Mild Effects of Sunscreen Agents on a Marine Flatfish: Oxidative Stress, Energetic Profiles, Neurotoxicity and Behaviour in Response to Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles and Oxybenzone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. TiO2 Nanoparticles Characterization
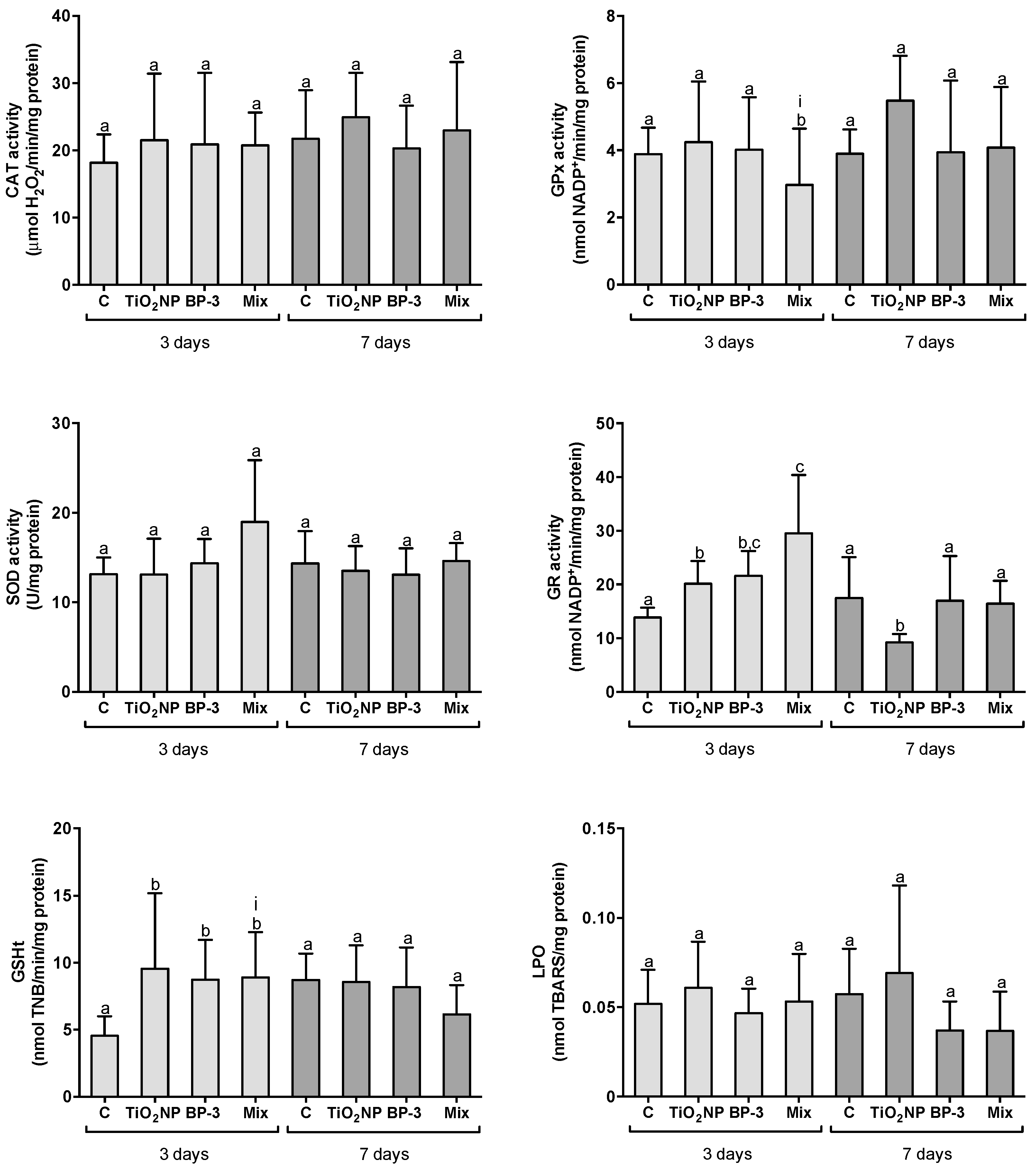
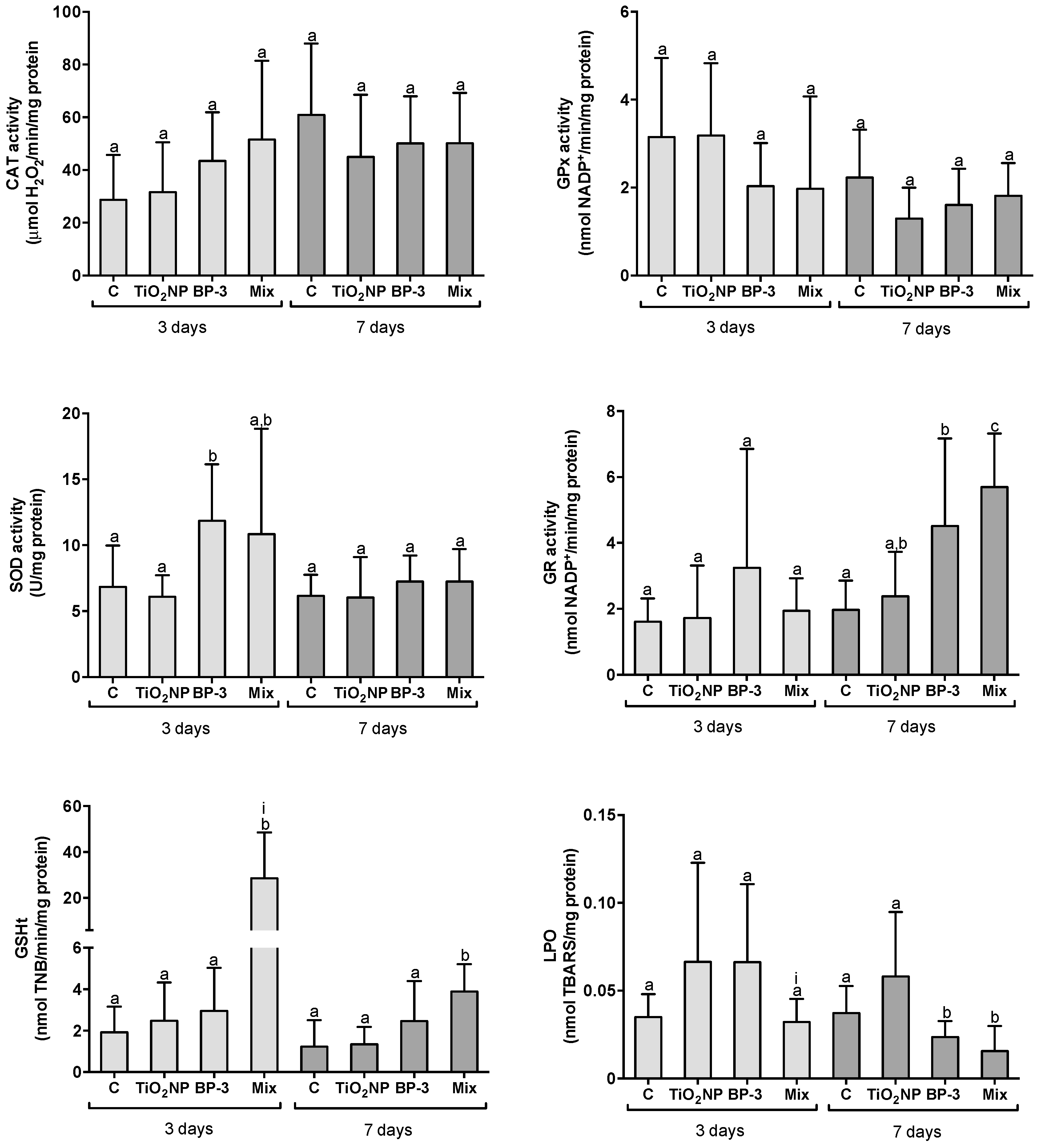
2.2. Organ-Specific Oxidative Stress Profiles
2.2.1. Responses in the Intestine
2.2.2. Responses in the Kidney
2.2.3. Responses in the Liver
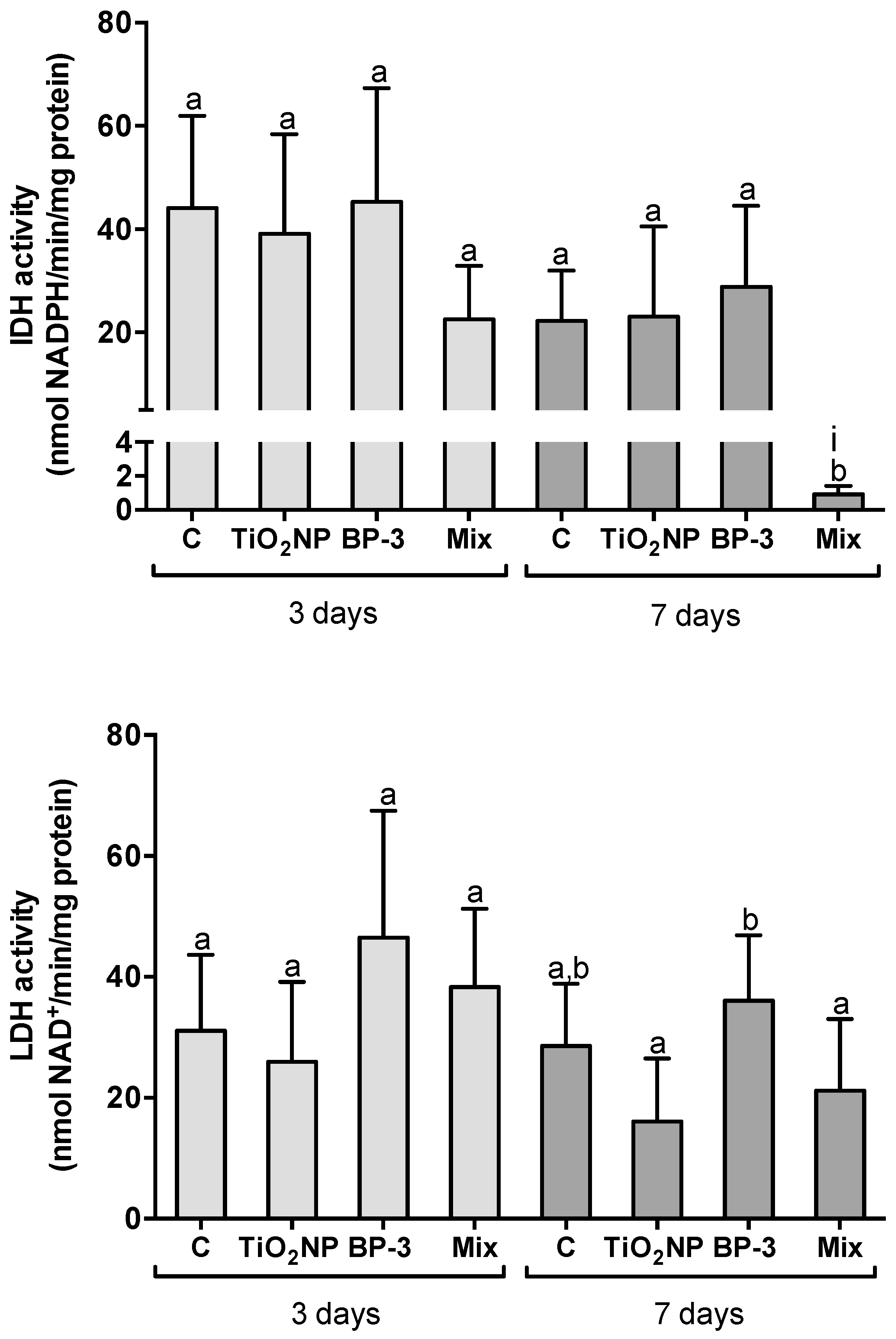
2.3. Hepatic Metabolic Profile
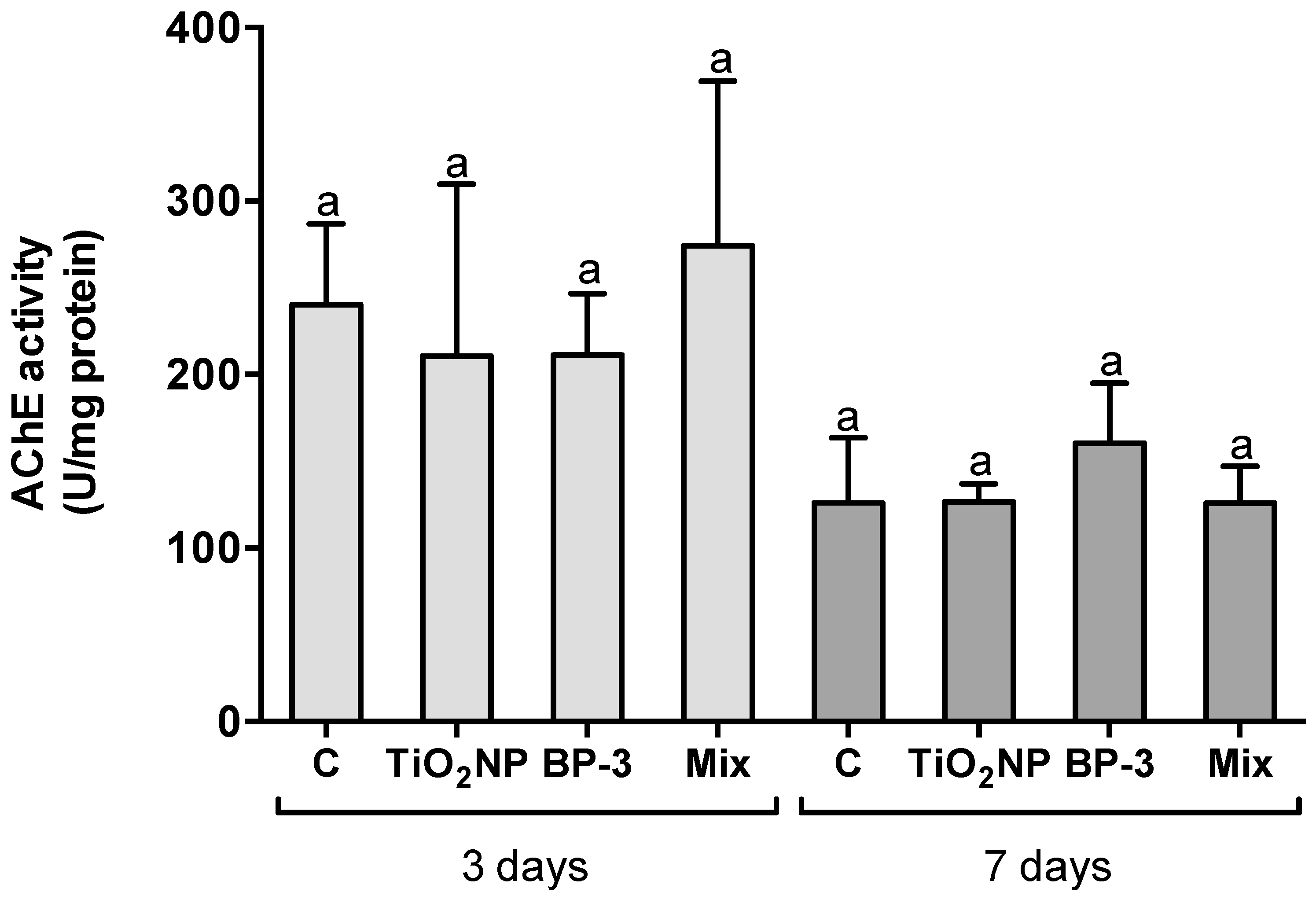
2.4. Neurotoxicity
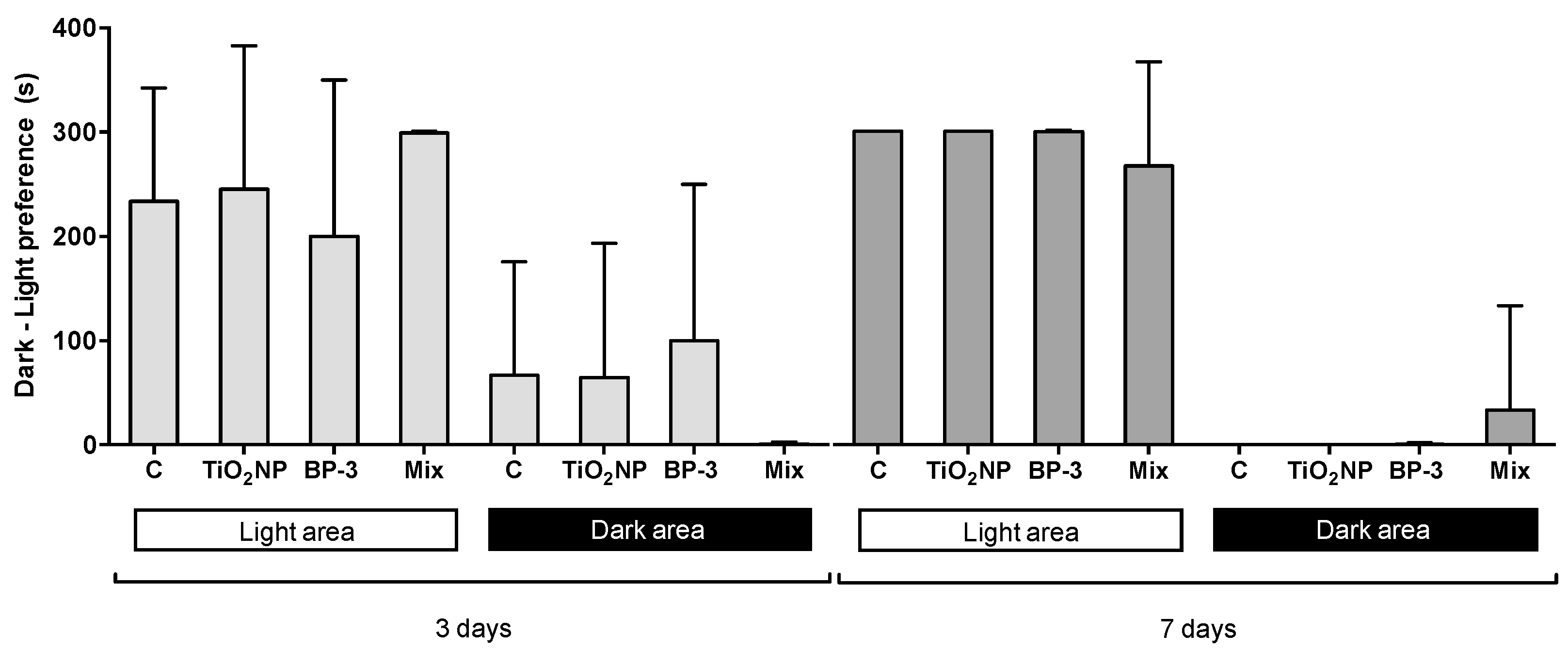
2.5. Behavioural Alterations
3. Discussion
3.1. Organ-Specific Oxidative Stress Profiles
3.2. Hepatic Metabolic Profile
3.3. Neurotoxicity
3.4. Fish Behavioural Analysis
3.5. Identifying Chemical-Chemical Interactions under Simultaneous Exposure
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Fish Maintenance
4.2. Preparation and Characterization of Titanium Dioxide Suspensions
4.3. Preparation of Oxybenzone Solutions
4.4. Exposures to TiO2 Nanoparticles and Oxybenzone
4.5. Sampling and Biochemical Analyses
4.6. Fish Behavioural Assessment
- -
- Total distance travelled (mm)—Represents the sum of all the displacements for each fish while it moved freely during the whole time period of the test; only movements that were able to move the centre of mass were considered displacement;
- -
- Average speed (mm s−1)—Represents the average of instantaneous speeds for each fish during the whole assay time, where the instantaneous speed Si corresponding to the time ti is calculated according to the formulac is a sampling distance.
- -
- Mobility rate (%)—The percentage of whole assay time that each fish remained in motion for, including movements in great lengths or within the same area;
- -
- Exploration rate (%)—Each recorded arena was divided into regular non-overlapping zones in a total of 28 zones; then, the use of each zone was computed for each arena by dividing the total number of detections in the zone by the total number of detections. This parameter can provide information on to what extent the exploratory behaviour of fish was affected.
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mao, F.; He, Y.; Gin, K.Y.H. Occurrence and fate of benzophenone-type UV filters in aquatic environments: A review. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar-Sánchez, A.; Sánchez-Quiles, D.; Rodríguez-Romero, A. Massive coastal tourism influx to the Mediterranean Sea: The environmental risk of sunscreens. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giokas, D.L.; Salvador, A.; Chisvert, A. UV filters: From sunscreens to human body and the environment. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danovaro, R.; Bongiorni, L.; Corinaldesi, C.; Giovannelli, D.; Damiani, E.; Astolfi, P.; Greci, L.; Pusceddu, A. Sunscreens Cause Coral Bleaching by Promoting Viral Infections. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar-Sánchez, A.; Sánchez-Quiles, D.; Basterretxea, G.; Benedé, J.L.; Chisvert, A.; Salvador, A.; Moreno-Garrido, I.; Blasco, J. Sunscreen Products as Emerging Pollutants to Coastal Waters. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.S.; Sanz, M.R.; Rodríguez, J.R.B. Occurrence of eight UV filters in beaches of Gran Canaria (Canary Islands). An approach to environmental risk assessment. Chemosphere 2015, 131, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, S.L.; Lim, H.W. Review of environmental effects of oxybenzone and other sunscreen active ingredients. J. Am. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gago-Ferrero, P.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. An overview of UV-absorbing compounds (organic UV filters) in aquatic biota. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 2597–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoffrey, K.; Mwangi, A.N.; Maru, S.M. Sunscreen products: Rationale for use, formulation development and regulatory considerations. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Quiles, D.; Tovar-Sánchez, A. Are sunscreens a new environmental risk associated with coastal tourism? Environ. Int. 2015, 83, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Nanda, A. Enhanced sun protection of nano-sized metal oxide particles over conventional metal oxide particles: An in vitro comparative study. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2014, 36, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.J.; Fang, S.W.; Cheng, W.L.; Huang, S.C.; Huang, M.C.; Cheng, H.F. Characterization of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles in sunscreen powder by comparing different measurement methods. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Choi, K. Occurrences, toxicities, and ecological risks of benzophenone-3, a common component of organic sunscreen products: A mini-review. Environ. Int. 2014, 70, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruszkiewicz, J.A.; Pinkas, A.; Ferrer, B.; Peres, T.V.; Tsatsakis, A.; Aschner, M. Neurotoxic effect of active ingredients in sunscreen products, a contemporary review. Toxicol. Rep. 2017, 4, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüthgen, N.; Meili, N.; Chew, G.; Odermatt, A.; Fent, K. Accumulation and effects of the UV-filter octocrylene in adult and embryonic zebra fish (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476–477, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronado, M.; De Haro, H.; Deng, X.; Rempel, M.A.; Lavado, R.; Schlenk, D. Estrogenic activity and reproductive effects of the UV-filter oxybenzone (2-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl-methanone) in fish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 90, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gago-Ferrero, P.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. UV filters bioaccumulation in fish from Iberian river basins. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 518–519, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Kojima, H.; Takeuchi, S.; Uramaru, N.; Sanoh, S.; Sugihara, K.; Kitamura, S.; Ohta, S. Metabolism of UV-filter benzophenone-3 by rat and human liver microsomes and its effect on endocrine-disrupting activity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 282, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Fan, Y.; Jin, J.; Xiong, S.; Liu, J.; Tang, C. Bioaccumulation and biomagnification of ultraviolet absorbents in marine wildlife of the Pearl River Estuarine, South China Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, M.M.P.; Lam, J.C.W.; Ng, T.Y.; Ang, P.O.; Murphy, M.B.; Lam, P.K.S. Occurrence, Distribution, and Fate of Organic UV Filters in Coral Communities. EnvIron. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4182–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.; Fernandes, J.O.; Pena, A.; Cunha, S.C. Occurrence, profile and spatial distribution of UV-filters and musk fragrances in mussels from Portuguese coastline. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 138, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molins-Delgado, D.; Muñoz, R.; Nogueira, S.; Alonso, M.B.; Torres, J.P.; Malm, O.; Ziolli, R.L.; Hauser-Davis, R.A.; Eljarrat, E.; Barceló, D.; et al. Occurrence of organic UV filters and metabolites in lebranche mullet (Mugil liza) from Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal-Liñán, L.; Villaverde-de-Sáa, E.; Rodil, R.; Quintana, J.B.; Beiras, R. Bioaccumulation of UV filters in Mytilus galloprovincialis mussel. Chemosphere 2018, 190, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, A.N.; Hayes, C.E.; Kerr, J.J.; Lee, R.C.; Flaherty, D.B. Acute toxicity testing of TiO 2 -based vs. oxybenzone-based sunscreens on clownfish (Amphiprion ocellaris). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 14513–14520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Dong, X.; Xin, Y.; Zhao, M. Effects of titanium dioxide nano-particles on growth and some histological parameters of zebrafish (Danio rerio) after a long-term exposure. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 101, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignardi, C.P.; Hasue, F.M.; Sartório, P.V.; Cardoso, C.M.; Machado, A.S.D.; Passos, M.J.A.C.R.; Santos, T.C.A.; Nucci, J.M.; Hewer, T.L.R.; Watanabe, I.S.; et al. Genotoxicity, potential cytotoxicity and cell uptake of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in the marine fish Trachinotus carolinus (Linnaeus, 1766). Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 158, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canesi, L.; Corsi, I. Effects of nanomaterials on marine invertebrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureda, A.; Capó, X.; Busquets-Cortés, C.; Tejada, S. Acute exposure to sunscreen containing titanium induces an adaptive response and oxidative stress in Mytillus galloprovincialis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 149, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo, D.G.; Tasat, D.; Guglielmotti, M.B.; Cabrini, R.L. Titanium transport through the blood stream. An experimental study on rats. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2003, 14, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazipura, M.; McGowan, R.; Arslan, A.; Hossain, T. Exposure to benzophenone-3 and reproductive toxicity: A systematic review of human and animal studies. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 73, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNardo, J.C.; Downs, C.A. Dermatological and environmental toxicological impact of the sunscreen ingredient oxybenzone/benzophenone-3. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüthgen, N.; Zucchi, S.; Fent, K. Effects of the UV filter benzophenone-3 (oxybenzone) at low concentrations in zebra fish (Danio rerio). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 263, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Fuentes, G.; Sandoval-Gío, J.J.; Arroyo-Silva, A.; Noreña-Barroso, E.; Escalante-Herrera, K.S.; Olvera-Espinosa, F. Evaluation of the estrogenic and oxidative stress effects of the UV filter 3-benzophenone in zebrafish (Danio rerio) eleuthero-embryos. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 2015, 115, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mieiro, C.L.; Martins, M.; Silva, M.; Coelho, J.P.; Lopes, C.B.; Alves, A.; Alves, J.; Pereira, E.; Pardal, M.; Costa, M.H.; et al. Advances on assessing nanotoxicity in marine fish—the pros and cons of combining an ex vivo approach and histopathological analysis in gills. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 217, 105322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barmo, C.; Ciacci, C.; Canonico, B.; Fabbri, R.; Cortese, K.; Balbi, T.; Marcomini, A.; Pojana, G.; Gallo, G.; Canesi, L. In vivo effects of n-TiO2 on digestive gland and immune function of the marine bivalve Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 132–133, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auguste, M.; Lasa, A.; Pallavicini, A.; Gualdi, S.; Vezzulli, L.; Canesi, L. Exposure to TiO2 nanoparticles induces shifts in the microbiota composition of Mytilus galloprovincialis hemolymph. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canesi, L.; Fabbri, R.; Gallo, G.; Vallotto, D.; Marcomini, A.; Pojana, G. Biomarkers in Mytilus galloprovincialis exposed to suspensions of selected nanoparticles (Nano carbon black, C60 fullerene, Nano-TiO2, Nano-SiO2). Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 100, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Z.; Xie, Z.; Dupont, S.; Huang, W.; Wu, F.; Kong, H. Oxidative stress induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles increases under seawater acidi fi cation in the thick shell mussel Mytilus coruscus. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 137, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, M.; Bernardeschi, M.; Costagliola, D.; Della Torre, C.; Frenzilli, G.; Guidi, P.; Lucchesi, P.; Mottola, F.; Santonastaso, M.; Scarcelli, V.; et al. n-TiO2 and CdCl2 co-exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles and cadmium: Genomic, DNA and chromosomal damage evaluation in the marine fish European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 168, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oost, D.; Beyer, J.; Vermeulen, N.P.E. Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 13, 57–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, S.E.; Gallagher, E.P.; Batley, G.E. The Role of Biomarkers in the Assessment of Aquatic Ecosystem Health. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2014, 10, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connon, R.E.; Geist, J.; Pfeiff, J.; Loguinov, A.V.; Abronzo, L.S.D.; Wintz, H.; Vulpe, C.D.; Werner, I. Linking mechanistic and behavioral responses to sublethal esfenvalerate exposure in the endangered delta smelt; Hypomesus transpacificus (Fam. Osmeridae). BMC Genom. 2009, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, G.R.; Sloman, K.A. The effects of environmental pollutants on complex fish behaviour: Integrating behavioural and physiological indicators of toxicity. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 68, 369–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, A.S.; Salierno, J.D.; Brewer, S.K. Fish models in behavioral toxicology: Automated techniques, updates and perspectives. In Methods in Aquatic Toxicology; Ostrander, G.K., Ed.; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Hsieh, C.; Ko, F.; Cheng, J. Effect of the UV- filter benzophenone-3 on intra-colonial social behaviors of the false clown anemone fish (Amphiprion ocellaris). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 1625–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, D.; Al-bairuty, G.A.; Ramsden, C.S.; Sloman, K.A.; Henry, T.B.; Handy, R.D. Subtle alterations in swimming speed distributions of rainbow trout exposed to titanium dioxide nanoparticles are associated with gill rather than brain injury. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 126, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canesi, L.; Frenzilli, G.; Balbi, T.; Bernardeschi, M.; Ciacci, C.; Corsolini, S.; Della, C.; Fabbri, R.; Faleri, C.; Focardi, S.; et al. Interactive effects of n-TiO2 and 2,3,7,8-TCDD on the marine bivalve Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 153, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbi, T.; Smerilli, A.; Fabbri, R.; Ciacci, C.; Montagna, M.; Grasselli, E.; Brunelli, A.; Pojana, G.; Marcomini, A.; Gallo, G.; et al. Co-exposure to n-TiO2 and Cd2+ results in interactive effects on biomarker responses but not in increased toxicity in the marine bivalve. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, G.; Shaw, B.J.; Handy, R.D. Toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Gill injury, oxidative stress, and other physiological effects. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 84, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Wang, Z.; Xing, B. Effect of sub-acute exposure to TiO2 nanoparticles on oxidative stress and histopathological changes in Juvenile Carp (Cyprinus carpio). J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsden, C.S.; Henry, T.B.; Handy, R.D. Sub-lethal effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the physiology and reproduction of zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 126, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushothaman, S.; Raghunath, A.; Dhakshinamoorthy, V.; Panneerselvam, L.; Perumal, E. Acute exposure to titanium dioxide (TiO2) induces oxidative stress in zebrafish gill tissues. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2014, 96, 890–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammel, T.; Wassmur, B.; Mackevica, A.; Chen, C.L.; Sturve, J. Mixture toxicity effects and uptake of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles and 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl (PCB77) in juvenile brown trout following co-exposure via the diet. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 213, 105195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donovan, S.; Mestre, N.C.; Abel, S.; Fonseca, T.G.; Carteny, C.C.; Willems, T.; Prinsen, E.; Cormier, B.; Keiter, S.S.; João, M. Effects of the UV filter, oxybenzone, adsorbed to microplastics in the clam Scrobicularia plana. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz, M.S.; De Matos, A.P.A.; Lourenço, J.; Castro, L.; Peres, I.; Mendonça, E.; Picado, A. Liver Alterations in Two Freshwater Fish Species (Carassius auratus and Danio rerio) Following Exposure to Different TiO2 Nanoparticle Concentrations. Microsc. Microanal. 2013, 19, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, P.; Liu, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z. Hepatic oxidative stress biomarker responses in freshwater fish Carassius auratus exposed to four benzophenone UV filters. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 2015, 119, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.; Lin, J.-F.; Tian, T.; Xie, D.; Xu, R.-H. NADPH homeostasis in cancer: Functions, mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Signal Transduct. Targeted Ther. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Kuang, S.; Tang, L.; Wu, P. Differential growth performance, intestinal antioxidant status and relative expression of Nrf2 and its target genes in young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) fed with graded levels of leucine. Aquaculture 2014, 434, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, R.D.; McGeer, J.C.; Allen, H.E.; Drevnick, P.E.; Gorsuch, J.W.; Green, A.S.; Lundebye, A.K.; Hook, S.E.; Mount, D.R.; Stubblefield, W.A. Toxic effects of dietborne metals: Laboratory studies. In Toxicity of Dietborne Metals to Aquatic Organisms; Meyer, J.S., Adams, W.J., Brix, K.V., Luoma, S.N., Mount, D.R., Stubblefield, W.A., Wood, C.M., Eds.; SETAC Press: Pensacola, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 59–112. [Google Scholar]
- Handy, R.D.; Ramsden, C.S. Effects of manufactured nanomaterials on fishes: A target organ and body systems physiology. J. Fish Biol. 2011, 44, 821–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, W.; Cai, P.; Chen, M.; Li, H.; Tang, J.; Xu, C. The relationship between prenatal exposure to BP-3 and Hirschsprung’s disease. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNardo, J.C.; Downs, C.A. Can oxybenzone cause Hirschsprung’s disease? Reprod. Toxicol. 2019, 86, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, R.D.; Henry, T.B.; Scown, T.M.; Johnston, B.D.; Tyler, C.R. Manufactured nanoparticles: Their uptake and effects on fish—A mechanistic analysis. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, D.; Fang, T.; Yu, L.; Sima, X.; Zhu, W. Effects of nano-scale TiO2, ZnO and their bulk counterparts on zebra fish: Acute toxicity, oxidative stress and oxidative damage. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langford, K.H.; Reid, M.J.; Fjeld, E.; Øxnevad, S.; Thomas, K.V. Environmental occurrence and risk of organic UV filters and stabilizers in multiple matrices in Norway. Environ. Int. 2015, 80, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okereke, C.S.; Abdel-Rhaman, M.S.; Friedman, M.A. Disposition of benzophenone-3 after dermal administration in male rats. Toxicol. Lett. 1994, 73, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fediuk, D.J.; Wang, T.; Chen, Y.; Parkinson, F.E.; Namaka, M.P.; Simons, K.J.; Burczynski, F.J.; Gu, X. Metabolic Disposition of the Insect Repellent DEET and the Sunscreen Oxybenzone Following Intravenous and Skin Administration in Rats. Int. J. Toxicol. 2012, 31, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnoni, L.J.; Novais, S.C.; Eding, E.; Leguen, I.; Lemos, M.F.L.; Ozório, R.O.A.; Geurden, I.; Prunet, P.; Schrama, J.W. Acute Stress and an Electrolyte- Imbalanced Diet, but Not Chronic Hypoxia, Increase Oxidative Stress and Hamper Innate Immune Status in a Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Isogenic Line. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Cho, H.; Park, J.-W.; Kwon, O.-S.; Lee, H.-S.; Huh, T.; Kang, B. NADP+-dependent cytosolic isocitrate dehydrogenase provides NADPH in the presence of cadmium due to the moderate chelating effect of glutathione. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 23, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, H.; Lee, S.; Son, B.; Lee, S.; Young, Z.; Chang, K.; Park, J.; Park, D.; Song, B.J.; Veech, R.L.; et al. Cytosolic NADP+-dependent Isocitrate Dehydrogenase Plays a Key Role in Lipid Metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 39968–39974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Rubio, H.F.; Vega-López, A. Fatty acid metabolism in fish species as a biomarker for environmental monitoring. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifi, K.; Soltani, N. Seasonal changes of two biomarkers of oxidative stress (LDH, MDA) in the edible mollusc Donax trunculus (Mollusca:Bivalvia) from the Gulf of Annaba (Algeria): Correlation with carbohydrate and lipid contents. Molluscan Res. 2019, 39, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlhoff, E.P. Biochemical indicators of stress and metabolism: Applications for Marine Ecological Studies. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2004, 66, 183–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Luo, Z.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, L.; Zhuo, M.; Hu, W. Differential induction of enzymes and genes involved in lipid metabolism in liver and visceral adipose tissue of juvenile yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco exposed to copper. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 136–137, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziarrusta, H.; Mijangos, L.; Picart-Armada, S.; Irazola, M.; Perera-Lluna, A.; Usobiaga, A.; Prieto, A.; Etxebarria, N.; Olivares, M.; Zuloaga, O. Non-targeted metabolomics reveals alterations in liver and plasma of gilt-head bream exposed to oxybenzone. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumalsamy, N.; Arumugam, K. Enzymes Activity in Fish Exposed to Heavy Metals and the Electro-Plating Effluent at Sub-Lethal Concentrations. Water Qual. Expo. Health 2013, 5, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.; Kurian, G.A. Differential effect of aqueous Desmodium gangeticum root extract mediated TiO2 nanoparticles on isolated mitochondria, cells and Wistar rats. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2017, 7, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, X.; Deneufbourg, P.; Paci, P.; Rugira, P.; Laurent, S.; Frau, A.; Stanicki, D.; Ris, L.; Nonclercq, D. Morphological alterations induced by the exposure to TiO2 nanoparticles in primary cortical neuron cultures and in the brain of rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 878–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wnuk, A.; Rzemieniec, J.; Staron, J.; Litwa, E.; Lason, W.; Bojarski, A.; Kajta, M. Prenatal exposure to benzophenone-3 impairs autophagy, disrupts RXRs/PPARγ signaling, and alters epigenetic and post-translational statuses in brain neurons. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 56, 4820–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, R.R.; Silveira, A.L.R.D.; De Jesus, I.P.; Grötzner, S.R.; Voigt, C.L.; Campos, S.X.; Garcia, J.R.E.; Randi, M.A.F.; Ribeiro, C.A.O.; Neto, F.F. Effects of realistic concentrations of TiO 2 and ZnO nanoparticles in Prochilodus lineatus juvenile fish. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 5179–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicari, T.; Carolina, A.; Klingelfus, T.; Limberger, G.; Sampaio, P.; Pereira, S.; Cristina, H.; De Assis, S.; Margarete, M. Co-exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles (NpTiO2) and lead at environmentally relevant concentrations in the Neotropical fish species Hoplias intermedius. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 1032–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, T.L.L.; Siqueira, P.R.; Azevedo, V.C.; Tavares, D.; Pesenti, E.C.; Cestari, M.M.; Martinez, C.B.R.; Fernandes, M.N. Overview of the toxic effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in blood, liver, muscles, and brain of a Neotropical detritivorous fish. Environ. Toxicol. 2019, 34, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeumer, R.; Galhano, V.; Monteiro, M.S.; Kuehr, S.; Knopf, B.; Meisterjahn, B.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Loureiro, S.; Lopes, I.; Schlechtriem, C. Chronic effects of wastewater-borne silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 137974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Lu, G.; Liu, J.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Y. Toxicological responses of Carassius auratus induced by benzophenone-3 exposure and the association with alteration of gut microbiota. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsden, C.S.; Smith, E.T.J.; Shaw, B.J.; Handy, E.R.D. Dietary exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles in rainbow trout, (Oncorhynchus mykiss): No effect on growth, but subtle biochemical disturbances in the brain. Ecotoxicology 2009, 7, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Bai, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Q.; Pan, W.; Dong, H.; Li, L.; Xu, H.; et al. Environmental relevant concentrations of benzophenone-3 induced developmental neurotoxicity in zebra fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.N.; Stoner, A.W.; Ryer, C.H. The Behaviour of Flatfishes. In Flatfishes: Biology and Exploitation; Gibson, R.N., Nash, R.D.M., Geffen, A.J., Van der Veer, H.W., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 314–345. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.H.; Wu, Y.T.; Ding, W.H. UV-filter benzophenone-3 inhibits agonistic behavior in male Siamese fighting fish (Betta splendens). Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximino, C.; de Brito, T.M.; Dias, C.A.; Gouveia, A., Jr.; Morato, S. Scototaxis as anxiety-like behavior in fish. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler de la Vega, A.C.; Molins-Delgado, D.; Barceló, D.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S. Nanosized titanium dioxide UV filter increases mixture toxicity when combined with parabens. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 2019, 184, 109565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, P.V.; Brabb, T.; Pekow, C.; Vasbinder, M.A. Administration of Substances to Laboratory Animals: Routes of Administration and Factors to Consider. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2011, 50, 600–613. [Google Scholar]
- Aita, K.; Irie, H.; Tanuma, Y.; Toida, S.; Okuma, Y.; Mori, S.; Shiga, J. Apoptosis in murine lymphoid organs following intraperitoneal administration of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2005, 79, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, R.P.; Draper, H.H. Comparative studies on different methods of malonaldehyde determination. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, D.W.; Tribess, T.; Gáspari, C.; Claudio, F.; Torres, M.; Magalhães, A.R. Seasonal changes in antioxidant defenses of the digestive gland of the brown mussel (Perna perna). Aquaculture 2001, 203, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claiborne, A. Catalase activity. In Handbook of Methods in Oxygen Radical Research; Greenwald, R.A., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1985; pp. 283–284. [Google Scholar]
- Giri, U.; Iqbal, M.; Athar, M. Porphyrine-mediated photosensitization has a weak tumor promoting activity in mouse skin: Possible role of in situ generated reactive oxygen species. Carcinogenesis 1996, 17, 2023–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, M.A.; Cerniglia, G.J.; Zaman, A. Microtiter plate assay for the measurement of glutathione and glutathione disulfide in large numbers of biological samples. Anal. Biochem. 1990, 190, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandeputte, C.; Guizon, I.; Genestie-Denis, I.; Vannier, B.; Lorenzon, G. A microtiter plate assay for total glutathione and glutathione disulfide contents in cultured/isolated cells: Performance study of a new miniaturized protocol. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 1994, 10, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cribb, A.E.; Leeder, J.S.; Spielberg, S.P. Use of a microplate reader in an assay of glutathione reductase using 5,5′-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid). Anal. Biochem. 1989, 183, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandas, J.; Marshall, J.; Duggins, G.; Horvath, J.; Tiller, D. Differential distribution of glutathione and glutathione related enzymes in rabbit kidney. Possible implications in analgesic neuropathy. Cancer Res. 1984, 44, 5086–5091. [Google Scholar]
- Athar, M.; Iqbal, M. Ferric nitrilotriacetate promotes N-diethylnitrosamine-induced renal tumorigenesis in the rat: Implications for the involvement of oxidative stress. Carcinogenesis 1998, 19, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, G.; Goldberg, D.M. An improved manual and semi-automatic assay for NADP-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase activity, with a description of some kinetic properties of human liver and serum enzyme. Clin. Biochem. 1971, 4, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, I.; Moreira, S.M.; Von Osten, J.R.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Guilhermino, L. Biochemical responses of the marine mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis to petrochemical environmental contamination along the North-western coast of Portugal. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1230–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassault, A. Lactate dehydrogenase. In Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, Enzymes: Oxirreductases Transferases; Bergmeyer, H.-U., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; Volume III, pp. 118–126. [Google Scholar]
- Diamantino, T.C.; Almeida, E.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Guilhermino, L. Lactate dehydrogenase activity as an effect criterion in toxicity tests with Daphnia magna straus. Chemosphere 2001, 45, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornall, A.C.; Bardawill, C.J.; David, M.M. Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1949, 177, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximino, C.; De Brito, T.M.; de Moraes, F.D.; de Oliveira, F.V.C. A Comparative Analysis of the Preference for Dark Environments in Five Teleosts. Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2007, 20, 351–367. [Google Scholar]
- Fairchild, E.A.; Howell, W.H. Factors affecting the post-release survival of cultured juvenile Pseudopleuronectes americanus. J. Fish Biol. 2004, 65, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Zhang, H.; Klaminder, J.; Brodin, T. ToxId: An efficient algorithm to solve occlusions when tracking multiple animals. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Zhang, H.; Klaminder, J.; Brodin, T.; Andersson, P.L. ToxTrac: A fast and robust software for tracking organisms. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N.; Walker, N.; Saveliev, A.A.; Smith, G.M. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; DebRoy, S.; Sarkar, D. Nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models; R Package Version 3.1-107; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2013; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=nlme (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology; R Package Version 2.5-6. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 3 February 2021).




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carvalhais, A.; Pereira, B.; Sabato, M.; Seixas, R.; Dolbeth, M.; Marques, A.; Guilherme, S.; Pereira, P.; Pacheco, M.; Mieiro, C. Mild Effects of Sunscreen Agents on a Marine Flatfish: Oxidative Stress, Energetic Profiles, Neurotoxicity and Behaviour in Response to Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles and Oxybenzone. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041567
Carvalhais A, Pereira B, Sabato M, Seixas R, Dolbeth M, Marques A, Guilherme S, Pereira P, Pacheco M, Mieiro C. Mild Effects of Sunscreen Agents on a Marine Flatfish: Oxidative Stress, Energetic Profiles, Neurotoxicity and Behaviour in Response to Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles and Oxybenzone. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(4):1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041567
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarvalhais, Ana, Bárbara Pereira, Mariangela Sabato, Rafaela Seixas, Marina Dolbeth, Ana Marques, Sofia Guilherme, Patrícia Pereira, Mário Pacheco, and Cláudia Mieiro. 2021. "Mild Effects of Sunscreen Agents on a Marine Flatfish: Oxidative Stress, Energetic Profiles, Neurotoxicity and Behaviour in Response to Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles and Oxybenzone" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 4: 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041567
APA StyleCarvalhais, A., Pereira, B., Sabato, M., Seixas, R., Dolbeth, M., Marques, A., Guilherme, S., Pereira, P., Pacheco, M., & Mieiro, C. (2021). Mild Effects of Sunscreen Agents on a Marine Flatfish: Oxidative Stress, Energetic Profiles, Neurotoxicity and Behaviour in Response to Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles and Oxybenzone. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(4), 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041567









