Factor XIII and Fibrin Clot Properties in Acute Venous Thromboembolism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Genetic Variants of FXIII
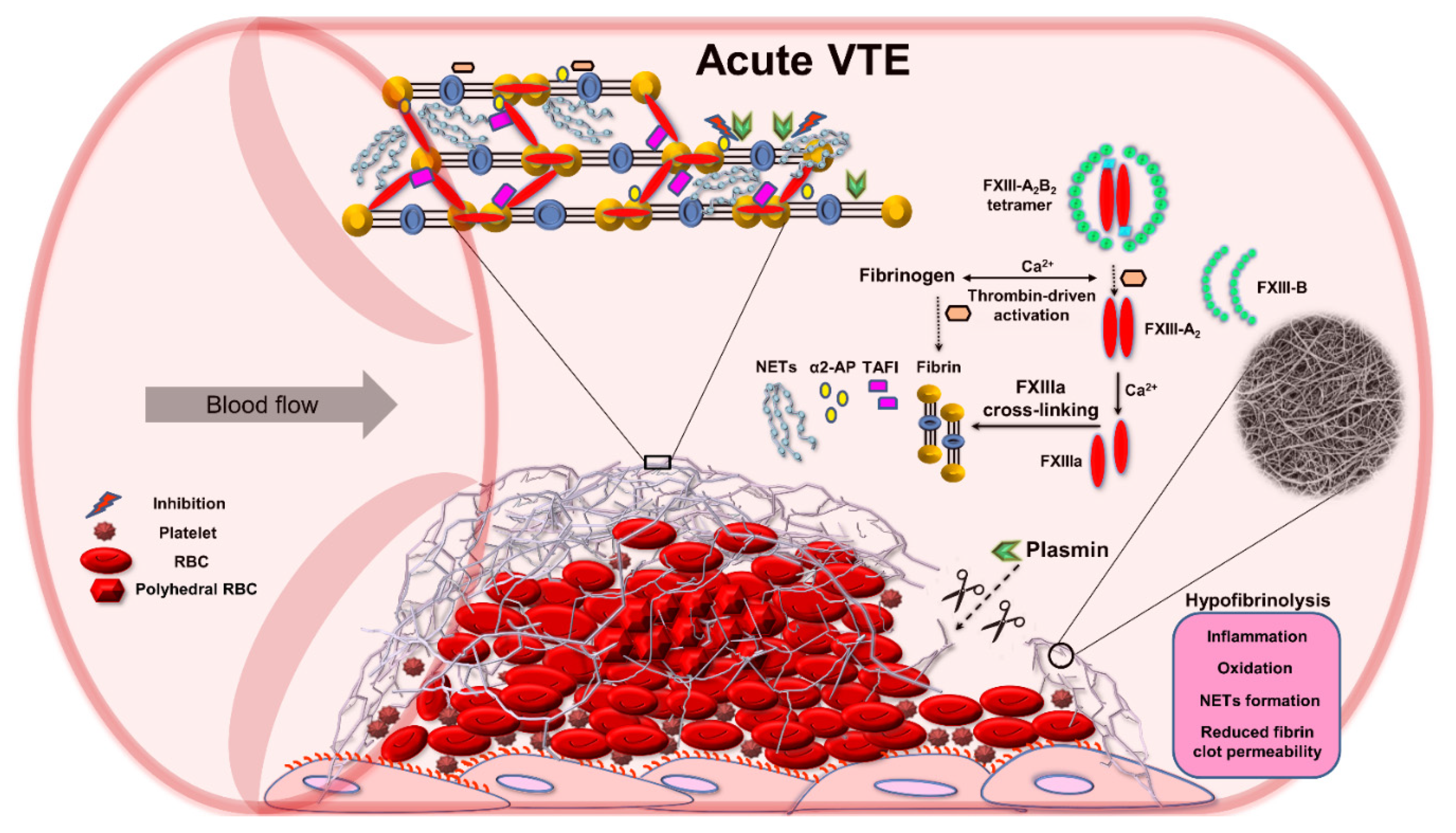
3. FXIII as a Modulator of Fibrin Clot Properties
4. Role of FXIII in Venous Thromboembolism (VTE)
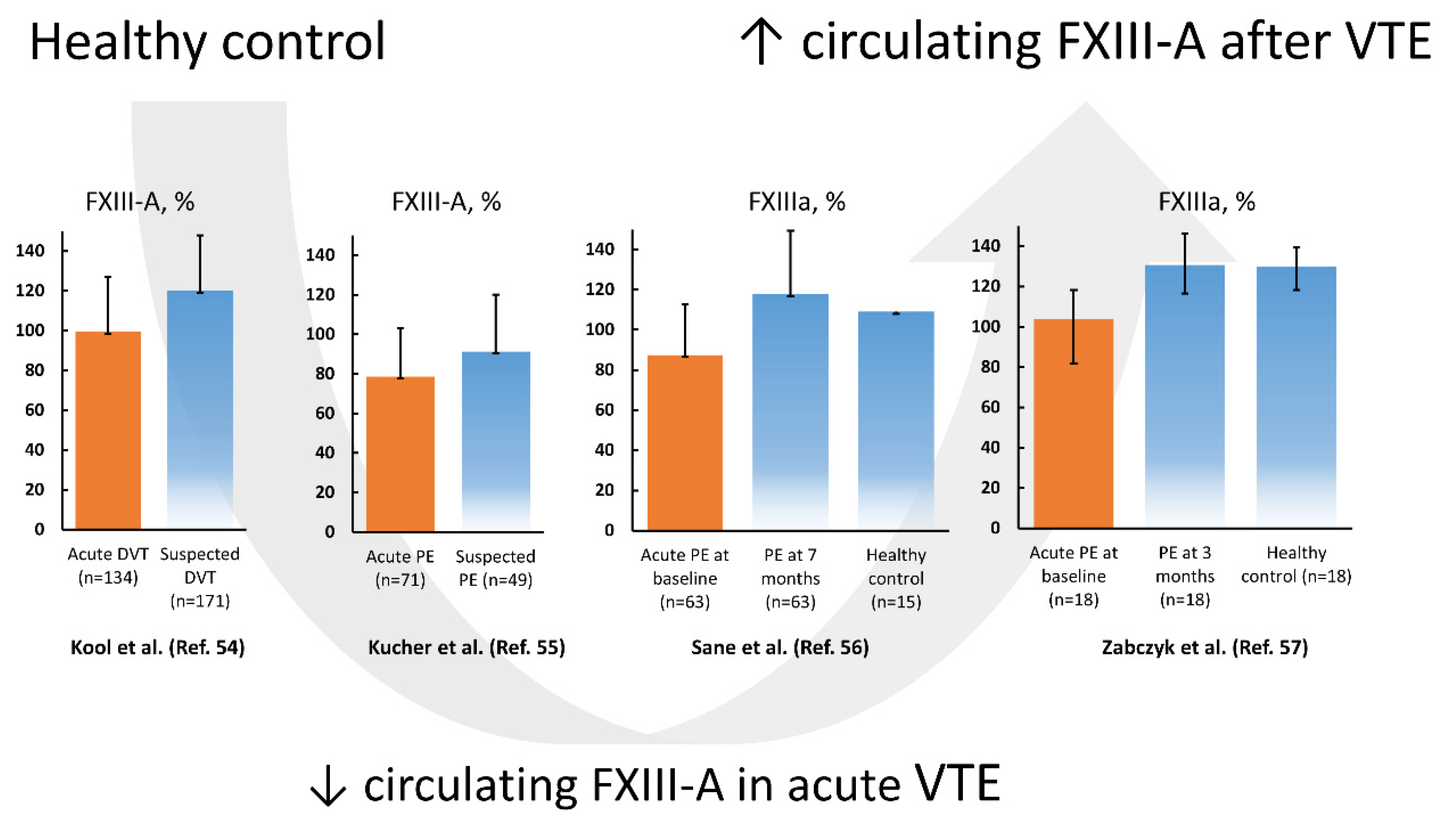
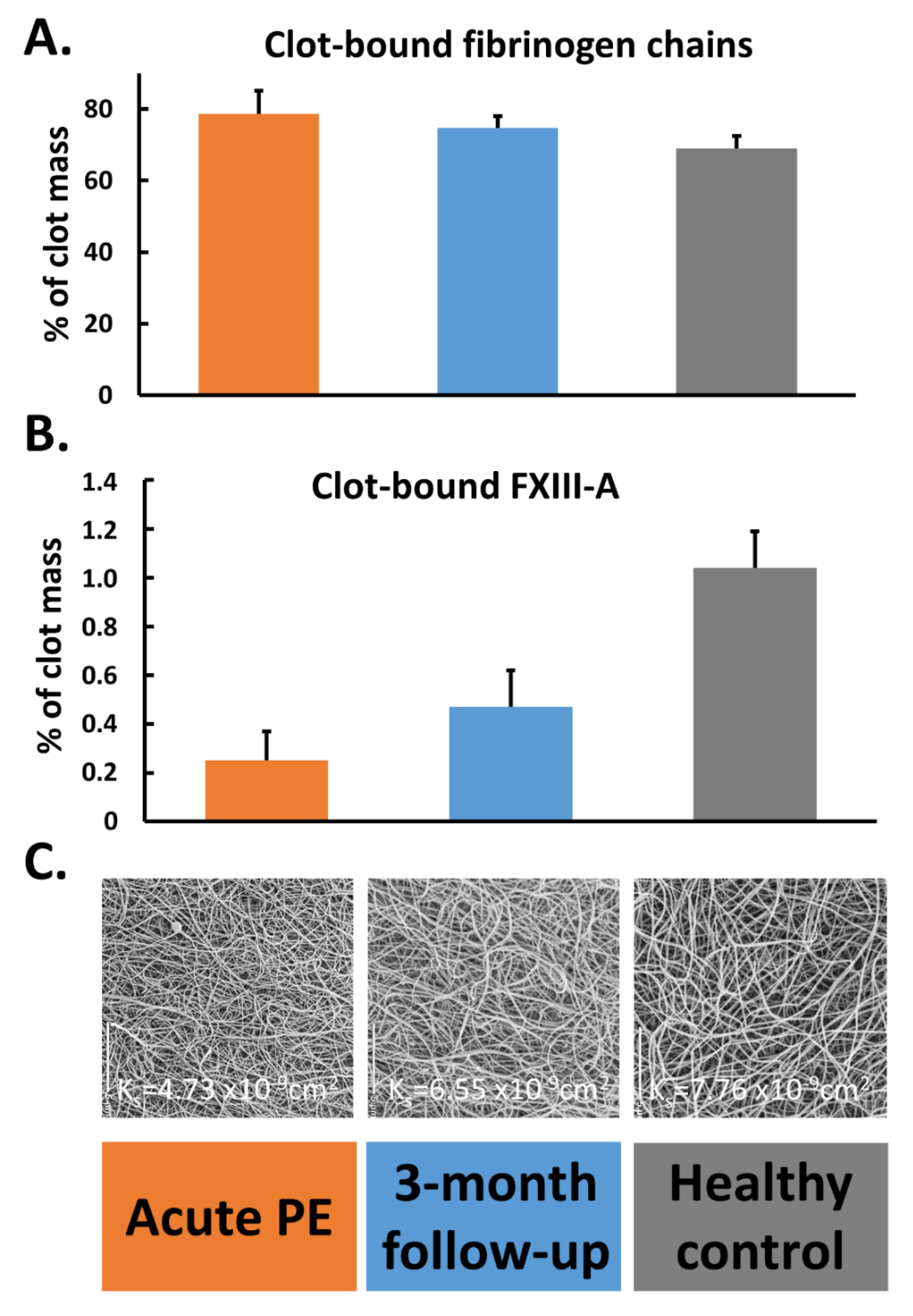
4.1. FXIII in Patients with Acute VTE
4.2. Drug Induced Effects on FXIII and Fibrin Properties
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Griffin, M.; Casadio, R.; Bergamini, C.M. Transglutaminases: Nature’s biological glues. Biochem. J. 2002, 368, 377–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muszbek, L.; Bereczky, Z.; Bagoly, Z.; Komáromi, I.; Katona, É. Factor XIII: A Coagulation Factor with Multiple Plasmatic and Cellular Functions. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 931–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bereczky, Z.; Muszbek, L. Factor XIII and Venous Thromboembolism. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2011, 37, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrnes, J.R.; Wilson, C.; Boutelle, A.M.; Brandner, C.B.; Flick, M.J.; Philippou, H.; Wolberg, A.S. The interaction between fi-brinogen and zymogen FXIII-A2B2 is mediated by fibrinogen residues γ390-396 and the FXIII-B subunits. Blood 2016, 128, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katona, É.; Pénzes, D.K.; Csapó, A.; Fazakas, F.; Udvardy, M.L.; Bagoly, Z.; Orosz, Z.Z.; Muszbek, L. Interaction of factor XIII subunits. Blood 2014, 123, 1757–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleman, M.M.; Byrnes, J.R.; Wang, J.-G.; Tran, R.; Lam, W.A.; Di Paola, J.; Mackman, N.; Degen, J.L.; Flick, M.J.; Wolberg, A.S. Factor XIII activity mediates red blood cell retention in venous thrombi. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3590–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katona, É.; Ajzner, É.; Tóth, K.; Kárpáti, L.; Muszbek, L. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the determination of blood coagulation factor XIII A-subunit in plasma and in cell lysates. J. Immunol. Methods 2001, 258, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgheznawy, A.; Shi, L.; Hu, J.; Wittig, I.; Laban, H.; Pircher, J.; Mann, A.; Provost, P.; Randriamboavonjy, V.; Fleming, I. Dicer Cleavage by Calpain Determines Platelet microRNA Levels and Function in Diabetes. Circ. Res. 2015, 117, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.L.; Lionikiene, A.S.; Fraser, S.R.; Whyte, C.S.; Booth, N.A.; Mutch, N.J. Functional factor XIII-A is exposed on the stimulated platelet surface. Blood 2014, 124, 3982–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolberg, A.S. Plasma factor XIII: Understanding the 99%. Blood 2014, 123, 1623–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, M.; Bereczky, Z.; Cohan, N.; Muszbek, L. Factor XIII deficiency. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2009, 35, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, Y.; Imamura, S.; Yamagata, Y.; Kitahara, A.; Saji, H.; Murachi, T.; Kannagi, R. Platelet factor XIII is activated by calpain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1987, 144, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszbek, L.; Polgár, J.; Boda, Z. Platelet Factor XIII Becomes Active without the Release of Activation Peptide during Platelet Activation. Thromb. Haemost. 1993, 69, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, V.; Kohler, H.P. Factor XIII: Structure and Function. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2016, 42, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Asahina, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Takeuchi, K.; Kanayama, N. Congenital Blood Coagulation Factor XIII Deficiency and Successful Deliveries: A Review of the Literature. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2007, 62, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, V.; Kohler, H.P. Factor XIII Deficiency: An Update. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2013, 39, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.T.S.; Rydz, N.; Goodyear, D.; Sholzberg, M. Acquired factor XIII deficiency: A review. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2018, 57, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, V.R.; Cordell, P.; Standeven, K.F.; Carter, A.M. Substrates of Factor XIII-A: Roles in thrombosis and wound healing. Clin. Sci. 2012, 124, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbal, A.; Lubetsky, A.; Krapp, T.; Castel, D.; Shaish, A.; Dickneitte, G.; Módis, L.; Muszbek, L.; Inbal, A. Impaired wound healing in factor XIII deficient mice. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 94, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardik, R.; Loscalzo, J.; Inbal, A. Factor XIII (FXIII) and angiogenesis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 4, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinose, A. Factor XIII is a key molecule at the intersection of coagulation and fibrinolysis as well as inflammation and infection control. Int. J. Hematol. 2012, 95, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malandrino, A.; Trepat, X.; Kamm, R.D.; Mak, M. Dynamic filopodial forces induce accumulation, damage, and plastic re-modeling of 3D extracellular matrices. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, M. Impact of crosslink heterogeneity on extracellular matrix mechanics and remodeling. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 3969–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malandrino, A.; Mak, M.; Kamm, R.D.; Moeendarbary, E. Complex mechanics of the heterogeneous extracellular matrix in cancer. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2018, 21, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spill, F.; Bakal, C.; Mak, M. Mechanical and Systems Biology of Cancer. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, B.R.; Houng, A.K.; Reed, G.L. Catalytic life of activated factor XIII in thrombi. Implications for fibrinolytic resistance and thrombus aging. Circulation 2000, 102, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.A.; Pease, R.J.; Avery, C.A.; Brown, J.M.; Adamson, P.J.; Cooke, E.J.; Neergaard-Petersen, S.; Cordell, P.A.; Ariëns, R.A.; Fishwick, C.W.; et al. The activation peptide cleft exposed by thrombin cleavage of FXIII-A (2) con-tains a recognition site for the fibrinogen α chain. Blood 2013, 121, 2117–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bagoly, Z.; Haramura, G.; Muszbek, L. Down-regulation of activated factor XIII by polymorphonuclear granulocyte proteases within fibrin clot. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 98, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorgalaleh, A.; Rashidpanah, J. Blood coagulation factor XIII and factor XIII deficiency. Blood Rev. 2016, 30, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszbek, L. Deficiency Causing Mutations and Common Polymorphisms in the Factor XIII-A Gene. Thromb. Haemost. 2000, 84, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariëns, R.A.; Philippou, H.; Nagaswami, C.; Weisel, J.W.; Lane, D.A.; Grant, P.J. The factor XIII V34L polymorphism accel-erates thrombin activation of factor XIII and affects cross-linked fibrin structure. Blood 2000, 96, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, H.-P. Role of blood coagulation factor XIII in vascular diseases. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2001, 131, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, P.S.; Anderson, J.L.; Scarvelis, D.K.; Doucette, S.P.; Gagnon, F. Factor XIII Val34Leu Variant Is Protective against Venous Thromboembolism: A HuGE Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 164, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivaskevicius, V.; Biswas, A.; Loreth, R.; Schroeder, V.; Ohlenforst, S.; Rott, H.; Krause, M.; Kohler, H.P.; Scharrer, I.; Oldenburg, J. Mutations affecting disulphide bonds contribute to a fairly common prevalence of F13B gene defects: Results of a genetic study in 14 families with factor XIII B deficiency. Haemophilia 2010, 16, 675–682. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, R.; Miloszewski, K.J. Factor XIII deficiency. Br. J. Haematol. 1999, 107, 468–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finlayson, J.S.; Aronson, D.L. Crosslinking of Rabbit Fibrin in Vivo. Thromb. Haemost. 1974, 31, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standeven, K.F.; Carter, A.M.; Grant, P.J.; Weisel, J.W.; Chernysh, I.; Masova, L.; Lord, S.T.; Ariëns, R.A. Functional analysis of fibrin {gamma}-chain cross-linking by activated factor XIII: Determination of a cross-linking pattern that maximizes clot stiff-ness. Blood 2007, 110, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Carlisle, C.R.; Sparks, E.A.; Guthold, M. The mechanical properties of single fibrin fibers. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rijken, D.C.; Abdul, S.; Malfliet, J.J.M.C.; Leebeek, F.W.; De Willige, S.U. Compaction of fibrin clots reveals the antifibrinolytic effect of factor XIII. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hethershaw, E.L.; La Corte, A.L.C.; Duval, C.; Ali, M.; Grant, P.J.; Ariëns, R.A.S.; Philippou, H. The effect of blood coagulation factor XIII on fibrin clot structure and fibrinolysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undas, A.; Casini, A. Congenital structural and functional fibrinogen disorders: A primer for internists. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2019, 129, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ząbczyk, M.; Stachowicz, A.; Natorska, J.; Olszanecki, R.; Wiśniewski, J.R.; Undas, A. Plasma fibrin clot proteomics in healthy subjects: Relation to clot permeability and lysis time. J. Proteom. 2019, 208, 103487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muszbek, L.; Bagoly, Z.; Bereczky, Z.; Katona, E. The involvement of blood coagulation factor XIII in fibrinolysis and throm-bosis. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents Med. Chem. 2008, 6, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, M.; Longstaff, C. Extracellular Histones Inhibit Fibrinolysis through Noncovalent and Covalent Interactions with Fibrin. Thromb. Haemost. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasternack, R.; Büchold, C.; Jähnig, R.; Pelzer, C.; Sommer, M.; Heil, A.; Florian, P.; Nowak, G.; Gerlach, U.; Hils, M. Novel inhibitor ZED3197 as potential drug candidate in anticoagulation targeting coagulation FXIIIa (F13a). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, M.; O’Meara, E.S.; Folsom, A.R.; Heckbert, S.R. Coagulation factors IX through XIII and the risk of future venous thrombosis: The Longitudinal Investigation of Thromboembolism Etiology. Blood 2009, 114, 2878–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezei, Z.A.; Katona, É.; Kállai, J.; Bereczky, Z.; Somodi, L.; Molnár, É; Kovács, B.; Miklós, T.; Ajzner, É.; Muszbek, L. Factor XIII levels and factor XIII B subunit polymorphisms in patients with venous thromboembolism. Thromb. Res. 2017, 158, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, S.R.; Zabczyk, M.; Macrae, F.L.; Duval, C.; Undas, A.; Ariёns, R. Recurrent venous thromboembolism patients form clots with lower elastic modulus than those formed by patients with non-recurrent disease. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohil, R.; Peck, G.; Sharma, P. The genetics of venous thromboembolism. A meta-analysis involving approximately 120,000 cases and 180,000 controls. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 102, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undas, A.; Brzezinska-Kolarz, B.; Brummel-Ziedins, K.; Musial, J.; Szczeklik, A.; Mann, K.G. Factor XIII Val34Leu polymor-phism and gamma-chain cross-linking at the site of microvascular injury in healthy and coumadin-treated subjects. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 2015–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tiedje, V.; Dunkler, D.; Ay, C.; Horvath, B.; Quehenberger, P.; Pabinger, M.; Zielinski, C.; Pabinger, I.; Mannhalter, C. The role of fibrinogen plasma levels, the-455G>A fibrinogen and the factor XIII A subunit (FXIII-A) Val34Leu polymorphism in can-cer-associated venous thrombosis. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 106, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariёns, R. Novel mechanisms that regulate clot structure/function. Thromb. Res. 2016, 141, S25–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłoczko, J.; Wojtukiewicz, M.; Bielawiec, M. Molecular subunits and transamidase activity of factor XIII in patients with deep vein thrombosis. Folia Haematol. 1986, 113, 810–814. [Google Scholar]
- Kool, R.O.; Kohler, H.P.; Coutinho, J.M.; Levi, M.; Coppens, M.; Meijers, J.C.M.; Schroeder, V. Coagulation factor XIII-A subunit and activation peptide levels in individuals with established symptomatic acute deep vein thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2017, 159, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucher, N.; Schroeder, V.; Kohler, H.P. Role of blood coagulation factor XIII in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Correlation of factor XIII antigen levels with pulmonary occlusion rate, fibrinogen, D-dimer, and clot firmness. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 90, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sane, M.; Granér, M.; Laukkanen, J.A.; Harjola, V.-P.; Mustonen, P. Plasma levels of haemostatic factors in patients with pulmonary embolism on admission and seven months later. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2017, 40, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ząbczyk, M.; Natorska, J.; Bagoly, Z.; Sarkady, F.; Barath, B.; Katona, E.; Bryk, A.; Zettl, K.; Wisniewski, J.R.; Undas, A. Plasma fibrin clots of pulmonary embolism patients present increased amounts of factor XIII and alpha2-antiplasmin at 3 months’ anticoagulation since the acute phase. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 71, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryk, A.H.; Natorska, J.; Ząbczyk, M.; Zettl, K.; Wiśniewski, J.R.; Undas, A. Plasma fibrin clot proteomics in patients with acute pulmonary embolism: Association with clot properties. J. Proteom. 2020, 229, 103946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ząbczyk, M.; Natorska, J.; Janion-Sadowska, A.; Metzgier-Gumiela, A.; Polak, M.; Plens, K.; Janion, M.; Skonieczny, G.; Mizia-Stec, K.; Undas, A. Prothrombotic fibrin clot properties associated with NETs formation characterize acute pulmonary embolism patients with higher mortality risk. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ząbczyk, M.; Natorska, J.; Janion-Sadowska, A.; Malinowski, K.P.; Janion, M.; Undas, A. Elevated Lactate Levels in Acute Pulmonary Embolism are Associated with Prothrombotic Fibrin Clot Properties: Contribution of NETs Formation. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilyeva, A.D.; Yurina, L.; Shchegolikhin, A.; Indeykina, M.I.; Bugrova, A.E.; Kononikhin, A.S.; Nikolaev, E.N.; Rosenfeld, M.A. The Structure of Blood Coagulation Factor XIII Is Adapted to Oxidation. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Undas, A.; Zawilska, K.; Ciesla-Dul, M.; Lehmann-Kopydłowska, A.; Skubiszak, A.; Ciepłuch, K.; Tracz, W. Altered fibrin clot structure/function in patients with idiopathic venous thromboembolism and in their relatives. Blood 2009, 114, 4272–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ząbczyk, M.; Natorska, J.; Janion-Sadowska, A.; Metzgier-Gumiela, A.; Polak, M.; Plens, K.; Janion, M.; Skonieczny, G.; Mizia-Stec, K.; Undas, A. Loose Fibrin Clot Structure and Increased Susceptibility to Lysis Characterize Patients with Central Acute Pulmonary Embolism: The Impact of Isolated Embolism. Thromb. Haemost. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaya, S.A.; Gani, D.M.; Weitz, J.I.; Kim, P.Y.; Gross, P.L. Factor XIII Prevents Pulmonary Emboli in Mice by Stabilizing Deep Vein Thrombi. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruszczyk, P.; Konstantinides, S. Where to treat patients with acute pulmonary embolism? Kardiol. Pol. 2020, 78, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Varin, R.; Mirshahi, S.; Mirshahi, P.; Klein, C.; Jamshedov, J.; Chidiac, J.; Perzborn, E.; Mirshahi, M.; Soria, C.; Soria, J. Whole blood clots are more resistant to lysis than plasma clots greater efficacy of rivaroxaban. Thromb. Res. 2013, 131, e100–e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, R.L.; Talbot, K.; Hur, W.S.; Meixner, S.C.; Van Der Gugten, J.G.; Holmes, D.T.; Côté, H.C.; Kastrup, C.J.; Smith, T.W.; Lee, A.Y.; et al. Rivaroxaban and apixaban induce clotting factor Xa fibrinolytic activity. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 2276–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frączek, P.; Krzysztofik, M.; Stanisz, A.; Undas, A. Clinical outcomes and plasma clot permeability and lysability in patients with venous thromboembolism on rivaroxaban: A cohort study. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2019, 129, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirshahi, S.; Varin, R.; Soria, J. Importance of clot permeability and clot degradability for determination of rivaroxaban efficacy. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2019, 129, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standeven, K.F.; Ariëns, R.A.; Whitaker, P.; Ashcroft, A.E.; Weisel, J.W.; Grant, P.J. The effect of dimethylbiguanide on thrombin activity, FXIII activation, fibrin polymerization, and fibrin clot formation. Diabetes 2002, 51, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undas, A.; Sydor, W.J.; Brummel, K.; Musial, J.; Mann, K.G.; Szczeklik, A. Aspirin Alters the Cardioprotective Effects of the Factor XIII Val34Leu Polymorphism. Circulation 2003, 107, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ząbczyk, M.; Natorska, J.; Undas, A. Factor XIII and Fibrin Clot Properties in Acute Venous Thromboembolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041607
Ząbczyk M, Natorska J, Undas A. Factor XIII and Fibrin Clot Properties in Acute Venous Thromboembolism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(4):1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041607
Chicago/Turabian StyleZąbczyk, Michał, Joanna Natorska, and Anetta Undas. 2021. "Factor XIII and Fibrin Clot Properties in Acute Venous Thromboembolism" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 4: 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041607
APA StyleZąbczyk, M., Natorska, J., & Undas, A. (2021). Factor XIII and Fibrin Clot Properties in Acute Venous Thromboembolism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(4), 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041607





