Calcineurin and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: The Rationale for Using Calcineurin Inhibitors in the Treatment of Lupus Nephritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Etiopathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
3. Characteristics of Lupus Nephritis
4. T Cell Dysregulation in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
5. Mechanisms Involved in T Cell Dysregulation: TCR Rewiring
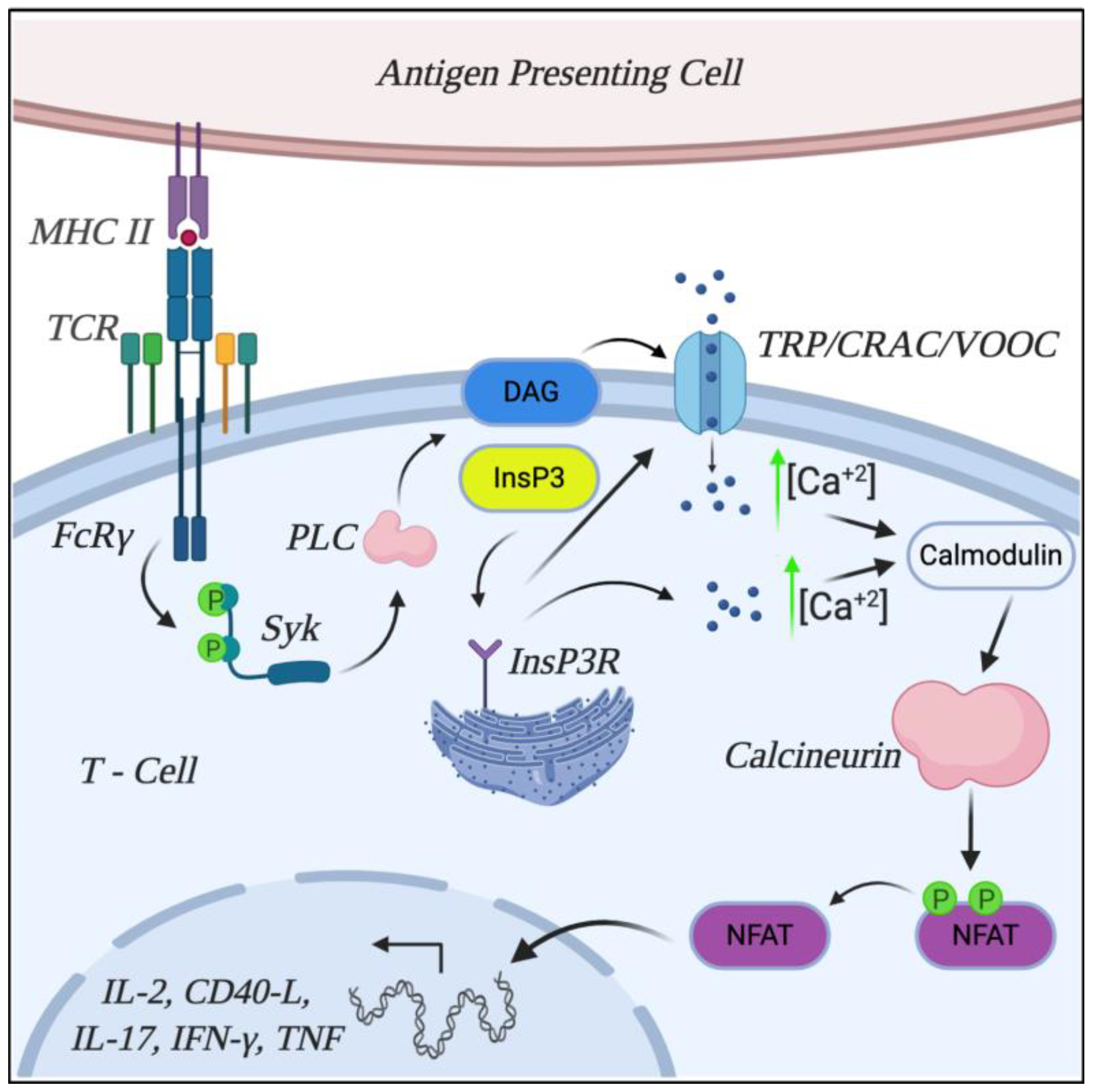
6. Calcineurin Role and Characterization
7. Calcineurin Inhibitors: Characterization and Mechanisms of Action
8. Calcineurin Inhibitors in Lupus Nephritis
9. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wardowska, A. The epigenetic face of lupus: Focus on antigen-presenting cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 81, 106262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsokos, G.C.; Lo, M.S.; Reis, P.C.; Sullivan, K.E. New insights into the immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 716–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulton, V.R.; Tsokos, G.C. T cell signaling abnormalities contribute to aberrant immune cell function and autoimmunity. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 2220–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katsuyama, T.; Tsokos, G.C.; Moulton, V.R. Aberrant T cell signaling and subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispín, J.C.; Kyttaris, V.C.; Terhorst, C.; Tsokos, G.C. T cells as therapeutic targets in SLE. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mok, C.C. Pro: The use of calcineurin inhibitors in the treatment of lupus nephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Wan, C.; Song, A.; Qiu, Y.; Xiong, W.; Zhang, C. Renal Fibrosis: Mechanisms and Therapies; Springer: Singapore, 2019; Volume 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ji, L.; Yang, L.; Tang, X.; Qin, W. The effect of calcineurin inhibitors in the induction and maintenance treatment of lupus nephritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2016, 48, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés Verdú, R.; Pego-Reigosa, J.M.; Seoane-Mato, D.; Morcillo Valle, M.; Palma Sánchez, D.; Moreno Martínez, M.J.; Mayor González, M.; Atxotegi Sáenz de Buruaga, J.; Urionagüena Onaindia, I.; Blanco Cáceres, B.A.; et al. EPISER2016 for the WGP. Prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus in Spain: Higher than previously reported in other countries? Rheumatology 2020, 59, 2556–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pons-Estel, G.J.; Ugarte-Gil, M.F.; Alarcón, G.S. Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 13, 799–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belot, A.; Cimaz, R. Monogenic forms of systemic lupus erythematosus: New insights into SLE pathogenesis. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2012, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.; Bang, S.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Okada, Y.; Han, B.; Saw, W.Y.; Teo, Y.Y.; Bae, S.C. The HLA-DRβ1 amino acid positions 11-13-26 explain the majority of SLE-MHC associations. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Odhams, C.A.; Cortini, A.; Chen, L.; Roberts, A.L.; Viñuela, A.; Buil, A.; Small, K.S.; Dermitzakis, E.T.; Morris, D.L.; Vyse, T.J. Cunninghame Graham DS. Mapping eQTLs with RNA-seq reveals novel susceptibility genes, non-coding RNAs and alternative-splicing events in systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 1003–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, Z.H.; Lu, X.; Miller, D.; Forney, C.R.; Lee, J.; Lynch, A.; Schroeder, C.; Parks, L.; Magnusen, A.F.; Chen, X.; et al. A plausibly causal functional lupus-associated risk variant in the STAT1-STAT4 locus. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 2392–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gateva, V.; Sandling, J.K.; Hom, G.; Taylor, K.E.; Chung, S.A.; Sun, X.; OrtmAnn, W.; Kosoy, R.; Ferreira, R.C.; Nordmark, G.; et al. A large-scale replication study identifies TNIP1, PRDM1, JAZF1, UHRF1BP1 and IL10 as risk loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lanata, C.M.; Nititham, J.; Taylor, K.E.; Chung, S.A.; Torgerson, D.G.; Seldin, M.F.; Pons-Estel, B.A.; Tusié-Luna, T.; Tsao, B.P.; Morand, E.F.; et al. Genetic contributions to lupus nephritis in a multi-ethnic cohort of systemic lupus erythematous patients. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Rodan, A.R.R.; Le, T.H.H.; Gaulton, K.J.J.; Haessler, J.; Stilp, A.M.M.; Kamatani, Y.; Zhu, G.; Sofer, T.; Puri, S.; et al. Trans-ethnic Fine Mapping Highlights Kidney-Function Genes Linked to Salt Sensitivity. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sawalha, A.H.; Jeffries, M.; Webb, R.; Lu, Q.; Gorelik, G.; Ray, D.; Osban, J.; Knowlton, N.; Johnson, K.; Richardson, B. Defective T-cell ERK signaling induces interferon-regulated gene expression and overexpression of methylation-sensitive genes similar to lupus patients. Genes Immun. 2008, 9, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meroni, P.L.; Penatti, A.E. Epigenetics and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Unmet Needs. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 50, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, C.G.; de Souza Espindola Santos, A.; Barbhaiya, M.; Costenbader, K.H. Understanding the role of environmental factors in the development of systemic lupus erythematosus. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 31, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernatsky, S.; Boivin, J.F.; Joseph, L.; Manzi, S.; Ginzler, E.; Gladman, D.D.; Urowitz, M.; Fortin, P.R.; Petri, M.; Barr, S.; et al. Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2550–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danila, M.I.; Pons-Estel, G.J.; Zhang, J.; Vilá, L.M.; Reveille, J.D.; Alarcón, G.S. Renal damage is the most important predictor of mortality within the damage index: Data from LUMINA LXIV, a multiethnic US cohort. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yap, D.Y.; Yung, S.; Chan, T. Lupus nephritis: An update on treatments and pathogenesis. Nephrology 2018, 23, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mok, C.C.; Kwok, R.C.L.; Yip, P.S.F. Effect of renal disease on the standardized mortality ratio and life expectancy of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 2154–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurkovich, M.; Vostretsova, K.; Chen, W.; Aviña-Zubieta, J.A. Overall and cause-specific mortality in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 66, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo-Izquierdo, M.; Rodriguez-Almaraz, E.; Pego-Reigosa, J.M.; López-Longo, F.J.; Calvo-Alén, J.; Olivé, A.; Fernández-Nebro, A.; Martinez-Taboada, V.; Vela-Casasempere, P.; Freire, M.; et al. Characterization of patients with lupus nephritis included in a large cohort from the Spanish society of rheumatology registry of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (RELESSER). Medicine 2016, 95, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanly, J.G.; O’Keeffe, A.G.; Su, L.; Urowitz, M.B.; Romero-Diaz, J.; Gordon, C.; Bae, S.C.; Bernatsky, S.; Clarke, A.E.; Wallace, D.J.; et al. The frequency and outcome of lupus nephritis: Results from an international inception cohort study. Rheumatology 2015, 55, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imran, T.F.; Yick, F.; Verma, S.; Estiverne, C.; Ogbonnaya-Odor, C.; Thiruvarudsothy, S.; Reddi, A.S.; Kothari, N. Lupus nephritis: An update. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2016, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, J.; Eisenberger, U.; de Groot, K. Lupus nephritis. Internist 2019, 60, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balow, J.E. Clinical presentation and monitoring of lupus nephritis. Lupus 2005, 14, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajema, I.M.; Wilhelmus, S.; Alpers, C.E.; Bruijn, J.A.; Colvin, R.B.; Cook, H.T.; D’Agati, V.D.; Ferrario, F.; Haas, M.; Jennette, J.C.; et al. Revision of the International Society of Nephrology/Renal Pathology Society classification for lupus nephritis: Clarification of definitions, and modified National Institutes of Health activity and chronicity indices. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, J.J.; Mocanu, M.; Berns, J.S. The native kidney biopsy: Update and evidence for best practice. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 11, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostopoulou, M.; Fanouriakis, A.; Cheema, K.; Boletis, J.; Bertsias, G.; Jayne, D.; Boumpas, D.T. Management of lupus nephritis: A systematic literature review informing the 2019 update of the joint EULAR and European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association (EULAR/ERA-EDTA) recommendations. RMD Open 2020, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, L.E.; Hatton, R.D.; Mangan, P.R.; Turner, H.; Murphy, T.L.; Murphy, K.M.; Weaver, C.T. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.O.; Chang, S.H.; Nurieva, R.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.; Hood, L.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, Q.; et al. A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeachy, M.J.; Cua, D.J.; Gaffen, S.L. The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Health and Disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 892–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, P.; Rodríguez-Carrio, J.; Caminal-Montero, L.; Mozo, L.; Suárez, A. A pathogenic IFNα, BLyS and IL-17 axis in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispín, J.C.; Oukka, M.; Bayliss, G.; Cohen, R.A.; Van Beek, C.A.; Stillman, I.E.; Kyttaris, V.C.; Juang, Y.-T.; Tsokos, G.C. Expanded Double Negative T Cells in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Produce IL-17 and Infiltrate the Kidneys. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 8761–8766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdaca, G.; Colombo, B.M.; Puppo, F. The role of Th17 lymphocytes in the autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2011, 6, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doreau, A.; Belot, A.; Bastid, J.; Riche, B.; Trescol-Biemont, M.C.; Ranchin, B.; Fabien, N.; Cochat, P.; Pouteil-Noble, C.; Trolliet, P.; et al. Interleukin 17 acts in synergy with B cell-activating factor to influence B cell biology and the pathophysiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Yu, Y.C.; Deng, H.H.; Sun, J.Z.; Dai, Z.; Wu, Y.W.; Yang, M. Plasma IL-17A is increased in new-onset SLE patients and associated with disease activity. J. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 30, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.; Lit, L.C.W.; Tam, L.S.; Li, E.K.M.; Wong, P.T.Y.; Lam, C.W.K. Hyperproduction of IL-23 and IL-17 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Implications for Th17-mediated inflammation in auto-immunity. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 127, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Abed, U.; Goosmann, C.; Hurwitz, R.; Schulze, I.; Wahn, V.; Weinrauch, Y.; BrinkmAnn, V.; Zychlinsky, A. Novel cell death program leads to neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 176, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbandian, A.; Crispín, J.C.; Tsokos, G.C. Interleukin-17 and systemic lupus erythematosus: Current concepts. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 157, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studnicka-Benke, A.; Steiner, G.; Petera, P.; Smolen, J.S. Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha and its Soluble Receptors Parallel Clinical Disease and Autoimmune Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Rheumatology 1996, 35, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCarthy, E.M.; Smith, S.; Lee, R.Z.; Cunnane, G.; Doran, M.F.; Donnelly, S.; Howard, D.; O’Connell, P.; Kearns, G.; Ní Gabhann, J.; et al. The association of cytokines with disease activity and damage scores in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 1586–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Postal, M.; Appenzeller, S. The role of Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-α) in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Cytokine 2011, 56, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idborg, H.; Eketjäll, S.; Pettersson, S.; Gustafsson, J.T.; Zickert, A.; Kvarnström, M.; Oke, V.; Jakobsson, P.-J.; Gunnarsson, I.; Svenungsson, E. TNF-α and plasma albumin as biomarkers of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus Sci. Med. 2018, 5, e000260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, P.; Ma, L.; Shan, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y. Increased interleukin 21 and follicular helper T-like cells and reduced interleukin 10+ B cells in patients with new-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 41, 1781–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, R.; Botti, E.; Sarra, M.; Esposito, M.; Stolfi, C.; Diluvio, L.; Giustizieri, M.L.; Pacciani, V.; Mazzotta, A.; Campione, E.; et al. Involvement of interleukin-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1013–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harigai, M.; Kawamoto, M.; Hara, M.; Kubota, T.; Kamatani, N.; Miyasaka, N. Excessive Production of IFN-γ in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Its Contribution to Induction of B Lymphocyte Stimulator/B Cell-Activating Factor/TNF Ligand Superfamily-13B. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.M.; Yan, S.X.; Wei, W. IL-21 acts as a promising therapeutic target in systemic lupus erythematosus by regulating plasma cell differentiation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 12, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaud, G.; Lesourne, R.; Love, P.E. Regulatory mechanisms in T cell receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariuzza, R.A.; Agnihotri, P.; Orban, J. The structural basis of T-cell receptor (TCR) activation: An enduring enigma. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 914–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, A.H.; Lo, W.L.; Weiss, A. TCR Signaling: Mechanisms of Initiation and Propagation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2018, 43, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samelson, L.E. Signal Transduction Mediated by the T Cell Antigen Receptor: The Role of Adapter Proteins. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 371–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mak, A.; Kow, N.Y. The pathology of T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enyedy, E.J.; Nambiar, M.P.; Liossis, S.N.C.; Dennis, G.; Kammer, G.M.; Tsokos, G.C. Fcε receptor type I γ chain replaces the deficient T cell receptor ζ chain in T cells of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Chowdhury, B.; Tsokos, G.C. Autoimmunity in systemic lupus erythematosus: Integrating genes and biology. Semin. Immunol. 2006, 18, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsokos, G.C.; Nambiar, M.P.; Tenbrock, K.; Juang, Y.T. Rewiring the T-cell: Signaling defects and novel prospects for the treatment of SLE. Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, M.; Setoyama, Y.; Tsuzaka, K.; Yoshimoto, K.; Amano, K.; Abe, T.; Takeuchi, T. Defective expression and tyrosine phosphorylation of the T cell receptor zeta chain in peripheral blood T cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2002, 129, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambiar, M.P.; Fisher, C.U.; Warke, V.G.; Krishnan, S.; Mitchell, J.P.; Delaney, N.; Tsokos, G.C. Reconstitution of deficient T cell receptor ζ chain restores T cell signaling and augments T cell receptor/CD3-induced interleukin-2 production in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 1948–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Juang, Y.-T.; Chowdhury, B.; Magilavy, A.; Fisher, C.U.; Nguyen, H.; Nambiar, M.P.; Kyttaris, V.; Weinstein, A.; Bahjat, R.; et al. Differential Expression and Molecular Associations of Syk in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus T Cells. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 8145–8152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsokos, G.C.; Liossis, S.N.C. Immune cell signaling defects in lupus: Activation, anergy and death. Immunol. Today. 1999, 20, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, S.; Raz, E. Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) channels in T cells. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016, 38, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clipstone, N.A.; Fiorentino, D.F.; Crabtree, G.R. Molecular analysis of the interaction of calcineurin with drug- immunophilin complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 26431–26437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheftic, S.R.; Page, R.; Peti, W. Investigating the human Calcineurin Interaction Network using the i LxVP SLiM. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macian, F. NFAT proteins: Key regulators of T-cell development and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Yoo, S.A.; Kim, M.; Kim, W.U. The Role of Calcium–Calcineurin–NFAT Signaling Pathway in Health and Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.K.; Lin, X.; Gaffen, S.L. Crucial role for nuclear factor of activated T cells in T cell receptor-mediated regulation of human interleukin-17. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 52762–52771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.K.; Clements, J.L.; Gaffen, S.L. Signaling through the murine T cell receptor induces IL-17 production in the absence of costimulation, IL-23 or dendritic cells. Mol. Cells 2005, 20, 339–347. [Google Scholar]
- Kyttaris, V.C.; Zhang, Z.; Kampagianni, O.; Tsokos, G.C. Calcium signaling in systemic lupus erythematosus T cells: A treatment target. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2058–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavenstädt, H.; Kriz, W.; Kretzler, M. Cell biology of the glomerular podocyte. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 253–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakhi, H.; Moktefi, A.; Bouachi, K.; Audard, V.; Hénique, C.; Remy, P.; Ollero, M.; El Karoui, K. Podocyte Injury in Lupus Nephritis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, G.; Wang, L.; Spurney, R.F. TRPC Channels in Proteinuric Kidney Diseases. Cells 2019, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peleg, Y.; Bomback, A.S.; Radhakrishnan, J. The evolving role of calcineurin inhibitors in treating lupus nephritis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cribbs, J.T.; Strack, S. Reversible phosphorylation of Drp1 by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and calcineurin regulates mitochondrial fission and cell death. EMBO Rep. 2007, 8, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.Y.; Qi, R. Role of bad in podocyte apoptosis induced by puromycin aminonucleoside. Transplant. Proc. 2013, 45, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, M.; Bringhenti, R.N.; Rodrigues, P.G.; do Nascimento, J.F.; Pereira, S.V.; Zancan, R.; Monticielo, O.A.; Gasparin, A.A.; de Castro, W.P.; Veronese, F.V. Podocyte-associated mRNA profiles in kidney tissue and in urine of patients with active lupus nephritis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 4600–4613. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.S.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.M.; Han, N.Y.; Oh, J.M.; Ha, J.; Kim, Y.S. Pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus according to body composition in recipients of kidney transplants. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 31, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arriens, C.; Polyakova, S.; Adzerikho, I.; Randhawa, S.; Solomons, N. OP0277 AURORA Phase 3 study demonstrates voclosporin statistical superiority over standard of care in lupus nephritis (LN). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79 (Suppl. 1), 172–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahr, A. Cyclosporin Clinical Pharmacokinetics. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1993, 24, 472–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbarino, J.M.; Staatz, C.E.; Venkataramanan, R.; Klein, T.E.; Altman, R.B. PharmGKB summary: Cyclosporine and tacrolimus pathways. Pharm. Genom. 2013, 23, 563–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cardenas, M.E.; Hemenway, C.; Muir, R.S.; Ye, R.; Fiorentino, D.; Heitman, J. Immunophilins interact with calcineurin in the absence of exogenous immunosuppressive ligands. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 5944–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiederrecht, G.; Lam, E.; Hung, S.; Martin, M.; Sigal, N. The Mechanism of Action of FK-506 and Cyclosporin A. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 696, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponticelli, C.; Podestà, M.A. Calcineurin inhibitors in lupus nephritis. J. Nephrol. 2020, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bîrsan, T.; Dambrin, C.; Freitag, D.G.; Yatscoff, R.W.; Morris, R.E. The novel calcineurin inhibitor ISA247: A more potent immunosuppressant than cyclosporine in vitro. Transpl. Int. 2005, 17, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busque, S.; Cantarovich, M.; Mulgaonkar, S.; Gaston, R.; Gaber, A.O.; Mayo, P.R.; Ling, S.; Huizinga, R.B.; Meier-Kriesche, H.U. The PROMISE study: A phase 2b multicenter study of voclosporin (ISA247) versus tacrolimus in de Novo kidney transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 2675–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunnicliffe, D.J.; Palmer, S.C. Immunosuppressive Treatment for Proliferative Lupus Nephritis: Summary of a Cochrane Review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 72, 756–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuglstatter, A.; Mueller, F.; Kusznir, E.; Gsell, B.; Stihle, M.; Thoma, R.; Benz, J.; Aspeslet, L.; Freitag, D.; Hennig, M. Structural basis for the cyclophilin A binding affinity and immunosuppressive potency of E-ISA247 (voclosporin). Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, R.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Fan, J.; Peng, W.; Kong, Q.; He, H.; Yang, S.; Chen, W.; Tang, X.; et al. Tacrolimus protects podocytes from injury in lupus nephritis partly by stabilizing the cytoskeleton and inhibiting podocyte apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flint, J.; Panchal, S.; Hurrell, A.; van de Venne, M.; Gayed, M.; Schreiber, K.; Arthanari, S.; Cunningham, J.; Flanders, L.; Moore, L.; et al. BSR and BHPR guideline on prescribing drugs in pregnancy and breastfeeding-Part I: Standard and biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs and corticosteroids. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 1693–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andreoli, L.; Bertsias, G.K.; Agmon-Levin, N.; Brown, S.; Cervera, R.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Doria, A.; Fischer-Betz, R.; Forger, F.; Moraes-Fontes, M.F.; et al. EULAR recommendations for women’s health and the management of family planning, assisted reproduction, pregnancy and menopause in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and/or antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skorpen, C.G.; Hoeltzenbein, M.; Tincani, A.; Fischer-Betz, R.; Elefant, E.; Chambers, C.; Da Silva, J.; Nelson-Piercy, C.; Cetin, I.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; et al. The EULAR points to consider for use of antirheumatic drugs before pregnancy, and during pregnancy and lactation. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 795–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naesens, M.; Kuypers, D.R.J.; Sarwal, M. Calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 481–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Issa, N.; Kukla, A.; Ibrahim, H.N. Calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity: A review and perspective of the evidence. Am. J. Nephrol. 2013, 37, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, T.; Al-Otaibi, T.; Al-Wahaib, S.; Francis, I.; Nair, M.P.; Halim, M.A.; El-Sayed, A.; Nampoory, M.R.N. Posttransplantation calcineurin inhibitor-induced hemolytic uremic syndrome: Single-center experience. Transplant. Proc. 2010, 42, 814–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Kostopoulou, M.; Alunno, A.; Aringer, M.; Bajema, I.; Boletis, J.N.; Cervera, R.; Doria, A.; Gordon, C.; Govoni, M.; et al. 2019 Update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Kostopoulou, M.; Cheema, K.; Anders, H.J.; Aringer, M.; Bajema, I.; Boletis, J.; Frangou, E.; Houssiau, F.A.; Hollis, J.; et al. 2019 Update of the Joint European League against Rheumatism and European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association (EULAR/ERA-EDTA) recommendations for the management of lupus nephritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, S713–S723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Závada, J.; Pešičkova, S.S.; Ryšavá, R.; Olejárova, M.; Horák, P.; Hrnčíř, Z.; Rychlík, I.; Havrda, M.; Vítová, J.; Lukáč, J.; et al. Cyclosporine A or intravenous cyclophosphamide for lupus nephritis: The Cyclofa-Lune study. Lupus 2010, 19, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, G.; Doria, A.; Mosca, M.; Alberighi, O.D.C.; Ferraccioli, G.; Todesco, S.; Manno, C.; Altieri, P.; Ferrara, R.; Greco, S.; et al. A randomized pilot trial comparing cyclosporine and azathioprine for maintenance therapy in diffuse lupus nephritis over four years. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 1, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argolini, L.M.; Frontini, G.; Elefante, E.; Saccon, F.; Binda, V.; Tani, C.; Scotti, I.; Carli, L.; Gatto, M.; Esposito, C.; et al. Multicentric study comparing cyclosporine, mycophenolate mofetil and azathioprine in the maintenance therapy of lupus nephritis: 8 years follow up. J. Nephrol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Li, X.; Qu, L.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; He, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; et al. Tacrolimus versus cyclophosphamide as treatment for diffuse proliferative or membranous lupus nephritis: A non-randomized prospective cohort study. Lupus 2012, 21, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wu, X.; Xu, Y.; Shen, P.; Chen, N. Mycophenolate mofetil or tacrolimus compared with intravenous cyclophosphamide in the induction treatment for active lupus nephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 1467–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mok, C.C.; Ying, K.Y.; Yim, C.W.; Siu, Y.P.; Tong, K.H.; To, C.H.; Ng, W.L. Tacrolimus versus mycophenolate mofetil for induction therapy of lupus nephritis: A randomised controlled trial and long-term follow-up. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, H.; Liu, Z.H.; Xie, H.L.; Hu, W.X.; Zhang, H.T.; Li, L.S. Successful treatment of class V+IV lupus nephritis with multitarget therapy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Xing, C.; Fu, P.; Ni, Z.; Chen, J.; Lin, H.; Liu, F.; He, Y.; et al. Multitarget therapy for induction treatment of lupus nephritis: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Xing, C.; Lin, H.; Ni, Z.; Fu, P.; Liu, F.; et al. Multitarget therapy for maintenance treatment of lupus nephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 3671–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, J.; Casian, A.; D’Cruz, D. Tacrolimus use in lupus nephritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraai, J.T.; Bredewold, O.W.; Trompet, S.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Rabelink, T.J.; De Craen, A.J.M.; Teng, Y.K.O. TAC-TIC use of tacrolimus-based regimens in lupus nephritis. Lupus Sci. Med. 2016, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.C.; Tunnicliffe, D.J.; Singh-Grewal, D.; Mavridis, D.; Tonelli, M.; Johnson, D.W.; Craig, J.C.; Tong, A.; Strippoli, G.F.M. Induction and Maintenance Immunosuppression Treatment of Proliferative Lupus Nephritis: A Network Meta-analysis of Randomized Trials. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 70, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costenbader, K.H.; Desai, A.; Alarcón, G.S.; Hiraki, L.T.; Shaykevich, T.; Brookhart, M.A.; Massarotti, E.; Lu, B.; Solomon, D.H.; Winkelmayer, W.C. Trends in the incidence, demographics, and outcomes of end-stage renal disease due to lupus nephritis in the US from 1995 to 2006. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1681–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parikh, S.V.; Almaani, S.; Brodsky, S.; Rovin, B.H. Update on Lupus Nephritis: Core Curriculum 2020. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, B.K.; Montagnino, G.; del Castillo, D.; Margreiter, R.; Sperschneider, H.; Olbricht, C.J.; Krüger, B.; Ortuño, J.; Köhler, H.; Kunzendorf, U.; et al. Group for the ET vs CMRTS. Efficacy and safety of tacrolimus compared with cyclosporin A microemulsion in renal transplantation: 2 year follow-up results. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2005, 20, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rovin, B.H.; Solomons, N.; Pendergraft, W.F.; Dooley, M.A.; Tumlin, J.; Romero-Diaz, J.; Lysenko, L.; Navarra, S.V.; Huizinga, R.B.; AURA-LV Study Group. A randomized, controlled double-blind study comparing the efficacy and safety of dose-ranging voclosporin with placebo in achieving remission in patients with active lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2017, 389, 2328–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunkl, M.; Frascolla, S.; Amormino, C.; Volpe, E.; Tuosto, L. T Helper Cells: The Modulators of Inflammation in Multiple Sclerosis. Cells 2020, 9, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiricozzi, A.; Romanelli, P.; Volpe, E.; Borsellino, G.; Romanelli, M. Scanning the Immunopathogenesis of Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veale, D.J.; Fearon, U. The pathogenesis of psoriatic arthritis. Lancet 2018, 391, 2273–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanke, Y.; Yago, T.; Kotake, S. The Role of Th17 Cells in the Pathogenesis of Behcet’s Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugaya, M. The role of th17-related cytokines in atopic dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 1 December 2020).
- Kitahara, K.; Kawai, S. Cyclosporine and tacrolimus for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2007, 19, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, J.R.; Sayegh, M.H.; Mallat, S.G. Calcineurin Inhibitors: 40 Years Later, Can’t Live without …. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 5785–5791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rafael-Vidal, C.; Altabás, I.; Pérez, N.; Mourino Rodríguez, C.; Pego-Reigosa, J.M.; Garcia, S. Calcineurin and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: The Rationale for Using Calcineurin Inhibitors in the Treatment of Lupus Nephritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031263
Rafael-Vidal C, Altabás I, Pérez N, Mourino Rodríguez C, Pego-Reigosa JM, Garcia S. Calcineurin and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: The Rationale for Using Calcineurin Inhibitors in the Treatment of Lupus Nephritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(3):1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031263
Chicago/Turabian StyleRafael-Vidal, Carlos, Irene Altabás, Nair Pérez, Coral Mourino Rodríguez, Jose M. Pego-Reigosa, and Samuel Garcia. 2021. "Calcineurin and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: The Rationale for Using Calcineurin Inhibitors in the Treatment of Lupus Nephritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 3: 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031263
APA StyleRafael-Vidal, C., Altabás, I., Pérez, N., Mourino Rodríguez, C., Pego-Reigosa, J. M., & Garcia, S. (2021). Calcineurin and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: The Rationale for Using Calcineurin Inhibitors in the Treatment of Lupus Nephritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(3), 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031263






