Novel Transcript Discovery Expands the Repertoire of Pathologically-Associated, Long Non-Coding RNAs in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
Abstract
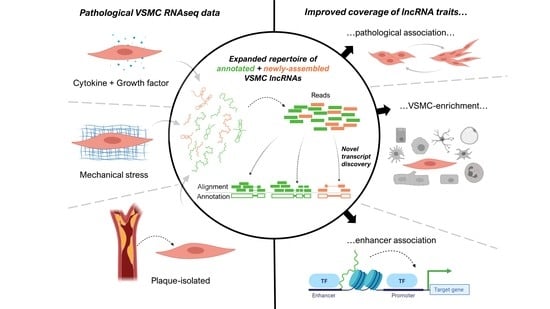
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. A Bioinformatic Approach to Provide a More Complete Annotation of lncRNAs Expressed in VSMCs in Basal and Pathological Conditions
2.2. Newly Assembled Genes Substantially Increase the Number of VSMC lncRNAs Detected in Response to Pathological Stimuli
2.3. Novel Transcript Discovery Increases the Representation of VSMC-Enriched lncRNAs with Pathological Association
2.4. Novel Transcript Discovery in VSMCs Increases Evidence of Enhancer-Transcribed lncRNAs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Transcriptome Assembly
4.2. Pipeline for Annotation of LncRNA (PLAR) + Classification of Transcripts
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alexander, M.R.; Owens, G.K. Epigenetic Control of Smooth Muscle Cell Differentiation and Phenotypic Switching in Vascular Development and Disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2012, 74, 13–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frismantiene, A.; Philippova, M.; Erne, P.; Resink, T.J. Smooth Muscle Cell-Driven Vascular Diseases and Molecular Mechanisms of VSMC Plasticity. Cell. Signal. 2018, 52, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, V.; Vickneson, K.; Kofidis, T.; Woo, C.C.; Lin, X.Y.; Foo, R.; Shanahan, C.M. Role of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Plasticity and Interactions in Vessel Wall Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, R.; Choong, A.M.; Woo, C.C.; Foo, R.; Sorokin, V. Genetic and Epigenetic Mechanisms Underlying Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Modulation in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykes, I.M.; Emanueli, C. Transcriptional and Post-Transcriptional Gene Regulation by Long Non-Coding RNA. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2017, 15, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haemmig, S.; Simion, V.; Yang, D.F.; Deng, Y.H.; Feinberg, M.W. Long Noncoding RNAs in Cardiovascular Disease, Diagnosis, and Therapy. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2017, 32, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volders, P.J.; Anckaert, J.; Verheggen, K.; Nuytens, J.; Martens, L.; Mestdagh, P.; Vandesompele, J. Lncipedia 5: Towards a Reference Set of Human Long Non-Coding Rnas. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D135–D139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Washietl, S.; Kellis, M.; Garber, M. Evolutionary Dynamics and Tissue Specificity of Human Long Noncoding RNAs in Six Mammals. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gloss, B.S.; Dinger, M.E. The Specificity of Long Noncoding RNA Expression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2016, 1859, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, M.D.; Pinel, K.; Dakin, R.; Vesey, A.T.; Diver, L.; Mackenzie, R.; Garcia, R.; Welsh, P.; Sattar, N.; Hamilton, G.; et al. Smooth Muscle Enriched Long Noncoding RNA (SMILR) Regulates Cell Proliferation. Circulation 2016, 133, 2050–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.J.; Zhang, W.; Lin, M.Y.; Wu, W.; Jiang, P.T.; Tou, E.; Xue, M.; Richards, A.; Jourd’heuil, D.; Asif, A.; et al. MYOSLID Is a Novel Serum Response Factor-Dependent Long Noncoding RNA That Amplifies the Vascular Smooth Muscle Differentiation Program. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 2088–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bell, R.D.; Long, X.C.; Lin, M.Y.; Bergmann, J.H.; Nanda, V.; Cowan, S.L.; Zhou, Q.; Han, Y.; Spector, D.L.; Zheng, D.Y.; et al. Identification and Initial Functional Characterization of a Human Vascular Cell-Enriched Long Noncoding RNA. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uszczynska-Ratajczak, B.; Lagarde, J.; Frankish, A.; Guigó, R.; Johnson, R. Towards a Complete Map of the Human Long Non-Coding RNA Transcriptome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENCODE Consortium. An Integrated Encyclopedia of DNA Elements in the Human Genome. Nature 2012, 489, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, C.C.; Ramilowski, J.A.; Harshbarger, J.; Bertin, N.; Rackham, O.J.L.; Gough, J.; Denisenko, E.; Schmeier, S.; Poulsen, T.M.; Severin, J.; et al. An Atlas of Human Long Non-Coding RNAs with Accurate 5’ Ends. Nature 2017, 543, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alvarez-Dominguez, J.R.; Hu, W.; Yuan, B.; Shi, J.; Park, S.S.; Gromatzky, A.A.; Van Oudenaarden, A.; Lodish, H.F. Global Discovery of Erythroid Long Noncoding RNAs Reveals Novel Regulators of Red Cell Maturation. Blood 2014, 123, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hudson, W.H.; Prokhnevska, N.; Gensheimer, J.; Akondy, R.; McGuire, D.J.; Ahmed, R.; Kissick, H.T. Expression of Novel Long Noncoding RNAs Defines Virus-Specific Effector and Memory CD8 + T Cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsoi, L.C.; Iyer, M.K.; Stuart, P.E.; Swindell, W.R.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Tejasvi, T.; Sarkar, M.K.; Li, B.; Ding, J.; Voorhees, J.J.; et al. Analysis of Long Non-Coding RNAs Highlights Tissue-Specific Expression Patterns and Epigenetic Profiles in Normal and Psoriatic Skin. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersson, R.; Gebhard, C.; Miguel-Escalada, I.; Hoof, I.; Bornholdt, J.; Boyd, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Schmidl, C.; Suzuki, T.; et al. An Atlas of Active Enhancers across Human Cell Types and Tissues. Nature 2014, 507, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, N.; Ulitsky, I. Production of Spliced Long Noncoding RNAs Specifies Regions with Increased Enhancer Activity. Cell Syst. 2018, 7, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.K.; Xu, T.; Assoian, R.K.; Rader, D.J. Mining the Stiffness-Sensitive Transcriptome in Human Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Identifies Long Noncoding RNA Stiffness Regulators. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alloza, I.; Goikuria, H.; Idro, J.L.; Triviño, J.C.; Fernández Velasco, J.M.; Elizagaray, E.; García-Barcina, M.; Montoya-Murillo, G.; Sarasola, E.; Vega Manrique, R.; et al. RNAseq Based Transcriptomics Study of SMCs from Carotid Atherosclerotic Plaque: BMP2 and IDs Proteins Are Crucial Regulators of Plaque Stability. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hezroni, H.; Koppstein, D.; Schwartz, M.G.; Avrutin, A.; Bartel, D.P.; Ulitsky, I. Principles of Long Noncoding RNA Evolution Derived from Direct Comparison of Transcriptomes in 17 Species. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G. GFF Utilities: GffRead and GffCompare. F1000Research 2020, 9, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirka, R.C.; Wagh, D.; Paik, D.T.; Pjanic, M.; Nguyen, T.; Miller, C.L.; Kundu, R.; Nagao, M.; Coller, J.; Koyano, T.K.; et al. Atheroprotective Roles of Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Modulation and the TCF21 Disease Gene as Revealed by Single-Cell Analysis. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, M.D.; Wakefield, M.J.; Smyth, G.K.; Oshlack, A. Gene Ontology Analysis for RNA-Seq: Accounting for Selection Bias. Genome Biol. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breschi, A.; Muñoz-Aguirre, M.; Wucher, V.; Davis, C.A.; Garrido-Martín, D.; Djebali, S.; Gillis, J.; Pervouchine, D.D.; Vlasova, A.; Dobin, A.; et al. A Limited Set of Transcriptional Programs Define Major Cell Types. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishilevich, S.; Nudel, R.; Rappaport, N.; Hadar, R.; Plaschkes, I.; Iny Stein, T.; Rosen, N.; Kohn, A.; Twik, M.; Safran, M.; et al. GeneHancer: Genome-Wide Integration of Enhancers and Target Genes in GeneCards. Database 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.Y.; Kang, Y.J.; Song, I.H.; Choi, H.C.; Kim, H.S. Upregulation of Interleukin-8/CXCL8 in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells from Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Hypertens. Res. 2008, 31, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, Y.; Fan, F.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wei, X.; Kohama, K.; Gordon, J.R.; Li, F.; Gao, Y. Recombinant Human CXCL8(3-72)K11R/G31P Regulates Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Migration through Blockage of Interleukin-8 Receptor. IUBMB Life 2013, 65, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Newman, W.H. Smooth Muscle Cell Migration Stimulated by Interleukin 6 Is Associated with Cytoskeletal Reorganization. J. Surg. Res. 2003, 111, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, U.; Ikeda, M.; Oohara, T.; Oguchi, A.; Kamitani, T.; Tsuruya, Y.; Kano, S. Interleukin 6 Stimulates Growth of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in a PDGF-Dependent Manner. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 1991, 260, H1713–H1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurozumi, A.; Nakano, K.; Yamagata, K.; Okada, Y.; Nakayamada, S.; Tanaka, Y. IL-6 and SIL-6R Induces STAT3-Dependent Differentiation of Human VSMCs into Osteoblast-like Cells through JMJD2B-Mediated Histone Demethylation of RUNX2. Bone 2019, 124, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.M.; Esmailzadeh, L.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X.; Asadi, A.; Krassilnikova, S.; Fassaei, H.R.; Luo, G.; Al-Lamki, R.S.M.; Takahashi, T.; et al. ESDN Is a Marker of Vascular Remodeling and Regulator of Cell Proliferation in Graft Arteriosclerosis. Am. J. Transplant. 2007, 7, 2098–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yaghini, F.A.; Song, C.Y.; Lavrentyev, E.N.; Ghafoor, H.U.B.; Fang, X.R.; Estes, A.M.; Campbell, W.B.; Malik, K.U. Angiotensin II-Induced Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Migration and Growth Are Mediated by Cytochrome P450 1b1-Dependent Superoxide Generation. Hypertension 2010, 55, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernard, K.; Logsdon, N.J.; Benavides, G.A.; Sanders, Y.; Zhang, J.; Darley-Usmar, V.M.; Thannickal, V.J. Glutaminolysis Is Required for Transforming Growth Factor-Β1–Induced Myofibroblast Differentiation and Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, F.A.; Yuhong, Q.; Zhou, G.; Tsai, M.J.; Tsai, S.Y. The Orphan Nuclear Receptor COUP-TFII Is Required for Angiogenesis and Heart Development. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 1037–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.N.; Li, Y.S.J.; Yeh, Y.T.; Lee, P.L.; Usami, S.; Chien, S.; Chiu, J.J. Synergistic Roles of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB and Interleukin-1β in Phenotypic Modulation of Human Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2665–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chappell, J.; Harman, J.L.; Narasimhan, V.M.; Yu, H.; Foote, K.; Simons, B.D.; Bennett, M.R.; Jørgensen, H.F. Extensive Proliferation of a Subset of Differentiated, yet Plastic, Medial Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Contributes to Neointimal Formation in Mouse Injury and Atherosclerosis Models. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.; Li, F.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; He, L.; Zhang, H.; Pu, W.; Liu, K.; et al. Arterial Sca1+ Vascular Stem Cells Generate De Novo Smooth Muscle for Artery Repair and Regeneration. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.; Trac, C.; Jin, W.; Lanting, L.; Akbany, A.; Saetrom, P.; Schones, D.E.; Natarajan, R. Novel Long Noncoding RNAs Are Regulated by Angiotensin II in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Vries, M.R.; Simons, K.H.; Jukema, J.W.; Braun, J.; Quax, P.H.A. Vein Graft Failure: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Outcomes. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 451–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangala, P.; Murphy, R.; Quinodoz, S.A.; Gellatly, K.; McDonel, P.; Guttman, M.; Garber, M. High-Resolution Mapping of Multiway Enhancer-Promoter Interactions Regulating Pathogen Detection. Mol. Cell 2020, 80, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Krueger, F. Trim Galore! 2012. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/trim_galore/ (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast Universal RNA-Seq Aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie Enables Improved Reconstruction of a Transcriptome from RNA-Seq Reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate Transcript Quantification from RNA-Seq Data with or without a Reference Genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulitsky, I. Pipeline for LncRNA Annotation from RNA-Seq Data (PLAR). 2018. Available online: https://www.weizmann.ac.il/Biological_Regulation/IgorUlitsky/PLAR (accessed on 1 February 2021).




| ElncRNA Name 1 | Interaction Evidence | PCG | VSMC Type + Stimulus | Stimulus Response | Max. FANTOM VSMC Enrichment | PCG VSMC Characterisation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VSMClnc6 (svSMC + stiff-culturing) | CHi-C, eRNA co-expression, Distance, GeneHancer eQTLs | CXCL8 | svSMC + IL-1α/PDGF-BB | Co-induced | LncRNA: 41-fold PCG: None | Activates VSMC proliferation + migration [30,31] |
| AC002480.3 | CHi-C, eRNA co-expression | IL-6 | svSMC + IL-1α/PDGF-BB | Co-induced | LncRNA: None (overlaps AC002480.4: 20-fold) PCG: 19-fold | Activates VSMC proliferation/migration + osteoblast phenotype [32,33,34] |
| LINC00973 | FANTOM eQTL analysis | DCBLD2 | All datasets | Co-induced with IL-1α/PDGF-BB Co-repressed with stiffness | LncRNA: 7-fold PCG: 5-fold | Regulates PDGFR + Il-8 expression, Marker of vascular remodelling [35] |
| AC009229.5 | FANTOM eQTL analysis | CYP1B | aoSMC + stiffness | Co-repressed | LncRNA: None PCG: None | Mediates angiotensin II-induced VSMC proliferation + migration [36] |
| MSTRG.10933 (svSMC) | Distance, GeneHancer eQTLs | GLS | svSMC + IL-1α/PDGF-BB | Co-repressed | LncRNA: None PCG: None | Required for TGFβ-induced myofibroblast differentiation + pro-fibrotic marker expression [37] |
| NR2F2-AS1 | GeneHancer eQTLs, CHi-C | NR2F2 (COUP-TFII) | svSMC + IL-1α/PDGF-BB | Co-repressed | LncRNA: None PCG: None | Ablation leads to osteoblast-like phenotype in mesenchymal precursors [38] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bennett, M.; Ulitsky, I.; Alloza, I.; Vandenbroeck, K.; Miscianinov, V.; Mahmoud, A.D.; Ballantyne, M.; Rodor, J.; Baker, A.H. Novel Transcript Discovery Expands the Repertoire of Pathologically-Associated, Long Non-Coding RNAs in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031484
Bennett M, Ulitsky I, Alloza I, Vandenbroeck K, Miscianinov V, Mahmoud AD, Ballantyne M, Rodor J, Baker AH. Novel Transcript Discovery Expands the Repertoire of Pathologically-Associated, Long Non-Coding RNAs in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(3):1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031484
Chicago/Turabian StyleBennett, Matthew, Igor Ulitsky, Iraide Alloza, Koen Vandenbroeck, Vladislav Miscianinov, Amira Dia Mahmoud, Margaret Ballantyne, Julie Rodor, and Andrew H. Baker. 2021. "Novel Transcript Discovery Expands the Repertoire of Pathologically-Associated, Long Non-Coding RNAs in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 3: 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031484
APA StyleBennett, M., Ulitsky, I., Alloza, I., Vandenbroeck, K., Miscianinov, V., Mahmoud, A. D., Ballantyne, M., Rodor, J., & Baker, A. H. (2021). Novel Transcript Discovery Expands the Repertoire of Pathologically-Associated, Long Non-Coding RNAs in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(3), 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031484