Novel Biallelic Variants and Phenotypic Features in Patients with SLC38A8-Related Foveal Hypoplasia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Molecular Variant Findings
2.2. Clinical Findings
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Genetic Analysis
4.2. Clinical Assessment
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, M.G.; Kumar, A.; Mohammad, S.; Proudlock, F.A.; Engle, E.C.; Andrews, C.; Chan, W.M.; Thomas, S.; Gottlob, I. Structural grading of foveal hypoplasia using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: A predictor of visual acuity? Ophthalmology 2011, 118, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rufai, S.R.; Thomas, M.G.; Purohit, R.; Bunce, C.; Lee, H.; Proudlock, F.A.; Gottlob, I. Can structural grading of foveal hypoplasia predict future vision in infantile nystagmus? A longitudinal study. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, H. Foveal hypoplasia and optical coherence tomographic imaging. Taiwan J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 8, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulter, J.A.; Al-Araimi, M.; Conte, I.; Van Genderen, M.M.; Sheridan, E.; Carr, I.M.; Parry, D.A.; Shires, M.; Carrella, S.; Bradbury, J.; et al. Recessive mutations in SLC38A8 cause foveal hypoplasia and optic nerve misrouting without albinism. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, Y.; Gradstein, L.; Flusser, H.; Markus, B.; Cohen, I.; Langer, Y.; Marcus, M.; Lifshitz, T.; Kadir, R.; Birk, O.S. Isolated foveal hypoplasia with secondary nystagmus and low vision is associated with a homozygous SLC38A8 mutation. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 22, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Al-Araimi, M.; Pal, B.; Poulter, J.A.; Van Genderen, M.M.; Carr, I.; Cudrnak, T.; Brown, L.; Sheridan, E.; Mohamed, M.D.; Bradbury, J.; et al. A new recessively inherited disorder composed of foveal hypoplasia, optic nerve decussation defects and anterior segment dysgenesis maps to chromosome 16q23.3-24.1. Mol. Vis. 2013, 19, 2165–2172. [Google Scholar]
- Hägglund, M.G.; Hellsten, S.V.; Bagchi, S.; Philippot, G.; Löfqvist, E.; Nilsson, V.C.; Almkvist, I.; Karlsson, E.; Sreedharan, S.; Tafreshiha, A.; et al. Transport of l-Glutamine, l-Alanine, l-Arginine and l-Histidine by the Neuron-Specific Slc38a8 (SNAT8) in CNS. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 1495–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toral, M.A.; Velez, G.; Boudreault, K.; Schaefer, K.A.; Xu, Y.; Saffra, N.; Bassuk, A.G.; Tsang, S.H.; Mahajan, V.B. Structural modeling of a novel SLC38A8 mutation that causes foveal hypoplasia. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2017, 5, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasseaux, E.; Plaisant, C.; Michaud, V.; Pennamen, P.; Trimouille, A.; Gaston, L.; Monfermé, S.; Lacombe, D.; Rooryck, C.; Morice-Picard, F.; et al. Molecular characterization of a series of 990 index patients with albinism. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2018, 31, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.; Ellingford, J.M.; Parry, N.R.A.; Fletcher, T.; Ramsden, S.C.; Gale, T.; Hall, G.; Smith, K.; Kasperaviciute, D.; Thomas, E.; et al. Clinical and genetic variability in children with partial albinism. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, C.; Hecht, I.; Rotenstreich, Y.; Guttman, S.; Or, L.; Morad, Y.; Shapira, G.; Shomron, N.; Pras, E. The pathogenicity of SLC38A8 in five families with foveal hypoplasia and congenital nystagmus. Exp. Eye Res. 2020, 193, 107958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuht, H.J.; Han, J.; Maconachie, G.D.; Park, S.E.; Lee, S.T.; McLean, R.; Sheth, V.; Hisaund, M.; Dawar, B.; Sylvius, N.; et al. SLC38A8 mutations result in arrested retinal development with loss of cone photoreceptor specialisation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2020, 29, 2989–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, D.; Malka, S.; Harding, P.; Palma, J.; Dunbar, H.; Moosajee, M. Molecular diagnostic challenges for non-retinal developmental eye disorders in the United Kingdom. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2020, 184, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, E.C.; Poulter, J.A.; Webster, A.R.; Sergouniotis, P.; Khan, K.N.; Benke, P.J.; Friedman, L.; Ali, M.; Inglehearn, C.F.; Toomes, C. Mutations in SLC38A8 and FOXD1 in patients with nystagmus and foveal hypoplasia. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 2786. [Google Scholar]
- Cornish, K.S.; Reddy, A.R.; McBain, V.A. Concentric macular rings sign in patients with foveal hypoplasia. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014, 132, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramtohul, P.; Comet, A.; Denis, D. Multimodal imaging correlation of the concentric macular rings sign in foveal hypoplasia: A distinctive henle fiber layer geometry. Ophthalmol. Retin. 2020, 4, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Rennie, C.; Chowdhury, S.; Khan, J.; Rajan, F.; Jordan, K.; Lamb, R.J.; Vivian, A.J. The prevalence and associated features of posterior embryotoxon in the general ophthalmic clinic. Eye 2004, 19, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, J.M.; Fufa, T.D.; Bharti, K.; Brooks, B.P.; Hufnagel, R.B.; McGaughey, D.M. Identifying core biological processes distinguishing human eye tissues with precise systems-level gene expression analyses and weighted correlation networks. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 3325–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, I.; Morita, H.; Kondo, H. Autosomal dominant foveal hypoplasia without visible macular abnormalities and PAX6 mutations. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 64, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, D.L.; Owen, N.; Tailor, V.; Corton, M.; Theodorou, M.; Moosajee, M. PAX6 missense variants in two families with isolated foveal hypoplasia and nystagmus: Evidence of paternal postzygotic mosaicism. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Ren, X.; Yang, X.; Guo, T.; Yao, Q.; Li, L.; Dai, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, M.; et al. Identification of a novel GPR143 mutation in a large Chinese family with congenital nystagmus as the most prominent and consistent manifestation. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 52, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.; Oh, E.H.; Shin, J.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Choi, S.Y.; Choi, K.-D.; Lee, C.; Choi, J.-H. Identification of a novel GPR143 mutation in X-linked ocular albinism with marked intrafamilial phenotypic variability. J. Genet. 2018, 97, 1479–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Kuht, H.J.; Moon, E.H.; Maconachie, G.D.; Thomas, M.G. Current and emerging treatments for albinism. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surace, E.M.; Domenici, L.; Cortese, K.; Cotugno, G.; Di Vicino, U.; Venturi, C.; Cellerino, A.; Marigo, V.; Tacchetti, C.; Ballabio, A.; et al. Amelioration of both Functional and Morphological Abnormalities in the Retina of a Mouse Model of Ocular Albinism Following AAV-Mediated Gene Transfer. Mol. Ther. 2005, 12, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargiulo, A.; Bonetti, C.; Montefusco, S.; Neglia, S.; Di Vicino, U.; Marrocco, E.; Della Corte, M.; Domenici, L.; Auricchio, A.; Surace, E.M. AAV-mediated Tyrosinase Gene Transfer Restores Melanogenesis and Retinal Function in a Model of Oculo-cutaneous Albinism Type I (OCA1). Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Deng, J.; Sui, T.; La, L.; Li, Z. Functional Validation of Albinism-Associated Tyrosinase T373K SNP by CRISPR-Cas9-Mediated Homology-Directed Repair (HDR) in Rabbit. SSRN Electron. J. 2018, 36, 517–525. [Google Scholar]
- Rim, J.H.; Lee, S.-T.; Gee, H.Y.; Lee, B.J.; Choi, J.R.; Park, H.W.; Han, S.-H.; Han, J. Accuracy of Next-Generation Sequencing for Molecular Diagnosis in Patients With Infantile Nystagmus Syndrome. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017, 135, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, C.; Scott, R.H.; Thomas, E.; Jones, L.; Murugaesu, N.; Pretty, F.B.; Halai, D.; Baple, E.; Craig, C.; Hamblin, A.; et al. The 100 000 Genomes Project: Bringing whole genome sequencing to the NHS. BMJ 2018, 361, k1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.L.; Arno, G.; Poulter, J.A.; Khan, K.N.; Morarji, J.; Hull, S.; Pontikos, N.; Martin, A.R.; Smith, K.R.; Ali, M.; et al. Association of Steroid 5α-Reductase Type 3 Congenital Disorder of Glycosylation With Early-Onset Retinal Dystrophy. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017, 135, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Adzhubei, I.; Jordan, D.M.; Sunyaev, S.R. Predicting functional effect of human missense mutations using PolyPhen-2. Curr. Protoc. Human Genet. 2013, 76, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, N.-L.; Kumar, P.; Hu, J.; Henikoff, S.; Schneider, G.; Ng, P.C. SIFT web server: Predicting effects of amino acid substitutions on proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W452–W457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Cooper, D.N.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster2: Mutation prediction for the deep-sequencing age. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
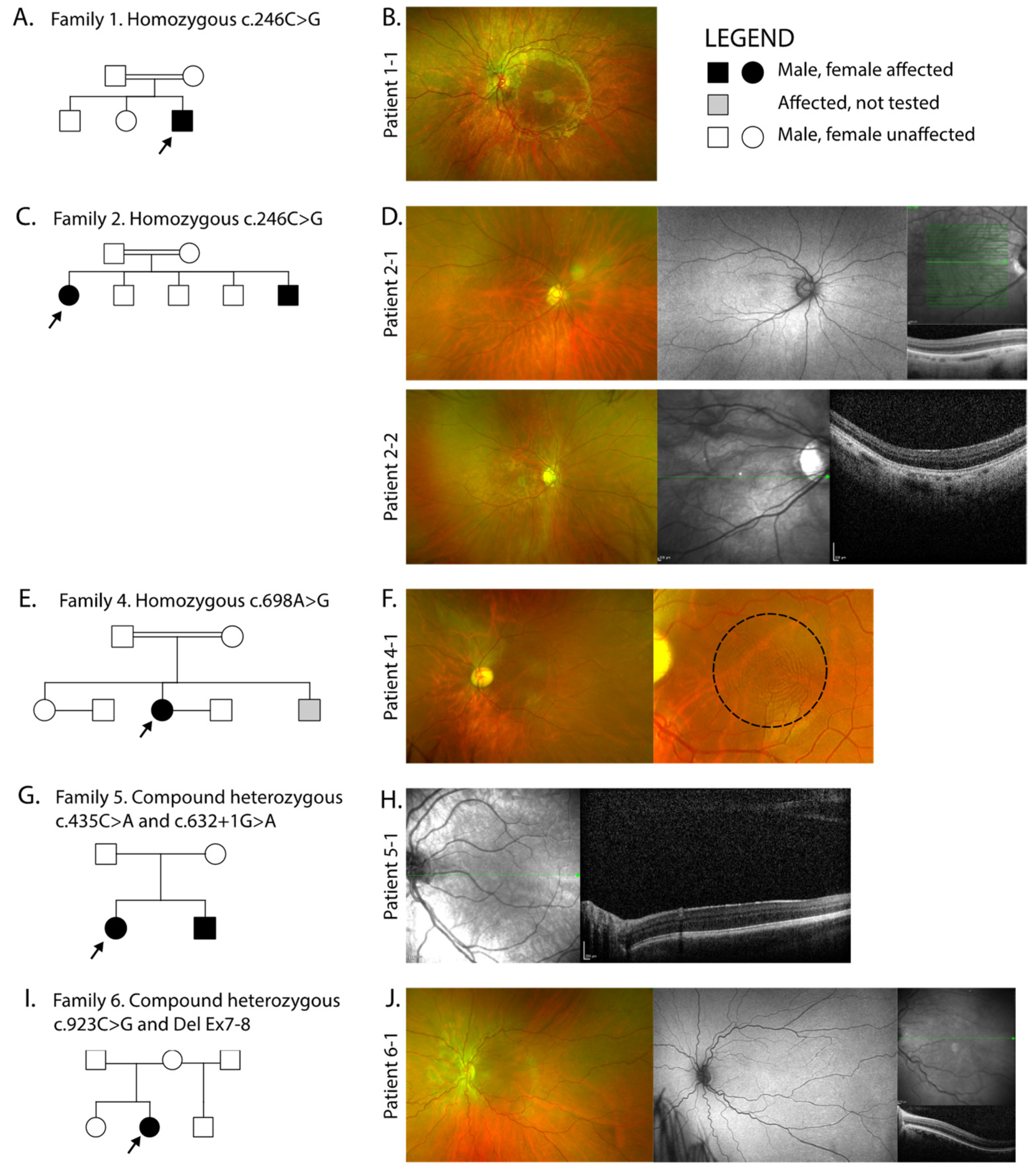
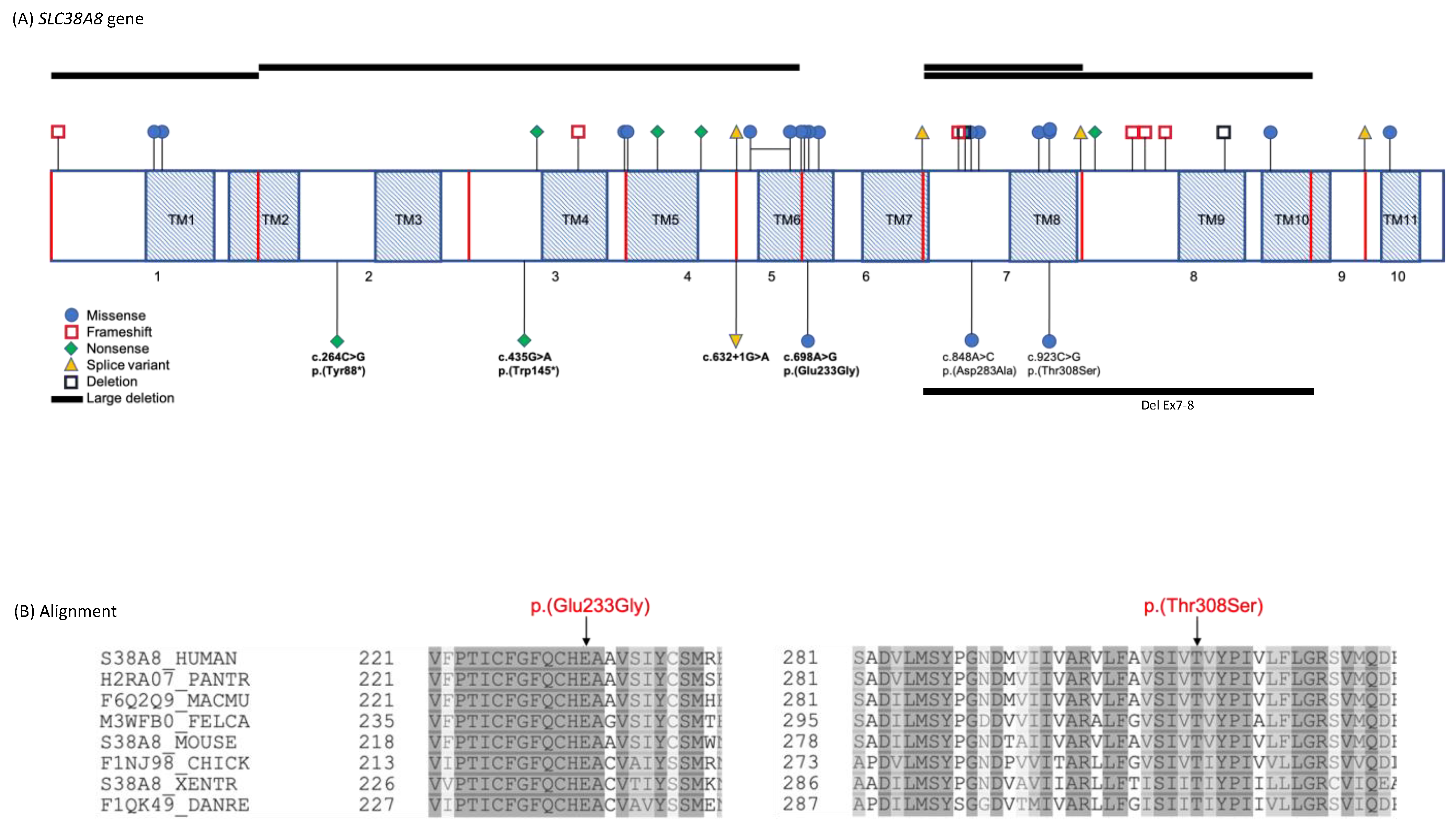
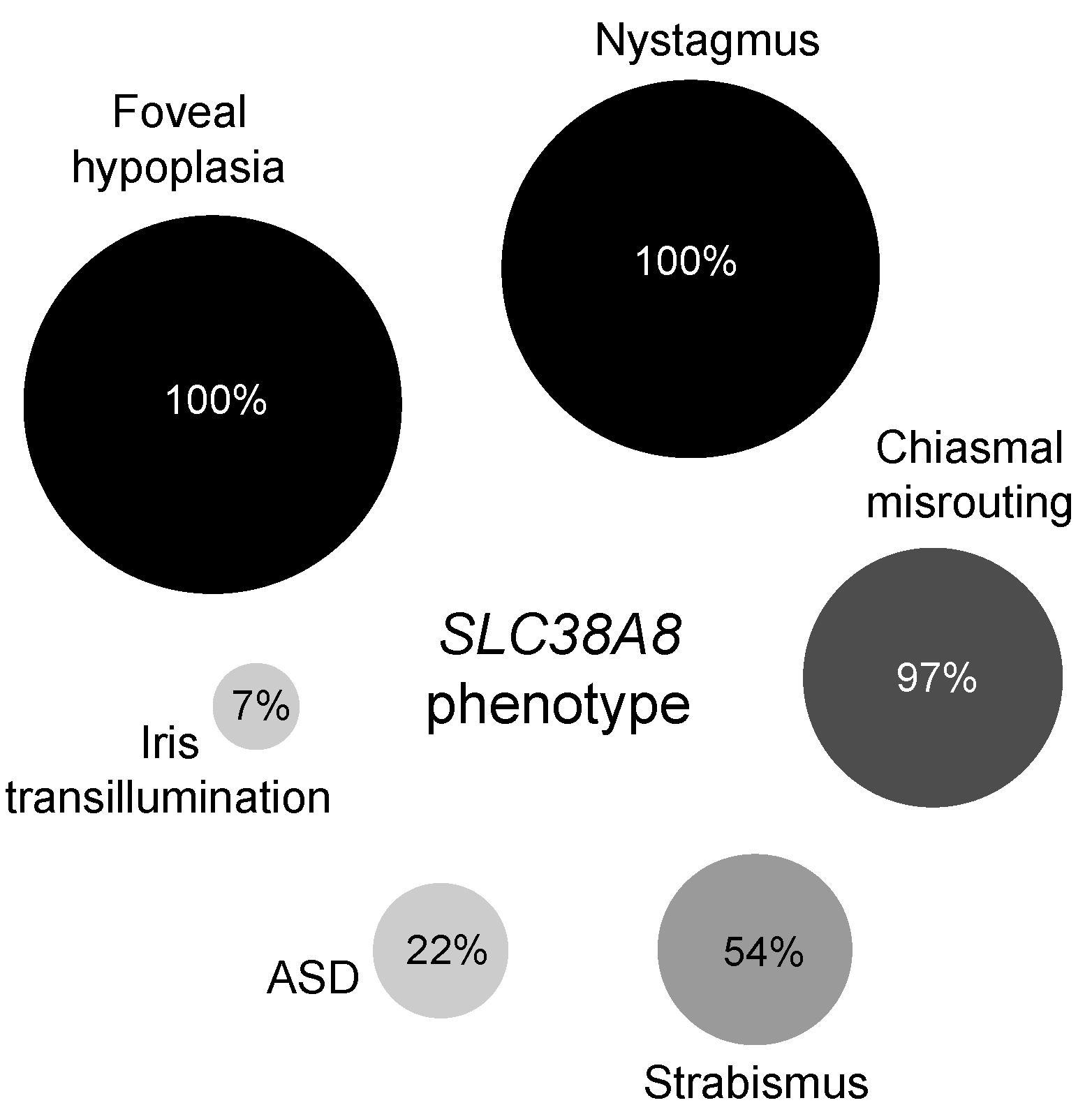
| Family ID | Ethnicity | Consanguinity | Variants | Exon | Consequence | Protein Domain | Zygosity | Reported | gnomAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (26320) | South Asian Bangladesh | Yes | c.264C>G p.(Tyr88*) | 2 | Nonsense | Intracellular between TM domains 1 and 2 | HOM | Novel | 0.0002614 in South Asians only |
| 2 (23089) | South Asian Indian | Yes | c.264C>G p.(Tyr88*) | 2 | Nonsense | Intracellular between TM domains 1 and 2 | HOM | Novel | 0.0002614 in South Asians only |
| 3 (26350) | South Asian Pakistan | Yes | c.264C>G p.(Tyr88*) | 2 | Nonsense | Intracellular between TM domains 1 and 2 | HOM | Novel | 0.0002614 in South Asians only |
| 4 (26364) | South Asian Sri-Lanka | Yes | c.698A>G p.Glu233Gly | 6 | Missense | TM6 | HOM | Novel | Absent |
| 5 (26237) | Caucasian British | No | c.435G>A p.Trp145* | 3 | Nonsense | Extracellular between TM domains 3 and 4 | HET | Novel | Absent |
| c.632+1G>A | IVS4 | Splice donor | Extracellular between TM domains 5 and 6 | HET | Novel | Absent | |||
| 6 (16812) | Caucasian Spanish-British | No | c.923C>G p.Thr308Ser Del Ex7-8 | 7 | Missense splice site impact Deletion | TM8 TM7-TM10 | HET HET | [9] [9] | Absent Absent |
| 7 (28327) | Caucasian Ashkenazi Jewish | No | c.848A>C p.(Asp283Ala) | 7 | Missense | Extracellular between TM domains 7 and 8 | HOM | [8,9] | 0.0002653 in gnomAD 0.006178 in AJs |
| Family ID/Patient | Ethnicity | Age (Years) | Gender | BCVA OD | BCVA OS | Refraction | Strabismus | Nystagmus | Anterior Segment | Foveal Hypoplasia | Electrodiagnostic Testing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-1 | South Asian Bangladesh | 3 | Male | Objects to occlusion | Objects to occlusion | R: +3.50/−2.50 × 180 L: +3.50/−3.50 × 180 | Left Exotropia | Pendular horizontal | Normal | Present | No evidence of chiasmal misrouting |
| 2-1 | South Asian Indian | 32 | Female | 0.6 | 0.6 | R: −1.75/−3.50 × 180 L: −7.00/−2.50 × 170 | Left Esotropia | Pendular horizontal | Normal | Grade 4 | Evidence of chiasmal misrouting |
| 2-2 | 16 | Male | 0.82 | 0.78 | R: −0.75/−3.50 × 10 L: +1.50/−4.00 × 175 | Right Exotropia | Pendular horizontal | Posterior embryotoxon | Grade 4 | Evidence of chiasmal misrouting | |
| 3-1 | South Asian Pakistan | 21 | Female | 0.7 | 0.9 | R: +0.75/−2.50 × 30 L: +0.75/−2.50 × 75 | Left Exotropia | Pendular horizontal | Normal | Present | Not undertaken |
| 4-1 | South Asian Sri-Lanka | 39 | Female | 0.6 | 0.6 | Not available | Left Exotropia | Pendular horizontal | Bilateral Posterior embryotoxon Bilateral peripheral iris adhesions to the cornea Bilateral blue dot cataract | Grade 4 | Evidence of chiasmal misrouting |
| 5-1 | Caucasian British | 5 | Female | 0.6 | 0.6 | R: +3.50DS L: +3.50DS | No deviation | Jerk with extended foveation | Normal | Grade 4 | Evidence of chiasmal misrouting |
| 5-2 | 2 | Male | Objects to occlusion | Objects to occlusion | R: +5.00/−0.75 × 180 L: +5.00/−0.75 × 180 | No deviation | Pendular horizontal | Normal | Present | Not undertaken | |
| 6-1 | Caucasian Spanish-British | 36 | Female | 0.9 | 1 | Not available | Left Esotropia | Rotary | Bilateral shallow anterior chamber | Grade 4 | Evidence of chiasmal misrouting |
| 7-1 | Caucasian Ashkenazi Jewish | 16 | Female | 0.42 | 0.4 | R: +2.50/−1.50 × 165 L: +1.50/−1.50 × 180 | Right Exotropia | Pendular horizontal | Peripheral iris transillumination | Grade 4 | Evidence of chiasmal misrouting |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schiff, E.R.; Tailor, V.K.; Chan, H.W.; Theodorou, M.; Webster, A.R.; Moosajee, M. Novel Biallelic Variants and Phenotypic Features in Patients with SLC38A8-Related Foveal Hypoplasia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031130
Schiff ER, Tailor VK, Chan HW, Theodorou M, Webster AR, Moosajee M. Novel Biallelic Variants and Phenotypic Features in Patients with SLC38A8-Related Foveal Hypoplasia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(3):1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031130
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchiff, Elena R., Vijay K. Tailor, Hwei Wuen Chan, Maria Theodorou, Andrew R. Webster, and Mariya Moosajee. 2021. "Novel Biallelic Variants and Phenotypic Features in Patients with SLC38A8-Related Foveal Hypoplasia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 3: 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031130
APA StyleSchiff, E. R., Tailor, V. K., Chan, H. W., Theodorou, M., Webster, A. R., & Moosajee, M. (2021). Novel Biallelic Variants and Phenotypic Features in Patients with SLC38A8-Related Foveal Hypoplasia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(3), 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031130








