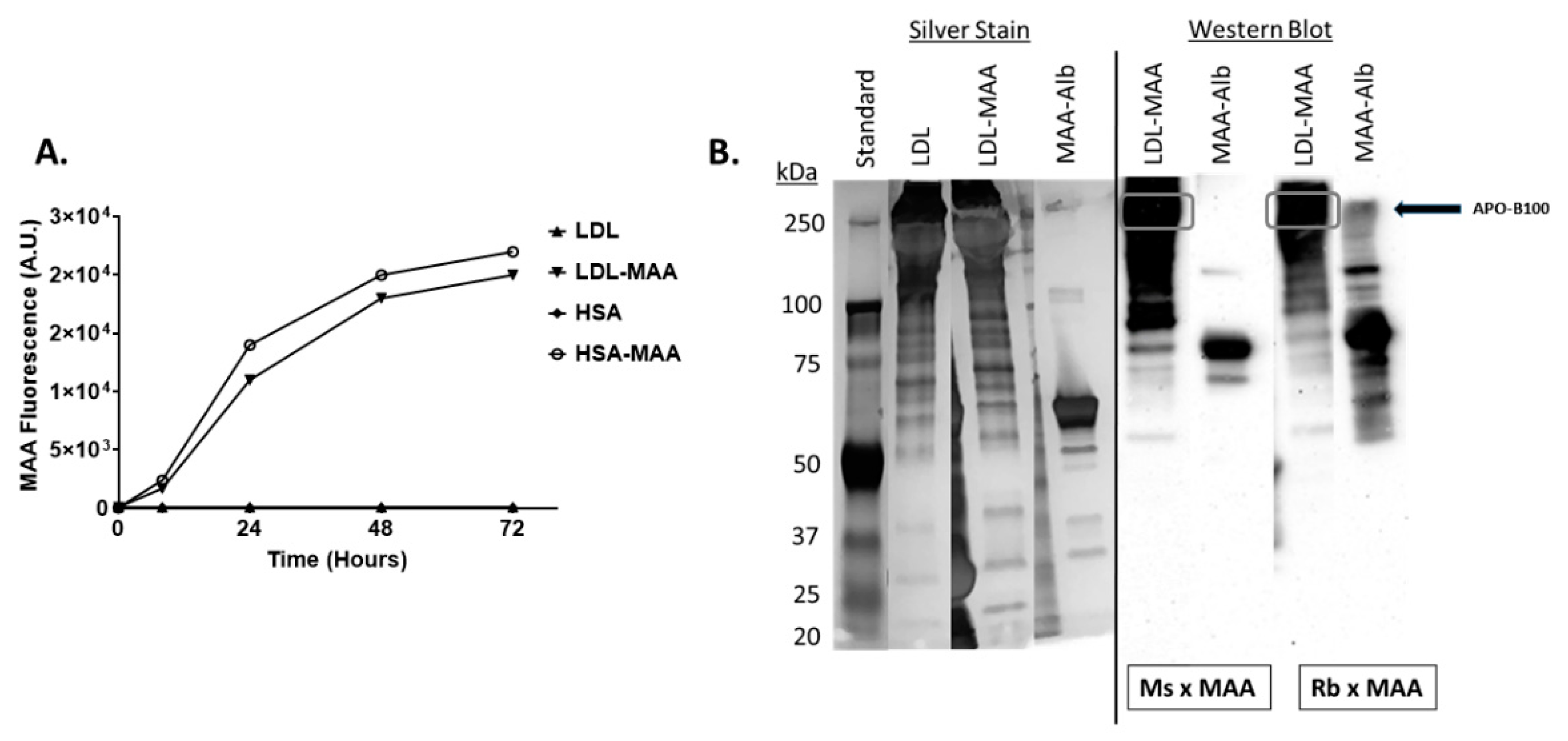
2.1. Proteins on LDL Are MAA Adducted
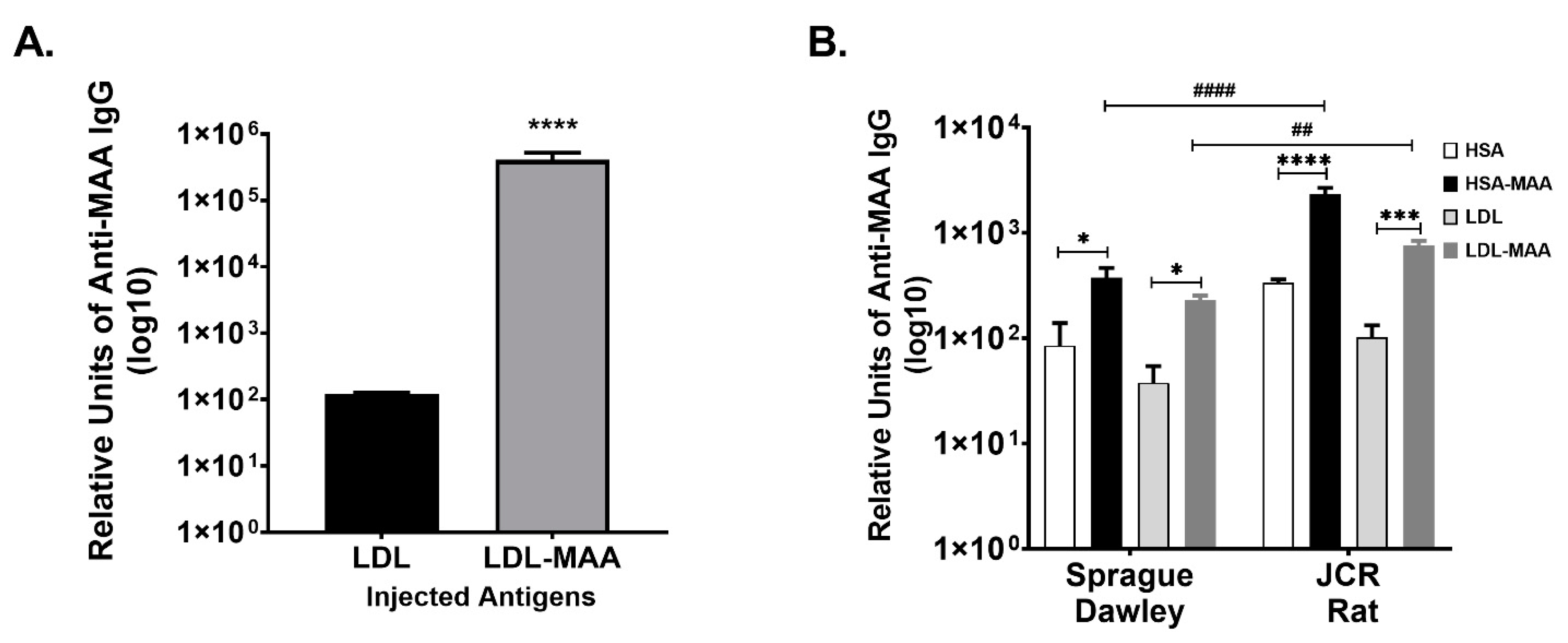
2.2. MAA Modified LDL Is Immunogenic
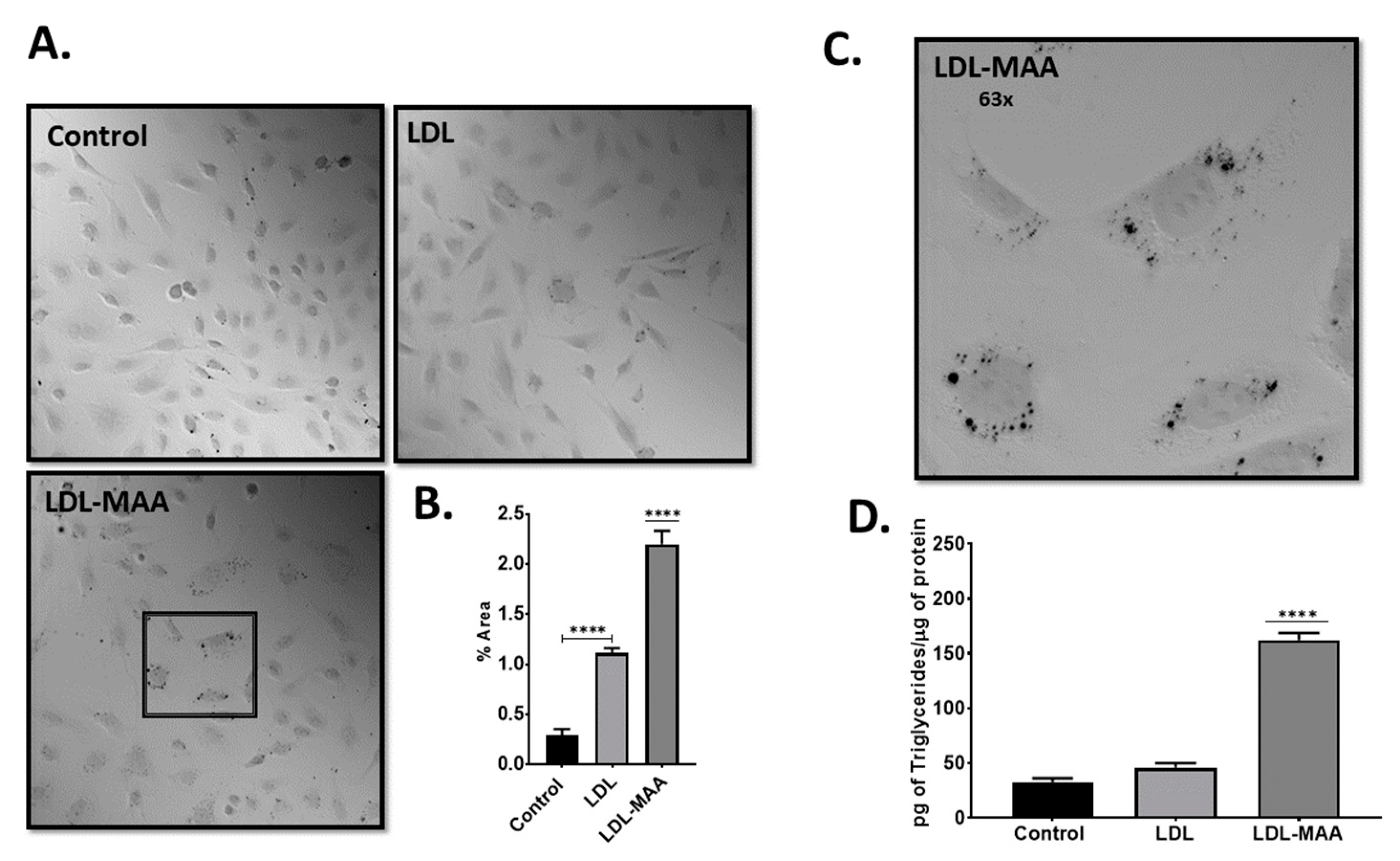
2.3. LDL-MAA Increases Fat Accumulation in Vascular Endothelial Cells
2.4. MAA Adducted Proteins Increase Adhesion Molecules and Cytokines in Vascular Endothelial Cells
2.5. LDL-MAA Increases Fat Accumulation in Mouse Macrophage
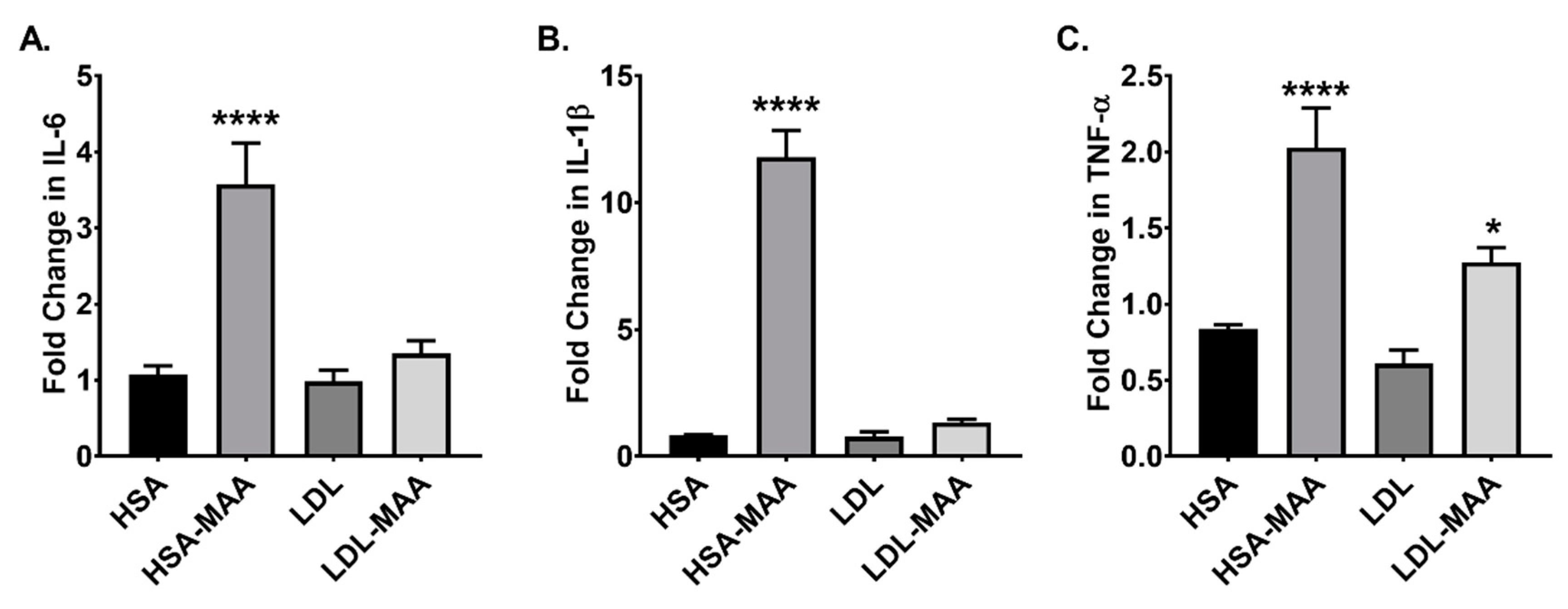
2.6. MAA-Modified Proteins Increase Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Macrophage
2.7. High Fat Diet and MAA Antigen Increase Aortic Fat Deposition (Key Finding)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Malondialdehyde-Acetaldehyde (MAA)-Protein Adduct Formation
4.2. Animal Studies
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Detection of Cellular Lipids
4.5. RT-PCR
4.6. Flow Cytometry
4.7. Immunohistochemistry
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benjamin, E.J.; Blaha, M.J.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; Deo, R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Floyd, J.; Fornage, M.; Gillespie, C.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e146–e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, G.K. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Libby, P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 2002, 420, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R. Atherosclerosis--an inflammatory disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madamanchi, N.R.; Hakim, Z.S.; Runge, M.S. Oxidative stress in atherogenesis and arterial thrombosis: The disconnect between cellular studies and clinical outcomes. J. Thromb. Haemost 2005, 3, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madamanchi, N.R.; Vendrov, A.; Runge, M.S. Oxidative stress and vascular disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kunsch, C.; Medford, R.M. Oxidative stress as a regulator of gene expression in the vasculature. Circ. Res. 1999, 85, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spychalowicz, A.; Wilk, G.; Sliwa, T.; Ludew, D.; Guzik, T.J. Novel therapeutic approaches in limiting oxidative stress and inflammation. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 2456–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, A.; Munoz, M.F.; Arguelles, S. Lipid peroxidation: Production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2014, 2014, 360438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esterbauer, H.; Schaur, R.J.; Zollner, H. Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1991, 11, 81–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaschler, M.M.; Stockwell, B.R. Lipid peroxidation in cell death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, C.J.; Chang, M.K.; Shaw, P.X.; Miller, Y.I.; Hartvigsen, K.; Dewan, A.; Witztum, J.L. Innate and acquired immunity in atherogenesis. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, C.J.; Papac-Milicevic, N.; Witztum, J.L. Innate sensing of oxidation-specific epitopes in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikugawa, K.; Ido, Y. Studies on peroxidized lipids. V. Formation and characterization of 1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarbaldehydes as model of fluorescent components in lipofuscin. Lipids 1984, 19, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuma, D.J.; Thiele, G.M.; Xu, D.; Klassen, L.W.; Sorrell, M.F. Acetaldehyde and malondialdehyde react together to generate distinct protein adducts in the liver during long-term ethanol administration. Hepatology 1996, 23, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele, G.M.; Tuma, D.J.; Willis, M.S.; Miller, J.A.; McDonald, T.L.; Sorrell, M.F.; Klassen, L.W. Soluble proteins modified with acetaldehyde and malondialdehyde are immunogenic in the absence of adjuvant. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1998, 22, 1731–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Thiele, G.M.; Kearley, M.L.; Haugen, M.D.; Klassen, L.W.; Sorrell, M.F.; Tuma, D.J. Epitope characterization of malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde adducts using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1997, 10, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, M.S.; Klassen, L.W.; Carlson, D.L.; Brouse, C.F.; Thiele, G.M. Malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde haptenated protein binds macrophage scavenger receptor(s) and induces lysosomal damage. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2004, 4, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, M.S.; Thiele, G.M.; Tuma, D.J.; Klassen, L.W. T cell proliferative responses to malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde haptenated protein are scavenger receptor mediated. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2003, 3, 1381–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.R.; Duryee, M.J.; Shurmur, S.W.; Um, J.Y.; Bussey, W.D.; Hunter, C.D.; Garvin, R.P.; Sayles, H.R.; Mikuls, T.R.; Klassen, L.W.; et al. Unique antibody responses to malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde (MAA)-protein adducts predict coronary artery disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duryee, M.J.; Klassen, L.W.; Schaffert, C.S.; Tuma, D.J.; Hunter, C.D.; Garvin, R.P.; Anderson, D.R.; Thiele, G.M. Malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde adduct is the dominant epitope after MDA modification of proteins in atherosclerosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1480–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Hansson, G.K. Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature 2011, 473, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viola, J.; Soehnlein, O. Atherosclerosis-A matter of unresolved inflammation. Semin. Immunol. 2015, 27, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, D.; Parthasarathy, S.; Carew, T.E.; Khoo, J.C.; Witztum, J.L. Beyond cholesterol. Modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 320, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, G.E.; Miller, J.A.; Baxter, B.T.; Klassen, L.W.; Duryee, M.J.; Tuma, D.J.; Thiele, G.M. Association of malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde (MAA) adducted proteins with atherosclerotic-induced vascular inflammatory injury. Atherosclerosis 1998, 141, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotis, L.; Agrogiannis, G.; Vlachos, I.S.; Pantopoulou, A.; Margoni, A.; Kostaki, M.; Verikokos, C.; Tzivras, D.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Perrea, D. Intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM)-1 at the early stages of atherosclerosis in a rat model. In Vivo 2012, 26, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moss, J.W.; Ramji, D.P. Cytokines: Roles in atherosclerosis disease progression and potential therapeutic targets. Future Med. Chem. 2016, 8, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stocker, R.; Keaney, J.F., Jr. Role of oxidative modifications in atherosclerosis. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 1381–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.R.; Duryee, M.J.; Anchan, R.K.; Garvin, R.P.; Johnston, M.D.; Porter, T.R.; Thiele, G.M.; Klassen, L.W. Albumin-based microbubbles bind up-regulated scavenger receptors following vascular injury. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 40645–40653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duryee, M.J.; Willis, M.S.; Freeman, T.L.; Kuszynski, C.A.; Tuma, D.J.; Klassen, L.W.; Thiele, G.M. Mechanisms of alcohol liver damage: Aldehydes, scavenger receptors, and autoimmunity. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 3145–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thiele, G.M.; Duryee, M.J.; Hunter, C.D.; England, B.R.; Fletcher, B.S.; Daubach, E.C.; Pospisil, T.P.; Klassen, L.W.; Mikuls, T.R. Immunogenic and inflammatory responses to citrullinated proteins are enhanced following modification with malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde adducts. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 83, 106433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, M.Z.; Sahu, A. Scavenger receptors: A key player in cardiovascular diseases. Biomol. Concepts. 2012, 3, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, K.J.; Freeman, M.W. Scavenger receptors in atherosclerosis: Beyond lipid uptake. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 1702–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clemens, D.L.; Duryee, M.J.; Hall, J.H.; Thiele, G.M.; Mikuls, T.R.; Klassen, L.W.; Zimmerman, M.C.; Anderson, D.R. Relevance of the antioxidant properties of methotrexate and doxycycline to their treatment of cardiovascular disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 205, 107413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duryee, M.J.; Clemens, D.L.; Opperman, P.J.; Thiele, G.M.; Duryee, L.M.; Garvin, R.P.; Anderson, D.R. Malondialdehyde-Acetaldehyde Modified (MAA) Proteins Differentially Effect the Inflammatory Response in Macrophage, Endothelial Cells and Animal Models of Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312948
Duryee MJ, Clemens DL, Opperman PJ, Thiele GM, Duryee LM, Garvin RP, Anderson DR. Malondialdehyde-Acetaldehyde Modified (MAA) Proteins Differentially Effect the Inflammatory Response in Macrophage, Endothelial Cells and Animal Models of Cardiovascular Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(23):12948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312948
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuryee, Michael J., Dahn L. Clemens, Patrick J. Opperman, Geoffrey M. Thiele, Logan M. Duryee, Robert P. Garvin, and Daniel R. Anderson. 2021. "Malondialdehyde-Acetaldehyde Modified (MAA) Proteins Differentially Effect the Inflammatory Response in Macrophage, Endothelial Cells and Animal Models of Cardiovascular Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 23: 12948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312948
APA StyleDuryee, M. J., Clemens, D. L., Opperman, P. J., Thiele, G. M., Duryee, L. M., Garvin, R. P., & Anderson, D. R. (2021). Malondialdehyde-Acetaldehyde Modified (MAA) Proteins Differentially Effect the Inflammatory Response in Macrophage, Endothelial Cells and Animal Models of Cardiovascular Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(23), 12948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312948





