Abstract
Electrical remodelling as a result of homeodomain transcription factor 2 (Pitx2)-dependent gene regulation was linked to atrial fibrillation (AF) and AF patients with single nucleotide polymorphisms at chromosome 4q25 responded favorably to class I antiarrhythmic drugs (AADs). The possible reasons behind this remain elusive. The purpose of this study was to assess the efficacy of the AADs disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone on human atrial arrhythmias mediated by Pitx2-induced remodelling, from a single cell to the tissue level, using drug binding models with multi-channel pharmacology. Experimentally calibrated populations of human atrial action po-tential (AP) models in both sinus rhythm (SR) and Pitx2-induced AF conditions were constructed by using two distinct models to represent morphological subtypes of AP. Multi-channel pharmaco-logical effects of disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone on ionic currents were considered. Simulated results showed that Pitx2-induced remodelling increased maximum upstroke velocity (dVdtmax), and decreased AP duration (APD), conduction velocity (CV), and wavelength (WL). At the concentrations tested in this study, these AADs decreased dVdtmax and CV and prolonged APD in the setting of Pitx2-induced AF. Our findings of alterations in WL indicated that disopyramide may be more effective against Pitx2-induced AF than propafenone and quinidine by prolonging WL.
1. Introduction
Although atrial fibrillation (AF) incidence increases with age, and with the context of concomitant cardiac pathologies [1], population-based genome-wide association studies (GWASs) showed that one-third of AF patients carry common genetic variants, suggesting that AF has a heritable component [2]. Recently, many AF-associated loci were identified in GWASs [3,4,5,6,7,8,9] and the most common AF susceptibility locus first identified in European, Chinese, and Japanese populations is located on chromosome 4q25 [10]. The gene-poor 4q25 region harbors paired-like homeodomain transcription factor 2 (Pitx2), which has been fundamentally linked to AF [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20], although the basis for this connection remains obscure. In early cardiac embryogenesis, Pitx2 suppresses left atrial automaticity and the formation of “sinus node-like structures” in the left atrium [21] and contributes to the formation of the pulmonary vein myocardium [13]. In the adult heart, Pitx2 is mainly expressed in the left atrium and pulmonary vein [11]. Experimental studies of Pitx2-induced AF have indicated that the downregulation of Pitx2 creates a predisposition to AF without marked structural changes in the atria [11,15,18,22] via shortened atrial repolarisation [22], a more depolarised resting membrane potential (RMP) [18], and abnormalities in calcium cycling [17,23,24]. Gene expression analyses highlighted that Pitx2 regulated genes of ion channels and gap junctions [11,12,17,22,23,25,26] in a dose-dependent manner. Based on these experimental data on changes in the expression of ion channels and gap junctions, we constructed multi-scale models of human atrial electrophysiology to investigate mechanisms by which Pitx2-induced remodelling promotes AF in our previous studies [27,28,29,30,31,32,33]. However, the effective management of AF remains a challenge, and is incompletely understood in the context of Pitx2-induced AF.
A population-based study assessed the influence of AF-associated loci on the response to antiarrhythmic drug (AAD) therapies and showed that carriers of the variant allele at rs10033646 on chromosome 4q25 responded favorably to class I AADs [34]. Class I AADs used in AF include flecainide, disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone [35]. The pharmacological effects of flecainide in Pitx2-induced AF were investigated by using a multi-scale computational model and simulated results demonstrated that flecainide is effective for the treatment of Pitx2-induced AF patients by preventing spontaneous calcium release [36]. However, the efficacy of other class I AADs, disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone, on human atrial arrhythmias mediated by Pitx2-induced remodelling remains elusive.
Although the efficacy of disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone on human atrial patho-electrophysiology associated with human Ether-à-go-go-Related Gene(hERG) -linked short QT syndrome has been investigated using a multi-scale computational model [37], mechanisms by which short QT mutations promote AF may be different from that underlying Pitx2-induced AF [27,28,29,30,31,32,36]. Additionally, both clinical [34] and theoretical [36] studies of pharmacotherapy for Pitx2-induced AF often ignored inter-subject variability in atrial electrophysiology properties. Population-based computational approaches that can capture key disease conditions have proven valuable for understanding inter-subject variability in electrophysiological properties [38,39,40] and cardiotoxicity [41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52]. Similarly, these methods were useful in the study of AF [53,54,55,56,57]. Recently, a novel Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Framework was proposed based on these population-based computational models and the effects of a multi-atrial-predominant potassium current block in AF were investigated [54].
Here, following the Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Framework developed by Ni et al. [54], we constructed populations of in silico models calibrated to values of action potential (AP) biomarkers reported in an experimental dataset on AP recordings [58]. Using these experimentally calibrated models, we simulated and assessed actions of class I AADs on human atrial electrophysiology. AP duration (APD) and maximum upstroke velocity (dVdtmax) were quantified to evaluate anti-AF effects of class I AADs on AP at the cellular level, while conduction velocity (CV) and wavelength (WL) were quantified to assess the effects of class I AADs on AP propagation at the tissue level. Sensitivity analyses of AP biomarkers were applied to understand the ionic mechanisms underlying Pitx2-induced AF and the efficacy of these AADs. Finally, we performed population-based simulations of Pitx2-induced remodelling and predicted a reduction in APD, CV, and WL and an increase in dVdtmax. Further simulations of actions of class I AADs on Pitx2-induced AF exhibited APD prolongation and a reduction in CV and dVdtmax. Our results showed that disopyramide led to WL prolongation compared to the drug-free AF conditions. These findings suggest that disopyramide may be effective against Pitx2-induced AF.
2. Results
2.1. Overview of In Silico Assessment of Class I Antiarrhythmic Drugs
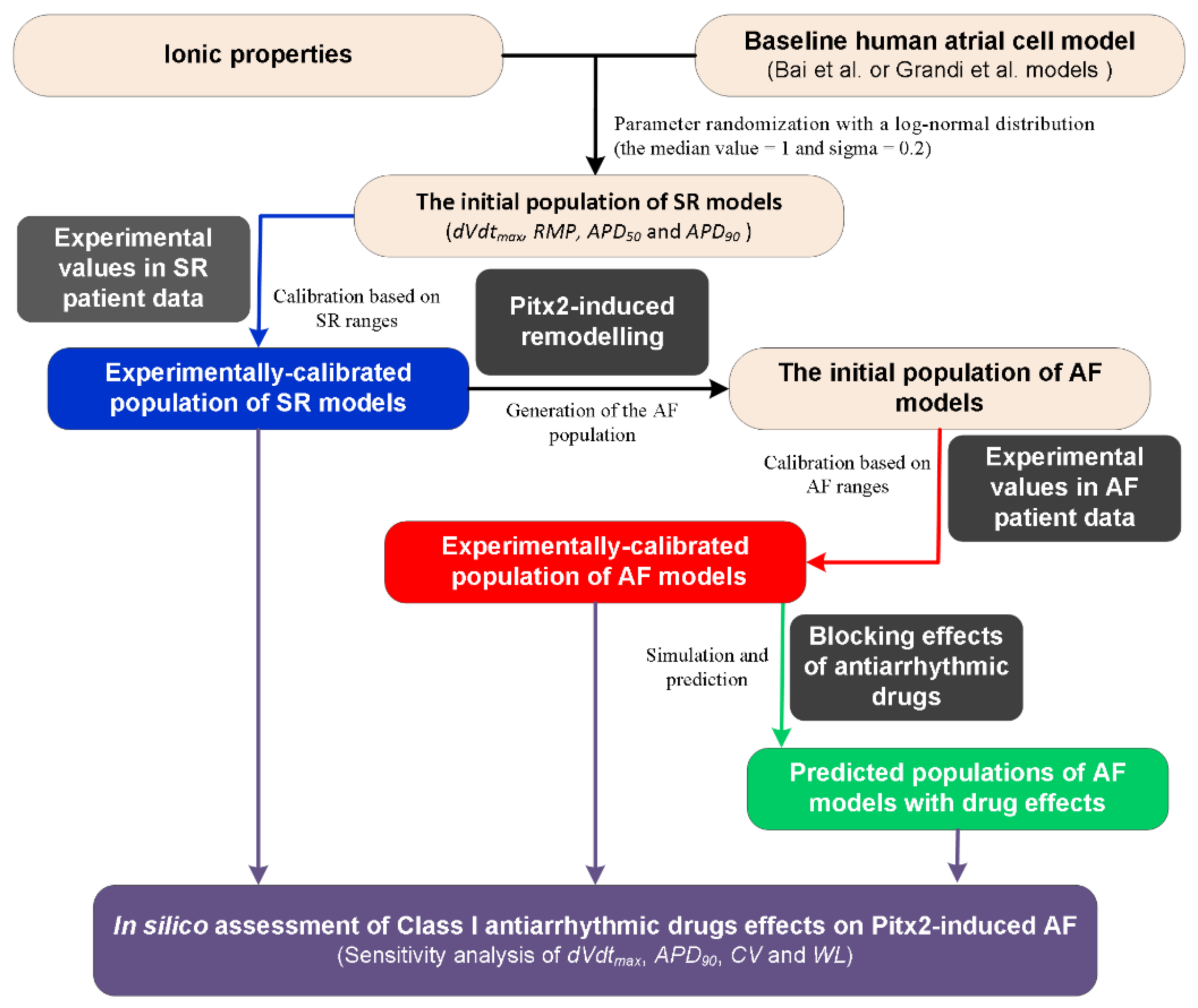
A flow chart illustrating the process for the in silico assessment of class I AADs effects on Pitx2-induced AF is presented in Figure 1. First, the initial population of sinus rhythm (SR) models was created by randomly perturbing parameters associated with ionic properties (Table 1) of the baseline human atrial cell models [41]. The Bai et al. model displaying a type-1 AP with notch-and-dome morphology [27] and the Grandi et al. model displaying a type-3 AP with a typical triangular shape [59] were chosen as the baseline human atrial cell models to represent distinct morphological subtypes of human atrial AP [60]. Parameters associated with ionic properties were allowed to vary independently according to a log-normal distribution and sigma was set to be 0.2 to cover a range of variability similar to that seen in experiments based on previous studies [41,54,61,62]. Second, we used the initial models to simulate human atrial AP by considering stimulation frequency (1 Hz) under the experimental conditions [58] and calculated the AP biomarkers of each initial model. The initial models generated in the previous step were selected to constitute the SR population whose simulated electrophysiological properties are in range with the same properties in experimental data on AP biomarkers (including dVdtmax, RMP, APD50, and APD90) in Table 2. This step yields the experimentally calibrated population of SR models [53]. Third, electrical remodelling due to impaired Pitx2 (Table 3) was introduced into SR model variants to generate the initial population of AF models. Fourth, we used experimental AP biomarkers to calibrate the AF population by excluding the model variants in which values of simulated biomarkers were outside the experimentally observed range (Table 3) reported by Ravens et al [58]. Fifth, the blocking effects of AADs on ion channels (Table 4) were incorporated into experimentally calibrated Pitx2-induced AF models to evaluate their effects on the virtual atrial myocytes. Finally, sensitivity analyses [41,54] of dVdtmax and APD90 at the cellular level and CV and WL at the tissue level were applied to understand modulations by ionic parameters of Pitx2-induced remodelling and ion channels affected by AADs. On the basis of model responses, AADs that eliminated the arrhythmogenic propensity of the atrial substrate arising from Pitx2-induced remodelling were selected.
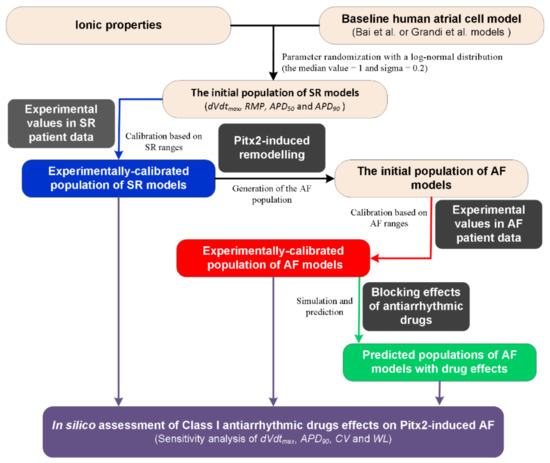
Figure 1.
A flow chart illustrating the process for in silico assessment of class I antiarrhythmic drug effects on Pitx2-induced atrial fibrillation (AF). Note: There are two distinct morphological subtypes of human atrial action potential (AP) [58] and therefore the Bai et al. model with a notch-and-dome AP morphology [27] and the Grandi et al. model with a triangular AP shape [59] were used in the present study. Class I antiarrhythmic drugs assessed include quinidine, disopyramide, and propafenone. Abbreviations: Pitx2: Homeodomain transcription factor 2, SR: Sinus rhythm; dVdtmax: Maximum upstroke velocity, RMP: Resting membrane potential, APD50 and APD90: AP duration at 50% and 90%, respectively, CV: Conduction velocity, and WL: Wavelength.

Table 1.
Parameters associated with ionic properties for constructing populations of atrial models.

Table 2.
Experimental data on AP biomarkers [58] under atrial fibrillation (AF) and sinus rhythm (SR) conditions.

Table 3.
Parameters associated with Pitx2-induced remodelling.

Table 4.
Parameters associated with blocking effects of antiarrhythmic drugs.
2.2. The Experimentally Calibrated Populations of Human Atrial Myocytes under SR and AF Conditions
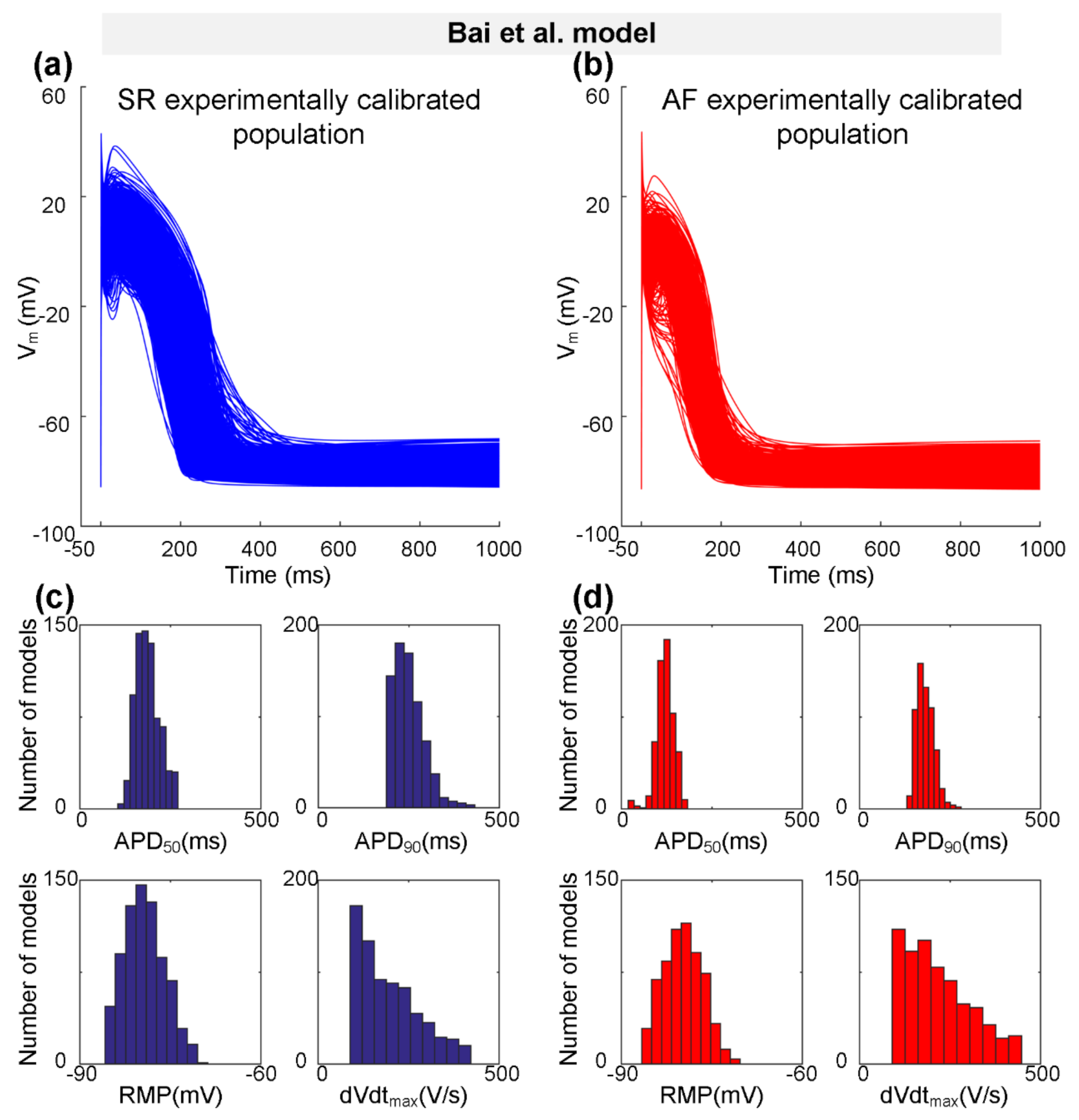
Representing a type-1 AP with notch-and-dome morphology, the Bai et al. model [27] was used to generate the initial SR population of human atrial cell model variants. According to the physiological range of AP biomarkers (dVdtmax, RMP, APD50, and APD90 values at 1 Hz pacing) measured experimentally (Table 2), populations of 745 SR models out of the initial pool of 1200 models were selected to generate the experimentally calibrated population of SR models. Next, we incorporated Pitx2-induced electrical remodelling (Table 3) into the SR population of 745 variants to generate the initial AF population, and then calibrated this AF population to the experimentally measured AP biomarkers (Table 2). Representative AP traces for the experimentally calibrated SR population of 745 models and AF population of 621 models, respectively, are shown in Figure 2a,b. Distributions of AP biomarkers of the experimentally calibrated SR models are compared to that of AF models (Figure 2c,d). In detail (Table 5), dVdtmax is increased from 197.87 ± 83.18 V/s for the SR condition to 219.21 ± 90.48 V/s for the AF condition, whereas APD90 (250.10 ± 41.59 ms vs. 181.93 ± 23.66 ms) and APD50 (187.84 ± 32.36 ms vs. 121.22 ± 24.13 ms) were abbreviated due to Pitx2-induced remodelling. No significant changes in RMP (−79.28 ± 3.29 mV vs. −79.81 ± 3.22 mV) were observed.
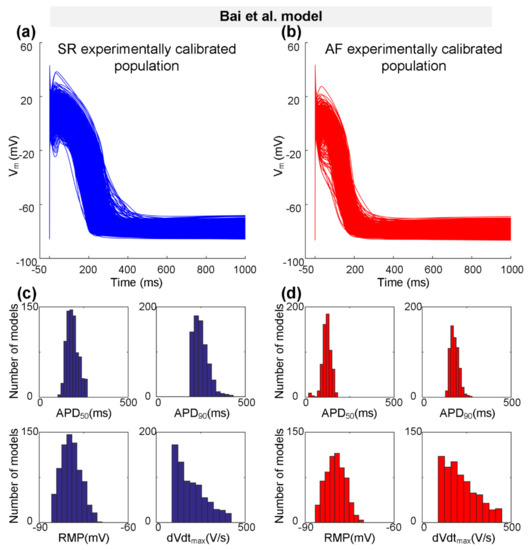
Figure 2.
The experimentally calibrated populations constructed with the Bai et al. model for sinus rhythm (SR, blue) and atrial fibrillation (AF, red) conditions. (a,b) Representative traces of action potential (AP) models in SR and Pitx2-induced AF conditions. (c,d) Distributions of AP biomarkers (including dVdtmax, RMP, APD50, and APD90) under SR and Pitx2-induced AF conditions.

Table 5.
AP biomarkers obtained from the Bai et al. model and the Grandi et al. model under atrial fibrillation (AF) and sinus rhythm (SR) conditions.
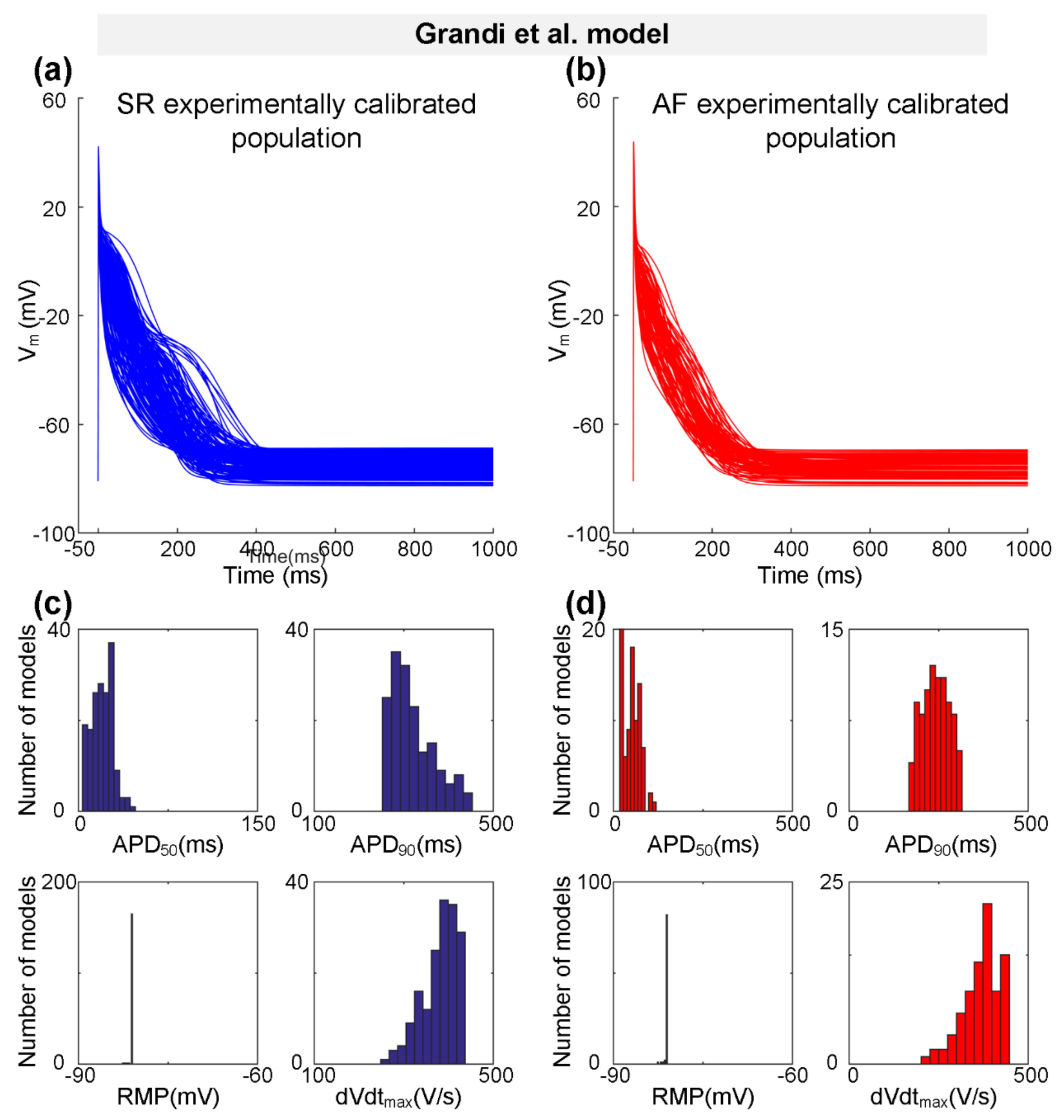
Representing a type-3 AP with a typical triangular shape, the Grandi et al. model [59] was also used to generate the experimentally calibrated populations according to the physiological range of AP biomarkers [58] measured experimentally (Table 2). One hundred and seventy SR models and 87 AF models were selected to constitute the SR population and the AF population, respectively. Figure 3 shows representative AP traces (Figure 3a,b) and distributions of AP biomarkers (Figure 3c,d) for the SR population and the AF population. Consistent with changes in AP biomarkers observed in the Bai et al. model (Figure 2c,d and Table 5), in particular, dVdtmax is increased from 351.14 ± 48.90 V/s for the SR population to 368.66 ± 52.15 V/s for the AF population, whereas APD90 is decreased from 251.08 ± 61.50 ms for the SR population to 241.82 ± 37.98 ms for the AF population (Table 5).
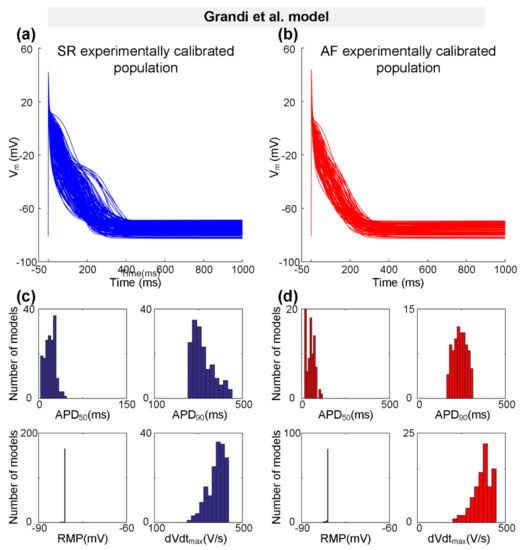
Figure 3.
The experimentally calibrated populations constructed with the Grandi et al. model for sinus rhythm (SR, blue) and atrial fibrillation (AF, red) conditions. (a,b) Representative traces of action potential (AP) models in SR and Pitx2-induced AF conditions. (c,d) Distributions of AP biomarkers (including dVdtmax, RMP, APD50, and APD90) under SR and Pitx2-induced AF conditions.
2.3. Sensitivity Analysis Revealed Alterations in Depolarisation and Repolarisation of AP
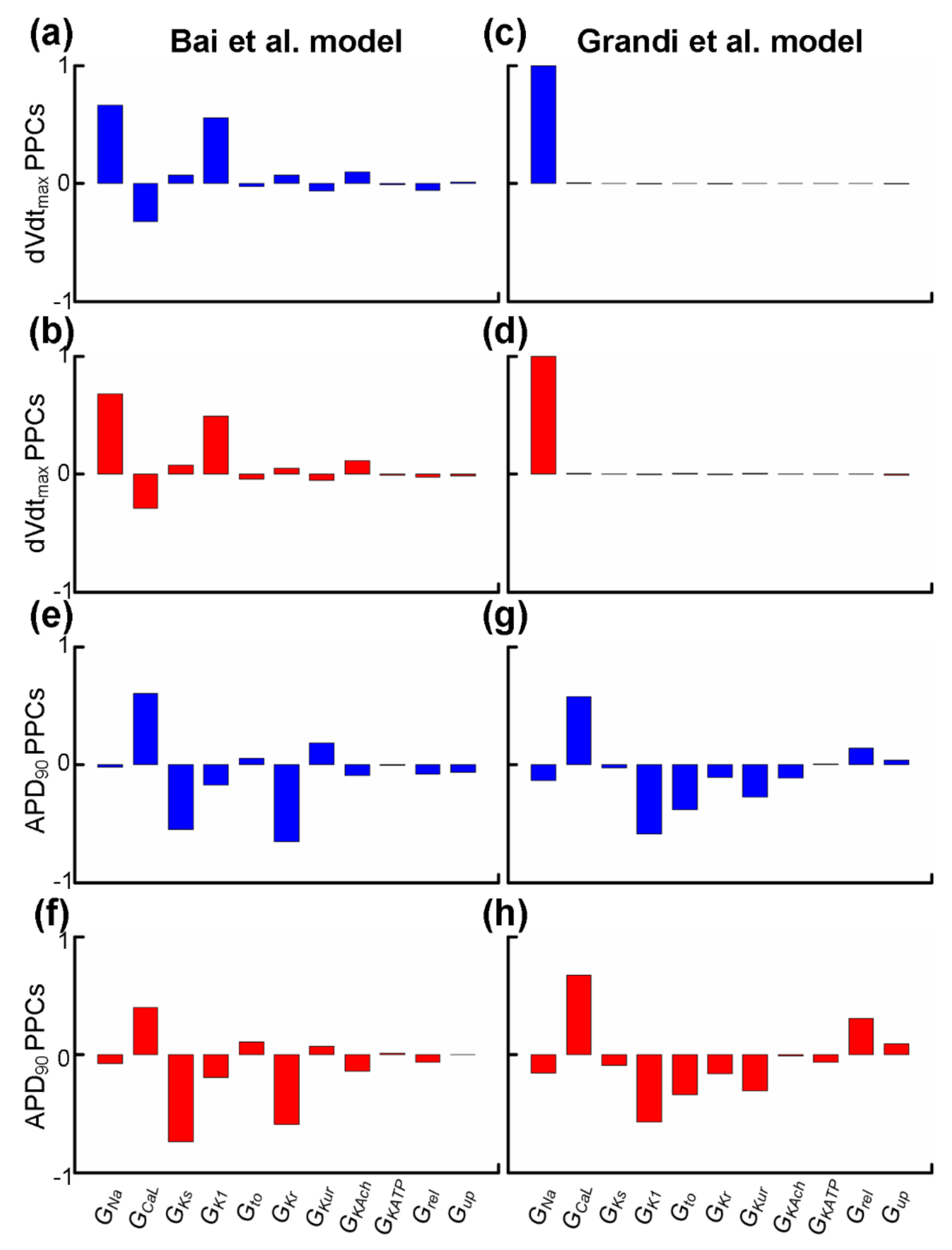
Experimental studies have demonstrated that sensitivity analyses of dVdtmax and APD90 can provide insights into alterations in the depolarisation rate [80,81,82,83] and the repolarisation time [84] of the cardiac tissue. We applied partial correlation analysis to predict alterations in dVdtmax and APD90 when electrical remodelling (listed in Table 3) due to impaired Pitx2 was introduced or ion channels (listed in Table 4) were blocked by class I AADs. Parameters associated with Pitx2-induced electrical remodelling include GNa, GCaL, GKs, GK1, Grel, and Gup, while parameters affected by actions of AADs (including disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone) include GNa, GCaL, Gto, GKs, GKr, GKur, GKATP, GKAch,Ado, and GK1. We used partial correlation analysis to calculate partial correlation coefficients (PCCs) to quantify correlations between the parameter values and dVdtmax and APD90. In Figure 4a,d, dVdtmax PPCs are positive for GNa in Bai et al. and Grandi et al. populations, suggesting that upregulated INa in Pitx2-induced remodelling would tend to increase the depolarisation rate and inhibit INa due to actions of AADs reducing depolarisation rate. In Figure 4e,h, APD90 PPCs are negative for GKs, GKr, GKAch,Ado, and GK1 but not for GCaL, indicating that upregulated GKs and downregulated GCaL in Pitx2-induced remodelling cause APD shortening and blocking these potassium currents (i.e., IKs, IKr, IKAch, and IK1) would tend to prolong APD. APD90 PPCs for Gto, GKATP, and GKur are also negative in Grandi et al. but not Bai et al. populations. Therefore, in Grandi et al. populations, APD90 PPCs for Gto, GKs, GKr, GKur, GKAch,Ado, GKATP, and GK1 are negative, suggesting that inhibiting these currents due to actions of AADs produces positive APD prolongation. In contrast, in Bai et al. populations, negative APD90 PPCs are seen for IKs, IKr, IKAch, and IK1 only, indicating that the blocking effects of class I drugs on IKs, IKr, IKAch, and IK1 are associated with positive APD prolongation, but the blocking effects of AADs on Gto, GKATP, and GKur with negative APD prolongation.
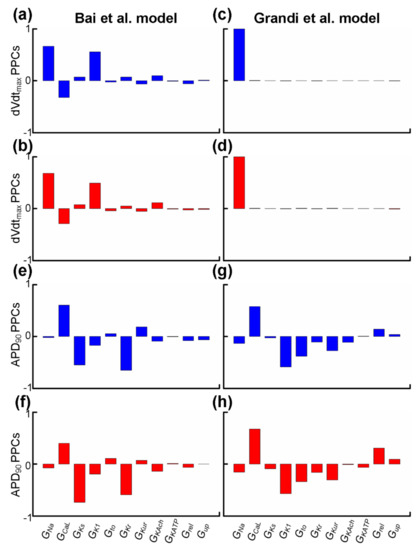
Figure 4.
Partial correlation coefficients (PPCs) between biomarkers (dVdtmax or APD90) and parameters associated with Pitx2-induced electrical remodelling (GNa, GCaL, GKs, GK1, Grel, and Gup) or actions (GNa, GCaL, Gto, GKs, GKr, GKur, GKATP, GKAch,Ado, and GK1) of antiarrhythmic drugs. PPCs between dVdtmax and GNa, GCaL, GKs, GK1, GKr, Gto, GKur, GKATP, GKAch,Ado, Grel, or Gup for the virtual atrial myocytes created by the Bai et al. model in SR (a, blue) and AF (b, red) are compared to those for virtual atrial myocytes in the SR (c, blue) and AF (d, red) populations created by the Grandi et al. model. PPCs of APD90 for virtual atrial SR (e, blue) and AF (f, red) myocyte populations created by the Bai et al. model are compared to those for the virtual atrial myocytes created by the Grandi et al. model in SR (g, blue) and AF (h, red).
2.4. Antiarrhythmic Effects of Class I Drugs on dVdtmax and APD90 at the Cellular Level
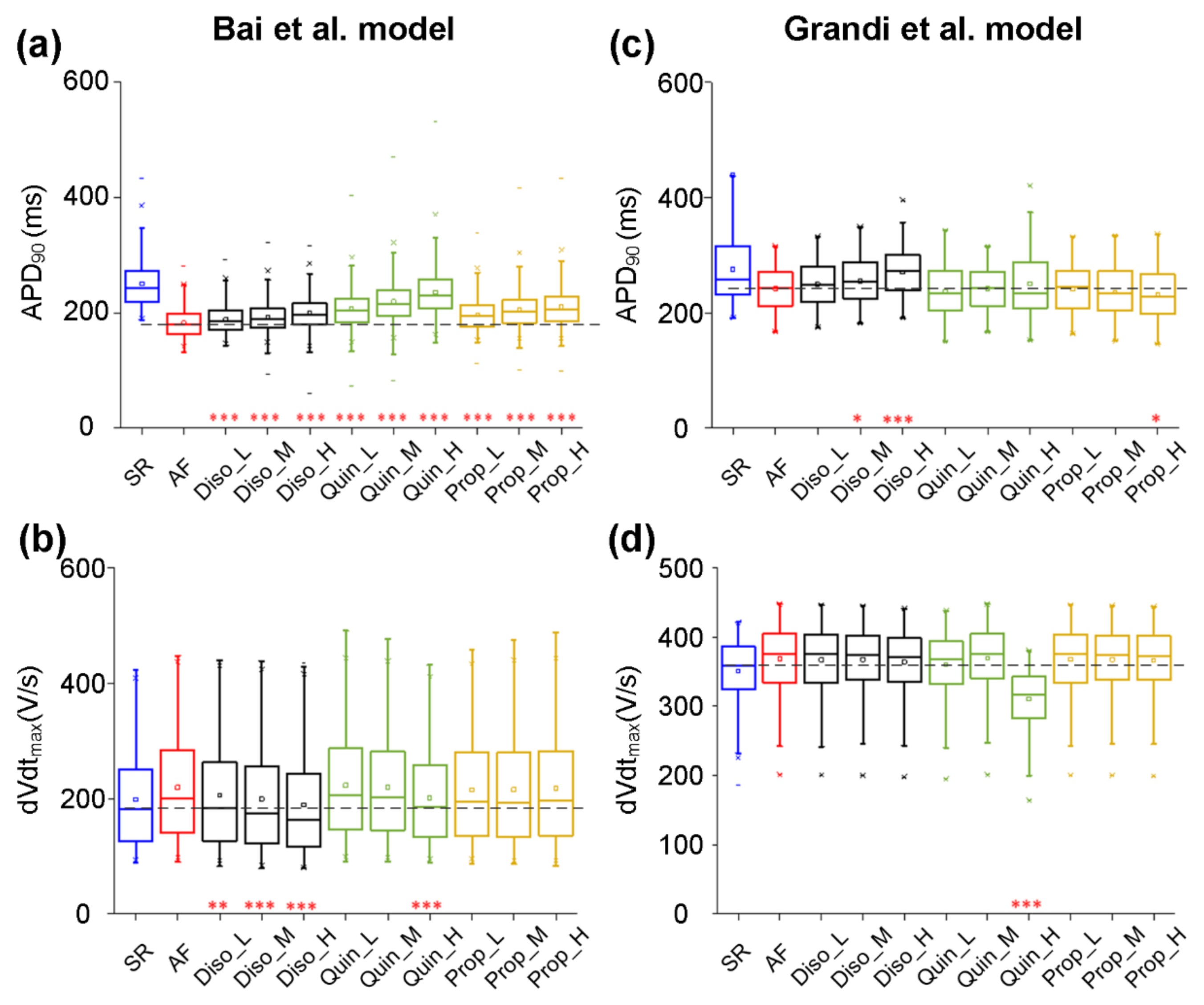
According to experimental data on actions of class I AADs on ion currents, their effects were incorporated into experimentally calibrated models in the AF population created with the Bai et al. model. Parameters associated with the effects of AADs were GNa, GCaL, Gto, GKs, GKr, GKATP, GKAch,Ado, GKur, and GK1 (Table 4). The class I AADs investigated here included disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone. Taking into account plasma protein binding, estimates of the most likely unbound concentrations of propafenone, disopyramide, and quinidine have been given as ~0.15–1 μM [85,86,87], 1 μM, and 2 μM [88], respectively. To encompass the likely total as well as unbound concentrations, we chose to simulate the effects of a wide range of concentrations of propafenone (low dose Prop_L: 0.2, medium dose Prop_M: 0.5, and high dose Prop_H: 0.8 μM), disopyramide (Diso_L: 1.0, Diso_M: 2.0, and Diso_H: 5.0 μM), and quinidine (Quin_L: 1.0, Quin_M: 2.0, and Quin_H: 5.0 μM) [37,89]. Figure 5 shows the actions of disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone on dVdtmax and APD90 in the AF condition. All drugs also prolonged APD90 in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 5a), with quinidine producing a slightly larger increase in APD90 across all concentrations investigated. In detail (Table 6), quinidine prolonged APD90 from 181.93 ± 23.66 ms in the drug-free AF condition to 199.32 ± 28.53 ms (Quin_L), 206.57 ± 32.27ms (Quin_M), and 219.08± 36.78 ms (Quin_H), whereas values of APD90 are 188.29 ± 24.57 ms (Diso_L), 192.17 ± 26.09 ms (Diso_M), and 199.32 ± 28.53 ms (Diso_H) upon application of disopyramide, and are 196.69 ± 27.72 ms (Prop_L), 205.60 ± 32.13 ms (Prop_M), and 210.37± 34.46 ms (Prop_H) upon application of propafenone. APD90 upon application of 5μM quinidine (Quin_H) in the AF condition is close to that in the drug-free SR condition (219.08 ± 36.78 vs. 250.10 ± 41.59). It can be seen in Figure 5b that disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone reduced dVdtmax in a dose-dependent manner, with disopyramide and quinidine decreasing dVdtmax to a greater extent than propafenone. Values of dVdtmax upon application of quinidine and propafenone were smaller than those in the drug-free AF condition, but were larger than those in the drug-free SR condition. However, values of dVdtmax upon the application of disopyramide were smaller than those under drug-free AF and SR conditions.
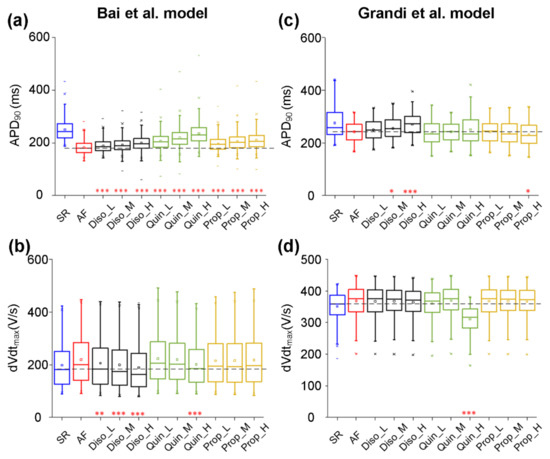
Figure 5.
Effects of low (L), medium (M), and high (H) doses of disopyramide (Diso), quinidine (Quin), and propafenone (Prop) on the atrial fibrillation (AF) population. Using the Bai et al. model, simulated changes in APD90 (a) and dVdtmax (b) following the application of drugs at different doses in comparison to the drug-free conditions in the AF population or in the normal population for sinus rhythm (SR). Using the Grandi et al. model, ranges of APD90 (c) and dVdtmax (d) in conditions of drug-free SR, drug-free AF, AF in the presence of disopyramide at low (Diso_L), medium (Diso_M), and high (Diso_H) doses, AF in the presence of quinidine at low (Quin_L), medium (Quin_M), and high (Quin_H) doses, and AF in the presence of propafenone at low (Prop_L), medium (Prop_M), and high (Prop_H) doses. Each boxplot represents the range covered by the ionic conductances: The edges of the box are the 1st and 3rd quartiles, the whiskers extend to the most extreme datapoints, the estimated median physiological value is the central horizontal line and the notch around the median is the 5% significance level (Mann–Whitney U test: * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001).

Table 6.
A quantitative summary of the effects of class I antiarrhythmic drugs on human atrial electrical activity using the Bai et al. model.
Based on the experimentally calibrated AF models created with the Grandi et al. model, the antiarrhythmic effects of disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone on dVdtmax and APD90 were investigated. Figure 5 shows all drugs prolonged APD90 (Figure 5c) and decreased dVdtmax (Figure 5d) in a dose-dependent manner. It can also be seen in Figure 5c that APD90 upon the application of disopyramide in the AF condition was larger than that in the drug-free AF condition, whereas values of APD90 upon the application of propafenone and quinidine in the AF condition were smaller than that in the drug-free AF condition. Quinidine decreased dVdtmax to a greater extent than disopyramide and propafenone. The value of dVdtmax upon the application of quinidine (Quin_H) was smaller than those under drug-free AF and SR conditions.
Together, our models developed by the Bai et al. model or the Grandi et al. model predicted that all drugs reduced dVdtmax and APD90 to different extents.
2.5. Antiarrhythmic Effects of Class I Drugs on CV and WL at the Tissue Level
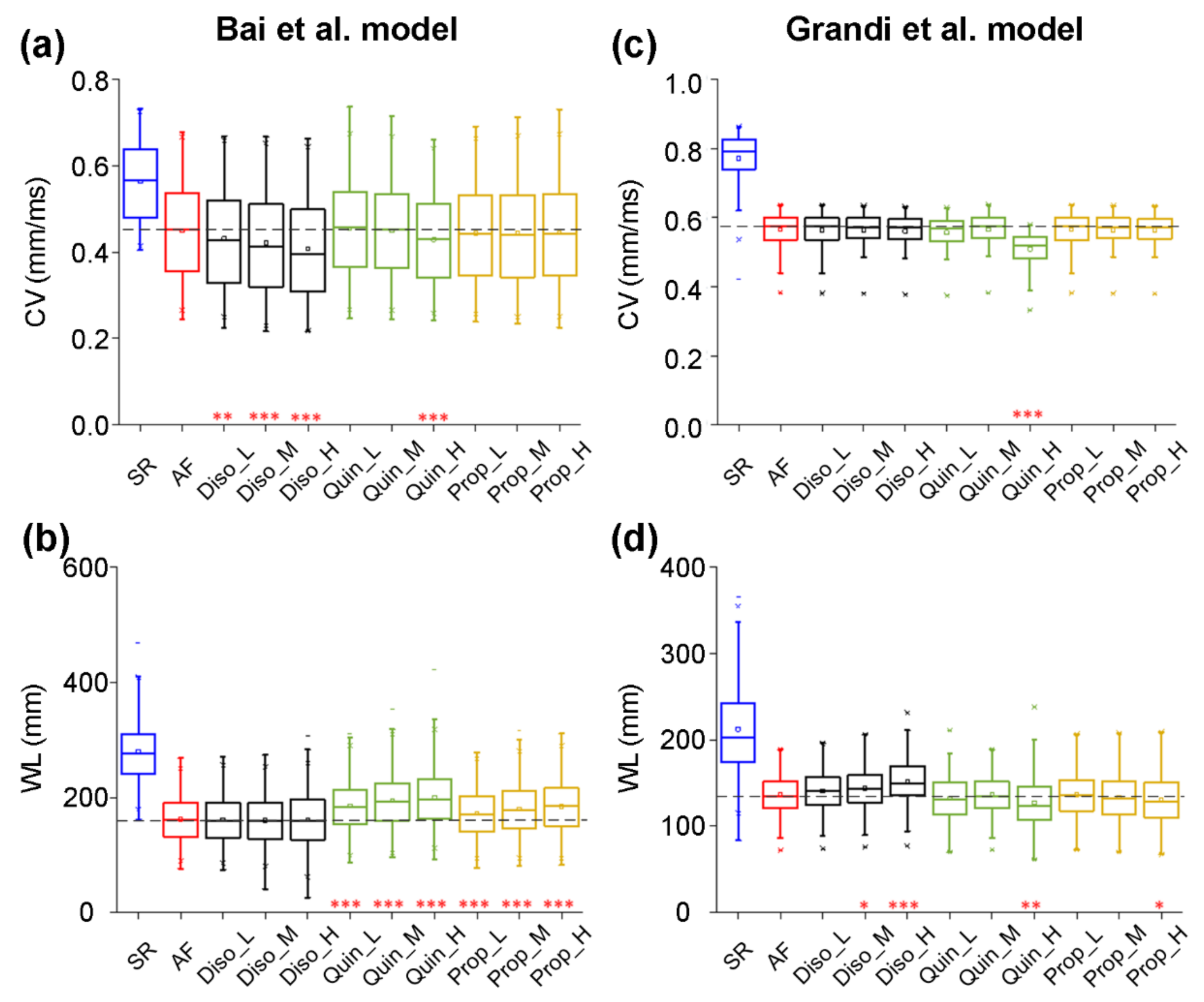
To evaluate the effects of class I drugs on CV and WL, we constructed one-dimensional (1D) models of human atrial strands with the Bai et al. model to investigate the responses of electrical waves to AADs in tissue. Figure 6 shows CV and WL upon the application of disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone in the AF condition, compared with those in the drug-free SR and AF conditions. CV was decreased from 0.56 ± 0.08 mm/ms for the SR condition to 0.45 ± 0.11 mm/ms for the AF condition. It can be seen in Figure 6a that disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone reduced CV in a dose-dependent manner, with disopyramide decreasing CV to a greater extent than quinidine and propafenone. Figure 6b shows values of WL under drug-free SR and AF conditions, and upon the application of various concentrations of disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone. WL was decreased from 139.62 ± 25.56 mm for the drug-free SR condition to 81.13 ± 18.91 mm for the drug-free AF condition. Compared with the drug-free AF condition, all drugs prolonged WL in a dose-dependent manner, with quinidine and propafenone increasing WL to a greater extent than disopyramide. In order of effects of AADs on WL, these drugs are quinidine, propafenone, and disopyramide.
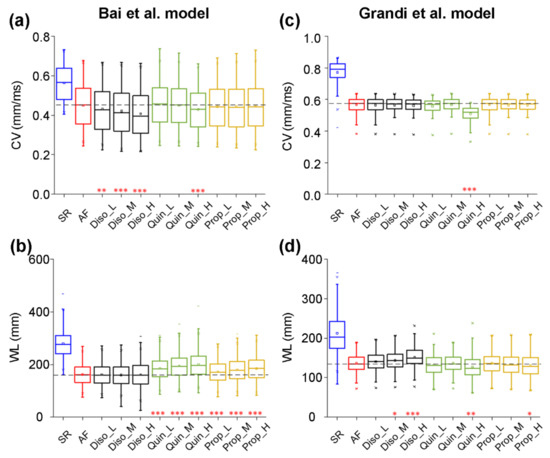
Figure 6.
Effects of low (L), medium (M), and high (H) doses of disopyramide (Diso), quinidine (Quin), and propafenone (Prop) on the virtual tissue population for atrial fibrillation (AF). Using the Bai et al. model, simulated changes in conduction velocity (CV, a) and wavelength (WL, b) following the applications of drugs at different doses in comparison to the drug-free conditions in the AF population or in the normal population for sinus rhythm (SR). Using the Grandi et al. model, ranges of CV (c) and WL (d) in conditions of drug-free SR, drug-free AF, AF in the presence of disopyramide at low (Diso_L), medium (Diso_M), and high (Diso_H) doses, AF in the presence of quinidine at low (Quin_L), medium (Quin_M), and high (Quin_H) doses, and AF in the presence of propafenone at low (Prop_L), medium (Prop_M), and high (Prop_H) doses. Each boxplot represents the range covered by the ionic conductances: The edges of the box are the 1st and 3rd quartiles, the whiskers extend to the most extreme datapoints, the estimated median physiological value is the central horizontal line and the notch around the median is the 5% significance level (Mann–Whitney U test: * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001).
Using 1D models of human atrial fibers developed with the Grandi et al. model, the antiarrhythmic effects of class I drugs on CV and WL were also investigated. All drugs decreased CV in a dose-dependent manner, with quinidine (Quin_H) decreasing CV to a greater extent than disopyramide and propafenone (Figure 6c). Figure 6d shows that disopyramide prolonged WL in a dose-dependent manner, whereas quinidine and propafenone shortened WL in a dose-dependent manner. In order of effects of AADs on WL, these drugs are disopyramide, propafenone, and quinidine.
Together, our models developed by the Bai et al. model or the Grandi et al. model predicted that all drugs reduced CV to different extents. However, only disopyramide can prolong WL in the Pitx2-induced AF condition. Quantitative summaries of the effects of class AADs on human atrial electrical activity in the Pitx2-induced AF condition are listed in Table 6 for the Bai et al. model and Table 7 for the Grandi et al. model. Alterations of electrophysiological properties are listed in Table 8.

Table 7.
A quantitative summary of the effects of class I antiarrhythmic drugs on human atrial electrical activity using the Grandi et al. model.

Table 8.
Alterations of electrophysiological properties.
3. Discussion
Population-based studies have assessed the influence of common single-nucleotide polymorphisms related to AF on the response to AAD therapies and showed that carriers of the variant allele at rs10033646 on chromosome 4q25 responded favorably to the class I AADs [34]. The actions of the class I AADs disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone were assessed in the context of Pitx2-induced AF using a population-based Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Framework [54]. Through sensitivity and statistical analyses of our atrial cell and tissue populations, we found that WL prolongation could be achieved by disopyramide. This study provides clinically relevant insights into the pharmacology of WL prolongation by evaluating and comparing the actions of all three drugs in the context of Pitx2-induced AF, offering an important step toward in silico optimization of pharmacological therapy in this context.
3.1. Main Findings
The major findings presented in this study are as follows. (1) Populations of models based on two human atrial AP models are able to mimic a wide range of inter-subject variability in human atrial AP properties, as exhibited in a set of AP measurements from over 379 SR and AF patients. (2) Pitx2-induced remodelling (as reported in [36]) predicts abbreviated APD90 and increased dVdtmax at the cellular level, and decreased CV and shortened WL at the tissue level in SR versus AF conditions, as reported in experimental studies [17,58] (Table 2). (3) AP biomarkers (namely, APD90 and dVdtmax) are correlated in both SR and AF cardiomyocytes created with the Bai et al. and the Grandi et al. models. dVdtmax is primarily determined by GNa, whereas APD90 is determined by GCaL, GKs, GKr, GKAch,Ado, and GK1. (4) The AADs disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone prolonged APD90 and decreased dVdtmax and CV in a dose-dependent manner in drug-free versus drug-bound AF conditions. (5) Disopyramide prolonged WL. Disopyramide is more effective against Pitx2-induced AF than quinidine and propafenone.
3.2. Compared to Other Forms of AF
AF is the most common cardiac arrhythmia with well-established clinical and genetic risk components. AF can be broadly divided into two types, genetic and acquired types, according to the factors that cause AF. Acquired AF usually begins in a self-terminating paroxysmal form (pAF) and this pattern often evolves to become a chronic form (cAF) [1]. In addition to acquired AF, genetic factors are presumed as key in the development of AF, especially in familial cases (fAF) without cardiac pathology. The total genetic contribution to fAF risk can be broadly divided into three components: Rare coding variation, common variation, and undiscovered variation [90].
For common variation, the genetic loci associated with fAF were first identified and are located on chromosome 4q25, upstream of the transcription factor gene Pitx2 [10]. Pitx2 deficiency resulted in electrical and structural remodelling, and impaired repair of the heart in murine models [18]. Then, meta-analysis of AF cases identified a novel locus for fAF (ZFHX3, rs2106261) [3]. Furthermore, a meta-analysis of multiple well-phenotyped GWASs identified six new susceptibility loci for fAF, including 1q24 (PRRX1), 7q3 (CAV1), 14q23 (SYNE2), 9q22 (FBP1 and FBP2), 15q24 (HCN4), and 10q22 (upstream of SYNPO2L and MYOZ1) [5]. By meta-analyses of SNP associations with AF, researchers discovered five novel loci near the genes NEURL (rs12415501 and rs6584555), GJA1 (rs13216675), TBX5 (rs10507248), CAND2 (rs4642101), and CUX2 (rs6490029)[9]. Five GWASs were conducted in 2017, with a total of no more than 30 novel loci identified. Roselli et al. conducted the largest GWAS meta-analysis, and found that there were 97 loci significantly associated with AF [8]. Nielsen et al. found 142 independent risk variants at 111 loci and prioritised 151 functional candidate genes likely to be involved in fAF. Of these, 80 loci have not been previously reported [91]. Among these common genes, the links between fAF and Pitx2 or TBX5 have been deeply investigated. Experimental studies demonstrated that TBX5 directly activated Pitx2, and TBX5 and Pitx2 antagonistically regulated the membrane effector genes SCN5A, GJA1, RYR2, DSP, and ATP2A2 [17].
For rare coding variation, S140G in the KCNQ1 gene was the first identified [92]. The potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E genes encode the regulatory β-subunits of the channels producing the delayed rectifier potassium current. Gain-of-function mutations in KCNE1, KCNE2, KCNE3, and KCNE5 have been associated with fAF. Furthermore, the genes (i.e., KCNA5, KCND3, and KCNH2) coding the α-subunit of the voltage-gated potassium channels Kv1.5, Kv4.3, and Kv11.1, and the α-subunit of the inwardly rectifying potassium channels Kir2.1, Kir3.4, and Kir6.1 (i.e., KCNJ2, KCNJ5, and KCNJ8) also showed significant associations with fAF risk. fAF-associated potassium channel variants have a gain of channel function, with an expected shortening of the atrial action potential duration and atrial refraction period. The fAF-associated sodium channel genes included SCN5A, SCN10A, and genes coding sodium voltage-gated channel β subunit 1–4 (SCN1B, SCN2B, SCN3B, and SCN4B). The mutations in SCN5A exhibited a compromised peak sodium current and an increased sustained sodium current. The related variations in SCN10A were implicated in the modulation of the late sodium current, while mutations in SCN1B-4B were engaged with the modulation of the inward sodium current. Several non-ion channel genes did not directly alter the action potential, but instead would be expected to instigate the onset of fAF through alternative mechanisms. These included NPPA, NUP155, LMNA, GJA5, AGT, and ACE [93].
For pAF, APD90, ICaL, and INcx were unaltered, indicating the absence of AF-induced electrical remodelling [94]. In contrast, there were increases in SR Ca2+ leaks and the incidence of delayed after-depolarisations in pAF. Ca2+ transient amplitude and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ load were larger in pAF. Ca2+ transient decay was faster in pAF, but the decay of caffeine-induced Ca2+ transients was unaltered, suggesting increased SERCA2a function. In agreement, phosphorylation (inactivation) of the SERCA2a inhibitor protein phospholamban was increased in pAF. Ryanodine receptor fractional phosphorylation was unaltered in pAF, whereas ryanodine receptor expression and single-channel open probability were increased. Increased diastolic sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ leaks and related delayed after-depolarisations promote cellular arrhythmogenesis in pAF patients. Biochemical, functional, and modelling studies point to a combination of increased sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ load related to phospholamban hyperphosphorylation and ryanodine receptor dysregulation as underlying mechanisms.
In addition to Ca2+ handling, cAF involves electrophysiological and structural remodelling. Differences in cardiomyocyte Ca2+-handling properties between patients with pAF and cAF point towards progressive changes in atrial Ca2+ handling due to AF itself [95]. Ca2+ transient amplitude is increased in pAF, but decreased in cAF [96]. Consistent with its role as a frequency sensor, CaMKII autophosphorylation and CaMKII-dependent RyR2 phosphorylation are elevated in cAF but not pAF. Rate induced Ca2+ loading causes enhanced binding of Ca2+ to calmodulin, which activates the phosphatase calcineurin. Calcineurin then dephosphorylates the nuclear factor of activated T cells, which translocates into the nucleus and inhibits the production of CACNA1C mRNA, decreasing the message for the ICaL α-subunit, thereby reducing its protein expression and ion transport function [97]. In parallel, the nuclear factor of activated T cells suppresses the production of microRNA (miR)-26 by binding to and negatively regulating sites upstream of the transcriptional start site in the human and mouse atrium [98]. One of the binding targets of the miR-26 seed site is KCNJ2, the gene encoding the IK1 channel. Reduced miR-26 expression caused by AF removes miR-26-induced destabilisation of the KCNJ2 message and inhibition of its translation. Inward rectifier current functional expression is enhanced by this mechanism, as well as by increased IKACh in human and canine models [99]. Recent work also shows that NLRP3 activation increases the gene expression of the channels subunits underlying the atrial selective currents IKur and IKACh [100]. In addition to these pathways, protein kinase isoform switches upregulate the constitutive activity of IKACh, and the upregulation of two-pore and Ca2+-dependent K+ channels [101]. In addition to AF-induced electrical remodelling, rapid cardiomyocyte firing leads to fibroblast activation via a diffusible substance in HL-1 atrial-derived cardiomyocytes, which seems to be ROS-derived from cardiomyocyte nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase stimulated by Ca2+ loading [102]. ROS are known to activate NLRP3 inflammasomes in other systems and NLRP3 inflammasome activation is known to cause atrial fibrosis [103].
3.3. Changes in Human Atrial Electrical Activity Are Linked to Pitx2-Induced Remodelling
Research studies on Pitx2-induced AF have demonstrated that Pitx2-induced remodelling contributes to atrial cellular electrophysiological changes in AF patients [11,17,26]. Experimental data showed that alterations in human atrial electrical activity included AP shortening, increased upstroke velocity, and decreased conduction velocity [58] and our simulated effects of Pitx2-induced remodelling on atrial electrical activity (Table 2 and Table 5) are concordant with these experimental findings.
Previous experiments on isolated human atrial myocytes have demonstrated that Pitx2-induced remodelling of ion channels, particularly for IKs and ICaL, may contribute to the clinically significant association between impaired Pitx2 and AF [26]. Further simulations in our previous study indicated the Pitx2-induced changes in IKs and ICaL led to APD shortening, facilitating sustained re-entry in 3D anatomical atrial geometry [30]. Our simulations in the Pitx2-induced AF population of models show that AP shortening is determined by ICaL and IKs, and APD is negatively correlated with IKs and positively correlated with ICaL (Figure 4). This is consistent with findings from previous studies that the upregulation of IKs and downregulation of ICaL due to Pitx2-induced remodelling critically contribute to the abbreviation of APD [30,33].
Increased upstroke velocity in Pitx2-induced AF may result from remodelled INa arising from impaired Pitx2. Previous experiments in atrial cardiomyocytes of Pitx2-deleted mice showed increased action potential amplitude and shortened APD [17]. Further gene analysis showed that a reduced Pitx2 dose caused an increase in the expression of SCN5A [17] encoding the alpha subunit of the human cardiac voltage-gated sodium channel (INa). In addition, an increase in the mRNA level of SCN1B encoding a beta-1 subunit of voltage-gated sodium channels (INa) was observed in patients with familial AF arising from the Pitx2c mutation p.Met207Val [63]. Decreased mRNA levels of SCN5A and SCN1B were also observed in atrial-specific Pitx2 mutant mice [22,25], but changes in T-box transcription factor Tbx5 was not investigated and the downregulation of sodium channel genes may result from impaired Tbx5. Previous experiments in atrial cardiomyocytes of Tbx5-deleted mice showed reduced Pitx2 and sodium channel genes, although reduced Pitx2 without alterations in Tbx5 caused an increase in sodium channel genes [17]. Based on these data on remodelled INa due to impaired Pitx2, a Pitx2-induced AF model was developed and predicted an increase in action potential amplitude and maximum upstroke velocity [36]. Consistent with these findings, our simulations in the Pitx2-induced AF population of models show that increased upstroke velocity is determined by INa and is positively correlated with INa (Figure 4).
Furthermore, slow conduction in Pitx2-induced AF may be associated with reduced gap junctions due to impaired Pitx2. Previous experiments in atrial cardiomyocytes of Pitx2-deleted mice showed a reduction of GJA1 encoding the protein connexin 43 (Cx43) [11,17,22,63]. Based on experimental data on remodelled Cx43, our previous simulations showed slow conduction velocity [29,36]. Consistent with these findings, our results in the present study predicted that reduced gap junctions led to the slow conduction of AP propagation.
3.4. Antiarrhythmic Effects of Class I Drugs in Pitx2-Induced AF
Despite the prevalence of AF and decades of research, antiarrhythmic therapies for AF continue to have limited efficacy and safety [35]. A population-based study assessed the influence of AF-associated loci on the response to antiarrhythmic drug therapies and showed that carriers of the variant allele at rs10033646 on chromosome 4q25 (Pitx2) responded favorably to class I AADs [34]. Class I AADs frequently used clinically include flecainide, disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone [35]. The antiarrhythmic effects of flecainide on Pitx2-induced AF were investigated in our previous study and simulation results indicated that flecainide has antiarrhythmic effects on AF due to impaired Pitx2 by preventing spontaneous calcium release and increasing wavelength [36]. In the present study using the Bai et al model, the effectiveness of disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone was assessed with WL. The simulated results showed that disopyramide and quinidine were moderately effective by prolonging WL, whereas propafenone was shown to be ineffective by abbreviating WL in Pitx2-induced AF. WL is the product of APD90 and CV. Increased APD90 and decreased CV occurred upon the application of disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone. Under the application of disopyramide or quinidine, the extent of AP prolongation is larger than the degree of CV reduction, resulting in an increase in WL. In contrast, the extent of CV reduction is much larger than the degree of AP prolongation, leading to a reduction in WL. Alterations in WL can be linked to blocking effects of class I drugs on ion channels which included GNa, GCaL, Gto, GKs, GKr, GKAch,Ado, GKATP, GKur, and GK1. Under the application of class I drugs in Pitx2-induced AF, the inhibition of sodium currents would decrease dVdtmax and thereby reduce CV, while the blocking of potassium currents would prolong APD90. Therefore, the antiarrhythmic effects of class I drugs in Pitx2-induced AF can be attributed to their potent blocking of sodium and potassium channels. The effectiveness of drugs is determined by the extent of their blocking effects on sodium and potassium channels. Consistent with findings obtained from the Bai et al. model, the results obtained from the Grandi et al. model show that disopyramide is more effective than propafenone in Pitx2-induced AF and this is because the extent of their blocking effects on potassium channels is larger than that on sodium channels. Collectively, our results demonstrate that a combined blocking of sodium and potassium currents can exert synergistic antiarrhythmic effects and therefore is a valuable therapeutic for Pitx2-induced AF.
By slowing the rate of atrial flutter/fibrillation, quinidine can decrease the degree of atrioventricular blocking and cause an increase, sometimes marked, in the rate at which supraventricular impulses are successfully conducted by the atrioventricular node, with a resultant paradoxical increase in ventricular rate [104]. The previous study showed that quinidine causes greater QT prolongation in women than in men at equivalent serum concentrations. This difference may contribute to the greater incidence of drug-induced torsades de pointes observed in women taking quinidine and has implications for other cardiac and noncardiac drugs that prolong the QTc interval. The adjustment of dosages based on body size alone is unlikely to substantially reduce the increased risk of torsades de pointes in women [105].
In addition, the direct effect of the class 1a AADs quinidine and disopyramide on APs is significantly modified by their anticholinergic actions. Inhibiting vagal activity can lead to a reduction in IKAch and an increase in sinoatrial rate. Quinidine depressed adenosine-induced IKAch, while the effect of disopyramide on the adenosine-induced current was much smaller than that on the Ach-induced current. An experimental study suggested that quinidine may inhibit the muscarinic K+ channel itself and/or G proteins, while disopyramide may mainly block functions of muscarinic Ach receptors in atrial myocytes [106]. Although disopyramide may effectively depress atrial rate during flutter, it may lead to an increase in ventricular rate because of an increase in the number of impulses conducted through the atrioventricular node, thereby requiring concomitant treatment with a beta blocker to slow atrioventricular nodal conduction.
3.5. Model and AP Shape Independence of Prediction of the Antiarrhythmic Effects of Class I Drugs
It is well known that human atrial myocytes display two distinct AP morphologies: the type-1 AP shows a notch-and-dome morphology and the type-3 AP shows a typical triangular morphology [58,60]. Therefore, the Bai et al. model displaying the type-1 AP [27] and the Grandi et al. model displaying the type-3 AP [59] were chosen to generate populations of human atrial AP. The Bai et al. model was developed by taking into account ionic differences between atrial and ventricular cells based on the previous human ventricular model (TP model) developed by ten Tusscher and Panfilov [107]. The TP model included a subspace calcium variable that controls the dynamics of the ICaL and the ryanodine receptor current. The phenomenological description of ICaL-induced calcium release was used with a reduced version of the ryanodine receptor Markov model developed by Stern et al. [108] and Shannon et al. [109]. The AP profile of the Bai et al. model is a spike-and-dome-type action potential and is comparable to the Courtemanche et al. model [110]. The Grandi et al. model was developed largely based on their previous human ventricular model, and therefore the formulation of transmembrane currents differs significantly from the Bai et al. and Courtemanche et al. models. In addition to the main transmembrane currents, the Grandi et al. atrial model also includes the formulation of two chloride currents and a potassium plateau current. The calcium subsystem model is based on the one in the rabbit ventricular model by Shannon et al. [109]. Therefore, the calcium transient of the Grandi et al. model is comparable to the Bai et al. model, but the Grandi et al. model with a triangular AP shape is different from the Bai et al. model. This difference can be reflected by the effects of ion currents on depolarisation and repolarisation. Consistent with this study [111], the excitability of the Bai et al. model is modulated by both INa and IK1, whereas that of the Grandi et al. model is regulated only by INa. During the repolarisation duration, Ito and IKur regulate the AP shape (the notch) at phase 1 and IKs and IKr are the important potassium currents that regulate APD90. These characteristics are derived from those of the base model (TP model). However, there is no notch shape in the AP of the Grandi et al. model and therefore all potassium currents (including Ito and IKur) are modulated APD90. Among these potassium currents, IKs, IKAch, and IKATP have small effects on APD90.
According to the stimulation protocol (1Hz) used in experiments [58], we ran simulations and reproduced Pitx2-induced AP morphology, with both dVdtmax increases and AP shortening being reported experimentally [58]. Further simulations predicted the antiarrhythmic effects of class I drugs on APD90 and dVdtmax, but their effects are dependent on the baseline AP morphology [112,113] seen in previous modelling [54]. While some of the differences in model responses might be related to distinct AP morphologies, we cannot exclude model dependencies due to distinct cellular model structure and models of ionic and calcium handling processes. Interestingly, analyses using both models demonstrated that the class I drugs disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone prolonged APD90 and reduced dVdtmax in a dose-dependent manner. Therefore, these results demonstrated that these class I drugs consistently produced anti-AF effects independent of the baseline electrophysiological characteristics.
Although the class I drugs disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone produced similar anti-AF effects (AP prolongation and dVdtmax and CV reduction), the degree of changes in APD90 and dVdtmax is different between the Bai et al. model and the Grandi et al. model. According to the extents of dVdtmax and CV reductions, drugs in both Bai et al. and Grandi et al. models are sorted as propafenone>quinidine>disopyramide. However, based on the degrees of AP prolongation, the drug ranking obtained with the Bai et al. model is quinidine>disopyramide>propafenone, whereas drugs whose effects were predicted with the Grandi et al. model are ranked as disopyramide>quinidine>propafenone. Different alterations in CV and APD90 lead to different changes in WL, which can be used as one of the indexes for evaluating the antiarrhythmic effects of drugs at the tissue level [54]. If the extent of AP prolongation is larger than that of CV reduction, WL is prolonged. Conversely, WL is shortened. For the Bai et al. model, WL is prolonged upon the application of quinidine and disopyramide, but is shortened upon the application of propafenone. However, for the Grandi et al. model, WL upon the application of disopyramide at various concentrations, quinidine at the low and medium concentrations, and propafenone at the low concentration is prolonged, but is shortened upon the application of quinidine at the high concentration and propafenone at the medium and high concentrations. Based on alterations in WL, the drug ranking obtained with the Bai et al. model is quinidine>disopyramide>propafenone, whereas drugs are sorted as disopyramide>quinidine>propafenone for the Grandi et al. model. Therefore, analyses using both models demonstrated that quinidine and disopyramide are more effective against Pitx2-induced AF than propafenone.
3.6. Limitations and Future Work
Several limitations specific to this study are addressed here. Firstly, the electrophysiological representation of AF-induced remodelling in the human atrial AP model is based on data from previous mouse models of Pitx2-induced AF because of the lack of experimental data on humans. Although shortened atrial repolarisation, a more depolarised resting membrane potential, and abnormalities in calcium cycling were observed in atrial cardiomyocytes of mice with reduced Pitx2 mRNA and these models (including Bai et al. and Grandi et al. models) could reproduce these phenomena in our previous study [27], Pitx2-induced AP data of human atrial cardiomyocytes and 3D whole atria for reproducing P waves [12] are not available to further validate the suitability and accuracy of our models to date. Special attention must be paid to the differences between mouse and human atrial cells [114]. In general, APD is approximately 50 ms in mice, compared to 250 ms in humans. The AP morphology reflects the contribution of numerous depolarising and repolarising currents. Even when the same type of ion channel is expressed in humans and mice, its contribution to the AP morphology may differ substantially, given the large difference in APD. In the mouse heart, ICaL contributes less to the AP than in humans and therefore the murine AP shows a gradual repolarisation rather than a distinct plateau phase. The much faster repolarisation in mice is mediated by transient outward K+ currents with a fast and slow recovery from inactivation, a slowly inactivating K+ current, and a non-inactivating, steady-state current. In humans, the transient outward K+ current with a fast recovery is mainly involved in phase 1 repolarisation, with more prominent expression in the epicardium. In addition, the rapid and slow delayed outward rectifier K+ currents are predominantly responsible for phase 3 repolarisation. However, studies in mice did observe the rapid and slow delayed rectifier K+ currents, but their contribution to repolarisation under physiological conditions is probably negligible or minor [115]. Further, we simulated AF model populations with all identified targets associated with impaired Pitx2 [11,17,18,22,23,26]. However, Pitx2-induced remodelling is different in published experimental studies [11,17,18,22,23,26], atrial cell types [11], AF stages [116], and AF patients of different ages [117]. The complexity of Pitx2-induced remodelling may present complex responses to these class I drugs and require more realistic heterogenous descriptions in cellular and tissue simulations. Secondly, we assumed that these changes in mRNA expression are quantitatively reflected at the final functional level of ion channels to obtain human AF myocyte models that reproduced the experimentally observed changes in the mRNA levels corresponding to key proteins under Pitx2-induced electrical remodelling conditions. Of note, mRNA alterations often do not match electrophysiological alterations and this is one of the main limitations. Thirdly, the effects of these class I AADs on ion currents were modelled by changing maximum current conductances with a simple pore blocking scheme based on IC50 and nH values, but it might be important to incorporate the state dependence and use dependence of antiarrhythmic drugs in evaluating realistic compounds [37,61,89]. Model variations for these characteristics (including the affinity of the drug compound to various gating modalities, binding kinetics, drug polarity, charge for the drug-channel interaction, and so on) are far beyond the scope of the current study and should be explored in future studies. In addition, IC50 values were chosen based on experimental data from atrial cells (where data are available) and large ventricular cells (where atrial data are not available), but the large variability in IC50 was influenced by various experimental conditions, including different species, different cell types [118], temperature [119], ionic concentrations, and voltage clamp protocols. Therefore, special attention should be paid to explain our simulated results. Fourthly, considering the stimulation protocol used under the experimental conditions [58], we performed all simulations only at 1Hz and rate-dependent APD modulation will be further investigated when experimental data at different frequencies are available. Here, we only used APD50, APD90, RMP, and dVdtmax as biomarkers to calibrate populations of human atrial AP models. Parameter unidentifiability, which can be attenuated if broader experimental datasets are available, is also a potential limitation. Fifthly, we analysed the effects of class I drugs by quantifying changes in APD90 and dVdtmax at the cellular level and CV and WL in tissue. This approach is consistent with the accepted mechanisms of action of class I drugs and is limited in that it did not account for composite metrics, including calcium-associated biomarkers, after-depolarisations, alternans, and AP propagation dynamics. Sixthly, [Ach]0 was set to 0 nM, but the contribution of GKAch,Ado to changes in AP could be under-estimated. Indeed, the “extracellular” concentration of adenosine and therefore GKAch,Ado could be variable [120]. The adenosine receptor is a Gi protein-coupled receptor and is predominantly expressed in atrial and nodal tissue. In the atrial myocardium, adenosine shortens both APD and causes RMP hyperpolarisation, thereby increasing the fraction of available sodium channels [121]. Such an increased sodium current, combined with shorter refractory periods, would be expected to increase the vulnerability and sustainability of AF. This action is mediated by the IKAch channel effector system under basal conditions. With increased adrenergic stimulation, adenosine attenuates the catecholamine-stimulated contractility and cyclic AMP accumulation. Adenosine attenuates both catecholamine-activated outward potassium and inward calcium currents, presumably by the inhibition of the phosphorylation of these channels, because adenosine inhibits adenylate cyclase activity and decreases the generation of cyclic AMP. The net electrophysiologic effect is the result of the direct adenosine-mediated activation of IKAch channels and the indirect adenosine-mediated inhibition of potassium and calcium currents. In the sinoatrial node, adenosine slows the heart rate. The pacemaker slowing caused by adenosine is due to a hyperpolarisation of the membrane which results in a decrease in phase 4 depolarisation. The hyperpolarisation is partly accomplished by the activation of IKAch channels through the Gi βγ-subunits and partly by the reduction in cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) through the Giα-subunit. Reduced cAMP levels decrease hyperpolarisation-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channel activity in pacemaker cells and decrease protein kinase A activity, thereby reducing ICaL [122]. These factors were not considered in the present study and special attention should be paid to explain our simulated results. Finally, further studies using populations of 3D atrial models should be conducted to show whether class I AADs really inhibit Pitx2-induced AF. However, whole heart simulations with complex models and large parameter dimensions are computationally expensive and generally require high-performance computing resources; running millions (or more) of simulations to obtain estimates of model outputs is likely to be prohibitively expensive. Further studies will be performed if conditions permit. Nevertheless, mechanisms underlying the actions of class I drugs are highly complex and future investigations should be carried out.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Dataset
The experimental dataset of AP recordings was used in the present study for calibration of human atrial electrophysiology. The dataset published in the previous study [58] comprised 480 instances from 379 patients: AP recordings from n = 256 right atrial appendages of N = 221 SR patients and from n = 224 right atrial appendages of N = 158 AF patients. Human myocytes were isolated enzymatically from atrial appendages and APs were recorded with standard intracellular microelectrodes in atrial trabeculae. Preparations were electrically stimulated at a single constant rate of 1 Hz for 60 min with isolated square-wave stimuli of a 1 ms duration, two times the threshold intensity. Obtained human atrial APs displayed spike-and-dome and more triangular conformations. The following parameters were quantified to characterise inter-subject variability in human atrial AP: dVdtmax, RMP, and APD50 and APD90. Compared with the APs of SR myocytes, APD50 and APD90 were reduced and dVdtmax was increased for the APs of AF atrial cells (Table 2). More information (including ethics approval, informed consent, and basic information of participants) regarding the experimental conditions under which the data were collected is available in the study of Ravens et al. [58].
4.2. Mathematical Models Representing Distinct Morphological Subtypes of Human Atrial AP
To represent the spike-and-dome and triangular conformations of human atrial APs observed in experiments [58,60], the Bai et al. model displaying a type-1 AP with notch-and-dome morphology and the Grandi et al. model displaying a type-3 AP with typical triangular shape were chosen as a base to construct the computational AP model populations.
The Bai et al. model developed by our group is able to reproduce human AP morphology, APD rate dependence, and triggered activity, i.e., early after-depolarisations (EADs), delayed after-depolarisations (DADs), and spontaneous depolarisations [27]. This biophysically detailed model of human atrial cellular electrophysiology was also used to investigate mechanisms underlying Pitx2-induced AF and here we provide a brief description. It includes representation of the 13 transmembrane ionic currents and 2 main intracellular calcium flows, including fast sodium current (INa), transient outward potassium current (Ito), rapid delayed rectifier potassium current (IKr), slow delayed rectifier potassium current (IKs), ultrarapid delayed rectifier potassium current (IKur), inward rectifier potassium current (IK1), L-type calcium current (ICaL), background sodium current (IBNa), background calcium current (IBCa), plateau potassium current (IPK), plateau calcium current (IPCa), sodium–potassium pump current (INaK), sodium–calcium exchange current (INcx), the calcium flow (Iup) through the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase (SERCA), and calcium release flow (Irel).
Comparative simulations were carried out using the human atrial cell model of Grandi et al. [59,123] (GB model). The baseline GB model was modified to generate the Grandi et al. model to facilitate AP propagation in tissue by replacing the INa formulation with that of the human cell model [107,124]. The Grandi et al. model includes representation of the 18 transmembrane ionic currents and 2 main intracellular calcium flows, including Ito, IKr, IKs, IKur, IK1, ICaL, IBNa, IBCa, IPK, IPCa, INaK, INcx, Iup, Irel, sodium current through the L-type calcium channel (ICaNa), potassium current through the L-type calcium channel (ICaK), calcium-activated chloride current (IClCa), background chloride current (IBCl), late sodium current (INaL), and INa. This INa model [107,124] is given by
where GNa (14.838 nS/pF) is the maximal conductance, m, h and j are three gate variables for INa, Vm is the membrane potential, and ENa is the sodium equilibrium potential. m∞, h∞, and j∞ denote steady-state activation, steady-state inactivation, and steady-state inactivation, respectively.τm, τh, and τj are the time constants for m∞, h∞, and j∞, respectively.
In additional to the original ion currents of the Bai et al. and Grandi et al. models, IKATP and IKAch were incorporated into these models. IKAch channel activation shortens both APD and the effective refractory period causes RMP hyperpolarisation, thereby increasing the fraction of available sodium channels. Such an increased sodium current, combined with shorter refractory periods, would be expected to increase the vulnerability and sustainability of AF. The effects of ATP are broadly similar to those of adenosine and activated IKAch channels will shorten the action potential and reduce the effective refractory period, a significant risk factor for the development of re-entrant arrhythmias like AF. This IKATP model [125] is given by
where GKATP is the maximal conductance, [ATP]i (6.8 mM for a normal value) is the intracellular nucleotide level, [K+]0 is extracellular potassium concentration, and EK is the sodium equilibrium potential. The IKAch model [126,127] is given by
where (0.135 nS/pF) is the maximal conductance, (0.0 nM for a normal value) is the extracellular Ach level, and r∞ and τr, respectively, denote the steady-state activation and the time constant. This model was developed based on these experimental data on IAch at the holding potential of −40 mV in the presence of different Ach concentrations [128].
Based on these models of ion channels, the electrophysiological behavior of human atrial cells can be modelled with the following differential equation:
In order to investigate the electrophysiological behavior of human atrial tissues, a multicellular model of homogeneous atrial tissue with 200 nodes spaced evenly by 0.15 mm was constructed to quantify APD90 and CV for calculating WL. The propagation of APs was governed by the partial differential equation:
where is a scalar coefficient describing the intercellular electrical coupling via gap junctions. In simulations, was set to be a constant value of 0.154 mm2ms−1 that gave a CV of 0.65 m/s for the Bai et al. model and 0.59 m/s for the Grandi et al. model. The resulting CVs were comparable to those seen in atrial tissue [129,130]. The time (t) step was 0.02 ms for the Bai et al. model and 0.005 ms for the Grandi et al. model.
4.3. Modelling Pitx2-Induced AF
To obtain human AF myocyte models that reproduced the experimentally observed changes in the mRNA levels corresponding to key proteins under Pitx2-induced electrical remodelling conditions, we assumed that these changes in mRNA expression are quantitatively reflected at the final functional level of ion channels [29] and incorporated alterations in the maximal conductances of ionic currents due to Pitx2-induced electrical remodelling into the Bai et al. (or the Grandi et al.) model. These Pitx2-induced changes in the ionic channel properties have been well characterised in many experimental studies [17,18,23,24,25,26,63]. However, the identified targets were different among these studies: While several studies showed no Pitx2-associated changes [18] and reductions [22,25] in sodium channel gene expression, significant increases [17,63] in this channel gene expression have also been well documented. Similarly, calcium channel gene expression was found to be decreased in this study [12], but increased in others [22,23,25,26]. Further, whereas the overexpression of the potassium gene encoding IK1 was identified in the study of Kirchhof et al. [11], the underexpression of this gene was observed in some studies [18,22]. In addition, all these studies have shown the upregulation of genes encoding IKs [11,12,15,26,63], Irel [12,17,23,25], and Iup [22,24,66,69,70]. Modifications made for each model are summarised in Table 3.
4.4. Simulations of Actions of Class I AADs in Pitx2-Induced AF
In our previous studies [37,89], the actions of the class I AADs disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone on human atrial electrophysiology were simulated in the setting of hERG-linked short QT syndrome [37]. The effects of these class I AADs on ion currents were modelled by changing maximum current conductances with a simple pore blocking scheme based on IC50 and nH [31]. Maximum current conductances associated with these drugs included GNa, GCaL, Gto, GKs, GKr, GKur, and GK1. For disopyramide, as measured in previous studies, values of IC50 for GNa, GCaL, Gto, GKs, GKr, and GKur, respectively, were taken to be 168.4 [64], 1036.7 [64], 20.9 [68], 88.1 [71], 14.4 [64], and 25.0 μM [74]. For quinidine, as observed in experimental studies, GNa, GCaL, Gto, GKs, GKr, GKur, and GK1 were decreased with an IC50 of 14.6 [64], 14.9 [66], 21.8 [69], 44.0
[72], 0.72 [64], 6.6 [69], and 42.6 μM [69], respectively. Propafenone decreased GNa, GCaL, Gto, GKr, GKur, and GK1 with an IC50 of 1.2 [65], 1.7 [67], 4.8
[70], 2.0 [73], 4.4 [75], and 16.8 μM [76], respectively. Taking into account plasma protein binging, estimates of the most likely unbound concentrations of disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone are given as 1–15 [88,131], 1–15 [88,131], and 0.15–1 μM [85,86,87]. The effects of low (L), medium (M), and high (H) doses within the therapeutic ranges of disopyramide (Diso_L: 1.0, Diso_M: 2.0, and Diso_H: 5.0 μM), quinidine (Quin_L: 1.0, Quin_M: 2.0, and Quin_H: 5.0 μM), and propafenone (Prop_L: 0.2, Prop_M: 0.5, and Prop_H: 0.8 μM) were studied.
4.5. Generation and Calibration of Populations of Models
To capture inter-subject variability, populations of sampled models of human atrial electrophysiology for SR were generated based on the Bai et al. and the Grandi et al. models. All models in each population shared the same equations but parameters of ionic current conductances in determining the human atrial AP were varied with respect to their original values. These parameters were independently varied following a log-normal distribution and sigma was set to be 0.2 to cover a range of variability similar to that seen in experiments of previous studies [41,54,61,62]. The size of the SR population was set to be 1200 for convergence of the sensitivity coefficients [132]. Following the ASME V&V40 Standard proposed by the Subcommittee of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) on Verification and Validation (V&V) in Computational Modeling of Medical Devices [133] for developing a structured approach for establishing the credibility of computational models for a specific use, we used the candidate models to simulate human atrial AP by considering stimulation frequency (1Hz) under the experimental conditions [58] and calculated AP biomarkers of each candidate model. The candidate models generated in the previous step were selected to constitute the SR population whose simulated electrophysiological properties are within 3 standard errors from the mean experimental values in SR patient data on AP biomarkers (including dVdtmax, RMP, APD50, and APD90) in Table 2. This step yields the experimentally calibrated population of models. Modifications to ionic currents due to Pitx2-induced remodelling (Table 3) were introduced into SR model variants to generate the candidate AF models. These candidate AF models were calibrated to 3 standard errors from the mean experimental values in AF patient data (Table 2). Then, actions of class I AADs on ion channels were incorporated into the experimentally calibrated AF models to investigate their effects on dVdtmax, APD90, CV, and WL.
4.6. Simulation Protocols
The stimulation protocol mimics the one used by Ravens et al. [58] to obtain AP measurements in SR and AF cardiomyocytes. Cell mathematical models were initially preconditioned by pacing at a basic cycle length of 1000 ms until the steady state was reached. A stimulus with an amplitude of −80 μA/μF and a duration of 0.5 ms was applied at each pace.
Considering the computational cost of reaching the steady state, a series of 10 conditioning waves was initiated by supra-threshold stimuli with an amplitude of −80 μA/μF and a duration of 1.0 ms to the 3 nodes at the strand end. The last beat was recorded for APD90 and CV analysis.
4.7. Sensitivity Analysis
To quantify the relative importance of ionic conductances in determining changes in AP biomarkers, PCCs were used on the SR and AF populations to evaluate the role of each ionic current [132]. Partial correlation is a method to find correlations between two variables, after accounting for the linear effects of one or more additional variables [134]. The PCC between and , given the set of additional variables , is then defined as the correlation coefficient between the residuals and [132]. and are the respective sample means or the following linear regression models:
where Cov(rx,ry) represents the covariance between rx and ry, while and are, respectively, the variance of and variance of .
4.8. Software, Numerical Methods, and Statistical Analysis
The Bai et al. (available from the repository CellML http://models.cellml.org/workspace/520) and the Grandi et al. models (freely available at https://github.com/drgrandilab) were implemented in MATLAB 2018a (The MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA) using the stiff ordinary differential equation solver ode15s and the analysis of biomarkers was also performed using MATLAB. In addition, the 1D models were implemented in C++. The ordinary differential equations (ODEs) were solved using the forward Euler method. Our user project containing newly created datasets and the simulation codes used in this study is available to download from the GitHub website (https://github.com/aspirerabbit). All simulations and data analyses were performed on a computing cluster with Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2690 v4 @ 2.60GHz 32 CPUs 28 CPUs (56 threads) + 128GB. The statistical significance of differences in ionic conductance distributions between populations was evaluated by using the Mann–Whitney U test. A probability <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, populations of models reproduce the variability in human atrial AP properties measured in samples obtained from patients and AF models predict AP shortening and slow conduction in Pitx2-induced remodelling conditions observed in experiments. State-of-the-art Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Framework simulations demonstrated that disopyramide, quinidine, and propafenone produce AP prolongation and slow conduction in the setting of Pitx2-induced AF. However, disopyramide was more effective in prolonging WL than propafenone and quinidine.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z., J.B., M.G., J.Z. and H.Z.; methodology, M.G. and Y.Z.; software, Y.Z.; validation, Y.Z., M.G. and J.B.; formal analysis, Y.Z., M.G. and J.B.; investigation, Y.Z., M.G. and J.B.; resources, Y.Z. and J.B.; data curation, Y.Z., M.G. and J.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.G. and J.B.; writing—review and editing, Y.Z., J.B., M.G., A.L., Y.L., J.Z. and H.Z.; visualization, Y.Z., M.G. and J.B.; supervision, J.B. and Y.L.; project administration, J.B. and Y.L.; funding acquisition, J.B. and Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 61901192 (J.B.), National Key Research and Development Project, grant number 2019YFC0120100 and 2019YFC0121907 (J.B. and Y.L.), and the “Young Talents” Project of Northeast Agricultural University under Grant 17QC21 (M.G.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| AF | atrial fibrillation |
| GWAS | genome-wide association studies |
| Pitx2 | paired-like homeodomain transcription factor 2 |
| AAD | antiarrhythmic drug |
| AP | action potential |
| APD | AP duration |
| dVdtmax | maximum upstroke velocity |
| CV | conduction velocity |
| WL | wavelength |
| SR | sinus rhythm |
| RMP | resting membrane potential |
| APD50 | AP duration at 50% |
| APD90 | AP duration at 90% |
| IC50 | half-maximal inhibitory concentration |
| nH | Hill-coefficient value |
| PCC | partial correlation coefficient |
| Prop_L | low dose of propafenone |
| Prop_M | medium dose of propafenone |
| Prop_H | high dose of propafenone |
| Diso_L | low dose of disopyramide |
| Diso_M | medium dose of disopyramide |
| Diso_H | high dose of disopyramide |
| Quin_L | low dose of quinidine |
| Quin_M | medium dose of quinidine |
| Quin_H | high dose of quinidine |
| 1D | one-dimensional |
| INa | fast sodium current |
| Ito | transient outward potassium current |
| IKr | rapid delayed rectifier potassium current |
| IKs | slow delayed rectifier potassium current |
| IKur | ultrarapid delayed rectifier potassium current |
| IK1 | inward rectifier potassium current |
| ICaL | L-type calcium current |
| IBNa | background sodium current |
| IBCa | background calcium current |
| IPK | plateau potassium current |
| IPCa | plateau calcium current |
| INaK | sodium-potassium pump current |
| INcx | sodium-calcium exchange current |
| Iup | the calcium flow through the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase (SERCA) |
| Irel | calcium release flow |
| ICaNa | sodium current through the L-type calcium channel |
| ICaK | potassium current through the L-type calcium channel |
| IClCa | calcium-activated chloride current |
| IBCl | background chloride current |
| INaL | late sodium current |
References
- Nattel, S.; Heijman, J.; Zhou, L.; Dobrev, D. Molecular Basis of Atrial Fibrillation Pathophysiology and Therapy: A Translational Perspective. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ouwerkerk, A.F.; Hall, A.W.; Kadow, Z.A.; Lazarevic, S.; Reyat, J.S.; Tucker, N.R.; Nadadur, R.D.; Bosada, F.M.; Bianchi, V.; Ellinor, P.T.; et al. Epigenetic and Transcriptional Networks Underlying Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Rice, K.M.; Arking, D.E.; Pfeufer, A.; van Noord, C.; Smith, A.V.; Schnabel, R.B.; Bis, J.C.; Boerwinkle, E.; Sinner, M.F.; et al. Variants in ZFHX3 are associated with atrial fibrillation in individuals of European ancestry. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 879–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophersen, I.E.; Rienstra, M.; Roselli, C.; Yin, X.; Geelhoed, B.; Barnard, J.; Lin, H.; Arking, D.E.; Smith, A.V.; Albert, C.M.; et al. Large-scale analyses of common and rare variants identify 12 new loci associated with atrial fibrillation. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellinor, P.T.; Lunetta, K.L.; Albert, C.M.; Glazer, N.L.; Ritchie, M.D.; Smith, A.V.; Arking, D.E.; Müller-Nurasyid, M.; Krijthe, B.P.; Lubitz, S.A.; et al. Meta-analysis identifies six new susceptibility loci for atrial fibrillation. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellinor, P.T.; Lunetta, K.L.; Glazer, N.L.; Pfeufer, A.; Alonso, A.; Chung, M.K.; Sinner, M.F.; de Bakker, P.I.; Mueller, M.; Lubitz, S.A.; et al. Common variants in KCNN3 are associated with lone atrial fibrillation. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, S.K.; Takahashi, A.; Ebana, Y.; Ozaki, K.; Christophersen, I.E.; Ellinor, P.T.; Ogishima, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Satoh, M.; Sasaki, M.; et al. Identification of six new genetic loci associated with atrial fibrillation in the Japanese population. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roselli, C.; Chaffin, M.D.; Weng, L.C.; Aeschbacher, S.; Ahlberg, G.; Albert, C.M.; Almgren, P.; Alonso, A.; Anderson, C.D.; Aragam, K.G.; et al. Multi-ethnic genome-wide association study for atrial fibrillation. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinner, M.F.; Tucker, N.R.; Lunetta, K.L.; Ozaki, K.; Smith, J.G.; Trompet, S.; Bis, J.C.; Lin, H.; Chung, M.K.; Nielsen, J.B.; et al. Integrating genetic, transcriptional, and functional analyses to identify 5 novel genes for atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2014, 130, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Arnar, D.O.; Helgadottir, A.; Gretarsdottir, S.; Holm, H.; Sigurdsson, A.; Jonasdottir, A.; Baker, A.; Thorleifsson, G.; Kristjansson, K.; et al. Variants conferring risk of atrial fibrillation on chromosome 4q25. Nature 2007, 448, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhof, P.; Kahr, P.C.; Kaese, S.; Piccini, I.; Vokshi, I.; Scheld, H.H.; Rotering, H.; Fortmueller, L.; Laakmann, S.; Verheule, S.; et al. PITX2c is expressed in the adult left atrium, and reducing Pitx2c expression promotes atrial fibrillation inducibility and complex changes in gene expression. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2011, 4, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, L.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Moon, A.M.; Kaminski, H.J.; Martin, J.F. Pitx2, an atrial fibrillation predisposition gene, directly regulates ion transport and intercalated disc genes. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2014, 7, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mommersteeg, M.T.; Brown, N.A.; Prall, O.W.; de Gier-de Vries, C.; Harvey, R.P.; Moorman, A.F.; Christoffels, V.M. Pitx2c and Nkx2-5 are required for the formation and identity of the pulmonary myocardium. Circ. Res. 2007, 101, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Tucker, N.R.; Weng, L.C.; Clauss, S.; Lubitz, S.A.; Ellinor, P.T. A Functional Variant Associated with Atrial Fibrillation Regulates PITX2c Expression through TFAP2a. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Klysik, E.; Sood, S.; Johnson, R.L.; Wehrens, X.H.; Martin, J.F. Pitx2 prevents susceptibility to atrial arrhythmias by inhibiting left-sided pacemaker specification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9753–9758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, L.A.; Alonso, M.E.; Badía-Careaga, C.; Rollán, I.; Arias, C.; Fernández-Miñán, A.; López-Jiménez, E.; Aránega, A.; Gómez-Skarmeta, J.L.; Franco, D.; et al. Long-range regulatory interactions at the 4q25 atrial fibrillation risk locus involve PITX2c and ENPEP. BMC Biol. 2015, 13, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadadur, R.D.; Broman, M.T.; Boukens, B.; Mazurek, S.R.; Yang, X.; van den Boogaard, M.; Bekeny, J.; Gadek, M.; Ward, T.; Zhang, M.; et al. Pitx2 modulates a Tbx5-dependent gene regulatory network to maintain atrial rhythm. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 354ra115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syeda, F.; Holmes, A.P.; Yu, T.Y.; Tull, S.; Kuhlmann, S.M.; Pavlovic, D.; Betney, D.; Riley, G.; Kucera, J.P.; Jousset, F.; et al. PITX2 Modulates Atrial Membrane Potential and the Antiarrhythmic Effects of Sodium-Channel Blockers. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1881–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Hill, M.C.; Kadow, Z.A.; Suh, J.H.; Tucker, N.R.; Hall, A.W.; Tran, T.T.; Swinton, P.S.; Leach, J.P.; Margulies, K.B.; et al. Long-range Pitx2c enhancer-promoter interactions prevent predisposition to atrial fibrillation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22692–22698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyat, J.S.; Chua, W.; Cardoso, V.R.; Witten, A.; Kastner, P.M.; Kabir, S.N.; Sinner, M.F.; Wesselink, R.; Holmes, A.P.; Pavlovic, D.; et al. Reduced left atrial cardiomyocyte PITX2 and elevated circulating BMP10 predict atrial fibrillation after ablation. JCI Insight 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mommersteeg, M.T.; Hoogaars, W.M.; Prall, O.W.; de Gier-de Vries, C.; Wiese, C.; Clout, D.E.; Papaioannou, V.E.; Brown, N.A.; Harvey, R.P.; Moorman, A.F.; et al. Molecular pathway for the localized formation of the sinoatrial node. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinchilla, A.; Daimi, H.; Lozano-Velasco, E.; Dominguez, J.N.; Caballero, R.; Delpón, E.; Tamargo, J.; Cinca, J.; Hove-Madsen, L.; Aranega, A.E.; et al. PITX2 insufficiency leads to atrial electrical and structural remodeling linked to arrhythmogenesis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2011, 4, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano-Velasco, E.; Hernández-Torres, F.; Daimi, H.; Serra, S.A.; Herraiz, A.; Hove-Madsen, L.; Aránega, A.; Franco, D. Pitx2 impairs calcium handling in a dose-dependent manner by modulating Wnt signalling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 109, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herraiz-Martínez, A.; Llach, A.; Tarifa, C.; Gandía, J.; Jiménez-Sabado, V.; Lozano-Velasco, E.; Serra, S.A.; Vallmitjana, A.; Vázquez Ruiz de Castroviejo, E.; Benítez, R.; et al. The 4q25 variant rs13143308T links risk of atrial fibrillation to defective calcium homoeostasis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Velasco, E.; Wangensteen, R.; Quesada, A.; Garcia-Padilla, C.; Osorio, J.A.; Ruiz-Torres, M.D.; Aranega, A.; Franco, D. Hyperthyroidism, but not hypertension, impairs PITX2 expression leading to Wnt-microRNA-ion channel remodeling. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Hernández, M.; Matamoros, M.; Barana, A.; Amorós, I.; Gómez, R.; Núñez, M.; Sacristán, S.; Pinto, Á.; Fernández-Avilés, F.; Tamargo, J.; et al. Pitx2c increases in atrial myocytes from chronic atrial fibrillation patients enhancing IKs and decreasing ICa,L. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 109, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Gladding, P.A.; Stiles, M.K.; Fedorov, V.V.; Zhao, J. Ionic and cellular mechanisms underlying TBX5/PITX2 insufficiency-induced atrial fibrillation: Insights from mathematical models of human atrial cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Lu, Y.; Lo, A.; Zhao, J. PITX2 overexpression leads to atrial electrical remodeling linked to atrial fibrillation. In Proceedings of the Computing in Cardiology (CinC), Singapore, 8–11 September 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Lu, Y.; Lo, A.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H. Proarrhythmia in the p.Met207Val PITX2c-Linked Familial Atrial Fibrillation-Insights From Modeling. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Lu, Y.; Lo, A.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H. PITX2 upregulation increases the risk of chronic atrial fibrillation in a dose-dependent manner by modulating I(Ks) and I(CaL) -insights from human atrial modelling. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, H. In silico study of the effects of anti-arrhythmic drug treatment on sinoatrial node function for patients with atrial fibrillation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Zhu, Y.; Lo, A.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, J. In silico assessment of genetic variation in PITX2 reveals the molecular mechanisms of calcium-mediated cellular triggered activity in atrial fibrillation. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 2353–2356. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Bai, J.; Lo, A.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, J. Mechanisms underlying pro-arrhythmic abnormalities arising from Pitx2-induced electrical remodelling: An in silico intersubject variability study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Parvez, B.; Vaglio, J.; Rowan, S.; Muhammad, R.; Kucera, G.; Stubblefield, T.; Carter, S.; Roden, D.; Darbar, D. Symptomatic response to antiarrhythmic drug therapy is modulated by a common single nucleotide polymorphism in atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, Y.S.; Rajamani, S.; Haldar, S.M.; Hüser, J. A New Therapeutic Framework for Atrial Fibrillation Drug Development. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 184–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Lo, A.; Gladding, P.A.; Stiles, M.K.; Fedorov, V.V.; Zhao, J. In silico investigation of the mechanisms underlying atrial fibrillation due to impaired Pitx2. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1007678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, D.G.; Hancox, J.C.; Zhang, H. In silico Assessment of Pharmacotherapy for Human Atrial Patho-Electrophysiology Associated With hERG-Linked Short QT Syndrome. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paci, M.; Casini, S.; Bellin, M.; Hyttinen, J.; Severi, S. Large-Scale Simulation of the Phenotypical Variability Induced by Loss-of-Function Long QT Mutations in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernik, D.C.; Yang, P.C.; Kurokawa, J.; Wu, J.C.; Clancy, C.E. A computational model of induced pluripotent stem-cell derived cardiomyocytes for high throughput risk stratification of KCNQ1 genetic variants. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1008109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernik, D.C.; Morotti, S.; Wu, H.; Garg, P.; Duff, H.J.; Kurokawa, J.; Jalife, J.; Wu, J.C.; Grandi, E.; Clancy, C.E. A computational model of induced pluripotent stem-cell derived cardiomyocytes incorporating experimental variability from multiple data sources. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 4533–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobie, E.A. Parameter sensitivity analysis in electrophysiological models using multivariable regression. Biophys. J. 2009, 96, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.X.; Sobie, E.A. Quantification of repolarization reserve to understand interpatient variability in the response to proarrhythmic drugs: A computational analysis. Heart Rhythm 2011, 8, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, M.A.; Dalal, P.J.; Bugana, M.; Severi, S.; Sobie, E.A. Comprehensive analyses of ventricular myocyte models identify targets exhibiting favorable rate dependence. PLos Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morotti, S.; Grandi, E. Logistic regression analysis of populations of electrophysiological models to assess proarrythmic risk. MethodsX 2017, 4, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passini, E.; Britton, O.J.; Lu, H.R.; Rohrbacher, J.; Hermans, A.N.; Gallacher, D.J.; Greig, R.J.H.; Bueno-Orovio, A.; Rodriguez, B. Human In Silico Drug Trials Demonstrate Higher Accuracy than Animal Models in Predicting Clinical Pro-Arrhythmic Cardiotoxicity. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, L.; Pueyo, E.; Fink, M.; Rodríguez, B. Impact of ionic current variability on human ventricular cellular electrophysiology. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 297, H1436–H1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.X.; Christini, D.J.; Sobie, E.A. Exploiting mathematical models to illuminate electrophysiological variability between individuals. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 2555–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pueyo, E.; Corrias, A.; Virág, L.; Jost, N.; Szél, T.; Varró, A.; Szentandrássy, N.; Nánási, P.P.; Burrage, K.; Rodríguez, B. A multiscale investigation of repolarization variability and its role in cardiac arrhythmogenesis. Biophys. J. 2011, 101, 2892–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotta, V.; Cools, F.; van Ammel, K.; Gallacher, D.J.; Visser, S.A.; Sannajust, F.; Morissette, P.; Danhof, M.; van der Graaf, P.H. Inter-study variability of preclinical in vivo safety studies and translational exposure-QTc relationships—A PKPD meta-analysis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 4364–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszkiewicz, A.; Liu, X.; Bueno-Orovio, A.; Lawson, B.A.J.; Burrage, K.; Casadei, B.; Rodriguez, B. From ionic to cellular variability in human atrial myocytes: An integrative computational and experimental study. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 314, H895–H916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.Q.X.; Sobie, E.A. Population-based mechanistic modeling allows for quantitative predictions of drug responses across cell types. NPJ Syst. Biol. Appl. 2018, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, T.R.; Allen, R.J.; Bystricky, L.; Chen, Y.; Colopy, G.W.; Cui, Y.; Gonzalez, A.; Liu, Y.; White, R.D.; Everett, R.A.; et al. Improving the generation and selection of virtual populations in quantitative systems pharmacology models. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2018, 139, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszkiewicz, A.; Britton, O.J.; Gemmell, P.; Passini, E.; Sánchez, C.; Zhou, X.; Carusi, A.; Quinn, T.A.; Burrage, K.; Bueno-Orovio, A.; et al. Variability in cardiac electrophysiology: Using experimentally-calibrated populations of models to move beyond the single virtual physiological human paradigm. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2016, 120, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, H.; Iseppe, A.F.; Giles, W.R.; Narayan, S.M.; Zhang, H.; Edwards, A.G.; Morotti, S.; Grandi, E. Populations of in silico myocytes and tissues reveal synergy of multi-atrial-predominant K(+) -current block in atrial fibrillation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 4497–4515. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vagos, M.R.; Arevalo, H.; de Oliveira, B.L.; Sundnes, J.; Maleckar, M.M. A computational framework for testing arrhythmia marker sensitivities to model parameters in functionally calibrated populations of atrial cells. Chaos 2017, 27, 093941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, B.A.J.; Drovandi, C.C.; Cusimano, N.; Burrage, P.; Rodriguez, B.; Burrage, K. Unlocking data sets by calibrating populations of models to data density: A study in atrial electrophysiology. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, e1701676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, H.; Morotti, S.; Grandi, E. A Heart for Diversity: Simulating Variability in Cardiac Arrhythmia Research. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravens, U.; Katircioglu-Öztürk, D.; Wettwer, E.; Christ, T.; Dobrev, D.; Voigt, N.; Poulet, C.; Loose, S.; Simon, J.; Stein, A.; et al. Application of the RIMARC algorithm to a large data set of action potentials and clinical parameters for risk prediction of atrial fibrillation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2015, 53, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandi, E.; Pandit, S.V.; Voigt, N.; Workman, A.J.; Dobrev, D.; Jalife, J.; Bers, D.M. Human atrial action potential and Ca2+ model: Sinus rhythm and chronic atrial fibrillation. Circ. Res. 2011, 109, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fermini, B.; Nattel, S. Delayed rectifier outward current and repolarization in human atrial myocytes. Circ. Res. 1993, 73, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinwood, N.; Dobrev, D.; Morotti, S.; Grandi, E. In Silico Assessment of Efficacy and Safety of I(Kur) Inhibitors in Chronic Atrial Fibrillation: Role of Kinetics and State-Dependence of Drug Binding. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, E.; Maleckar, M.M. Anti-arrhythmic strategies for atrial fibrillation: The role of computational modeling in discovery, development, and optimization. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 168, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechakra, A.; Footz, T.; Walter, M.; Aránega, A.; Hernández-Torres, F.; Morel, E.; Millat, G.; Yang, Y.Q.; Chahine, M.; Chevalier, P.; et al. A Novel PITX2c Gain-of-Function Mutation, p.Met207Val, in Patients with Familial Atrial Fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2019, 123, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, J.; Obejero-Paz, C.A.; Myatt, G.; Kuryshev, Y.A.; Bruening-Wright, A.; Verducci, J.S.; Brown, A.M. MICE models: Superior to the HERG model in predicting Torsade de Pointes. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zou, B.; Du, F.; Xu, K.; Li, M. Reporting sodium channel activity using calcium flux: Pharmacological promiscuity of cardiac Nav1.5. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 87, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Hancox, J.C. Mode-dependent inhibition by quinidine of Na+-Ca2+ exchanger current from guinea-pig isolated ventricular myocytes. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2002, 29, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancox, J.C.; Mitcheson, J.S. Inhibition of L-type calcium current by propafenone in single myocytes isolated from the rabbit atrioventricular node. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 121, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanada, E.; Ohtani, H.; Hirota, M.; Uemura, N.; Nakaya, H.; Kotaki, H.; Sato, H.; Yamada, Y.; Iga, T. Inhibitory effect of erythromycin on potassium currents in rat ventricular myocytes in comparison with disopyramide. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2003, 55, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenov, N.I.; Crumb, W.J., Jr.; Pigott, J.D.; Harrison, L.H., Jr.; Clarkson, C.W. Quinidine interactions with human atrial potassium channels: Developmental aspects. Circ. Res. 1998, 83, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, G.J.; Castle, N.A. Propafenone inhibition of human atrial myocyte repolarizing currents. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1998, 30, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, H. Comparative actions of cibenzoline and disopyramide on I(Kr) and I(Ks) currents in rat sino-atrial nodal cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 407, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Chen, X.L.; Wang, L.; Rampe, D. Interactions of the antimalarial drug mefloquine with the human cardiac potassium channels KvLQT1/minK and HERG. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 299, 290–296. [Google Scholar]
- Katchman, A.N.; Koerner, J.; Tosaka, T.; Woosley, R.L.; Ebert, S.N. Comparative evaluation of HERG currents and QT intervals following challenge with suspected torsadogenic and nontorsadogenic drugs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 316, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aréchiga, I.A.; Barrio-Echavarria, G.F.; Rodríguez-Menchaca, A.A.; Moreno-Galindo, E.G.; Decher, N.; Tristani-Firouzi, M.; Sánchez-Chapula, J.A.; Navarro-Polanco, R.A. Kv1.5 open channel block by the antiarrhythmic drug disopyramide: Molecular determinants of block. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 108, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Franqueza, L.; Valenzuela, C.; Delpón, E.; Longobardo, M.; Caballero, R.; Tamargo, J. Effects of propafenone and 5-hydroxy-propafenone on hKv1.5 channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 125, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorós, I.; Dolz-Gaitón, P.; Gómez, R.; Matamoros, M.; Barana, A.; de la Fuente, M.G.; Núñez, M.; Pérez-Hernández, M.; Moraleda, I.; Gálvez, E.; et al. Propafenone blocks human cardiac Kir2.x channels by decreasing the negative electrostatic charge in the cytoplasmic pore. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuta, H.; Okamoto, K.; Watanabe, Y. Blockade by antiarrhythmic drugs of glibenclamide-sensitive K+ channels in Xenopus oocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 107, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, E.; Mubagwa, K. Antiarrhythmic drugs and cardiac ion channels: Mechanisms of action. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1998, 70, 1–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inomata, N.; Ohno, T.; Ishihara, T.; Akaike, N. Antiarrhythmic agents act differently on the activation phase of the ACh-response in guinea-pig atrial myocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 108, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchard, U.; Boisten, M. Effect of flecainide on action potentials and alternating current-induced arrhythmias in mammalian myocardium. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1982, 4, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, M.; Hamamoto, T.; Ban, T. Sodium channel-blocking properties of flecainide, a class IC antiarrhythmic drug, in guinea-pig papillary muscles. An open channel blocker or an inactivated channel blocker. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1989, 339, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, A.; Chorro, F.J.; Cánoves, J.; Mainar, L.; Blasco, E.; Such, L. Effect of flecainide on longitudinal and transverse conduction velocities in ventricular myocardium. An experimental study. Revista Espanola de Cardiologia 2007, 60, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, C.; Pavlovic, D.; Rajpoot, K.; Winter, J. Examination of the Effects of Conduction Slowing on the Upstroke of Optically Recorded Action Potentials. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, F.L.; Cobbe, S.M. Dispersion of ventricular repolarization and refractory period. Cardiovasc. Res. 2001, 50, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slawsky, M.T.; Castle, N.A. K+ channel blocking actions of flecainide compared with those of propafenone and quinidine in adult rat ventricular myocytes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1994, 269, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duan, D.; Fermini, B.; Nattel, S. Potassium channel blocking properties of propafenone in rabbit atrial myocytes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1993, 264, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seki, A.; Hagiwara, N.; Kasanuki, H. Effects of propafenone on K currents in human atrial myocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 126, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagawa, K.; Mohri, K.; Shimada, S.; Shimizu, M.; Muramatsu, J. Disopyramide concentrations in human plasma and saliva: Comparison of disopyramide concentrations in saliva and plasma unbound concentrations. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1997, 52, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, D.G.; Ni, H.; Benson, A.P.; Hancox, J.C.; Zhang, H. Computational Analysis of the Mode of Action of Disopyramide and Quinidine on hERG-Linked Short QT Syndrome in Human Ventricles. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Li, G. The molecular genetic basis of atrial fibrillation. Hum. Genet. 2020, 139, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.B.; Thorolfsdottir, R.B.; Fritsche, L.G.; Zhou, W.; Skov, M.W.; Graham, S.E.; Herron, T.J.; McCarthy, S.; Schmidt, E.M.; Sveinbjornsson, G.; et al. Biobank-driven genomic discovery yields new insight into atrial fibrillation biology. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1234–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Xu, S.-J.; Bendahhou, S.; Wang, X.-L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.-Y.; Jin, H.-W.; Sun, H.; Su, X.-Y.; Zhuang, Q.-N.; et al. KCNQ1 Gain-of-Function Mutation in Familial Atrial Fibrillation. Science 2003, 299, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feghaly, J.; Zakka, P.; London, B.; MacRae, C.A.; Refaat, M.M. Genetics of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e009884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, N.; Heijman, J.; Wang, Q.; Chiang, D.Y.; Li, N.; Karck, M.; Wehrens, X.H.T.; Nattel, S.; Dobrev, D. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Atrial Arrhythmogenesis in Patients with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2014, 129, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, N.; Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; Trafford, A.W.; Abu-Taha, I.; Sun, Q.; Wieland, T.; Ravens, U.; Nattel, S.; et al. Enhanced Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ Leak and Increased Na+-Ca2+ Exchanger Function Underlie Delayed Afterdepolarizations in Patients with Chronic Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2012, 125, 2059–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijman, J.; Voigt, N.; Nattel, S.; Dobrev, D. Cellular and Molecular Electrophysiology of Atrial Fibrillation Initiation, Maintenance, and Progression. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1483–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.Y.; Yeh, Y.-H.; Xiao, L.; Burstein, B.; Maguy, A.; Chartier, D.; Villeneuve, L.R.; Brundel, B.J.J.M.; Dobrev, D.; Nattel, S. Cellular Signaling Underlying Atrial Tachycardia Remodeling of L-type Calcium Current. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Pan, Z.; Shan, H.; Xiao, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, N.; Lin, H.; Xiao, L.; Maguy, A.; Qi, X.-Y.; et al. MicroRNA-26 governs profibrillatory inward-rectifier potassium current changes in atrial fibrillation. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrev, D.; Friedrich, A.; Voigt, N.; Jost, N.; Wettwer, E.; Christ, T.; Knaut, M.; Ravens, U. The G Protein—Gated Potassium Current IK,ACh Is Constitutively Active in Patients With Chronic Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2005, 112, 3697–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Veleva, T.; Scott, L.; Cao, S.; Li, L.; Chen, G.; Jeyabal, P.; Pan, X.; Alsina, K.M.; Abu-Taha, I.; et al. Enhanced Cardiomyocyte NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling Promotes Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2018, 138, 2227–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.; Wiedmann, F.; Voigt, N.; Zhou, X.-B.; Heijman, J.; Lang, S.; Albert, V.; Kallenberger, S.; Ruhparwar, A.; Szabó, G.; et al. Upregulation of K2P3.1 K+ Current Causes Action Potential Shortening in Patients with Chronic Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2015, 132, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, B.; Qi, X.-Y.; Yeh, Y.-H.; Calderone, A.; Nattel, S. Atrial cardiomyocyte tachycardia alters cardiac fibroblast function: A novel consideration in atrial remodeling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 76, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theisen, K.; Scheininger, M. Electrophysiological effects of quinidine alone and of the combination quinidine-verapamil on AV conduction in humans. Clin. Cardiol. 1983, 6, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benton, R.E.; Sale, M.; Flockhart, D.A.; Woosley, R.L. Greater quinidine-induced QTc interval prolongation in women. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 67, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, T.; Kurachi, Y.; Ito, H.; Takikawa, R.; Sugimoto, T. Anti-cholinergic effects of quinidine, disopyramide, and procainamide in isolated atrial myocytes: Mediation by different molecular mechanisms. Circ. Res. 1989, 64, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ten Tusscher, K.H.; Panfilov, A.V. Alternans and spiral breakup in a human ventricular tissue model. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 291, H1088–H1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, M.D.; Song, L.-S.; Cheng, H.; Sham, J.S.K.; Yang, H.T.; Boheler, K.R.; Ríos, E. Local Control Models of Cardiac Excitation–Contraction Coupling: A Possible Role for Allosteric Interactions between Ryanodine Receptors. J. Gen. Physiol. 1999, 113, 469–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, T.R.; Wang, F.; Puglisi, J.; Weber, C.; Bers, D.M. A Mathematical Treatment of Integrated Ca Dynamics within the Ventricular Myocyte. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 3351–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtemanche, M.; Ramirez, R.J.; Nattel, S. Ionic mechanisms underlying human atrial action potential properties: Insights from a mathematical model. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 1998, 275, H301–H321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, A. Reciprocal Modulation of IK1–INa Extends Excitability in Cardiac Ventricular Cells. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wettwer, E.; Hála, O.; Christ, T.; Heubach, J.F.; Dobrev, D.; Knaut, M.; Varró, A.; Ravens, U. Role of IKur in controlling action potential shape and contractility in the human atrium: Influence of chronic atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2004, 110, 2299–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workman, A.J.; Kane, K.A.; Rankin, A.C. The contribution of ionic currents to changes in refractoriness of human atrial myocytes associated with chronic atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2001, 52, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, A.G.; Louch, W.E. Species-Dependent Mechanisms of Cardiac Arrhythmia: A Cellular Focus. Clin. Med. Insights Cardiol. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaese, S.; Verheule, S. Cardiac electrophysiology in mice: A matter of size. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nattel, S.; Dobrev, D. Electrophysiological and molecular mechanisms of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scridon, A.; Fouilloux-Meugnier, E.; Loizon, E.; Rome, S.; Julien, C.; Barrès, C.; Chevalier, P. Long-standing arterial hypertension is associated with Pitx2 down-regulation in a rat model of spontaneous atrial tachyarrhythmias. Eur. Eur. Pacing Arrhythm. Card. Electrophysiol. J. Work. Groups Card. Pacing Arrhythm. Card. Cell. Electrophysiol. Eur. Soc. Cardiol. 2015, 17, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Cannell, M.B.; Hancox, J.C. Differential responses of rabbit ventricular and atrial transient outward current (I(to)) to the I(to) modulator NS5806. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, J.I.; Varghese, A.; Lu, Y.; Bursill, J.A.; Mahaut-Smith, M.P.; Huang, C.L. Temperature dependence of human ether-a-go-go-related gene K+ currents. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 291, C165–C175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.K.; Kurachi, Y. Mechanisms of adenosine-mediated actions on cellular and clinical cardiac electrophysiology. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1995, 70, 274–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liang, B.; Skibsbye, L.; Olesen, S.P.; Grunnet, M.; Jespersen, T. GIRK channel activation via adenosine or muscarinic receptors has similar effects on rat atrial electrophysiology. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 62, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, S.J.; Morrison, R.R.; Teng, B.; Pelleg, A. Adenosine receptors and the heart: Role in regulation of coronary blood flow and cardiac electrophysiology. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2009, 193, 161–188. [Google Scholar]
- Grandi, E.; Pasqualini, F.S.; Bers, D.M. A novel computational model of the human ventricular action potential and Ca transient. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2010, 48, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten Tusscher, K.H.; Noble, D.; Noble, P.J.; Panfilov, A.V. A model for human ventricular tissue. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2004, 286, H1573–H1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, C.G.; Ripoll, C.; Lederer, W.J. ATP-sensitive potassium channel modulation of the guinea pig ventricular action potential and contraction. Circ. Res. 1991, 68, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, S.; Sarai, N.; Kuratomi, S.; Ono, K.; Noma, A. Role of individual ionic current systems in ventricular cells hypothesized by a model study. JPN J. Physiol. 2003, 53, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, T.; Takasugi, N.; Naruse, G.; Okura, H. Adenosine-induced atrial fibrillation arising from arrhythmogenic right atrial appendage. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2020, 31, 234–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiFrancesco, D.; Ducouret, P.; Robinson, R.B. Muscarinic modulation of cardiac rate at low acetylcholine concentrations. Science 1989, 243, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, A.; Holm, M.; Blomström, P.; Johansson, R.; Lührs, C.; Brandt, J.; Olsson, S.B. Right atrial free wall conduction velocity and degree of anisotropy in patients with stable sinus rhythm studied during open heart surgery. Eur. Heart J. 1998, 19, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krul, S.P.; Berger, W.R.; Smit, N.W.; van Amersfoorth, S.C.; Driessen, A.H.; van Boven, W.J.; Fiolet, J.W.; van Ginneken, A.C.; van der Wal, A.C.; de Bakker, J.M.; et al. Atrial fibrosis and conduction slowing in the left atrial appendage of patients undergoing thoracoscopic surgical pulmonary vein isolation for atrial fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2015, 8, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roden, D.M.; Woosley, R.L. Class I antiarrhythmic agents: Quinidine, procainamide and N-acetylprocainamide, disopyramide. Pharmacol. Ther. 1983, 23, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, O.J.; Bueno-Orovio, A.; Van Ammel, K.; Lu, H.R.; Towart, R.; Gallacher, D.J.; Rodriguez, B. Experimentally calibrated population of models predicts and explains intersubject variability in cardiac cellular electrophysiology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2098–E2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, T.M.; Hariharan, P.; Funkhouser, C.M.; Afshari, P.; Goodin, M.; Horner, M. Assessing Computational Model Credibility Using a Risk-Based Framework: Application to Hemolysis in Centrifugal Blood Pumps. ASAIO J. (Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1992) 2019, 65, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, S.; Hogue, I.B.; Ray, C.J.; Kirschner, D.E. A methodology for performing global uncertainty and sensitivity analysis in systems biology. J. Theor. Biol. 2008, 254, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).